1. Introduction
Cell-free plasma DNA (cfDNA) is composed of circulating extracellular DNA originating from apoptosis or cell necrosis. It is generally released from different cellular lines (neutrophils, eosinophils and macrophages), circulating as mononucleosomes, which protect it from degradation. Small amounts of cfDNA are normally present in the blood of healthy individuals, but its levels increase in the setting of different clinical conditions, such as hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis [
1], sepsis [
2,
3], myocardial infarction [
4], trauma [
5] and cancer [
6].
Inflammation is a common feature of chronic kideny disease (CKD), especially in end-stage renal disease, and it appears to play a pivotal role in the release of cfDNA [
7]. Increased levels of cfDNA have been demonstrated to be associated with higher mortality in patients with CKD, especially in those undergoing hemodialysis [
8].
Apoptosis is a homeostatic mechanism responsible for the maintenance of cellular populations in tissues. It may also occur in the setting of immune reactions or noxious agents [
9]. Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases, cysteine aspartases or cysteine-dependent aspartate-directed proteases) are a family of protease enzymes playing essential roles in apoptotic pathway. They are named caspases due to their specific cysteine protease activity [
10]. Three main apoptotic pathways have been described: the extrinsic or death receptor pathway, the intrinsic or mitochondrial pathway and a pathway involving T-cell mediated cytotoxicity and perforin-granzyme-dependent killing of the cell [
10]. All of them converge in the execution pathway, which is initiated by the cleavage of caspase-3, resulting in DNA fragmentation, degradation of cytoskeletal and nuclear proteins, formation of apoptotic bodies, expression of ligands finally uptaken by phagocytic cells [
10]. Therefore, caspase-3 is an effector caspase, responsible for the progression of apoptotic mechanisms.
The aim of our study was the evaluation of cfDNA levels and caspase-3 concentrations in patients with chronic kidney disease, in order to investigate the potential role of these molecules, deriving from inflammatory and apoptotic mechanisms, in the progression of renal damage.
We studied cfDNA levels in patients with CKD and compared their levels with cfDNA in healthy subjects. Furthermore, we evaluated the possible relationship between cfDNA concentrations and the severity of renal disease. Moreover, we analyzed caspase-3 levels in CKD patients and healthy subjects, focusing on its possible change according to CKD stage. Finally, we evaluated the relationship between cfDNA and caspase-3 levels and the correlation between them and uremic toxins (creatinine and urea) in this population of patients.
2. Methods
2.1. Enrollment and Blood Collection
In this study, we evaluated cfDNA levels in 25 CKD patients. In particular, we recruited blood samples from 25 CKD patients (5 for each stage) who came to our center (Nephrology Department at San Bortolo Hospital in Vicenza, Italy) for routine check-up. CKD patients with serious medical comorbidities, including active infection, autoimmune disease, and malignant, pulmonary or hepatic disease were excluded from the study. Serum creatinine (SCr) was measured by an enzymatic method, isotope dilution mass spectrometry traceable by an automatic analyzer (Dimension Vista; Siemens Healthcare, Tarrytown, NY, USA), and eGFR was calculated with the CKD-EPI equation. Blood urea, sodium and potassium were measured by standard laboratory techniques with an automatic analyser (Dimension Vista, Siemens Healthcare, Tarrytown, NY, USA) Haemoglobin and Platelet count (PLT) were measured by the automated haematology analysers XN 9000 (SYSMEX, KOBE, Japan). Comorbidities, such as diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD), were recorded for all patients.
Demographic and clinical characteristics and laboratory parameters were recorded for all patients. In addition, 10 healthy volunteers (CTR) were enrolled as control group. Healthy subjects were recruited in the Blood Center of St. Bortolo Hospital, and blood from these subjects was kindly provided by the blood bank of St. Bortolo Hospital. Each volunteer, with any condition that influence kidney function, was excluded.
2.2. Biological Sample Collection
Blood samples were collected from all subjects into EDTA tube and processed within 30 minutes after venipuncture. Samples were subsequently centrifuged for 10 minutes at 3500 rpm. Plasma was carefully removed without touching the cell pellet and re-centrifuged at 13000 rpm for 15 minutes. After centrifugation, the supernatant was placed into a clean polypropylene tube and stored at -80°C until use.
2.3. Isolation and cfDNA Extraction
Within the first 30 minutes after drawing fresh plasma samples from all patients, DNA was isolated from 250 µl of plasma using a DNA isolation kit (ArrowDNA Kit; NorDiag, Holliston, MA) by automatic extractor NorDiag Arrow (NorDiag, Holliston, MA), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The DNA was eluated in 35 µl of elution buffer and cfDNA concentration was measured using a Picodrop Spectrophotometer (Bulldog Bio, Portsmouth, NH).
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
Plasma cfDNA was measured using real-time quantitative assay in RotorGene 6000 (Qiagen, Milan, Italy) for the β-actin gene. The primers sequences were as following: Forward(5’–3’) GCGCCGTTCCGAAAGTT; Reverse(5’–3’): CGGCGGATCGGCAAA.
A volume of 10 µl of cfDNA (template) was added to each reaction mixture (total of 15 μL), which consisted of 4.95 μL of deionized water, 1.25μL of Eva Green (Biotium, Hayward, CA), 5 μL of Real Time PCR Buffer, magnesium free (TakaRa, Shiga, Japan); 1.5 μL of Magnesium (TakaRa, Shiga, Japan); 0,5 μL of dNTP Mixture (TakaRa, Shiga, Japan); 5 μM of each primer and 0,3 μL of Takara Ex Taq R-PCR (TakaRa, Shiga, Japan).
Each run included an activation step at 95°C for 3 minutes followed by 50 amplification cycles of 30 seconds denaturation, 30 seconds annealing at 65°C (touchdown 1°C for 10 cycles) and 30 seconds elongation, and a final elongation step at 72°C for 5 minutes, with fluorescence acquired on the green channel. The PCR products were heated to 99 ºC and cooled for heteroduplex formation, and melt was monitored by fluorescence emission using appropriate denaturation range (50-99°C).
For each run, one aliquot of stock DNA was serially diluted with deionized water to generate a 6-point standard calibration curve (200000-20000-2000-200-20-2 pg/ml). A conversion factor of 6.6 pg of DNA per diploid cell was used. Results are expressed as genome equivalents (GE)/ml; 1 GE/ml equals 6.6 pg DNA.
We performed PCR runs 2 times in triplicate with samples and standard curves. A blank reaction and several negative controls were included in every run. Melt-curve analysis showed a single product-specific melting temperature with a mean of 93.5°C for β-actin gene.
2.5. Determination of Caspase-3 Activity
Plasma samples were assayed for cell free-caspase-3. Caspase-3 concentration was measured by Human Caspase-3 Instant Enzyme-Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) Kit (eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA) with a fluorometric assay at 450 nm by VICTORX4 Multilabel Plate Reader (PerkinElmer Life Sciences, Waltham MA, USA). Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Caspase-3 concentrations (ng/mL) were calculated from the standard curve (10-5-2.5-1.25-0.63-0.31-0.16 ng/mL) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Standard samples ranged from 0.16 to 10.0 ng/mL. Human Caspase-3 Instant ELISA Kit sensitivity is 0.12 ng/mL.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS Software package and Excel. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results are presented as percentages, or media and standard deviation (parametric variables) or medians and interquartile ranges (nonparametric variables). The Mann–Whitney U test or T test was used for comparison of two groups when appropriate. The Kruskal–Wallis test or ANOVA test for multiple comparisons were applied to compare the groups when appropriate. Correlation coefficients were calculated with the Spearman’s rank or Pearson’s test, as appropriate.
3. Results
A total of 25 CKD patients were included in this study. 14/25 patients were male. The mean age of enrolled patients was 57±17 years old.
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) was attributed to diabetic nephropathy (7 patients), to hypertension (8 patients), nephroangiosclerosis (3 patients), polycystic kidney disease (2 patients), other causes (3 patients) or unknown causes (2 patients).
For our propose, we divided patients according to CKD stage. Each stage was composed of 5 patients.
Table 1 reports comorbidities and biochemical parameters for each stage of CKD (
Table 1).
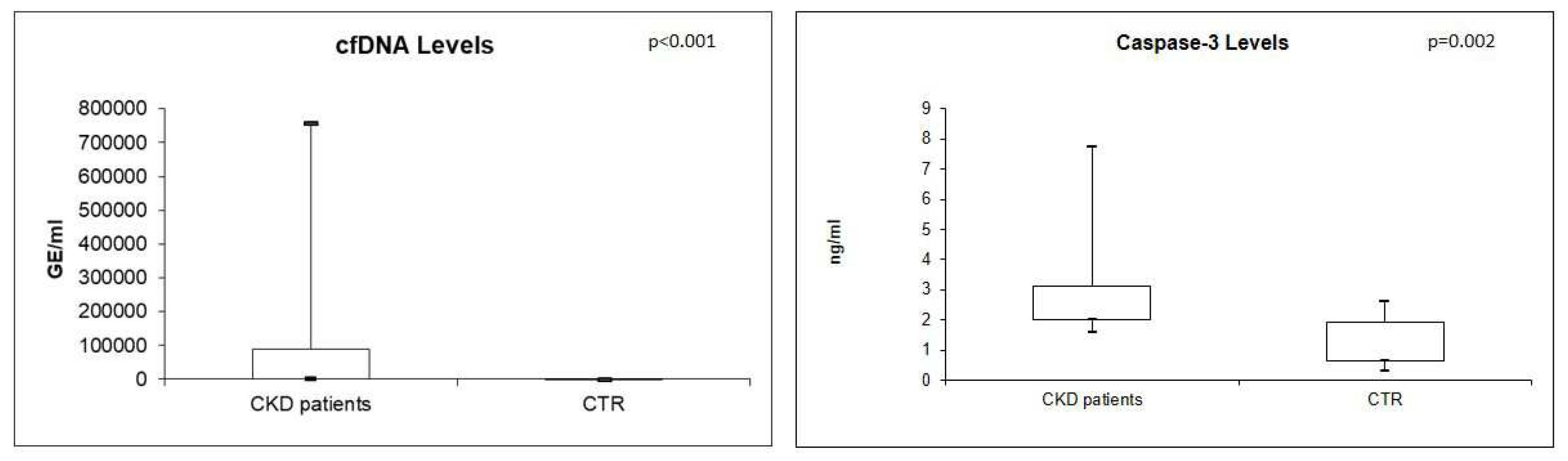
Real-time quantitative analysis showed significantly higher levels of plasma cfDNA and Caspase-3 in CKD patients compared with CTR (both p<0.05) (
Figure 1).
In particular, the median value of cfDNA resulted 37537 GE/ml (IQR: 1495.4-90326.09) in CKD patients compared with 186.7 GE/ml (IQR 122.95-285.8) in controls. In the same way, the median value of caspase-3 resulted 2.20 ng/ml (IQR: 1.99-3.12) in CKD patients compared with 1.114 ng/ml (IQR: 0.6-1.9) in healthy individuals.
Furthermore, we analyzed cfDNA and caspase-3 levels in CKD patients with different comorbidities. Median values of cfDNA and Caspase-3 did not differ significantly between patients with (n=4) and without diabetes (cfDNA p=0.20, Caspase-3 p=0.37), with (n=13) hypertension and without (cfDNA p=0.11, Caspase-3 p=0.21), with (n=5), with cardiovascular comorbidity and without (cfDNA p=0.17, Caspase-3 p=0.35).
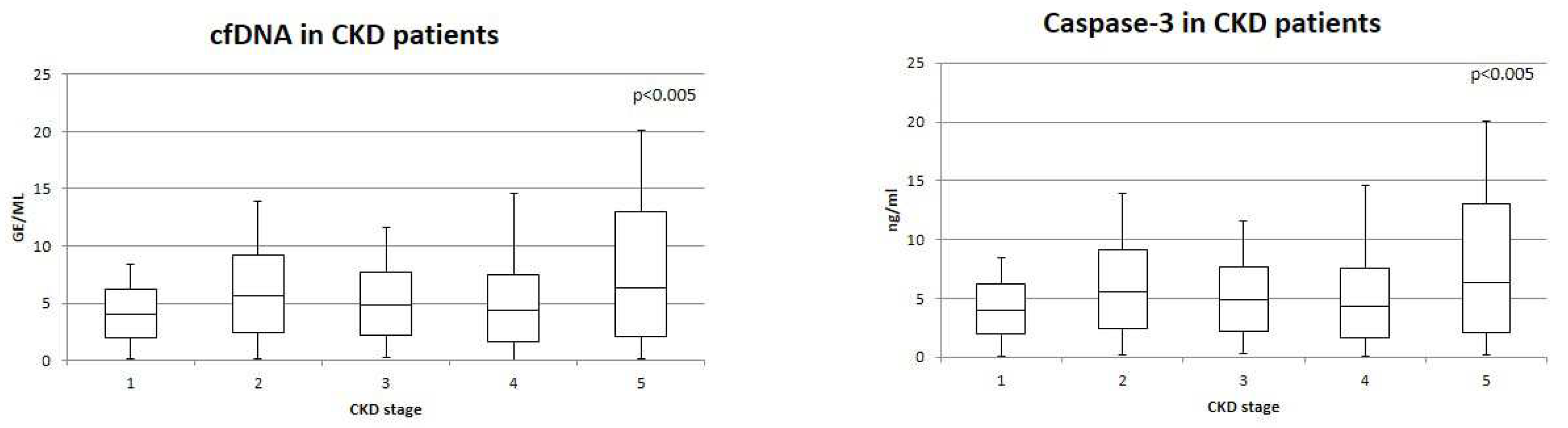
Furthermore, we analyzed cfDNA and caspase-3 levels in each stage of CKD. CfDNA and Caspase-3 levels were significantly different comparing CKD stages (both p<0.05) (
Figure 2). In particular, cfDNA and Capsase-3 values were lower in patients with CKD stage G1, while they resulted higher in patients with CKD stage G5. Furthermore, cfDNA and Caspase-3 levels did not differ significantly between CKD G1 and CKD G2 and CKD G3. CfDNA e Caspase-3 values resulted significantly higher in CKD G5 compared with all CKD stages (p=0.04 and p=0.05, respectively).
In addition, we investigated the relationship between cfDNA and Caspase-3 and urea and serum creatinine. A very strong significant positive correlation was observed between cfDNA and Caspase-3 levels (Sperman’s rho=0.7, p<0.001). In addition, positive correlations were observed between urea/cfDNA (Sperman’s rho=0.57, p=0.01) and urea/Caspase-3 (Sperman’s rho=0.53, p=0.02), serum creatinine/cfDNA (Sperman’s rho=0.49, p=0.03) and serum creatinine/Caspase-3 (Sperman’s rho=0.40, p=0.05). We summarized correlation data in
Table 2. (
Table 2)
4. Discussion
In our study, we evaluated cfDNA levels and caspase-3 concentrations in patients with chronic kidney disease, in order to investigate the potential role of these molecules, deriving from inflammatory and apoptotic mechanisms, in the progression of renal damage.
CfDNA has been isolated from blood and urine of healthy subjects, but its levels increase in the setting of sepsis [
2,
3], myocardial infarction [
4], trauma [
5] and cancer [
6]. Also patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis have been reported to have increased levels of cfDNA [
1]. In particular, compared with concentrations before hemodialysis session, higher cfDNA levels have been found during the treatment, decreasing to the pre-dialysis concentrations within 30 minutes after the procedure [
11].
According to these data, in our study, cfDNA levels were higher in patients with CKD compared to healthy subjects. Moreover, its levels increased in patients with CKD stage G5 compared to all CKD stages. These data suggest a possible relationship between cfDNA release and the progression of renal disease. Indeed, in a recent study, cfDNA has been demonstrated to be closely associated with diabetic kidney disease, predicting its worsening in patients with type 2 diabetes [
12]. Furthermore, a previous study has analyzed the role of cf-DNA in acute kidney injury induced by ischaemia, suggesting its possible effect in the amplification of renal damage [
13].
In our study, hypertension, diabetes and cardiovascular comorbidities did not affect cfDNA concentrations, which may increase as the result of the contemporaneous presence of all these factors. Our data have also demonstrated a positive correlation between cfDNA and creatinine and urea, thus suggesting an increased cfDNA release secondary to the uremic status. Urea, as well as other uremic toxins (indoles, p-cresylsulfate and phosphate), is known to induce oxidative stress by expanding reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and triggering leukocyte free radical production, thus resulting in endothelial dysfunction and apoptosis [
14]. Both mechanisms may be involved in the increased release of cfDNA.
We have also found higher levels of caspase-3 in patients with chronic kidney disease compared to healthy subjects, and its concentrations increased with the worsening of renal damage. Indeed, caspase-3 levels were higher in patients with CKD stage G5, like cfDNA concentrations. Moreover, a positive correlation was found between caspase-3 levels and creatinine and urea concentrations. A relationship between cf-DNA and caspase-3 levels was observed as well.
In higher organisms, apoptosis is known to be one of the main sources of cf-DNA and to be mediated by caspases, a family of cysteine proteases cleaving after an aspartate residue in their substrates [
15]. In particular, caspase-3 plays a pivotal role in the in the execution pathway of apoptotis which is one of the main mechanisms involved in the progression of renal disease, together with endothelial dysfunction [
10,
14]. Furthermore, it is known that elevated urea levels can lead to molecular changes responsible for the generation of reactive oxygen species and apoptosis. Also hemodialysis is known to induce apoptosis of leukocytes, as shown by the appearance of typical ladders after electrophoresis [
16].
Therefore, it is clear that cfDNA and caspase-3 levels are tightly connected in the setting of renal disease progression and their concentrations increase with the severity of kidney damage, thus reflecting the effect of the uremic toxins. Indeed, our data suggest that inflammation and apoptosis may be responsible for the higher levels of cfDNA in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Our study has some limitations. First, the study population consists of 25 CKD patients; second, we evaluated caspase-3 concentrations, whose role is fundamental in the execution pathway, therefore we are not able to indicate the specific apoptotic mechanism activated in this population of patients. Future studies are needed to investigate the role of other caspases in the progression of chronic kidney disease.
5. Conclusion
CfDNA and caspase-3 concentrations are higher in patients with chronic kidney disease compared with healthy subjects and their levels increase with the worsening of renal damage. They are tightly related and they reflect the activation of apoptotic and inflammatory mechanisms playing a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of CKD. Future studies should focus on the analysis of the specific apoptotic pathways which may be involved in chronic kidney disease.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, X.X. and Y.Y.; methodology, X.X.; software, X.X.; validation, X.X., Y.Y. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, X.X.; investigation, X.X.; resources, X.X.; data curation, X.X.; writing—original draft preparation, X.X.; writing—review and editing, X.X.; visualization, X.X.; supervision, X.X.; project administration, X.X.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”, please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
Please add: “This research received no external funding” or “This research was funded by NAME OF FUNDER, grant number XXX” and “The APC was funded by XXX”. Check carefully that the details given are accurate and use the standard spelling of funding agency names at
https://search.crossref.org/funding, any errors may affect your future funding.
Acknowledgments
In this section you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
Declare conflicts of interest or state “The authors declare no conflict of interest.” Authors must identify and declare any personal circumstances or interest that may be perceived as inappropriately influencing the representation or interpretation of reported research results. Any role of the funders in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results must be declared in this section. If there is no role, please state “The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results”.
References
- Korabecna, M.; Opatrna, S.; Wirth, J.; Rulcova, K.; Eiselt, J.; Sefrna, F.; Horinek, A. Cell-Free Plasma DNA during Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis and in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnacho-Montero, J.; Huici-Moreno, M.J.; Gutiérrez-Pizarraya, A.; López, I.; Márquez-Vácaro, J.; Macher, H.; Guerrero, J.M.; Puppo-Moreno, A. Prognostic and diagnostic value of eosinopenia, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and circulating cell-free DNA in critically ill patients admitted with suspicion of sepsis. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R116–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, A.; Virzì, G.M.; Brocca, A.; Pastori, S.; de Cal, M.; Marcante, S.; Granata, A.; Ronco, C. The Role of Cell-Free Plasma DNA in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis. Blood Purif. 2015, 41, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.P.-Y.; Chia, R.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Tsao, K.-C.; Sun, C.-F.; Wu, J.T. Elevated cell-free serum DNA detected in patients with myocardial infarction. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 327, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoham Y, Krieger Y, Perry ZH, Shaked G, Bogdanov-Berezovsky A, SilbersteinE, Sagi A, Douvdevani A. Admission cell free DNA as a prognostic factor inburns: quantification by use of a direct rapid fluorometrictechnique. BiomedRes Int. 2014, 2014, 306580.
- Kim K, Shin DG, Park MK, Baik SH, Kim TH, Kim S, Lee S. Circulating cell-freeDNA as a promising biomarker in patients with gastric cancer: diagnostic validity and significant reduction of cfDNA after surgical resection. AnnSurgTreat Res. 2014, 86, 136–142.
- Kohlova, M.; Ribeiro, S.; Sameiro-Faria, M.D.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Fernandes, J.; Reis, F.; Miranda, V.; Quintanilha, A.; Belo, L.; Bronze-Rocha, E.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA levels in hemodialysis patients and its association with inflammation, iron metabolism, and rhEPO doses. Hemodial. Int. 2013, 17, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovbin, D.; Novack, V.; Wiessman, M.P.; Elkadir, A.A.; Zlotnik, M.; Douvdevani, A. Circulating cell-free DNA in hemodialysis patients predicts mortality. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbury CJ, Hickson ID. Cellular responses to DNA damage. Annu Rev Pharmaco Toxicol. 2001, 41, 367–401. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Moreira V, de la Cera Martínez T, Gago González E, Prieto García B,Alvarez Menéndez FV. Increase in and clearance of cell-free plasma DNA in hemodialysis quantified by real-time PCR. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2006, 44, 1410–1415.
- Li, X.; Hu, R.; Luo, T.; Peng, C.; Gong, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Li, Q. Serum cell-free DNA and progression of diabetic kidney disease: a prospective study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, V.; Abu Hamad, R.; Berman, S.; Efrati, S. Renoprotective Effects of DNAse-I Treatment in a Rat Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Nephrol. 2016, 43, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Chamieh, C.; Liabeuf, S.; Massy, Z. Uremic Toxins and Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease: What Have We Learned Recently beyond the Past Findings? Toxins 2022, 14, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Prior, P.; Salvesen, G.S. The protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity, activation and inhibition. Biochem J. 2004, 384, 201–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atamaniuk, J.; Ruzicka, K.; Stuhlmeier, K.M.; Karimi, A.; Eigner, M.; Mueller, M.M. Cell-Free Plasma DNA: A Marker for Apoptosis during Hemodialysis. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).