1. Introduction
Hematite is a typical iron oxide ore used as a major raw material for the iron and steel industry. As the continuous exploitation of hematite resources, the reserves of rich ore are getting more scarce. Hematite ores also gradually become lower in grade, finer in grain size, and more complex in compositions, which makes the separation of hematite ores more difficult [
1]. In China, 55% of iron ore is known as Anshan-type iron ore. Approximately 40% of Anshan-type ores are low-grade hematite ores with nonuniform mineral dissemination sizes along with complex mineral compositions [
2,
3].
At present, the separation process of Chinese Anshan-type hematite ores typically adopts a combined beneficiation process including several stages of grinding, gravity separation, magnetic separation and flotation, which has achieved good industrial applications in many mineral processing plants such as Diaojuntai, Qidashan and Gongchangling et al. in China [
1,
4]. This beneficiation process can obtain good separation performance and its main advantage is that the coarse liberated iron minerals can be separated from the gangue minerals in advance by staged grinding, which reduces the grinding energy consumption and enhances the separation efficiency of the subsequent magnetic separation [
1]. The ground product is separated into coarse and fine size fractions by the hydrocyclone. The coarse particle fraction of the ground product is usually separated by a combination process with spiral chute and low-intensity magnetic separation (LIMS) to obtain the final concentrate and tailings directly, which has been well applied in industry. The fine particle fraction of the ground product is usually separated by a combination process with low-intensity magnetic separation (LIMS) and high-intensity magnetic separation (HIMS)) and flotation. A partially qualified concentrate can be obtained by LIMS and its tailing is fed to HIMS to remove slimes, providing a feed with higher TFe grade to the subsequent anionic reverse flotation process [
1]. The primary advantages of anionic reverse flotation include a decreased sensitivity to slimes and a lower collector dosage. The fatty acids produced from the paper industry as a waste are often used as the flotation collector [
1,
5].
The flotation feed in this study was a mixture of low and high intensity magnetic concentrates from the typical combined beneficiation process of hematite ore. Jiang et al. [
6] characterized the particle size of the flotation feed from a Qidashan processing plant with process mineralogical properties similar to the sample used this study. Their analysis showed that the flotation feed contained a large number of fine particles with particle sizes of only a few microns or even less than one micron. For such fine particles, flotation is considered to be the most effective separation techniques [
7] but the flotation results obtained with conventional flotation processes are always unsatisfactory [
8]. Many studies have been conducted on flotation reagents and flotation equipment to further improve the flotation separation performance of similar hematite flotation feed to meet the production needs in the recent years. Luo et al. [
9] applied the RA-315 anionic collectors developed by Changsha Mining and Metallurgy Research Institute in China to the Qishan beneficiation plant (Anshan Steel Company, China) and upgraded the iron concentrate to 65.33% TFe grade with a recovery of 80.72%. RA series collectors have also been applied to Donganshan and Gongchangling beneficiation plants that deal with refractory iron ores [
1]. Mei et al. [
10] used a novel KS-VI collector for desilication of iron ore by anionic reverse flotation process with one rougher, one cleaner and two stages of scavenger and their flotation test results showed that the tailing TFe grade decreased by 3.50% and the concentrate TFe recovery increased by 3.27% compared with four RA series collectors at the same concentrate TFe grade of 68.5%. Pu et al. [
11] used flotation column to conduct reverse flotation tests of hematite ore and obtained a concentrate of 68.17% TFe grade with a recovery of 84.10% by a shorter process of one rougher flotation and two stages of scavenger flotation, which not only shortened the flotation process but also reduced the collector dosage. In summary, previous studies have shown that the iron concentrate obtained with the Anshan-type iron ore by rougher flotation only is poor regardless of flotation reagents and device and the ideal flotation performance can only be obtained by the complex closed-circuit process with several stages of cleaner flotation and scavenger flotation.
The Mineral Liberation Analyzer (MLA) is widely used to evaluate process mineralogy including mineral composition, particle size and liberation characteristics [
12,
13]. In the recent years, the process mineralogical characterization of Chinese Anshan-type iron ore has been performed with the MLA with a focus on understanding its inefficient flotation behavior. For example, Hou et al. [
14] used MLA to determine mineral composition and liberation degree of the flotation feed from the Anqian processing plant to evaluate the feasibility of effective flotation separation and similar work was done by Tao et al. [
8] and Sobhy et al [
15]. Jiang et al. [
6] comparatively investigated the process mineralogy of two flotation feed samples from Gongchangling and Qidashan processing plants, respectively and concluded that the fine particle size of siderite and its complex association with other iron minerals are the main reasons for poor flotation performance with the flotation feed from Gongchangling processing plant.
This study was conducted to systematically and quantitatively investigate the effect of mineral composition, particle size distribution and association characteristics etc. on the flotation performance of flotation feed samples from Anqian processing plant in China with the use of advanced MLA. Combined with other characterization and analysis methods the MLA process mineralogy results provided the critical information needed for elucidating the mechanisms of poor flotation behavior of the Chinese Anshan-type iron ore and providing valuable guidance for achieving more efficient flotation of the ore.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Minerals and Reagents
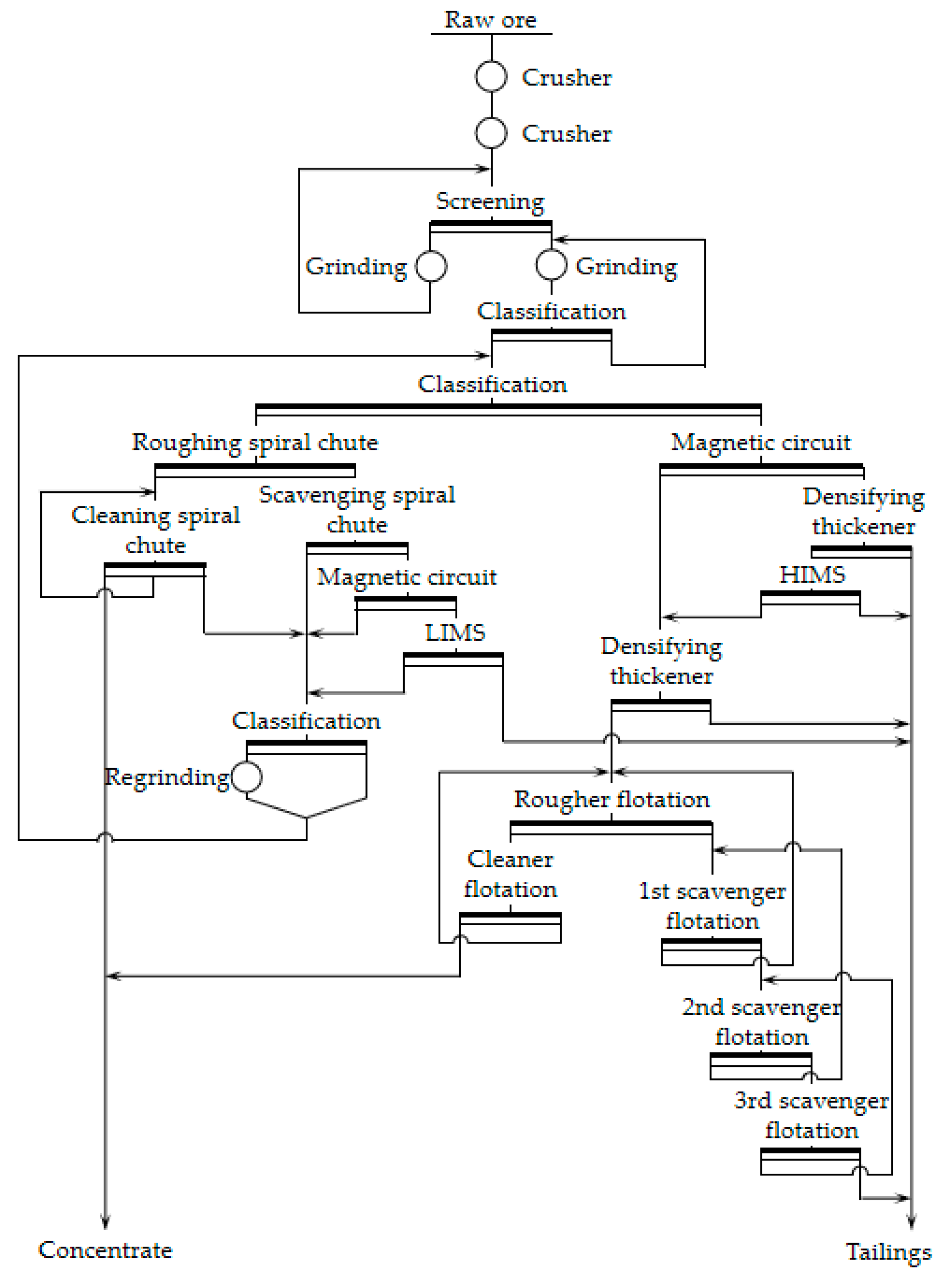
A 1 kg representative flotation feed sample was collected every day for about one month for a total sample of approximately 30 kg from Anqian processing plant’s flotation shop of Anshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd., Anshan city, China. The collected sample was mixed and homogenized thoroughly, fractionated immediately after its arrival at the lab and dried outdoors for later usage. The beneficiation process of the Anqian processing plant is shown in
Figure 1.
As can be seen in
Figure 1, the coarse liberated iron minerals from hydrocyclone classification are recovered by spiral gravity separation. The fine particles from classification hydrocyclone and non-magnetic coarse gangue minerals are beneficiated by LIMS and HIMS magnetic separations and the mixture of LIMS and HIMS concentrates are employed as the flotation feed. The flotation feed contains a high concentration of slimes, as described in many previous publications [
1,
6,
7,
8].
Flotation reagents, including sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as pH regulator, corn starch as hematite depressant, lime (CaO) as quartz activator, and anionic collector TD-II as quartz collector, were commercial products (the purity is more than 90%) acquired from the Anqian processing plant of Anshan Iron and Steel Co., Ltd. The adjustment of pulp pH value to ~11.5 using NaOH is essential for effective reverse anionic flotation of hematite because the surface charges on oxide particles are increased to the level that significant electrostatic repulsion exists between mineral particles and slime coatings [
16]. On the other hand, surface activation of quartz surface by lime in the form of Ca(OH)+ is most effective for changing quartz surface charge to positive values even at strong alkaline pH value of 11.5 to 13.5 [
17], while the negative charge of the hematite surface is very high (about 30 mV) [
8]. Soluble ionic species RCOO- or dimers (RCOO)22- of fatty acids are predominate forms of the collector in alkaline solutions [
18,
19] both of which can physically adsorb on positively charged quartz surfaces [
20] while their adsorption on hematite is negligible [
1,
5]. Starch is one of the most popular depressants applied in the reverse flotation of hematite [
1,
21]. The chemical complex is formed by the strong chemical interactions between the hydroxyl groups on the starch molecules and the hydroxylated metal sites on the hematite surface [
22], thus hindering the adsorption of fatty acids collector on the hematite surface and causing fine hematite particle aggregation [
8]. NaOH, corn starch and CaO can be obtained in the common chemical market. The collector TD-II is made from Tianxiang industry technology Co., Ltd, Anshan. Tap water with pH 7.8 from the city of Anshan was used in all experiments.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Sample Characterization
A 100 g homogenized sample was screened with standard screens of 74 μm and 30 μm to obtain three size fractions of +74 μm, 74-30 μm, and -30 μm, respectively for MLA analysis with higher efficiency and better accuracy as specified by the manufacturer. The yield of each size fraction was 16.0%, 20.2%, and 63.8%, respectively. A 3 g sample of each size fraction was used to make sample pellets with epoxy resin for liberation characterization of all minerals using an MLA apparatus (FEI MLA650F) consisting of an FEI scanning electron microscope with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX) energy spectrum. Since the analytical principle of MLA determines mineral species through elemental compositions, it is difficult to distinguish minerals such as magnetite and hematite with small differences in elemental compositions and therefore magnetite and hematite are both referred to as hematite without distinction in this study.
2.2.2. Flotation Tests
The rough reverse flotation test was performed with a 1 L XFD-III mechanical agitation flotation machine (Jilin Exploration Machinery Co., China) under the same conditions as Anqian processing plant: pH value of 11.5 (adjusted by NaOH), flotation temperature of 35oC, solid concentration of 25wt%, corn starch dosage of 1.25 kg/t conditioned for 3 min, lime dosage of 0.40 kg/t conditioned for 3 min, collector TD-II dosage of 0.76 kg/t conditioned for 2 min, rotation speed of 2000 r/min for the rotor of the mechanical cell, flotation aeration by natural aspiration, and flotation time of 3 min. Among all flotation conditions flotation temperature is one of the most important factors for fatty acid collectors in the anionic reverse flotation of hematite. The pulp temperatures at 35oC to 45oC can enhance collector’s effectiveness and their solubility in solution, thus obtaining a higher flotation efficiency [
23]. For performance evaluation, flotation concentrate and tailing products were filtered, dried, weighed, sampled, and assayed for TFe contents by the Chinese national standard GB/T 6730.8-1986.
2.2.3. Bubble Size Measurements
Online particle imaging system (Pixact, Finland) was employed to measure the bubble size distribution in the conventional 1 L mechanical agitation flotation machines (Jilin Exploration Machinery Co., China) and the flotation column with a static mixer (Yilong Mechanical & Electrical Technology Co., China), respectively. The measurement position was at the middle of mechanical flotation cell under the condition of rotation speed 2000 rpm and flotation aeration 100 L/h and feed entry point of the flotation column under the condition of MIBC frother concentration 20 ppm and gas flow rate 0.75 cm/s, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical Composition
The main element chemical analysis of flotation feed sample of iron ore was performed according to Chinese national standard GB/T 6730.8-1986 for TFe and GB/T 6730.10-2014 for SiO2 and the results show that flotation feed sample mainly contained 49.11% TFe and 35.26% SiO2.
The MLA analysis results of mineralogical compositions of the flotation feed sample of iron ore used in this study are shown in
Table 1, which indicates that the major minerals were hematite and quartz, accounting for 74.76% and 19.02%, respectively. In addition, the sample contained small amounts of actinolite, ophiolite, dolomite, calcite and ankerite. Therefore, high purity iron concentrates can be obtained by efficiently removing quartz only due to the lower content of other gangue minerals.
3.2 Distribution of Major Minerals
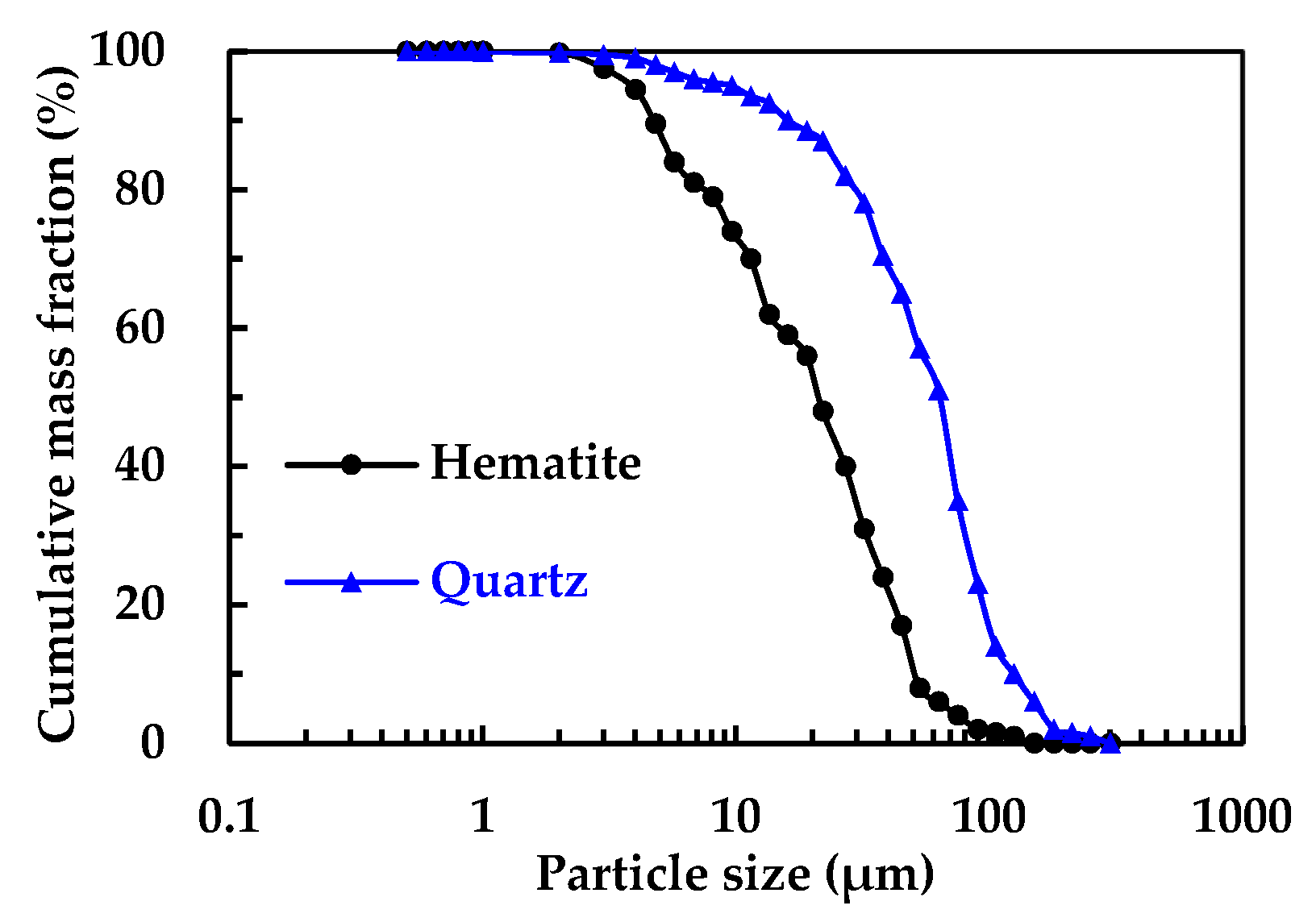
Figure 2 shows the MLA measurement results of particle size distribution of main minerals. It can be determined that the particle size of quartz is significantly coarser than that of hematite. For the hematite, the fine particle size less than 45 μm accounted for 85.93% and the ultrafine particle size less than 20 μm accounted for 51.08%. For the quartz, the fine particle size less than 45 μm accounted for 34.77% and the ultrafine particle size less than 20 μm accounted for 13.77%.
The yield, grade and iron distribution results from wet screening 500 g feed sample are given in
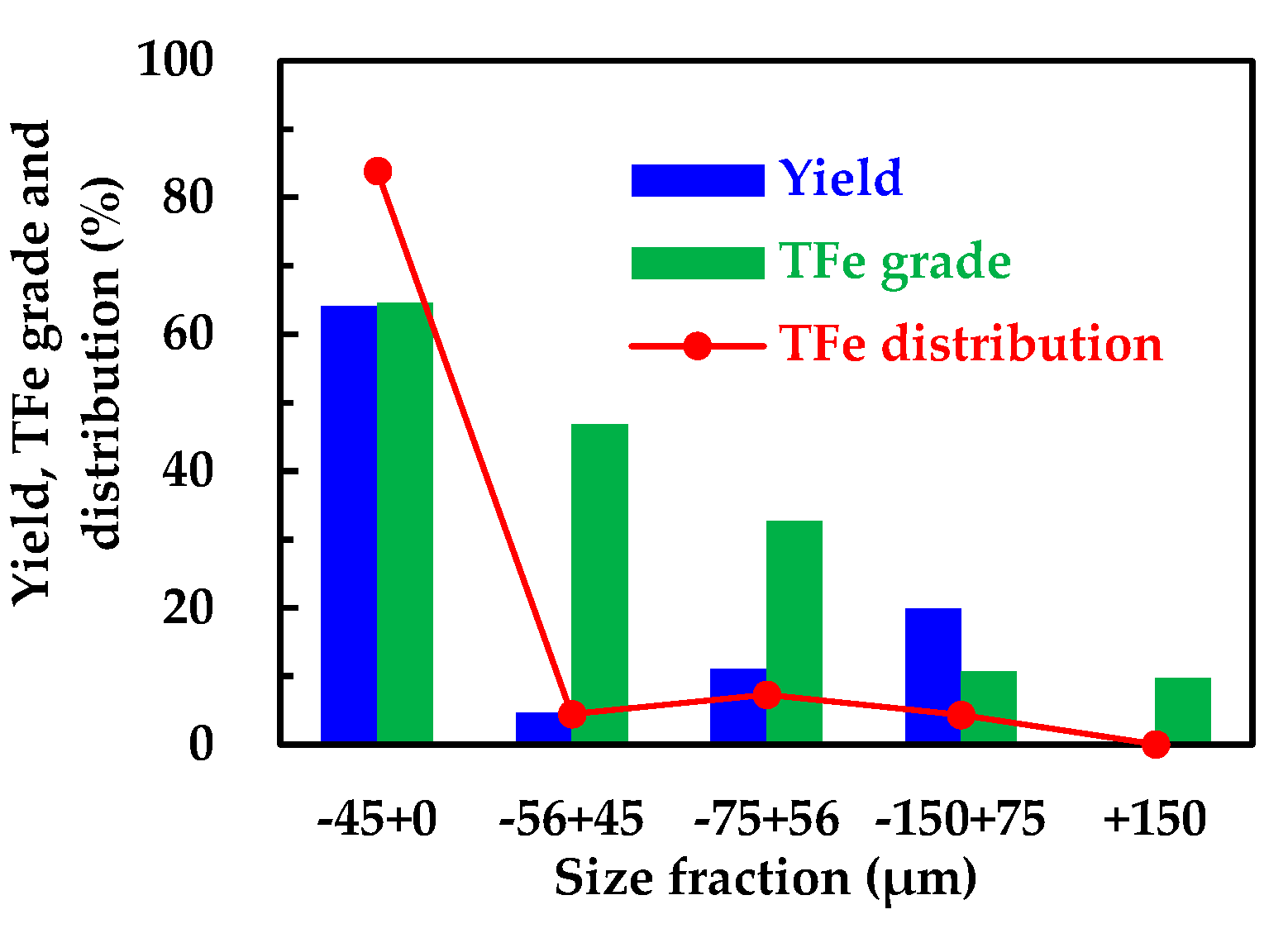
Figure 3. It can be seen from
Figure 3 that a total of 64.10% particles were in the 0-45 μm size fraction. The content of 45-75 μm size fraction was 15.74% and the 75-150 μm particles only accounted for 19.92%. The content of +150 μm size fraction is very low, i.e., less than 1%. Most of the particles existed in the fine size fractions. The TFe grade of 0-45 μm size fraction was 64.59%. The TFe grade of 45-56 μm and 56-75 μm size fraction was 46.85% and 32.63%, respectively. The TFe grade of remaining finer size fraction was only about 10%. The TFe grade increased with decreasing particle size, which also resulted in most of the iron being distributed in the fine particle size of less than 45 μm. The TFe distribution of 0-45 μm size fraction was 83.88% and the remaining size fractions only accounted for only less than 10%. Therefore, the flotation performance of particles with 0-45 μm size fraction is the key to achieving efficient flotation.
3.3. Mineral Liberation of Major Minerals
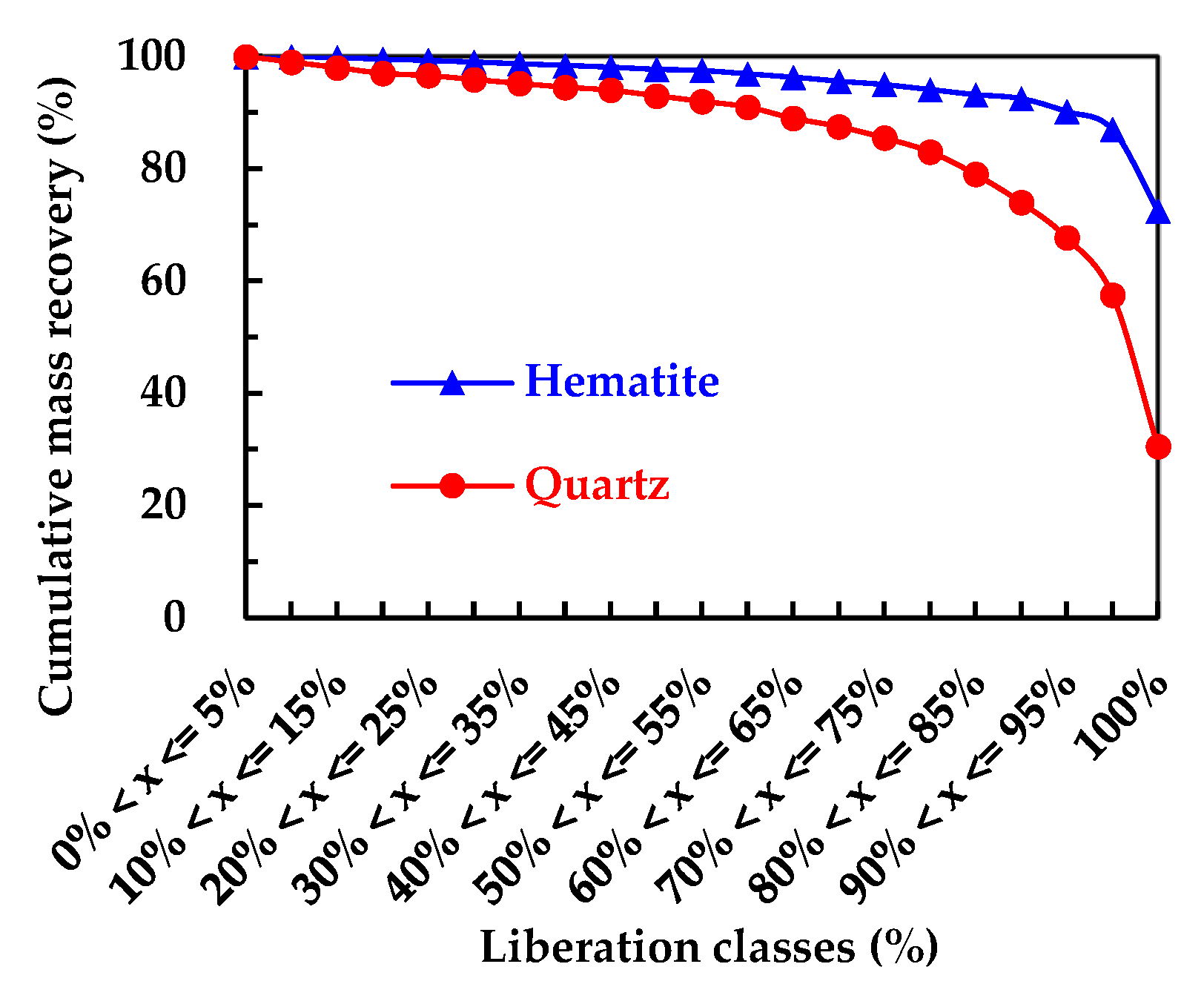
The mineral liberation results from MLA are given in
Figure 4. As shown in
Figure 4, hematite had a high degree of mineral liberation with the liberation degree of 90.19% while quartz had a relatively low degree of liberation of 67.72%.
The quantitative mineral liberation characteristics of hematite and quartz were analyzed separately in order to further explore the association characteristics of the main minerals. The purity of the mineral surface can directly affect mineral hydrophobicity during flotation and so the degree of liberation is generally expressed as free surface liberation. The liberation value of each particle is determined by calculating the perimeter of minerals particle in the MLA analysis. The liberation degree of flotation feed sample is quantified by the quantity of particles with varying liberation classes. Even though other minerals may be contained within the mineral particles with 100% free surface liberation, they can still be referred to as liberated particle because the floatability is not affected by the minerals contained inside.
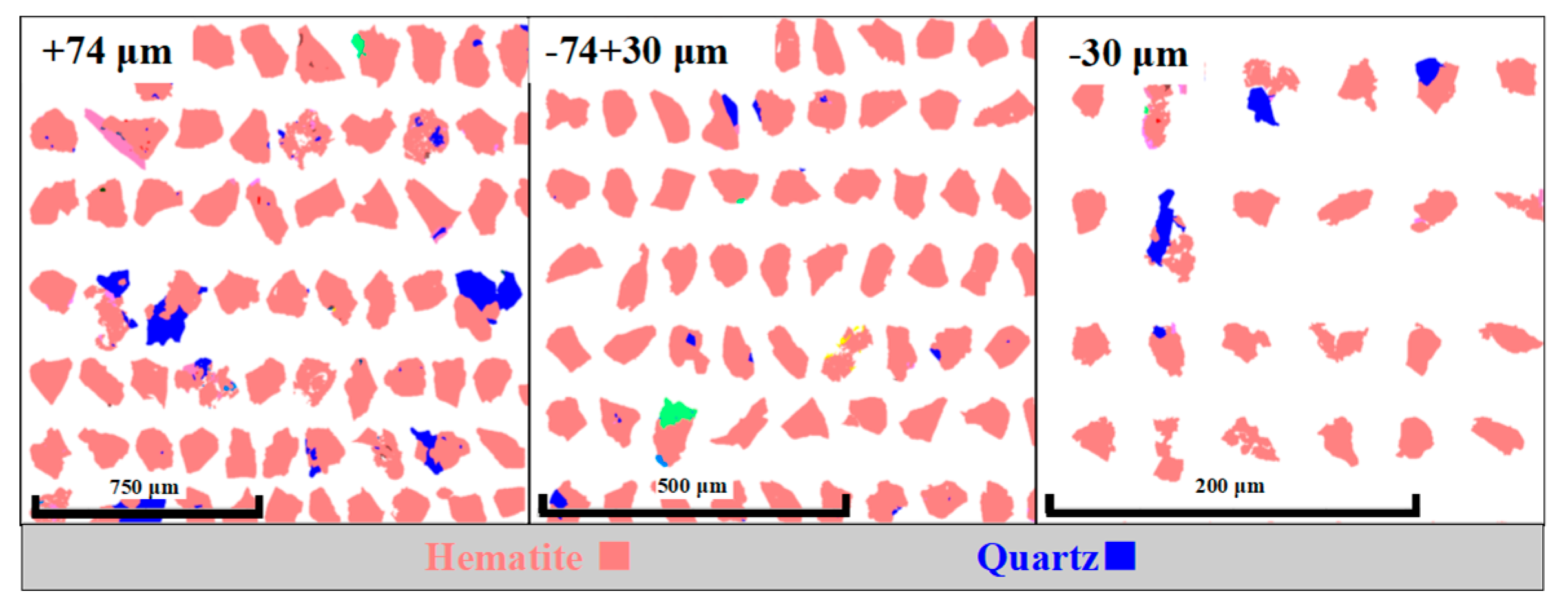
Hematite is the valuable mineral to be recovered and its association with gangue minerals will directly affect the separation performance of the iron sample. As can be seen in
Table 2, the iron sample contains 87.05% liberated hematite. Besides, only 7.15% and 5.80% of the hematite are associated with quartz and other gangue minerals, respectively.
Association data of hematite with quartz and other minerals is shown in
Figure 5. Most of the hematite minerals were separated from gangue mineral and only small numbers of hematite particles were associated with quartz and other gangue mineral. Most of hematite intergrows with quartz in a relatively big lumps whereas quartz remains at the edge of hematite and is closely associated with it in the form of small lumps and strips. Farrokhpay et al. [
24] concluded that the existence of composite particles will lead to poor separation efficiency due to the heterogeneous hydrophobicity of particle surfaces. Therefore, during the process of reverse flotation of iron ore, the composite particles with high contents of hematite were left in the underflow, resulting in a lower iron grade in the concentrate. In contrast, the composite particles with low contents of hematite likely entered the tailings along with the quartz, resulting in a lower iron recovery in the concentrate. It is worth noting that a small amount of ultrafine quartz was wrapped in the hematite in this flotation feed with two size fraction of +74μm and -74+30 μm and inevitably entered the underflow, resulting in a lower iron grade in the concentrate.
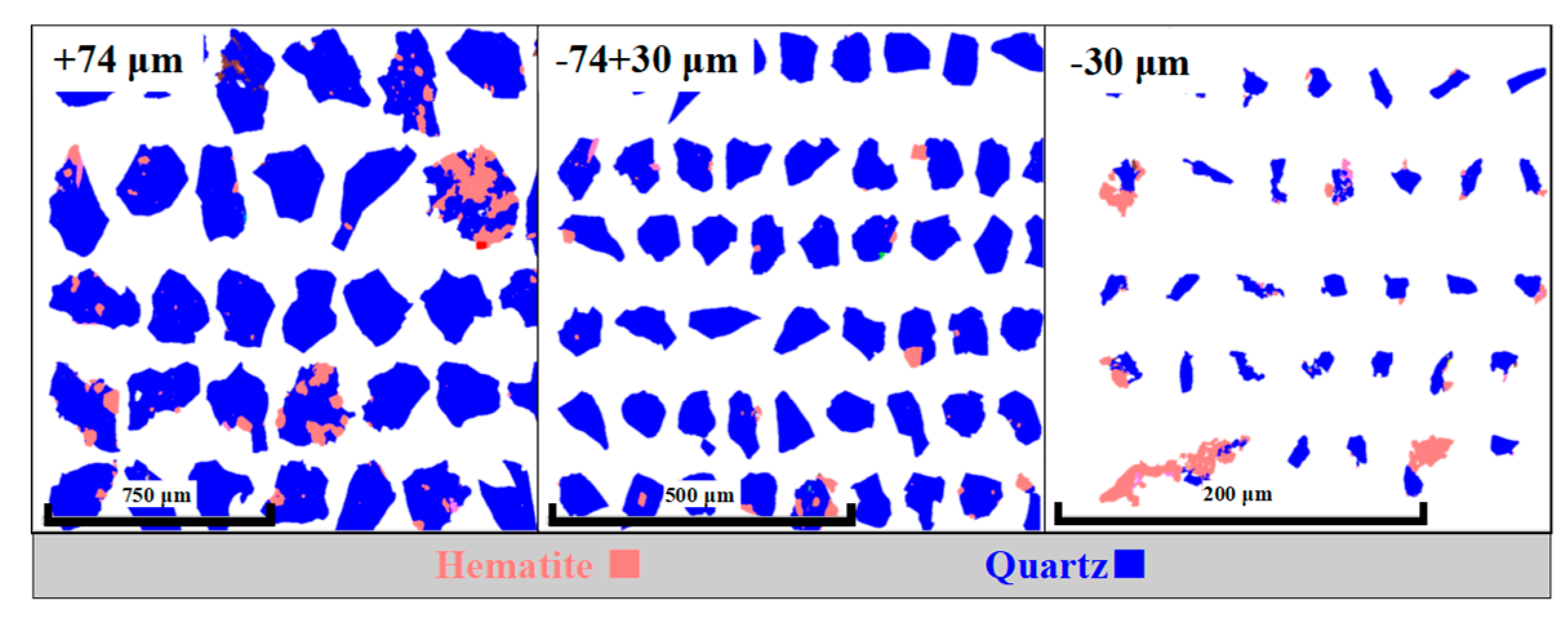
Quartz was the main siliceous gangue mineral with this iron ore and its association data is shown in
Table 3. Only 57.61% quartz existed in the form of liberated particles whereas 36.44% and 5.95% quartz particles were associated with hematite and other minerals, respectively. However, the composite particles of quartz and other gangue minerals had little influence on the flotation performance and qualified iron concentrate can be obtained by removing them at the same time in the flotation process. As can be seen in
Figure 6, hematite was wrapped as mosaic type in most of the quartz particles in the +74 μm coarse size fraction and these quartz particles had a relatively high degree of free surface liberation. Therefore, during the flotation process, the wrapped hematite likely entered the tailings along with the coarse quartz particles, resulting in a low iron recovery in the concentrate. Liu et al. [
25] investigated the mineral liberation and separation properties of Anshan-type hematite under different comminution flowsheets and concluded that the “Mosaic-type” locked-particles produced by comminution show no greater likelihood of better liberation in downstream ball mill grinding. A small quantity of hematite remained at the edge of quartz in this flotation feed with two size fraction of -74+30 and -30 μm and was closely associated with it as small lumps and strips. A small amount of hematite disseminated with quartz and the particle size of this portion of locked hematite was mostly less than 10 μm.
3.4. Kinetic Flotation Tests
The kinetic flotation experiments were performed to show the behavior of iron mineral during the flotation process.
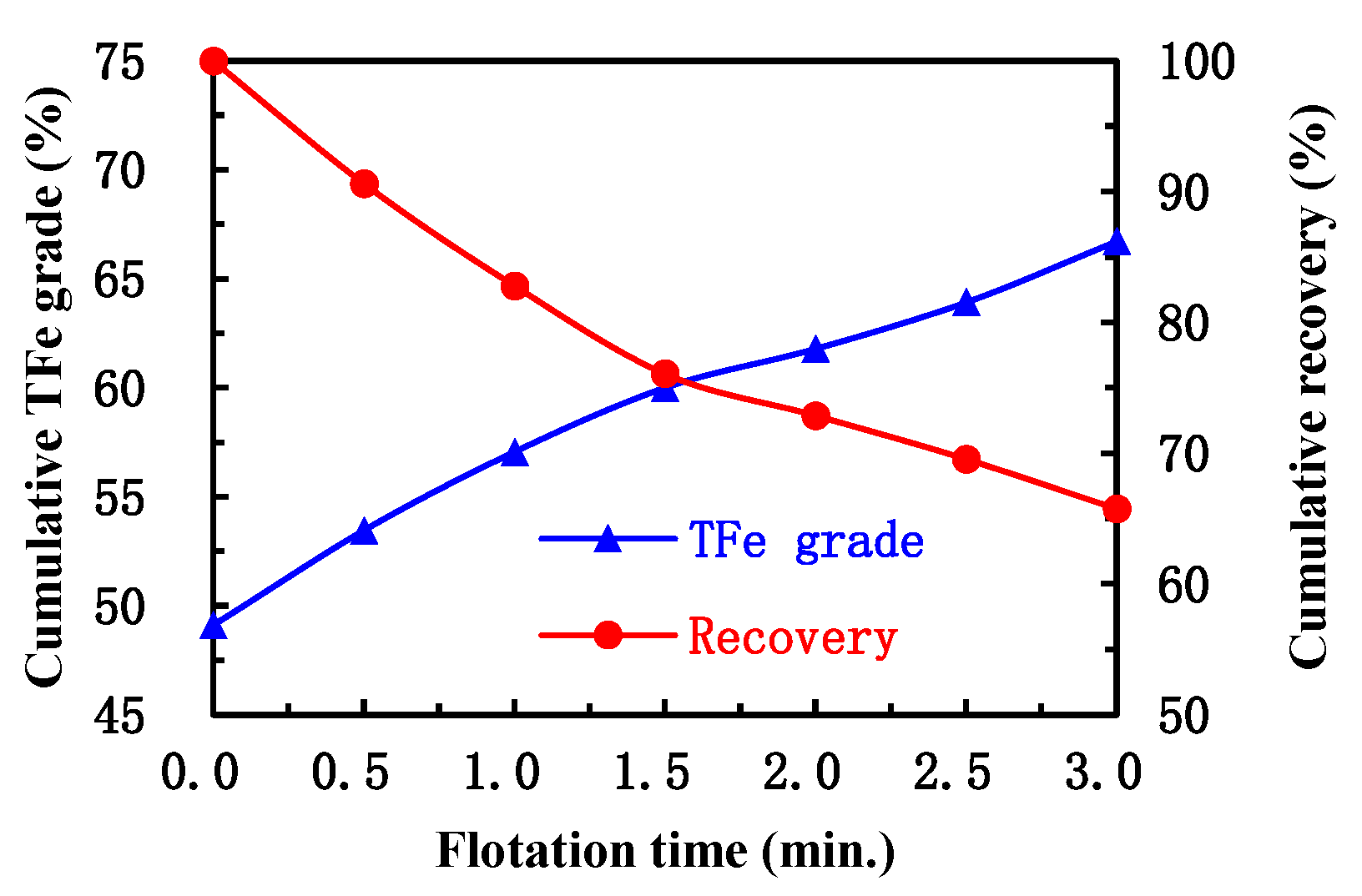
Figure 7 shows the concentrate TFe grade and recovery as a function of flotation time.
It is clear that the rougher flotation process with a flotation time of 3 min resulted in a concentrate of 66.73% TFe grade and 65.45% recovery, which was considerably below the target of 68.5% TFe grade and 85% recovery. Chen et al. [
26] obtained a concentrate with 68.21% TFe grade and 88.01% recovery by a closed-circuit process flowsheet of rougher, cleaner and two stages of scavenger flotation using the same flotation reagents. Their TFe grade and recovery were 0.39 percentage points and 19.25 percentage points higher than the above data obtained in this study, suggesting that the process flowsheet with cleaner and scavenger flotation stages improved the flotation performance.
When the flotation time increased from 0 min to 3 min the concentrate TFe grade increased from 49.11% to 66.71% but recovery decreased from 100% to 65.76%. About 66.5% TFe grade of concentrate can be obtained in approximately 3 min, but the recovery was only about 65.5%. It is worth noting that the recovery decreased sharply in the range from 0 to 3 min nearly linearly. Since the hematite in the flotation feed sample had a high degree of liberation (
Figure 4), it was considered that the fine hematite particles may be responsible for the sharp decrease in recovery, which will be discussed in the next section.
3.5. Screening Analysis of Rougher Flotation Products
In order to better understand iron components’ flotation behavior, wet screening analysis was performed with the rougher concentrate and tailings to evaluate the separation performance of hematite in each size fraction during the reverse flotation process. The results of the screening analysis are shown in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
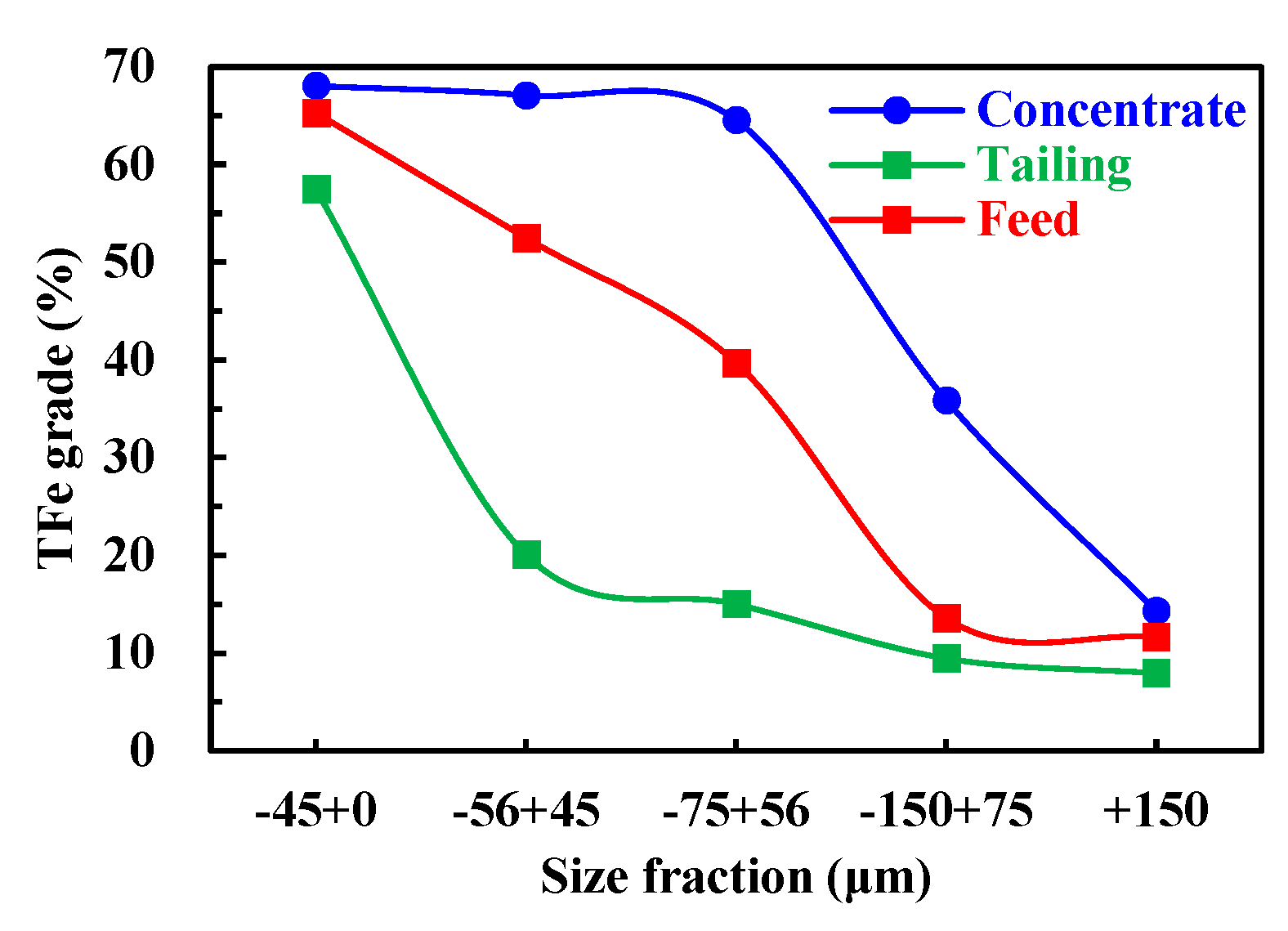
Figure 8 shows that the TFe grade increased with decreasing particle size in all products (feed, concentrate and tailing). Particle size ranging from 0 to 150 μm had a high separation efficiency, due to the significant grade difference between concentrate and tailings. With the concentrate curve, the TFe grade decreased sharply and linearly with the particle size larger than 56 μm, indicating that the coarser mineral particle in this range contained more composite particles and the liberation characteristics became gradually worse with increasing particle size. Therefore, it is necessary to add the cleaner flotation to remove the lower TFe grade composite particles to improve the final concentrate TFe grade.
Figure 9 shows that only 3.31% TFe recovery was associated with the +45 μm size fraction of the tailings. Up to 25.46% of the Fe recovery was lost in the -45 μm fine particle size of the tailings and the TFe grade of that size fraction was 49.99% (
Figure 8), which was significantly higher than the TFe grade of the other particle size fractions in the tailings. The actual recovery of each particle size was expressed as the effective TFe recovery in order to more directly show the separation performance of the mineral particles of each particle size. As shown in
Figure 9, the effective TFe recovery increased with decreasing particle size when the particle size was larger than 45 μm. When the particle size was less than 45 μm, the effective TFe recovery decreased sharply to 69.46 %, indicating that the separation efficiency of the fine particle was very low. In summary, the main reasons for the poor quality of rougher flotation concentrate were the ineffective recovery of +56 μm coarse composite particles and the low separation efficiency of -45 μm fine particles.
It is well known that the mineral liberation increases with decreasing particle size. Therefore, when the particle is coarse, the incomplete liberation of hematite and quartz causes portions of the high grade hematite composite particles to enter the underflow stream, resulting in a decrease in TFe grade of the concentrate. Meanwhile, some low grade hematite composite particles enter the froth tailings stream , resulting in a lower TFe recovery of the concentrate. Although fine particles (-45 μm) have a sufficient mineral liberation, their non-selective hydraulic entrainment into froth product will also reduce the TFe recovery of the concentrate and increase the TFe grade of the tailing during the reverse flotation [
27]. In addition, the adverse entrainment effect of fine particles leads to a drop in flotation kinetics of the fine floatable quartz particles and an increase in entrainment of fine hematite particles [
13].
3.6. Approaches for Flotation Performance Improvement
The above process mineralogical, kinetic flotation tests and screening analyses showed that the high content of fine particle size (64.10% feed was in the -45 μm size fraction) and incomplete liberation (the quartz liberation degree was only 67.72%) were the main reasons for the poor flotation performance of this hematite sample. Therefore, it is critical for achieving better flotation performance to improve the degree of liberation without producing a large quantity of fine particles, and find an effective method for fine particle flotation.
The method of liberation of conventional ball milling is referred to as comminution liberation due to the mechanical decrease of particle size in rocks and minerals. It is possible that minerals are liberated only when the geometry size of a particle is smaller than the mineral grain. Therefore, the mineral liberation degree is directly proportional to the grinding fineness in comminution liberation [
25]. For fine-grained composite particles, the high liberation degree is achieved only with fine grinding. Previous research has shown that the random fracture is considered to be the dominating mechanism of mineral fracture during the crushing operation [
28]. Non-random fracture mechanisms can be divided into preferential fracture and phase boundary fracture [
29]. Phase boundary fracture, also known as an intergranular fracture, is the ideal form of liberation. With regard to the grinding process, Chen and Yin [
28] concluded that the conventional ball mill resulted in more transgranular breakage of particles, which led to a poor liberation degree of minerals at a given particle size. The grinding media in the ball mill are mainly in the cataracting mode and the falling balls can readily fracture and break mineral particles by impact and attrition, diminishing the size of mineral particles [
30]. It is difficult to achieve complete liberation by the conventional grinding technology because the probability of fracture of fine particles by the grinding media can be drastically reduced. In this study we have demonstrated that hematite was well liberated but the high degree of liberation was achieved in the presence of large quantities of fine and ultrafine mineral particles that are partially responsible for the poor performance of flotation. Some previous research on advanced comminution technology has shown that the comminution process such as crushing and grinding is a non-random process only if intragranular and intergranular micro-cracks are generated in iron ores by crushing and intragranular cracks are more favorable for a higher degree of liberation at a given particle size [
31]. Compared to conventional crushing processes such as jaw crusher and cone crusher, high-pressure grinding roller (HPGR) has made inroads in the comminution circuit as an energy-efficient comminution equipment due to its potential processing benefits in terms of energy efficiency, improved exposure or liberation, particle weakening, induced micro-cracks, high throughput and high reduction ratio [
32]. The morphology image of the HPGR product surface with microcracks, liberated iron mineral with minor abrasion and the intergranular breakage produced by compressive forces. The microcracks within the particles generated by HPGR will result in more intergranular fracture during the subsequent grinding process to obtain a higher degree of liberation [
30,
33]. Emmanuel et al. [
33] investigated the effect of superfine crusher and HPGR on mineral liberation of iron ore and their results showed that the coarser HPGR product yielded a higher rejection of gangue than the finer product of the superfine crusher, indicating that the HPGR product achieved a higher degree of liberation at a coarser particle size.
Froth flotation is one of the most effective beneficiation process for fine particles and it is usually accomplished using mechanical flotation cell and flotation column. Mechanical flotation cells are widely used in the iron flotation industry in China. However, mechanical flotation cells have a relatively low separation efficiency for very fine mineral particles (<45 μm). Bu et al. [
34] reported that the mechanical flotation cells are being gradually replaced by the large flotation columns by technical retrofitting of old plants in China. Flotation columns characterized with a 5-30 cm thick froth can effectively minimize the entrainment of hydrophilic particles and is often capable of upgrading the fine flotation feed in a single step with which the conventional mechanical flotation cells may require several sequential stages [
35]. Bubble size is also a key factor in determining flotation efficiency. The bubble size distributions in the middle of the mechanical flotation cell and near the feed entry point of the flotation column are shown in
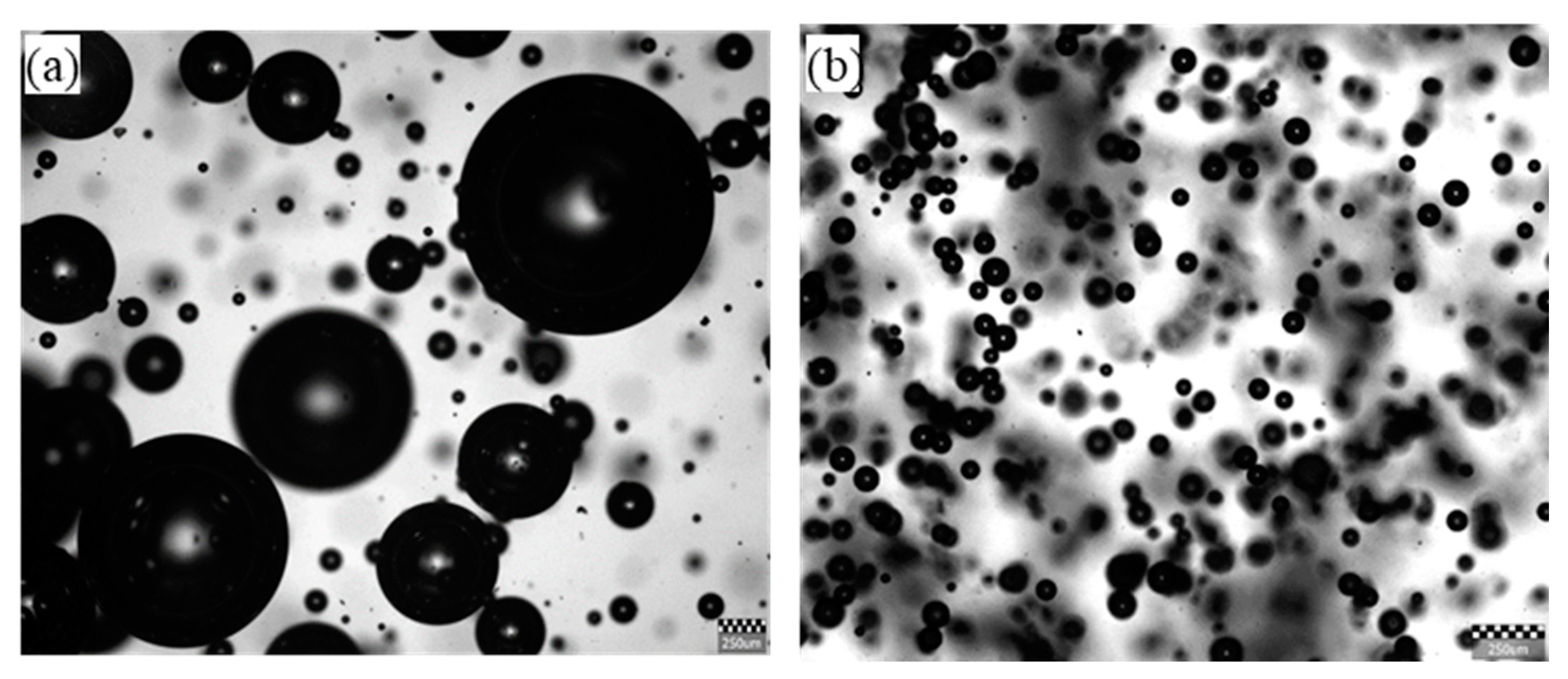
Figure 10. For the mechanical flotation cell the sizes of bubbles were mostly larger than 250 μm and some bubbles were several times larger than 250 μm in size. For the flotation column the bubbles were substantially smaller in size and more uniform compared to those in the mechanical flotation cell. Most of the bubbles in the flotation column were smaller than 100 μm.
The conclusion that the collection probability during flotation increases with decreasing bulk bubble size was reached in several previous studies conducted by Tao et al [
8], Ahmed et al [
15]. At present, flotation with the introduction of nanobubbles is the most widely used separation process for fine/ultrafine particle mineral processing. Nanobubbles refer to bubbles with a size less than 1 μm (usually between 300-700 nm), which are much smaller than conventional bubbles. Surface nanobubbles produced by cavitation can selectively be formed on the surface of hydrophobic particles and serve as preferred sites for attachment to conventional sized bubbles [
8,
15]. The introduction of nanobubbles in flotation can also significantly promote agglomeration of fine hydrophobic particles due to capillary bridging attraction caused by the formation of surface nanobubble on hydrophobic surfaces [
8]. It has also been shown that when nanobubbles were integrated into the conventional flotation, coarse quartz recovery increased by 24% [
36], fine and ultrafine quartz recovery improved by 20-30% as a result of increased quartz contact angle and agglomeration of ultrafine quartz particles [
37]. In fact, Tao et al. [
8] introduced nanobubbles into reverse anionic flotation of hematite and their rougher flotation results showed that the concentrate grade and recovery were approximately 67% and 68%, respectively without nanobubbles and 67% and 84%, respectively with nanobubbles under the reagent dosages of 2 kg/t starch, 0.25 kg/t lime, and 0.3 kg/t collector. Nanobubbles significantly increased concentrate Fe recovery and shortened the flotation process compared with the conventional flotation process [
26].
In summary, the above results and analysis have demonstrated that HOGR, flotation column and nanobubble flotation processes are promising approaches for achieving the enhanced separation performance with the Anshan-type hematite ore. These approaches should also prove applicable to other types of refractory and finely disseminated iron minerals.
4. Conclusions
Based on the process mineralogy characteristics of a typical refractory flotation feed of Chinese Anshan-type hematite iron ore, the main reasons for the poor rougher flotation performance were investigate by laboratory-scale anionic reverse flotation tests.
The MLA results show that the particle size of flotation feed was rather fine, with 85.93% mineral grains smaller than 45 μm and 51.08% smaller than 20 μm. The particle size of quartz was relatively large, with only 34.77% of quartz particles smaller than 45 μm in size. Moreover, the Fe distribution and TFe grade reached 83.35% and 62.27% in the fine size fraction of 0~45 μm, respectively, and the higher enrichment of iron minerals in the fine size fraction is not beneficial for effective flotation separation. The liberation degree of hematite and quartz were 90.19% and 67.72%, respectively. The interior of liberated quartz particles with free surface contained hematite as their impurities and the content of composite quartz particle with hemitate reached 36.44%. Ideally, the flotation feed with a high liberation degree of hematite can obtain a good separation performance. However, the reagent dosages for the reverse flotation of hematite were determined to be 1.25 kg/t starch, 0.4 kg/t lime, and 0.76 kg/t collector under which the concentrate grade and recovery were only 67.82% and 68.76%, respectively. The screening results of rougher flotation products indicate that the difficult collection of coarse low-grade composite particles larger than 65.5 μm and the low separation efficiency of fine particles smaller than 45 μm are mainly responsible for the poor flotation performance. Depending to the process mineral analysis and the flotation behavior of main minerals in the flotation feed, HOGR, column flotation and nanobubble flotation are the new promising techniques to be adopted by the iron ore beneficiation industry in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.T. and Y.T.; methodology, Z.W.; investigation, Z.W., H.H. and H.S.; resources, D.T. and Z.W.; data curation, Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.W.; writing—review and editing, D.T.; supervision, D.T.; funding acquisition, Y.T. and D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51874303), a government grant No. 2020SNPT0006, and a research contract from private company ZBJF-20210326-6.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competitive financial interests or personal relationships, which could affect the work reported in this paper.
References
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Han, Y.; Parra-Alvarez, N.; Claremboux, V.; Kawatra, S.K. Flotation of Iron Ores: A Review. Miner. Process. Extr. M. 2021, 42, 184–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Q. Process in China’s beneficiation technology for complex refractory iron ore. Metal Mine. 2006, 11–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.X.; Yuan, Z.T.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, B.C. Advances in mineral processing technology of China’s metallic mine and its development orientation. Metal Mine. 2006, 34–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G. New development of mineral processing technology for iron mines in China. Sci. Tech. Infor. 2013, 9, 431. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Cao, Y.D. Reverse Flotation of Quartz From Magnetite Ore with Modified Sodium Oleate. Miner. Process. Extr. M. 2013, 34, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.L.; Fu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Suo, M.M.; Jiang, X.J. Mineral analysis and refractory reasons of fine ore of An steel Gongchangling beneficiation plant. China Mining Magazine. 2019, 28, 126–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.X.; Lu, S.C. Hydrophobic flocculation of fine hematite, siderite, and rhodochrosite particles in aqueous-solution. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 1994, 166, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, D.P.; Wu, Z.X.; Sobhy, A. Investigation of nanobubble enhanced reverse anionic flotation of hematite and associated mechanisms. Powder Technol. 2021, 379, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Han, Y. Flotation and adsorption of a new collector α-Bromodecanoic acid on quartz surface. Miner. Eng. 2015, 77, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.T.; Wang, L.; Hao, R.A.; Yan, W. Experimental Investigation of New Collector for Anqian Iron Ores. Mining Eng. 2013, 11, 15–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.C.; Liu, J.T.; Cao, Y.J.; Wang, D.P. Industrial Test of Flotation Column in Short Process of Reverse Floatation of Hematite. Metal Mine. 2011, 419, 81–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.X.; Tao, D.P. Mineralogical Analysis of Collophane in Yunnan Using AMICS and Exploration of Difficult Flotation Mechanisms. Chin. J. Eng. 2021, 43, 503–511. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, D.H.; Kupka, N.; Peuker, U.A.; Rudolph, M. Flotation study of fine grained carbonaceous sedimentary apatite ore - Challenges in process mineralogy and impact of hydrodynamics. Miner. Eng. 2018, 121, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Sobhy, A. Application of uniform test design in optimizing the flotation reagents of iron anionic reverse flotation circuit. Physicochem. Probl. Mi. 2022, 58, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhy, A.; Wu, Z.X.; Tao, D.P. Statistical analysis and optimization of reverse anionic hematite flotation integrated with nanobubbles. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M. Froth Flotation of Iron Ores. Int. J. Min. Eng. Miner. Process. 2012, 1, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.D.; Zhu, Y.M.; Han, Y.X.; Wei, Y.H. Effects and Activation Mechanism of Calcium lon on the Flotation of Quartz with fattyacid Collector. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science). 2018, 39, 409–415. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Quast, K. Use of conditioning time to investigate the mechanisms of interactions of selected fatty acids on hematite. Part 1: Literature survey. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, K. Use of conditioning time to investigate the mechanisms of interactions of selected fatty acids on hematite Part II laboratory investigations. Miner. Eng. 2015, 79, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.X.; Wang, L.G.; Cao, Y.J.; Li, C. Collecting Agent-Mineral Interactions in the Reverse Flotation of Iron Ore: A Brief Review. Minerals. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.S.; Sahoo, H. A Review on the Application of Starch as Depressant in Iron Ore Flotation. Miner. Process. Extr. M. 2022, 43, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, N.A.; Yassin, K.E.; Selim, K.A.; Rao, K.H.; Kandel, A.H. Effect of starch type on selectivity of cationic flotation of iron ore. Miner. Process. Extr. M. 2012, 121, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.B.; Zhu, Y.M.; Sun, C.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Han, Y.X. Reverse flotation of iron ore using amphoteric surfactant: 2-((2-(decyloxy)ethyl)amino)lauric acid. Physicochem. Probl. Mi. 2021, 57, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhpay, S.; Fornasiero, D. Flotation of coarse composite particles: Effect of mineral liberation and phase distribution. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, Q.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.C. Comparison of of different comminution flowsheets in terms of minerals liberation and separation properties. Miner. Eng. 2018, 125, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Zhu, Y.M.; Han, Y.X.; Li, W. A New Depressant DHY to Reverse Flotation of the Mixed Magnetic Concentrate from Anqian. Metal Mine. 2016, 475, 72–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.Z.; Wang, D.H.; Drelich, J.W.; Yang, B.; Li, D.; Zhu, Z.L.; Yao, J. Reverse flotation separation of hematite from quartz assisted with magnetic seeding aggregation. Miner. Eng. 2019, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Q.; Yin, W.Z. Investigation of Liberation Properties and Mineral Fracture Mechanisms of Iron Ores with Different Mineral Grain Sizes at Different Grinding Degrees. Miner. Process. Extr. M. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, L.; Mainza, A.N.; Becker, M.; Wiese, J.G. Using mineralogical and particle shape analysis to investigate enhanced mineral liberation through phase boundary fracture. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.Y.; Tao, D.P.; Tao, Y.J.; Liu, S.Y. An innovative flake graphite upgrading process based on HPGR, stirred grinding mill, and nanobubble column flotation. Int. J. Min. Sci. Techno. 2021, 31, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Z.T.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, P. Comparison of low-grade hematite product characteristics in a high-pressure grinding roller and jaw crusher. Miner. Metall. Proc. 2012, 29, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadangi, J.K.; Das, S.P. Potential of High-Pressure Grinding Roll (HPGR) for Size Reduction of Hard Banded Iron Ore. T. Indian. I. Metals. 2022, 75, 1797–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baawuah, E.; Kelsey, C.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Skinner, W. Comparison of the performance of different comminution technologies in terms of energy efficiency and mineral liberation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 156, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.N.; Xie, G.Y.; Peng, Y.L.; Chen, Y.R. Kinetic modeling and optimization of flotation process in a cyclonic microbubble flotation column using composite central design methodology. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 157, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Q.; Bu, X.N.; Mao, Y.Q.; Ni, C.; Peng, Y.L.; Xie, G.Y. Combined column and cell flotation process for improving clean coal quality: Laboratory-scale and industry-scale studies. Energ. Source Part A 2020, 42, 2678–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, S.; Shafaei Tonkaboni, S.Z.; Gharabaghi, M.; Ahmadi, R.; Shahbazi, B. Quartz particles flotation using nano-micro bubbles; Publisher: The first national conference of nano from syntesis to industry, Tehran, 2017.
- Ahmadi, R.; Khodadadi, D.A.; Abdollahy, M.; Fan, M. Nano-microbubble flotation of fine and ultrafine chalcopyrite particles. Int. J. Min. Sci. Techno. 2014, 24, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).