1. Introduction
Splanchnic-artery aneurysms are relatively rare, with an incidence of 0.1% to 2% in the general population. Among them, 2% and 1.5% are located on the pancreaticoduodenal arteries (PDA) and gastroduodenal arteries, respectively [
1,
2,
3]. False aneurysms are more common than true aneurysms and may complicate pancreatitis, pancreatic trauma, infection, and surgery [
4]. They will not be discussed here as they differ substantially from true aneurysms [
1].
True PDA aneurysms may be associated with celiac-artery occlusion secondary to atherosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia, or compression by the median arcuate ligament (MAL) [
5,
6]. Celiac-trunk stenosis due to extrinsic compression by the MAL, known as MAL syndrome, occurs in about 4% of the general population and is usually an incidental discovery. MAL syndrome seems independent from age, sex, and presence of calcified aortic plaque. Celiac-trunk compression increases the retrograde blood flow from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) to the celiac artery via the posterior and anterior PDA collaterals, thereby promoting the development of high-flow aneurysms [
6,
7,
8,
9].
Several studies suggest that the risk of PDA-aneurysm rupture may be independent from patient age and from aneurysm size, number, and cause. Reported mortality rates after rupture range from 20% to 50% [
3,
10,
11,
12,
13]. Previous work emphasizes the importance of recognizing and treating PDA aneurysms as quickly as possible [
4,
14,
15].
PDA aneurysms can be treated surgically or by a variety of transarterial embolization (TAE) techniques. A review of the literature until 2002 identified 37 patients with PDA aneurysms, of whom 2 were left untreated due to patient refusal or comorbidities, 23 were treated surgically, and 12 were managed by TAE [
16]. No new cases of surgical treatment occurred after 1999. Over the last two decades, TAE has become the reference standard treatment of PDA aneurysms due to its high success rate and lower mortality compared to surgery [
17]. However, few data are available on the TAE techniques used and on patient outcomes after TAE for ruptured or unruptured PDA aneurysms.
The objective of this study was to describe the TAE techniques used and their effectiveness in excluding PDA aneurysms due to MAL syndrome. To this end, we evaluated our experience acquired over 12 years at a highly experienced interventional-radiology unit in a university hospital.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
Consecutive patients admitted to the Dijon-Bourgogne University Hospital (Dijon, France) between January 2010 and May 2022 and treated by TAE for ruptured or unruptured PDA aneurysms due to MAL syndrome were identified retrospectively. Inclusion criteria were celiac-trunk stenosis greater than 50% and one or more PDA aneurysms eligible for TAE.
Exclusion criteria were false aneurysm, true aneurysm without celiac-trunk stenosis, and celiac-trunk stenosis due to a cause other than compression by the MAL.
2.2. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization Procedure
All TAE procedures were performed by two radiologists with more than 10 years of experience in TAE. Pain control was by local puncture-site anesthesia and mild sedation. The Seldinger technique with insertion of a 6 French (Fr) introducer into the right femoral artery was used in all patients. The first step was celiac-trunk catheterization with a 5-Fr catheter (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) inserted through the 6-Fr introducer. Competitive flow in the PDA from the SMA due to celiac-trunk stenosis was documented at this step. However, in 7 patients, the celiac trunk was completely occluded by the MAL and could not be catheterized. The second step was insertion of a catheter into the SMA and supra-selective catheterization of the afferent aneurysmal artery using a 2.4-Fr Progreat microcatheter (Terumo).
The operator then chose between, or combined, two techniques, depending on the presentation of the aneurysm and clinical circumstances. In the trapping (or sandwich) technique, controlled-detachable non-fibered microcoils are released to embolize the vessels on either side of the aneurysm [
18]. This procedure has the disadvantage of sacrificing the parent artery. The other method, known as the packing technique, consists in super-selective embolization of the aneurysmal sac with microcoils of decreasing size and a liquid embolic agent or biological cyanoacrylate glue, while maintaining permeability of the parent artery [
18,
19,
20].
A final angiogram was obtained to confirm total exclusion of the aneurysm and to check the patency of the SMA and of the celiac-trunk branches, including the hepatic artery. No anticoagulant or antiplatelet treatment was given following the procedure.
2.3. Outcomes and Follow-Up
Technical success was defined as total exclusion of the aneurysm, with no intra-aneurysmal flow after opacification of the afferent artery during the final angiogram. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with intravenous contrast injection and standard protocols including arterial-phase image acquisition was performed at least 1 month after TAE; some patients underwent several other imaging studies during their follow-up.
Clinical success was defined as the absence of symptoms in previously asymptomatic patients and as the resolution of clinical and laboratory abnormalities in patients with aneurysmal rupture responsible for symptoms (e.g., abdominal pain and/or hemorrhagic shock).
Complications were defined as minor if they had no impact on hospital stay length. Major complications required either hospitalization of previously discharged patients or prolongation of hospitalization in non-discharged patients. Early complications were defined as occurring within the first 30 days after TAE and late complications as occurring after day 30.
2.4. Data Analysis
The study variables were described as number (%) or mean±SD depending on distribution.
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
We included 14 patients (7 women and 7 men) with a mean age of 64.0±13.2 years (range, 35–82 years). Their main characteristics extracted from our hospital database are reported in
Table 1.
None of the patients had a known vascular disease before TAE. In 1 patient, giant-cell arteritis was diagnosed a few weeks after TAE. The main comorbidities were controlled hypertension (n=5, 36%), current smoking (n=3, 21%), type 2 diabetes (n=2, 14%), and dyslipidemia (n=2, 14%). Mean body mass index was 24.2 ± 4.7 (range, 15.0–33.0). One patient (#8) had cirrhosis of the liver and presented with acute alcoholic pancreatitis. In another (#4), the aneurysm was discovered during evaluation for a liver tumor, which turned out to be a hepatocellular carcinoma. Finally, in another patient (#13), the aneurysm was found by investigations done for follow-up of colon cancer with liver metastases.
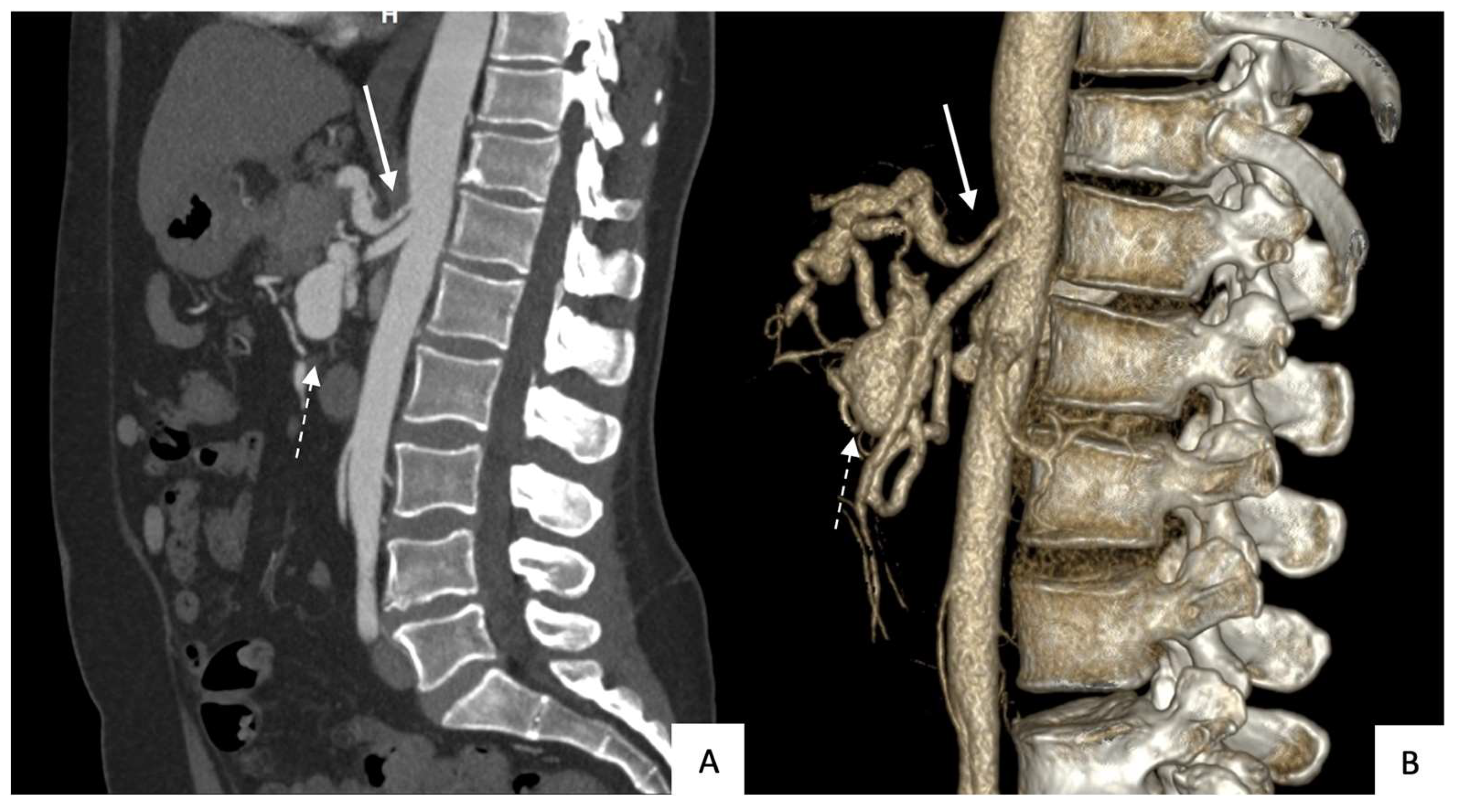
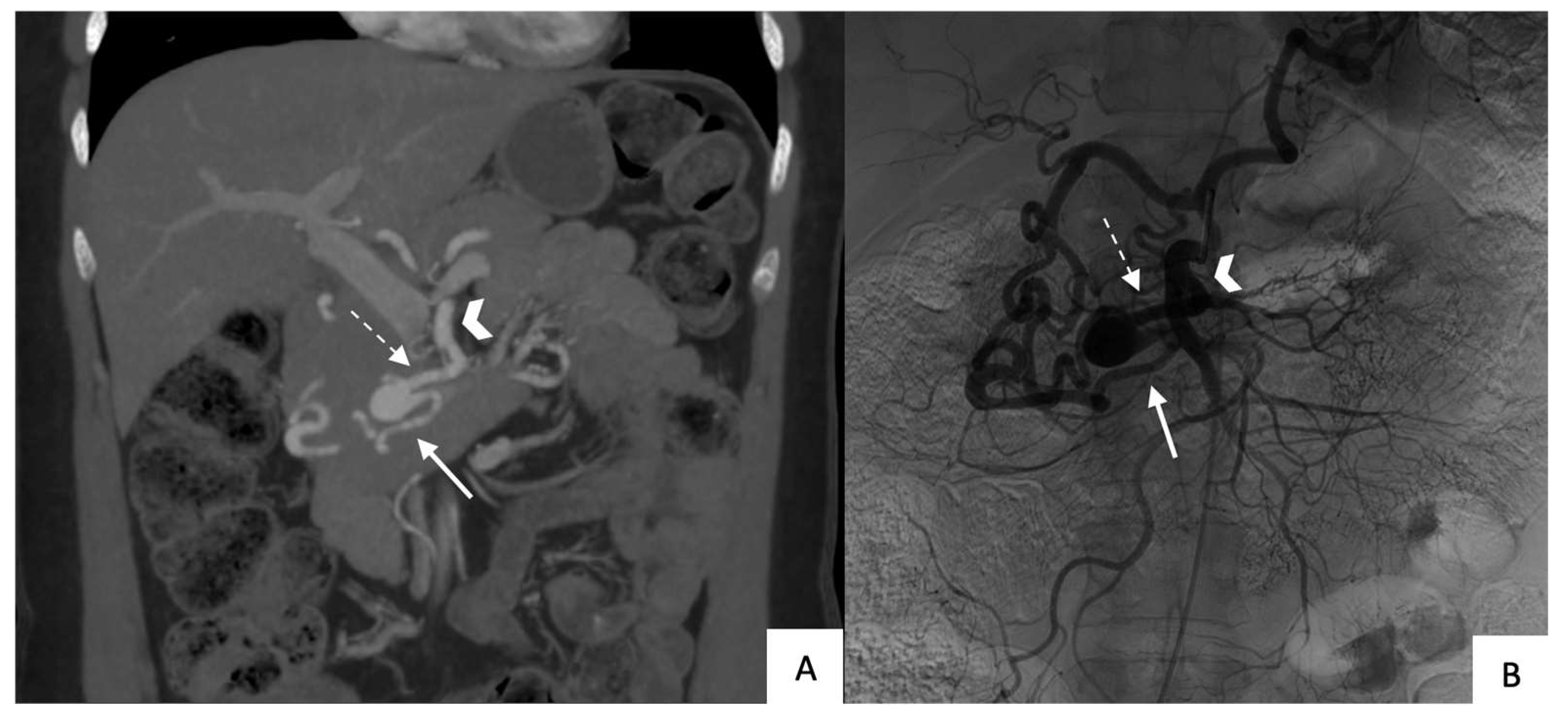
All patients underwent contrast-enhanced CT with multiplanar-reformation and maximum-intensity-projection reconstructions before TAE to accurately determine the location, size, and shape (saccular or fusiform) of the aneurysm and to determine whether rupture had occurred (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). All 14 aneurysms were saccular.
Table 1 reports data on size, location, circumstances of the diagnosis, and celiac-trunk stenosis. Thirteen patients each had a single aneurysm. The anterior or posterior branch of the inferior PDA was affected in 79% of cases.
3.2. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization
Table 2 provides information on the operating time, fluoroscopy duration, dosimetry, and embolization technique.
Packing was performed alone in 3 (21%) patients, using only coils (#5, unruptured), only co-polymer (#9, ruptured), or only cyanoacrylate (#10, ruptured), respectively. The coils were controlled-detachable non-fibered microcoils with diameters of 5–20 mm (Concerto, Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN) or 20 mm (Retracta, Cook Medical France, Charenton Le Pont, France), deployed over a 0.035-inch guidewire. The co-polymer was 34% Onyx® (LES, Covidien, Plymouth, MN), an elastic compound composed of ethylene-vinyl-alcohol co-polymer dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide and mixed with micronized tantalum powder. For this patient (#9, ruptured aneurysm), a balloon catheter was placed into the afferent artery. With the balloon occluded, Onyx® was injected slowly via the catheter until it entirely filled the aneurysmal sac. Finally, for the remaining patient, cyanoacrylate glue (n-butyl cyanoacrylate metacryloxysulfolane, Glubran®2; GEM, Viareggio, Italy) mixed with ultrafluid ethiodized alcohol (Lipiodol®; Ultra Fluid, Guerbet, Villepinte, France) in a 1:1 ratio was used because of life-threatening bleeding. The aneurysmal sac and parent postero-inferior PDA were occluded with the glue.
Trapping was used alone in 4 (29%) patients. In 3 of these patients (#6 and #7, unruptured; and #12, ruptured), only microcoils were injected. First, controlled-detachable non-fibered microcoils (Concerto, Medtronic; Ruby® Coil, Penumbra, Alameda, CA) were used to ensure good anchorage in the efferent artery, thereby minimizing the risk of downstream migration. Then, non-detachable fibered microcoils (Nester, Cook Medical France) 20 or 40 mm in diameter were injected to complete occlusion of the aneurysmal sac and, if necessary, of the afferent artery. In the remaining patient (#14, ruptured), the catheter could not be passed downstream of the aneurysm and occlusion was therefore achieved using only a liquid co-polymer (SquidPeri18®, BALT Group, Montmorency, France).
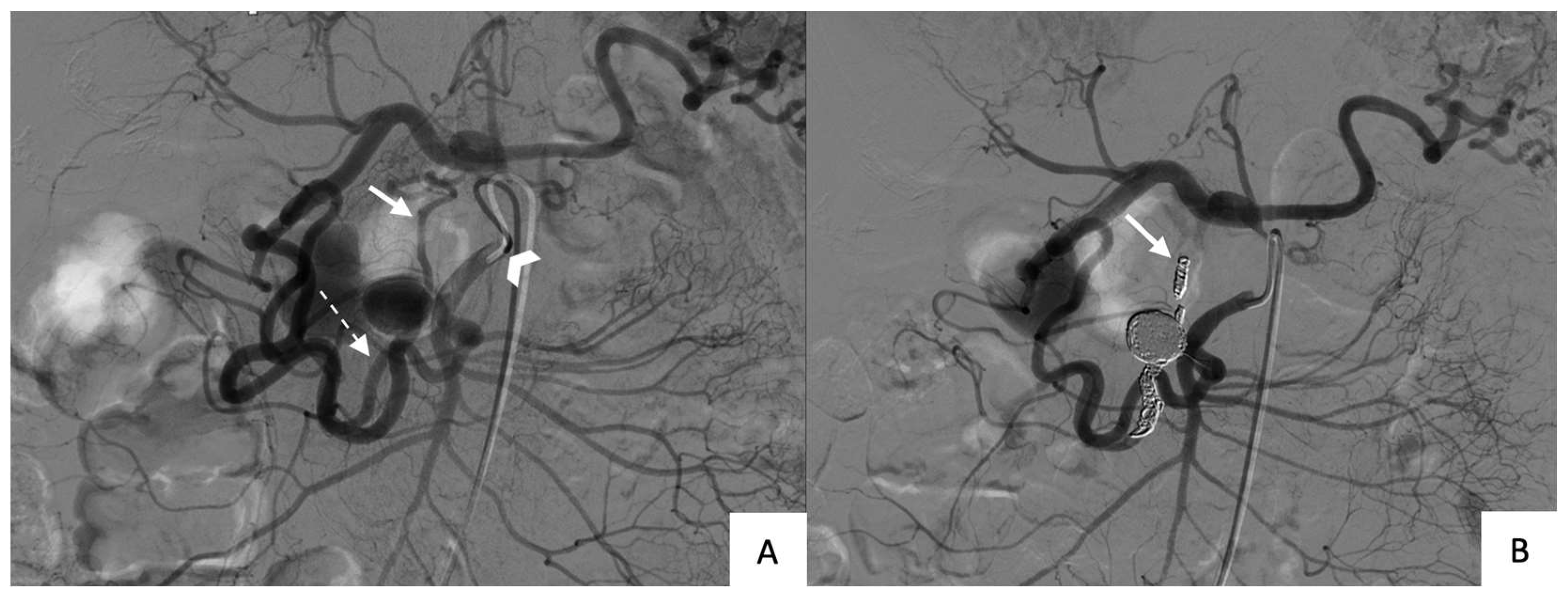
Finally, both packing and trapping were used in 7 (50%) patients (
Figure 3). Microcoils were used alone in 3 of these patients (#1, #2, and #13; all unruptured) and both microcoils and co-polymer (34% Onyx®, LES, Covidien) in 4 patients (#3, #4, and #8, unruptured; and #11, ruptured).
3.3. Outcomes
Results of the TAE procedures are presented in
Table 3.
3.3.1. Technical Succes
The final angiogram showed complete aneurysm exclusion in 13 (93%) patients. TAE failed in the remaining patient (#12), who was treated hemorrhagic shock due to aneurysmal rupture. Catheterization of the parent artery was not feasible and embolization of the gastroduodenal artery failed to exclude the aneurysm. This patient died of hemorrhagic shock after celiac-trunk ostium dissection, on day 15 of the hospital stay.
In 12 (86%) patients, the parent artery was occluded by the embolization material. One of the patients managed with packing only (#5) had a persistently patent parent artery.
3.3.2. Clinical Succes
In addition to patient #12 with failed TAE, one other patient died (#10), on day 1 of the hospital stay, after rupture of an 8-mm aneurysm responsible for severe hemodynamic instability that required emergency packing with cyanoacrylate glue.
The remaining 12 patients were alive at last follow-up, with no aneurysm-related symptoms, yielding a clinical success rate of 86% (12/14 patients).
3.3.3. Complications
One major and two minor complications of TAE occurred within the first 30 days.
About the major complication: in 1 patient (#4), two microcoils initially placed in the afferent aneurysmal artery were carried by the high flow via the PDAs then gastroduodenal arteries into the right branch of the hepatic artery, causing septic necrosis of the right lobe of the liver. This patient recovered with antibiotic therapy.
About the minor complication: two other patients experienced vascular dissection, of the right iliac artery (#11) and celiac-trunk ostium (#12), respectively. Patient #11 recovered, was discharged on day 7, and had no evidence of further complications on follow-up imaging studies. Patient #12 died on day 15 as described above.
3.3.4. Other Outcomes
Mean hospital stay length in the 9 patients whose aneurysms were asymptomatic was 3.0±4.8 days (range, 0–16 days). In 1 of these patients (#4), coil migration resulted in prolongation of the hospital stay to 16 days. The range in the other 6 patients was 0 to 4 days, and 3 patients were discharged on the day of TAE.
Of the 12 survivors, 1 (#3) was lost to follow-up after the procedure. In 2 patients, follow-up since TAE was less than 1 month at the time of this writing. The remaining 9 patients underwent CT or MRI at least 1 month after the procedure. The longest follow-up was 84 months (range, 1–84 months; median, 6 months). None of the follow-up imaging studies showed evidence of aneurysm recanalization or recurrence.
4. Discussion
This retrospective review identified 14 patients with PDA aneurysms caused by MAL syndrome and managed by TAE over a 12-year period in a single, highly experienced, interventional-radiology department. Among them, 5 were treated on an emergency basis after aneurysmal rupture, including 2 who died of complications from hemorrhagic shock and 3 who recovered. One patient presented with abdominal pain. Of the remaining 8 patients who had no symptoms related to the aneurysm, 5 had their aneurysm discovered fortuitously and 3 during evaluation for another condition. TAE had very high technical and clinical success rates, of 93% and 86%, respectively. The 2 patients who died presented with severe hemorrhagic shock due to aneurysmal rupture. The complications of TAE consisted of celiac-trunk dissection in 1 of the patients who died and of right-iliac-artery dissection and coil migration, respectively, in 2 survivors.
True PDA aneurysms account for only about 2% of all splanchnic aneurysms, and those caused by compression of the celiac trunk by the MAL are even less common [
1,
2,
3]. The MAL is a band of fibrous tissue that connects the diaphragmatic crura surrounding the aortic hiatus and is usually situated above the celiac-trunk ostium. However, 10% to 24% of individuals have a low riding MAL that puts pressure on the root of the celiac trunk, which is thus variably narrowed [
8,
21,
22]. This stenosis may increase blood flow in the pancreatic arterial network due to collateral supply from the SMA, potentially causing formation of an aneurysm [
2,
9,
23,
24]. Dilation of the peripancreatic arteries has been reported in 80% of patients with celiac-trunk stenosis [
25].
Although PDA aneurysms due to MAL syndrome are less common than those related to atherosclerosis, the risk of life-threatening rupture is just as high. Unlike other splanchnic-artery aneurysms, size does not correlate with the risk of rupture. Thus, in one study, the mean size of ruptured PDA aneurysms was only 4.6 mm (range, 2–10 mm) [
26]. In the absence of rupture, the diagnosis is often fortuitous, although some patients present with abdominal pain or other symptoms.
In the past, surgery consisting in ligation, resection, exclusion, or endoaneurysmorrhaphy was the standard reference treatment. However, these procedures carry high morbidity and mortality rates [
27]. Advances in imaging and intervention-radiology techniques have allowed the development of TAE as a safer alternative to surgery. Our findings support the use of TAE as the preferred treatment for PDA aneurysms due to MAL syndrome, for several reasons. The technical and clinical success rates in the 9 patients without aneurysmal rupture were 100%. These results are consistent with earlier studies reporting no recurrences after TAE [
13,
23,
26,
27]. Of these 9 patients, 4 were discharged on the same day and 3 on the day after TAE, reflecting the limited invasiveness of the procedure, with less anesthetic exposure compared to surgery. It must be noted, however, that 3 of these 9 patients did not have their first follow-up CT or MRI scan to assess for recanalization or recurrence, 2 because their TAE procedure was too recent at the time of writing and 1 who was lost to follow-up. The 9 patients with follow-up imaging studies had no evidence of recanalization or recurrence.
The treatment of celiac-trunk stenosis remains controversial, and no clear consensus exists for patients with PDA aneurysm. Given the absence of reported aneurysm recurrences, celiac-trunk revascularization procedures may be best reserved for those patients who have symptoms due to adverse effects on the hepatic blood supply [
26,
27]. Some groups, however, have advocated celiac-trunk revascularization to prevent recurrence by reestablishing the normal pancreatic arterial circulation [
16,
28,
29].
The limitations of our study include the retrospective design, which may have resulted in data-retrieval bias. Moreover, the single-center recruitment resulted in a small sample size and may have induced selection bias. We did not compare TAE to surgery. However, TAE is now the reference standard treatment for PDA aneurysms. None of our patients received treatment for the celiac-trunk stenosis, precluding an evaluation of TAE effects on hemodynamics within the pancreaticoduodenal arcades. Finally, follow-up to document the continuing absence of symptoms and the absence of recanalization and recurrence on imaging studies was short.
5. Conclusions
In patients with high-flow PDA aneurysms, TAE may be the treatment of choice both to prevent rupture and to stop bleeding after rupture. When the celiac-trunk stenosis is left untreated, flow remains high within the PDAs. Consequently, longer follow-ups are needed to collect data on the risk of recanalization and development of new aneurysms. It may be of interest to assess all patients treated for PDA due to MAL syndrome using TAE or surgery, in order to compare these two strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.S. and R.L..; methodology, V.S and O.C..; software, A.M.; validation, V.S., O.C. and R.L.; formal analysis, N.F.; investigation, P.O.C.; resources, V.S.; data curation, V.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.S., O.C., N.F. and R.L.; writing—review and editing, A.M., P.O.C. and R.L.; visualization, R.L.; supervision, R.L.; project administration, N.F.; funding acquisition, R.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional review board was not required for this study due to its retrospective nature, but our ethics committee approved the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived in compliance with French legislation on retrospective studies of anonymized data.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors. The data are not publicly available due to identity reason.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stanley, J.C.; Wakefield, T.W.; Graham, L.M.; Whitehouse, W.M.; Zelenock, G.B.; Lindenauer, S.M. Clinical importance and management of splanchnic artery aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 1986, 3, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandy, F.C.; Sell, K.A.; Eliason, J.L.; Coleman, D.M.; Rectenwald, J.E.; Stanley, J.C. Pancreaticoduodenal and Gastroduodenal Artery Aneurysms Associated with Celiac Artery Occlusive Disease. Ann Vasc Surg. 2017, 41, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasha, S.F.; Gloviczki, P.; Stanson, A.W.; Kamath, P.S. Splanchnic Artery Aneurysms. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007, 82, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffroy, R.; Favelier, S.; Pottecher, P.; Genson, P.Y.; Estivalet, L.; Gehin, S. Endovascular management of visceral artery aneurysms: When to watch, when to intervene? World J Radiol. 2015, 7, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, J.D.; Molnar, W.; Beman, F.F.; Marable, S.A. Compression of the celiac trunk and abdominal angina. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1965, 95, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, K.M.; Talamini, M.A.; Fishman, E.K. Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome: Evaluation with CT Angiography. RadioGraphics. 2005, 25, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, H.B.; Shin, S.J.; Park, J.H. ; Celiac Axis Stenosis: Incidence and Etiologies in Asymptomatic Individuals. Korean J Radiol. 2001, 2, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.N.; Lamb, K.; Relles, D.; Moudgill, N.; DiMuzio, P.J.; Eisenberg, J.A. ; Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome—Review of This Rare Disease. JAMA Surg. 2016, 151, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.; Lawton, G. ; Coeliac stenosis or occlusion with aneurysm of the collateral supply. Clin Radio. 1973, 24, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.K. Clinical impact of collateral circulation in patients with median arcuate ligament syndrome. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018, 24, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, M.; Gushimiyagi, M.; Takara, H.; Mototake, H. True Aneurysm of the Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries: A Single Institution Experience. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010, 14, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Perrot, M.; Berney, T.; Deléaval, J.; Bühler, L.; Mentha, G.; Morel, P. Management of true aneurysms of the pancreaticoduodenal arteries. Ann Surg. 1999, 229, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, K.; Nicholson, A. Inferior Pancreaticoduodenal Artery Aneurysms Associated with Occlusive Lesions of the Celiac Axis: Diagnosis, Treatment Options, Outcomes, and Review of the Literature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013, 36, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonardelli, S.; Spampinato, B.; Ravanelli, M.; Cuomo, R.; Zanotti, C.; Paro, B. The role of emergency presentation and revascularization in aneurysms of the peripancreatic arteries secondary to celiac trunk or superior mesenteric artery occlusion. J Vasc Surg. 2020, 72, 46S–55S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, M.R.; Ergul, E.A.; Cambria, R.P.; Patel, V.I.; Lancaster, R.T.; Kwolek, C.J. The presentation and management of aneurysms of the pancreaticoduodenal arcade. J Vasc Surg. 2016, 64, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducasse, E.; Roy, F.; Chevalier, J.; Massouille, D.; Smith, M.; Speziale, F. Aneurysm of the pancreaticoduodenal arteries with a celiac trunk lesion: current management. J Vasc Surg. 2004, 39, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratby, M.J.; Lehmann, E.D.; Bottomley, J.; Kessel, D.O.; Nicholson, A.A.; McPherson, S.J. Endovascular embolization of visceral artery aneurysms with ethylene-vinyl alcohol (Onyx): a case series. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006, 29, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikoma, A.; Nakai, M.; Loffroy, R.; Midulla, M.; Kamisako, A.; Higashino, N. Transcatheter arterial embolization of a splenic artery aneurysm with N-butyl cyanoacrylate/lipiodol/ethanol mixture with coil-assisted sandwich technique. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2019, 9, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffroy, R.; Rao, P.; Ota, S.; Lin, M.D.; Kwak, B.K.; Krause, D. Packing Technique for Endovascular Coil Embolisation of Peripheral Arterial Pseudo-aneurysms with Preservation of the Parent Artery: Safety, Efficacy and Outcomes. Eur J of Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010, 40, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulmalak, G.; Chevallier, O.; Falvo, N.; Di Marco, L.; Bertaut, A.; Moulin, B. Safety and efficacy of transcatheter embolization with Glubran®2 cyanoacrylate glue for acute arterial bleeding: a single-center experience with 104 patients. Abdom Radiol. 2018, 43, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, H.H.; Kemprud, E. A Clinicoanatomical Study of the Arcuate Ligament of the Diaphragm. Arch Surg. 1971, 103, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.H.; Pfeifer, K.J.; Tato, F.; Reiser, M.; Rieger, J. Transcatheter Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm of the Pancreatico-duodenal Artery with Occluded Celiac Trunk. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005, 28, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Tachi, Y.; Ito, S.; Maruyama, K.; Mori, Y.; Komada, T. Endovascular Management of Ruptured Pancreaticoduodenal Artery Aneurysms Associated with Celiac Axis Stenosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008, 31, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrottes, A.; Mariage, D.; Baqué, P.; Massalou, D. Pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysms due to median arcuate ligament syndrome: what we need to know. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018, 40, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, R.M.; Coldwell, D.M.; Ben-Menachem, Y. Ligamentous compression of the celiac axis: CT findings in five patients. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1991, 156, 1101–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivot, C.; Rebibo, L.; Robert, B.; Regimbeau, J.M.; Yzet, T. Ruptured Pancreaticoduodenal Artery Aneurysms Associated with Celiac Stenosis Caused by the Median Arcuate Ligament: A Poorly Known Etiology of Acute Abdominal Pain. Eur J of Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016, 51, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniak, R.; Grabowska-Derlatka, L.; Maciąg, R.; Ostrowski, T.; Nawrot, I.; Gałązka, Z. Treatment Algorithm of Peripancreatic Arteries Aneurysm Coexisting with Coeliac Artery Lesion: Single Institution Experience. Biomed Res Int. 2018, e5745271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bageacu, S.; Cuilleron, M.; Kaczmarek, D.; Porcheron, J. True aneurysms of the pancreaticoduodenal artery: Successful non-operative management. Surg. 2006, 139, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, Y.W.; Kao, H.L.; Wang, H.P. ; Celiac artery stenting: a new strategy for patients with pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysm associated with stenosis of the celiac artery. J Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).