Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
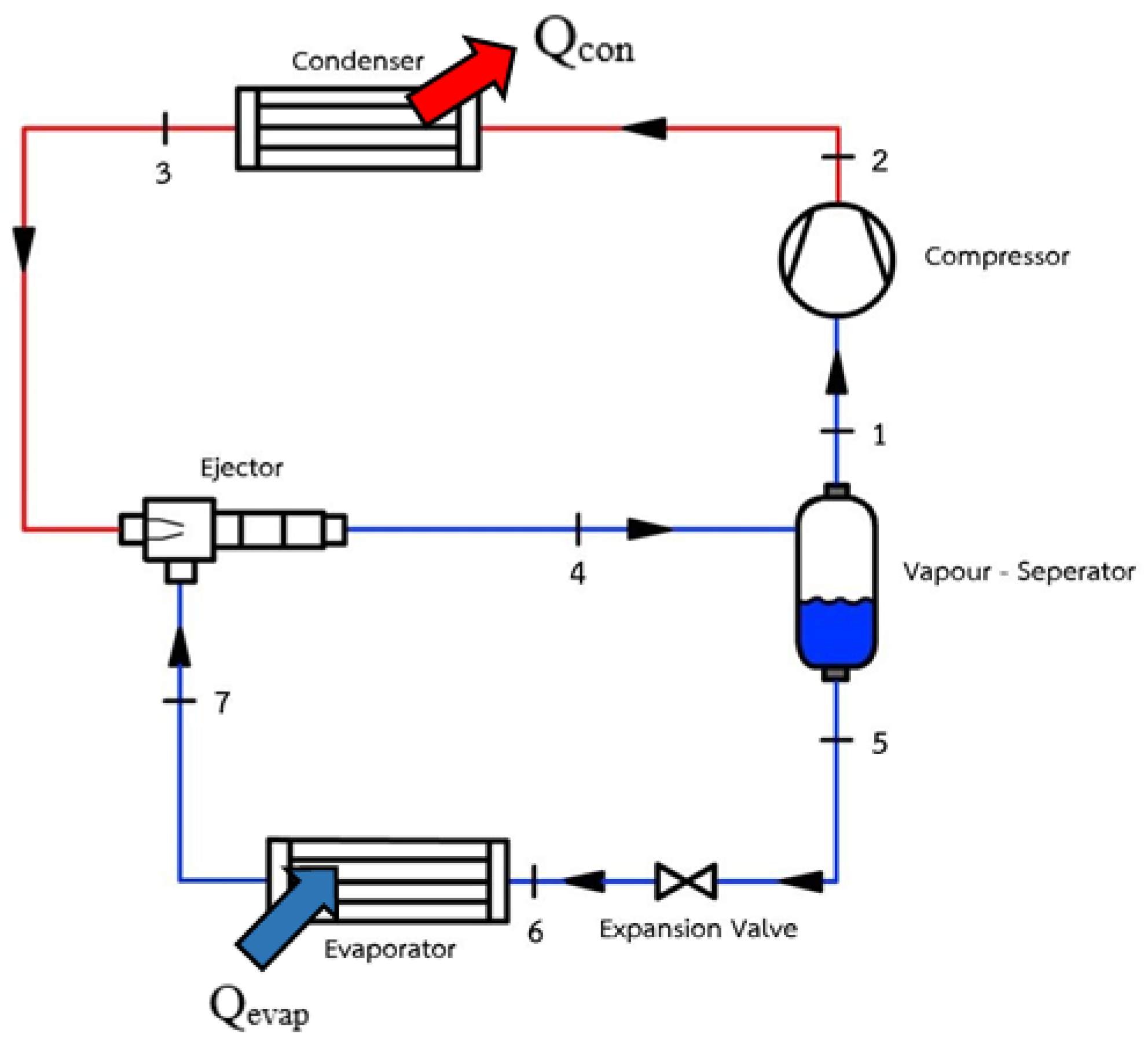
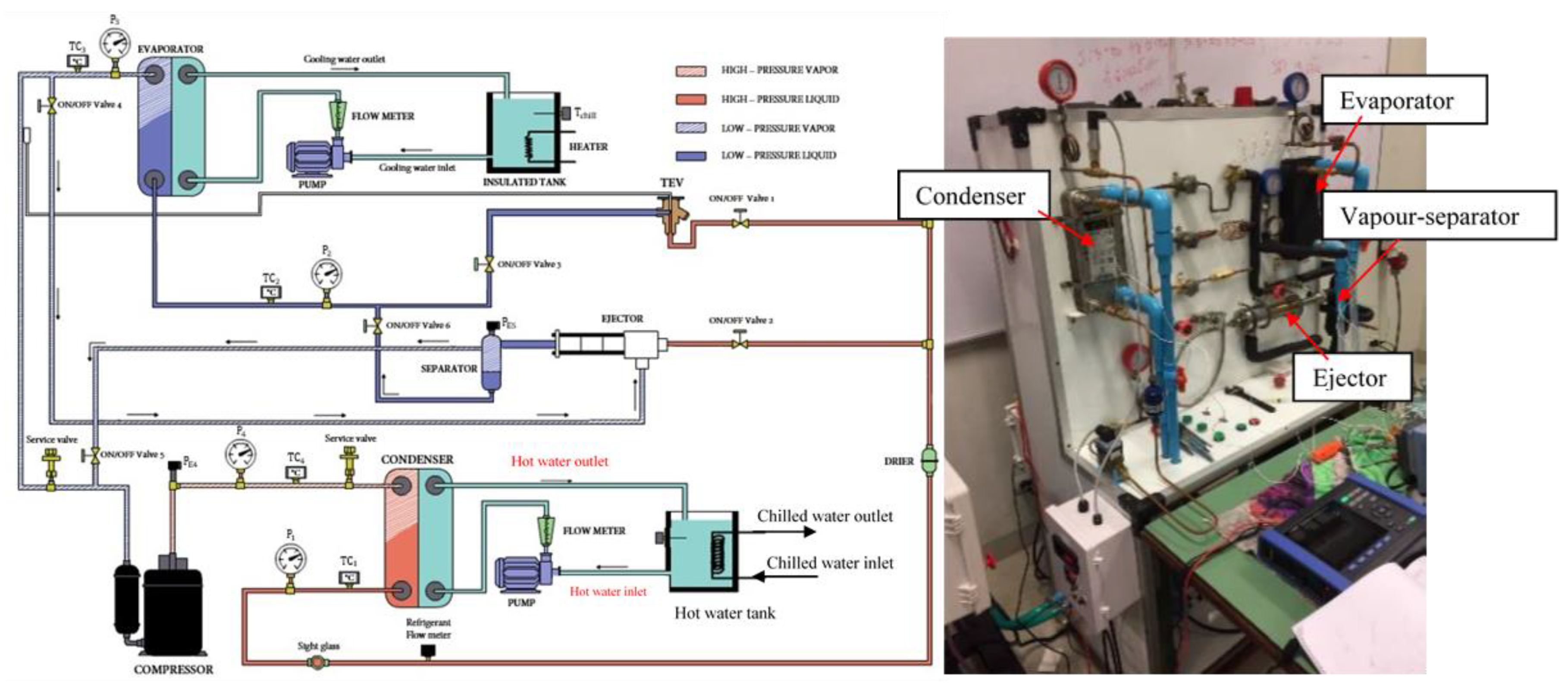
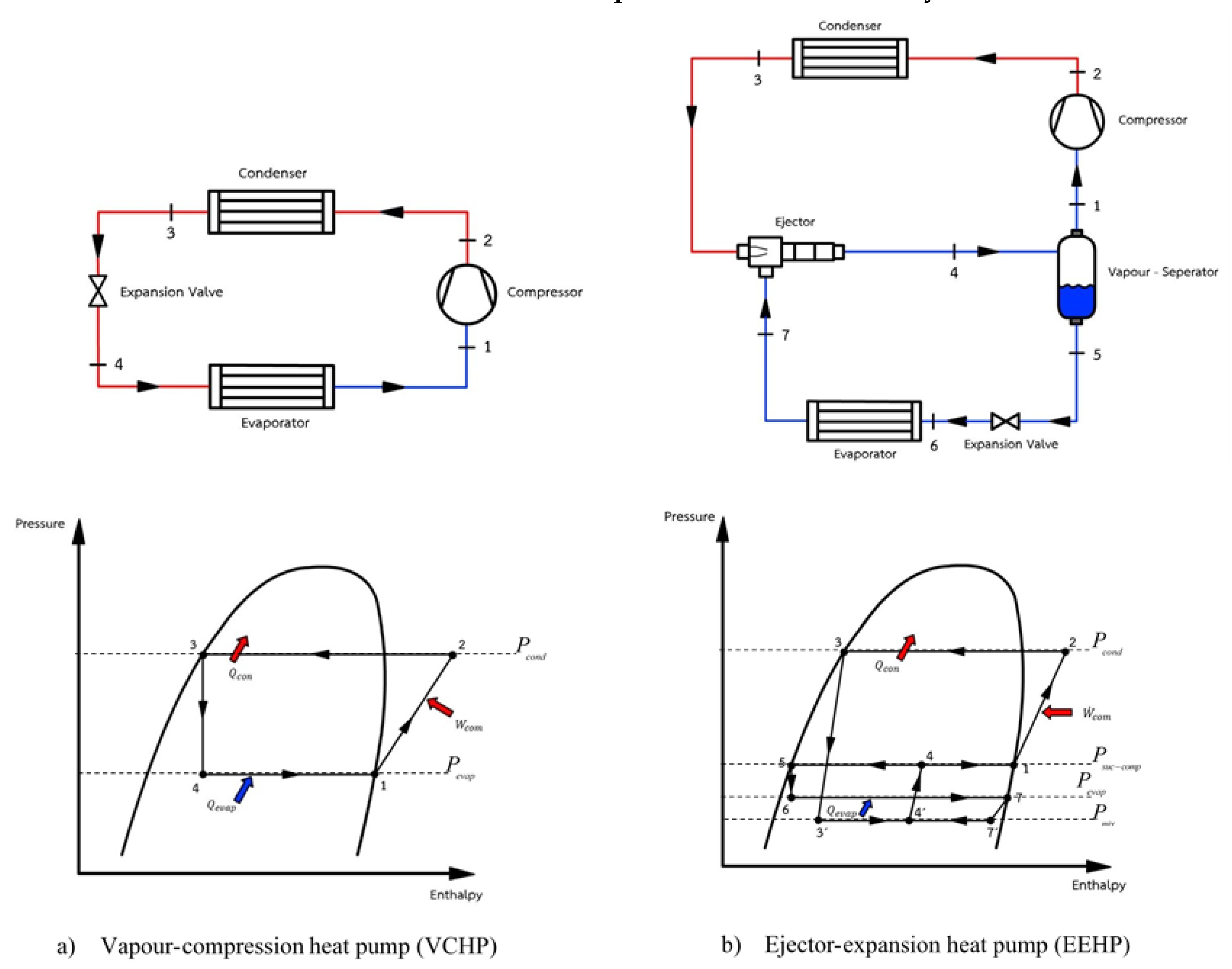
2.1. Test Based on the VCHP
2.2. Test Based on the EEHP
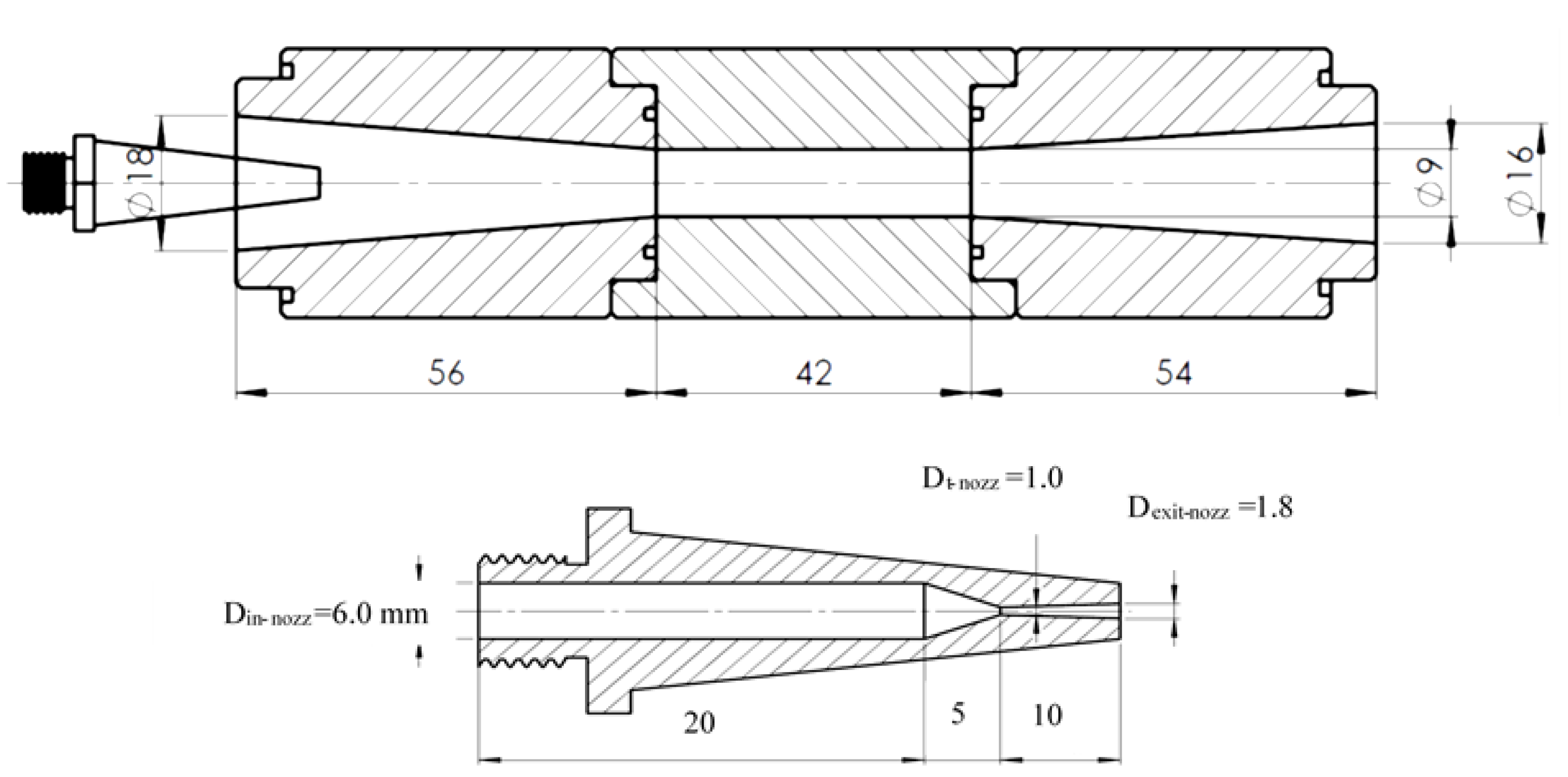
2.4. Instrumentations and Data Reduction
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Performance Comparison of an Ejector-Expansion Heat Pump with a Vapour-Compression Heat Pump
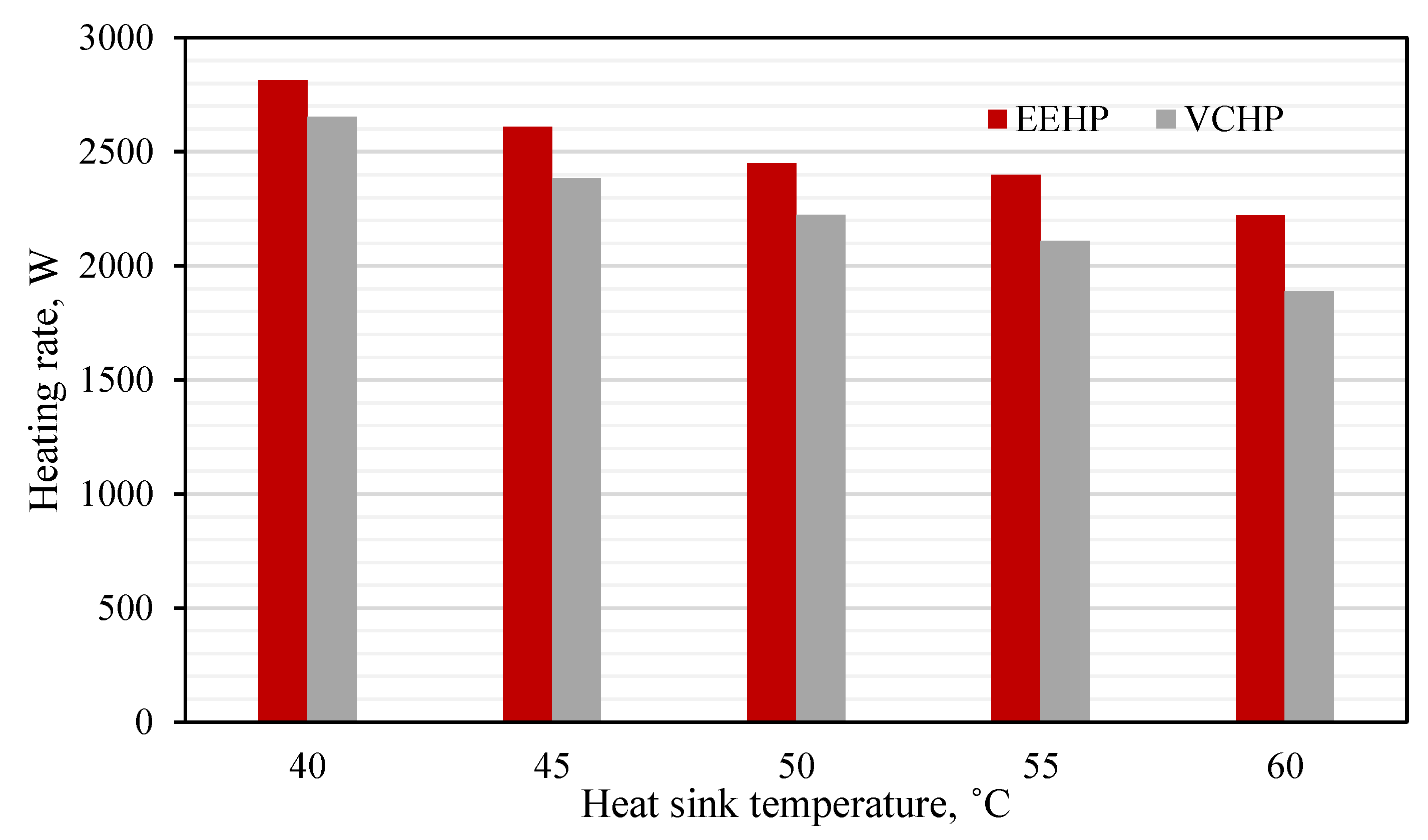
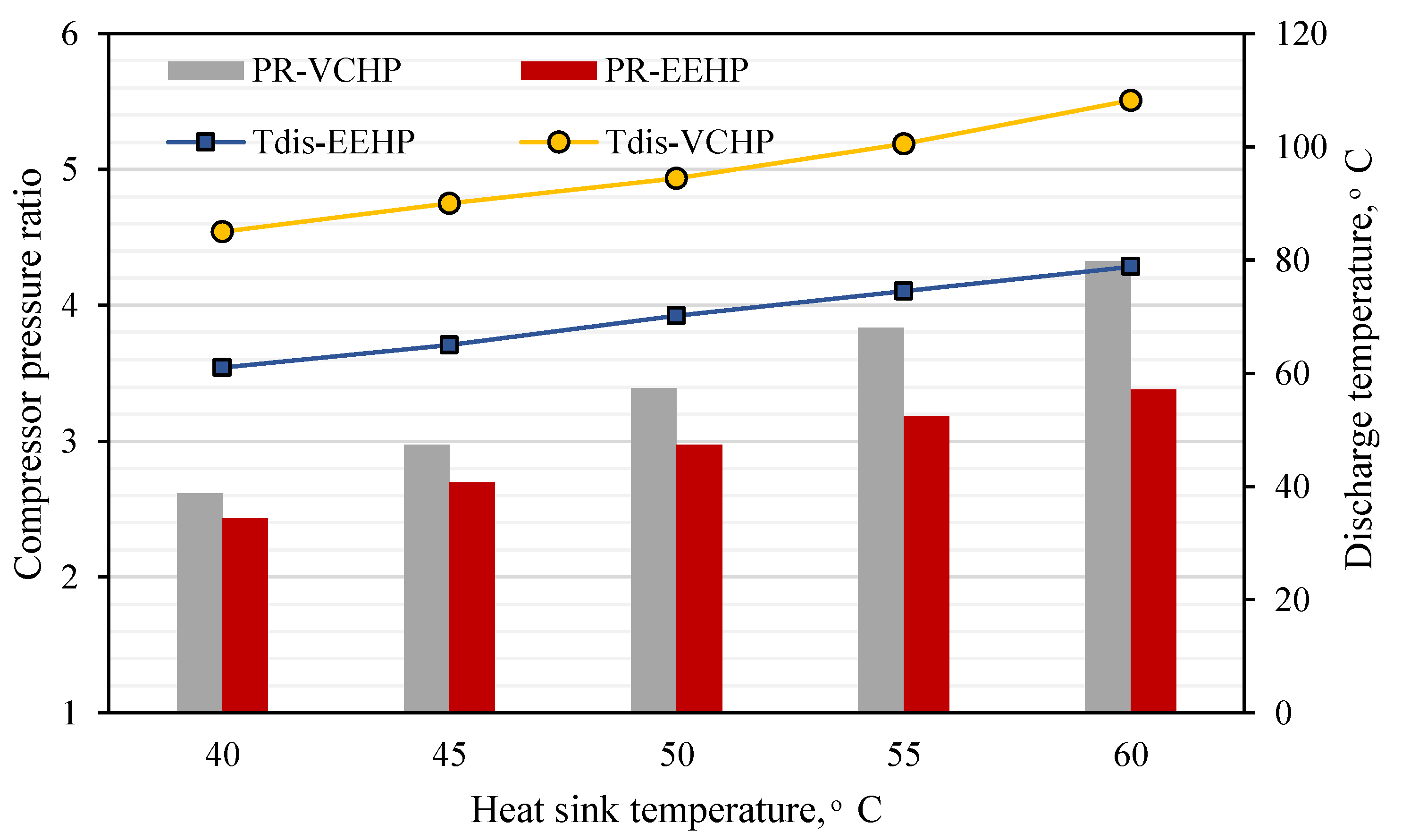
3.1.1. Impact of Heat Sink Temperature’s Variations
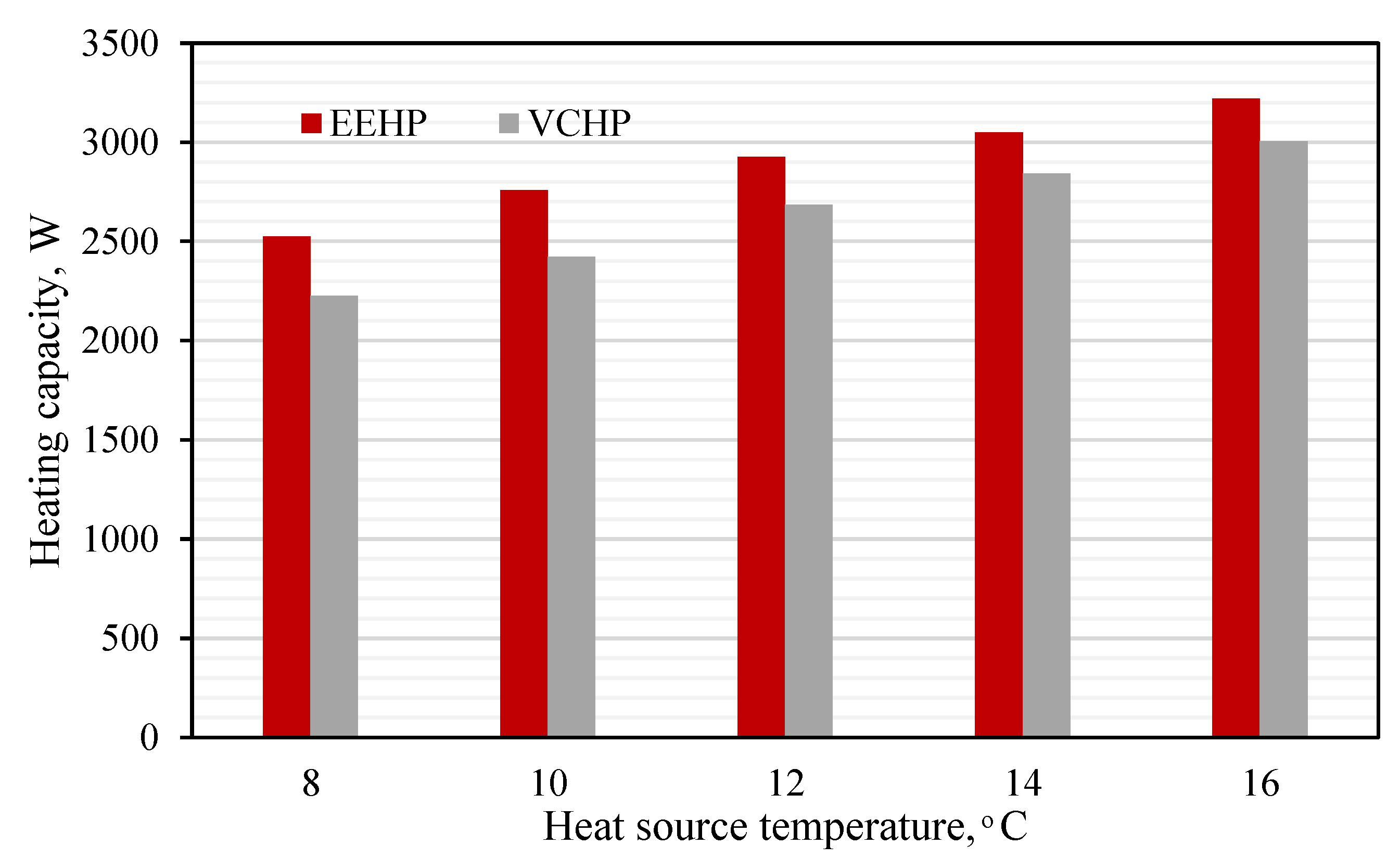
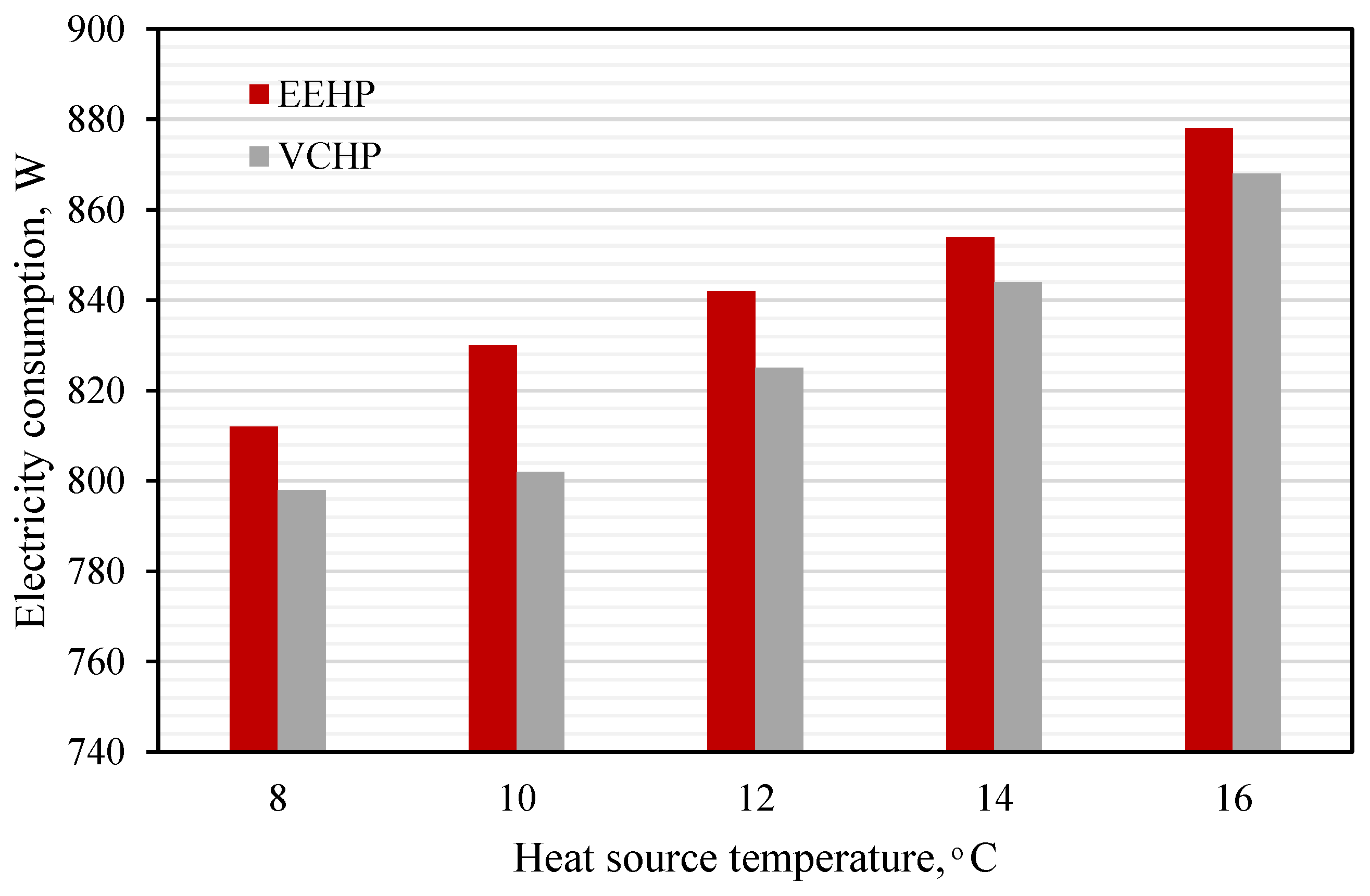
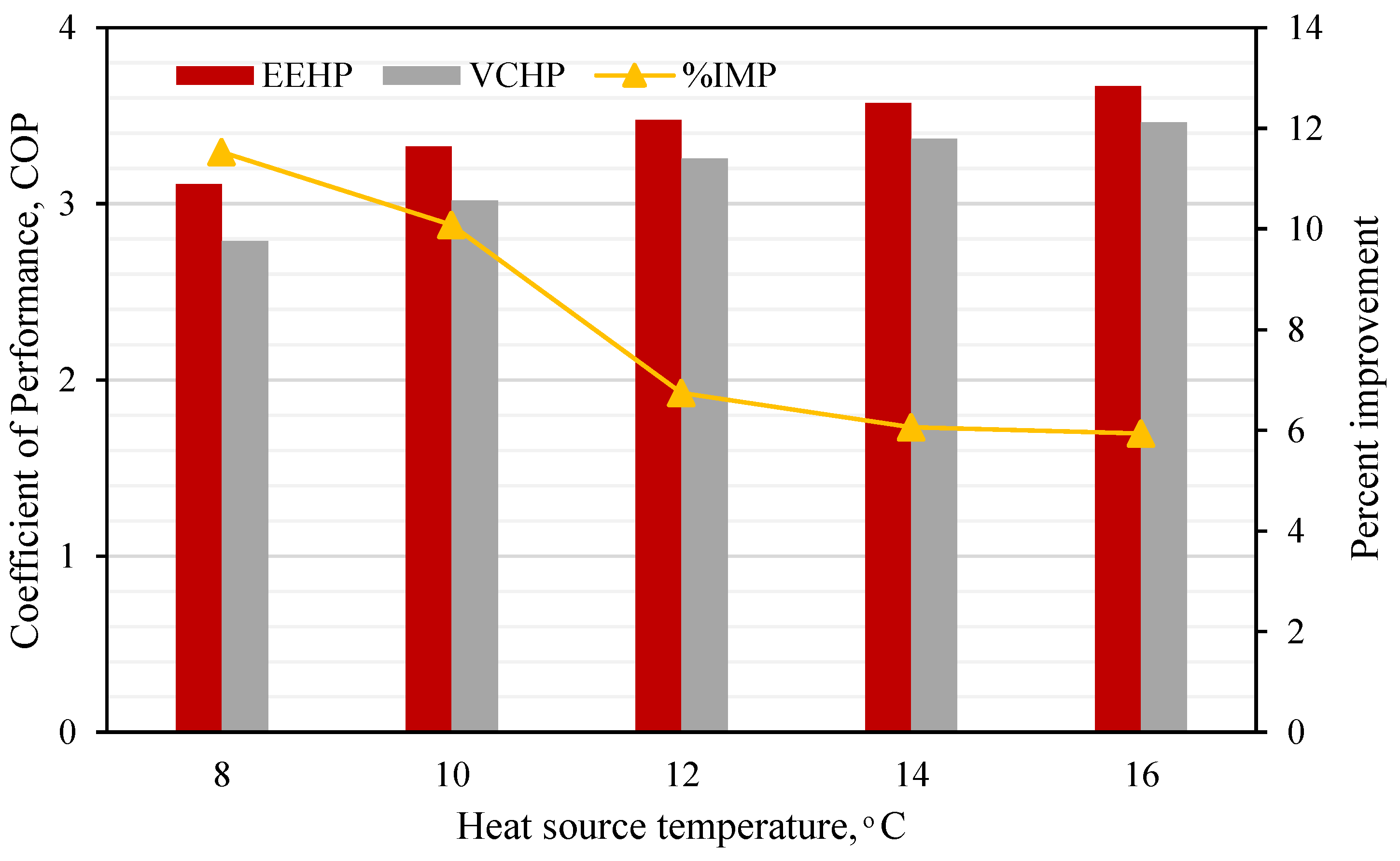
3.1.1. Impact of Heat Source Temperature’s Variations
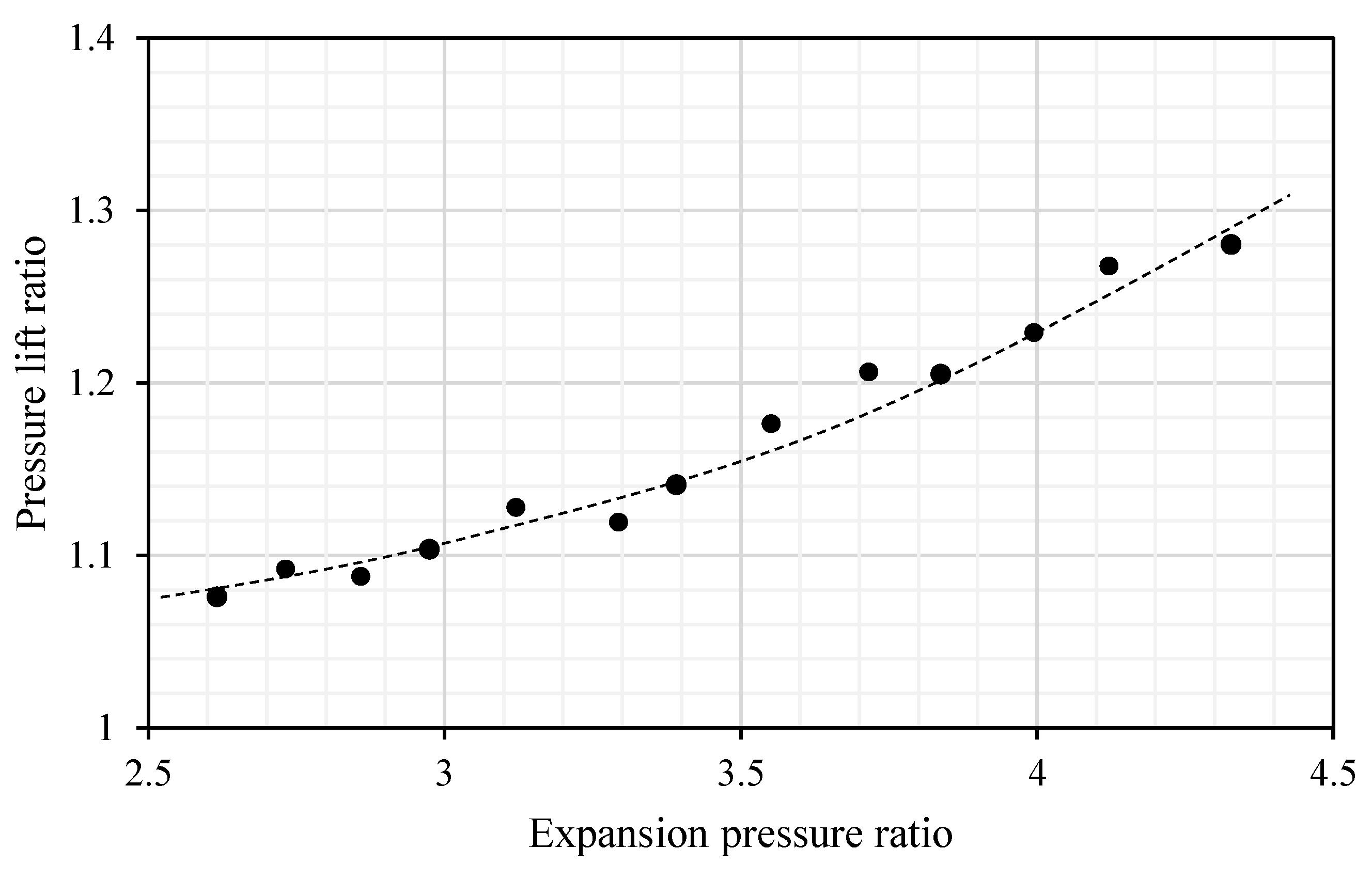
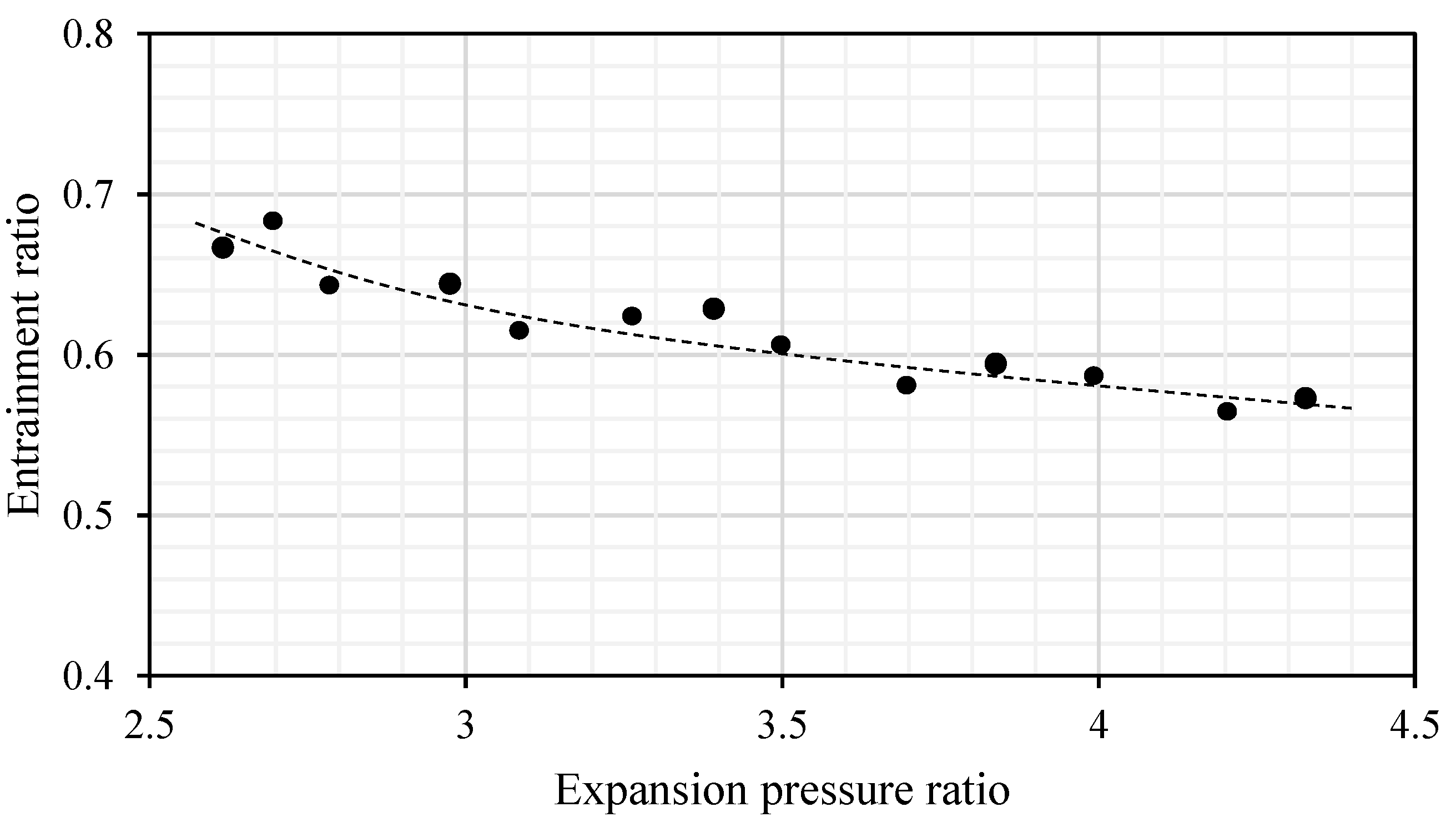
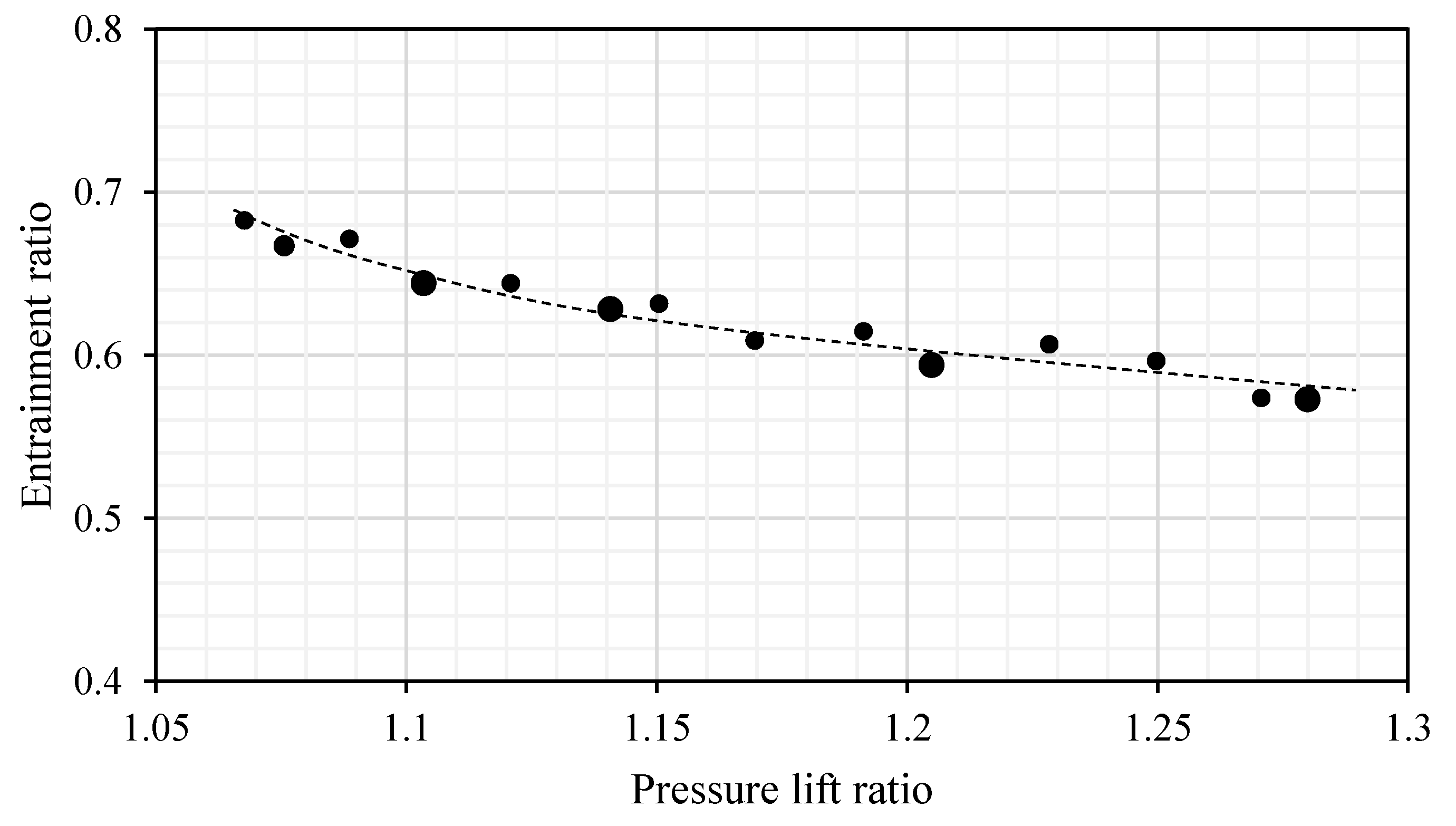
3.2. Impact of the Expansion Pressure Ratio to the Two-Phase Ejector Performance
4. Conclusions
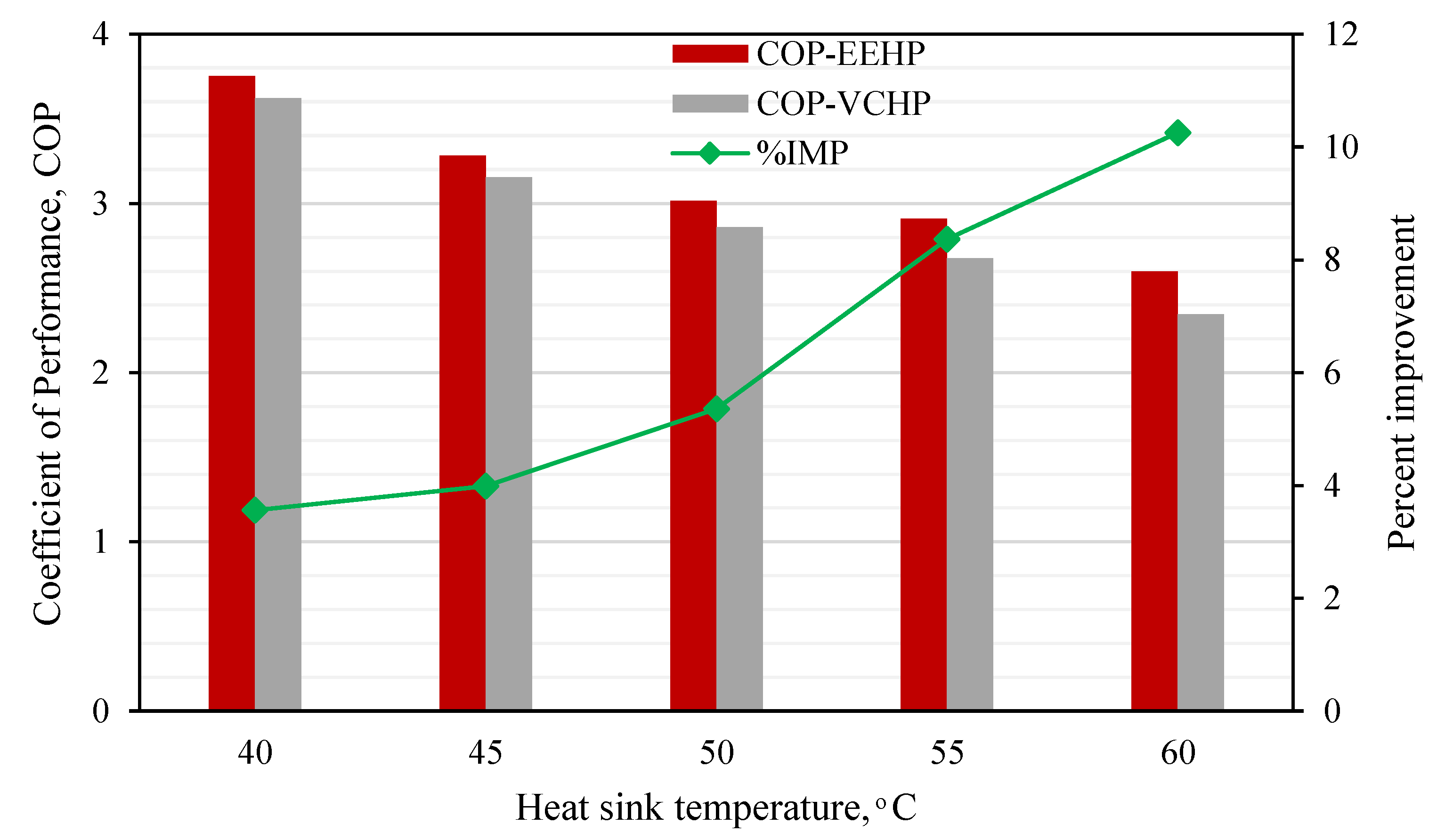
- The EEHP can produce a higher QH and COPHP than the VCHP under the heat sink (TL) between 40 and 60 °C. The percent improvement is 6.1 – 11.8% compared to the VCHP (conventional system). A higher percent improvement is achieved when increasing the TL.
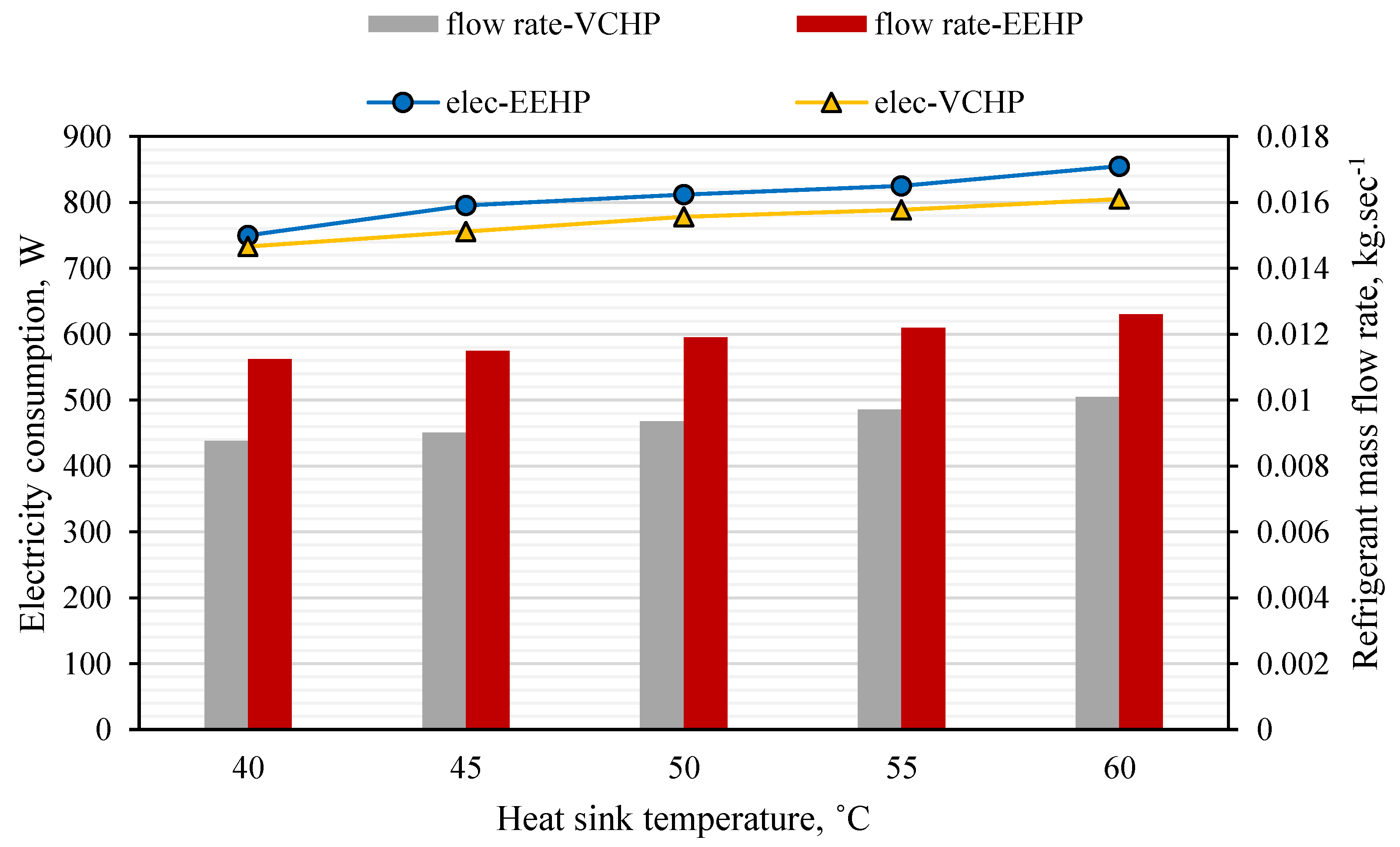
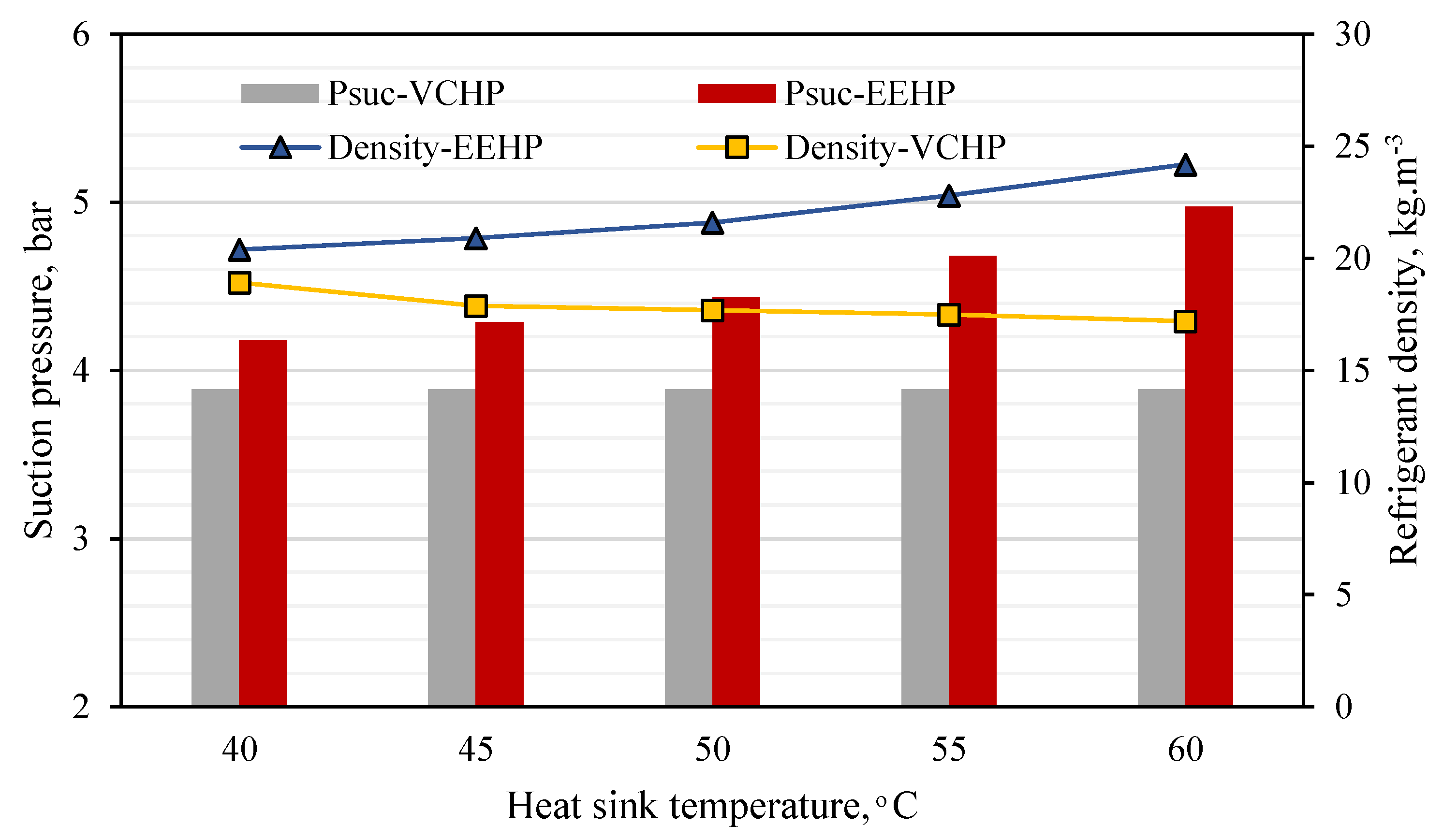
- The key to the performance improvement is the use of the two-phase ejector. This is because of the pressure lift effect and mass entrainment performance. Additionally, an increase in the compressor suction pressure via the pressure lift causes the refrigerant density to be increased which results in a higher mass flow rate (at a fixed compressor rotational speed) through the compressor and condenser. Hence, the EEHP yields higher heating rate than the VCHP.
- As the TL is increased while the TH is held constant, the EEHP performs at a higher heating rate and COPHP than the VCHP throughout the investigated range of the heat source temperature. The percent improvement is 5.8 - 11.4%. Lower heat source temperature yields a higher percent improvement.
- The key performance improvement of the EEHP is mainly dependent on the expansion pressure ratio (pressure ratio between the heat sink and heat source) which significantly relates the two-phase ejector operation as indicated by the entrainment performance and pressure lift ratio.
- The two-phase ejector performance is important to the overall system performance of the EEHP because it is a key to recovery expansion work. There is a trade-off between the pressure lift ratio and entrainment ratio for a certain expansion pressure ratio. The heating capacity of the EEHP is associated with such parameters which demonstrates the actual working condition.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A | Cross-sectional Area (m2) |
| COP | Coefficient of Performance |
| EEHP | Ejector expansion heat pump |
| ER | Entrainment ratio |
| Elec | Electricity consumption |
| h | Refrigerant Specific enthalpy (kJ kg–1) |
| VCHP | Vapour-compression heat pump |
| m | Mass flow rate (kg s–1) |
| P | Pressure (bar) |
| PR | Pressure ratio |
| Q | Heat transfer rate (kW) |
| T | Temperature (°C) |
| Subscripts |
| chill | representing the chilled water |
| comp | representing the compressor |
| con | representing the condenser |
| dis-comp | representing the compressor discharge |
| evap | representing the evaporator |
| evap-out | representing the evaporator outlet |
| exit-nozz | condition at the primary nozzle exit |
| expan | representing the expansion process |
| H | refers to as the heat sink |
| hot | refers to hot water |
| in-nozz | inlet nozzle condition |
| lift | lift ratio |
| mix | condition at the ejector mixing |
| suc-comp | condition at the compressor suction |
| pri | representing the primary fluid |
| sec | representing the secondary fluid |
| t-ej | the ejector mixing chamber throat |
| t-nozz | the primary nozzle throat |
References
- Huang, Z. and Li, T., 2023. Experimental Investigation of Gravity Effect on a Vapor Compression Heat Pump System. Energies, 16(11), p.4412.
- Szymiczek, J. , Szczotka, K., Banaś, M. and Jura, P., 2022. Efficiency of a Compressor Heat Pump System in Different Cycle Designs: A Simulation Study for Low-Enthalpy Geothermal Resources. Energies, 15(15), p.5546.
- Zhou, Y. , Peng, B. and Zhu, B., 2023. Assessment of Optimal Operating Range and Case Verification of a Waste Heat Air-Source Heat Pump Water Heater Based on a Semiempirical Parametric Model. Energies, 16(5), p.2289.
- Navarro-Esbrí, J. and Mota-Babiloni, A., 2023. Experimental analysis of a high temperature heat pump prototype with low global warming potential refrigerant R-1336mzz (Z) for heating production above 155° C. International Journal of Thermofluids, 17, p.100304.
- Trancossi, M. , Cannistraro, G. and Pascoa, J., 2020. Thermoelectric and solar heat pump use toward self sufficient buildings: The case of a container house. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 18, p.100509.
- Zanetti, E. , Azzolin, M., Bortolin, S., Busato, G. and Del Col, D., 2022. Experimental data and modelling of a dual source reversible heat pump equipped with a minichannels evaporator. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 35, p.101471.
- hossein Shiravi, A. , Ghanbarpour, M. and Palm, B., 2023. Experimental evaluation of the effect of mechanical subcooling on a hydrocarbon heat pump system. Energy, p.127406.
- Zhang, Q. , Huang, H., Zhai, H., Zhao, W. and Lü, X., 2023. Experimental research on direct expansion heat pump flue gas waste heat recovery and humidification nitrogen reduction system. Journal of Cleaner Production, p.137000.
- Hu, Z. , Li, Y., El-Mesery, H.S., Yin, D., Qin, H. and Ge, F., 2022. Design of new heat pump dryer system: a case study in drying characteristics of kelp knots. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 32, p.101912.
- Yuan, Y. , Hassan, A., Zhou, J., Zeng, C., Yu, M. and Emmanuel, B., 2022. Experimental and numerical investigation on a solar direct-expansion heat pump system employing PV/T & solar thermal collector as evaporator. Energy, 254, p.124312.
- Wang, Y. , Zong, S., Song, Y., Cao, F., He, Y. and Gao, Q., 2021. Experimental and techno-economic analysis of transcritical CO2 heat pump water heater with fin-and-tube and microchannel heat exchanger. Applied Thermal Engineering, 199, p.117606.
- Chiriboga, G. , Capelo, S., Bunces, P., Guzmán, C., Cepeda, J., Gordillo, G. and Montesdeoca, D.E., 2021. Harnessing of geothermal energy for a greenhouse in Ecuador employing a heat pump: design, construction, and feasibility assessment. Heliyon, 7(12), p.e08608.
- Lim, H. , Kim, C., Cho, Y. and Kim, M., 2017. Energy saving potentials from the application of heat pipes on geothermal heat pump system. Applied Thermal Engineering, 126, pp.1191-1198.
- Ye, J. and Ni, L., 2023. Experimental study on heating performance of air source heat pump fresh air unit with fresh air and return air mixing in severe cold regions. Energy and Buildings, 283, p.112839.
- Leonzio, G. , Fennell, P.S. and Shah, N., 2022. Air-source heat pumps for water heating at a high temperature: State of the art. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 54, p.102866.
- Wu, J. , Sun, S., Song, Q., Wang, D. and Sun, D., 2022. Subcritical recuperative air-to-water heat pump with zeotropic mixtures: Comparative and performance assessment. Energy Reports, 8, pp.13682-13697.
- Huang, M.J. and Hewitt, N.J., 2013. The experimental analysis of the effect of ambient factors on the defrosting of economised vapour injection compressor air source heat pump in marine climates. International journal of refrigeration, 36(3), pp.820-827.
- Li, K. , Ma, J., Zhang, B., Su, L., Liu, N., Zhang, H., Dou, B., He, Q., Zhou, X. and Tu, R., 2023. Experimental study on low temperature heating performance of different vapor injection heat pump systems equipped with a flash tank and economizers for electric vehicle. Applied Thermal Engineering, 227, p.120428.
- Yang, T. , Zou, H., Tang, M., Tian, C. and Yan, Y., 2022. Experimental performance of a vapor-injection CO2 heat pump system for electric vehicles in− 30° C to 50° C range. Applied Thermal Engineering, 217, p.119149.
- Li, J. , Fan, Y., Zhao, X., Bai, X., Zhou, J., Badiei, A., Myers, S. and Ma, X., 2022. Design and analysis of a novel dual source vapor injection heat pump using exhaust and ambient air. Energy and Built Environment, 3(1), pp.95-104.
- Boccardi, G. , Botticella, F., Lillo, G., Mastrullo, R., Mauro, A.W. and Trinchieri, R., 2017. Experimental investigation on the performance of a transcritical CO2 heat pump with multi-ejector expansion system. International Journal of Refrigeration, 82, pp.389-400.
- Ghazizade-Ahsaee, H. and Askari, I.B., 2020. The application of thermoelectric and ejector in a CO2 direct-expansion ground source heat pump; energy and exergy analysis. Energy Conversion and Management, 226, p.113526.
- Zhu, Y. , Huang, Y., Li, C., Zhang, F. and Jiang, P.X., 2018. Experimental investigation on the performance of transcritical CO2 ejector–expansion heat pump water heater system. Energy conversion and management, 167, pp.147-155.
- Zhang, Z. , Feng, X., Tian, D., Yang, J. and Chang, L., 2020. Progress in ejector-expansion vapor compression refrigeration and heat pump systems. Energy Conversion and Management, 207, p.112529.
- Li, S. , Lu, J., Li, W., Huang, S. and Tian, L., 2023. Comparative performance of ternary azeotropic mixtures as substitutes for R134a in dual-temperature air source heat pump combined ejector. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 37, p.101577.
- Fan, C. , Yan, G. and Yu, J., 2019. Thermodynamic analysis of a modified solar assisted ejector-compression heat pump cycle with zeotropic mixture R290/R600a. Applied Thermal Engineering, 150, pp.42-49.
- Al-Sayyab, A.K.S. , Navarro-Esbrí, J. and Mota-Babiloni, A., 2022. Energy, exergy, and environmental (3E) analysis of a compound ejector-heat pump with low GWP refrigerants for simultaneous data center cooling and district heating. International Journal of Refrigeration, 133, pp.61-72.
- Sutthivirode, K. and Thongtip, T., 2022. Experimental investigation of a two-phase ejector installed into the refrigeration system for performance enhancement. Energy Reports, 8, pp.7263-7273.
- Zhang, Y. , Wei, X. and Qin, X., 2022. Experimental study on energy, exergy, and exergoeconomic analyses of a novel compression/ejector transcritical CO2 heat pump system with dual heat sources. Energy Conversion and Management, 271, p.116343.
- Nemati, A. , Nami, H. and Yari, M., 2017. A comparison of refrigerants in a two-stage ejector-expansion transcritical refrigeration cycle based on exergoeconomic and environmental analysis. International journal of refrigeration, 84, pp.139-150.
- Bilir N, Ersoy HK. Performance improvement of the vapour compression refrigeration cycle by a two-phase constant area ejector. Int J Energy Res 2009;33(5):469-480.
- Ersoy HK, Bilir N. The influence of ejector component efficiencies on performance of ejector expander refrigeration cycle and exergy analysis. Int J Exergy 2010;7(4):425-438.
| Item | Uncertainty | Model |
|---|---|---|
| Data acquisition | ±0.15% | Yokogawa GP10-1-E-F/UC20 |
| Power meter | ±0.2% | Hioki PQ3100 |
| Thermocouple | 3.0 - 5.0% | Type-K |
| Pressure transducer | 1.0%FS | Dixell, PF11 |
| Volume flow meter | 3.5 - 5.0% | Burkert, 8030SE30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





