1. Introduction
Muscle strength and muscle hypertrophy adaptation by resistance training can be changed by rest interval between sets [
1,
2,
3,
4] and correction [
5,
6,
7] is possible according to the goal of training. The rest interval during resistance exercise means the time set between sets [
8]) and is an important factor that affects one-time response and long-term adaptation [
7] On the other hand, the intensity of exercise is defined as the percentage of 1RM used in a given exercise [
8,
9]. In the aspect of the Loading zone continuum, the resistance training of light loads (65%1RM or less) is provided by the corresponding process, which is mostly fast, with the energy required for more than 15 repetitions per set and for muscle contraction of 45 sec or more, and is also associated with a large amount of metabolic stress [
10].
In addition, the resistance training of intermediate load (65-85 %1RM) is provided by the fast corresponding process with most energy required for repetition of 15 or fewer times per set and muscle contraction of 20 to 40 sec, but it is optimally provided with a combination of mechanical tension and metabolic stress required for hypertrophy adaptation by generating higher metabolic stress due to the difference in exercise load [
11]. This shows that changing the rest period between sets during a resistance workout can change the metabolic stress (fatigue) and the number of repetitions depending on how the set is going and that there may be variations in the energy metabolism contribution needed for muscular contraction. In terms of energy metabolism, physiological recovery has a positive correlation between exercise and muscle contraction intensity and heart rate [
12] and a series of responses in which heart rate increases immediately after maximum exercise decreases to stable levels by homeostasis mechanism [
13,
14,
15,
16].
It is reported that these physiological recovery responses were relatively fast in healthy and well-trained athletes, suggesting that the rapid heart rate recovery level for the preceding exercises could bepositive for the next exercise task [
13]. In the previous studies on the strength of exercise and rest interval, 50%-90%1RM intensity and 3-5min rest interval between sets were considered to be able to perform more repetition times up to 3 sets because the ability to maintain mechanical tension is higher than the short rest interval even if the number of sets increases [
6,
17,
18]. However, the 30sec rest interval between sets was considered to be a factor that reduces the momentum of more than 50% during 5 set at 10RM load given by increased metabolic stress according to set progression [
18] and [
19] increased metabolic stress as 90sec rest interval condition progressed over 5min during resistance exercise under the same muscle hypertrophy load condition [
10] reported that the amount of exercise decreased.
As described above, various studies are being conducted on the combination of metabolic s According to the different rest interval circumstances between sets during resistance exercise, several studies are being undertaken on the combination of metabolic stress and exercise performance, exercise intensity, and rest interval. However, the study that presented the rest interval conditions between sets using the same exercise intensity in 6 ways has not yet been found. Additionally, the 65%1RM exercise intensity recommended in this study is thought to be both the maximum load for muscular endurance training that incorporates aerobic exercise elements [
20] and the lowest load for hypertrophy training [
9]. Furthermore, comparing the cardiovascular response brought on by muscle contraction during resistance training with the number of repetitions, heart rate, and heart rate recovery percentage (%) by rest interval conditions between sets will be important from an academic perspective. Therefore, this study aims to present more objectively the exercise performance level (repeated number) and physiological variables (heart rate and heart rate recovery rate (%) according to rest interval conditions between 6 sets during resistance exercise using the same intensity (65%1RM).
2. Materials and Methods
Research Process
1. Subject
The subjects of this study were eight students who had more than six months of resistance exercise experience attending C university. After fully understanding and recognizing the explanation of the purpose of the study before the experiment, the consent was signed. The physical characteristics of the subjects are shown in (
Table 1).
2. Experimental design and procedure
In order to determine the squat weight to be applied in this study, the [
27] literature was referred. One week before the experiment, the subjects' repetition maximum weight of one repetition of bench press was measured, and 65%1RM was measured based on this. Experiments were conducted by random assignment according to six rest interval conditions (30sec, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5min). The experiment was carried out with maximum effort for each set, and a second experiment was conducted in the same manner after one week. A total of six experiments were conducted in this way, and the experimental design of the study is shown in (
Figure 1,
Figure 2).
Measuring instrument and method
1) Repetition
The number of repetitions was based on the repetition by the maximum effort of each set and the one time within 1.5~2sec. When the repetition was not completed within a fixed time, the set was terminated and the number of repetitions at that time was measured and recorded.
2) Heart Rate
The heart rate was measured in a chair position using a radio heart rate measuring device (Polar S610i), and each was measured seven times immediately after each set exercise and after rest time according to six rest interval conditions (30sec, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5min).
3) Data processing
Data were processed by repeated measures two-way ANOVA using the SPSS 26.0 statistical program. The difference between the conditions was examined using the post-comparison (repeated) method if there was a statistically significant difference between the number of repetitions for each set according to the six rest conditions and the heart rate just after exercise and after rest. The significance level was set to =.05.
3. Results
3.1. Repetition
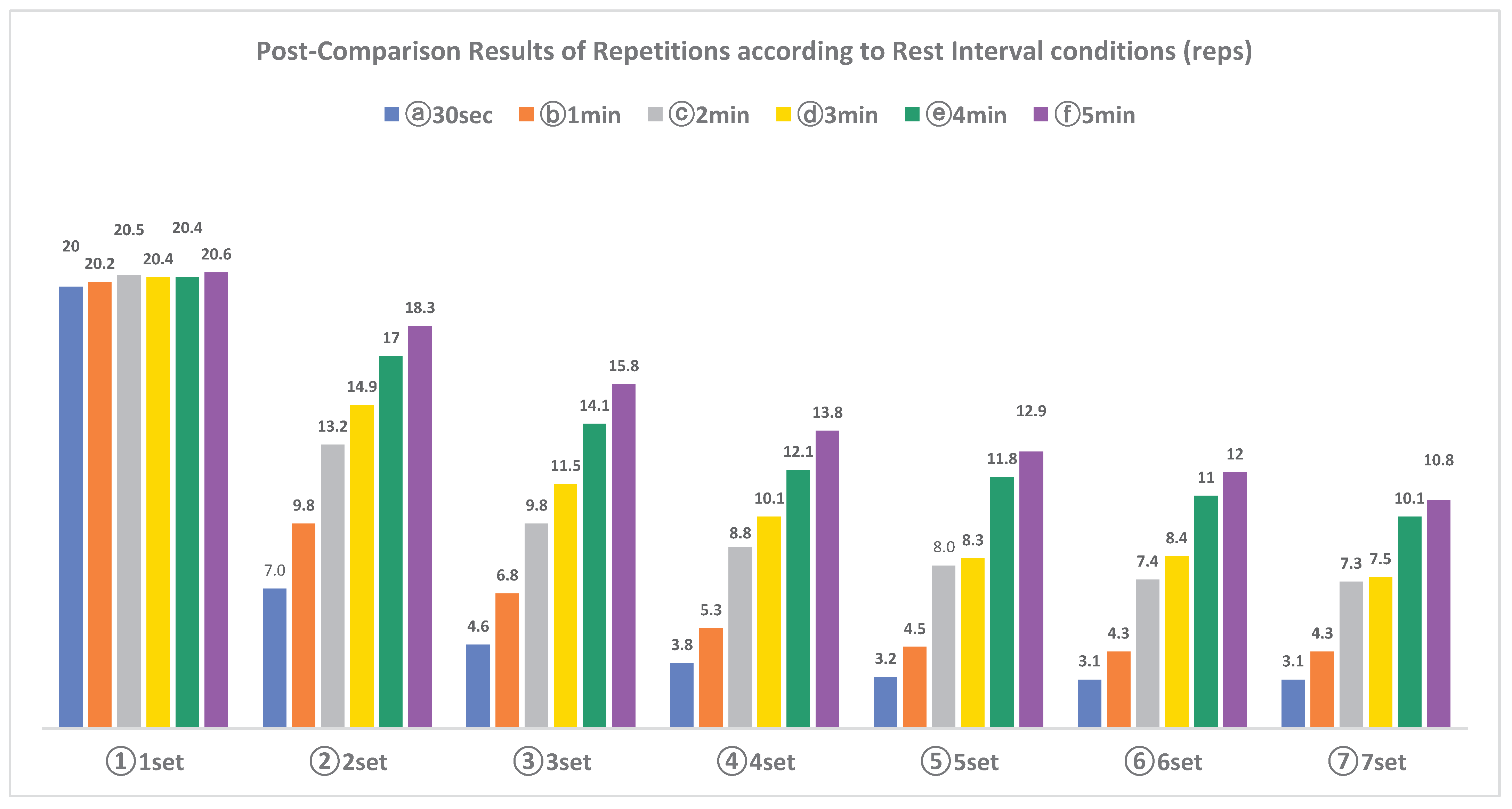
The results of the number of repetitions according to the rest interval six conditions and seven sets are as follows: <
Table 2>, <
Table 3>. The number of repetitions according to the rest interval condition showed a statistically significant difference (p<.000). The number of repetitions according to the set progression also showed a statistically significant difference (p<.000), and the interaction effect between rest interval conditions and sets also showed statistical significance (p<.000). As a result of post-comparison, the number of repetitions according to the rest interval condition decreased significantly in the 30sec, 1, 2, and 3min, and similarly in the 4 or 5min condition. The number of repetitions according to set progression decreased significantly from 2set, 30sec, 1min rest interval condition decreased significantly to 5set, 2min rest interval condition decreased to 3-5set, 4min rest interval condition decreased to 3set. It has typically remained at the same level since each set.
Table 2.
Post-Comparison Results of Repetitions according to Rest Interval conditions (reps).
Table 2.
Post-Comparison Results of Repetitions according to Rest Interval conditions (reps).
Rest
Interval |
①
1set |
②
2set |
③
3set |
④
4set |
⑤
5set |
⑥
6set |
⑦
7set |
|
p |
Contrast |
ⓐ
30sec |
20.0
±1.5 |
7.0
±2.5 |
4.6
±1.4 |
3.8
±1.7 |
3.2
±1.4 |
3.1
±1.2 |
3.1
±1.5 |
Rest
Interval
(RI) |
.000*** |
ⓐ<ⓑ<ⓒ<ⓓ=ⓔ=ⓕ |
ⓑ
1min |
20.2
±1.3 |
9.8
±2.0 |
6.8
±1.6 |
5.3
±1.5 |
4.5
±1.1 |
4.3
±1.3 |
4.3
±1.0 |
ⓒ
2min |
20.5
±1.0 |
13.2
±2.4 |
9.8
±2.8 |
8.8
±2.4 |
8.0
±1.8 |
7.4
±2.3 |
7.3
±2.0 |
Sets(S) |
.000*** |
①=②>③=④>⑤>⑥>⑦ |
ⓓ
3min |
20.4
±1.5 |
14.9
±2.9 |
11.5
±3.0 |
10.1
±3.1 |
8.3
±1.4 |
8.4
±2.6 |
7.5
±2.8 |
ⓔ
4min |
20.4
±1.4 |
17.0
±3.3 |
14.1
±3.0 |
12.1
±3.6 |
11.8
±3.2 |
11.0
±3.4 |
10.1
±3.2 |
(RI)×(S) |
.000*** |
|
ⓕ5
min |
20.6
±1.4 |
18.3
±2,0 |
15.8
±3.8 |
13.8
±3.8 |
12.9
±3.1 |
12.0
±3.0 |
10.8
±3.2 |
| (M±SD), *p<.05, **p<.001, ***p<.001 |
Table 3.
Mean and standard deviation of the number of repetitions by rest interval (M±SD).
Table 3.
Mean and standard deviation of the number of repetitions by rest interval (M±SD).
Rest
Interval |
①
1set |
②
2set |
③
3set |
④
4set |
⑤
5set |
⑥
6set |
⑦
7set |
| ⓐ30sec |
20.0±1.5 |
7.0±2.5 |
4.6±1.4 |
3.8±1.7 |
3.2±1.4 |
3.1±1.2 |
3.1±1.5 |
| ⓑ1min |
20.2±1.3 |
9.8±2.0 |
6.8±1.6 |
5.3±1.5 |
4.5±1.1 |
4.3±1.3 |
4.3±1.0 |
| ⓒ2min |
20.5±1.0 |
13.2±2.4 |
9.8±2.8 |
8.8±2.4 |
8.0±1.8 |
7.4±2.3 |
7.3±2.0 |
| ⓓ3min |
20.4±1.5 |
14.9±2.9 |
11.5±3.0 |
10.1±3.1 |
8.3±1.4 |
8.4±2.6 |
7.5±2.8 |
| ⓔ4min |
20.4±1.4 |
17.0±3.3 |
14.1±3.0 |
12.1±3.6 |
11.8±3.2 |
11.0±3.4 |
10.1±3.2 |
| ⓕ5min |
20.6±1.4 |
18.3±2,0 |
15.8±3.8 |
13.8±3.8 |
12.9±3.1 |
12.0±3.0 |
10.8±3.2 |
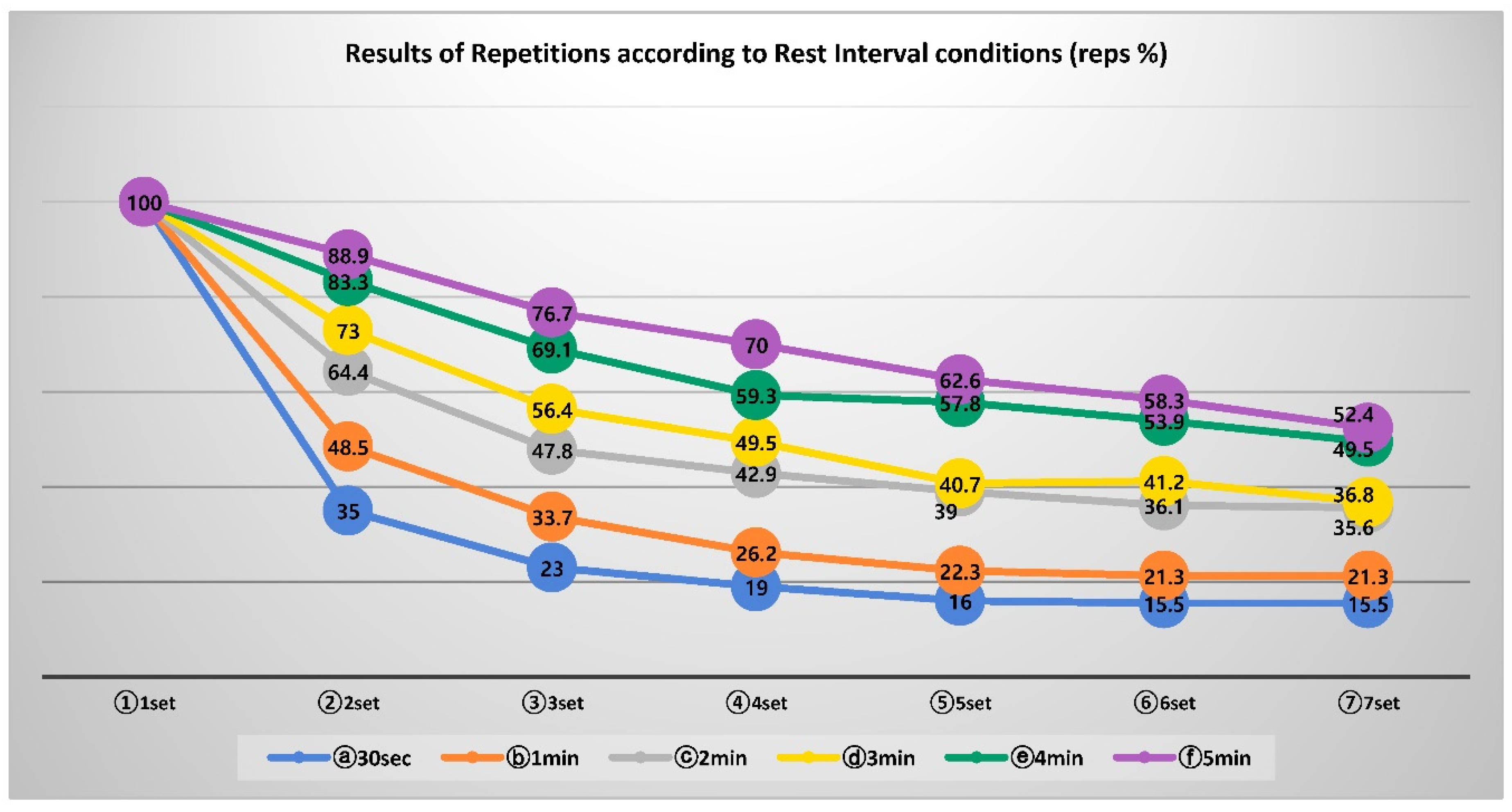
Figure 3.
Post-Comparison Results of Repetitions according to Rest Interval conditions (reps).
Figure 3.
Post-Comparison Results of Repetitions according to Rest Interval conditions (reps).
There was a statistically significant difference (p<.000) in the number of repetitions according to the rest interval between sets. There was also a statistically significant difference (p<.000) in the number of repetitions according to the set progress. The rest interval between sets and the interaction effect according to the set also showed a statistically significant difference (p<.000). As a result of post-comparison, the number of repetitions according to the interval between sets decreased from 30sec to 1, 2 and 3min, and the 4 and 5min conditions showed similar level. The number of repetitions according to the set progression significantly decreased every set after 2 sets.
As a result of the post-comparison based on the interaction effect, the number of repetitions was significant up to 5set for the 30sec rest interval and 1min condition, between 3-5set for the 2 and 3min condition, and up to 3set for the 4 and 5min condition decreased significantly. They frequently remained at the same level after each set.
3.2. Heart rate
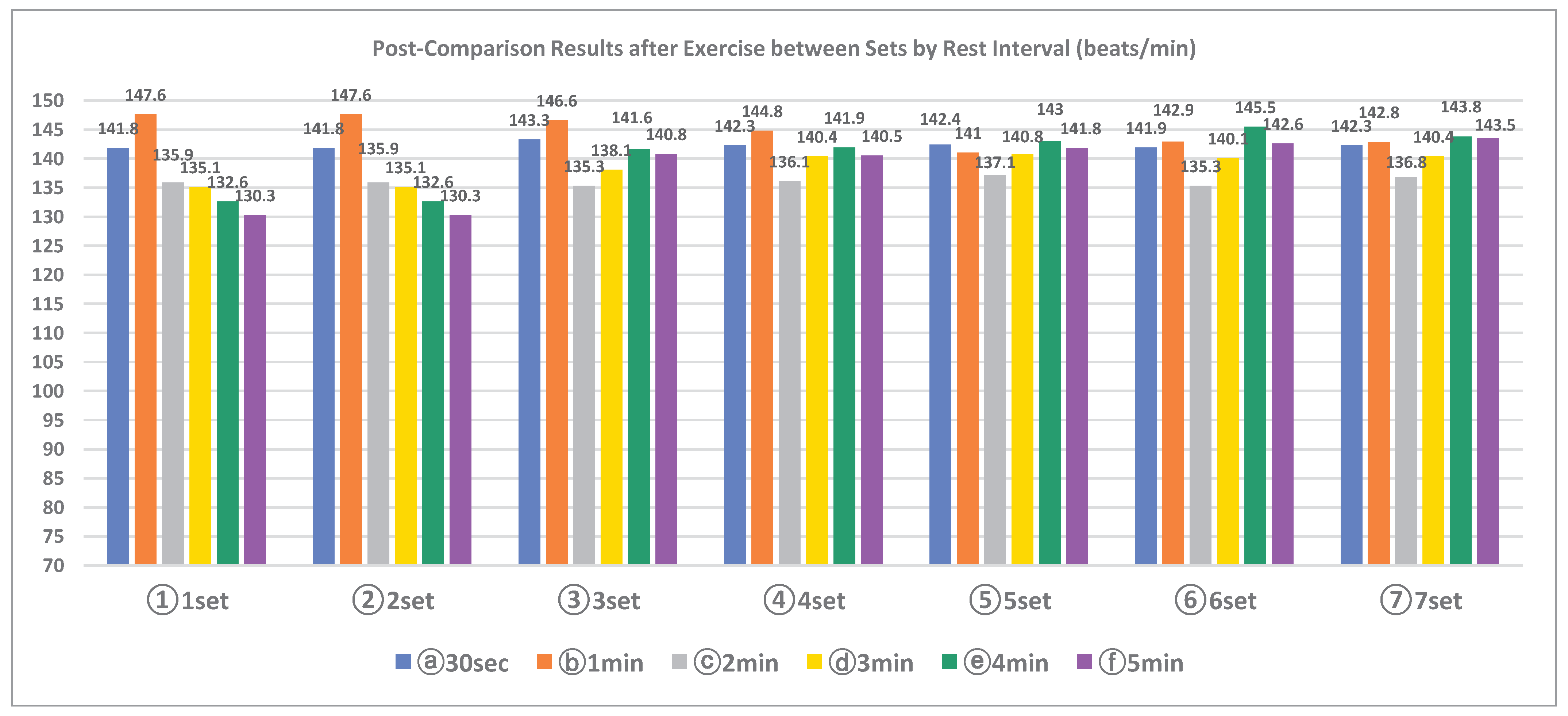
3.2.1. Heart rate immediately after exercise
According to the rest interval six conditions and seven sets, the change in heart rate immediately following exercise is the same as (
Table 4).
The heart rate after exercise according to the rest interval condition did not show statistically significant difference. There was no statistically significant difference in the interaction effect between sets and rest intervals. However, the heart rate after exercise according to the set showed statistical significance(p<.001). The post-comparison results showed that the heart rate was similar in the 30sec, 1min rest interval condition, maintained or increased in the 2, 3min rest interval condition, and continued to increase in the 4, 5min condition. There was no statistically significant difference in heart rate immediately after exercise according to rest interval conditions. The heart rate after exercise according to the set showed a statistically significant difference(p<.001). There was no statistical significance in the interaction effect between the set rest interval and set. As a result of post comparison of heart rate immediately after exercise according to set, the heart rate was maintained similarly in 30 sec and 1min rest intervals, maintained or increased in 2 and 3min rest interval, and showed a tendency to increase continuously in 4 and 5min rest time.
Table 4.
sPost-Comparison Results after Exercise between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Table 4.
sPost-Comparison Results after Exercise between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Rest
Interval |
Pre-
Exercise |
①
1set |
②
2set |
③
3set |
④
4set |
⑤
5set |
⑥
6set |
⑦
7set |
|
p |
Contrast |
ⓐ
30sec |
91
±15.2 |
141.8
±14.9 |
141.8
±14.9 |
143.3
±14.0 |
142.3
±13.6 |
142.4
±13.2 |
141.9
±11.6 |
142.3
±11.0 |
Rest Interval (RI) |
.352 |
|
ⓑ
1min |
93
±14.6 |
147.6
±28.2 |
147.6
±28.2 |
146.6
±25.4 |
144.8
±22.6 |
141.0
±24.3 |
142.9
±22.4 |
142.8
±22.8 |
ⓒ
2min |
88
±16.9 |
135.9
±30.0 |
135.9
±30.0 |
135.3
±27.5 |
136.1
±22.7 |
137.1
±19.7 |
135.3
±23.3 |
136.8
±22.0 |
Sets(S) |
.005* |
①=②<③<④=⑤<⑥<⑦ |
ⓓ
3min |
89
±15.2 |
135.1
±22.6 |
135.1
±22.6 |
138.1
±19.1 |
140.4
±20.0 |
140.8
±16.6 |
140.1
±18.2 |
140.4
±17.6 |
ⓔ
4min |
89
±13.8 |
132.6
±22.8 |
132.6
±22.8 |
141.6
±15.6 |
141.9
±14.6 |
143.0
±11.8 |
145.5
±11.3 |
143.8
±10.7 |
(RI)×(S) |
.982 |
|
ⓕ
5min |
87
±15.5 |
130.3
±17.5 |
130.3
±17.5 |
140.8
±16.1 |
140.5
±17.8 |
141.8
±16.7 |
142.6
±12.9 |
143.5
±19.0 |
| (M±SD), *p<.05, **p<.001, ***p<.001 |
Figure 4.
Post-Comparison Results after Exercise between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Figure 4.
Post-Comparison Results after Exercise between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
3.2.2. Heart rate immediately after rest
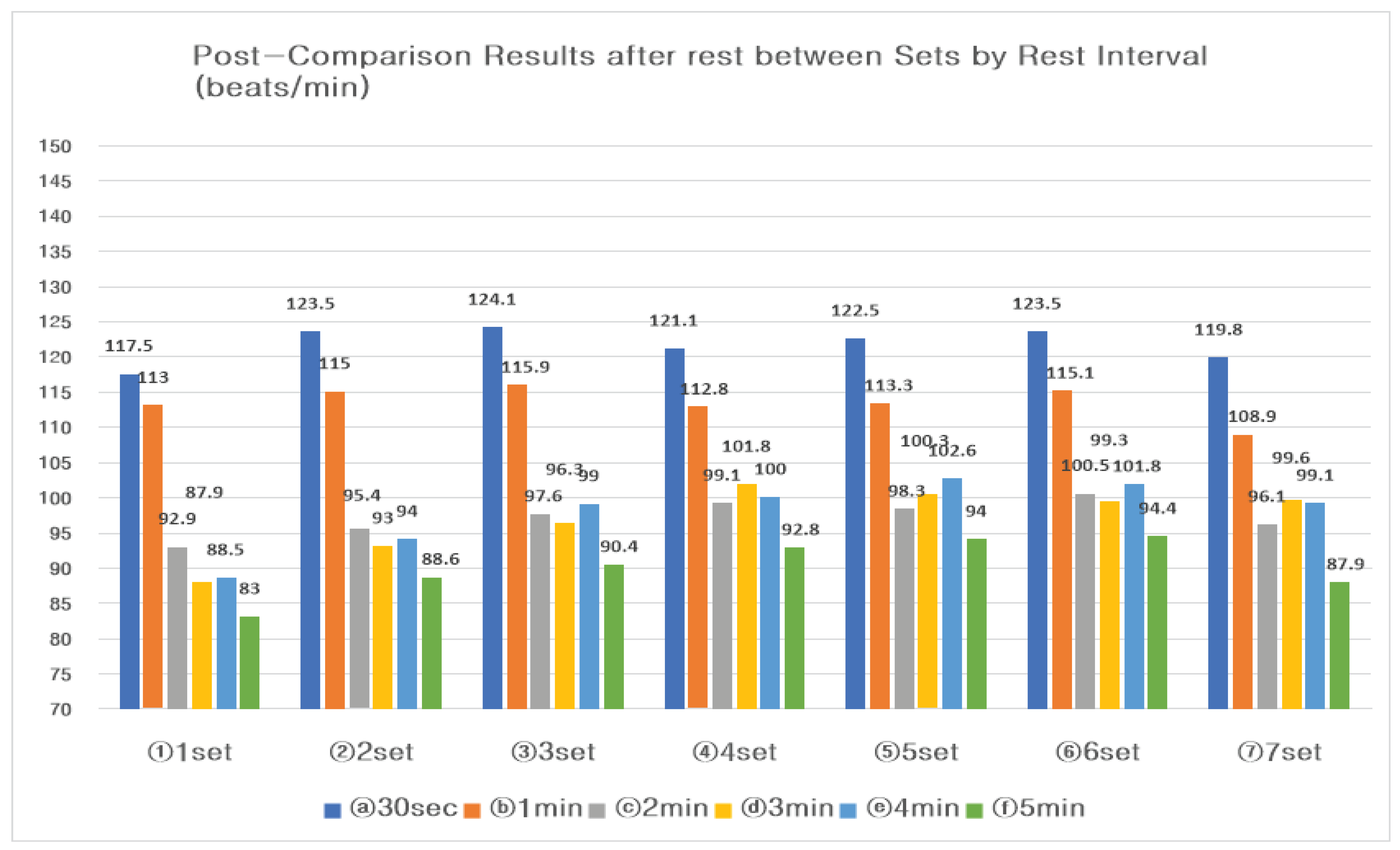
The result of the change of heart rate after rest according to the rest interval six conditions and seven sets is the same as <
Table 5>. The heart rate after rest according to the rest interval condition showed statistical significance(p<.020), and the heart rate after rest according to the set progression showed a significant difference(p<.000). The post-comparison results showed that the heart rate after resting according to the resting interval condition was significantly different in the 30sec and 1min rest interval condition and the 4 and 5min rest interval condition. After rest heart rate showed a significant difference in 1, 2, 6, and 7 set, and there was no interaction effect between rest interval conditions and sets.
Table 5.
Post-Comparison Results after rest between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Table 5.
Post-Comparison Results after rest between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Rest
Interval |
①
1set |
②
2set |
③
3set |
④
4set |
⑤
5set |
⑥
6set |
⑦
7set |
|
p |
Contrast |
ⓐ
30sec |
117.5
±18.7 |
123.5
±18.1 |
124.1
±16.5 |
121.1
±16.6 |
122.5
±15.4 |
123.5
±18.5 |
119.8
±15.5 |
Rest
Interval
(RI) |
.020** |
ⓐ,ⓑ>ⓒ>ⓓ,ⓔ>ⓕ |
ⓑ
1min |
113.0
±20.0 |
115.0
±19.5 |
115.9
±17.7 |
112.8
±17.2 |
113.3
±16.3 |
115.1
±16.9 |
108.9
±15.3 |
ⓒ
2min |
92.9
±19.8 |
95.4
±21.3 |
97.6
±21.5 |
99.1
±19.8 |
98.3
±18.4 |
100.5
±20.5 |
96.1
±18.2 |
Sets(S) |
.000*** |
①<②=③=④=⑤=⑥>⑦ |
ⓓ
3min |
87.9
±15.2 |
93.0
±15.0 |
96.3
±15.5 |
101.8
±13.1 |
100.3
±12.5 |
99.3
±13.5 |
99.6
±11.2 |
ⓔ
4min |
88.5
±15.0 |
94.0
±15.3 |
99.0
±12.9 |
100.0
±11.6 |
102.6
±8.6 |
101.8
±10.9 |
99.1
±10.7 |
(RI)×(S) |
.540 |
|
ⓕ
5min |
83.0
±14.6 |
88.6
±13.7 |
90.4
±15.2 |
92.8
±17.4 |
94.0
±16.2 |
94.4
±17.6 |
87.9
±13.0 |
| (M±SD), *p<.05, **p<.001, ***p<.001 |
Figure 5.
Post-Comparison Results after rest between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
Figure 5.
Post-Comparison Results after rest between Sets by Rest Interval (beats/min).
3.2.3. Heart rate recovery rate (%)
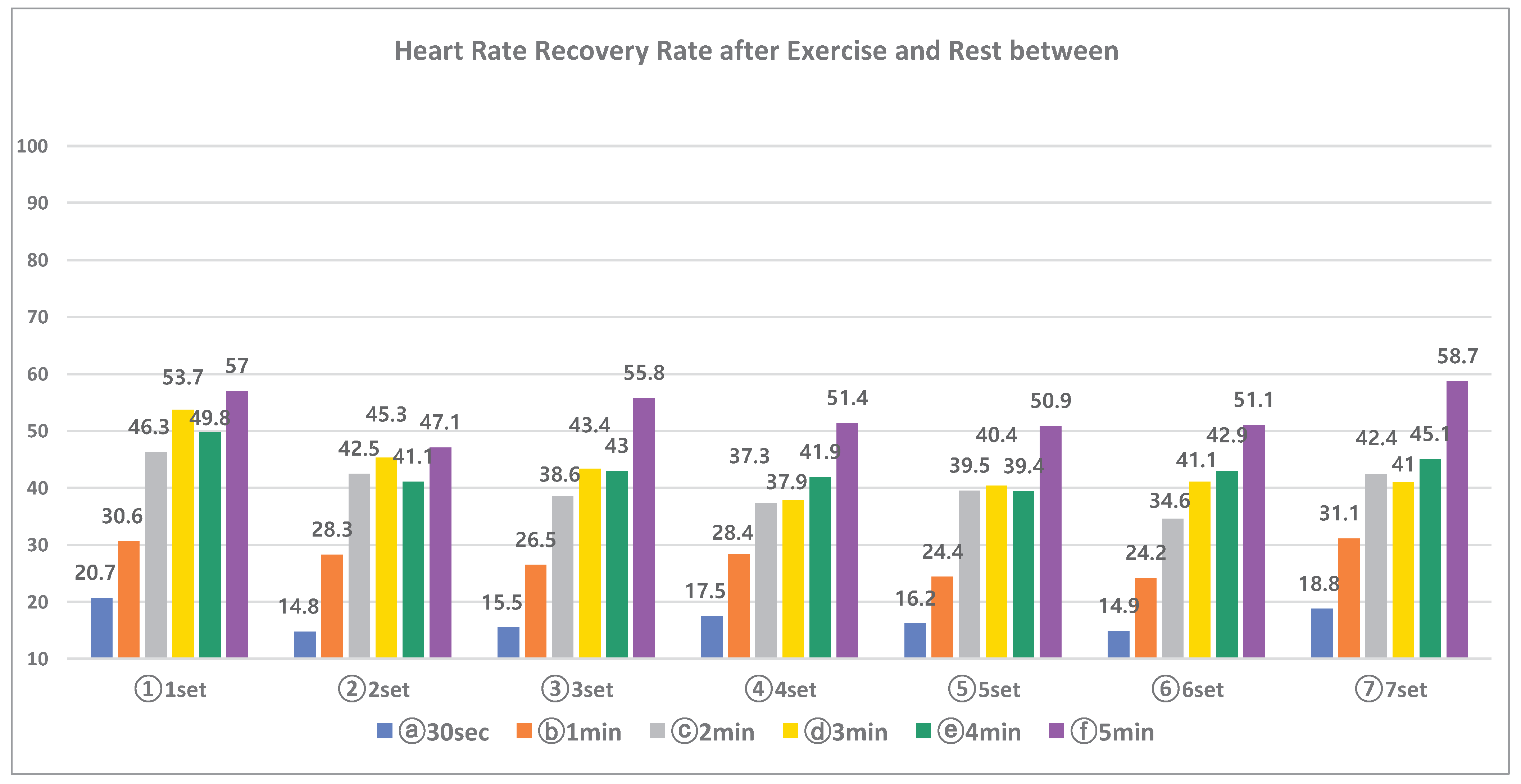
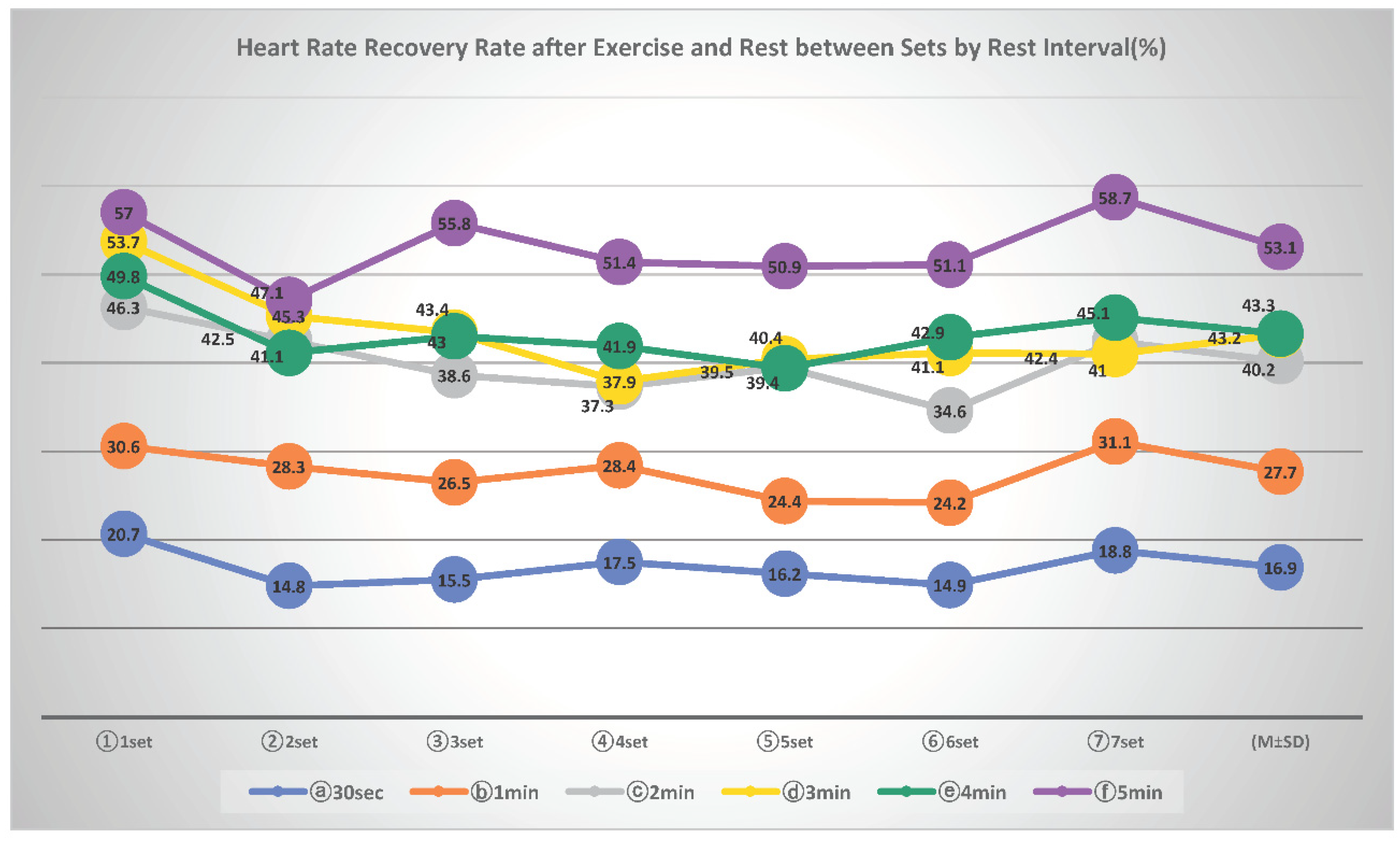
The result of the change of heart rate recovery rate according to the rest interval six conditions and seven sets is the same as <
Table 6>. The heart rate recovery rate (%) was calculated by subtracting the heart rate after rest from the heart rate after exercise, multiplying it by 100, and dividing it into the heart rate after rest. The relationship between heart rate recovery rate and exercise performance ability was examined. The recovery rate of heart rate (%) according to the rest interval condition showed statistical significance(p<.039), and the heart rate recovery rate according to the set progression also showed statistical significance in 1 and 2set, 6 and 7set(p<.026). The heart rate recovery rate was fairly constant from 3 to 7 sets in all rest interval conditions, according to post-comparison results for the 30sec and 1min rest interval condition, 1 and 2min rest interval condition, 2min and 3-5set, 3 and 4min rest interval condition, and 4 and 5min rest interval condition.
Table 6.
Post- Comparison of after Exercise and Rest between Sets by Rest Interval (%).
Table 6.
Post- Comparison of after Exercise and Rest between Sets by Rest Interval (%).
Rest
Interval |
①
1set |
②
2set |
③
3set |
④
4set |
⑤
5set |
⑥
6set |
⑦
7set |
(M±SD) |
|
p |
Contrast |
ⓐ
30sec |
20.7 |
14.8 |
15.5 |
17.5 |
16.2 |
14.9 |
18.8 |
16.9±2.2 |
Rest
Interval
(RI) |
.039** |
ⓐ<ⓑ<ⓒ<ⓓⓔⓕ |
ⓑ
1min |
30.6 |
28.3 |
26.5 |
28.4 |
24.4 |
24.2 |
31.1 |
27.7±2.8 |
ⓒ
2min |
46.3 |
42.5 |
38.6 |
37.3 |
39.5 |
34.6 |
42.4 |
40.2±3.9 |
Heart Rate
Recovery
(HRR) |
.026** |
①<②=③=④=⑤=⑥<⑦ |
ⓓ
3min |
53.7 |
45.3 |
43.4 |
37.9 |
40.4 |
41.1 |
41.0 |
43.2±5.2 |
ⓔ
4min |
49.8 |
41.1 |
43.0 |
41.9 |
39.4 |
42.9 |
45.1 |
43.3±3.4 |
(RI)×(HRR) |
.000*** |
|
ⓕ
5min |
57.0 |
47.1 |
55.8 |
51.4 |
50.9 |
51.1 |
58.7 |
53.1±4.1 |
| (M±SD), *p<.05, **p<.001, ***p<.001 |
Figure 6.
Heart Rate Recovery Rate after Exercise and Rest between Sets by Rest Interval (%).
Figure 6.
Heart Rate Recovery Rate after Exercise and Rest between Sets by Rest Interval (%).
4. Discussion
4.1. Change in the number of repetitions for each set of rest interval conditions
The number of repetitions and the performance speed during resistance exercises are strength and inverse correlation [
28]. The exercise performance is relatively fast in low-intensity load compared to high-intensity load, but as the number of repetitions increases, metabolic stress increases, and the speed decreases [
9]. When the rest interval conditions between sets were performed at 75% of one's maximum bench press weight, previous studies on the number of repetitions according to exercise intensity and rest interval conditions [
29] reported that the number of repetitions from 2set after 1 set decreased due to an increase in metabolic stress when the rest interval conditions were performed at 1, 3, and 5min. In the study of [
30], it was reported that it is impossible to continue in 5 sets with 15RM when the rest interval between sets is applied to 30sec, 1, and 2min during resistance exercise. The results of this study were consistent with previous studies, and the short rest interval (30sec, 1, 2, 3min rest interval) was lower than the long rest interval condition (4, 5min rest interval).
However, considering that there are no previous studies that suggested six rest interval conditions during resistance training, the change and ratio of the number of repetitions in
Table 2,
Table 3, and
Figure 3 is judged to indicate the difference in exercise performance and exercise amount level between rest interval conditions during 65%1RM resistance training. In addition, the short rest interval condition was due to the lack of time for physiological recovery such as energy re-compensation [
31,
32] and oxygen transfer in the muscle compared to the long rest interval condition after the set performance. It is thought that the reduction of energy utilization ability and accumulation of metabolic stress caused by this decreased the number of repetitions significantly as the set progressed. As a result of post-comparison according to set and set interval, the number of repetitions according to set interval conditions decreased statistically significantly from 30sec to 1, 2 and 3min, and the 4 and 5min conditions showed similar levels. This is judged to mean the level of energy replenishment [
31,
32] as well as the level of metabolic stress [
33,
34,
35] for each rest interval during resistance exercise at 65% 1RM intensity. Therefore, it was found that energy replenishment through physiological recovery was relatively higher in the long rest interval condition (4, 5min rest interval) compared to the short rest interval condition. In addition, it is believed that this is because it had less effect on the exertion and reduction of mechanical tension [
18] due to metabolic stress caused by exercise performance.
Therefore, it is thought that the decrease in the number of repetitions was different as the set progressed. This suggests that the set performance under short rest intervals between sets can cause high metabolic stress levels, which can affect muscle endurance improvement. However, based on the assumption that incomplete recovery and next exercise performance are prerequisites for endurance training improvement, 30sec and 1 min rest interval conditions are the mechanical tension efficiency by metabolic stress [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38] is low, so there is a limit to expect muscle endurance improvement. Therefore, it is thought that a 2-3min rest period between sets during 65%1RM bench press exercise can be suggested as muscular endurance training.
On the other hand, there was no difference in muscle size between the circumstances in [
21]'s study on adaptation to muscular hypertrophy, which examined two exercise intensity conditions under 60%1RM (Below 60%1RM) and over 60%1RM (Above 60%1RM). This suggests that exercise load is not a factor that determines the increase in muscle mass, and that the effective factors for improving muscle hypertrophy are failure of muscle contraction through maximum effort and the number of repetitions.
Therefore, the most number of repetitions of each set in the relatively long rest time conditions (4, 5min) of this study is thought to be consistent with the previous studies, and it is considered that it can be proposed as a rest interval of the muscle hypertrophy improvement program using 65%1RM intensity.
In conclusion, it is considered that muscle hypertrophy and endurance training will be possible according to the application of rest intervals between sets during resistance training using 65%1RM identical load. Exercise intensity and rest interval between sets are important factors for resistance exercise program [
39] are considered to be able to support the claim.
4.2. Changes in heart rate and heart rate recovery rate (%) immediately after exercise and after rest for each set of rest interval conditions
The strength of muscle contraction affects the size and speed of heart rate increase, and the increase of exercise intensity affects heart rate and stroke volume, and the higher the exercise intensity, the more heart rate response is shown [
12]. In addition, heart rate and cardiac output respond differently according to the nutrient and oxygen demand of cells in the environment of various exercise conditions [
40]. According to the study's rest interval conditions in between sets, the heart rate was not statistically significant immediately following exercise, and there was no interaction impact either. This result is thought to be because it was measured immediately after the exercise was performed with the maximum effort using the same exercise intensity(65%1RM). However, the heart rate after exercise according to the set showed statistical significance(p<.005).
As a result of post-comparison, the heart rate was maintained similarly in 30sec and 1min rest intervals, the 2 and 3min rest interval condition was maintained or increased, and the 4 and 5min rest time condition was continuously increased. This is because the heart rate immediately after exercise by the maximum repetition (effort) performance from the first set, so it is thought that there is no significant difference between all rest interval conditions. In addition, the short rest interval condition (30sec, 1min) is a relatively short time to recover metabolic stress increased by the maximum set exercise, so it is thought that the heart rate was maintained high immediately after exercise even though the number of repetitions decreased according to the set progression. This means the maximum heart rate of physiological recovery response to metabolic stress in short rest interval conditions when 65%1RM bench press exercise is performed. In addition, the heart rate after exercise of 2 and 3min rest interval condition was maintained or increased, and the heart rate after exercise of 4 and 5min rest interval condition gradually increased. This is thought to explain that the response phenomenon of increasing stroke volume without increasing heart rate (contraction frequency) at the same time as starting exercise is maintained up to 3set under the conditions of 2, 3, 4, and 5min of rest. After that, it is thought that the heart rate increased immediately after exercise due to the increase in the number of repetitions and the increase in accumulated metabolic stress.
On the other hand, there was a significant difference in the heart rate after rest and the heart rate after rest according to the set progression according to the rest interval condition, and there was a significant difference in the rest interval condition and the interaction effect between the sets. This is thought to indicate high metabolic stress levels and low physiological recovery levels in relatively short rest interval conditions. As the set progresses at the same time, the ratio of energy required for recovery was higher than that of long rest interval conditions than that of the energy used for muscle contraction [
31,
32].
The average heart rate recovery rate (%) according to the rest interval condition was 16.9±2.2% in the 30sec rest interval condition, 27.7±2.83% in the 1min rest interval condition, 40.2±3.9% in the 2min rest interval condition, and 43.2±5.2% in the 3min rest interval condition, 43.3 ± 3.4% in the 4min rest interval condition and 53.1 ± 4.1% in the 5min rest interval condition, and the heart rate recovery rate in the relatively long rest interval (3, 4, 5min) conditions was higher than the short rest interval (30sec, 1, 2min) conditions. As shown in
Figure 7 and
Figure 8, the heart rate recovery rate (%) and repetition rate (%) according to the rest interval condition and the set is the rate of repetition number of all rest interval conditions after performing 1set of exercises. 35%, 23%, 19%, 16%, 15.5%, and 15.5% were shown, 48.5%, 33.7%, 26.2%, 22.3%, 21.3%, 21.3%, 2min rest interval condition 64.4%, 47.8%, 42.9%, 39%, 36.1%, 35.6%, 73%, 56.4%, 49.5%, 40.7%, 41.2%, 36.8%, and 83.3 at the 4min rest interval condition %, 69.1%, 59.3%, 57.8%, 53.9, 49.5%, and 88.9%, 76.7%, 70%, 62.6%, 58.3%, and 52.4% in the 5min rest interval condition. Afterward, as the set progressed, the ratio of the number of repetitions increased as the heart rate recovery ratio between the rest interval conditions increased. This difference can be explained by the previous study that the relatively long rest interval between sets during resistance exercise can perform a lot of exercise [
35] because there is enough time to supplement energy compared to the short rest interval, and it is considered to indirectly infer the difference of metabolic stress between each rest interval condition. A decrease in relative muscle strength for absolute muscle strength results from the short rest interval conditions' low heart rate recovery rate, which also means that metabolic stress accumulation [
31,
32] is relatively high as the set progresses. This is different from the relatively long rest interval conditions, which are thought to have decreased exercise performance (number of repetitions) from the start of the set.
5. Conclusions
In this study, 8 students who had more than 6 months of resistance exercise experience at C university were selected and the number of repetitions, heart rate (after exercise, after rest), and heart rate recovery rate (%) according to 6 rest interval conditions were examined when performing 65%1RM bench press.
First, the lower heart rate recovery rate (%) of the short rest interval condition than the long rest interval condition showed that the rate of energy used for physiological recovery was higher than the rate of energy available in the next set, and the decrease in the number of repetitions was higher as the set progressed. Hence, it is considered that applying short rest interval conditions (30sec, 1min) with low heart rate recovery rate (%) to the muscular endurance training program will have limitations in terms of volume (number of repetitions) and energy use.
Second, considering that incomplete recovery between sets during resistance training is a prerequisite for muscle endurance improvement, it is thought that the 2-3min rest interval condition during the 65%1RM bench press resistance training conducted in this study can be effective in improving muscle endurance. In addition, the long rest interval (4, 5min), which showed the highest number of repetitions with a relatively high energy recovery level, is considered to be effective in applying the muscle hypertrophy exercise program, which is positively correlated with exercise volume(volume load or Dose-response relationship). However, it is judged that the long-term resistance training program applying the inter-set rest interval(2, 3, 4, 5min) under the load intensity of 65%1RM is likely to affect all muscle hypertrophy improvements.
References
- Rhea MR, Alvar BA, Burkett LN. Single versus multiple sets for strength: a meta-analysis to address the controversy. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2002.73(4):pp. 485–8. [CrossRef]
- Rhea, M. R., Alvar, B. A., Burkett, L. N., & Ball, S. D. A meta-analysis to determine the dose response for strength development. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 2003.35(3), pp. 456-464. [CrossRef]
- Wernbom M, Augustsson J, Thomee´ R. The influence of frequency, intensity, volume and mode of strength training on whole muscle cross-sectional area in humans. Sports Med. 2007.37(3): pp. 225–64. [CrossRef]
- American College of Sports Medicine. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Progression models in resistance training for healthy adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009.41(3):pp.687–708. [CrossRef]
- Ahtiainen JP, Pakarinen A, Alen M, et al. Short vs. long rest period between the sets in hypertrophic resistance training: influence on muscle strength, size, and hormonal adaptations in trained men. J Strength Cond Res. 2005.19(3):pp 572–82. [CrossRef]
- Willardson, J.M. A brief review: factors affecting the length of the rest interval between resistance exercise sets. J Strength Cond Res.2006. 20(4):pp.978–84. [CrossRef]
- De Salles BF, Sima˜o R, Miranda F, et al. Rest interval between sets in strength training. Sports Med. 2009.39(9):pp.765–77. [CrossRef]
- SCHOENFELD, Brad J. The mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application to resistance training. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, 2010.24.10: pp.2857-2872. [CrossRef]
- Bompa, T.O. , & Buzzichelli, C. Periodization-: theory and methodology of training. Human kinetics. 2018.
- Schoenfeld, BJ, Contreras, B, Willardson, JM, Fontana, F, and Tiryaki-Sonmez, G. Muscle activation during low- versus high-load resistance training in well-trained men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014.114: pp.2491-2497. [CrossRef]
- Durand, RJ, Castracane, VD, Hollander, DB, Tryniecki, JL, Bamman, MM, O’Neal, S, Hebert, EP, and Kraemer, RR. Hormonal responses from concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003.35: pp.937-943. [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vidotti HG, Mendes RG, Simoes RP, Castello-Simoes V, Catai AM, Borghi-Silva A. Cardiac autonomic responses during upper versus lower limb resistance exercise in healthy elderly men. Braz J Phys Ther; 2014.18: pp.9–18. [CrossRef]
- Imai, K. , Sato, H., Hori, M., Kusuoka, H., Ozaki, H., Yokoyama, H.,... & Kamada, T. Vagally mediated heart rate recovery after exercise is accelerated in athletes but blunted in patients with chronic heart failure. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 1994.24(6), pp.1529-1535. [CrossRef]
- Cole CR, Foody JM, Blackstone EH, Lauer MS. Heart rate recovery after submaximal exercise testing as a predictor of mortality in a cardiovascular healthy cohort. Ann Intern Med. 2000.132:pp.552–555. [CrossRef]
- Morshedi-Meibodi A, Larson MG, Levy D, O'Donnell CJ, Vasan RS. Heart rate recovery after treadmill exercise testing and risk of cardiovascular disease events (the Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2002.90:pp.848–852. [CrossRef]
- Byung-ro Kim, Seol-joong Kang, & Lee Dong-gyu. Cardiopulmonary function and heart rate recovery response in obese adolescents after maximal exercise. Kinesiology, 2010.19(1), pp.89-96.
- Kraemer, W.J. A series of studies: the physiological basis for strength training in American football: fact over philosophy. J Strength Cond Res 1997.11: pp.131-134. [CrossRef]
- Ratamess, NA, Falvo, MJ, Mangine, GT, Hoffman, JR, Faigenbaum, AD, and Kang, J. The effect of rest interval length on metabolic responses to the bench press exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007.100:pp.1-17. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, G, Mcloughlin, G, Bissas, A, and Ispoglou, T. Do the acute biochemical and neuromuscular responses justify the classification of strength and hypertrophy-type resistance exercise J. Strength Cond Res. 2014. [CrossRef]
- KRAEMER, William J.; RATAMESS, Nicholas A. Fundamentals of resistance training: progression and exercise prescription. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 2004.36.4: pp.674-688. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, BJ, Grgic, J, Ogborn, D, and Krieger, JW. Strength and Hypertrophy Adaptations Between Low- vs. High-Load Resistance Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Strength Cond Res. 2017.31: pp.3508-3523. [CrossRef]
- Salles, B., Simao, R., Miranda, F., da Silva Novaes, J., Lemos, A., & Willardson, J. M. Rest interval between sets in strength training. Sports medicine, 2009.39(9), pp.765-777. [CrossRef]
- Burgomaster, K.A. , Howarth, K. R., Phillips, S. M., Rakobowchuk, M., MacDonald, M. J., McGee, S. L., & Gibala, M. J. Similar metabolic adaptations during exercise after low volume sprint interval and traditional endurance training in humans. The Journal of physiology, 2008.586.1: pp.151-160. [CrossRef]
- Willardson, J.M. , & Burkett, L. N. The effect of rest interval length on the sustainability of squat and bench press repetitions. The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research, 2006.20(2), pp.400-403.
- De Souza, TP,Jr, Fleck, SJ, Simao, R, Dubas, JP, Pereira, B, de Brito Pacheco, EM, da Silva, AC, and de Oliveira, PR. Comparison between constant and decreasing rest intervals: influence on maximal strength and hypertrophy. J. Strength Cond Res. 2010. 24: pp.1843-1850. [CrossRef]
- Abdessemed, D, Duche, P, Hautier, C, Poumarat, G, and Bedu, M. Effect of recovery duration on muscular power and blood lactate during the bench press exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999. 20:pp.368-373. [CrossRef]
- FINN, Mary E. Investigation of the NSCA minimal readiness standards for upper extremity strength, speed, and performance of high intensity plyometrics in NCAA college athletes. University of South Alabama, 2015.
- KRAEMER, WILLIAM J., et al. Changes in muscle hypertrophy in women with periodized resistance training. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 2004.36.4: pp.697-708. [CrossRef]
- HASS, Christopher J.; FEIGENBAUM, Matthew S.; FRANKLIN, Barry A. Prescription of resistance training for healthy populations. Sports medicine, 2001.31.14: 953-964. [CrossRef]
- WILLARDSON, Jeffrey M. A brief review: factors affecting the length of the rest interval between resistance exercise sets. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2006.20.4: pp.978. [CrossRef]
- Pincivero, D.M. , Lephart S.M., and Karunakara R. G. Effects of rest interval on isokinetic strength and functional performance after short term high intensity training. Br J Sports Med, 1997.31: pp.229-234. [CrossRef]
- O'Shea, P. Effects of selected weight training programs on the development of strength and muscle hypertrophy. Research Quarterly. 2000. [CrossRef]
- Schott, J, McCully, K, and Rutherford, OM. The role of metabolites in strength training. II. Short versus long isometric contractions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1995.71: pp.337-341. [CrossRef]
- Smith, RC, and Rutherford, OM. The role of metabolites in strength training. I. A comparison of eccentric and concentric contractions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1995.71: pp.332-336. [CrossRef]
- Suga, T, Okita, K, Morita, N, Yokota, T, Hirabayashi, K, Horiuchi, M, Takada, S, Takahashi, T, Omokawa, M, Kinugawa, S, and Tsutsui, H. Intramuscular metabolism during low-intensity resistance exercise with blood flow restriction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009.106: pp.1119-1124. [CrossRef]
- Tesch, PA, Colliander, EB, and Kaiser, P. Muscle metabolism during intense, heavy-resistance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1986.55: pp.362-366. [CrossRef]
- Rooney, KJ, Herbert, RD, and Balnave, RJ. Fatigue contributes to the strength training stimulus. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1994.26: pp.1160-1164. [CrossRef]
- Suga, T, Okita, K, Morita, N, Yokota, T, Hirabayashi, K, Horiuchi, M, Takada, S, Omokawa, M, Kinugawa, S, and Tsutsui, H. Dose effect on intramuscular metabolic stress during low-intensity resistance exercise with blood flow restriction. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010.108: pp.1563-1567. [CrossRef]
- Gordan, R. , Gwathmey, J. K., & Xie, L. H. Autonomic and endocrine control of cardiovascular function. World journal of cardiology, 2015.7(4), pp.204. [CrossRef]
- Bottaro, M. , Martins, B., Gentil, P., & Wagner, D. Effects of rest duration between sets of resistance training on acute hormonal responses in trained women. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport, 2009. 12(1), pp.73-78. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).