Submitted:
06 June 2023
Posted:
07 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
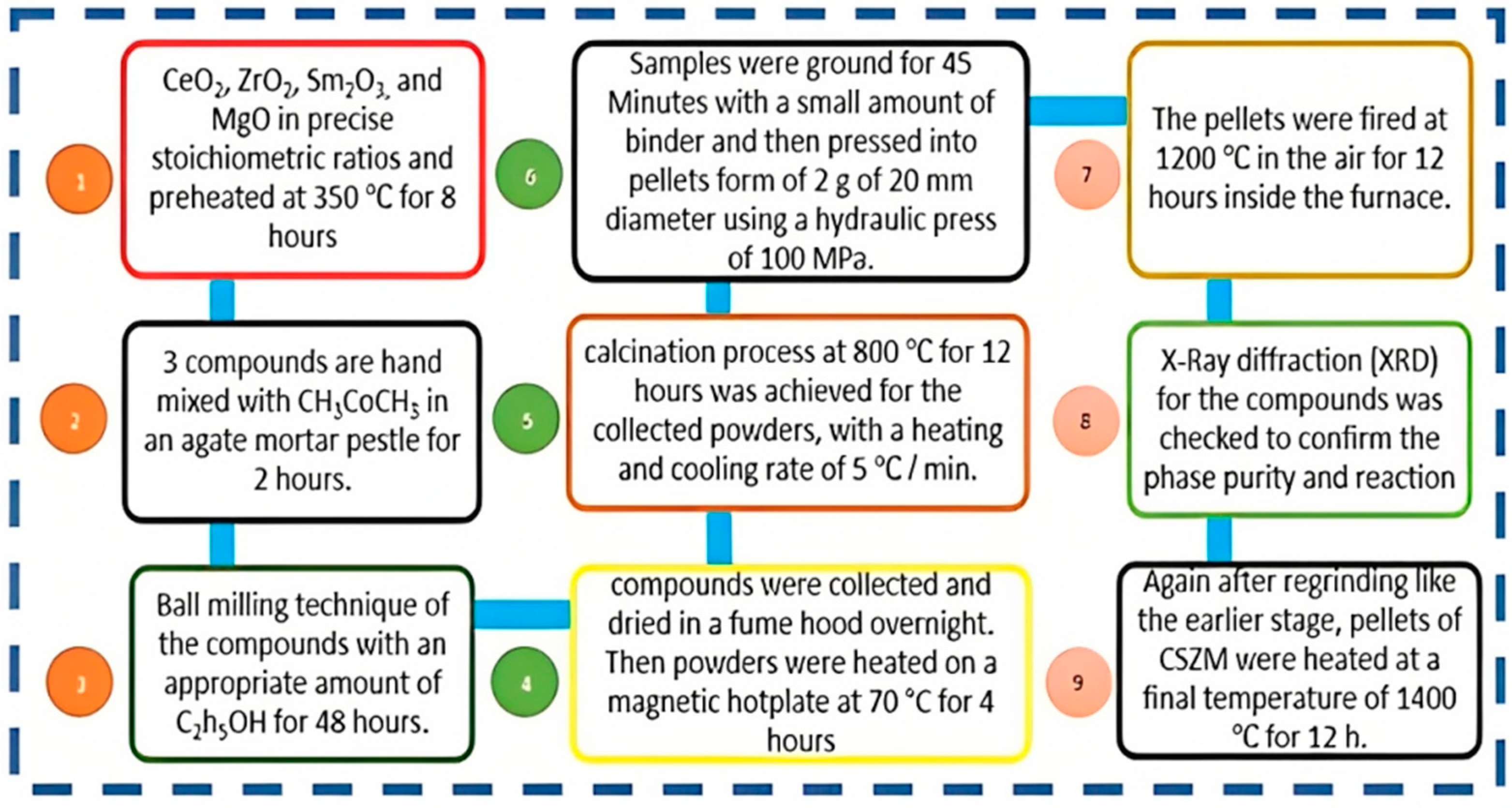
2.1. CSZM materials synthesis
2.2. Characterizations of the samples
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Structural and phase analysis of XRD data
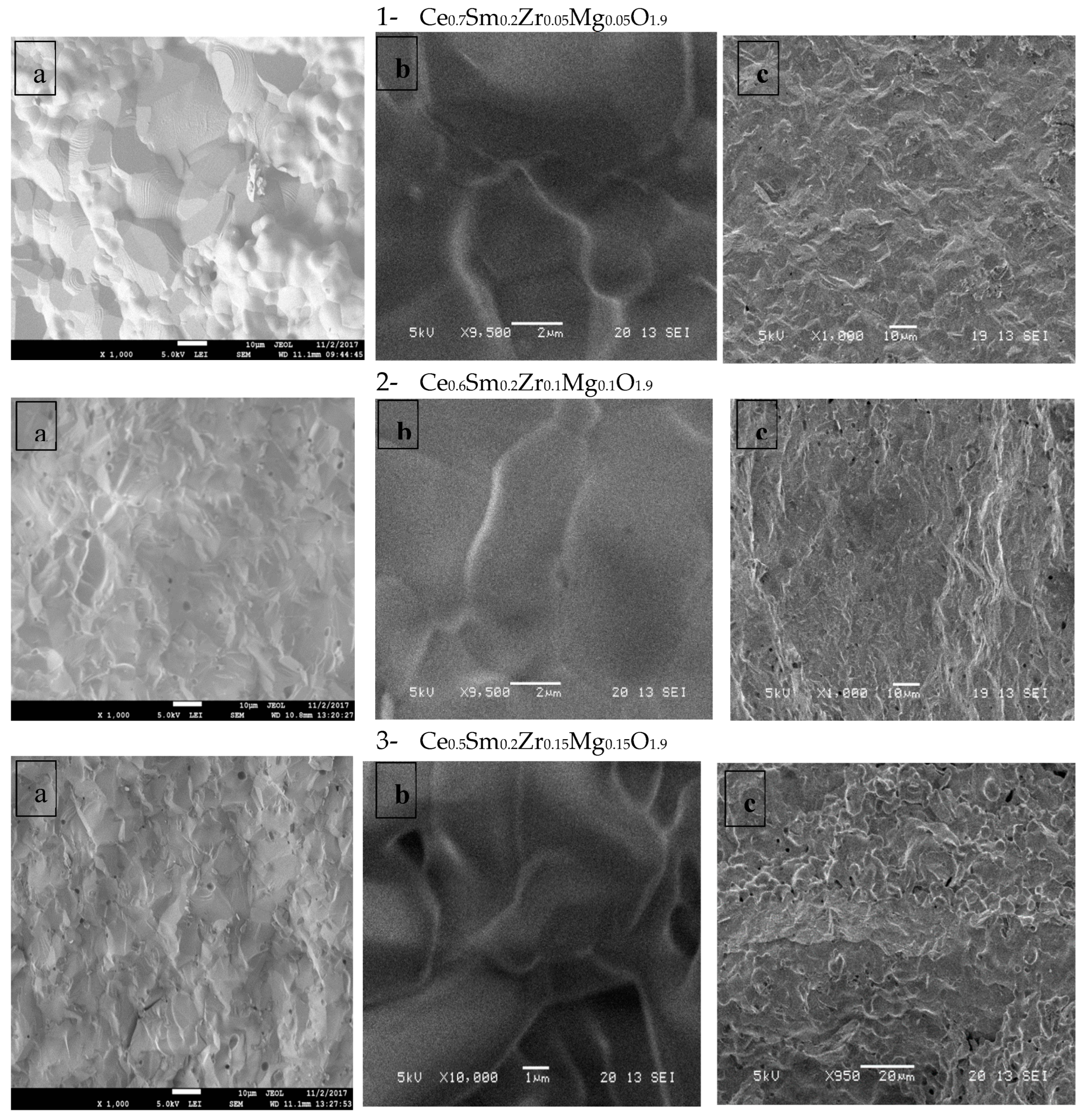
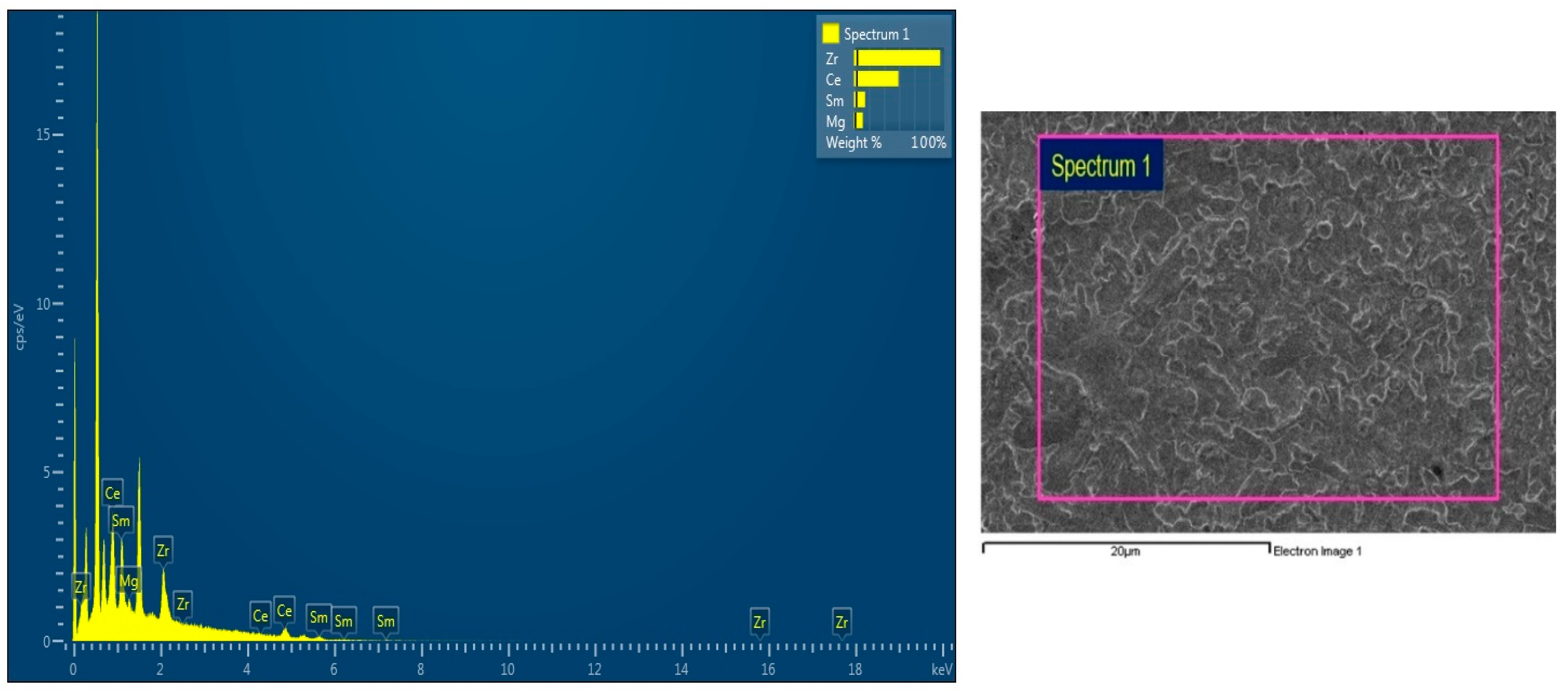
- Surface morphology of synthesized samples using SEM & EDX
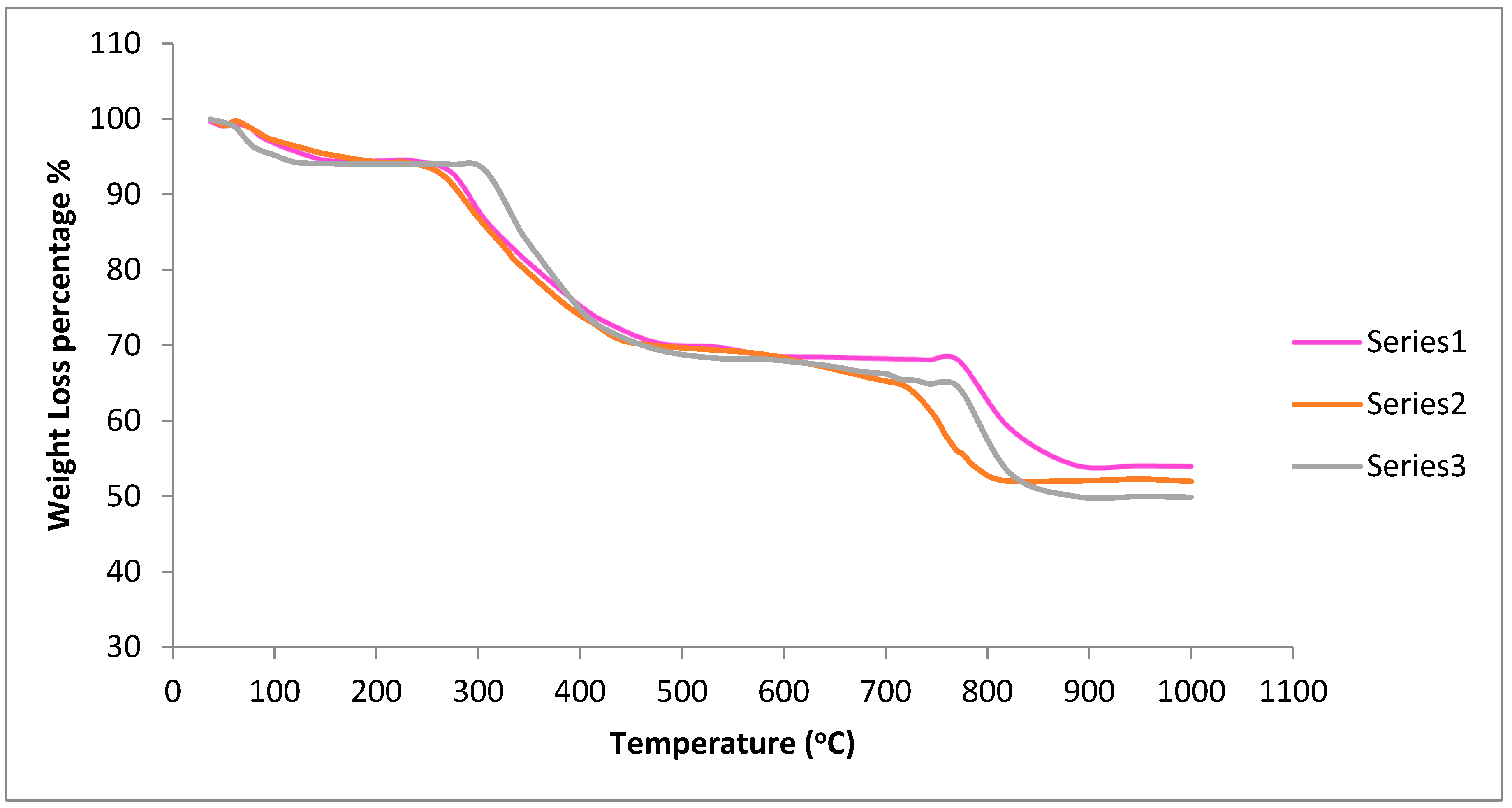
- Thermogravimetric (TGA) of the synthesized series of Mgx/2 doped Ce0.8-xSm0.2Zrx/2O2-d
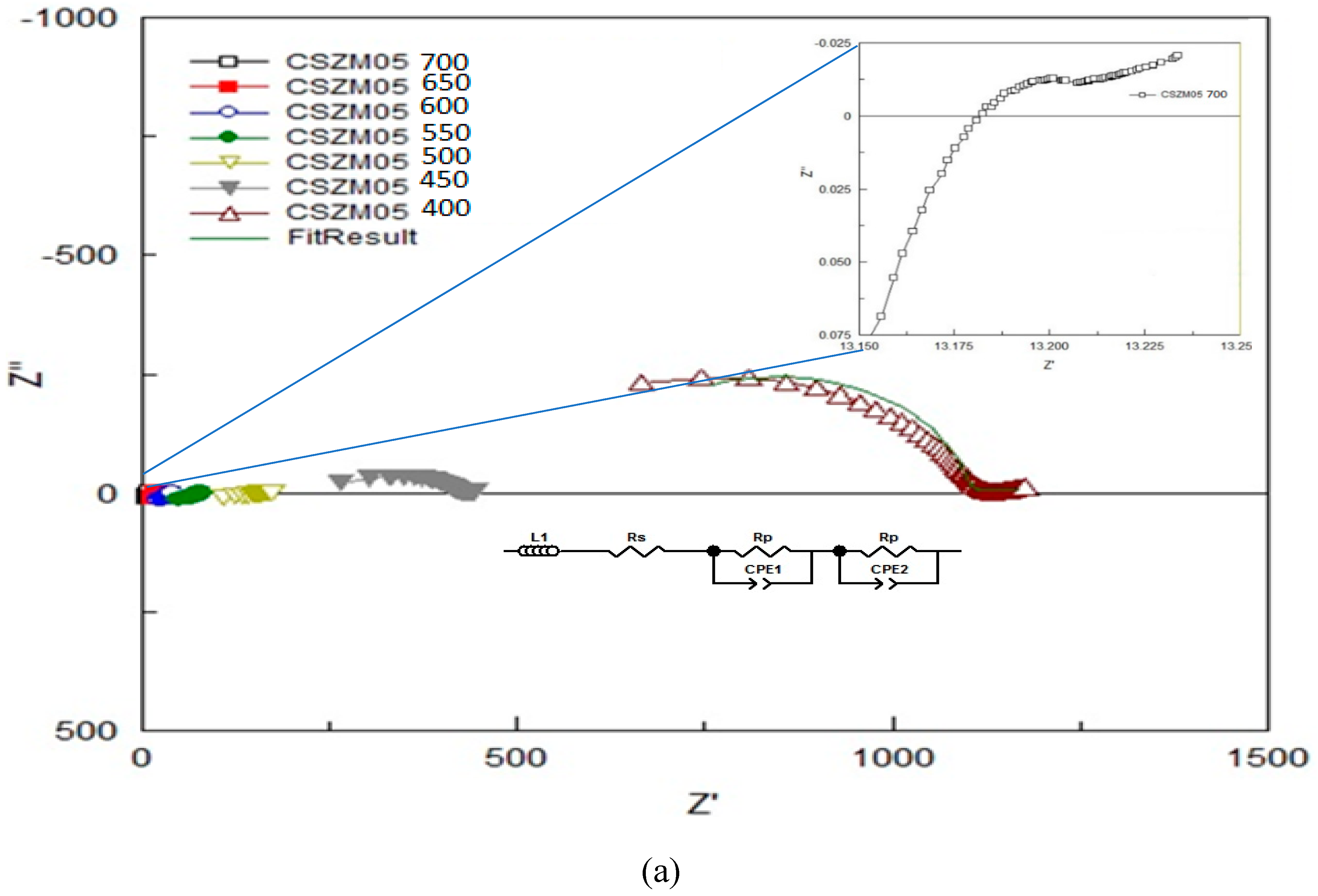
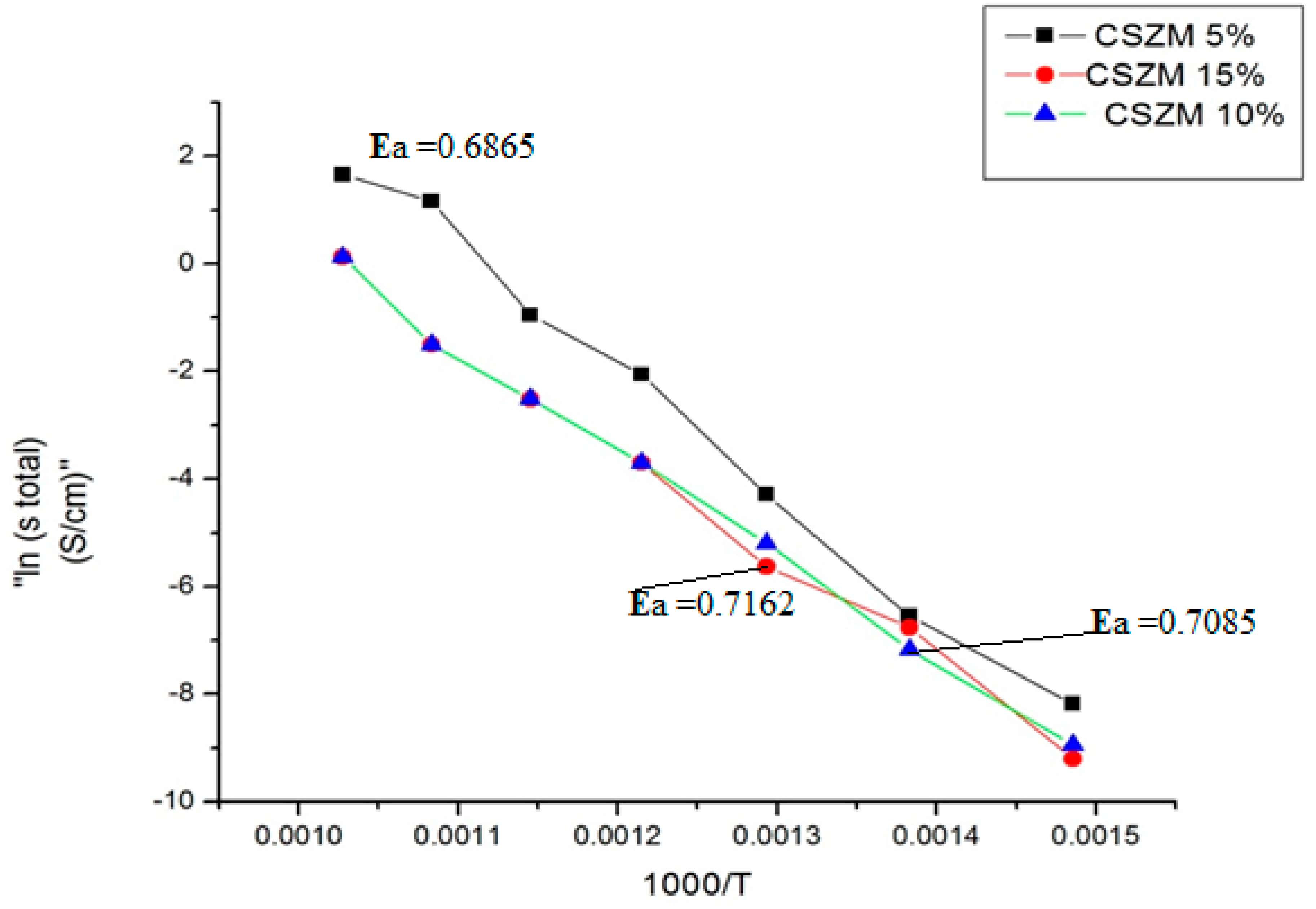
- Electrochemical Impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of the prepared samples under 5 % H2/Ar.
4. Conclusion and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfram T, Ellialtioglu S, Electronic and Optical Properties of d-Band Perovs, in: Univ. Press. Cambridge, 2006.
- Tejuca L.G, Fierro J.L.G, Tascón J.M.D, Structure and Reactivity of Perovskite-Type Oxides, Adv. Catal. 1989. [CrossRef]
- Hossain S, Abdalla AM, Jamain SNB, Zaini JH, Azad AK. A review on proton conducting electrolytes for clean energy and intermediate temperature-solid oxide fuel cells. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2017,79,750–64. [CrossRef]
- Levy M.R, Chapter 3: Perovskite Perfect Lattice, in: Cryst. Struct. Defect Prop. Predict. Ceram. Mater., 2005.
- Johnsson M, Lemmens P, Crystallography and Chemistry of Perovskites, in: Handb. Magn. Adv. Magn. Mater., 2007.
- Taimoor Raza , Jingjing Yang , Ruoming Wang , Chen Xia ,Rizwan Raza , Bin Zhu , Sining Yun "Recent advance in physical description and material development for single component SOFC: A mini-review" Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 444, 15 September 2022, 136533.
- Muneeb Irshad,Naila Kousar,Muhammad Bilal Hanif, Asif Nadeem Tabish, Abdul Ghaffar, Muhammad Rafique, Khurram Siraj, Zeeshan Aslam,Mohammed A. Assiri, Muhammad Imran, Michał Mosiałek, Zuzana Zmrhalovahi and Martin Motola "Investigating the microstructural and electrochemical performance of novel La0.3Ba0.7Zr0.5X0.3Y0.2 (X = Gd, Mn, Ce) electrolytes at intermediate temperature SOFCs.Sustainable Energy Fuels, 2022,6, 5384-5391.
- Zia UdDin, Z.A.Zainal, Biomass integrated gasification–SOFC systems: Technology overview, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 53,1356–1376.
- Radenahmad, N., Azad, A.T., Saghir, M., Taweekun, J., Bakar, M.S.A., Reza, M.S., Azad, A.K., “A review on biomass derived syngas for SOFC based combined heat and power application”, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 119, 109560.
- Giovanni Capurso et al., Nanoconfined mixed Li and Mg borohydrides as materials for solid state hydrogen storage, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 14, 10768-10773. [CrossRef]
- N. Radenahmad, J. Taweekun, A. Afif, J. I. Lee, J.-Y. Park, J. Zaini, A. K. Azad, “Syngas Fuelled High Performance Solid Oxide Fuel Cell”, ECS Transactions, 2019, 91(1), 1621-1629. [CrossRef]
- P.V. Aravind, T.Woudstra, N.Woudstra, H. Spliethoff, Thermodynamic evaluation of small-scale systems with biomass gasifiers, solid oxide fuel cells with Ni/GDC anodes and gas turbines , Journal of Power Sources 2009,190, 461–475. [CrossRef]
- Pukazhselvan D, K Sandhya, Nasani N, Paul D. Chemical transformation of additive phase in MgH2/CeO2 hydrogen storage system and its effect on catalytic performance. Appl Surf Sci 2021,561,150062.
- Q. Zhang, W.J. Liu, J. Wang, D. Liu, Z.H.C. Sun, Processing of perovskite La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ electrolyte by glycine-nitrate combustion method, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021,46,61, 31362-31369.
- Nagar R, Vinayan B, Samantaray P, Ramaprabhu S. Recent advances in hydrogen storage using catalytically and chemically modified graphene nanocomposites. J Mater Chem A 2017;5(44):22897-912. [CrossRef]
- Peng D, Ding Z, Fu Y, Wang Y, Bi J, Li Y, Han S. Enhanced H2 sorption performance of magnesium hydride with hard-carbon-sphere-wrapped nickel. RSC Adv 2018;8(50): 28787-96. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhang X, Hu J, Gao M, Pan H. Empowering hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 by nanoengineering and nanocatalysis. Mater Today Nano 2020,9,100064. [CrossRef]
- Ma Z, Zhang Q, Zhu W, Khan D, Hu C, Huang T, Ding W, Zou J. Nano Fe and Mg2Ni derived from TMA-TM (TM=Fe, Ni) MOFs as synergetic catalysts for hydrogen storage in MgH2. Sustain Energ Fuels 2020;4(5):2192-200.
- Abdalla A, Hossain S, Nisfindy O, Azad A, Dawood M, Azad A. Hydrogen production, storage, transportation and key challenges with applications: A review. Energ Convers Manage 2018,165,602-27. [CrossRef]
- Mohtadi R, Orimo S. The renaissance of hydrides as energy materials. Nat Rev Mater 2016;2(3):16091. [CrossRef]
- Serge Nyallang Nyamsi et al., 200 NL H2 hydrogen storage tank using MgH2eTiH2eC nanocomposite as H2 storage Material, Int.J. Hydrogen Energy,2021, 46 ,36, 19046-19059.
- Ouyang L, Chen K, Jiang J, Yang X, Zhu M. Hydrogen storage in light-metal based systems: A review. J Alloys Compd 2020,829,154597. [CrossRef]
- Huang Z, Guo Z, Calka A, Wexler D, Lukey C, Liu H. Effects of iron oxide (Fe2O3, Fe3O4) on hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based composites. J Alloys Compd 2006;422,1-2,299-304. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Wang K, Zhang X, Hu J, Gao M, Pan H, Liu Y. Synthesis process and catalytic activity of Nb2O5 hollow spheres for reversible hydrogen storage of MgH2. Int J Energ Res 2020;45,2,3129-41.
- Shahi R, Tiwari A, Shaz M, Srivastava O. Studies on de/rehydrogenation characteristics of nanocrystalline MgH2 co-catalyzed with Ti, Fe and Ni. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2013;38,6,2778-84. [CrossRef]
- Shevlin S, Guo Z. MgH2 Dehydrogenation Thermodynamics: Nanostructuring and Transition Metal Doping. J Phys Chem C 2013;117,21,10883-91. [CrossRef]
- Ponthieu M, Calizzi M, Pasquini L, Fernández J, Cuevas F. Synthesis by reactive ball milling and cycling properties of MgH2-TiH2 nanocomposites: Kinetics and isotopic effects. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2014;39,18,9918-23. [CrossRef]
- Souza ECC De, Muccillo R. Properties and applications of perovskite proton conductors. Mater Res 2010,13,385–94.
- Haugsrud R, Norby T. Proton conduction in rare-earth ortho-niobates and ortho-tantalates. Nat Mater 2006,5,193–6. [CrossRef]
- Fabbri E, Pergolesi D, Traversa E. Materials challenges toward proton conducting oxide fuel cells: a critical review. Chem Soc Rev 2010,39,4355–69. [CrossRef]
- Duan C, Tong J, Shang M, Nikodemski S, Sanders M, Ricote S, et al. Readily processed protonic ceramic fuel cells with high performance at low temperatures. Sci Rep 2015,349,1321–6. [CrossRef]
- Kreuer KD. Proton-Conducting Oxides. Annu Rev Mater Res 2003,33,333–59.
- Muneeb Irshad, Mehak Khalid, Muhammad Rafique, Naveed Ahmad, Khurram Siraj, Rizwan Raza, Muhammad Sadiq, Muhammad Ahsan, Abdul Ghaffarg and Amina Ashfaq "Evaluation of BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.2−xNixO3−δ perovskite cathode using nickel as a sintering aid for IT-SOFC,RSC Adv., 2021,11, 14475-14483.
- Wei Zhang, Yun Hang Hu "Recent progress in design and fabrication of SOFC cathodes for efficient catalytic oxygen reduction Author links open overlay panel" Catalysis Today Volume 409, 1 February 2023, Pages 71-86.
- Fabbri E, Pergolesi D, Traversa E. Electrode materials: A challenge for the exploitation of protonic solid oxide fuel cells. Sci Technol Adv Mater 2010,11,044301. [CrossRef]
- Bonano N, Ellis B, Mahmood MN. Construction and operation of fuel cells based on the solid electrolyte BaCeO3,Gd. Solid State Ionics 1991;44,305-11. [CrossRef]
- Ma GL, Shimura T, Iwahara H. Ionic conduction and nonstoichiometry in BaxCe0.90Y0.10O3-δ. Solid State Ionics 1998,110,103–10. [CrossRef]
- Schober T, Bohn HG. Water vapor solubility and electrochemical characterization of the high temperature proton conductor BaZr0.9Y0.1O2.95. Solid State Ionics 2000,127,351-60. [CrossRef]
- Kreuer KD, Adams S, Münch W, Fuchs A, Klock U, Maier J. Proton conducting alkaline earth zirconates and titanates for high drain electrochemical applications. Solid State Ionics, 2001;145,295-306. [CrossRef]
- V.A. Yartys et al., Magnesium based materials for hydrogen based energy storage: Past, present and future, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019,44, 15, 7809-7859. [CrossRef]
- Jianjiang Hu, Maximilian Fichtner, Marcello Baricco Preparation of Li-Mg-N-H hydrogen storage materials for an auxiliary power unit , Int.J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27, 17144-17148.
- Jingfeng Xue, Yu Shen, Qingjun Zhou, Tianmin He, Yanhong Han Combustion synthesis and properties of highly phase-pure perovskite electrolyte Co-doped La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 for IT-SOFCs Int. J. Hydrogen Energy2010, 35,1, 294-300.
- Jos_e Juan Alvarado Flores et al., Advances in the knowledge of the double perovskites derived from the conformation and substitution of the material Sr2MgMoO6-d as anode with potential application in SOFC cell, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021,46,51, 26152-26162.
- Daniel Friedrich, Marc Schlosser, and Arno Pfitzner. Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Physical Properties of Two Polymorphs of CsGaSe2, and High-Temperature X-ray Diffraction Study of the Phase Transition Kinetics. J Cryst. Growth Des. 2016,16 3983−399.
- Lufaso MW, Woodward PM. research papers Prediction of the crystal structures of perovskites using the software program J. Acta Crystallography B, 2001,725–38.
- Mustafa Anwar, Muhammed Ali S.A, Abdalla M. Abdalla, Mahendra Rao Somalu, Andanastuti Muchtar, Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and ionic conductivity of Ce0.8Sm0.1Ba0.1O2-d electrolyte, Processing and Application of Ceramics 2017,11,1,67–74. [CrossRef]
- Muneeb Irshad , Raazia Idrees, Khurram Siraj, Imran Shakir , Muhammad Rafique , Qurat ul Ain , Rizwan Raza. "Electrochemical evaluation of mixed ionic electronic perovskite cathode LaNi1-xCoxO3-δ for IT-SOFC synthesized by high temperature decomposition Author links open overlay panel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Volume 46, Issue 17, 8 March 2021, Pages 10448-10456.
- Risheng Pei, Sandra Korte-Kerzel, Talal Al-Samman "Normal and abnormal grain growth in magnesium: Experimental observations and simulations" Journal of Materials Science & Technology, Volume 50, 1 August 2020, Pages 257-270.
- W.D. Kingery, H.K. Bowen, D.R. Uhlmann, Introduction to Ceramics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1976.
- M.N. Rahaman, Ceramic Processing and Sintering, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1995. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen, D.F. Zhou, Y. Wang, X.F. Zhu, J. Meng, “Enhanced sintering of Ce0.8Nd0.2O2, La0.8Sr0.2Ga0.8Mg0.2O3, using CoO as a sintering aid”, Ceram. Int., 2017,43,4,3583–3589.
- J. Xiong, C. Jiao, M. Han, W. Yi, J. Ma, C. Yan, W. Cai, H. Cheng, “Effect of Li2O additions upon the crystal structure, sinterability and electrical properties of yttria stabilized zirconia electrolyte”, RSC Adv.2016,6, 106555–106562.
- Cun Xin Guo, Jian Xin Wang, Chang Rong He, Wei Guo Wang, Effect of alumina on the properties of ceria and scandia co-doped zirconia for electrolyte-supported SOFC, Ceram.In, 2013, 39,8, 9575-9582. [CrossRef]
- S. Gill, R. Kannan, N. Maffei V.Thangadurai ”Effect of Zr substitution for Ce in BaCe0.8Gd0.15Pr0.05O3−δ on the chemical stability in CO2 and water, and electrical conductivity” RSC Adv., 2013,3, 3599-3605.
- Kannan, R., Singh, K., Gill, S. et al. Chemically Stable Proton Conducting Doped BaCeO3 -No More Fear to SOFC Wastes. Sci Rep 3, 2138 (2013). [CrossRef]
- E. Barsoukov and J. R. Macdonald, Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2005.
- D. Chen, R. Ran, K. Zhang, J. Wang, and Z. Shao. Intermediate-temperature electrochemical performance of a polycrystalline PrBaCo2O5+δ cathode on samarium-doped ceria electrolyte. J. Power Sources. 2009,188,1 96–105. [CrossRef]
- Bin Lin, Songlin Wang, Xingqin Liu, Guangyao Meng, Simple solid oxide fuel cells, J. A.& Compounds, 2010,490, 1–2, 214-222.
- Riccardo Polini, Arianna Pamio, Enrico Traversa, Effect of synthetic route on sintering behaviour, phase purity and conductivity of Sr- and Mg-doped LaGaO3 perovskites, J. E. Ceramic Society 2004, 24,6, 1365-1370. [CrossRef]
- J. Yang, B. Ji, J. Si, Q. Zhang, Q. Yin, J. Xie, C. Tian, Synthesis and properties of ceria based electrolyte for ITSOFCs”, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41,36,15979– 15984. [CrossRef]
- X. Sha, Z. Lü, X. Huang, J.Miao, Z. Liu, X. Xin, Y. Zhang, W. Su, “Influence of the sintering temperature on electrical property of the Ce0.8Sm0.1Y0.1O1.9 electrolyte”, J. Alloys Compd., 2007,433,1-2, 274–278.
- S.J. Hong, A.V. Virkar, “Lattice parameters and densities of rare-earth oxide doped ceria electrolytes”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1995,78,2, 433–439. [CrossRef]
- M. Kahlaoui, S. Chefi, A. Inoubli, A. Madani, C. Chefi, Synthesis and electrical properties of co-doping with La3+, Nd3+, Y3+, and Eu3+ citric acid-nitrate prepared samarium-doped ceria ceramics”, Ceram. Int 2013, 39,4, 3873–3879.
- Jin Peng, Shuang Zhao, Asif Hassan Raza, Yan Wu. Energy band modulation of Mg-doped ZnO electrolyte for low-temperature advanced fuel cells" Int. J. of Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 15, 6088-6098.
- Mahmood Hameed Majeed , Murat Aycibin , Arife Gencer Imer"Study of the electronic, structure and electrical properties of Mg and Y single doped and Mg/Y co-doped ZnO: Experimental and theoretical studies" Optik,Volume 258, May 2022, 168949.
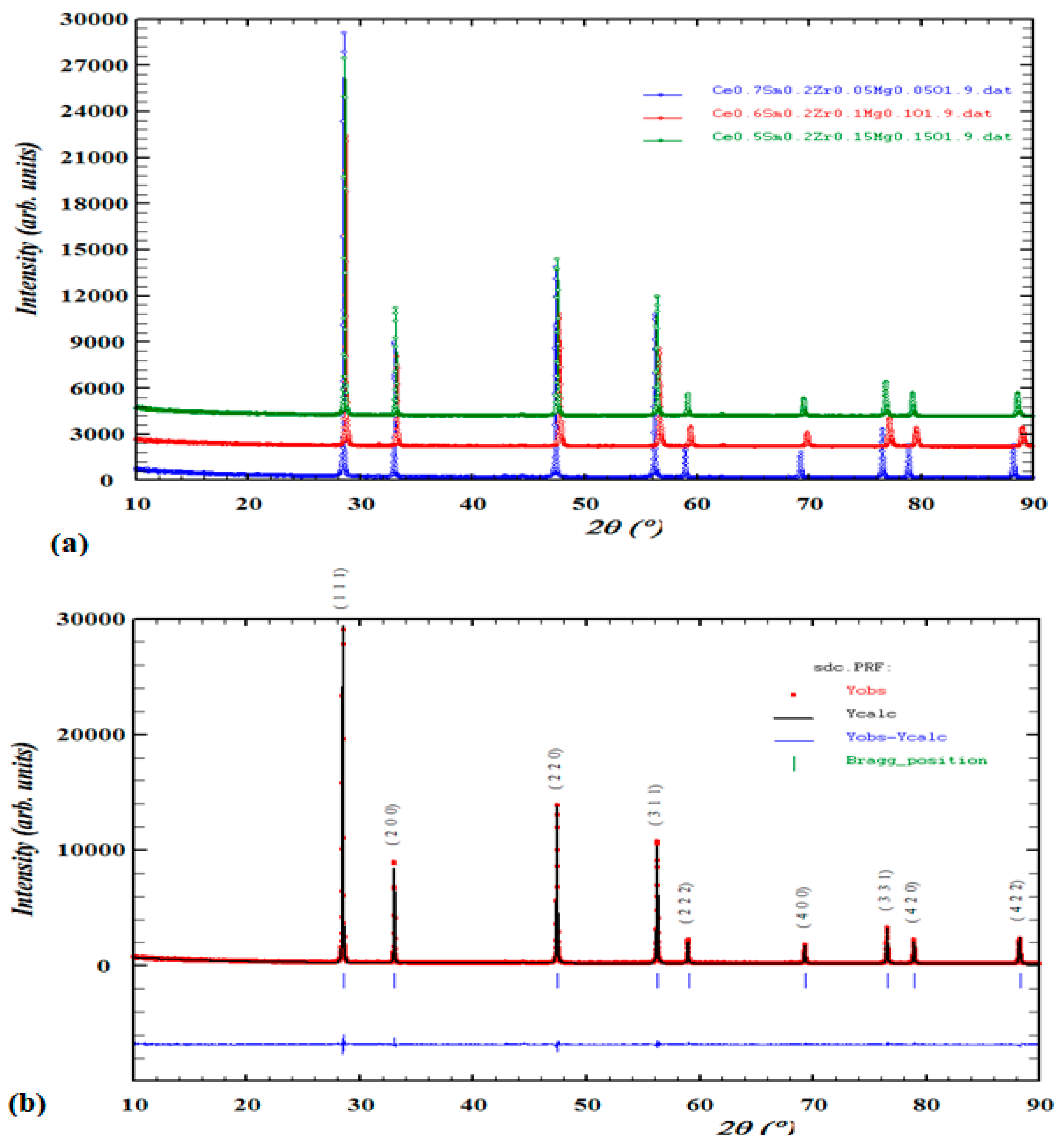

| Chemical Compounds | Space group | a =b = c | Volume | X2 | Rp | Rwp | Rexp | Theoretical density | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce0.7Sm0.2Zr0.05Mg0.05O1.9 | F m-3m | 5.401742 | 159.1092 | 1.63 | 5.16 | 6.79 | 5.32 | 7.623 | |
| Ce0.6Sm0.2Zr0.1Mg0.1O1.9 | F m-3m | 5.390912 | 155.80007 | 2.13 | 5.88 | 7.75 | 5.31 | 8.319 | |
| Ce0.5Sm0.2Zr0.15Mg0.15O1.9 | F m-3m | 5.401577 | 157.5144 | 2.34 | 6.36 | 8.37 | 5.47 | 8.908 | |
| Atomic positions | |||||||||
| Ce0.7Sm0.2Zr0.05Mg0.05O1.9 (x , y, z) & Occ | Ce0.6Sm0.2Zr0.1Mg0.1O1.9 (x , y, z) |
Ce0.5Sm0.2Zr0.15Mg0.15O1.9 (x , y, z) |
|||||||
| Ce | (0, 0 0) | 0.7 | (0, 0 0) | 0.6 | (0, 0 0) | 0.5 | |||
| Sm | (0, 0 0) | 0.2 | (0, 0 0) | 0.2 | (0, 0 0) | 0.2 | |||
| Zr | (0, 0 0) | 0.05 | (0, 0 0) | 0.1 | (0, 0 0) | 0.15 | |||
| Mg | (0, 0 0) | 0.05 | (0, 0 0) | 0.1 | (0, 0 0) | 0.15 | |||
| O | (0.25,0.25,0.25) | 1.9 | (0.25,0.25,0.25) | 1.9 | (0.25,0.25,0.25) | 1.9 | |||
| Material | Outer diameter (mm) | Pt diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Weight without Pt (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Compound | A | B | |||
| CSZM05 | Ce0.7Sm0.2 Zr0.05 Mg0.05O1.9 | 9.8367 | 7.0067 | 7.0500 | 1.6100 | 0.4920 |
| CSZM10 | Ce0.6Sm0.2 Zr0.1 Mg0.1O1.9 | 9.6667 | 6.6367 | 6.8933 | 1.5667 | 0.4855 |
| CSZM15 | Ce0.5Sm0.2 Zr0.15 Mg0.15O1.9 | 9.7267 | 6.8933 | 7.0867 | 1.4900 | 0.4965 |
| T (°C) |
1/T (K-1) |
s total (S/cm) |
ln (s total) (S/cm) |
Ohmic Resistance (Ω) |
Capacitance | ASR | Polarization resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 | 0.001027591 | 1.0461E+01 | 2.347653318 | 2.3898E-01 | 4.45E-03 | 8.37E-04 | 3.35E-03 |
| 650 | 0.001083248 | 3.7979E+00 | 1.33445878 | 6.5825E-01 | 2.32E-04 | 2.31E-03 | 9.22E-03 |
| 600 | 0.001145279 | 6.0300E-01 | -0.505841294 | 4.1460E+00 | 2.83E-04 | 1.45E-02 | 5.81E-02 |
| 550 | 0.001214845 | 1.3315E-01 | -2.016275199 | 1.8776E+01 | 6.85E-04 | 6.58E-02 | 2.63E-01 |
| 500 | 0.00129341 | 2.7329E-02 | -3.599815363 | 9.1479E+01 | 1.73E-03 | 3.20E-01 | 1.28E+00 |
| 450 | 0.001382839 | 5.8143E-03 | -5.147432299 | 4.2997E+02 | 6.27E-10 | 1.51E+00 | 6.03E+00 |
| 400 | 0.001485553 | 9.2890E-04 | -6.981506424 | 2.6913E+03 | 1.16E-10 | 9.43E+00 | 3.77E+01 |
| T (°C) |
T (K) |
s total (S/cm) |
ln (s total) (S/cm) |
Ohmic Resistance (Ω) | Capacitance | ASR | Polarization resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 | 0.001027591 | 2.2639E+00 | 0.81709542 | 1.1043E+00 | 8.54E-03 | 3.87E-03 | 1.55E-02 |
| 650 | 0.001083248 | 4.4590E-01 | -0.807654027 | 5.6066E+00 | 1.55E-04 | 1.96E-02 | 7.86E-02 |
| 600 | 0.001145279 | 1.6106E-01 | -1.825958391 | 1.5522E+01 | 6.46E-05 | 5.44E-02 | 2.18E-01 |
| 550 | 0.001214845 | 4.9418E-02 | -3.007438747 | 5.0589E+01 | 2.49E-05 | 1.77E-01 | 7.09E-01 |
| 500 | 0.00129341 | 7.1712E-03 | -4.937684105 | 3.4862E+02 | 4.14E-05 | 1.22E+00 | 4.89E+00 |
| 450 | 0.001382839 | 2.3180E-03 | -6.067037035 | 1.0785E+03 | 5.95E-08 | 3.78E+00 | 1.51E+01 |
| 400 | 0.001485553 | 2.0162E-04 | -8.509132304 | 1.2400E+04 | 5.20E-11 | 4.34E+01 | 1.74E+02 |
| T (°C) |
T (K) |
s total (S/cm) |
ln (s total) (S/cm) |
Ohmic Resistance (Ω) |
Capacitance | ASR | Polarization resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700 | 0.001027591 | 2.2639E+00 | 0.81709542 | 1.1043E+00 | 8.54E-03 | 3.87E-03 | 1.55E-02 |
| 650 | 0.001083248 | 4.4590E-01 | -0.807654027 | 5.6066E+00 | 1.55E-04 | 1.96E-02 | 7.86E-02 |
| 600 | 0.001145279 | 1.6106E-01 | -1.825958391 | 1.5522E+01 | 6.46E-05 | 5.44E-02 | 2.18E-01 |
| 550 | 0.001214845 | 4.9418E-02 | -3.007438747 | 5.0589E+01 | 2.49E-05 | 1.77E-01 | 7.09E-01 |
| 500 | 0.00129341 | 1.1081E-02 | -4.502482338 | 2.2560E+02 | 1.01E-05 | 7.90E-01 | 3.16E+00 |
| 450 | 0.001382839 | 1.5281E-03 | -6.483742838 | 1.6360E+03 | 1.07E-06 | 5.73E+00 | 2.29E+01 |
| 400 | 0.001485553 | 2.6192E-04 | -8.247487205 | 9.5450E+03 | 5.34E-11 | 3.34E+01 | 1.34E+02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





