Introduction
The use of resins and non-metallic materials is increasingly present in both temporary and permanent prosthetic rehabilitation.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a synthetic, linear, thermoplastic, polymetric material and has been used as a biomaterial in medicine for many years, especially in orthopaedic surgery [
1,
2].
The monomeric unit of PEEK is ethereterketone and the reaction polymerizes dialkylation of bis-phenolate to form polyetheretherketone.
Compared to other materials used as restorative prosthetics, PEEK has a low modulus of elasticity (4 GPa), similar to that of bone. Therefore, this material better withstands functional stresses, reducing the occlusal forces that are transmitted to the permanent teeth [
3].
Since the PEEK material has a greyish-white opaque colour, there was a need for veneering with composite materials in order to achieve satisfactory aesthetic criteria [
4,
5]. Prosthetic restorations should last a long time in the patient's mouth, and in order to obtain a chemically inert surface, BioHPP is veneered or glazed [
6,
7].
PEEK materials are used as frame materials in dental prosthetics, where fillers (ceramic particles of size 0.3-0.5 𝛍m) are added due to better mechanical resistance. It is a partially crystalline, synthetic material, thermoplastic, stable and insoluble. Unlike metal alloys, it does not release ions, does not corrode, so it is recommended for patients with metal allergies. This material also has one quality from a technical point of view, which is that it is easily polished to a high gloss, which makes it plaque non-adherent and resistant to pigments. From the physical-mechanical aspect, PEEK materials have a modulus of elasticity like bone and are subject to torsion like bone which makes them suitable for restorations of a larger range. Its high-pressure resistance (3.6 GPa), fracture resistance (1200 N) and low specific weight (1.31g/m3) are qualities that make BioHPP a better choice, compared to dental alloys and Zirconia.
BioHPP can be used in prosthetic dentistry for all kinds of prosthetic restorations and can be applied as pure, not polished (the inside surface of an internal telescopic crown), polished (removable partial dentures) or veneered with composite (external telescopic crowns, skeletal prosthesis hook, all esthetic kind of dental prosthetic restorations, implant supported fixed restorations, All on four complete dentures [
8,
9,
10]. In recent years, PEEK materials have been improved by adding different fillers, depending on the purpose. In implantology, PEEK can be used as an implant body, implant abutment or as a superstructure. As a material in implantology, Peek has weaker osteoconductive properties than titanium, but this can be improved by the addition of various bioactive materials. In implantology, it appears that PEEK's time is yet to come [
11].
All of these dental restorations need to be cleaned by the patient, but also at the dentists. This paper should give us an advice what cleaning method to apply, to make no damage to the investigated PEEK material.
In order for this material to be used in dentistry, it had to meet certain biological and mechanical criteria. This was achieved by enhancing pure PEEK with ceramics particles (less than 0.5 µm in diameter) [
12]. Modified PEEK polymer, reinforced with ceramic particles (BioHPP, Bredent, GmbH, Senden, Germany) has excellent mechanical properties, good wear resistance, chemical inertness and good biocompatibility [
13]. Thanks to that, BioHPP ® is the only material that achieves an ideal balance between elasticity and stiffness [
14]. The surface of this material can easily be technically processed to a high gloss surface, polishing down to <0.02 µm, resulting in less plaque adhesion [
15]. This material also has one property that is important for clinical diagnostics, BioHPP is radiolucent and does not create imaging artifacts.
From an aesthetic point of view, compared to dental alloys, PEEK materials has the advantage of being white in colour. Also, it can be veneered with composites in order to achieve high aesthetics. Dental composites are metal-free, multiphase materials consisting of an organic matrix, an inorganic filler and a binder. Inorganic fillers are dispersed inorganic particles.
Thanks to a colour that is more similar to the colour of the teeth than the colour of metal alloys, its metal-free composition and its modulus of elasticity, which is similar to the elasticity of tooth dentin, PEEK has found wide application in dental prosthetics in fixed and removable dental prostheses, dental implants, implant-supported fixed prostheses, implant-retained overdentures and hybrid dentures [
16].
The complete dental hygiene of the oral cavity involves the care of all natural teeth, soft tissues, and dental prosthetic restorations and any supporting implants. Patients with prostheses are more prone to tooth decay and periodontal infections due to the accumulation of biofilm present at the margins of the restorations and under the pontic elements [
17].
For the longevity of prosthetic restorations, remaining teeth, and soft tissues, the most important thing is good and proper oral hygiene. Also, it is very important to know the type and materials properties that the prosthetic restorations are made from.
Based on different kind of prosthetic restorations, some of them can be removed from oral cavity before the hygiene session, but some have to be instrumented within the oral cavity. In order to provide hygiene we use manual and mechanical instruments, such as curettes and ultrasound.
Ultrasonic scaling and brushing are a form of professional oral hygiene maintenance procedure that is carried out every 2-3 times a year. This measure prevents the formation of dental plaque and the growth of calculus [
18].
There are many different procedures by which the dentist maintains the hygiene of teeth and prosthetic restorations, the most common of which are the use of a brush and professional abrasive paste and ultrasonic scaling. This paper aims to show whether these recommended dental procedures are harmless or can lead to damage to the surfaces of prosthetic restorations. More precisely, from this paper we should conclude and give advice on how careful and attentive the dentist should be in daily practice when performing the procedure of tooth cleaning and prosthetic restorations.
Surface characteristics of dental restorations, such as surface roughness and hydrophobicity, are associated with the adhesion of microorganisms [
19,
20]. It has been reported that rough restoration surfaces increase the accumulation of dental plaque and calculus, as well as microbial adhesion [
21], which are directly related to the development of periodontal disease. There are numerous studies that prove the connection between surface roughness and biofilm adhesion [22, 23]. In all these studies, the conclusion can be drawn that a rougher surface equals the accumulation and retention of more plaque. However, in most studies, materials that have been in use for many years were studied, unlike BioHPP, which is a newer generation material and there is not much data on this topic in the literature
Consequently, the aim of this study is to determine whether routine brushing and ultrasonic scaling procedures affect the surface properties of polished and composite-glazed BioHPP prosthetic restorations.
The following surface characteristics of prosthetic restorations made of BioHPP material will be analysed:
- (i)
surface roughness (SR),
- (ii)
wetting contact angle (WCA),
- (iii)
X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), before and after surface treatment by brushing and ultrasonic scaling.
The null hypothesis of this study was that different methods of professional oral hygiene (brushing and ultrasonic scaling) would not affect either SR, WCA or XRD values on the tested materials.
Material and Method
In this study, a PEEK material called BioHPP (Bredent) was investigated. The name is derived from the abbreviation for Bio- biocompatible and HPP- high performance polymer. It is a thermoplastic material, which is used both in fixed and mobile prosthetics, for the production of combined restorations and restorations on implants.
Sample Collection Protocol of BioHPP Samples
All samples were made with dimensions of 10x10x2mm. The total number of samples was n=66
Samples were manufactured in 3 ways [
24]:
1. The first group of 22 samples (in the following text, samples of this group will be designated as BioHPP) was obtained by pressing in the For2press apparatus.
The samples were first cut out of the wax block, in the specified dimensions.
The wax tiles thus obtained were placed in a cuvette and melted in a wax annealing furnace at 930⁰C. After cooling the cuvette to 400⁰C, granulate material BioHPP® Bredent was introduced.
The material was melted for 10 minutes and then pressed in a For2press® vacuum press. The first group of samples was not further processed (no additional polishing).
2. The second group of 22 samples (BioHPP-P) was made by cutting in a CAD/CAM machine in the specified dimensions. The machine is VHF/K5®, five-axis simultaneous cutting.
All samples were processed with milling cutters for processing high-performance polymers ("Generation M") and prepared for polishing. Tungsten carbide cutters were used, coated with a layer of diatite (a protective layer that reduces heating and vibrations).
The second group of samples was polished according to the manufacturer's protocol, to a high gloss. The first step was treatment with an abrasive diamond brush (Abraso Fix). The second step is polishing with a horsehair brush (Rodeo) in combination with Acrypol paste. The third step is polishing with a goat hair brush in combination with Abraso-Star Glanz paste. The last step is polishing with a woolen brush to achieve a high gloss.
3. The third group of 22 samples (BioHPP-C) was veneered with composite. The samples were sandblasted with 110 µ aluminum oxide, at 2.5 Bar. Than they were cleaned and conditioned with Visio.link® primer. The primer was applied and polymerized in a polymerization lamp, Bre.Lux® power Unit for 90 seconds, on each sample. The nano-hybrid composite Crea.lign® was applied to all samples from the third group.
The composite was polished according to a standard protocol to a high gloss [
25,
26].
All processing and polishing materials are Bredent® products, as well as all used devices. The sample polishing procedure was carried out according to the protocol recommended by the manufacturer.
The second (BioHPP-P) and third (BioHPP-C) group of samples were divided into 3 subgroups:
- 0-
no treatment (control samples),
- 1-
exposed to brushing (with a professional dental cleaning brush and abrasive paste, Super Polish, Kerr),
- 2-
exposed to ultrasonic scaling (with a ultrasonic scaler incorporated in a dental unit).
Application of brushing or ultrasound on each of the samples from the second or third subgroup of samples was for 1 minute [
27].
Materials Characterization
The surface morphology was investigated by atomic force microscopy (AFM) with NanoScope 3D (Veeco, USA) microscope, operated in contact mode under ambient conditions. Silicon Nitride probes with spring constant of 20-60 N/m were used. Image analysis was done by NanoScope image processing software. Image data was expressed in height mode.
The image roughness (RMS) is calculated as the root mean square average of height deviations taken from the mean data plane, where
Zi is the maximum vertical distance between the highest and lowest data points in the image:
Phase composition of the representative samples was analyzed by XRD RIGAKU Ultima IV diffractometer, with Ni-filtered Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.54178 Å). The X-ray diffraction data were collected over the 2θ range from 5° up to 80° with the step of 0.02° and scanning rate of 5°/min.
The wettability measurements were performed on a homemade device equipped with CCD detector. During the measurements, a blue LED lamp (Kingbright Electronic Co., Ltd.) was used for the samples lightening. All samples were measured in the same conditions (room temperature) and each sample was evaluated by 5 drops of polar liquid – deionized water.
Results
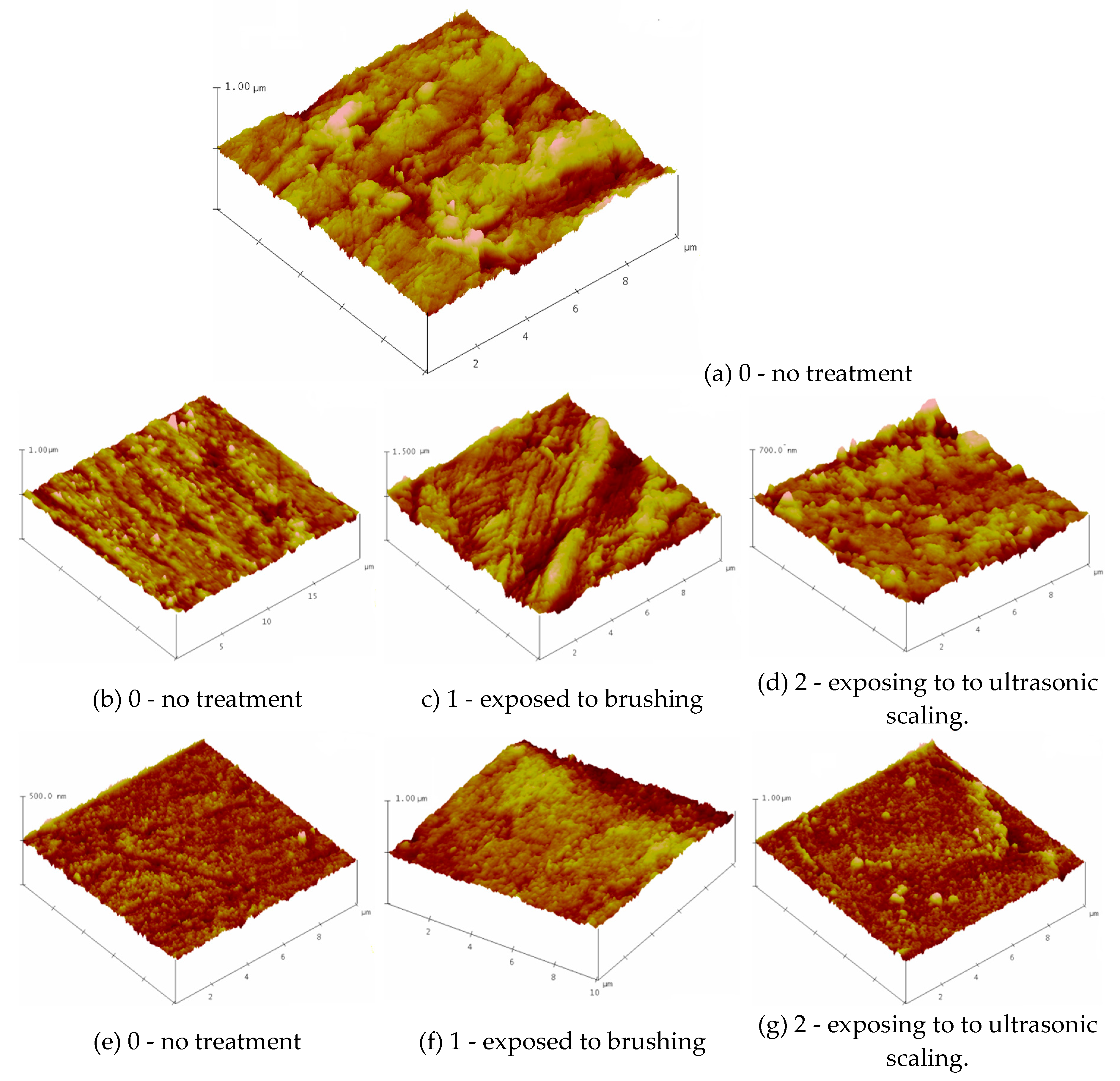
Figure 1: depicts the three-dimensional morphology of the representative samples using AFM. Surface Plot image displays the selected image with color-coded height information in a three-dimensional perspective.
The surfaces of the (a) BioHPP (b) BioHPP-P and (e) BioHPP-C specimens into condition marked with 0 (no treatment), exhibited different morphologies. The tested three groups of samples were treated in different ways: the first group of samples was not polished after pouring, so the tested surface showed roughness as expected, in contrast to the second and third groups of samples, where the surface of the second group was coated with a composite and processed according to the protocol, until high gloss, and in the third group polished to a high gloss, also according to the manufacturer's protocol.
The surface roughness of the samples was evaluated via root mean square (RMS) parameters, as shown in
Table 1. The roughness of the non-treated specimens (0) decreased in the line 59.181→28.839→14.515nm. Treatment of the samples by brushing and ultrasonic scaling leads to an increase of surface roughness.
These values are higher after brush treatment (samples 1 - exposed to brushing BioHPP-P, 1 (101.82 nm), BioHPP-C, 1 (41.57 nm) than exposing to ultrasonic scaling BioHPP-P, 2 (36.9 nm), BioHPP-C, 2 (31.92 nm).
The surface roughness of biomaterials highly affects bacterial responses, including their adhesion and spread. Generally speaking, smoother surfaces on a material better prevent bacterial adhesion and growth over its surface [
28].
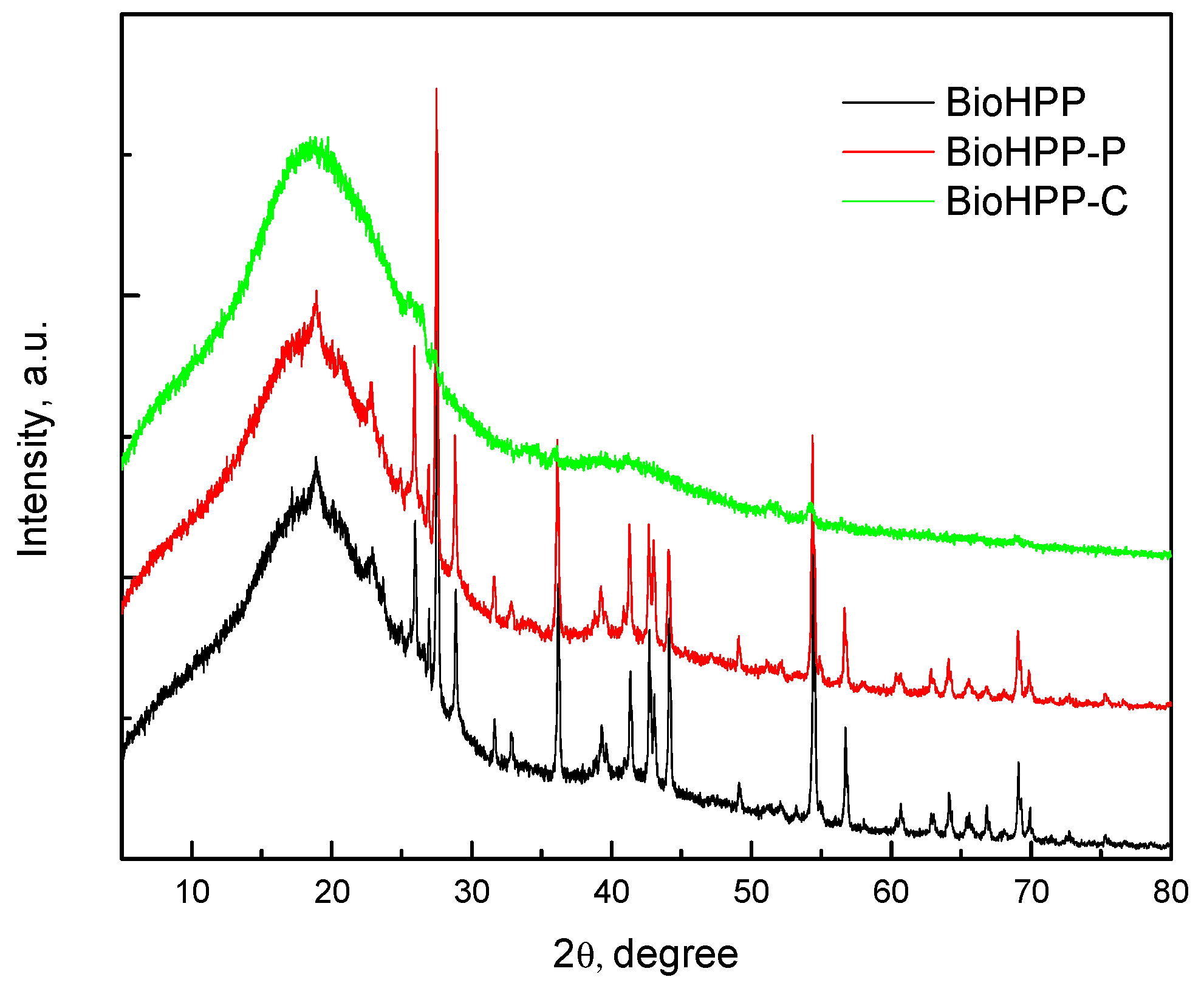
Figure 2 shows the XRD spectrum of the BioHPP as well as BioHPP-P and BioHPP-C. The wide diffraction peak, at approximately 2θ ≈ 18.5° corresponded to characteristic peak of PEEK [29, 30, 31] and the peaks at approximate 2θ 25.8º, 27.5°, 28.8°, 36.3º, 54.5° and the others were the peaks of ceramic particles.
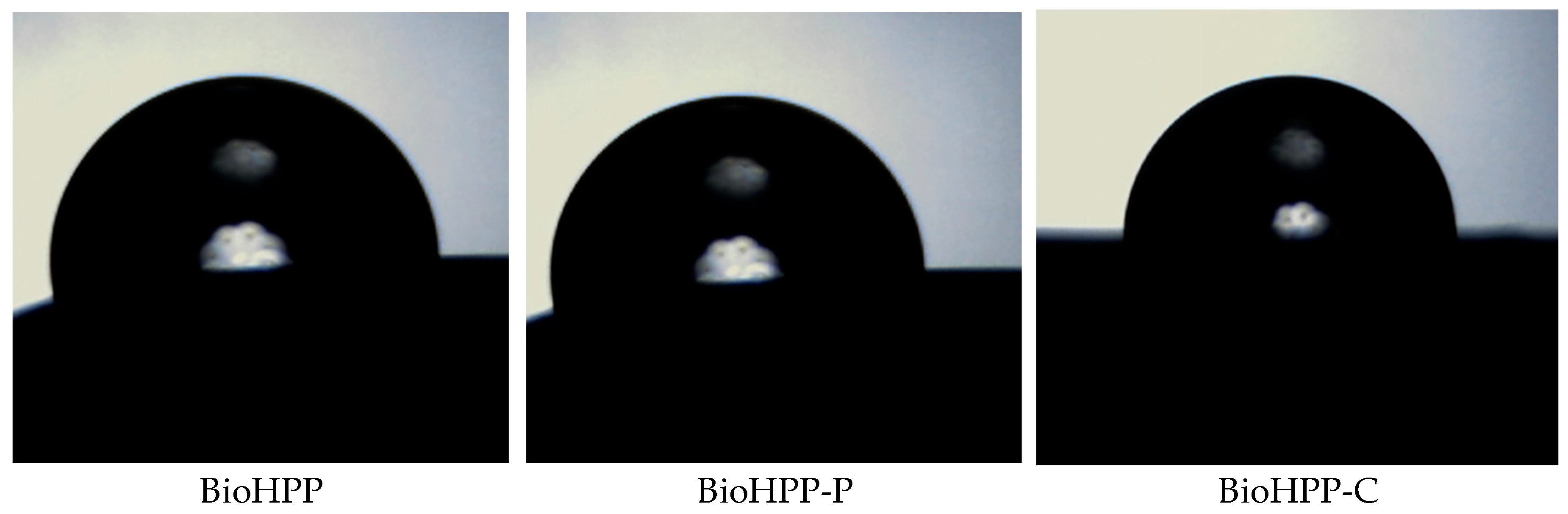
In order to assess the relative hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties of the BioHPP the water contact angle of the surface of the representative samples was determined.
Table 2 represents the variation of the contact angle of various prepared samples.
Wetting angles with water were determined from the images given below, using Drop Analysis software
Different surface treatment influences on surface morphology (
Figure 3) and therefore wettabality. The water contact angle of the samples BioHPP-P, 0, 1, 2 and BioHPP-C, 0, 2 was > 90º indicating a hydrophobic nature. On the contrary, the lowest contact angles and most hydrophilic surfaces were those on the samples BioHPP, 0 and BioHPP-C, 1, where the water contact angle was < 90º. [
32]
These observations indicate that the wetting behaviour is not only governed by surface morphology but probably also by physical characteristics of materials.
The wettability characterization is sensitive to detect very small variation in treatment, but no one can expect wettability tests to be used as a substitute for topographical analysis. In some cases, comparative tests may be envisaged [
33].
Discussion
In everyday dental practice, professional teeth cleaning, as a routine procedure, is recommended every six months. Brushes and abrasive professional pastes combined with ultrasonic scaling are the most often used procedures for these purposes. This paper should give us an answer to the question of whether these recommended professional cleaning methods affect the quality of the surface of dental restorations made of BioHPP. Therefore, the following surface properties were analysed: surface roughness, wetting angle and XRD analysis.
The results showed that there are differences in values of surface properties between the tested groups, as well as between subgroups, whose surface was treated differently. Therefore, the first null hypothesis can be rejected.
Important factor in the prevention of alteration of the surface properties of prosthetic restorations is the polishing and final finishing process [
34]. That is one of the significant conclusions from this study and from literature data, as well.
Brushing with abrasive paste and ultrasonic scaling increased the surface roughness values of all BioHPP material samples. There is evidence that brushing and ultrasonic scaling increase the surface roughness of many other restorative prosthetic materials such as ceramics, alloys, resins [
35,
36,
37].
The differences in the surface roughness values between the different BioHPP samples can be explained by the fact that the BioHPP samples veneered with composite make the surface mechanically more resistant and the composite covering the BioHPP surface acts as a protective layer.
Polished forms of BioHPP (BioHPP-P-0,1,2) samples showed the highest surface roughness values and also deeper surface scratches after brushing with abrasive paste and ultrasonic scaling [
38].
Rougher surface forms a greater adhesion surface for microorganisms and therefore may contribute to the formation of microbial biofilm [
39]. The results of the studies showed that the threshold value above the threshold of 0.2 µm of surface roughness affected the accumulation of bacteria or the formation of biofilm [
40]. As the mean surface roughness of all BioHPP samples after brushing and ultrasonic scaling exceeds 0.2 µm, so we can assume that they will have a greater receptivity to microbial biofilm. However, they were within the tongue detection threshold of 0.25–0.5 μm, except for BioHPP-P samples after ultrasonic scaling [
41].
Studies show that the hydrophobicity of the material as well as the high surface energy of the material can affect microbial adhesion [
42]. BiohHPP-C samples had larger contact angles and were considered to be more hydrophobic than BioHPP-P. Also, the samples after ultrasonic scaling had the highest wetting contact angles.
XRD analysis provides recording of the diffraction or reflection of rays on solid (crystalline) surfaces. In this case, those solid particles represent particles of ceramic fillers that are added to BioHpp to improve the physical and mechanical properties of this material. The composite layer that covers one group of the tested samples represents a barrier to XRD rays and that is why ceramic particles present in deeper layers, under the composite, could not be detected.
Plaque adhesion on PEEK differs from that of other dental restorative materials such as ceramics and metals [
43,
44].
It has been confirmed that materials with a more hydrophobic surface facilitate the growth of hydrophobic bacteria.
Candida albicans, which is generally considered to be the main cause of denture stomatitis, is considered to be hydrophobic, and this is an important factor for the initial adhesion of
Candida albicans [
45].
The rough surface favours not only adhesion of dental plaque, but also easier discolouration. BioHPP coated with composite has greater resistance to damaging caused by brushing and ultrasonic scaling, and therefore to the retention of microorganisms and discoloration. Bearing in mind that BioHPP represents a newer material, but also a material from which much is expected in the future, we are witnessing that there are more and more attempts to apply this material to implantology.
In daily practice, apart from brushing and ultrasound, other manual and mechanical instruments are used, such as, for example, steel, graphite and titanium curettes. Unlike manual instruments, the use of mechanical instruments is less dependent on the dexterity and skills of the dentist.
In this regard, it is of great importance to choose an adequate hygiene maintenance technique, in order to maintain the optimal properties of the material. Polishing of the surface has a great influence on the durability of the color. Any mechanical damage also affects the increased accumulation of plaque and pigments from food and drinks, as well as smoking [
46]. Aging, as a universal process, affects the color stability of the restorative materials in prosthetics, considering the fact that permanent restorations stays in the patient's mouth for a long time. The color stability depends on the free surface energy and the roughness of the surface of the material, which is influenced by the surface polishing treatment. Many studies have proven that there is a positive correlation between surface roughness and discoloration [47, 48, 49]. Also, a better polished surface reflects more light than a rough surface, and this is also one of the important optical factors.
The in vitro design is the major limitation of this study. The effects of saliva, formation microbial biofilm, temperature changes, parafunctional habits and aging of the BioHPP material may influence the results in actual clinical conditions. Additional clinical studies are needed to confirm the results of this study.
Conclusion
Based on this study, we can conclude that both the brush and the ultrasonic scalar increase the roughness of different surfaces of BioHPP material, with the brush leaving a rougher surface. BioHPP veneered with composite has a more resistant surface to damaging that may occur by these two routine methods of maintaining oral hygiene.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Č., M.P. and V.M.; data curation, A.Č., M.P., V.M., D.S. and S.S.; investigation, A.Č., M.P. and A.Š.G.; methodology, A.Č., M.P., D.S. and V.M.; project administration, S.S. and M.P.; resources, V.M., S.S. and A.Š.G.; software, V.M., S.S.; supervision, A.Č. D.S. and M.P.; validation, M.V., D.S.; visualization, V.M. and S.S.; writing—original draft, A.Č. M.P. and V.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was performed thanks to financial support from the School of Dental Medicine, University of Belgrade.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
BioHPP materials were provided free of charge by BREDENT, Serbia
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lümkemann, N.; Eichberger, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Bond strength between a high-performance thermoplastic and a veneering resin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najeeb, S.; Zafar, M.S.; Khurshid, Z.; Siddiqui, F. Applications of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) in oral implantology and prosthodontics. Journal of Prosthodontic Research. 2016, 60(1), 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stawarczyk, B.; Keul, C.; Beuer, F.; Roos, M.; Schmidlin, P.R. Tensile bond strength of veneering resins to PEEK: Impact of different adhesives. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, S, M; Caglar, I. The effect of different surface pretreatments on the bond strength of veneering resin to polyetheretherketone. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 2220–2231. [CrossRef]
- Zeighami, S.; Mirmohammadrezaei, S.; Safi, M.; Falahchai, S.M. The effect of core and veneering design on the optical properties of polyether ether ketone. Eur J Prosthodont Restor Dent. 2017, 25: 201-208. [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.H; Hyde, B; Hurst, M; Harris, B.T; Lin, W.S. Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK), a framework material for complete fixed and removable dental prostheses: A clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2018, 119: 867-872. [CrossRef]
- Basnyat, S.K.; Sapkota, B.; Shrestha, S. Oral Hygiene and Gingival Health in Patients with Fixed Prosthodontic Appliances—A Six Month Follow-up. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. (KUMJ) 2015, 13, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechir, E.S., Bechir, A., Gioga, C., Manu, R., Burcea, A., Dascalu, I.T. The advantages of BioHPP polymer as superstructure material in oral implantology. Mater. Plast. 2016, 53:394–398.
- Iyer, R.S., Suchitra, S.R., Hedge, D., Coutinho, C.A., Priya, A. Biohpp: Properties and Applications in Prosthodontics A Review. J. Res. Dent. 2019, 7:72–76. [CrossRef]
- Qin, L., Yao, S., Zhao, J., Zhou, C., Oates, T.W., Weir, M.D., Wu, J., Xu H.H.K. Review on development and dental applications of polyetheretherketone-based biomaterials and restorations. Materials. 2021, 14:408. [CrossRef]
- Zoidis, P.; Papathanasiou, I.; Polyzois, G. The Use of a Modified Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone (PEEK) as an Alternative Framework Material for Removable Dental Prostheses. A Clinical Report. J of prosthodontics, 2016, 25(7), 580-584. [CrossRef]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Papavasiliou, G.; Kamposiora, P.; Zoidis, P. Effect of Staining Solutions on Color Stability, Gloss and Surface Roughness of Removable Partial Dental Prosthetic Polymers. J. prosthodontics. 2022, 31(1), 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, R.; Zanza, A.; Galli, M.; De Biase, A.; Testarelli, L.; Di Nardo, D. Applications and Clinical Behavior of BioHPP in Prosthetic Dentistry: A Short Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6(3), 90. [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-Y.; Teng, M.-H.; Wang, Z.-J.; Li, X.; Liang, J.-Y.; Wang, W.-X.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, B.-D. Comparative evaluation of BioHPP and titanium as a framework veneered with composite resin for implant-supported fixed dental prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanasiou, I.; Kamposiora, P.; Papavasiliou, G.; Ferrari, M. The use of PEEK in digital prosthodontics: A narrative review. BMC Oral Health. 2020, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porojan, L.; Toma, F.R.; Vasiliu, R.D.; Matichescu, A. Surface roughness and color changes of dental PEEK related to staining beverages and cleaning methods. Materials today:proceedings. 2023, 78(2), 221-22. [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P.; Lindhe, J. Effect of controlled oral hygiene procedures on caries and periodontal disease in adults. J. Clin Periodontol. 1981; 8: 239-248. [CrossRef]
- Checketts, M.R.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Asar, N.V. An investigation of the effect of scaling-induced surface roughness on bacterial adhesion in common fixed dental restorative materials. J. Prosthet. Dent, 2014,112: 1265-1270. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.S.; Luke Yeo, I.S.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J. Effects of ultrasonic scaling on the optical properties and surface characteristics of highly translucent CAD/CAM ceramic restorative materials: An in vitro study. Ceramics International. 2019; 45 (12): 14594-14601. [CrossRef]
- Heimer, S.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Stawarczyk, B. Effect of different cleaning methods of polyetheretherketone on surface roughness and surface free energy properties. Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials, 2016, 14(3): e248-e255. [CrossRef]
- Garechahi, M.; Moosavi, H.; Forghani, M. Effect of surface roughness and materials composition. Journal of Biomaterials and nanobiotechnology. 2012, 03(04):541-546. [CrossRef]
- Giti, R.; Dabiri, S.; Motamedifar, M. Surface roughness, plaque accumulation and cytotoxicity of provisional restaurative materials fabricated by different methods. Journal. Pone. 2021, 0249551. [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Ishida, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Effect of polishing protocols on the surface roughness of polyetheretherketone. Journal of Oral Science. 2020, 62, 1, 40-42. [CrossRef]
- Heimer, S.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Roos, M.; Stawarczyk, B. Surface properties of polyetheretherketone after different laboratory and chairside polishing protocols. J Prosthet Dent. 2017, 117, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonson, S.A.; Yazici, A.R.; Kilinc, E.; Antonson, D.E.; Hardigan, P.C. Comparison of different finishing/polishing systems on surface roughness and gloss of resin composites. J Dent. 2011, 39, e9-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, F.; Erdem, M.B.; Tekin, S.; Caliskan, C. Effect of ultrasonic scaling and air polishing on the surface roughness of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) materials. Am J Dent. 2022, 35(4):200-204.
- Wu H., Liu T., Xu Z., Qian J., Shen X., Li Y., Pan Y., Wang D., Zheng K., Boccaccini A.R. Enhanced bacteriostatic activity, osteogenesis and osseointegration of silicon nitride/polyetherketoneketone composites with femtosecond laser induced micro/nano structural surface. Appl. Mater. Today. 2020, 18: 100523. [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Guo, D. Evaluating the bioactivity of a hydroxyapatite-incorporated polyether etherketone biocomposite. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.M.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, H.E.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, K.N.; Ha, Y.; et al. The electron beam deposition of titanium on polyether etherketone (PEEK) and the resulting enhanced biological properties. Biomaterials. 2010, 31:3465‒70. [CrossRef]
- Erik, A.; Hughes, B.; Grover, L.M. Characterization of a novel poly (ether etherketone)/calcium sulphate composite for bone augmentation. Biomaterials Research, 2017, 21:7. [CrossRef]
- Erjavec, A.K.; Črešnar, K. P.; Švab, I.; Vuherer, T.; Zigon, M.; Bruncko, M. Determination of Shear Bond Strength between PEEK Composites and Veneering Composites for the Production of Dental Restorations, Materials, 2023, 16(9), 3286. [CrossRef]
- Ourahmoune, R.; Salvia, M.; Mathia, T.G.; Mesrati, N. Surface Morphology and Wettability of Sandblasted PEEK and Its Composites, Scanning. 2014, 36, 64-75. [CrossRef]
- Baldi, D.; Menini, M.; Pera, F.; Ravera, G.; Pera, P. Plaque accumulation on exposed titanium surfaces and peri-implant tissue behaviour. A preliminary 1-year clinical study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2009. 22, 447–455.
- Hjerppe, J.; Rodas, S.; Korvala, J.; Pesonen, P.; Kaisanlahti, A.; Özcan, M.; Suojanen, J.; Reunanen, J. Surface Roughness and Streptococcus mutans Adhesion on Metallic and Ceramic Fixed Prosthodontic Materials after Scaling. Materials 2021, 14(4), 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.S.; Luke Yeo, I.S.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J. Effects of ultrasonic scaling on the optical properties and surface characteristics of highly translucent CAD/CAM ceramic restorative materials: An in vitro study. Ceramics International. 2019, 45 (12): 14594-14601. [CrossRef]
- Checketts, M.R.; Turkyilmaz, I.; Asar, N.V. An investigation of the effect of scaling-induced surface roughness on bacterial adhesion in common fixed dental restorative materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014,112: 1265-1270. [CrossRef]
- Kurahashi, K.; Matsuda, T.; Ichikawa, T. Effect of polishing protocols on the surface roughness of polyethertehrtketone. J. oral Sci. 2020;62(1): 40-42. [CrossRef]
- Renner, L.D.; Weibel, D.B. Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollen, C.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.S.; Billington, R.W.; Pearson, G.J. The in vivo perception of roughness of restorations. Br. Dent. J., 2004, 196, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzaniga, G.; Ottobelli, M.; Ionescu, A.C.; Paolone, G.; Gherlone, E.; Ferracane, J.L.; Brambilla, E. In vitro biofilm formation on resin-based composites after different finishing and polishing procedures. J. Dent. 2017, 67, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasawa, M.; Tsutsumi-Arai, C.; Takakusaki, K.; Oya, T.; Fueki, K.; Wakabayashi, N. Superhydrophilic Co-polymer Coatings on Denture Surfaces Reduce Candida Albicans Adhesion—An In Vitro Study. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 87, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, L.T.; Bezerra, A.P.; Schimmel, M.; Rodrigues Garcia, R.C.M.; de Luca Canto, G.; Gonçalves, T.M.S.V. Clinical Performance of Polymer Frameworks in Dental Prostheses: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu,Y; Fang, M; Zhao, R; Liu, H; Tian, K Li, M; Niu, L; Xie, R; Shizhu B. Clinical Applications of Polyetheretherketone in Removable Dental Prostheses: Accuracy, Characteristics, and Performance. Polymers, 2022, (21), 4615. [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S. (2021). In Vitro Effect of Denture Cleansers on the Color Stability of Polyetheretherketone and Other Denture Base Polymers. Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences, 24(2), 47–56. [CrossRef]
- Heimer, S.; Schmidlin, PR. Discoloration of PMMA, composite, and PEEK. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21:1191–1200. [CrossRef]
- Gönülol, N.; Yilmaz, F. The effects of finishing and polishing techniques on surface roughness and color stability of nano-composites. J. Dent. 2012, 40: e64–e70. [CrossRef]
- Türkün, L.S.; Leblebicioglu, E.A. Stain retention and surface characteristics of posterior composites polished by one-step sys-tems. Am. J. Dent. 2006, 19:343–347.
- Rahmitasari, F., Ishida Y., Kosuke Kurahashi K., Matsuda T., Watanabe M, Ichikawa T. PEEK with Reinforced Materials and Modifications for Dental Implant Applications. Dental J (Basel) 2017. 5(4):35. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).