1. Introduction
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have drawn the extensive interest researchers since their discovery because of their superior electrical, thermal, mechanical, and physical attribute [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Due to these excellent properties, CNTs are widely used in the development of nano-electro-mechanical systems (NEMS) [
6,
7,
8,
9]; The structural properties of CNTs can be used for nanofluid fluid conveying and hydrogen storage [
10]. Additionally, CNTs can be used to make composites with metals, cements, and glass fibers to compensate for the inadequacies of each material and create high strength, high performance composites [
11,
12]. Therefore, it is very significance to study the mechanical attribute of carbon nanotubes. Since experimental methods can only measure some basic mechanical constants of carbon nanotubes, Losts of researchers have used molecular dynamics simulations (MDS) and continuum mechanics methods to simulate and calculate the kinetic properties of more complex CNTs. However, MDS calculations of the molecular forces between each carbon atom are time and resource consuming, in general, continuum mechanics theory has become the primary method for studying the kinetic properties of CNTs [
13,
14].
Classical continuum mechanics ignores small-scale effects, surface effects and intermolecular interactions at the microscopic level, but in the microscopic case these factors play an important role in material properties and cannot be ignored. Therefore, most scholars have adopted the non-local theory of elasticity proposed by Eringen et al. [
15]. This theory can effectively model the mechanical properties of carbon nanostructures at the microscopic level. Yoon et al. [
16,
17] studied the fluid conveying of CNTs dynamic response characteristics and flow velocity induced chattering instability of cantilevered nanobeams. Wang et al. [
18,
19] investigated the shear and flexural waves behaviour of moving fluids on SWCNT in complex physical environment. the results illustrate that changes in magnetic field and temperature have a large effect on wave frequency Li et al. [
20,
21] discusses the free vibration and small-scale effects of CNTs under varying boundary conditions. Bahaadini et al. [
22,
23] constructed a nonlocal strain gradient Timoshenko(NSGT) model, and investigated the influence of cantilevered carbon nanobeam chattering instability due to the flow velocity.
Lim et al. [
24] combined strain gradient theories and Eringen’s nonlocal theories to obtain a new nonlocal strain gradient higher order continuum theory. deriving Timoshenko beam wave equations in the context of a new theory. Some new dispersion relations for wave propagation are obtained by arithmetic examples. Li and Hu et al. [
25,
26,
27] studied surface effects on the wave behaviour of viscoelastic SWCNT. the numerical results indicated that increasing the magnetic field and decreasing the damping can lead to an increasing phase velocity, and that the frequency value increases when surface effects are considered. Wang and Bian [
28] analysed vibration behaviour of SWCNT in fluid forces and magnetic field change, It was indicated that non-local parameters, fluid velocity and magnetic field change have a remarkable influence on the vibration frequency SWCNT. Rajendran et al. [
29] investigated the non-linear vibrational response of embedded CNTs in temperature and magnetic fields. Ebrahimi et al. [
30,
31] investigated the wave behaviour of non-linear functionally graded beams in temperature change.
Amiri et al. [
32] considered the dynamic characterisation of instability fluid conveying nanotube system based on NSGT flexoelectricity nanobeams model. Yang et al. [
33] studied on the kinetic characterization of non-local stress fields in microfluidic channels and the material parameters effects of carbon nanotube wave propagation. Zhen et al. [
34,
35] studied wave behaviour of fluid-conveying viscoelastic SWCNT in longitudinal magnetic field, temperature change and surface effect. the numerical results indicated that increasing the magnetic field and decreasing the temperature can lead to an incre asing phase velocity. Arani et al. [
36] investigated that surface effects and initial stresses have important Influence on the wave behaviour characteristics of CNTs. Bahaadini and Ghane et al. [
37,
38] constructed a NSGT cantilevered Timoshenko nanobeam to analyse dynamic flutter instability of fluid moving CNTs in magnetic field change, It was revealed that the magnetic field effect leads to an increase in the critical flow velocity, resulting in an increasingly stable system.
There is little discussion of the influence of the combined longitudinal magnetic field and fluid velocity on the phase velocities and surface effects of SWCNT in the available papers, this work mainly considered fluid conveying SWCNT with surface effects in longitudinal magnetic fields and embedded elastic foundations, and constructed a non-local strain gradient Timoshenko beam model, Using Hamilton principle, the control equations are derived. The influence of nonlocal coefficients, strain gradient coefficients, fluid flow, fluid density, magnetic flux, foundation medium and surface effect on the waves behaviour of CNTs are discussed in detail.
2. Non-local strain gradient constitutive equation theory
According to the nonlocal strain gradient higher order continuum theory by Lim[
24], the classical nonlocal stress
, the higher-order nonlocal stress
and the total stress can be denoted as:
In the above equation,
represent the length of the beam,
and
are both material-related constants,
stand for the length of the internal C-C bond of the carbon nanotube,
and
are non-local decay functions, and
denotes the material scale coefficient.; according to the NSGT developed by Lim[
24], the internal material size instanton equation for CNTs can be presented as:
Here
stand for the one-dimensional laplace operators,
and
are nonlocal parameters;
denote the material related parameter, and if
=
=
, then the Eq .(5) can be simplified as:
3. Timoshenko beam theory
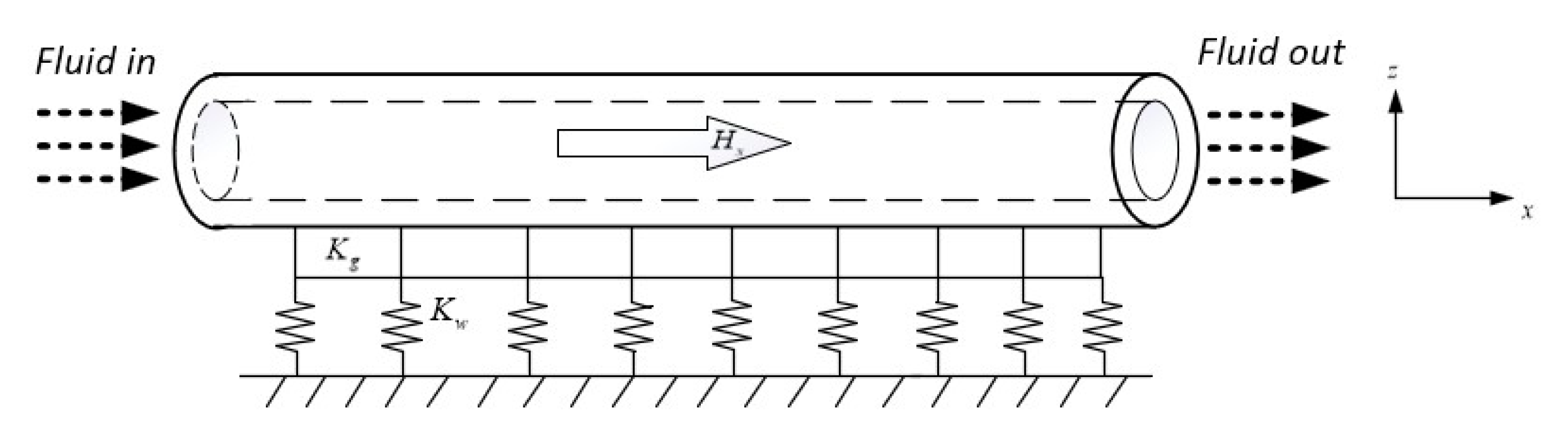
To better understand the fluid conveying carbon nanotube wave behaviour of SWCNT under the action of magnetic fields and foundations, the Timoshenko beam model illustrated in
Figure 1 is used, Assuming that the fluid inside the nanobeam is considered to be ideally incompressible and flowing uniformly, It is also assumed that the beam is not axially loaded and that the magnetic field strength inside and outside is the same in SWCNT, The geometric properties of SWCNT are taken as: Outer radius
, inner radius
,, density
, length
and simply supported Timoshenko beams embedded in Pasternak elastic foundation with elastic stiffness coefficient
and shear stiffness coefficient
.
According to the Timoshenko beams theory, their axial and transverse displacements can be expressed as:
where
denote the axial displacements, and
denote transverse displacements on the middle axis, and
and
denote the time and the rotation of the cross section, respectively.
According to the theory of Timoshenko beams, Axial and shear strains are written as:
The kinetic energy generated by the fluid flow internal to the CNTs is given by:
where
represent the mass of fluid per unit length within CNTs,
denote the mean flow velocity and
denote the fluid mass moment of inertia.
The kinetic energy of a carbon nanotube is given by:
where
represent the mass per unit length of carbon nanotube and
represent the mass moment of inertia of CNTs.
Carbon nanotube strain energy is given by:
where
denotes the cross-sectional area of the CNTs,
denotes the normal resultant force,
denotes transverse shear force and bending moment
can be defined as:
The work done by the external load can be denoted as:
where
denotes the magnetic field force per unit length in the z direction, and
represents the transverse distributed load caused by residual stresses on the surface.
The magnetic field force per unit length in the z direction can be expressed as:
where
denotes the magnetic fields permeability of CNTs material-related, and
denotes the component of magnetic flux in the
direction.
According to the literature [
35] the transverse distribution force due to the effect surface tension of SWCNT can be denoted as:
where
denote a constant, defined as
where
denotes the surface residual stress,
denotes the diameter of the CNTs, and
denotes the wall thickness. due to surface elasticity effects the effective flexural stiffness is given by
, where
denotes the surface Young’s modulus of CNTs,
.
Hamilton’s variational principle can be obtained as:
By substituting Eqs.(9), (10), (11) and (13) into Eq (16).integrating by parts and taking the coefficients of
and
to vanish, the differential equation of motion for the CNT is expressed as:
The axial displacement of the carbon nanotubes is neglected, the shear force
in equation (17) above is expressed as:
where
denotes the shear correction factor, and
denotes the shear modulus.
By submitting Eqs.(6) and (8) into Eq (12).the bending moment
can be obtained:
To take the first order partial derivative of
in equation (19) gives:
By submitting Eqs. (18) and (20).The final equation for the control equation of the Eq.(17) fluid-conveying SWCNT can be obtained as:
4. Wave Propagation Analysis
The solution to the wave equation of Eqs. (21) can be stated as:
where
and
denote the amplitude of the vibration of the simple harmonic and the amplitude of the angular vibration, respectively,
denotes the wavenumber, and
denote the excitation frequency, and
.
By substituting Eqs.(22) into Eq (21), The matrix equation for
and
can be obtained as:
Where
,
For a system of linear equations with non-singular solutions, let the coefficient matrix determinant (23) to zero:
The four solutions of frequency
can be obtained by solving the determinant, according to the literature [
39]; the low frequency of the real part represents the flexural wave; the high frequency of the real part represents the shear wave, this paper mainly studies the propagation characteristics of the flexural behaviour, the wave frequency is known, we can get the phase velocity of the carbon nanotube can be expressed as:
5. Numerical results and discussions
Through the above derivation and analysis, the propagation vibration equation of SWCNT bending wave is solved, The effect of different factors on the wave frequency of the fluid-conveying SWCNT wave propagation is discussed in the next. Material parameters for CNTs in the calculation can be obtained as:the Young’s modulus , the outer radius , the inner radius , the effective thickness of SWCNT , the Poisson’s ratio , the density of CNTs , Shear factor , the magnetic permeability , the surface Young’s modulus , the surface residual tension , the length of nanotube .
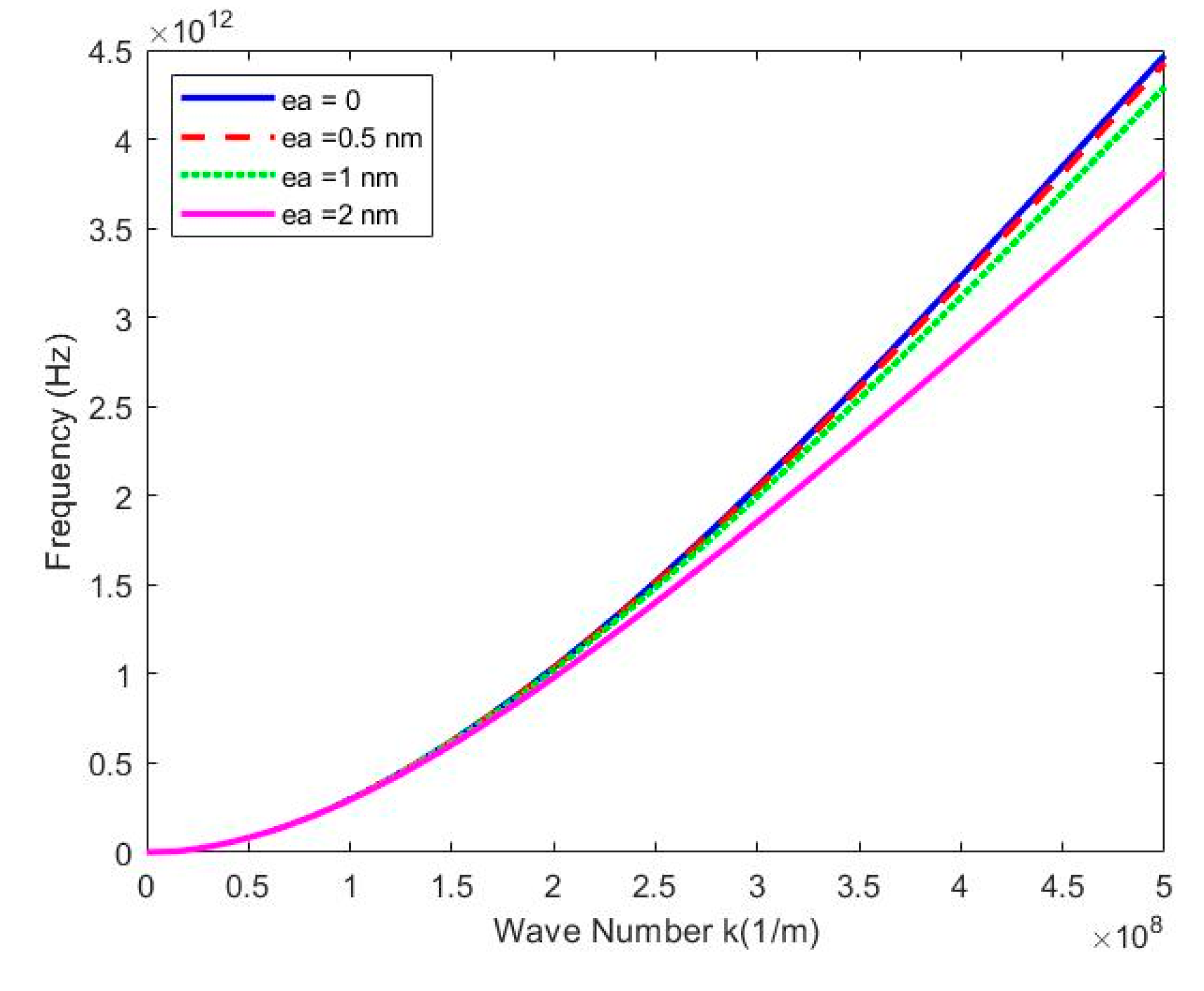
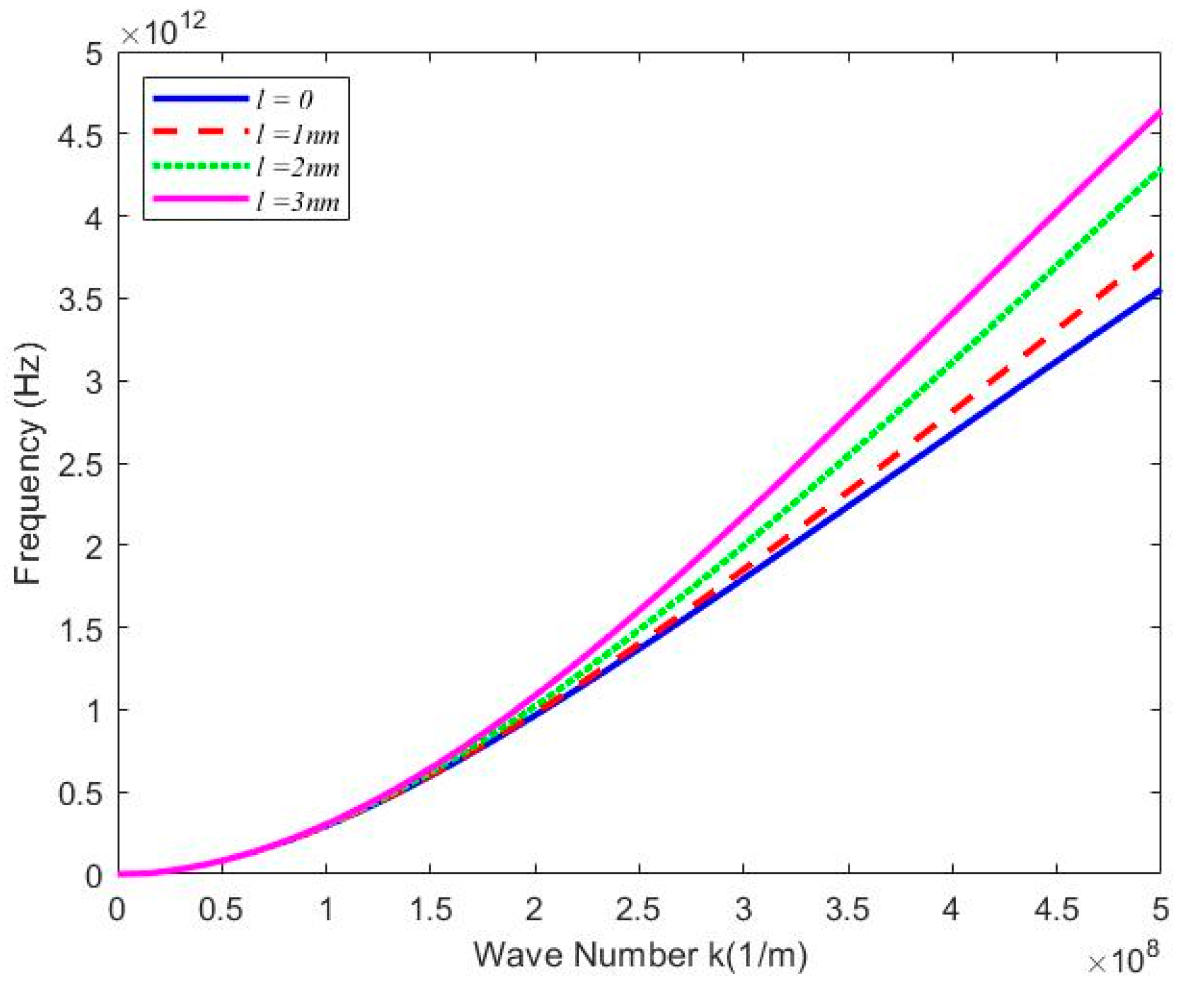
SWCNT with strain gradient coefficients
are considered, neglecting magnetic field and influence of surrounding elastic medium;With
.
, and fluid density
, The correlation between the flexural frequency and the wavenumber k for different values of the nonlocal coefficient is shown in
Figure 2, SWCNT wave frequency increases as wavenumber
increases, it is observed that for the same numberwaves
, the wave frequency of CNTs decreases as the nonlocal coefficients increases, which means that increasing the nonlocal coefficients hinders wave propagation. As shown in
Figure 3, nonlocal parameters
, other parameters are the same as above, SWCNT wave frequency increases with the increase of wavenumber
, as the strain gradient increases, the flexural frequency increases; which implies that the wave propagation is reinforced owing to strain gradient effect. When the wave number
, this variation will be more apparent. The conclusion is the same as that reached by Yu et al. [
40].With
. small scale parameters
.
, and fluid density
,
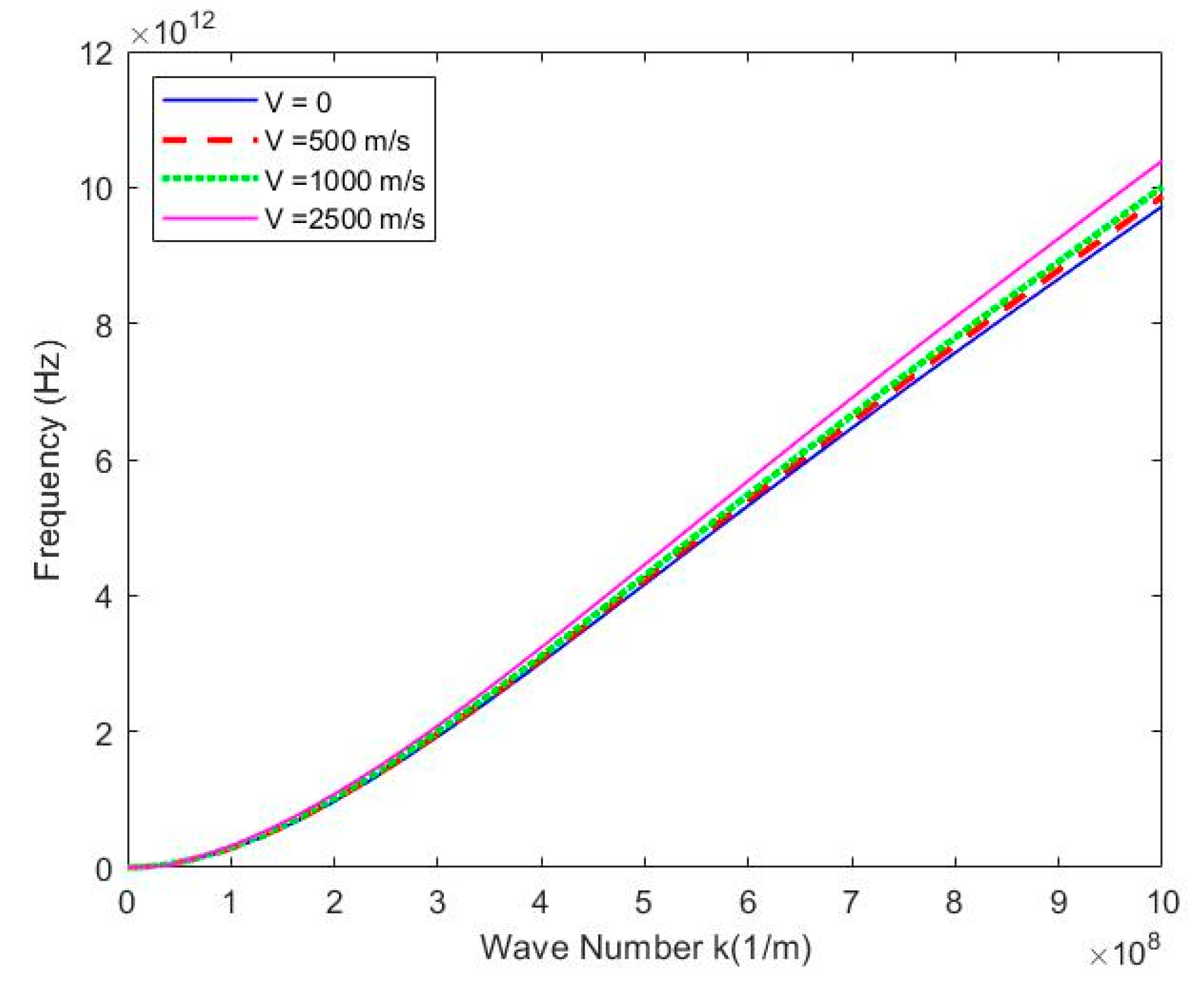
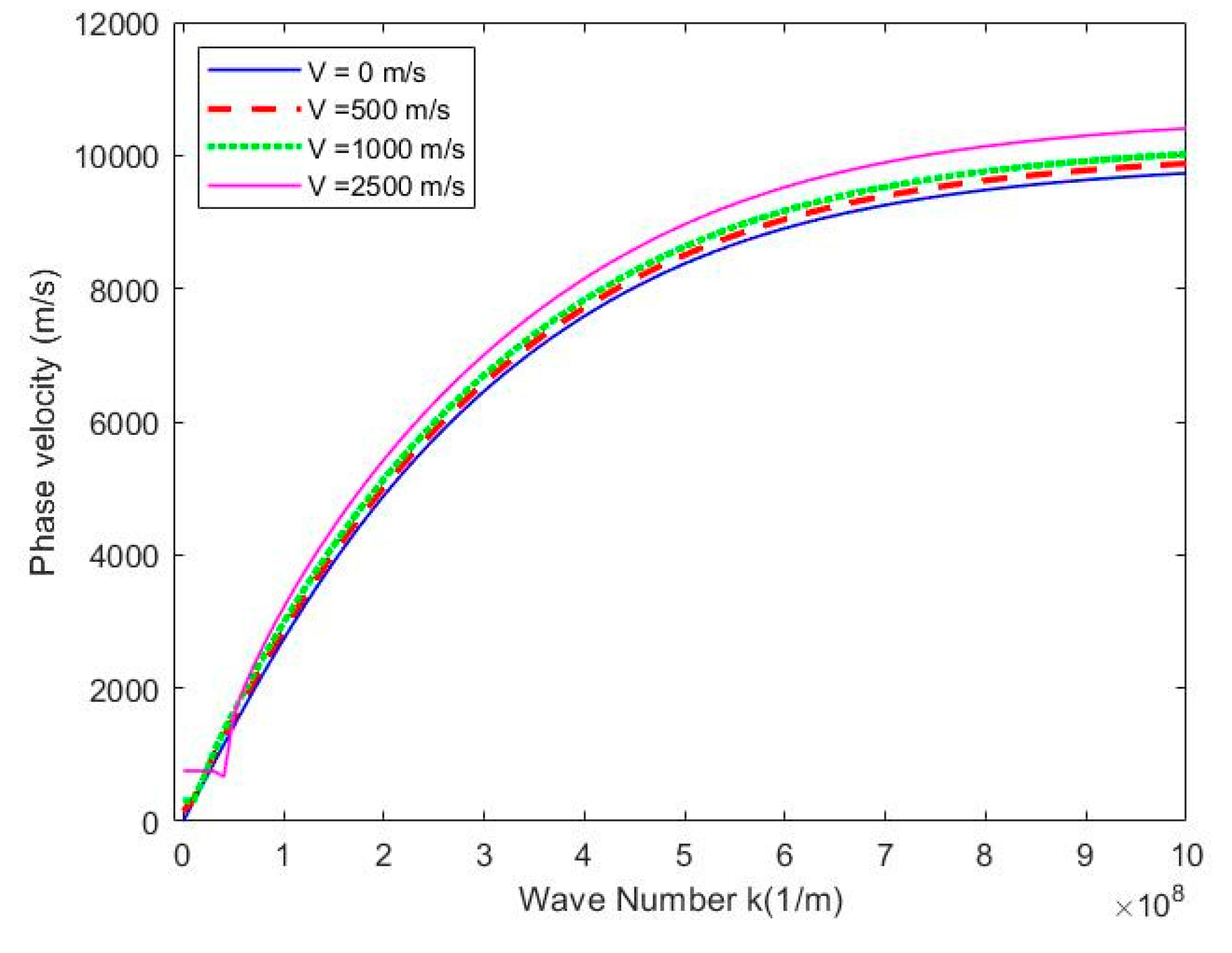
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 represent the variation of flexural frequency with and phase velocity with different flow velocity, As the fluid flow velocity increases, the flexural frequency of SWCNT are gradually increasing. When wave number
, the influence of increasing wavenumber on the phase velocity of CNT is noticeable.
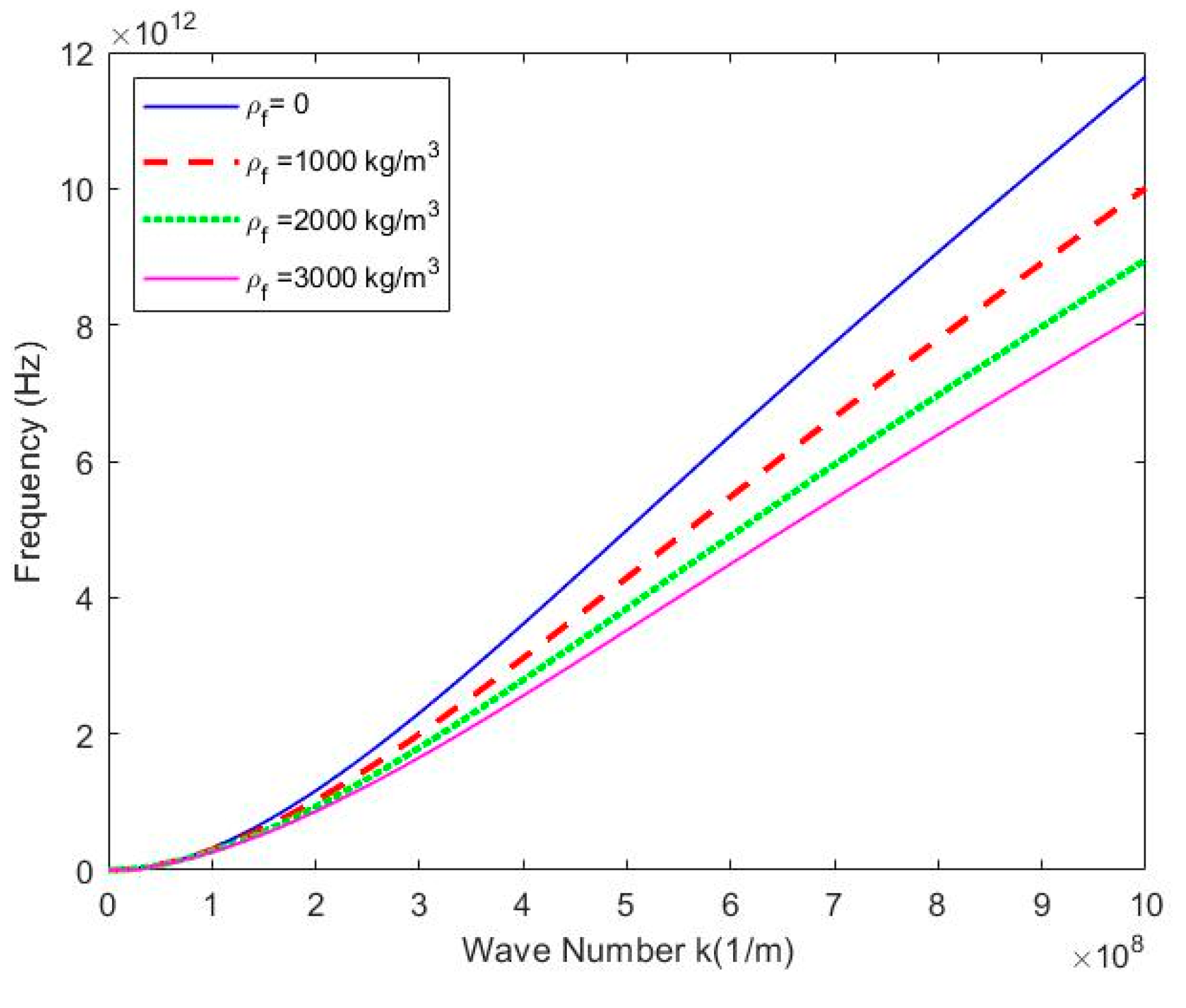
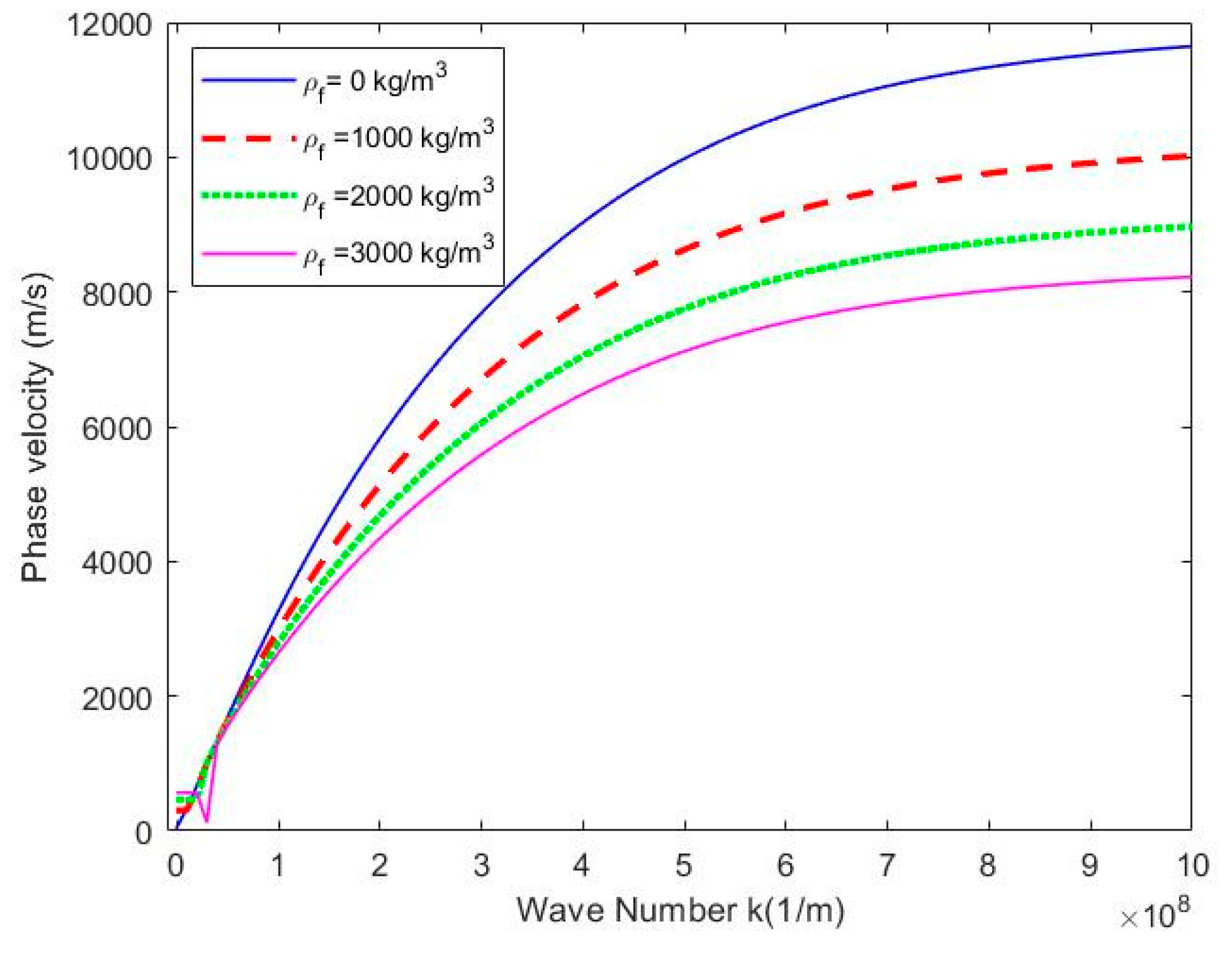
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 shows the effect flexural frequency and phase velocity variations of SWCNT under different fluid density respectively. Wih small scale parameters
, If not specified, the other physical parameters are neglected when a parameter variable is considered. It is worth noting that for the same wavenumber
, with the increases of the density of fluid, both the flexural frequency and phase velocity decrease, which indicates that the increase in fluid density can make the SWCNT stiffer.
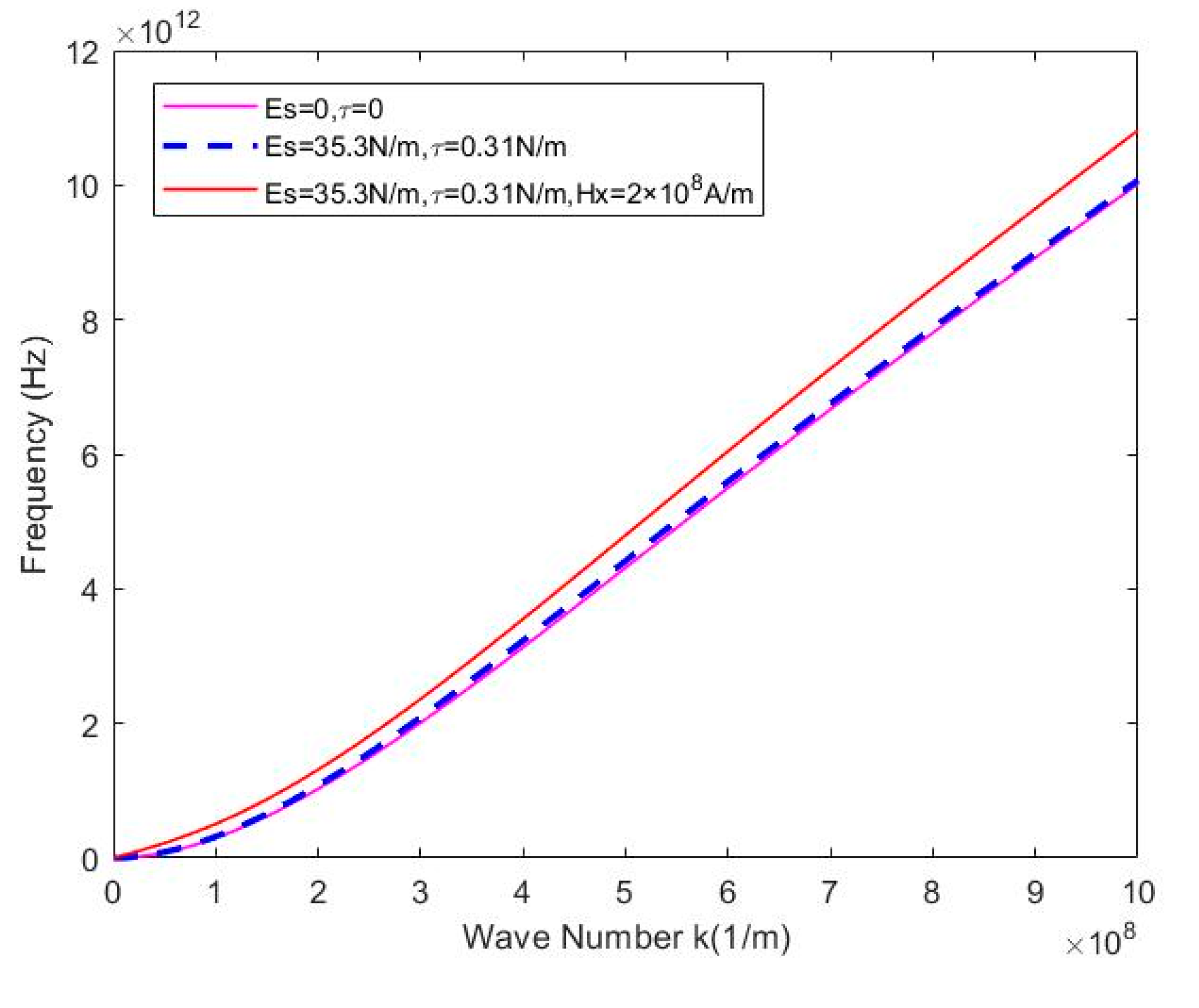
Figure 8 depicts the influence of with or without surface effect on the wave frequency characteristics, With
, the surrounding elastic medium is neglected. From
Figure 8, it can be concluded that the frequency of waves with surface effects is higher than the frequency of waves without surface effects. In addition, in the presence of both magnetic fields and surface effects, the wave frequencies increases significantly.
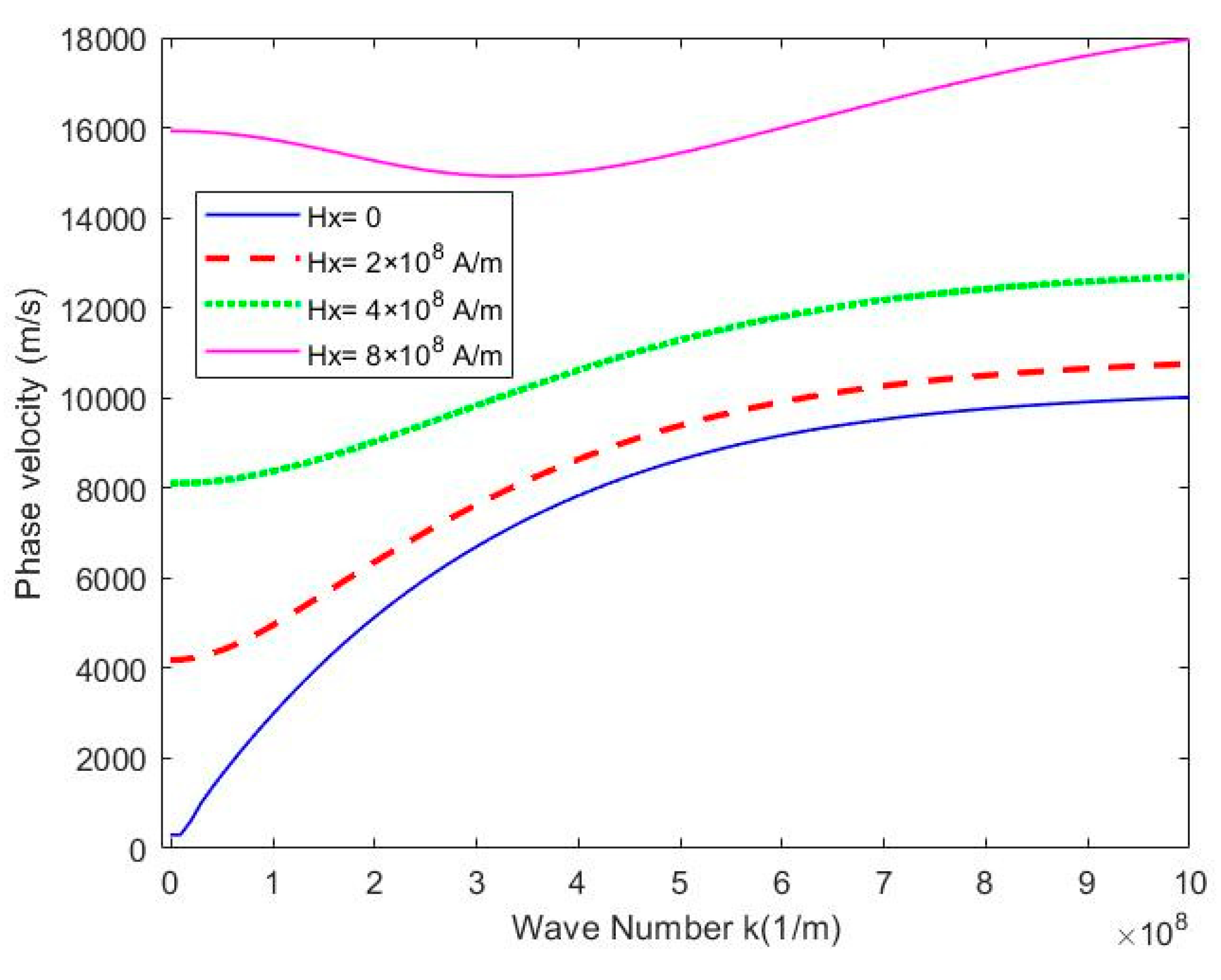
Figure 9 illustrates the SWCNT phase velocity variation with different magnetic field fluxes, With
, the shear stiffness coefficients, elastic stiffness coefficients and surface effect are neglected. as the wavenumber increases, the phase velocity gradually increases. It is not difficult to find that with the increase of magnetic field flux, the SWCNT phase velocity also increases.
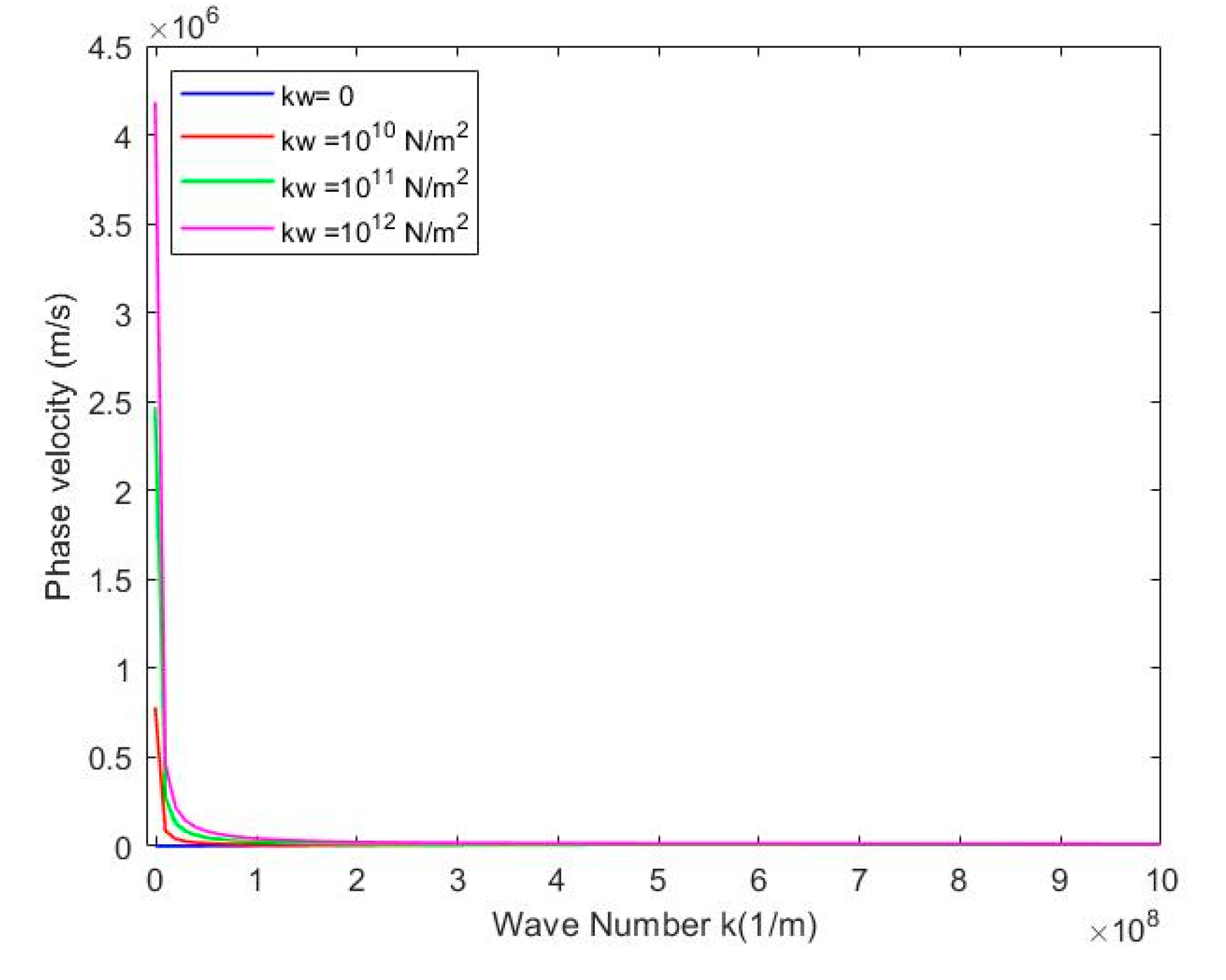
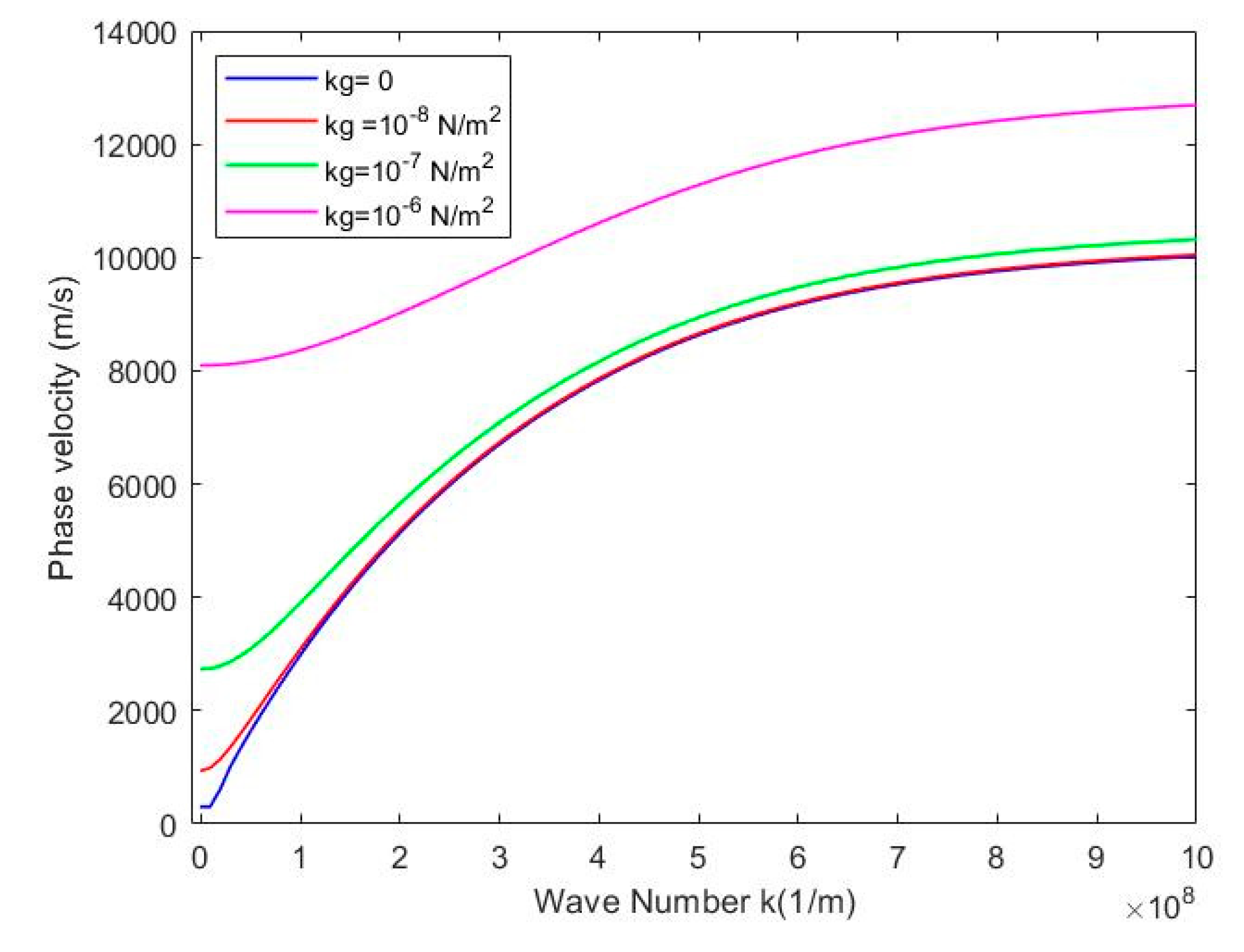
Figure 10 and
Figure 11 represents the effect of the elastic stiffness coefficient
and the shear stiffness coefficient
on the dynamic response, respectively. From
Figure 10, it can be found that when the wavenumber started to increase, the phase velocity decreases sharply, and eventually it comes close to a minimum value; as shown in
Figure 11, with an increases of shear stiffness coefficient, the phase velocity increases.
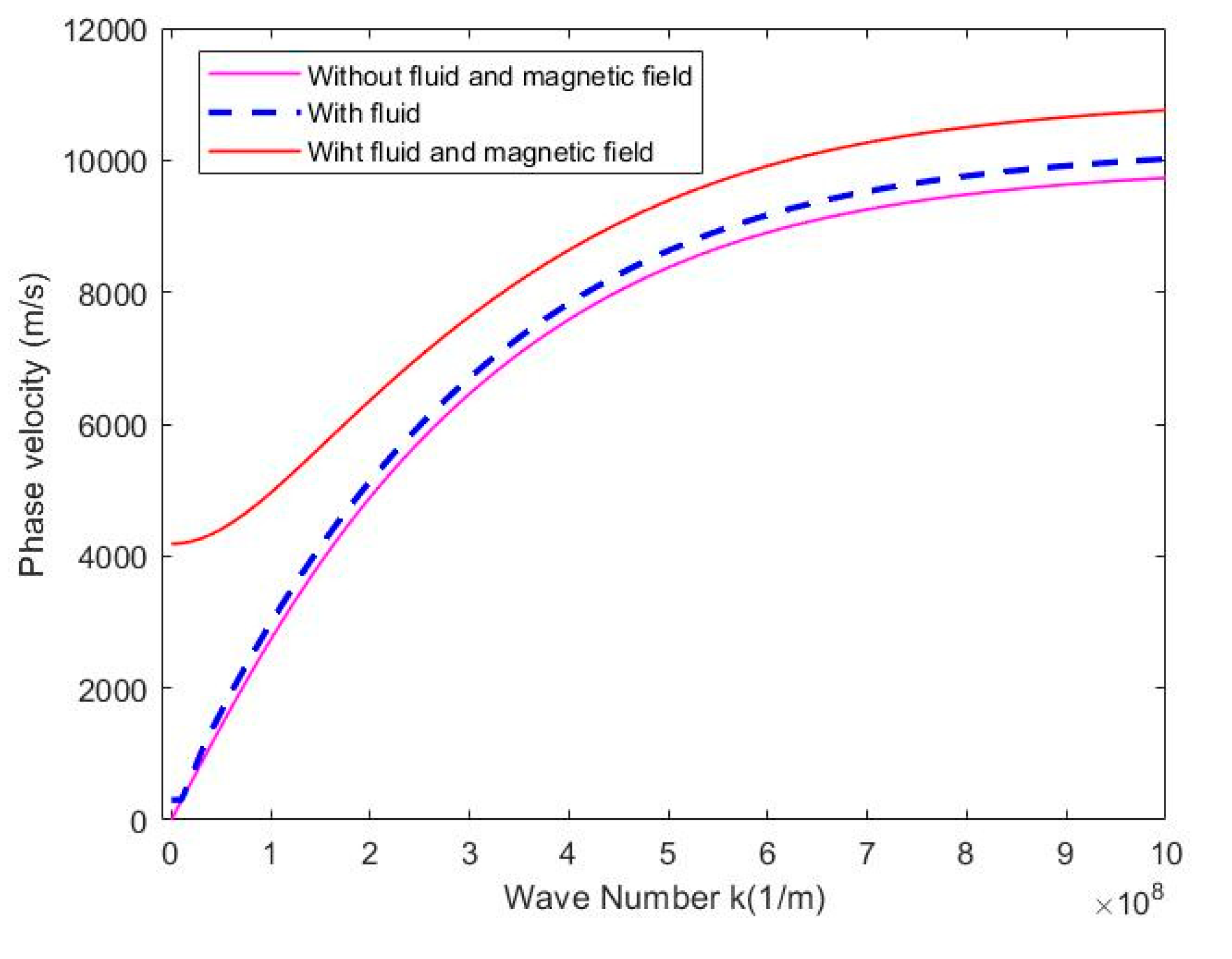
Figure 12 describes the phase velocity propagation characteristics of the SWCNT with and without magnetic field or fluid velocity, With
the elastic stiffness
the shear stiffness
, and surface effect are neglected. as shown in
Figure 12, It is noted that at the same wavenumber, In the presence of the magnetic field, the phase velocity of the CNT increases with the increase of the fluids flow.
6. Conclusion
Based on the theory of non-local strain gradients, this paper investigates the wave behaviour characteristics in the complex physical environment, Using Timoshenko beam theory and the Hamiton’s variational principle to derive the control equations for the fluid-conveying SWCNT, The influence of flow velocity, fluid density, small-scale parameters, magnetic field change, shear stiffness coefficients, elastic stiffness coefficients and surface effects on the elastic waves of carbon nanotubes is discussed and analysed.
The research indicates that: For the fluid-conveying SWCNT increasing the non-local coefficients hander carbon nanotube wave propagation, however, increasing the strain gradient coefficients promotes wave propagation. the phase velocity gets larger for CNTs due to the increase in magnetic flux strength and the existence of surface effects, the density of fluid increases make the stiffness of the CNTs, .In addition, The fluid velocity and surrounding elastic medium also play an noticeable role in the flexural frequency and phase velocity of the fluid-conveying SWCNT. The above derivative study can provide some theoretical support for nanodevice design and development.
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. nature, 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd G E, Blackford M, Moricca S, et al. The world’s smallest gas cylinders?. Science, 1997, 277, 933–936.
- Hummer G, Rasaiah J C, Noworyta J P. Water conduction through the hydrophobic channel of a carbon nanotube. nature, 2001, 414, 188–190.
- Wong E W, Sheehan P E, Lieber C M. Nanobeam mechanics: elasticity, strength, and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. science, 1997, 277, 1971–1975.
- Wilder J W G, Venema L C, Rinzler A G, et al. Electronic structure of atomically resolved carbon nanotubes. Nature, 1998, 391, 59–62.
- Yan Z, Jiang L. Electromechanical response of a curved piezoelectric nanobeam with the consideration of surface effects. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2011, 44, 365301.
- Bian L, Gao M. Nanomechanics model for properties of carbon nanotubes under a thermal environment. Acta Mechanica, 2018, 229, 4521–4538.
- El Jarroudi, M. A third gradient elastic material resulting from the homogenization of a von Kármán ribbon-reinforced composite. ZAMM-Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics/Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 2018, 98, 1666–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian L, Li H, Cheng Y. Temperature and size-dependent modeling for predicting mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 98, 518–536.
- Chang W J, Lee H L. Free vibration of a single-walled carbon nanotube containing a fluid flow using the Timoshenko beam model. Physics Letters A, 2009, 373, 982–985.
- Selvaraj R, Ramamoorthy M. Dynamic analysis of laminated composite sandwich beam containing carbon nanotubes reinforced magnetorheological elastomer. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2021, 23, 1784–1807.
- Shahedi S, Mohammadimehr M. Nonlinear high-order dynamic stability of AL-foam flexible cored sandwich beam with variable mechanical properties and carbon nanotubes-reinforced composite face sheets in thermal environment. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials, 2020, 22, 248–302.
- Mitra M, Gopalakrishnan S. Wave propagation in multi-walled carbon nanotube. Computational materials science, 2009, 45, 411–418.
- Peigney A, Laurent C, Flahaut E, et al. Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon, 2001, 39, 507–514.
- Eringen A C, Wegner J L. Nonlocal continuum field theories. Appl. Mech. Rev., 2003, 56, B20–B22.
- Yoon J, Ru C Q, Mioduchowski A. Vibration and instability of carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. Composites Science and Technology, 2005, 65, 1326–1336.
- Yoon J, Ru C Q, Mioduchowski A. Flow-induced flutter instability of cantilever carbon nanotubes. International journal of solids and structures 2006, 43, 3337–3349. [CrossRef]
- Wang B, Deng Z, Ouyang H, et al. Wave characteristics of single-walled fluid-conveying carbon nanotubes subjected to multi-physical fields. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2013, 52, 97–105.
- Wang B, Deng Z, Ouyang H, et al. Wave propagation analysis in nonlinear curved single-walled carbon nanotubes based on nonlocal elasticity theory. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2015, 66, 283–292.
- Ming Z H, Ming L, Bo Z, et al. Effect of shear strain on the deflection of a clamped magnetostrictive film–substrate system. Journal of magnetism and magnetic materials, 2011, 323, 3251–3258.
- Li M, Zheng H, Luo X. Additional small-scale boundary effects on free vibration of carbon nanotubes and their macroscopic energy meaning. International Journal of Materials Research, 2014, 105, 1018–1024.
- Bahaadini R, Saidi A R, Hosseini M. Flow-induced vibration and stability analysis of carbon nanotubes based on the nonlocal strain gradient Timoshenko beam theory. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2019, 25, 203–218.
- Bahaadini R, Saidi A R, Hosseini M. On dynamics of nanotubes conveying nanoflow. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2018, 123, 181–196.
- Lim C W, Zhang G, Reddy J N. A higher-order nonlocal elasticity and strain gradient theory and its applications in wave propagation. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2015, 78, 298–313.
- Li L, Hu Y. Buckling analysis of size-dependent nonlinear beams based on a nonlocal strain gradient theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2015, 97, 84–94.
- Li L, Hu Y, Ling L. Flexural wave propagation in small-scaled functionally graded beams via a nonlocal strain gradient theory. Composite Structures, 2015, 133, 1079–1092.
- Li L, Hu Y, Ling L. Wave propagation in viscoelastic single-walled carbon nanotubes with surface effect under magnetic field based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2016, 75, 118–124.
- Wang Y, Bian L, Gao M. A non-local modeling for the influence of fluid forces on vibration characteristics of carbon nanotubes. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2021, 272, 115348.
- Selvamani R, Jayan M M S, Dimitri R, et al. Nonlinear magneto-thermo-elastic vibration of mass sensor armchair carbon nanotube resting on an elastic substrate. Curved and Layered Structures, 2020, 7, 153–165.
- Ebrahimi F, Haghi P. Wave propagation analysis of rotating thermoelastically-actuated nanobeams based on nonlocal strain gradient theory. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2017, 30, 647–657.
- Ebrahimi F, Reza Barati M. Surface effects on the vibration behavior of flexoelectric nanobeams based on nonlocal elasticity theory. The European Physical Journal Plus, 2017, 132, 1–13.
- Amiri A, Vesal R, Talebitooti R. Flexoelectric and surface effects on size-dependent flow-induced vibration and instability analysis of fluid-conveying nanotubes based on flexoelectricity beam model. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2019, 156, 474–485.
- Yang Y, Jinrui W, Wuhuai Y. Study on Dynamic Characteristics of Microchannel Fluid–Solid Coupling Systems in Nonlocal Stress Fields. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 2019, 7, 477–485.
- Zhen Y X, Fang B. Nonlinear vibration of fluid-conveying single-walled carbon nanotubes under harmonic excitation. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 2015, 76, 48–55.
- Zhen Y, Zhou L. Wave propagation in fluid-conveying viscoelastic carbon nanotubes under longitudinal magnetic field with thermal and surface effect via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Modern Physics Letters B, 2017, 31, 1750069.
- Arani A G, Roudbari M A. Surface stress, initial stress and Knudsen-dependent flow velocity effects on the electro-thermo nonlocal wave propagation of SWBNNTs. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2014, 452, 159–165.
- Bahaadini R, Hosseini M, Jamalpoor A. Nonlocal and surface effects on the flutter instability of cantilevered nanotubes conveying fluid subjected to follower forces. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2017, 509, 55–61.
- Ghane M, Saidi A R, Bahaadini R. Vibration of fluid-conveying nanotubes subjected to magnetic field based on the thin-walled Timoshenko beam theory. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2020, 80, 65–83.
- Pang M, Wang P, Zhang Y. Wave propagation in fluid-conveying nanotubes under multi-physical fields based on non-local higher-order strain gradient model. Micro & Nano Letters, 2019, 14, 922–927.
- Yang Y, Wang J, Yu Y. Wave propagation in fluid-filled single-walled carbon nanotube based on the nonlocal strain gradient theory. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2018, 31, 484–492.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).