Submitted:
18 June 2023
Posted:
19 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Hardaliye Samples
2.2. Microbial Cultures
2.3. High Hydrostatic Pressure
2.4. Measurement of Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Measurement of Bioactive Properties
2.6. Inactivation of Endogenous Microflora
2.7. Sensory Analyses
2.8. Shelf-life Studies
2.9. Experimental Design
2.10. Optimization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in the Properties of Hardaliye Processed by High Hydrostatic Pressure
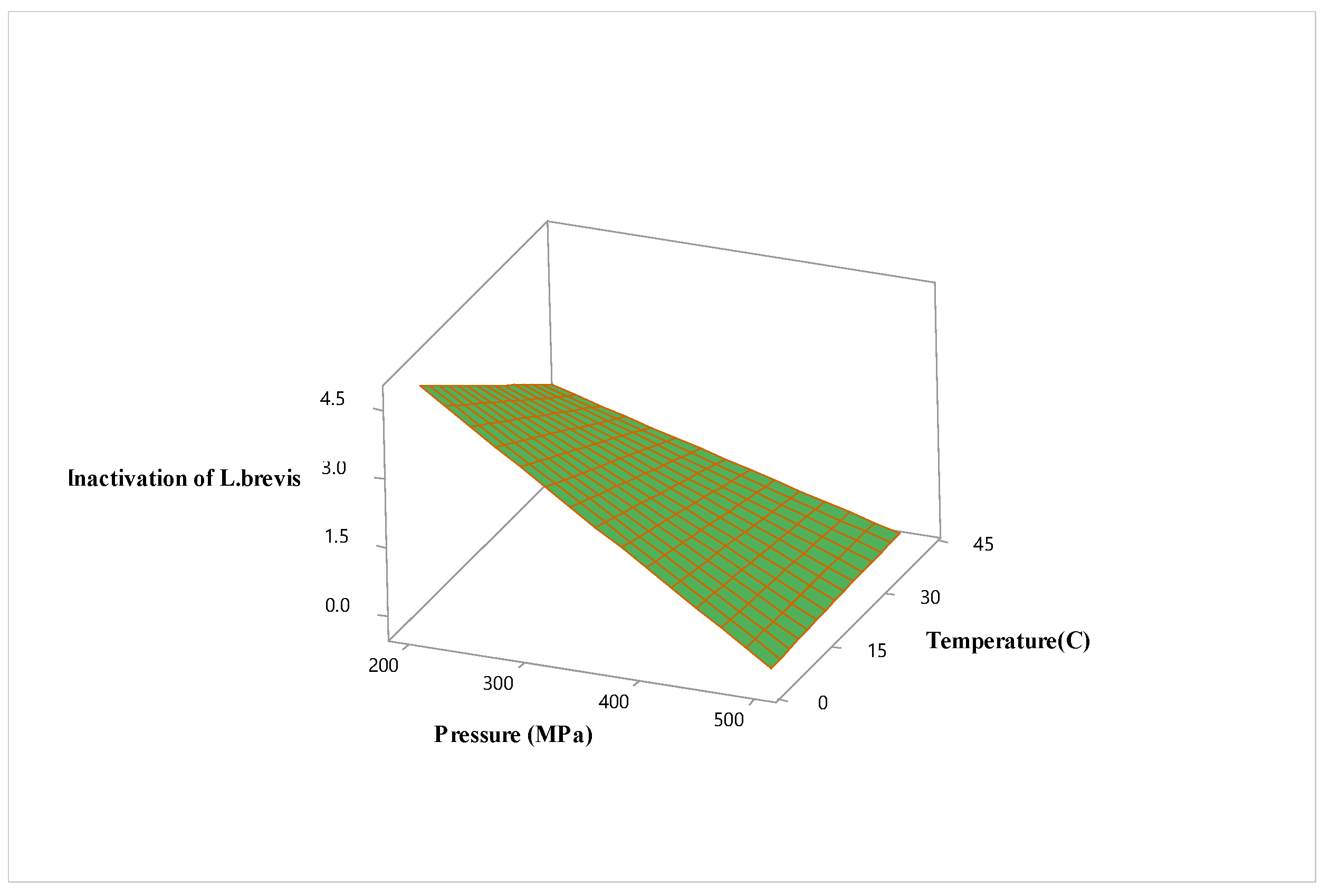
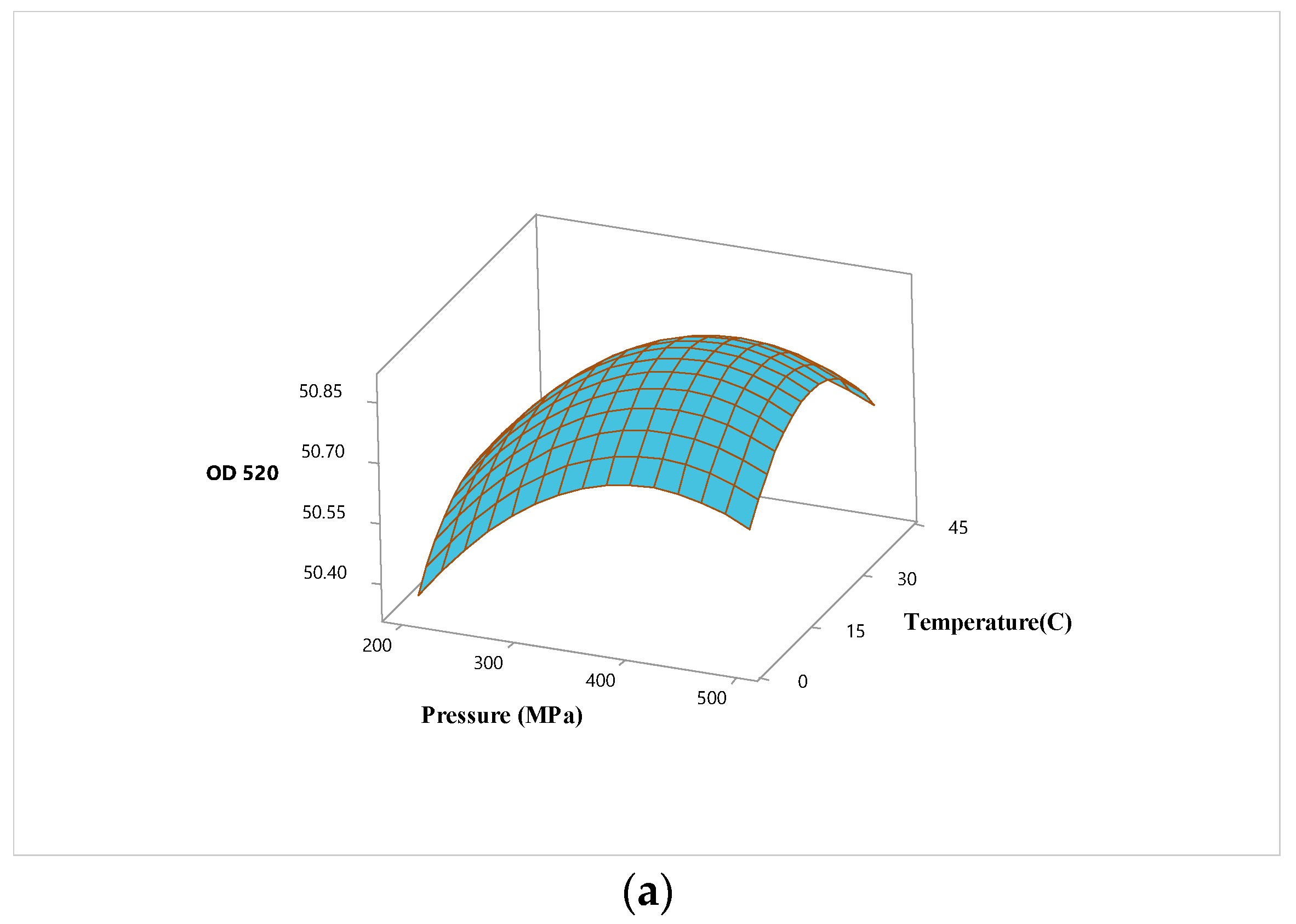
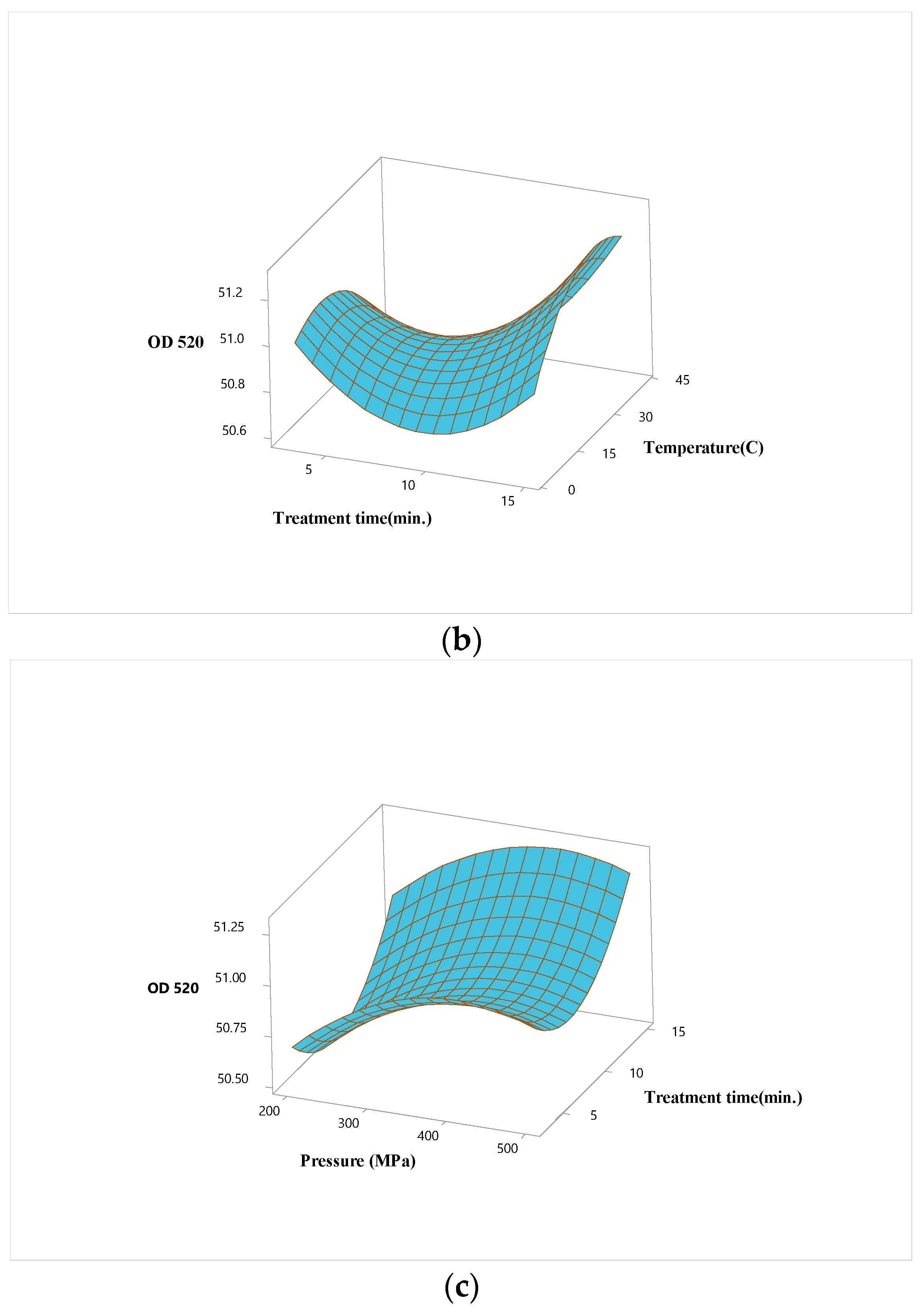
3.2. Optimization of High Hydrostatic Pressure Conditions for Hardaliye Drink
3.3. Shelf-life Studies of Hardaliye Drink
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arici, M.; Coskun, F. Hardaliye: Fermented Grape Juice as a Traditional Turkish Beverage. Food Microbiology 2001, 18, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, F.C.; Parada, J.L.; Pandey, A.; Soccol, C.R. Trends in Non-Dairy Probiotic Beverages. Food Research International 2008, 41, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiray, M. Geleneksel hardaliye içeceğinin yenilikçi proses teknolojileri ile pastörizasyonu. masterThesis, Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ates, C.; Akdemir Evrendilek, G.; Uzuner, S. High-Pressure Processing of Shalgam with Respect to Quality Characteristics, Microbial Inactivation, and Shelflife Extension. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2021, 45, e15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Beltrán, J.A.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing of Fruit and Vegetable Products. Food Reviews International 2005, 21, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inada, K.O.; Torres, A.G.; Perrone, D.; Monteiro, M. High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Affects the Phenolic Profile, Preserves Sensory Attributes and Ensures Microbial Quality of Jabuticaba (Myrciaria Jaboticaba) Juice. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2018, 98, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Roque, M.J.; de Ancos, B.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Cano, M.P.; Elez-Martínez, P.; Martín-Belloso, O. Impact of Food Matrix and Processing on the in Vitro Bioaccessibility of Vitamin C, Phenolic Compounds, and Hydrophilic Antioxidant Activity from Fruit Juice-Based Beverages. Journal of Functional Foods 2015, 14, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, N.; Si, X.; Pang, X.; Lv, J.; Zhang, S. Preparation and Quality Assessment of Processed Cream Cheese by High Hydrostatic Pressure Combined Thermal Processing and Spore-Induced Germination. Journal of Food Engineering 2023, 341, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elez-Martínez, P.; Escolà-Hernández, J.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.C.; Martín-Belloso, O. Inactivation of Lactobacillus Brevis in Orange Juice by High-Intensity Pulsed Electric Fields. Food Microbiology 2005, 22, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wyk, S.; Silva, F.V.M. High Pressure Inactivation of Brettanomyces Bruxellensis in Red Wine. Food Microbiology 2017, 63, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, E.; Dubourdieu, D.; Darriet, P. Characterization of Key-Aroma Compounds of Botrytized Wines, Influence of Grape Botrytization. Food Chemistry 2007, 103, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Jana, M.L.; Sengupta, D.; Naskar, A.K. A Note on the Estimation of Microbial Glycosidase Activities by Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2000, 53, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdemir Evrendilek, G.; Tanriverdi, H.; Demir, I.; Uzuner, S. Shelf-Life Extension of Traditional Licorice Root “Sherbet” with a Novel Pulsed Electric Field Processing. Frontiers in Food Science and Technology 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir Evrendilek, G.; Bakay, S.; Uzuner, S. High Pressure Processing of Licorice Drink with Respect to Quality Characteristics, Microbial Inactivation, and Shelf-Life Extension. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2021, 45, e15465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, M.; Esİn, Y.; Kaya, C.; İlhan, M.; Akın, G.; Etdöğer, R. Determination of some properties of hardaliye produced with Müșküle grapes by traditional method. Akademik Gida 2015, 13, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- AŞKIN, B.; ATİK, A. Color, Phenolic Composition, and Antioxidant Properties of Hardaliye(Fermented Grape Beverage) under Different Storage Conditions. Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 2016, 40, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Wu, S.-J.; Shyu, Y.-T. Quality Changes in High Hydrostatic Pressure and Thermal Pasteurized Grapefruit Juice during Cold Storage. J Food Sci Technol 2018, 55, 5115–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Ossandón, M.J.; Castillo, L.; Ah-Hen, K.S.; Vega-Gálvez, A. Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure Processing on Phytochemicals, Antioxidant Activity, and Behavior of Botrytis Cinerea in White Grape Juice Concentrate. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2020, 44, e14864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pan, S.; Chen, J.; Pang, X.; Guo, X.; Gao, L.; Liao, X.; Wu, J. Comparing the Effects of High Hydrostatic Pressure and Ultrahigh Temperature on Quality and Shelf Life of Cloudy Ginger Juice. Food Bioprocess Technol 2016, 9, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Process | Proses code |
Pressure (P, MPa) |
Treatment time (t, min) |
Temperature (T, °C) |
pH |
Titratable acidity (g/L) |
TSS (°Brix) |
Conductivity (mS/cm) |
Turbidity (NTU) |
Reducing sugar (g/L) |
| Control | Kontrol | ̶ | ̶ | ̶ | 3.80 ± 0.00ef | 5.80 ± 0.09ab | 27.02 ± 0.17a | 3.61 ± 0.02f | 862.89 ± 3.97a | 220.32 ± 2.07bcde |
| HHP1 | YHB1 | 350 | 3 | 40 | 3.78 ± 0.00g | 5.35 ± 0.17cdef | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.67 ± 0.03bc | 439.53 ± 2.521c | 211.39 ± 7.29de |
| HHP2 | YHB2 | 200 | 3 | 22 | 3.80 ± 0.01ef | 5.55 ± 0.15abcde | 27.02 ± 0.04a | 3.67 ± 0.02bc | 359.41 ± 2.09fgh | 242.50 ± 12.54abc |
| HHP3 | YHB3 | 350 | 15 | 40 | 3.81 ± 0.00bcde | 5.65 ± 0.17abc | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.62 ± 0.01ef | 340.48 ± 1.27ı | 227.66 ± 8.58abcde |
| HHP4 | YHB4 | 350 | 9 | 22 | 3.79 ± 0.01f | 5.50 ± 0.179abcde | 27.02 ± 0.04a | 3.69 ± 0.0b | 357.27 ± 1.90h | 245.41 ± 17.56ab |
| HHP5 | YHB5 | 200 | 15 | 22 | 3.80 ± 0.00def | 5.65 ± 0.09abc | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.64 ± 0.03cdef | 373.92 ± 2.02de | 226.79 ± 5.78bcde |
| HHP6 | YHB6 | 350 | 3 | 4 | 3.80 ± 0.00cdef | 5.20 ± 0.09def | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.63 ± 0.03cdef | 373.84 ± 2.77de | 218.99 ± 3.95cde |
| HHP7 | YHB7 | 500 | 3 | 22 | 3.80 ± 0.00cdef | 5.30 ± 0.09cdef | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.65 ± 0.06cdef | 369.98 ± 4.52defg | 219.56 ± 3.46bcde |
| HHP8 | YHB8 | 350 | 15 | 4 | 3.81 ± 0.00abcd | 5.35 ± 0.23cdef | 26.87 ± 0.12a | 3.62 ± 0.01ef | 358.90 ± 2.90gh | 208.32 ± 1.52e |
| HHP9 | YHB9 | 500 | 9 | 4 | 3.80 ± 0.00cdef | 5.60 ± 0.23abcd | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.67 ± 0.01bc | 482.19 ± 10.91b | 253.19 ± 5.36a |
| HHP10 | YHB10 | 350 | 9 | 22 | 3.82 ± 0.00ab | 4.95 ± 0.00f | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.70 ± 0.01b | 363.84 ± 2.46efgh | 220.43 ± 8.72bcde |
| HHP11 | YHB11 | 500 | 15 | 22 | 3.82 ± 0.00a | 5.25 ± 0.15cdef | 26.89 ± 0.10a | 3.62 ± 0.01def | 381.23 ± 1.10d | 238.74 ± 11.61abc |
| HHP12 | YHB12 | 200 | 9 | 40 | 3.81 ± 0.01bcdef | 5.15 ± 0.09ef | 26.89 ± 0.10a | 3.76 ± 0.05a | 371.21 ± 3.98def | 237.30 ± 5.99abcd |
| HHP13 | YHB13 | 200 | 9 | 4 | 3.81 ± 0.00abc | 5.90 ± 0.17a | 26.98 ± 0.04a | 3.67 ± 0.02bcd | 479.29 ± 5.00b | 232.14 ± 3.06abcde |
| HHP14 | YHB14 | 500 | 9 | 40 | 3.81 ± 0.00bcde | 5.45 ± 0.09bcde | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.78 ± 0.01a | 370.57 ± 0.97defg | 238.21 ± 13.99abc |
| HHP15 | YHB15 | 350 | 9 | 22 | 3.82 ± 0.00a | 5.45 ± 0.17bcde | 27.00 ± 0.00a | 3.66 ± 0.01bcde | 364.69 ± 3.77efgh | 228.44 ± 8.17abcde |
| Process | L* | a* | b* | C* | h0 | ΔE |
Color intensity (IC) |
Color tone | %OD420 | %OD520 | %OD620 |
| Control | 3.33 ± 0.22ab | 8.37 ± 0.76b | 0.95 ± 0.26abcd | 8.44 ± 0.71b | 0.12 ± 0.04bcde | ― | 4.85 ± 0.01ab | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.44 ± 0.04b | 50.41 ± 0.09de | 28.15 ± 0.08ab |
| HHP1 | 2.89 ± 0.28abcde | 8.74 ± 0.44ab | 0.63 ± 0.32cd | 8.77 ± 0.47ab | 0.07 ± 0.03de | 0.75 ± 0.11bc | 4.85 ± 0.01abc | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.60 ± 0.11ab | 50.57 ± 0.16cde | 27.83 ± 0.06bcd |
| HHP2 | 2.22 ± 0.08de | 8.14 ± 0.82b | 1.67 ± 0.32ab | 8.32 ± 0.86b | 0.20 ± 0.02a | 1.62 ± 0.15abc | 4.79 ± 0.02d | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.61 ± 0.07ab | 50.73 ± 0.25bcde | 27.65 ± 0.26cdef |
| HHP3 | 2.33 ± 0.10de | 8.71 ± 1.15ab | 1.71 ± 0.52a | 8.89 ± 1.23ab | 0.19 ± 0.03ab | 1.607 ± 0.48abc | 4.74 ± 0.01e | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 21.48 ± 0.27ab | 51.28 ± 0.20a | 27.24 ± 0.24fg |
| HHP4 | 2.35 ± 0.19de | 9.07 ± 1.06ab | 1.73 ± 0.41a | 9.24 ± 1.12ab | 0.19 ± 0.02ab | 1.58 ± 0.40abc | 4.81 ± 0.01bcd | 0.42 ± 0.01ab | 21.64 ± 0.29ab | 50.91 ± 0.36abcd | 27.46 ± 0.20defg |
| HHP5 | 3.27 ± 0.09abc | 10.64 ± 1.11a | 1.74 ± 0.49a | 10.78 ± 1.17a | 0.16 ± 0.03abc | 2.08 ± 1.19a | 4.80 ± 0.03cd | 0.43 ± 0.01ab | 21.76 ± 0.31ab | 50.89 ± 0.12abcd | 27.35 ± 0.23efg |
| HHP6 | 2.29 ± 0.09de | 8.08 ± 0.59b | 1.47 ± 0.17abc | 8.23 ± 0.60b | 0.18 ± 0.01ab | 1.41 ± 0.17abc | 4.79 ± 0.01d | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.78 ± 0.12ab | 50.91 ± 0.11abcd | 27.31 ± 0.12fg |
| HHP7 | 3.50 ± 0.49a | 8.72 ± 0.76ab | 0.61 ± 0.44cd | 8.75 ± 0.79ab | 0.07 ± 0.04de | 0.93 ± 0.01abc | 4.81 ± 0.01cd | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.58 ± 0.17ab | 51.09 ± 0.07ab | 27.32 ± 0.14fg |
| HHP8 | 2.31 ± 0.13de | 7.95 ± 0.13b | 0.70 ± 0.06cd | 7.99 ± 0.12b | 0.09 ± 0.01cde | 1.33 ± 0.12abc | 4.80 ± 0.03cd | 0.43 ± 0.01ab | 21.64 ± 0.17ab | 51.03 ± 0.22abc | 27.34 ± 0.06fg |
| HHP9 | 3.55 ± 0.81a | 8.36 ± 0.57b | 0.99 ± 0.16abcd | 8.43 ± 0.57b | 0.12 ± 0.02bcde | 0.95 ± 0.318abc | 4.81 ± 0.01bcd | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.53 ± 0.14ab | 50.61 ± 0.19bcde | 27.86 ± 0.11bcd |
| HHP10 | 2.38 ± 0.09de | 8.14 ± 0.40b | 0.85 ± 0.26abcd | 8.19 ± 0.42b | 0.10 ± 0.03cde | 1.18 ± 0.31abc | 4.82 ± 0.01bcd | 0.42 ± 0.00ab | 21.48 ± 0.04ab | 50.84 ± 0.07abcd | 27.68 ± 0.10cdef |
| HHP11 | 3.46 ± 0.21a | 8.84 ± 0.50ab | 0.43 ± 0.08d | 8.85 ± 0.50ab | 0.05 ± 0.01e | 0.72 ± 0.18bc | 4.80 ± 0.01d | 0.42 ± 0.00b | 21.39 ± 0.13b | 51.09 ± 0.13ab | 27.51 ± 0.08cdefg |
| HHP12 | 2.45 ± 0.27cde | 8.82 ± 0.47ab | 0.82 ± 0.24bcd | 8.86 ± 0.50ab | 0.09 ± 0.03cde | 1.02 ± 0.22abc | 4.84 ± 0.01abcd | 0.42 ± 0.00ab | 21.61 ± 0.15ab | 50.46 ± 0.06de | 27.94 ± 0.16bc |
| HHP13 | 2.97 ± 0.21abcd | 8.41 ± 0.46b | 1.09 ± 0.14abcd | 8.48 ± 0.45b | 0.13 ± 0.01abcd | 0.67 ± 0.33c | 4.87 ± 0.01a | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.36 ± 0.17b | 50.21 ± 0.13e | 28.43 ± 0.06a |
| HHP14 | 2.05 ± 0.04e | 7.38 ± 0.29b | 1.18 ± 0.11abcd | 7.48 ± 0.30b | 0.16 ± 0.01abc | 1.90 ± 0.23ab | 4.84 ± 0.02abcd | 0.43 ± 0.00ab | 21.53 ± 0.12ab | 50.68 ± 0.11bcde | 27.79 ± 0.19bcde |
| HHP15 | 2.56 ± 0.07bcde | 8.41 ± 0.23b | 1.25 ± 0.19abcd | 8.51 ± 0.21b | 0.15 ± 0.02abc | 0.94 ± 0.14abc | 4.81 ± 0.02bcd | 0.43 ± 0.01a | 21.97 ± 0.19a | 50.83 ± 0.18abcd | 27.19 ± 0.062g |
| Process | TPSC (mg/L) | TAC (%) | TMAC (mg/L) |
| Control | 2310.02 ± 22.91abc | 70.20 ± 0.91a | 126.91 ± 9.30b |
| HHP1 | 2222.18 ± 36.64c | 71.09 ± 0.87a | 137.21 ± 8.56ab |
| HHP2 | 2312.55 ± 25.87abc | 69.80 ± 0.92a | 133.03 ± 2.92ab |
| HHP3 | 2278.35 ± 14.39bc | 70.03 ± 1.34a | 136.42 ± 6.06ab |
| HHP4 | 2340.01 ± 32.51ab | 71.06 ± 1.36a | 140.04 ± 4.43ab |
| HHP5 | 2236.12 ± 12.31c | 70.75 ± 0.99a | 140.41 ± 2.10ab |
| HHP6 | 2332.83 ± 28.64ab | 70.29 ± 0.85a | 135.12 ± 2.29ab |
| HHP7 | 2348.03 ± 30.49ab | 70.79 ± 0.94a | 131.23 ± 9.34ab |
| HHP8 | 2351.83 ± 33.21ab | 68.95 ± 0.26a | 123.25 ± 1.12b |
| HHP9 | 2382.24 ± 17.14a | 69.51 ± 0.77a | 130.53 ± 4.26ab |
| HHP10 | 2277.93 ± 47.65bc | 69.57 ± 0.86a | 137.63 ± 8.94ab |
| HHP11 | 2346.76 ± 45.35ab | 69.81 ± 0.71a | 139.25 ± 7.98ab |
| HHP12 | 2347.61 ± 27.65ab | 69.61 ± 0.87a | 133.17 ± 3.57ab |
| HHP13 | 2302.84 ± 37.46abc | 69.97 ± 0.89a | 128.58 ± 15.18ab |
| HHP14 | 2236.12 ± 12.04c | 68.91 ± 1.02a | 130.67 ± 10.85ab |
| HHP15 | 2290.38 ± 18.81abc | 69.07 ± 0.89a | 150.71 ± 7.34a |
| Process |
TMAB inactivation (log cfu/mL) |
TMY inactivation (log cfu/mL) |
Brettanomyces bruxellensis inactivation (log cfu/mL) |
Lactobacillus brevis inactivation (log cfu/mL) |
| Control | ̶ | ‒ | - | - |
| HHP1 | 3.06 ± 0.04d | 3.21 ± 0.00b | 0.56 ± 0.42e | 1.57 ± 0.23cd |
| HHP2 | 0.46 ± 0.04k | 0.57 ± 0.06h | 0.50 ± 0.30e | 0.16 ± 0.03g |
| HHP3 | 5.10 ± 0.00a | 4.21 ± 0.00a | 4.36 ± 0.43a | 3.94 ± 0.48b |
| HHP4 | 2.56 ± 0.05ef | 2.73 ± 0.03c | 0.92 ± 0.45cde | 1.77 ± 0.30cd |
| HHP5 | 1.10 ± 0.03j | 1.17 ± 0.05g | 0.75 ± 0.42de | 0.75 ± 0.23efg |
| HHP6 | 2.36 ± 0.04g | 2.51 ± 0.05e | 0.53 ± 0.44e | 1.13 ± 0.14def |
| HHP7 | 4.10 ± 0.00b | 4.21 ± 0.00a | 4.38 ± 0.40a | 5.05 ± 0.22a |
| HHP8 | 3.62 ± 0.03c | 3.21 ± 0.00b | 2.44 ± 0.14b | 1.66 ± 0.61cd |
| HHP9 | 5.10 ± 0.00a | 4.21 ± 0.00a | 5.38 ± 0.68a | 4.05 ± 0.16b |
| HHP10 | 2.56 ± 0.03e | 2.73 ± 0.03c | 2.04 ± 0.16bc | 1.71 ± 0.74cd |
| HHP11 | 4.10 ± 0.00b | 4.21 ± 0.00a | 5.38 ± 0.59a | 5.05 ± 0.18a |
| HHP12 | 1.76 ± 0.05h | 1.77 ± 0.04f | 1.07 ± 0.84cde | 1.17 ± 0.22de |
| HHP13 | 1.56 ± 0.05ı | 1.69 ± 0.03f | 1.54 ± 0.36bcde | 0.46 ± 0.16fg |
| HHP14 | 5.10 ± 0.00a | 4.21 ± 0.00a | 1.90 ± 0.15a | 5.05 ± 0.38a |
| HHP15 | 2.46 ± 0.03f | 2.61 ± 0.04d | 1.97 ± 0.34bcd | 2.23 ± 0.34c |
| Term | OD520 | Inactivation of Lactobacillus brevis | ||||
| Coeff. | VIF | p value | Coeff. | VIF | p value | |
| Regression | ||||||
| Linear | ||||||
| X1 (P) | 0.148 | 1.00 | 0.000 | -1.754 | 1.00 | 0.000 |
| X2 (T) | -0.645 | 1.00 | 0.012 | |||
| X3 (Trt) | 0.124 | 1.00 | 0.002 | |||
| Square | ||||||
| X1∗X1 | -0.182 | 1.01 | 0.002 | |||
| X2∗X2 | -0.187 | 1.01 | 0.001 | |||
| X3∗X3 | 0.276 | 1.01 | 0.000 | |||
| Interaction | ||||||
| X1∗X2 | 0.731 | 1.00 | 0.040 | |||
| X1∗X3 | ||||||
| X2∗X3 | 0.151 | 1.00 | 0.006 | |||
| Lack-of-fit | 0.163 | 0.316 | ||||
| Constant | 50.86 | 0.000 | 1.608 | 0.000 | ||
| R2 | 0.70 | 0.61 | ||||
| R2(adj) | 0.65 | 0.58 | ||||
| R2(pred) | 0.58 | 0.54 | ||||
| Storage temperature | |||||
| 4°C | 22°C | ||||
| pH | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 3.69 ± 0.03Ba | 3.83 ± 0.02Aa | 3.78 ± 0.03A | 3.77 ± 0.03Aa | |
| 15 | 3.52 ± 0.04Bb | 3.85 ± 0.04Aa | 3.76 ± 0.04Ab | ||
| 30 | 3.72 ± 0.03Abc | 3.71 ± 0.02Ab | |||
| 45 | 3.74 ± 0.04 Ab | 3.75 ± 0.03Aab | |||
| 66 | 3.80 ± 0.03 Aab | 3.74 ± 0.03 Aab | |||
| 87 | 3.66 ± 0.09Ac | 3.72 ± 0.07Ab | |||
| 108 | 3.69 ± 0.02Abc | 3.66 ± 0.09Ab | |||
| 142 | 3.68 ± 0.05Abc | ||||
| 180 | 3.68 ± 0.04Abc | ||||
| 228 | 3.69 ± 0.04Abc | ||||
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 3.42 ± 0.03Aa | 3.42 ± 0.03A | 3.43 ± 0.03A | 3.42 ± 0.03Aa | |
| 15 | 3.41 ± 0.03Ba | 3.41 ± 0.03Ba | 3.48 ± 0.05Aa | ||
| 30 | 3.50 ± 0.04A | 3.50 ± 0.04Aa | |||
| 45 | 3.47 ± 0.04Aa | 3.52 ± 0.04Aa | |||
| 66 | 3.51 ± 0.03Aa | 3.52 ± 0.03Aa | |||
| 87 | 3.44 ± 0.03Aa | 3.48 ± 0.04Aa | |||
| 108 | 3.45 ± 0.04Ba | 3.51 ± 0.03Aa | |||
| 142 | 3.42 ± 0.04Aa | ||||
| 180 | 3.42 ± 0.04Aa | ||||
| 228 | 3.47 ± 0.04Aa | ||||
| Color L* | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 11.81 ± 1.64Aa | 11.59 ± 0.93Aa | 9.48 ± 0.84B | 11.81 ± 1.64Aa | |
| 15 | 2.98 ± 0.02Bb | 3.98 ± 0.12Ab | 3.60 ± 0.36Ab | ||
| 30 | 3.79 ± 0.35Ab | 3.67 ± 0.45Ab | |||
| 45 | 3.68 ± 0.33Ab | 3.40 ± 0.43Ab | |||
| 66 | 3.52 ± 0.24Ab | 3.33 ± 0.35Ab | |||
| 87 | 3.52 ± 0.36Ab | 3.10 ± 0.58Ab | |||
| 108 | 3.53 ± 0.25Ab | 3.13 ± 0.45Ab | |||
| 142 | 3.42 ± 0.34Ab | ||||
| 180 | 3.42 ± 0.34Ab | ||||
| 228 | 3.47 ± 0.34Ab | ||||
| Color a* | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 32.96 ± 0.64Aa | 32.75 ± 3.24A | 32.84 ± 0.99A | 32.82 ± 1.99Aa | |
| 15 | 14.04 ± 0.12Bb | 13.46 ± 2.22Ab | 12.49 ± 1.12b | ||
| 30 | 12.68 ± 1.15Ab | 8.78 ± 1.10Ac | |||
| 45 | 12.42 ± 1.17Ab | 8.51 ± 0.60Ac | |||
| 66 | 12.49 ± 1.15Ab | 5.95 ± 0.19Ad | |||
| 87 | 12.14 ± 1.14Ab | 5.10 ± 0.58Ad | |||
| 108 | 12.16 ± 1.25Ab | 5.11 ± 0.45Ad | |||
| 142 | 11.42 ± 1.34Ab | ||||
| 180 | 9.76 ± 0.34Ac | ||||
| 228 | 8.47 ± 0.34Ad | ||||
| Color b* | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 12.87 ± 1.58Aa | 12.19 ± 1.42Aa | 12.26 ± 1.01A | 13.80 ± 2.58Aa | |
| 15 | 3.26 ± 0.11Ab | 3.27 ± 0.18Ab | 3.10 ± 0.14Ab | ||
| 30 | 3.25 ± 0.06Ab | 2.49 ± 0.10Bc | |||
| 45 | 3.27 ± 0.16 Ab | 2.44 ± 0.20Bc | |||
| 66 | 3.24 ± 0.13 Ab | 2.47 ± 0.30 Bc | |||
| 87 | 3.12 ± 0.36Ab | 2.31 ± 0.31Bc | |||
| 108 | 3.09 ± 0.68Ab | 2.36 ± 0.17Bc | |||
| 142 | 2.57 ± 0.64Ac | ||||
| 180 | 2.08 ± 0.34Ac | ||||
| 228 | 3.03 ± 0.08Ac | ||||
| Chroma | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 15.47 ± 2.78Aa | 17.24 ± 1.44Aa | 15.41 ± 1.44A | 13.89 ± 2.58Aa | |
| 15 | 12.41 ± 0.41Ab | 13.81 ± 0.52Ab | 13.86 ± 0.43Aa | ||
| 30 | 13.04 ± 0.14Ab | 9.07 ± 0.80Bb | |||
| 45 | 12.85 ± 0.16 Abc | 6.87 ± 0.55Bc | |||
| 66 | 12.86 ± 0.12 Abc | 6.57 ± 0.49 Bc | |||
| 87 | 12.52 ± 0.10Abc | 6.50 ± 0.38Bc | |||
| 108 | 12.16 ± 1.49Abc | 5.62 ± 0.89Bd | |||
| 142 | 11.99 ± 1.31Abc | ||||
| 180 | 10.36 ± 0.76Abc | ||||
| 228 | 9.98 ± 0.20Ad | ||||
| Hue | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 0.36 ± 0.03Aa | 0.34 ± 0.08Aa | 0.33 ± 0.22A | 0.38 ± 0.03Aa | |
| 15 | 0.23 ± 0.01Ab | 0.22 ± 0.01Ab | 0.24 ± 0.01Ab | ||
| 30 | 0.22 ± 0.01Ab | 0.25 ± 0.01Bb | |||
| 45 | 0.23 ± 0.03 Ab | 0.23 ± 0.03Ab | |||
| 66 | 0.25 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.23 ± 0.03Ab | |||
| 87 | 0.24 ± 0.02Ab | 0.22 ± 0.02Ab | |||
| 108 | 0.25 ± 0.03Ab | 0.17 ± 0.02Bd | |||
| 142 | 0.24 ± 0.03Ab | ||||
| 180 | 0.23 ± 0.02Ab | ||||
| 228 | 0.21 ± 0.04Ab | ||||
| Total color difference | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 0.00 ± 0.00Ba | 1.32 ± 0.12Aa | 0.00 ± 0.00B | 1.38 ± 0.13Aa | |
| 15 | 0.21 ± 0.02Ab | 1.22 ± 0.11Aa | 1.24 ± 0.11Aa | ||
| 30 | 1.22 ± 0.10Aa | 1.25 ± 0.10Aa | |||
| 45 | 1.20 ± 0.11 Aa | 1.20 ± 0.11Aa | |||
| 66 | 1.25 ± 0.12 Aa | 1.21 ± 0.11Aa | |||
| 87 | 1.24 ± 0.22Aa | 1.22 ± 0.10Aa | |||
| 108 | 1.25 ± 0.13Aa | 1.24 ± 0.12Aa | |||
| 142 | 1.24 ± 0.12Aa | ||||
| 180 | 1.23 ± 0.12Aa | ||||
| 228 | 1.21 ± 0.14A | ||||
| Color intensity | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 4.90 ± 0.37Aa | 4.90 ± 0.36Aa | 4.59 ± 0.33A | 4.29 ± 0.40Aa | |
| 15 | 3.87 ± 0.04Ab | 3.97 ± 0.12Ab | 4.05 ± 0.14Aa | ||
| 30 | 4.16 ± 0.23Ab | 4.39 ± 0.24a | |||
| 45 | 4.07 ± 0.14 Ab | 4.11 ± 0.17Aa | |||
| 66 | 4.00 ± 0.21 Ab | 4.29 ± 0.15Aa | |||
| 87 | 2.65 ± 0.32Ac | 3.20 ± 0.13Ab | |||
| 108 | 2.28 ± 0.16Ac | 3.24 ± 0.21Ab | |||
| 142 | 2.24 ± 0.10Ac | ||||
| 180 | 2.23 ± 0.12Ac | ||||
| 228 | 2.22 ± 0.13Ac | ||||
| Storage temperature | |||||
| 4 °C | 22 °C | ||||
| TMAB | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 4.00 ± 0.49Aa | 0.00 ± 0.00Bd | 4.00 ± 0.33A | 0.3 ± 0.02Be | |
| 15 | 6.56 ± 0.24Ab | 0.47 ± 0.10Cc | 1.02 ± 0.0Bd | ||
| 30 | 0.49 ± 0.13Bc | 1.12 ± 0.24Ad | |||
| 45 | 0.58 ± 0.11 Ac | 1.31 ± 0.16Ad | |||
| 66 | 1.38 ± 0.21 Ab | 2.06 ± 0.15Ac | |||
| 87 | 1.40 ± 0.18Ab | 2.61 ± 0.16Ab | |||
| 108 | 2.62 ± 0.20Aa | 3.56 ± 0.30Aa | |||
| 142 | 2.24 ± 0.10Aa | ||||
| 180 | 2.31 ± 0.12Aa | ||||
| 228 | 2.62 ± 0.13Aa | ||||
| TMY | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 3.33 ± 0.26Aa | 0.00 ± 0.00Be | 3.67 ± 0.44A | 0.00 ± 0.02g | |
| 15 | 4.37 ± 0.22Ab | 0.00 ± 0.00Ce | 0.56 ± 0.0Bf | ||
| 30 | 0.00 ± 0.00e | 0.84 ± 0.16Ae | |||
| 45 | 0.38 ± 0.10 Ad | 1.04 ± 0.06Ad | |||
| 66 | 1.55 ± 0.20Ac | 1.46 ± 0.10Ac | |||
| 87 | 1.86 ± 0.18Ac | 2.02 ± 0.47Ab | |||
| 108 | 1.98 ± 0.16Ac | 2.84 ± 0.28Aa | |||
| 142 | 2.12 ± 0.14Ab | ||||
| 180 | 2.48 ± 0.18Ab | ||||
| 228 | 2.78 ± 0.14Aa | ||||
| Storage temperature | |||||
| 4 °C | 22 °C | ||||
| Clarity-Cloudiness | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 9.33 ± 0.89Aa | 9.60 ± 0.44Aa | 9.00 ± 0.50A | 9.88 ± 0.43Aa | |
| 15 | 6.77 ± 0.22Bb | 9.00 ± 0.66Aa | 8.44 ± 0.72Aa | ||
| 30 | 8.60 ± 0.80Aa | 8.33 ± 0.20Aa | |||
| 45 | 7.80 ± 0.10Aab | 7.04 ± 0.26Ab | |||
| 66 | 7.68 ± 0.32Ab | 6.32 ± 0.14Bc | |||
| 87 | 7.22 ± 0.18Ab | 6.05 ± 0.22Bc | |||
| 108 | 6.98 ± 0.26Ac | 5.94 ± 0.20Bc | |||
| 142 | 6.88 ± 0.34Ac | ||||
| 180 | 6.58 ± 0.28Ac | ||||
| 228 | 6.56 ± 0.24Ac | ||||
| Shininess-Dullness | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 9.22 ± 0.38Aa | 9.66 ± 0.41Aa | 9.21 ± 0.50A | 9.33 ± 0.28Aa | |
| 15 | 5.40 ± 0.23Cb | 9.10 ± 0.60Aa | 8.12 ± 0.60Bab | ||
| 30 | 8.96 ± 0.46Aa | 8.00 ± 0.23Ab | |||
| 45 | 8.14 ± 0.13Aab | 7.65 ± 0.32Bb | |||
| 66 | 8.08 ± 0.30b | 7.50 ± 0.22Bb | |||
| 87 | 7.69 ± 0.26Ab | 7.42 ± 0.26Ab | |||
| 108 | 7.62 ± 0.24Ac | 7.02 ± 0.32Ab | |||
| 142 | 7.22 ± 0.39Ac | ||||
| 180 | 7.11 ± 0.42Ac | ||||
| 228 | 7.05 ± 0.28Ac | ||||
| Color intensity | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 7.33 ± 1.56Aa | 8.46 ± 0.38Aa | 7.33 ± 0.44A | 8.22 ± 0.38Aa | |
| 15 | 6.44 ± 0.49Cb | 8.23 ± 0.46Aa | 8.01 ± 0.35Bb | ||
| 30 | 8.11 ± 0.32Aa | 7.89 ± 0.26Ab | |||
| 45 | 7.98 ± 0.39Aab | 7.33 ± 0.43bc | |||
| 66 | 7.65 ± 0.42b | 7.22 ± 0.38Bc | |||
| 87 | 7.03 ± 0.36Ab | 7.02 ± 0.16Ac | |||
| 108 | 6.82 ± 0.28Ab | 6.14 ± 0.38Ad | |||
| 142 | 6.18 ± 0.42Abc | ||||
| 180 | 6.01 ± 0.32Ac | ||||
| 228 | 6.00 ± 0.24Ac | ||||
| Flavor-aroma | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 7.03 ± 1.44Aa | 8.46 ± 0.38Aa | 7.00 ± 0.44A | 8.22 ± 0.37Aa | |
| 15 | 6.44 ± 0.49Bb | 8.23 ± 0.46Aa | 8.01 ± 0.35Ab | ||
| 30 | 8.11 ± 0.32Aa | 7.89 ± 0.26Ab | |||
| 45 | 7.98 ± 0.39Aab | 7.33 ± 0.43Ac | |||
| 66 | 7.65 ± 0.42Ab | 7.22 ± 0.38Ac | |||
| 87 | 7.03 ± 0.36Ab | 7.02 ± 0.16Ac | |||
| 108 | 6.82 ± 0.28Ab | 6.14 ± 0.25Ad | |||
| 142 | 6.18 ± 0.42Abc | ||||
| 180 | 6.01 ± 0.32Ac | ||||
| 228 | 6.00 ± 0.24Ac | ||||
| Bitter taste | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 4.44 ± 0.72Aa | 3.66 ± 0.66Aa | 4.33 ± 0.524A | 4.02 ± 0.42Aa | |
| 15 | 6.41 ± 0.59Cb | 3.67 ± 0.40Aa | 4.08 ± 0.28Bb | ||
| 30 | 3.65 ± 0.36Aa | 4.09 ± 0.20Ab | |||
| 45 | 3.76 ± 0.30Aab | 4.03 ± 0.23bc | |||
| 66 | 3.78 ± 0.40b | 4.12 ± 0.30Bc | |||
| 87 | 3.80 ± 0.32Ab | 4.22 ± 0.26Ac | |||
| 108 | 3.96 ± 0.20Ab | 4.34 ± 0.30Ad | |||
| 142 | 3.98 ± 0.40Abc | ||||
| 180 | 4.04 ± 0.30Ac | ||||
| 228 | 4.02 ± 0.28Ac | ||||
| Sour taste | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 4.42 ± 0.50Aa | 3.44 ± 0.40Aa | 4.33 ± 0.52A | 4.02 ± 0.42Aa | |
| 15 | 6.98 ± 0.58Cb | 3.40 ± 0.43Aa | 4.08 ± 0.28Bb | ||
| 30 | 4.01 ± 0.42Aa | 4.09 ± 0.20Ab | |||
| 45 | 4.02 ± 0.38Aab | 4.03 ± 0.23bc | |||
| 66 | 3.78 ± 0.40Ab | 4.12 ± 0.30Bc | |||
| 87 | 3.80 ± 0.32Ab | 4.22 ± 0.26Ac | |||
| 108 | 3.96 ± 0.20Ab | 4.34 ± 0.30Ad | |||
| 142 | 3.98 ± 0.40Abc | ||||
| 180 | 4.04 ± 0.30Ac | ||||
| 228 | 4.02 ± 0.28Ac | ||||
| After taste | Days | Control | HHP treated | Control | HHP treated |
| 0 | 6.78 ± 0.22Aa | 7.84 ± 0.40Aa | 6.32 ± 0.55A | 7.04 ± 0.39Aa | |
| 15 | 3.48 ± 0.58Cb | 7.64 ± 0.60Aa | 6.68 ± 0.28Bb | ||
| 30 | 7.33 ± 0.39Aa | 6.29 ± 0.35Ab | |||
| 45 | 7.34 ± 0.44Aa | 6.20 ± 0.42bc | |||
| 66 | 7.67 ± 0.36Aa | 6.18 ± 0.36Bb | |||
| 87 | 7.56 ± 0.44Aa | 6.08 ± 0.42Bb | |||
| 108 | 7.49 ± 0.38Aa | 5.67 ± 0.50Bb | |||
| 142 | 7.41 ± 0.39Aa | ||||
| 180 | 7.38 ± 0.49Aa | ||||
| 228 | 7.26 ± 0.51Aa | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





