Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. New energy vehicle industry
2.2. Patent collaboration network
2.3. Social network analysis
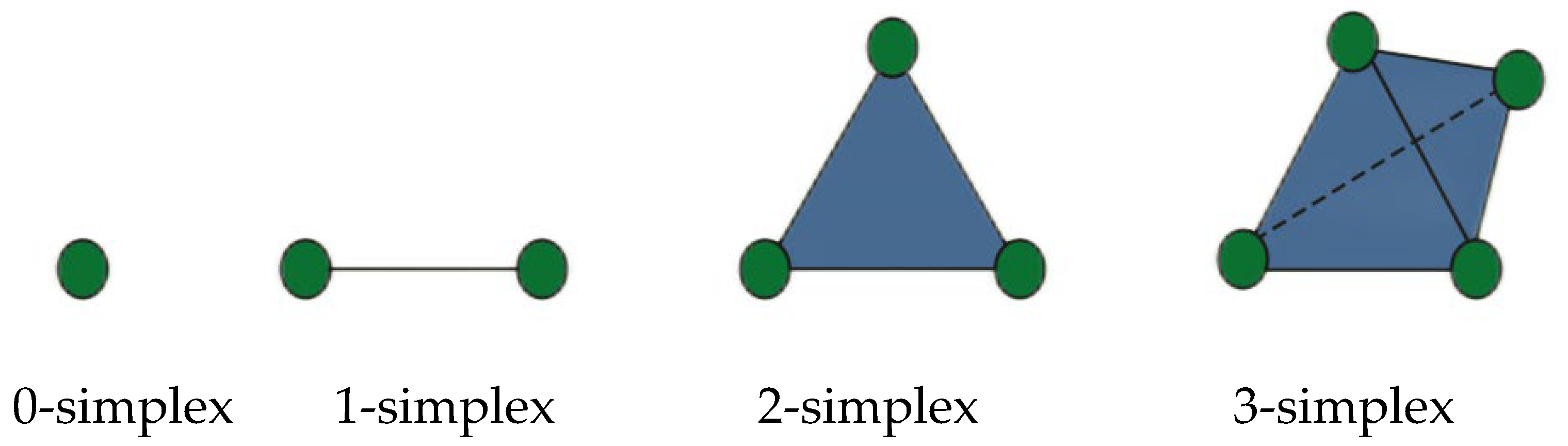
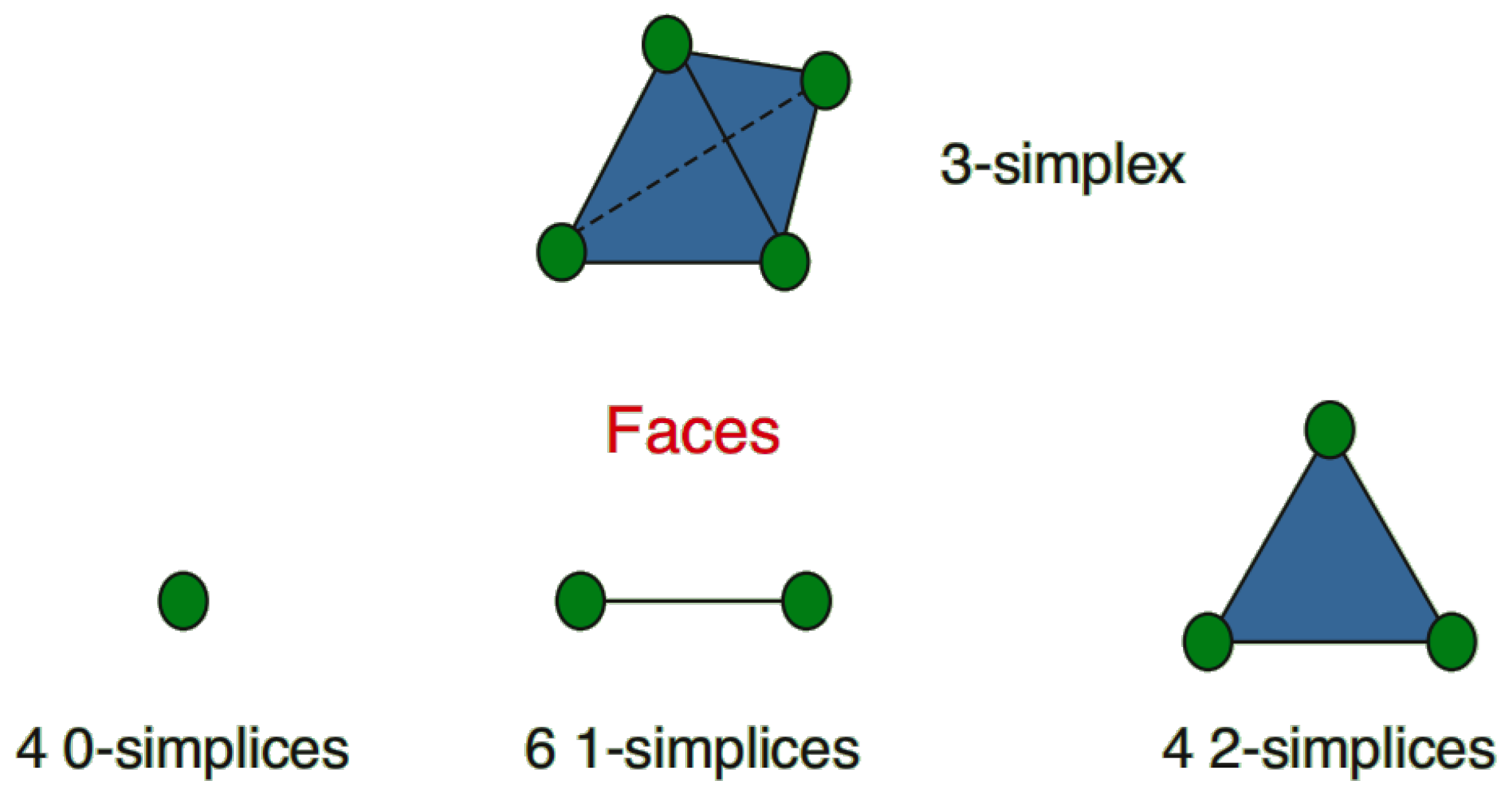
3. Construction of Higher-Order Interaction Cooperation Innovation Networks
3.1. Basic Properties of Higher-Order Networks
3.2. Generalized Degree
3.3. Spatial analysis of patent cooperation activities
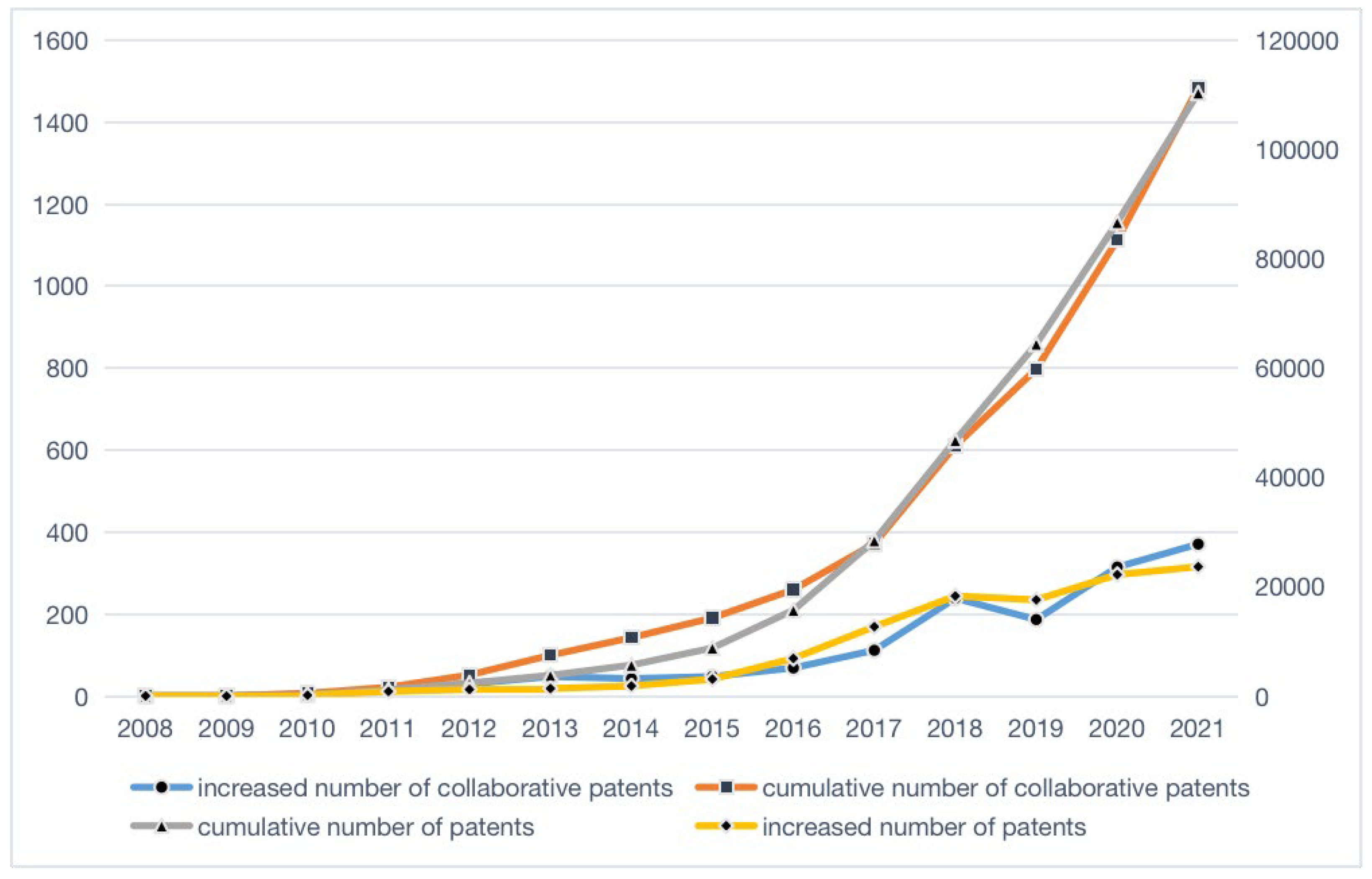
4. Data and Life Cycle Division
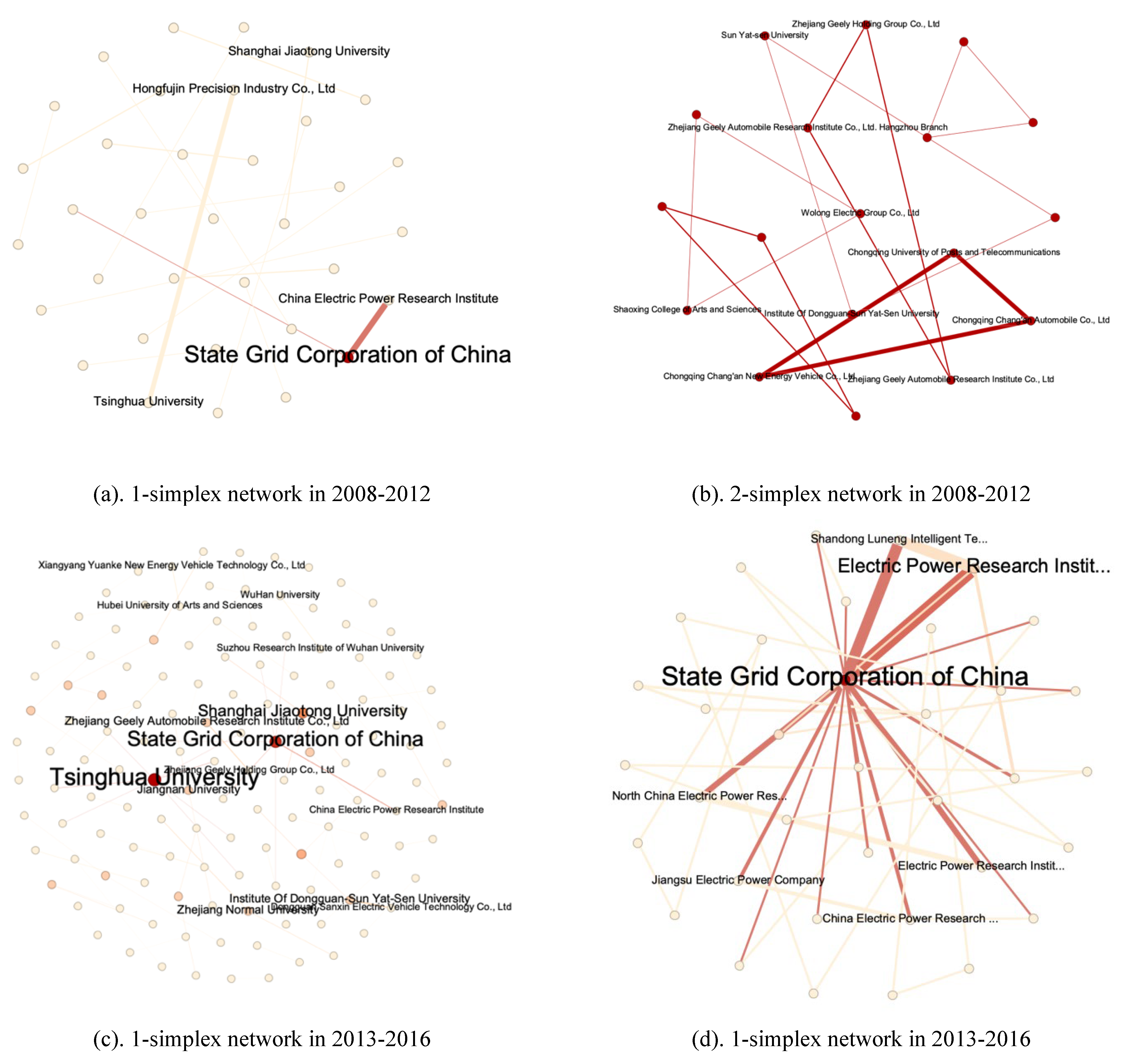
5. Evolution Analysis of Higher-order Network
5.1. Higher-order collaboration network dynamics
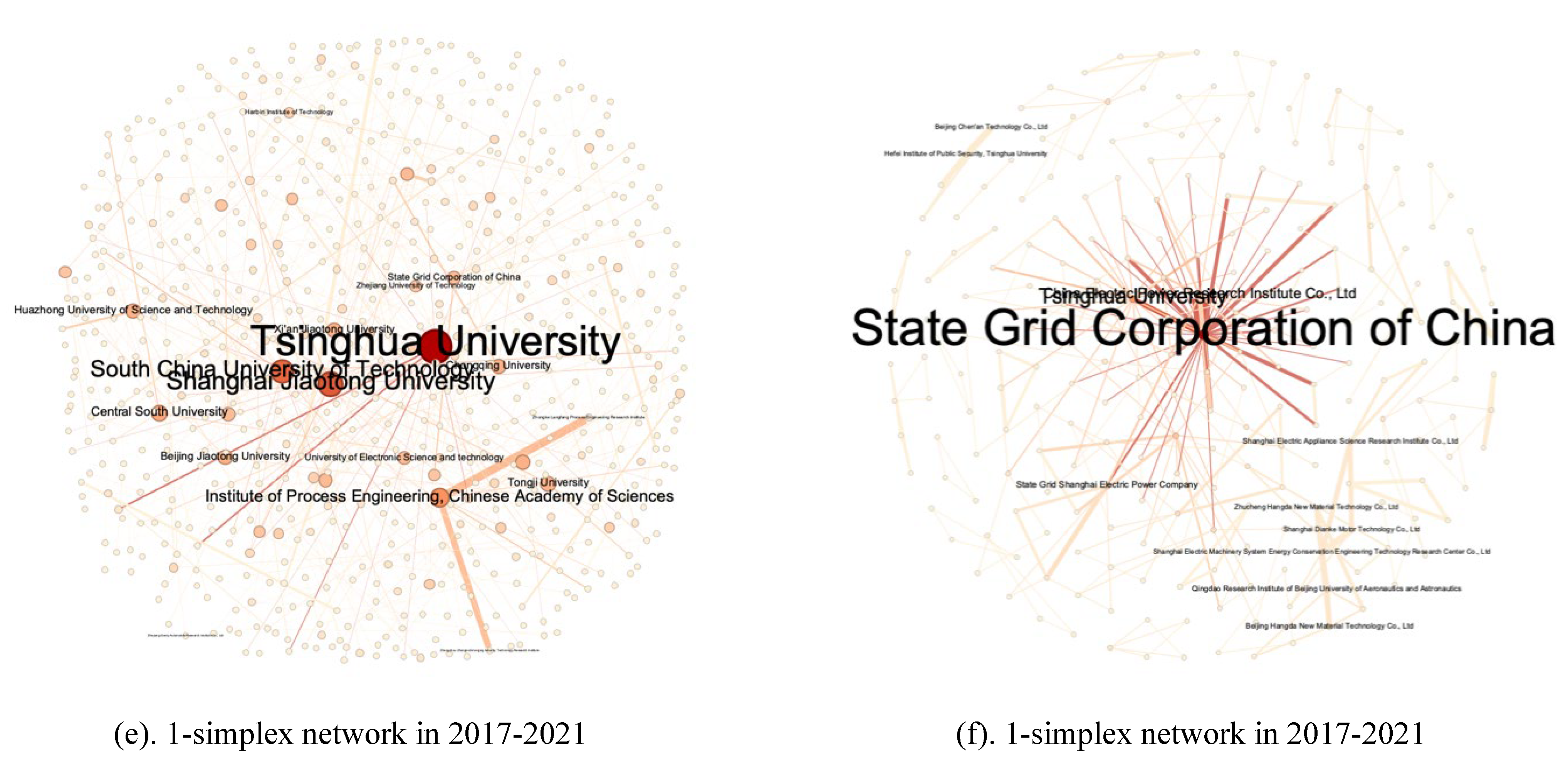
5.2. Higher-order collaboration network structure
6. Evolution characteristics of nodes and edges
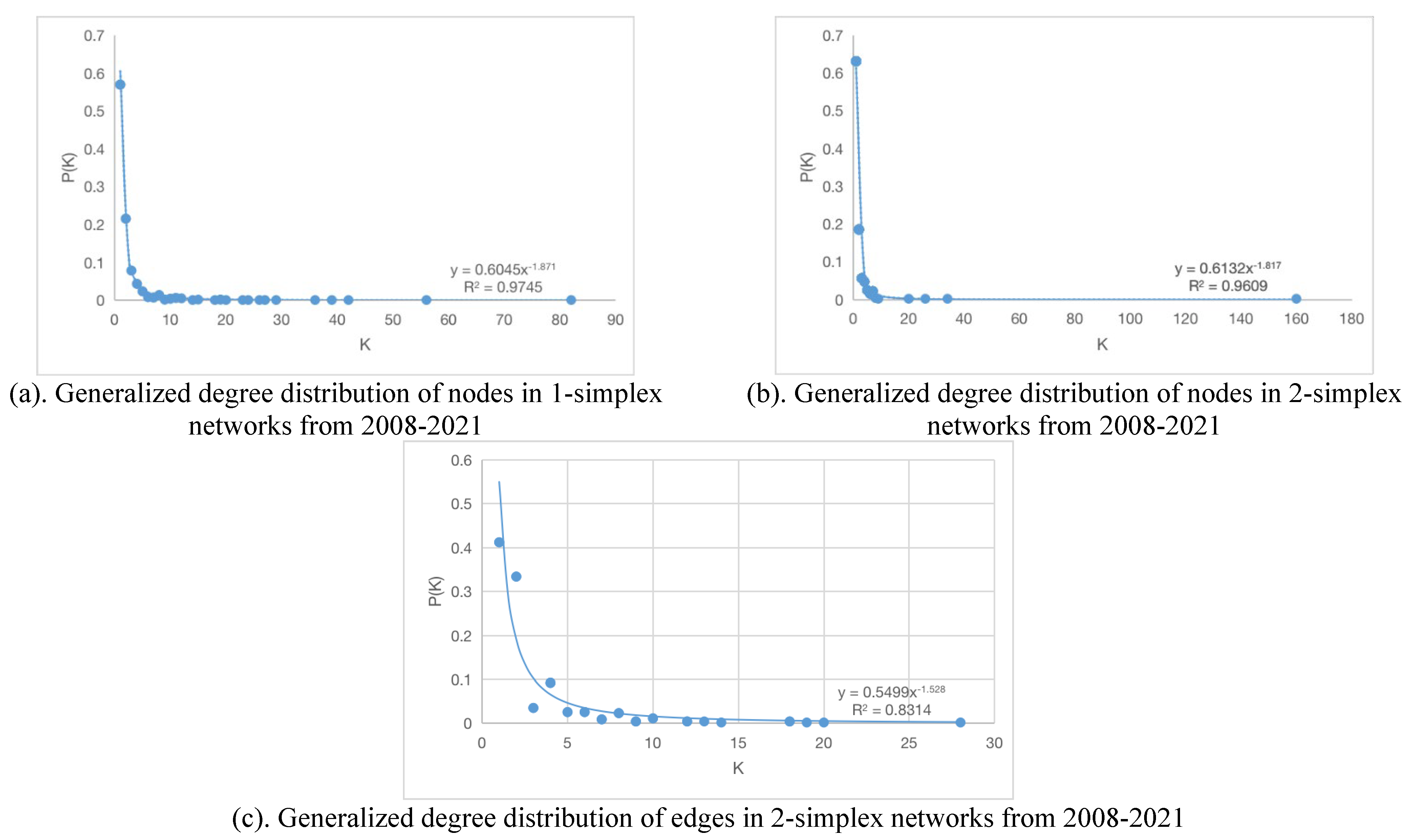
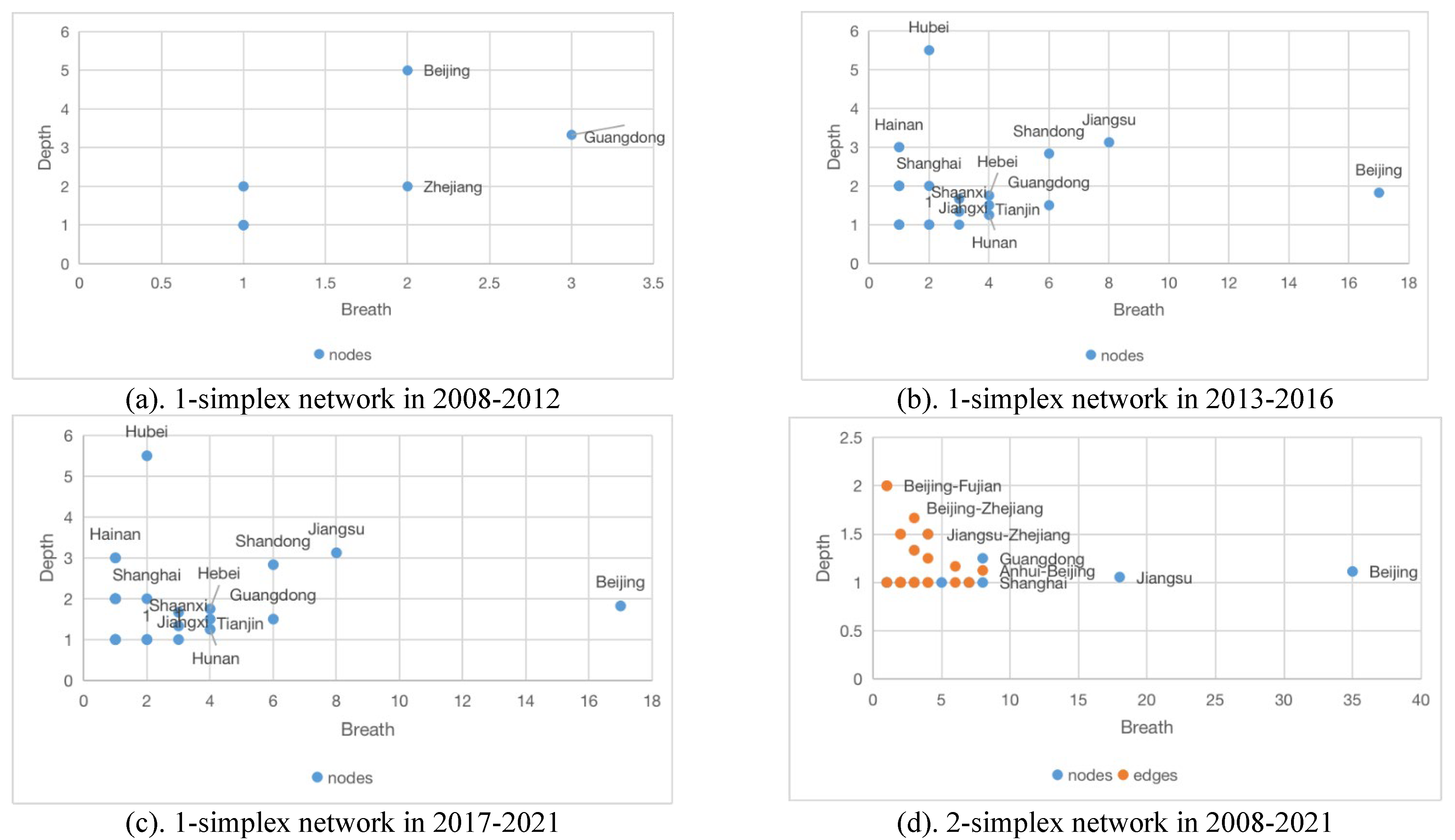
6.1. Generalized degree distribution of nodes and edges
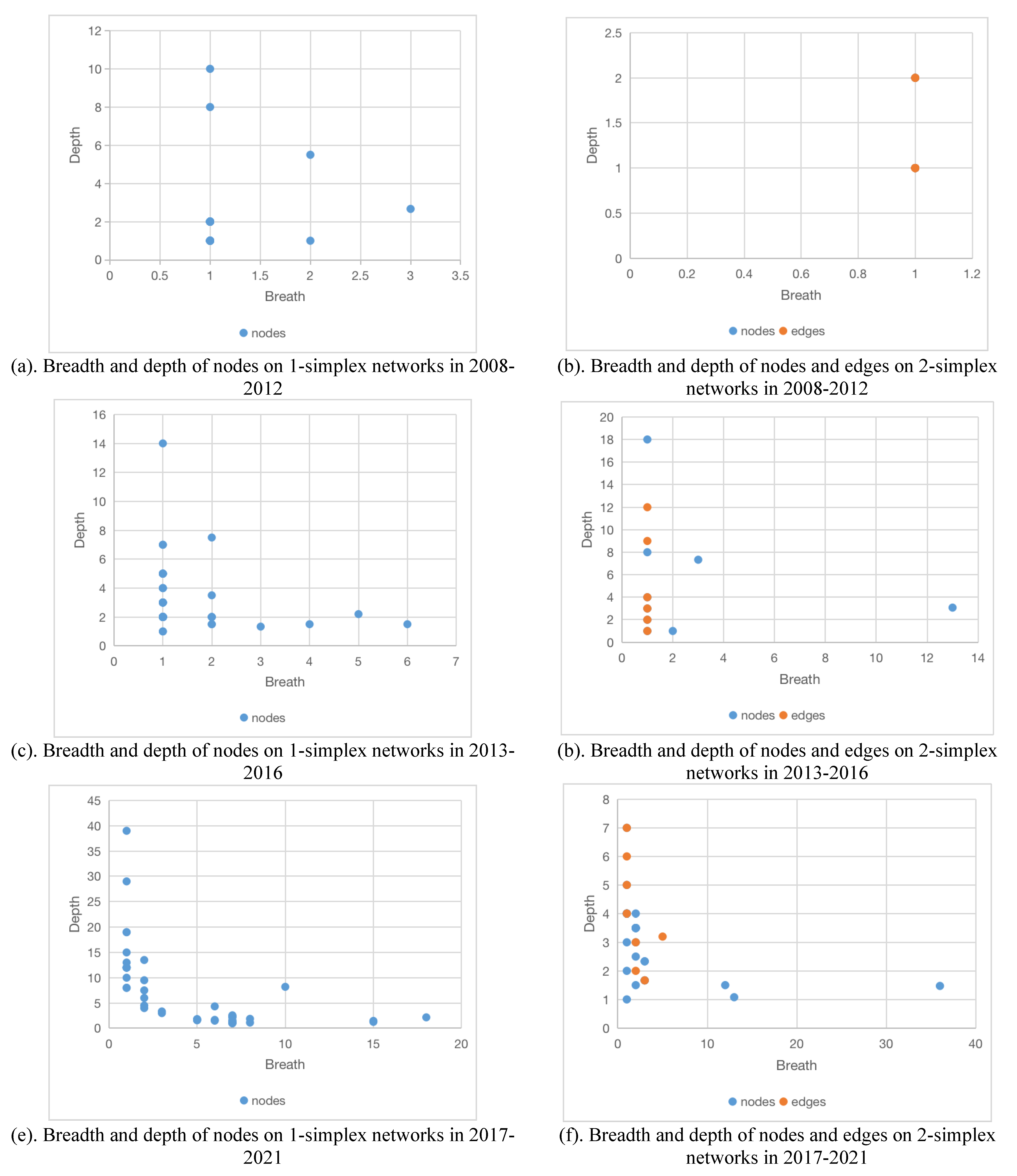
6.2. Collaboration breadth and depth of nodes and edges
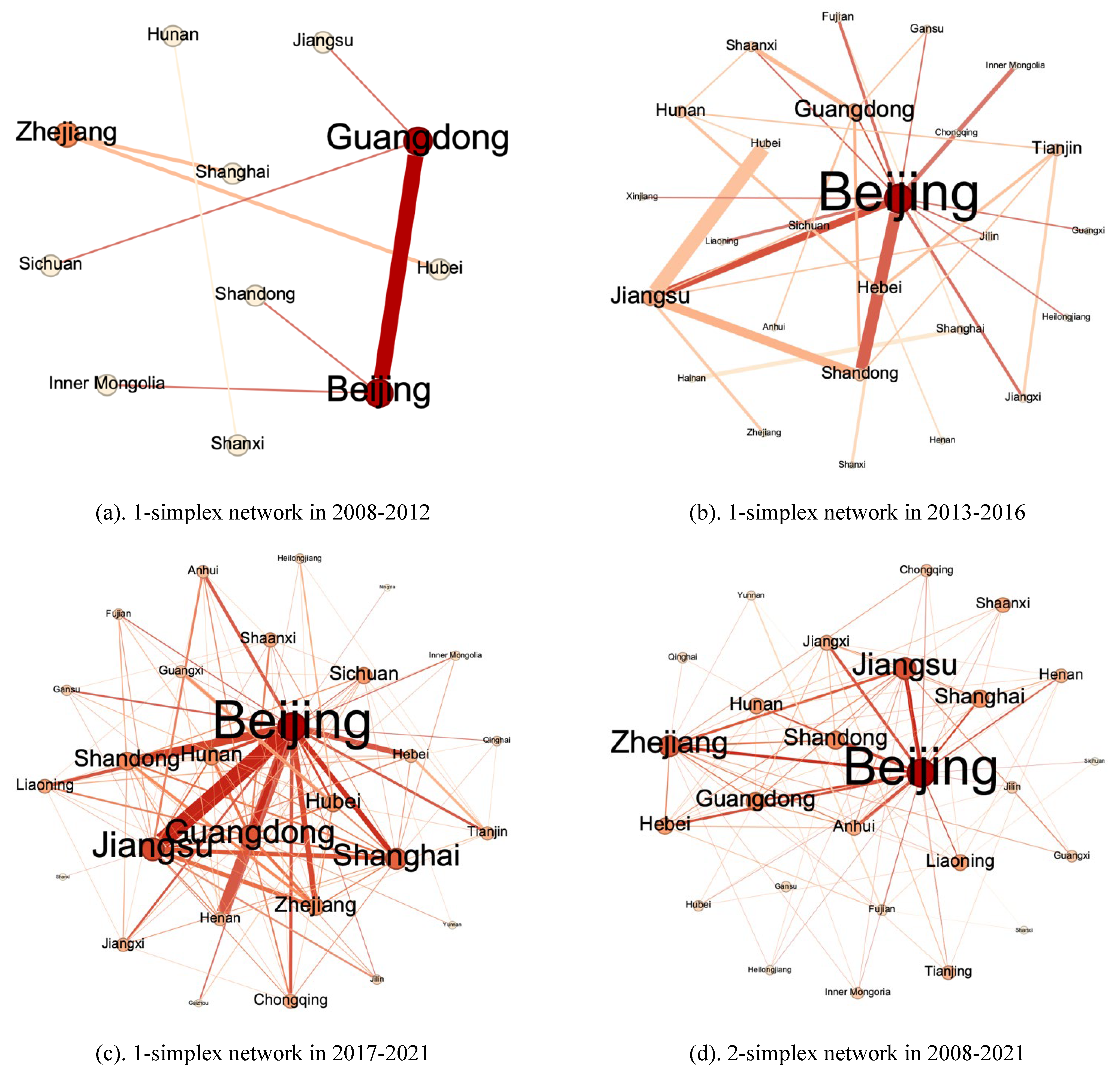
7. Evolutionary Analysis of Regional Cooperation
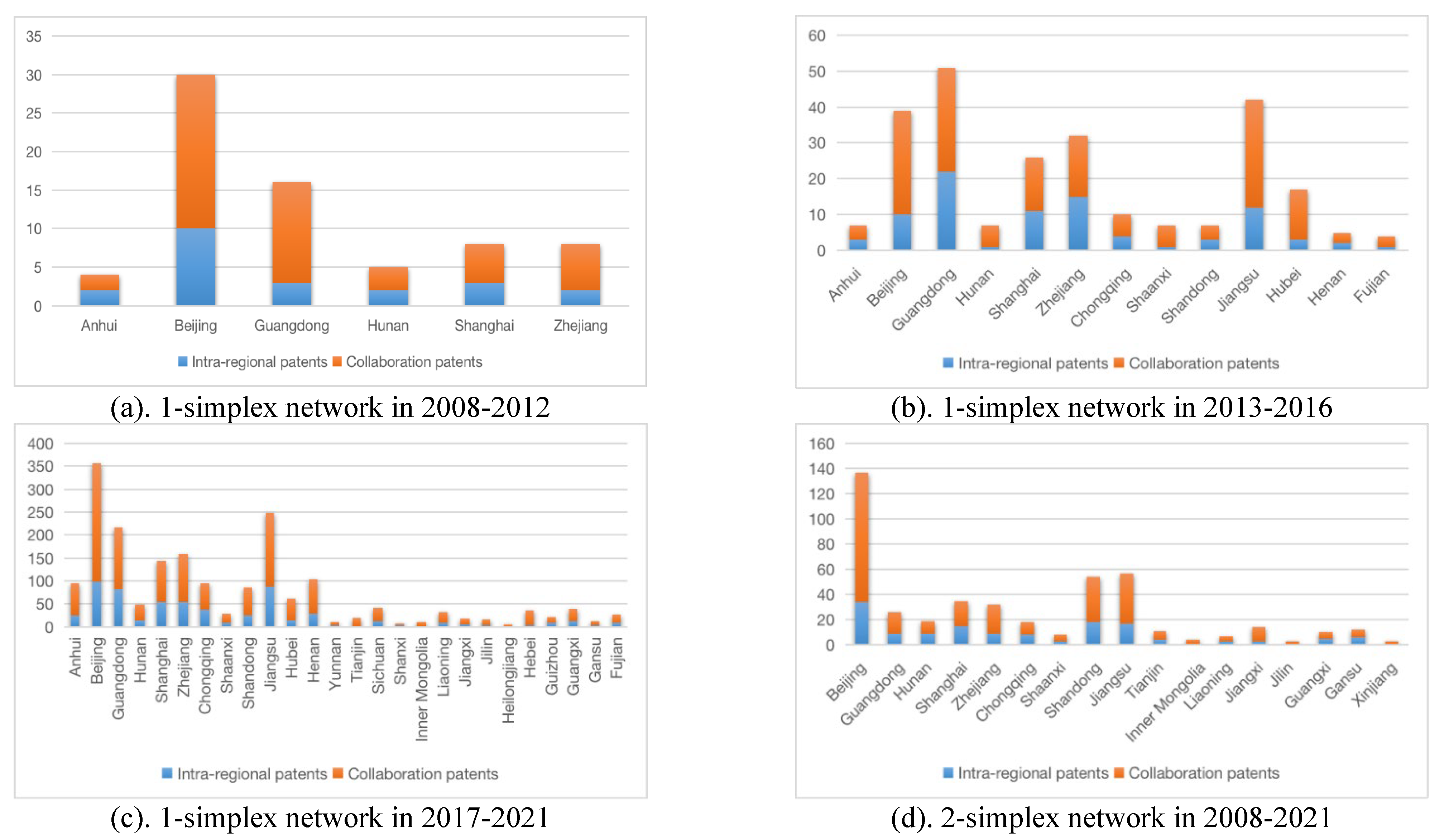
7.1. Evolution analysis of intra-regional cooperation
7.2. Evolution analysis of cross-regional cooperation
8. Conclusion and future work
8.1. Conclusion
8.2. Future work
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alstott, J.; Triulzi, G.; Yan, B.; Luo, J. Mapping Technology Space by Normalizing Patent Networks. Scientometrics 2017, 110, 443–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, A.B.; de Rassenfosse, G. Patent citation data in social science research: Overview and best practices. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, L.; Cao, B.; Fan, X. Benefit distribution and stability analysis of enterprises’ technological innovation cooperation alliance. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 161, 107637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, R.L.-T.; Liu, J.S.; Ho, M.H.-C. The development of autonomous driving technology: perspectives from patent citation analysis. Transp. Rev. 2021, 41, 685–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, M.-Y.; Liu, Z.-W. Analysis of the patent cooperation network in global artificial intelligence technologies based on the assignees. World Pat. Inf. 2020, 63, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Song, Y.; Bi, K. Exploring the patent collaboration network of China’s wind energy industry: A study based on patent data from CNIPA. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, G. Examining the moderating effect of technology spillovers embedded in the intra- and inter-regional collaborative innovation networks of China. Scientometrics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liu, Z.; Qing, Q. Optimal electric vehicle production strategy under subsidy and battery recycling. Energy Policy. 2017, 109, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Zuo, J. The development of new energy vehicles for a sustainable future: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ni, L.; Liu, K. Does China’s new energy vehicle industry innovate efficiently? A three-stage dynamic network slacks-based measure approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 2021, 173, 121161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Chen, K.; Hao, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. Technology development for electric vehicles under new energy vehicle credit regulation in China: scenarios through 2030. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, L. 4(3H)-Quinazolone regulates innate immune signaling upon respiratory syncytial virus infection by moderately inhibiting the RIG-1 pathway in RAW264.7 cell. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; He, L.-Y. Fuel demand, road transport pollution emissions and residents’ health losses in the transitional China. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2016, 42, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, Q. China’s new energy vehicle policies: Evolution, comparison and recommendation. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2018, 110, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, A.B.; Lichtenberg, S.; Brauer, B.; Nastjuk, I.; Kolbe, L.M. Improving Electric Vehicle Utilization in Carsharing: A Framework and Simulation of an E-Carsharing Vehicle Utilization Management System. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2018, 64, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiong, Y. Innovation strategies of Chinese new energy vehicle enterprises under the influence of non-financial policies: Effects, mechanisms and implications. Energy Policy. 2022, 164, 112946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Research on the impact mechanism of green finance on the green innovation performance of China’s manufacturing industry. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, D.; Petković, D.; Nikolić, V.; Milovančević, M.; Denić, N. DETERMINATION OF IMPORTANT PARAMETERS FOR PATENT APPLICATIONS. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2017, 15, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Chen, Z. Patent collaboration and international knowledge flow. Inf. Process. Manag. 2012, 48, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.; C. K. Iii; Juda, A.I. Small Worlds and Regional Innovation. Organ. Sci. 2006, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternitzke, C.; Bartkowski, A.; Schramm, R. Visualizing patent statistics by means of social network analysis tools. World Pat. Inf. 2008, 30, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M. The relation between R&D spending and patents: The moderating effect of collaboration networks. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management. 2017, 46, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.Q.; Ma, F.; Wang, H. The effect of intellectual property treaties on international innovation collaboration: a study based on USPTO patents during 1976–2017. Libr. Hi Tech. 2021, ahead-of-print. [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Kudic, M.; Vermeulen, B. The influence of the structure of technological knowledge on inter-firm R&D collaboration and knowledge discovery: An agent-based simulation approach. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 129, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kogler, D.F.; Lee, D. Capturing information on technology convergence, international collaboration, and knowledge flow from patent documents: A case of information and communication technology. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, C. Intra- and inter-regional research collaboration across organizational boundaries: Evolving patterns in China, Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 2015, 96, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. The structure and dynamics of intra- and inter-regional research collaborative networks: The case of China (1985–2008). Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2016, 108, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, Z. Regional innovation paths selection in complex environments of China: A configurational perspective. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Bi, K. Exploring and Visualizing the Patent Collaboration Network: A Case Study of Smart Grid Field in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Geng, Y.; Hu, L.; Shi, L.; Xu, T. Measuring China’s new energy vehicle patents: A social network analysis approach. Energy 2018, 153, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, N.; Cao, C. An evolutionary process of global nanotechnology collaboration: A social network analysis of patents at USPTO. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Gu, H.; Zhang, S. Measuring technological collaborations on carbon capture and storage based on patents: A social network analysis approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, X. Exploring the Technological Collaboration Characteristics of the Global Integrated Circuit Manufacturing Industry. Sustainability 2018, 10, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liu, X.; Xiao, R. Data-driven Product Functional Configuration: Patent Data and Hypergraph. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, E.; Rodríguez-Velázquez, J.A. Subgraph centrality and clustering in complex hyper-networks. Phys. Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2006, 364, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W. Cooperative knowledge creation in an uncertain network environment based on a dynamic knowledge supernetwork. Scientometrics 2019, 119, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiston, F.; Cencetti, G.; Iacopini, I.; Latora, V.; Lucas, M.; Patania, A.; Young, J.-G.; Petri, G. Networks beyond pairwise interactions: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2020, 874, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L. Network science. Nature 2012, 489, 507–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, G. Higher-Order Networks, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: 2021. [CrossRef]
- Cinardi, N.; Rapisarda, A.; Bianconi, G. Quantum statistics in network geometry with fractional flavor. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2019, 2019, 103403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopini, I.; Petri, G.; Barrat, A.; Latora, V. Simplicial models of social contagion. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, G.; Ziff, R.M. Topological Percolation on Hyperbolic Simplicial Complexes. Phys. Rev. E. 2018, 98, 052308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, O.T.; Bianconi, G. Generalized network structures: The configuration model and the canonical ensemble of simplicial complexes. Phys. Rev. E. 2016, 93, 062311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Li, J.; Li, J. Urban innovation and intercity patent collaboration: A network analysis of China’s national innovation system. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change. 2020, 160, 120185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patania, A.; Petri, G.; Vaccarino, F. The shape of collaborations. EPJ Data Sci. 2017, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liegsalz, J.; Wagner, S. Patent examination at the state intellectual property office in China. Res. Policy. 2013, 42, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ahmad, S.Z.; Yang, D. ; Matthew effect, ABC analysis and project management of scale-free information systems. J. Syst. Softw. 2013, 86, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahemia, H.; Squire, B.; Cousins, P. A multi-dimensional approach for managing open innovation in NPD. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 |
| Dimension | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Patent applications | 1145 | 247 | 66 | 21 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| period | 2008-2012 | 2013-2016 | 2017-2021 | |||
| dimension | d=1 | d=2 | d=1 | d=2 | d=1 | d=2 |
| nodes | 35 | 9 | 132 | 36 | 727 | 236 |
| Number of simplexes | 21 | 2 | 82 | 20 | 527 | 119 |
| Number of patents | 39 | 12 | 144 | 47 | 962 | 188 |
| Maximum node Generalized degree | 3 | 1 | 6 | 13 | 12 | 36 |
| Maximum link Generalized degree | - | 1 | - | 1 | - | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




