1. Introduction
Basal cell carcinomas (BCC) occur primarily on the face, yet their prognosis is excellent as they do not possess an aggressive biological behavior. The suggested treatment for BCC is surgical excision [
1] with adequate margins [
2], which however results in a scar that can significantly impact the aesthetic appearance of the patient. Notably, an untreated BCC also shares key visual characteristics with scars, i.e., similar alterations of the skin relief (usually a protrusion) and of the local qualities of the texture and of the color of the body surface. Therefore, for the efficient management of BCC and the evaluation of not only the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions, but also of the respective long-term sequelae it is crucial to conduct reliable assessments to better understand the visual impact of both tumors and post-treatment scars. In view of the generally non-aggressive nature of BCC, alternative to surgery methods of treatment have been developed. One of these is immunocryosurgery, i.e. the combination of imiquimod and cryosurgery in a fixed-time protocol [
3]. One of the advantages of this minimally invasive approach are the reasonably good resulting scars.
Scar assessment and response to therapy have been previously assessed with subjective scar scales [
4,
5]; however, in the meanwhile noninvasive, objective, and quantitative measurement devices have been developed that seem to supersede them [
6]. Technology-based scar assessment tools allow their accurate and reproducible evaluation. Lee et al. [
7] reviewed objective devices for burn scar analysis classified according to the features they may assess. These included color and texture (measured by digital photographs and laser imaging); scar dimensions (using 3D photographic imaging and ultrasound); pliability and elasticity (measured by cutometers, tissue tonometry, and elasticity probes). However, the high cost of these devices, the complexity of their usage, and time-constrains of the clinicians involve, are significant obstacles to their wider adoption. Therefore, these promising, noninvasive devices are still primarily used for research purposes and have not been incorporated in the daily clinical practice [
6,
8].
On the other hand, clinical photography [
9,
10,
11], coupled to computerized image analysis [
12,
13] is a cost-effective approach alternative to be used in lieu of live patient assessments to assess scars’ features. Among the different parameters characterizing a scar, color and texture appearance are the leading parameters that contribute to the assessment of its visibility [
4]. Color deviations relate to alterations of the underlying local blood perfusion rates and the concentrations of other chromophores. Texture aberrations are perceived as alterations of the smoothness, roughness, and irregularity confined to the skin surface of the scar. A previous study [
12] has outlined a machine-learning-assisted tool for automated burn scar severity rating (classification) based on the Vancouver Scar Scale. For implementing their multi-classifier to predict scores of the scars, the authors considered only color and texture features as input information for the classification process.
In a recent study [
13], we have verified the applicability of the modified scar rating system (MSRS) [
8] to evaluate the impact of immunocryosurgery on the visibility of the BCC harboring skin area after treatment compared to the pretreatment visual perception of the tumor. In essence, this user-friendly scale consists of three components (‘texture,’ ‘color,’ and ‘height’) and utilizes patient photographs to evaluate the appearance of a specific skin area. The visibility of the target site is subjectively assessed based on increasing levels of dissimilarity when compared to the characteristics of the surrounding skin.
However, MSRS relies on subjective visual inspection. A more reliable and valid assessment of these items might help clinicians measure outcomes, develop, and evaluate treatment strategies. Herein, we strike forward, breaking down visual similarity into two major sub-problems (color and texture assessments) and exploring relevant descriptors and metrics, using computerized image analysis, that best predict perceptual similarity. Although such an approach is appealing for producing transparent scoring rules, it faces immense challenges to device features that capture the way experts perceive color and texture differences. For this, we explored a variety of similarity metrics in different color spaces, and we utilized distances between images in the embedding space of a pre-trained deep convolutional neural network (CNN), exploiting the emergent property of deep visual presentations in predicting perceptual similarity [
14]. Herewith, through analysis of BCC treatment data, we present a promising, clinical photographs based, robust, high-speed, and affordable computerized image analysis modality to reliably assess visibleness of skin lesions and monitor treatment outcomes in clinical settings.
To the best of our knowledge, our work represents the initial attempt to predict perceptual similarity accurately and reliably, based on clinical photography, in the field of dermatology.
2. Materials and Methods
The use of archival photographic material for this study was approved by the Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of the University Hospital of Ioannina (approval nr.: 3/17-2-2015[θ.17)].
We used 176 photographs from 100 patients (57 males, 43 females; age range: 45–85 years) routinely treated for a facial BCC. Sixty-seven photographs were acquired from treated BCC tumors (post-treatment scars; 21 scars after standard surgical excision; 46 scars after immunocryosurgery). The rest 109 photographs were from untreated BCC tumors at the patient’s first examination.
The data acquisition procedure consisted of two steps. In the first step six physicians (four dermatologists and two plastic surgeons) independently graded the pre-and post-treatment BCC lesions using the scale of Mecott et al. [
9]. The same photographs were then used for the subsequent second digital imaging analysis study step. More precisely, the physicians assessed the resemblance of the target, ‘lesional’, and the perilesional, ‘healthy’ skin areas on a 4-scores scale of increasing color and texture visual deviation: ‘1’ (indistinguishable from the surrounding skin) ‘2’ (slight), ‘3’ (moderate) and ‘4’ (strong deviation).
Internal consistency and interrater agreement were estimated using Cronbach’s α [
14] and weighted Gwet’s AC2 [
15], respectively. The mean color and texture visual deviation score was estimated and used as the “gold standard” to validate the quantitative descriptors derived from image analysis.
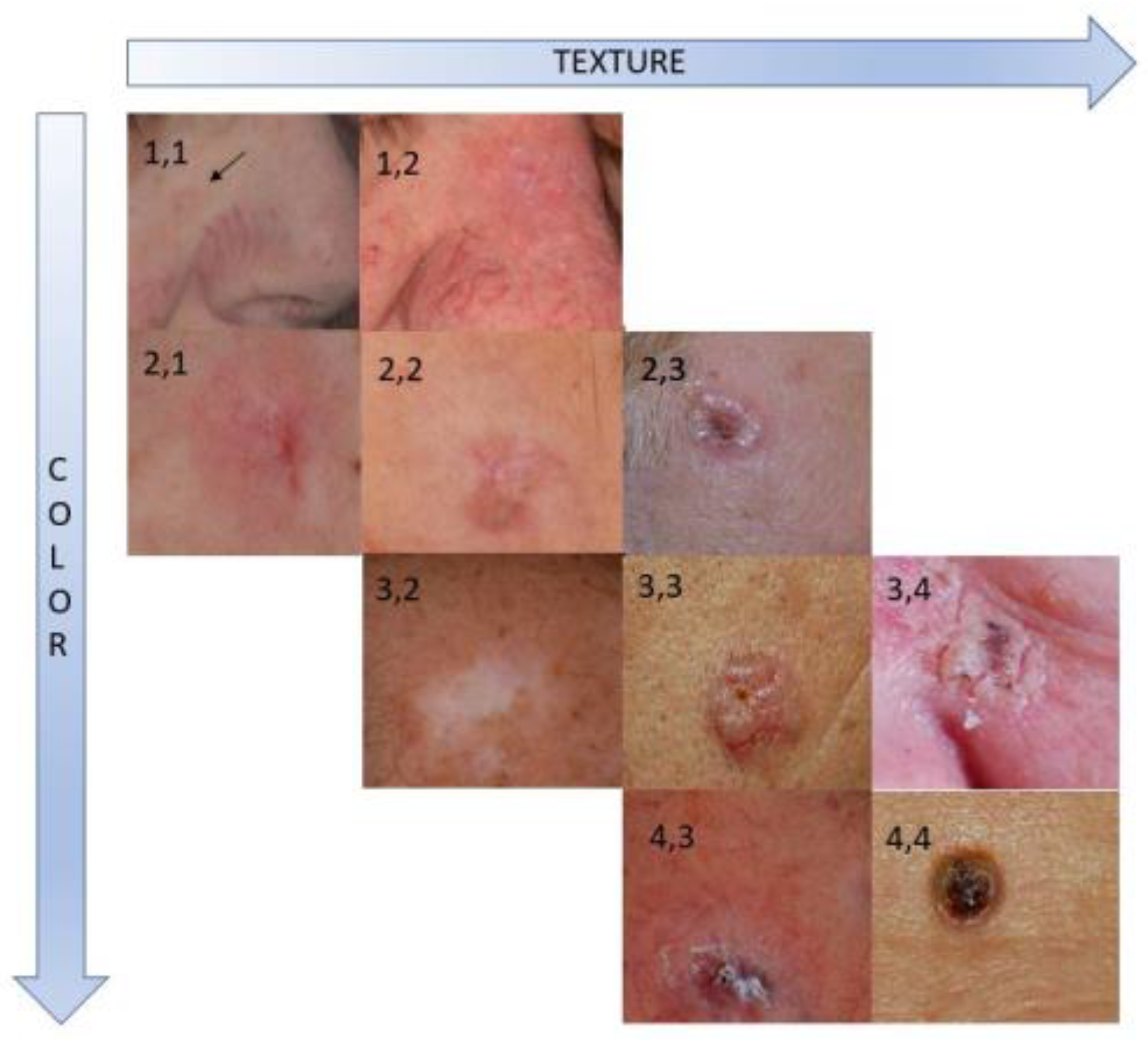
Figure 1 demonstrates examples of averaged color and texture scores for BCC sites.
2.1. Color and texture similarities using clinical photographs
From each photo, three patches of arbitrary size were manually cropped: one patch from the target skin area (S) and two sample patches (S1, S2) from the perilesional skin area. Similarity was estimated as the mean “distance” of the target patch S from the perilesional skin patches S1 and S2:
where M is a “distance” metric that measures the degree of color and texture deviation of the target skin area from the surrounding healthy skin.
2.1.1. Perceptual Color similarity
To measure color similarity, the metric M (Equation (1)) operates on the patches’ mean color vectors. Humans perceive colors differently from the way colors are presented in different color spaces. Aiming to measure color similarity as perceived by human raters, we explored different color spaces (RGB, YIQ, CIELAB) and metrics (Euclidean distance, Bray-Curtis distance, deltaE94).
Color modeling is essential in various image-processing applications based on skin color information [
16,
17]. Many color spaces have been developed to represent the color information of color images. The default color space for most image-capturing and storing devices is RGB (Red, Green, Blue). However, in computer vision and image processing, RGB color space is converted into other color spaces through linear or non-linear transformations.
Important color spaces successfully used in skin lesion applications are the YIQ and CIELAB color models [
18,
19,
20]. The YIQ color model was explicitly designed to consider the non-linear response of the human eye to different colors. YIQ separates the luminance (Y) and color information (I, Q components). The I component ranges from blue to orange, and the Q component from green to purple. The CIELAB color space, also referred to as L*a*b*, was intended as a pseudo-uniform color space, such that the Euclidean distance between two specified colors in this space is proportional to the color difference between these colors perceived by a standard observer. The L*a*b* color model also separates brightness L* from chromaticity components (a*b*). Chromaticity a* ranges from green to red, and chromaticity b* from blue to yellow.
Color differences were estimated using the standard Euclidean and the Bruy-Curtis Distance (BCD). For example, in CIELAB color space, assuming the mean color vectors
of image patch
and
of image patch
their Euclidean distance and BCD are given by:
Likewise, we estimate color differences in YIQ and RGB color spaces.
The Euclidean distance between two color vectors in CIELAB color space (Equation (2)) is known as the DeltaE Color difference. DeltaE has been successfully employed in several studies to quantify skin color differences using digital photography [
21,
22,
23]. In the present study, we additionally explored DeltaE94, a modified formula that is proposed to represent the human perception of color differences better than DeltaE [
24].
BCD metric is often used in environmental science, and biology but recent studies have highlighted the performance of BCD in medical information [
25], and medical image retrieval [
26,
27]. BCD is a normalized metric, that treats alike the variations among low and high values, with a nice property for positive values (in our case skin color has positive values in YIQ/ L*a*b* color spaces): BCD lies between 0 and 1, where zero means actual similarity.
2.1.2. Perceptual Texture similarity
In computer vision, a large body of literature has been devoted to texture feature extraction to perform tasks such as image classification, segmentation, and retrieval [
28]. However, in a survey study on perceptual textural similarity estimation, Dong et al. [
29] demonstrated that there is no simple relationship between the perceptual attributes and the computational features of texture images. The survey concluded that features from image embeddings derived from pre-trained CNNs outperform the conventional features. The latter verified the observations of Zhang et al. [
30], who first revealed that perceptual similarity is an emergent property shared across deep visual presentations. In a subsequent study, Gao et al. [
31] proposed a framework to predict fine-grained perceptual texture similarity by combining layer-wise deep feature similarity and similarity between images’ contour maps.
Motivated by the studies above, we used the VGG16 [
32] network pre-trained on ImageNet [
33] for feature extraction and texture similarity estimation. Consequently, to measure texture differences, the metric M (Equation (1)) operates on the deep representations of the patches obtained through the VGG16 network.
CNNs process images by convolving multiple filters over the input image to extract local patterns and features. The output of each filter is a two-dimensional feature map that captures the filter’s response at each spatial location of the input image. A convolutional layer with N filters (channels) generates N feature maps. Subsequent convolutional layers combine these feature maps to form higher-level features that capture increasingly complex visual patterns.
Assuming a pair of image patches S1 and S2, we denote their pair of activations as:
and are the activations of image patches S1 and S2 from layer L, respectively.
The cosine similarity estimates the texture similarity of pair F [
31]. Considering final image embeddings from the fully connected layers, the cosine distance is estimated between the corresponding deep feature vectors.
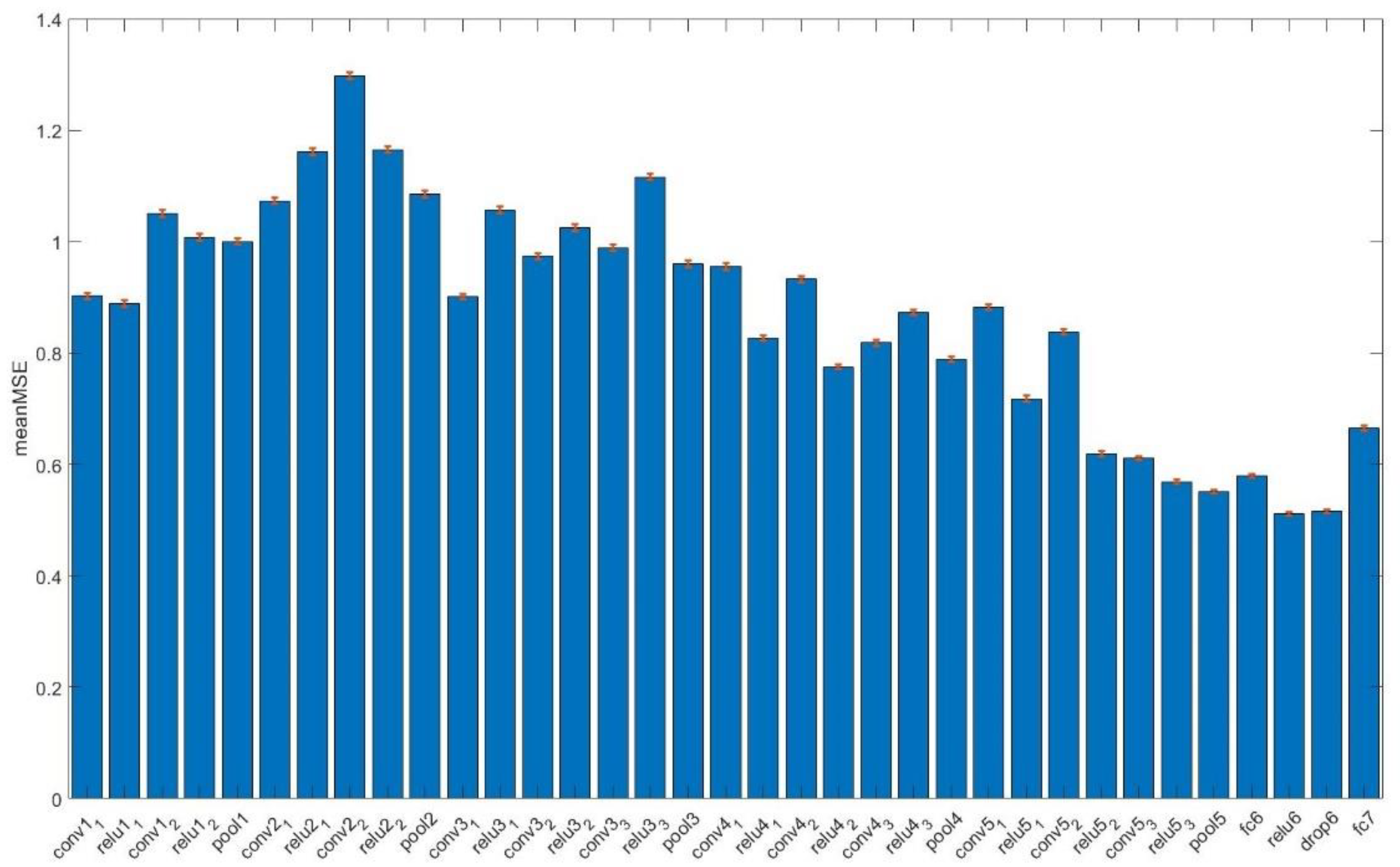
The cosine similarity between feature maps is estimated as follows: For each spatial position, a vector with a length equaling the number of filters in the layer exists. For the same spatial position of and we calculate the cosine similarity of the two vectors. The final similarity in the Lth layer is the average similarity across the spatial positions. The expressive ability of different layers of VGG16 was tested for the texture similarity calculation.
2.2. Validation of similarity metrics
To validate how accurately our metrics predict the perceptual color and texture scores, we transform the calculated similarities into discrete values from 1 to 4 using ordinal logistic regression (OLREG) models. We randomly split the data set into training and validation sets. The model construction uses the training set and the validation set to calculate its accuracy. As we aim to predict perceptual similarity as accurately as possible, to select from different options for calculated similarity metrics, we used the mean squared error (MSE), which is defined as:
where
and
are the mean perceptual and predicted (automated) scores, respectively, and N is the number of validated scores. We repeated the random splitting process multiple times to prevent biases and provide more reliable and robust estimates.
Best similarity metrics minimized mean error (); for these metrics, mean absolute accuracy and mean adjacent accuracy were also reported. Absolute accuracy refers to the exact agreement between predicted and perceptual scores. Adjacent accuracy refers to the adjacent agreement where predicted and perceptual scores do not differ more than one level. With this method we identified the ‘automated’ similarity metrics that best predicted the physicians’, ‘human’ perceptual scores.
We employed K-means cluster analysis to highlight how the chosen similarity metrics effectively capture perceptual similarities in a meaningful manner.
2.2.1. “Human” versus automated score agreement compared to between-experts agreement
To enquire further the performance of the ‘automated’ image similarity metrics we compare the level of agreement between raters’ and automatically generated scores (‘Human-System’ agreement) versus the level of agreement between scores assigned by the different expert raters (‘Human-Human’ agreement). We aimed to determine whether our proposed framework has the potential to perform at a level similar to that of an expert. Consistency and agreement assessments were conducted on a random validation round, using Cronbach’s α and quadratic Cohen’s Kappa [
14]. We utilized a box plot analysis to visualize the levels of agreement between the two groups: ‘Human-System’ (‘H-S’) and ‘Human-Human’ (’H-H’).
3. Results
All experts yielded ‘excellent’ consistency (α > 0.9) with at least ‘good’ reliability (AC2 > 0.70) for both texture and color assessments. For each target skin area (BCC or post-treatment scar), the rounded mean score was calculated and used to validate the color and texture similarity metrics.
Table 1 and
Table 2 present the distribution of mean scores for color and texture deviations, respectively.
To ensure a balanced representation of the four scales during training of the OLREG models, the training set consisted of 20 samples randomly selected from each scale in each split. (Train set: N = 80, validation set: N = 96). Different color and texture models were validated in terms of MSE over one hundred repetitions.
Considering the color similarity, the metric that minimized
was BCD in the YIQ model (
= 0.564, 95% CI: 0.560–0.567), which also yielded mean absolute accuracy
0.543 (95% CI: 0.541–0.545) and mean adjacent accuracy
0.964 (95% CI: 0.963–0.965).
Figure 3 depicts
performance for different color spaces and distance metrics.
Figure 2.
Color metrics rated with increasing mean Mean Square Errors (; red bars: 95% CI) values.
Figure 2.
Color metrics rated with increasing mean Mean Square Errors (; red bars: 95% CI) values.
Perceptual texture scores were best predicted by employing deep representations from the rectified layers ‘relu6’ ( = 0.512, 95% CI: 0.509–0.515), with absolute accuracy 0.538 (95% CI: 0.535–0.540) and mean adjacent accuracy 0.983 (95% CI: 0.982–0.984).
Figure 3 summarizes the performance of different layers of VGG16 in predicting perceptual scores.
Figure 3.
Layer-wise performance (mean MSE, Mean Square Error with corresponding 95% CI as red bars) in predicting perceptual texture scores. Layer ‘relu6’ representations were the most accurate according to the minimization of the mean MSE.
Figure 3.
Layer-wise performance (mean MSE, Mean Square Error with corresponding 95% CI as red bars) in predicting perceptual texture scores. Layer ‘relu6’ representations were the most accurate according to the minimization of the mean MSE.
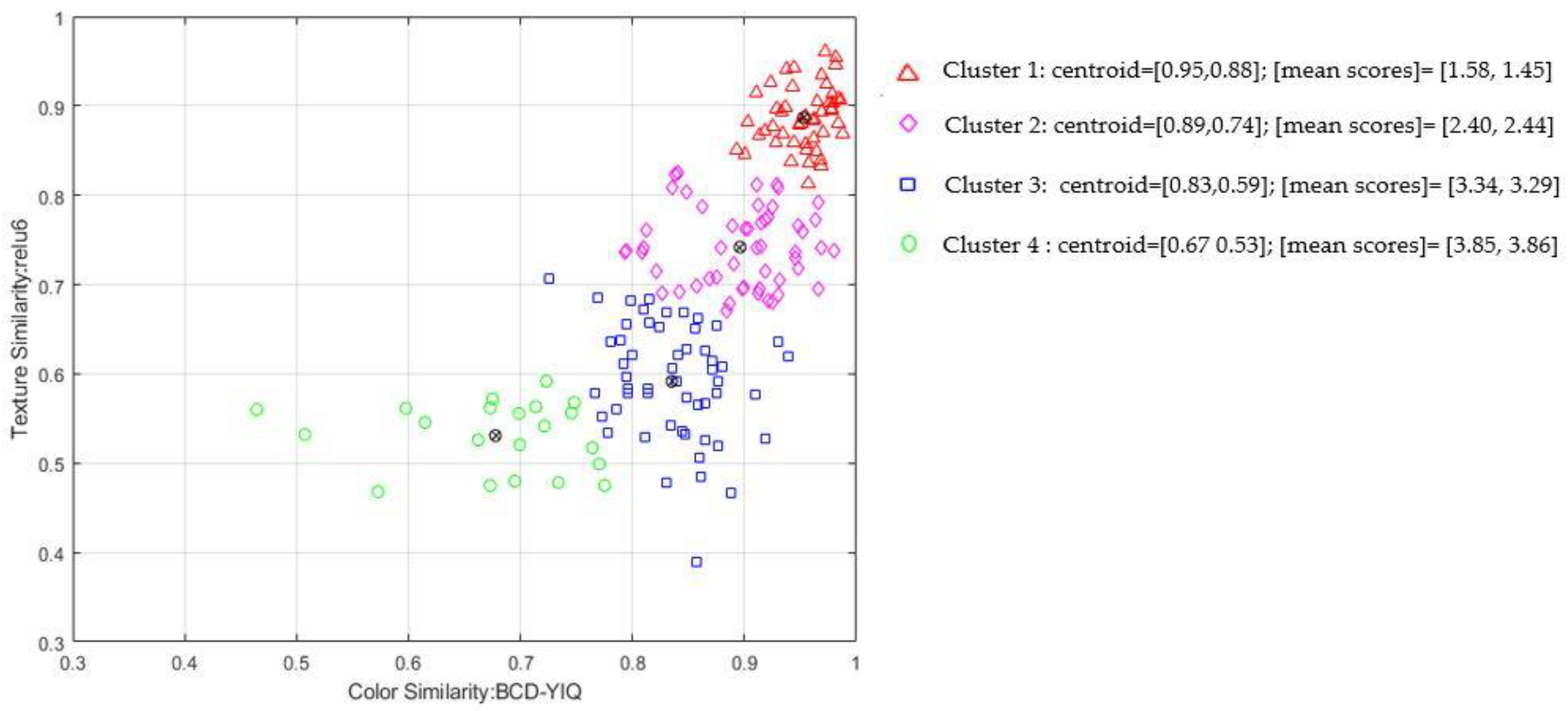
Figure 4 presents a qualitative k-means cluster analysis with k = 4 using color (BCD-YIQ) and texture (relu6) similarity metrics. For each cluster we estimated the mean perceptual score for color and texture similarity. The similarity metrics successfully cluster the perceptual scores in a consistent manner, that is items within the same cluster have similar perceptual scores for both color and texture similarity. For example, the first cluster gather BCCs sites that are perceptually similar to healthy skin.
3.1. Comparing the ‘between humans’ agreement with that between humans and the system
For a random run using the best-resulted metrics (color: ‘BCD-YIQ’, ‘texture: relu6’), we got the color and texture similarity predictions for the validation set (N = 96). Assuming that automated scores were produced from a 7th rater, we analyzed the consistency of ratings among seven raters using Cronbach’s alpha coefficient. The initial Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for the ratings was 0.937 for color and 0.958 for texture, indicating an excellent level of internal consistency. A rater removal analysis was conducted to investigate further the impact of individual raters on the overall consistency. Each rater was removed one at a time, and Cronbach’s alpha was recalculated for the remaining six raters. Upon rater removal, Cronbach’s alpha coefficient ranged from 0.917 to 0.934 for color and 0.950 to 0.953 for texture, suggesting that the presence of systems predictions did not influence the overall consistency of the ratings.
We further assessed the agreement using Cohen’s kappa for each pair of raters. The mean agreement for all 15 rater combinations (taking all combinations of six by two) was 0.65 (SD = 0.1) and 0.76 (SD = 0.03) for color and texture scores, respectively. Likewise, the mean agreement resulting from the six machine-human pairs was 0.64 (SD = 0.04) and 0.75 (SD = 0.02) for color and texture, respectively.
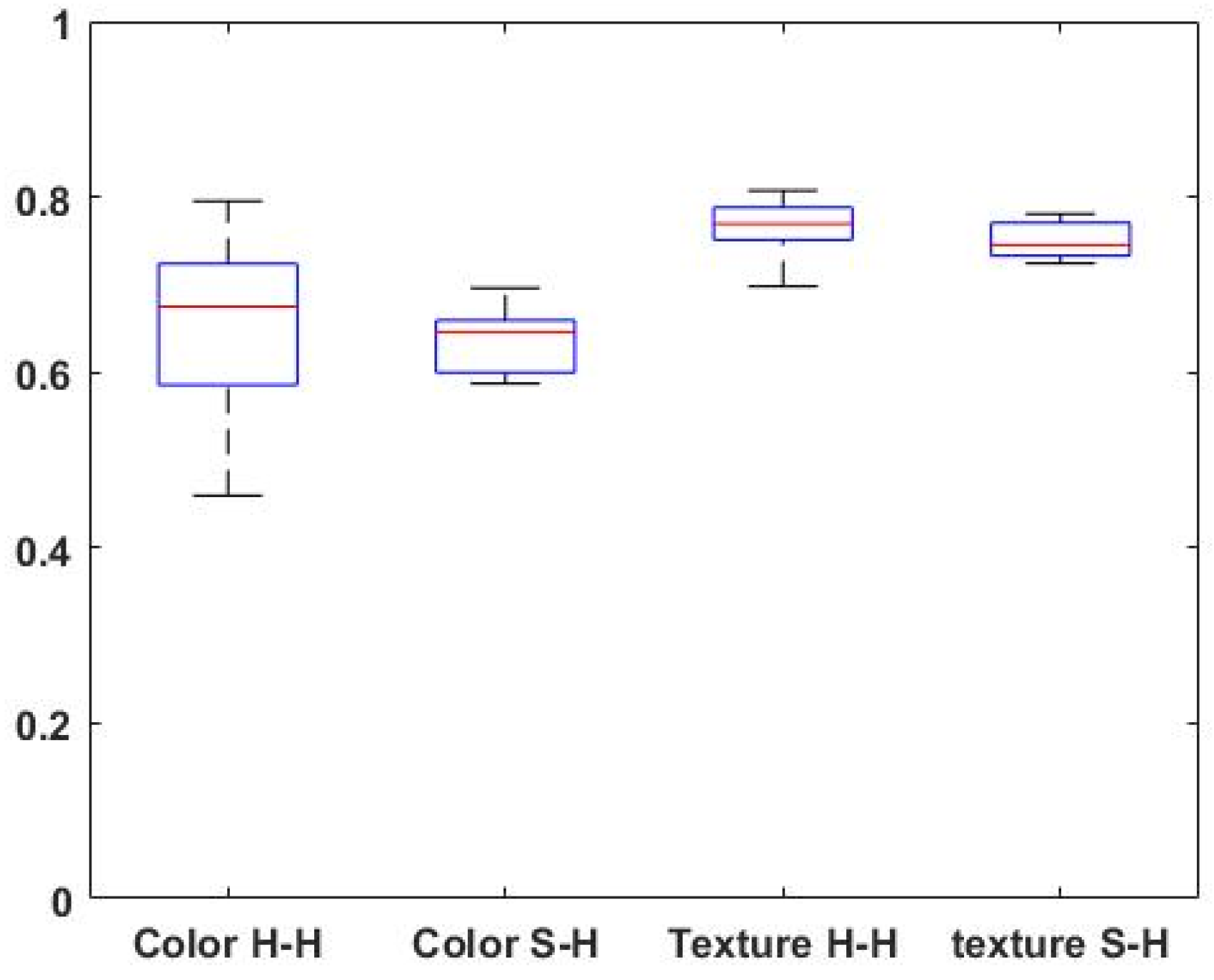
Figure 5 depicts a box plot analysis comparing the groups of human-human agreements (N = 15 pair agreements) and the human-system agreement (N = 6 pair agreements) regarding the color and texture appearance.
Overall, the distributions of the Cohen’s kappa values the groups ‘S-H’ and ‘H-H’ are quite similar, suggesting comparable central tendencies among the human-human and system-human agreement for both color and texture scores (p > 0.05; Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
The analysis of perceptual agreement between humans for color (‘Color H-H’) and texture (Texture ‘H-H’) revealed that perceptual texture agreement was higher than color perceptual agreement (p < 0.01; Wilcoxon rank-sum test).
Figure 5.
Box plot analysis of the agreement groups (pair-wise Cohen’s kappa): between two human raters (‘H-H’ group) and the humans to system comparisons (‘S-H’ group) for rating color and texture similarity. The samples’ medians are shown in red.
Figure 5.
Box plot analysis of the agreement groups (pair-wise Cohen’s kappa): between two human raters (‘H-H’ group) and the humans to system comparisons (‘S-H’ group) for rating color and texture similarity. The samples’ medians are shown in red.
4. Discussion
To ensure effective decision-making for managing BCC and evaluating therapeutic interventions, it is essential to perform accurate assessments that provide insight into the visual characteristics of tumors and post-treatment scars.
Given that color and texture are critical attributes that describe the clinical aspect of skin lesions, our focus was on quantifying deviations of these characteristics from the surrounding healthy skin through image analysis and propose similarity models that are congruent with the way experts make their judgments.
In the context of color similarity, we tested popular approaches including L2 Euclidean distance but also BCD in alternative to RGB color spaces (YIQ/ L*a*b*). Interestingly our results revealed an outstanding performance of BCD metric in the tested color spaces. Better normalization and goodness to the fit to the ordinal proximity data are the foremost benefits of BCD also verified by previous studies in medical information and image retrieval.
Considering perceptual texture similarity, our study builds upon and contributes to the existing body of research in this area that involves the use of internal activations of deep convolutional network trained for large-scale image classification tasks, to measure perceptual similarity. In general, CNNs consist of convolutional and fully connected layers. Convolutional layers learn progressively from fine to large spatial extend image representations, whereas the top fully connected layers learn to capture image wide global information. Our experiments indicated that rectified embeddings from fully connected layer ‘fc6’ (relu6 layer), are the most predictive for target skin texture similarity. A result that agrees with the intuition behind deep embeddings and visual perception. Moreover, the ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) layer is a key component of the VGG16 architecture that sets all negative values to zero while leaving positive values unchanged and is responsible for capturing and emphasizing relevant patterns and information while suppressing less important or irrelevant features.
The proposed similarity metrics produce scores, that are comparable in terms of internal consistency and agreement with those obtained from human raters. This finding aligns with and supports our aim of devising valid computational metrics to predict perceptual color and texture similarity. Moreover, estimated metrics enable a quantitative analysis of skin properties that were previously reliant on subjective descriptions. Quantifying these properties is crucial because discrete categories (‘1’,‘2’,‘3’,‘4’) struggle to capture subtle changes in skin appearance. K-means cluster analysis not only highlights the effectiveness of the selected similarity metrics to represent perceptual similarities in a meaningful way but also provides evidence of subtle discrimination of perceptually similar cases in the continuous similarity space (
Figure 4). Our continuous similarity metrics can provide more informative measurements, allowing for increased sensitivity in detecting and tracking changes in BCC sites over time.
In the box plot analysis (
Figure 5), the median values for texture perception agreement were noticeably higher, indicating a stronger consensus among human raters. On the other hand, color perception showed relatively more variability, as evidenced by the wider spread of the box plot. These findings suggest that experts tend to have higher agreement levels when evaluating texture than color appearance. It is noteworthy that the same relationships between color and texture perception as found in the hu-man-to-human comparisons are also evident in the pairwise human-to-machine evaluations: a higher degree of agreement in the evaluation of texture compared to color, while at the same time a proportionally higher degree of dispersion of Cohen’s kappa estimates in the case of color evaluation. Taken together, these latter observations support our hypothesis that the currently configured “machine” behaves similarly to a “human evaluator” when it comes to assessing the visual similarity of selected confined skin lesions from their surrounding skin
One of the main limitations of our study is the careful selection of image patches, which can potentially impact the accurate estimation of similarity. Particularly for color similarity, it is crucial to choose a rectangular area within the target patch that includes the minimal amount of perilesional skin. In addition, the inclusion of shiny skin patches due to light reflections affects the estimated metrics.
In the future, efforts should be made to expand the BCC image dataset, including the judgments of experts, and ensure that the dataset captures a wide range of variations and characteristics associated with BCC. Also, there is a need to improve perceptual color similarity metrics and enable better quantification of color relationships based on human perception.
5. Conclusions
Overall, the reported experimental results promise a robust, high-speed, and affordable modality to monitor BCC treatment outcomes in clinical settings. The proposed metrics allow quantified examination of a skin area which is of great importance towards reliable skin visibleness assessments. Moreover, our approach to model color and texture lesion similarity from the surrounding healthy skin is a promising paradigm for further development of a valid and reliable scar assessment tool.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.D.B. and P.S; methodology; P.S., A.L., I.D.B. and G.G.; formal analysis, P.S; investigation; I.B.D., K.S. and G.G.; data curation, A.Z., K.S., V.S., L.F., K.H., I.D.B., and G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.S.; writing—review and editing, I.D.B., G.G., K.S. and L.F.; funding acquisition, N/A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The use of archival photographic material for this study was approved by the Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of the University Hospital of Ioannina (approval nr.: 3/17-2-2015[θ.17)].
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this paper are not publicly available at this time but may be obtained from the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 |
In the graph color similarity is estimated as 1-BCD so higher values indicate greater similarity between the colors. |
References
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Garbe, C.; Kaufmann, R.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; del Marmol, V.; Dummer, R.; Harwood, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma: European Consensus–Based Interdisciplinary Guidelines. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 10–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretis, K.; Thomaidis, V.; Karpouzis, A.; Tamiolakis, D.; Tsamis, I. Epidemiology of Surgical Treatment of Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck in Greece. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitanis, G.; Bassukas, I.D. A Review of Immunocryosurgery and a Practical Guide to Its Applications. Diseases 2021, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, A.M.H.; Ong, Y.S.; Issa, F. Scar Assessment Tools: How Do They Compare? Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, P.T.L.; Echevarriá-Guanilo, M.E.; Goncąlves, N.; Girondi, J.B.R.; Da Costa Goncąlves, A. Subjective Tools for Burn Scar Assessment: An Integrative Review. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2021, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Bamford, A.; Gardiner, F.; Agovino, A.; ter Horst, B.; Bishop, J.; Sitch, A.; Grover, L.; Logan, A.; Moiemen, N.S. Investigating the Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability of a Panel of Subjective and Objective Burn Scar Measurement Tools. Burns 2019, 45, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.; Dretzke, J.; Grover, L.; Logan, A.; Moiemen, N. A Systematic Review of Objective Burn Scar Measurements. Burn. Trauma 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basson, R.; Bayat, A. Skin Scarring: Latest Update on Objective Assessment and Optimal Management. Front. Med. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecott, G.A.; Finnerty, C.C.; Herndon, D.N.; Al-Mousawi, A.M.; Branski, L.K.; Hegde, S.; Kraft, R.; Williams, F.N.; Maldonado, S.A.; Rivero, H.G.; et al. Reliable Scar Scoring System to Assess Photographs of Burn Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 199, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramly, E.P.; Eisemann, B.S.; Kantar, R.S.; Alfonso, A.R.; Wang, M.; Diaz-Siso, J.R.; Staffenberg, D.A.; Flores, R.L. Unilateral Cleft Lip Repair: A Quantitative Scale Assessment of Postoperative Lip and Nose Scars Across 2 Operative Techniques. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2019, 83, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantor, J. Reliability and Photographic Equivalency of the Scar Cosmesis Assessment and Rating (SCAR) Scale, an Outcome Measure for Postoperative Scars. JAMA Dermatology 2017, 153, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplyi, V.; Grebchenko, K. Evaluation of the Scars’ Vascularization Using Computer Processing of the Digital Images. Ski. Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Nidey, N.; Miller, S.F.; Moreno Uribe, L.M.; Baum, C.L.; Hamilton, G.S.; Wehby, G.L.; Dunnwald, M. Digital Imaging Analysis to Assess Scar Phenotype. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVellis, R.F. Inter-Rater Reliability. Encycl. Soc. Meas. 2005, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwet, K.L. Handbook of Inter-Rater Reliability: The Definitive Guide to Measuring the Extent of Agreement among Raters: Vol 2: Analysis of Quantitative Ratings. Handbook of Inter-Rater Reliability: the Definitive Guide to Measuring the Extent of Agreement among Raters Series; Advanced Analytics, LLC, 2021; ISBN 9781792354649. [Google Scholar]
- Kakumanu, P.; Makrogiannis, S.; Bourbakis, N. A Survey of Skin-Color Modeling and Detection Methods. Pattern Recognit. 2007, 40, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, S.; Jalab, H.A.; Kareem, S.A. A Survey on Skin Detection in Colored Images. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 1041–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Malik, A.S.; Kamel, N.; Dass, S.C.; Affandi, A.M. Segmentation of Acne Lesion Using Fuzzy C-Means Technique with Intelligent Selection of the Desired Cluster. In 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC); 2015; pp. 3077–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridonos, P.; Gaitanis, G.; Likas, A.; Bassukas, I.D. Automatic Discrimination of Actinic Keratoses from Clinical Photographs. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 88, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisar, H.; Ch’ng, Y.K.; Chew, T.Y.; Yap, V.V.; Yeap, K.H.; Tang, J.J. A Color Space Study for Skin Lesion Segmentation. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Systems (ICCAS); 2013; pp. 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Yates, J.M.; Zardawi, F.; Sueeprasan, S.; Liao, N.; Gill, L.; Li, C.; Wuerger, S. Characterising the Variations in Ethnic Skin Colours: A New Calibrated Data Base for Human Skin. Ski. Res. Technol. 2017, 23, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, M.M.; Sladen, C.; Crone, M.; Banner, E.; Newton, V.L.; Allen, A.; Bell, M.; Marlow, I.; Acevedo, S.F.; Jiang, L.I. A Validated Photonumeric Scale for Infraorbital Dark Circles and Its Application in Evaluating the Efficacy of a Cosmetic Treatment Product in a Split-Face Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-R.; Chen, S.-G.; Chen, J.-C.; Liu, S.-C. Validation of Fespixon in Postoperative Scar Cosmesis Using Quantitative Digital Photography Analysis. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2023, 43, NP427–NP437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Wu, W.; Dalal, E.N. The CIEDE2000 Color-Difference Formula: Implementation Notes, Supplementary Test Data, and Mathematical Observations. Color Res. Appl. 2005, 30, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Mehrotra, D.; Bansal, A.; Bala, M. Analysis and Implementation of the Bray–Curtis Distance-Based Similarity Measure for Retrieving Information from the Medical Repository BT—International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications. Bhattacharyya, S., Hassanien, A.E., Gupta, D., Khanna, A., Pan, I., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2019; pp. 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, J.; Doyle, S.; Basavanhally, A.; Ganesan, S.; Feldman, M.D.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Madabhushi, A. A Boosted Distance Metric: Application to Content Based Image Retrieval and Classification of Digitized Histopathology. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2009: Computer-Aided Diagnosis; SPIE 3 March 2009. Volume 7260, p. 72603F.
- Samantaray, A.K.; Rahulkar, A.D. Comparison of Similarity Measurement Metrics on Medical Image Data. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT); IEEE July 2019. ; pp. 1–5.
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Fieguth, P.; Zhao, G.; Chellappa, R.; Pietikäinen, M. From BoW to CNN: Two Decades of Texture Representation for Texture Classification. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 127, 74–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Dong, J.; Chantler, M.J. Perceptual Texture Similarity Estimation: An Evaluation of Computational Features. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2429–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2018; pp. 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gan, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhou, H.; Dong, X.; Dong, J. A Perception-Inspired Deep Learning Framework for Predicting Perceptual Texture Similarity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 3714–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Li, F.-F. ImageNet: A Large-Scale Hierarchical Image Database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; IEEE 1 June 2009. ; pp. 248–255.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).