1. Introduction
Poor management of organic wastes is a major cause of pollution. Indeed, organic by-products from food industries, farming and animal husbandry may pose a hygiene threat when aerobically decomposed (1,2). However, such wastes can be appropriately managed using anaerobic digestion (AD) systems to transform waste into energy, which may decrease the environmental impact and increase reusability (1). Especially, AD refers to the biological digestion of organic matter under anaerobic conditions, occurring in aquatic environments and involving different microorganisms, wherein a diverse community of microorganisms converts complex organic matter into biogas and whole digestate (WD) (3). Although AD is a highly favorable waste treatment technology, particularly from an environmental standpoint, it cannot achieve complete waste stabilization (4).
During the digestion of various animal wastes, particularly those of cattle, pig, poultry, and sheep manure, pathogenic microbes (Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Clostridium perfringens, Campylobacter jejuni, Cryptosporidium parvum, Giardia intestinalis, and Clostridium botulinum) are able to survive the digestive process and remain in the digestate (5). Consequently, it is of outermost importance to apply proper disinfection processes to avoid pathogens’ transportation from agricultural land through the food chain to humans.
Whole digestate (WD) sanitation is based on several factors, such as the quality of substrates fed into the reactor, reactor performance, digestion temperature, slurry retention time, pH, and NH3 concentration (6). Methods, including pasteurization, chlorine treatment, UV-light exposure, ozone treatment (7), and high-pressure treatment within a within a vessel (8), can be performed in order to reduce the pathogen load in the final WD effluent.
Alternative methods (i.e., electro-technology, microwave treatment, pressurization, and ultrasound treatment) have been developed and performed to reduce bacterial populations. In 2018, Uggetti et al. presented a sustainable approach to managing wastewater, which is considered a process for resource recovery waste treatment (9). During this research, an experimental microalgae-based wastewater treatment system has been developed using three semi-closed horizontal photo bioreactors under the European project INCOVER to reuse it and produce added-value products. There were low energy requirements for growing microalgae, using agricultural and sewage wastewater as feedstock. Their findings were very encouraging, while biomass production reached almost 2.2 kg VSS/d and with compensatory wastewater treatment performances (<2 mg/L for phosphates, <10 mg/L for ammonia, and <15 mg/L for nitrites and nitrates) ((9).
A recent study by Shi et al. has indicated a novel electrodialysis system development utilizing in situ the anode electrodialysis for the electrochemical oxidation and effective removal of antibiotics in the course of nutrient recovery from pig manure digestate(10). At the same time, electrochemical oxidation had no significant effect on the nutrient recovery efficiency but the pathogenic microorganism indicators were efficiently inactivated in the first 30 min. Though by this process a high concentration of disinfection by-products was generated, they were absorbed by anode electrodialysis, resulting in wastewater of very low trihalomethanes and haloacetic acids concentrations (10).
Moreover, in the study of Maynaud et al., it was reported that pathogenic bacteria in digestates can be inactivated by competition with indigenous bacteria. In the view of the PRObiotic project the activity of digestate microorganisms, which is related to competition for available nutrients and how it influences the inactivation of pathogenic bacteria was investigated. Based on the findings, when the availability of organic material and microbial activity increase, Salmonella enterica serotype Derby's survival in digestates decreases. Generally, the results of this study demonstrate how understanding the biotic processes involved can help improve microbial control dynamics and microbiological risk management (11).
For the rapid removal of nutrients and ecological inactivation of the pathogens Clostridium spp. and Arcobacter spp. in swine wastewater, the co-culture of vetiver and Dictyosphaerium sp. has been developed by the scientific team of Xinjie et al. Regarding their results, on the 15th day of the culture period, the bacterial community shifted from pathogen-dominant to photobacterial-dominant in the original wastewater. Furthermore, the plant-algae co-culture has decreased the levels of NH4+—N (from 102 mg L-1 to 5 mg L-1) and phosphorus below acceptable limits, as well as significantly reduced salinity and inactivated pathogens at wastewater treatment facilities within 15 days. The plant-algae co-culture also showed further significant interactions between microalgae and plants, such as water acidification via plant root respiration, algal growth with lower ammonia toxicity, and bicarbonate stress mitigation by microalgae and plant growth with reduced hypoxic stress, among others (12).
Prior research by Koziel et al. performed treatment of infectious animal carcasses digestate utilizing ammonia. Regarding the results, the minimum inhibitory concentration of NH3 was 0.1 M (~1.468 NH3—N mg/L), and 0.5 M NH3 (~7.340 NH3—N mg/L) for ST4232 & MRSA43300 bacterial strains, respectively, at 24 h and pH = 9 ± 0.1. Furthermore, the increase of NH3 concentration and/or time of treatment increased bacteria inactivation. Though the complexity of chemistry and microbiology of the digestate, the treatment with NH3 was effective and consistent with the minimum inhibitory concentration determined in sterile saline solution except for ST4232 in the late-phase ability of aerobic digestion scenario where the minimum inhibitory concentration was five times greater. Nevertheless, within 24 h, both pathogens were completely inactivated (13).
Management of the digestion residue, if intended for either soil improver or organic fertilizer, should comply with Circular Letter 3891/134991, 1-12-2016 "Management of livestock and slaughterhouses manure, and digestion residue from biogas plants" and the Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 as regards animal by-products. Application of the digestion residue from a biogas plant as a fertilizer or soil conditioner requires the application of various sanitary precautions depending on the type and risk category of the animal raw material used. According to the European Union (EU) Regulation) No 142/2011, representative samples of decomposition residues must comply with limits set by the regulation regarding the microorganisms Escherichia coli, Enterococcaceae, and Salmonella (14).
However, the corresponding circular letter offers suggestions for alternative sanitation methods, while pasteurization is a non-effective practice regarding economic and energetic aspects. Therefore, novel alternative strategies for microbial load reduction are developed so that the decomposition residue utilized in the fields does not constitute a risk to public health. In fact, circular letter 969/14986/21-6-2019 of the Department of the Directorate of Health and Safety of the Hellenic Ministry of Rural Development and Food defines the critical parameters that must be proven to be reduced to develop a method to be approved as sanitizing for digestate (15).
In this project, our aim was to develop a pilot sanitation unit using a subsequent filtration with decreasing porosity in liquid digestate to achieve a clear, purified liquid, which would then be used for unlimited irrigation and other industrial uses of recirculated cooling water according to Hellenic Joint Ministerial Decision 145116/02-02-2011 (Table 1) (17).
Table 1.
Limits for microbiological and conventional parameters, as well as the minimum required treatment for reuse of treated liquid waste, as per the Hellenic Joint Ministerial Decision 145116/02-02-2011 (Official Government Gazette B 354/2011) (17).
Table 1.
Limits for microbiological and conventional parameters, as well as the minimum required treatment for reuse of treated liquid waste, as per the Hellenic Joint Ministerial Decision 145116/02-02-2011 (Official Government Gazette B 354/2011) (17).
| Type of re-use |
Escherichia coli (cfu/100mL) |
BOD5 (mg/L) |
Suspended Solids (SS) (mg/L) |
Turbidity (NTU) |
Minimal
treatment |
Total N (mg/L) |
Total P (mg/L) |
| Limited irrigation & disposable cooling water |
≤200 median value |
≤25 |
- |
- |
Secondary with disinfection |
<45 |
- |
Unlimited irrigation & recirculated cooling water (boilers,
processes) |
≤5 for 80% of samples & ≤50 for 95% of samples |
≤10 for 80% of samples |
≤10 for 80% of samples |
≤2 median value |
Secondary & tertiary with disinfection |
<15 |
<2 |
| Urban use & Enrichment of underground aquifers & peri-urban green areas (groves, forests) |
Total coliforms ≤2 for 80% & ≤20 for 95% of samples |
≤10 for 80% of samples |
≤2 for 80% of samples |
≤2 median value |
Secondary & advanced with disinfection |
<15 |
<2 |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Equipment for WD treatment
WD was utilized after AD in a biogas plant (Biogas Lagada S.A.) of 1 MW electrical production capacity. The plant operates with two anaerobic digesters (D1 and D2, 4000 m3 each) connected in series. D1 is fed on an hourly basis by an underground 550 m3 tank (liquid feedstock) and a solid feeder (moving floor unit) for solid biomass. After the digestion, the effluents are stored in two storage tanks (ST1 and ST2, 8000 m3 each) and applied further as soil improver in nearby fields.
From D2 the WD can be separated with the use of a mechanical separator CRI–MAN, SM300/75 Pro (CRI–MAN S.p.A., Correggio, Italy) in primary solid and liquid fractions. Then it was further separated with a centrifugal separator Alfa Laval Aldec 45 (Alfa Laval AB, Lund, Sweden) in secondary solid and liquid fractions. With the help of a pumping system consisting of three progressive cavity pumps from Roto Pump Ltd, Noida, India (models: RMC 542 x2 and RLCB 571 x1) and a direct drive plunger pump (Model: 2SF05SEEL from CAT PUMPS, Minneapolis, USA) the fluid was led to all filtration units and intermediate tanks. Filtration units were acquired from Pentek, USA (bag filter), microfiltration and nanofiltration from Atech Innovations GmbH, Germany.
2.2. Fractionation and filtration procedure of digestate
2.2.1. First treatment stage
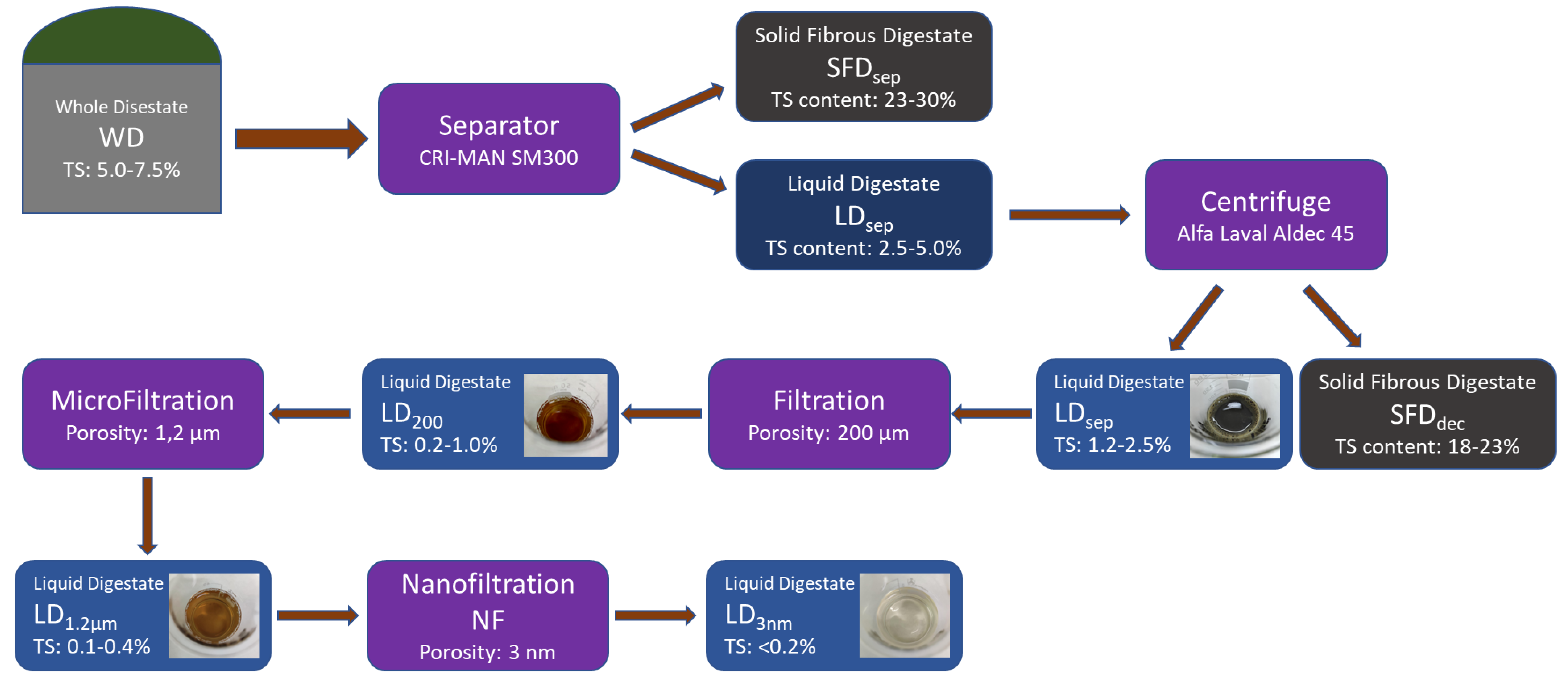
During the first stage of the pilot scale treatment, the initial whole digested residue (WD), which contains 5.0–7.5% solids depending on the seasonal feedstock, is introduced to the mechanical separator (screw press) at a flow rate of 30 m3/h from the digestion tank of the biogas plant. There, it is separated into the solid fibrous digested residue (SFDsep) which now contains 23.0–30.0% of solids, and into the liquid digested residue (LDsep) which consists of the remaining 2.5–5.0% of the original solids. The solid fibrous digestate (SFDsep) returns to the digestion tank to repeat the process of AD or is stored in a stockpile for field application as a solid organic soil improver, while the liquid digestate (LDsep) is transferred to a 20-m3 tank for further treatment. Additionally, the solids that will settle in the tank will again return through a secondary piping circuit to the separator so they can be further separated.
2.2.2. Second treatment stage
In the second stage of the treatment process, the liquid digested residue (LDsep) is channeled via the 20 m3 tank to the centrifugal separator (decanter) at a speed of 5 m3/h using an industrial progressive cavity pump appropriate for sludge and sewage transport. At this point, the wastewater that has already been treated undergoes more thorough separation. Specifically, the centrifuge (decanter) separates the liquid digested residue that contains 2.5–5.0% solids into a new solid fibrous digested residue (SFDdec) that contains 18.0 to 23.0% of the solids and a liquid digested residue (LDdec) that has the remaining 1.2 to 2.5% of solids (7). The newly separated (secondary) solid residue (SFDdec), with the use of a screw conveyor, ends up in a storage tank of 5 m3; while the newly separated liquid residue is transferred with a progressive cavity pump at a speed of 3 m3/h to a 6 m3 tank, that serves as an intermediate tank for the following stage. At this point, the outgoing liquid residue (LDdec) will be recirculated from a secondary piping circuit in order to dilute the incoming wastewater (LDsep). The goal of this procedure is to minimize the number of solids in the outgoing wastewater.
2.2.3. Third treatment stage
Then, the third stage of the treatment process follows, which is referred to as filtering and microfiltration (MF) which makes effluent suitable for the fourth and final stage. In the course of this, a progressive cavity pump moves the liquid fraction at a flow rate of 2–3 m3/h initially through a polypropylene bag filter which will retain solids larger than 200 μm that do not settle as sediment in the centrifuge. Following that, the liquid fraction passes through the MF assembly which allows only solids equal to or less than 1.2 μm to pass through.
Figure 1.
Microfiltration unit.
Figure 1.
Microfiltration unit.
Then the filtrate exits the MF system at a flow rate of 0.2 m3/h and ends up in a 1 m3 storage tank, where it is checked by sensors for electrical conductivity and turbidity.
2.2.4. Fourth treatment stage
In the fourth and last stage, a triple piston pump draws the sample from the 1 m3 tank and pushes it to the nanofiltration unit with a flow rate of 50 L/h. This unit is able to remove the remnants of organic pollutants and pathogenic organisms from wastewater through nanofiltration.
After the last NF stage, the water is collected in a 300-liter tank in which on an automated basis, electric conductivity and turbidity measurements are made.
A central computer with Lab View is responsible for the aforementioned process, while it monitors the values prior to and following NF unit, checks the system's flow and peripheral pressure as well as determines centrifugation data from a Decanter.
The above-described procedure is controlled by a central computer with Lab View, which monitors the values prior to and following NF unit, checks the system's flow and peripheral pressure as well as determines centrifugation data from a Decanter.
Following the above, the pilot plant had the following mechanical systems and equipment requirements:
A separator (screw press),
Centrifuge (Decanter),
Three pumps,
A microfiltration system,
Six tanks of different sizes,
A screw conveyor for the removal of solid digested residue,
One bag filter,
A nanofiltration unit with its support scaffold,
An electrical panel of dimensions 1.0x1.0 m,
An air conditioner for temperature reduction inside the container,
Two ventilation outlets,
And a host computer for entire pilot plant management.
Apart from the screw conveyor and the tanks, everything else was placed inside a container.
Figure 2.
Photographs of (a) mechanical separator; (b) centrifugal separator; (c) microfiltration and nanofiltration units.
Figure 2.
Photographs of (a) mechanical separator; (b) centrifugal separator; (c) microfiltration and nanofiltration units.
Figure 3.
Digestate treatment flowchart according to project Photosan.
Figure 3.
Digestate treatment flowchart according to project Photosan.
2.3. Physicochemical methods
The determination of values on the pH scale was carried out with the method APHA 4500-H+ (18) using a HACH instrument (HACH Model HQ30D) equipped with a universal pH measuring electrode (924 001) and a temperature measuring electrode (027 500). Before each measurement, the pH meter was adjusted. The electrode was gently cleaned with absorbent paper and rinsed with deionized water before every measurement. The device adjusts for the pH level at 25 °C.
The determination of EC was based on EN 13038 Standard–Determination of electrical conductivity. The sample was initially diluted with deionized water and then was measured using HQ30D Digital multimeter kit, Conductivity electrode (HACH Model HQ30D).
For the TS determination a quantity of 2–5 g sample was placed in a dried and pre-weighed dish, and the weight of the sample was recorded. The dish containing the sample was placed in the drying oven at 105 °C, overnight. Afterward, the dish was cooled in desiccator to ambient temperature, and weighed. The method was based on the Total Solids Dried at 103–105°C methodology: APHA 2540-B (19). For TSS the method was based on Total Suspended Solids APHA 2540-D (18,20).
For the VS determination the sample was dried before being placed in the muffle furnace. The dish was weighed with the sample within, was ignited for 4 hours at 550 °C, was cooled in a desiccator and the weight was recorded. The method was based on Fixed and Volatile Solids Ignited at 550°C: APHA 2540-E (18,19). For VSS the method was based on APHA 2540-E (18,19).
An Agilent 7850 ICP-MS (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with the ORS4 collision cell was used for the analysis of macro-elements and trace metals. Sampling was performed using an Agilent SPS 4 autosampler. The 7850 ICP-MS was configured with the standard ISIS 3 injection system. The IntelliQuant function in the ICP-MS MassHunter 5.1 software provides the capability of a full mass-spectrum scan with only two seconds additional measurement time, though the samples were quantitated by internal standard seven-point calibration. The samples were prepared for analysis according to the digestion procedure outlined in ISO 17294 Part I & II and APHA 3125 (20–22).
The sample is decomposed in acid at a high digestion vessel pressure with the help of a Milestone Ethos Up microwave oven and the resulting solution is analyzed. First, an amount of sample (0.5–1.0 g) was weighed and HNO3 and H2O2 were added to the sample followed by digestion gradually up to 210°C. The sample was then diluted and analyzed by ICP-MS. Its concentration calculation occurs using templates.
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) was held by using a commercial spectrometer HACH DR 3900 as described elsewhere (23–25) based on Closed Reflux, Colorimetric Method APHA 5220-D (23). Briefly, a volume of sample (2 mL) is transferred in a COD test tube, homogenized if necessary, and after proper agitation it is transferred in the preheated digester at 150 ± 2οC for 2 h. After the completion of the reaction, when the test tubes have a temperature <120°C, the samples are measured spectrophotometrically at 448 nm (COD: 15─150 mg/L) and 605 nm (COD: 100─2000 mg/L) with the appropriate dilution.
Total phosphorus was carried out by the Molybdovanadate method and using Hach reagents and the HACH DR3900 spectrophotometer. The determination of nitrate-nitrogen concentration is based on APHA 4500-NO3--Ultraviolet Spectrophotometric Screening Method and measurements were conducted at 220 nm with a JASCO V-630 Spectrophotometer (26). The determination of ammonium-nitrogen concentration was held photometrically with a JASCO V-630 Spectrophotometer at 420 nm according to Nitrogen (ammonia) APHA 4500-NH3 B & C method (27). Turbidity was analyzed with a UV-Vis spectrophotometer, COD3 Plus Colorimeter (LaMotte, Chestertown, MD, USA) determined according to method APHA 2540-E (19)
2.4. Microbiological methods
2.4.1. Detection of bacteria Salmonella spp
The detection of Salmonella spp method was based on ISO 6579-1:2017. Colony-forming microorganisms on solid selective substrates, when tested according to the protocol, demonstrate defined biochemical and serological characteristics. Initially, the sample is pre-enriched in Buffered Peptone Water, at ambient temperature and incubation at 34─38°C for 18h. Subsequently, the culture obtained from the first stage was inoculated in two selective substrates and the resulting cultures were recovered and coated in two solid selective substrates, in Xylose Lysine Deoxycholate Agar (XLD agar) and in a supplement to XLD agar. Finally, the colonies of potential Salmonella were subcultured in a non-selective substrate (nutrient agar), and their identity was confirmed by means of appropriate biochemical and serological tests.
2.4.2. Enumeration of bacteria Enterococcus faecalis
Enumeration of Enterococcus faecalis is based on a combination of ISO 7899-2:2000 (Detection and Enumeration of Enterococci in water) and CEN-TR 16193:2013 (Detection and quantification of Escherichia coli in sewage sludge, treated biowaste and soil).
The initial dilution (Dilution A) was prepared by weighing 10 g (wet weight) and adding an appropriate amount of peptone saline solution up to a final volume of 100 mL. Then, the material was mixed in the homogenizer for 90 s, aliquoted into containers and centrifuged (1600 rpm, 3 min, 10±1°C). The supernatant (1mL) was aseptically vacuum filtered through a 0.45 μm Whatman membrane and the membrane was placed in an SB plate. The plates were incubated inverted at 36±2°C for 44±4 h. The decimal dilutions of the supernatant were filtered accordingly. After incubation, in the case of typical colonies (brown – red color) development, the membrane is transferred to Bile aesculin azide agar medium (preheated to 44±0.5°C as a confirmatory step). Black color development on Bile aesculin azide agar after 2 h indicates the bacterial growth of E. faecalis. Method precision was confirmed by measurements of laboratory inoculated suspension material containing the certified reference material E. faecalis WDCM 00009 Vitroid.
2.4.3. Enumeration of bacteria Escherichia coli
Method of detection and enumeration of Escherichia coli in the digester material is based on the CEN-TR 16193 (2013) standard. The method is based on a membrane filtration process for quantitative detection, by culturing the individual colonies in a chromogenic culture medium. The method is suitable for estimating the logarithmic reduction of Escherichia coli in sanitation processes.
Method precision was tested using different size inoculations of the digester material with suspensions of E. coli WDCM 00090 Vitroids and Enterobacter aerogenes NCTC (SIGMA-ALDRICH, St Louis, MO, USA).
3. Results & Discussion
Limited irrigation (no sprinkler application) refers to areas where public access is not expected, such as forage crops, industrial crops, pastures, and non-fruit trees, with the premise that the fruits are not in contact with the soil, seed crops, and product crops which undergo further processing before consumption. Disposable cooling water for industrial use refers to the supply of underground aquifers by infiltration of an intermediate soil layer with sufficient thickness and suitable characteristics. Unlimited irrigation applies to all crops whose products are consumed raw. In unlimited irrigation, sprinkler application is allowed. Urban use involves watering large urban areas without sprinkler application, extinguishing fires, use for decorative fountains, and street cleaning (
Table 1).
For this purpose, we conducted and presented the Continuing Professional Development (CPD) study that concerns the preliminary unit design as well as the preparation of the overall process flow diagram. The goal of CPD studies is to establish the mass and energy balance equations, incorporate Key Performance Indicators KPIs of the process (system productivity per time and volume, pressure drop, liquid speed, water perviousness, and solute rejection efficiency), and apply the mathematical description of the filtration process and other cutting-edge technologies (reference cases). With the help of the created CPD tools, it will be possible to evaluate the Photosan pilot unit for the elimination of several organic and inorganic pollutants, bacteria, and pathogenic organisms in typical applications.
The process of wastewater filtration through the membranes, that allows the retention of solids that are larger than the diameter of the membrane's pores is called Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF). Tangential Flow Filtration is a filtration method in which the feed flow runs tangentially to the surface in the channels of the tubular membranes, so that retained particles and larger molecules do not accumulate on the membrane surface. In this way, no layer of the filtered particles remains on the membranes (28). The MF unit has an inlet for the wastewater and outlets for the retentate and permeate (filtrate) effluents. High overflow rate (OVR) of 2─4 m/s, which is a measure of the velocity of the fluid inside the channels, allow for more effective removal of the retained particles due to turbulent flow and the concomitant large buoyancy forces. However large OVR in combination with the existence of particles may lead to attrition of the thin microfiltration layer. For that reason, we worked with a total feed flow of 2–3 m3/h which gave a medium OVR of 0.13 m/s and we applied frequent backpulsing (every 5 minutes) to remove the small cover layer that was formed. With the prerequisite that we don’t have irreversible pore blocking, the momentary application of backflow where the direction of solution’s flow is reversed, is sufficient to restore the membrane’s permeability. In this particular pilot system, backflow is applied with automatic timing, with the aim of preserving the membranes good functioning and balancing their internal pressure.
The dimensions of both the NF unit outer shell and the components inside are estimated according to the requirements of productivity and purity of the water treated by the system. Additionally, optimal parameters of operation were determined. This included: (i) the dimensions of the NF unit to reach the required productivity; (ii) the materials and the thickness of the stainless steel shell and flanges to withstand the required operating pressure; (iii) the determination of the optimal influent pretreatment process prior the usage of NF, with the aim of ensuring continuous operation and minimizing the necessity for frequent membrane cleaning, while also mitigating the risk of irreversible membrane damage; (iv) design, engineering study, development, and operation of a small prototype, including a single set of reactor internals, to test all of the components that will be used to seal the membranes, glass tubes, and glass sleeves, and to hermetical separation of the filtrate from the retentate at the bottom of the reactor unit; (v) design of the integrated treatment system laboratory-scale wastewater treatment; (vi) design of the integrated wastewater treatment system at a 50 L/h aqueous fraction purification volume scale.
Evaluation of data
Samples of solid and liquid digestate were taken from the anaerobic digester of Lagada Biogas plant from each stage as described above and the physicochemical and microbiological properties were measured and presented in Tables 2 and 3 below.
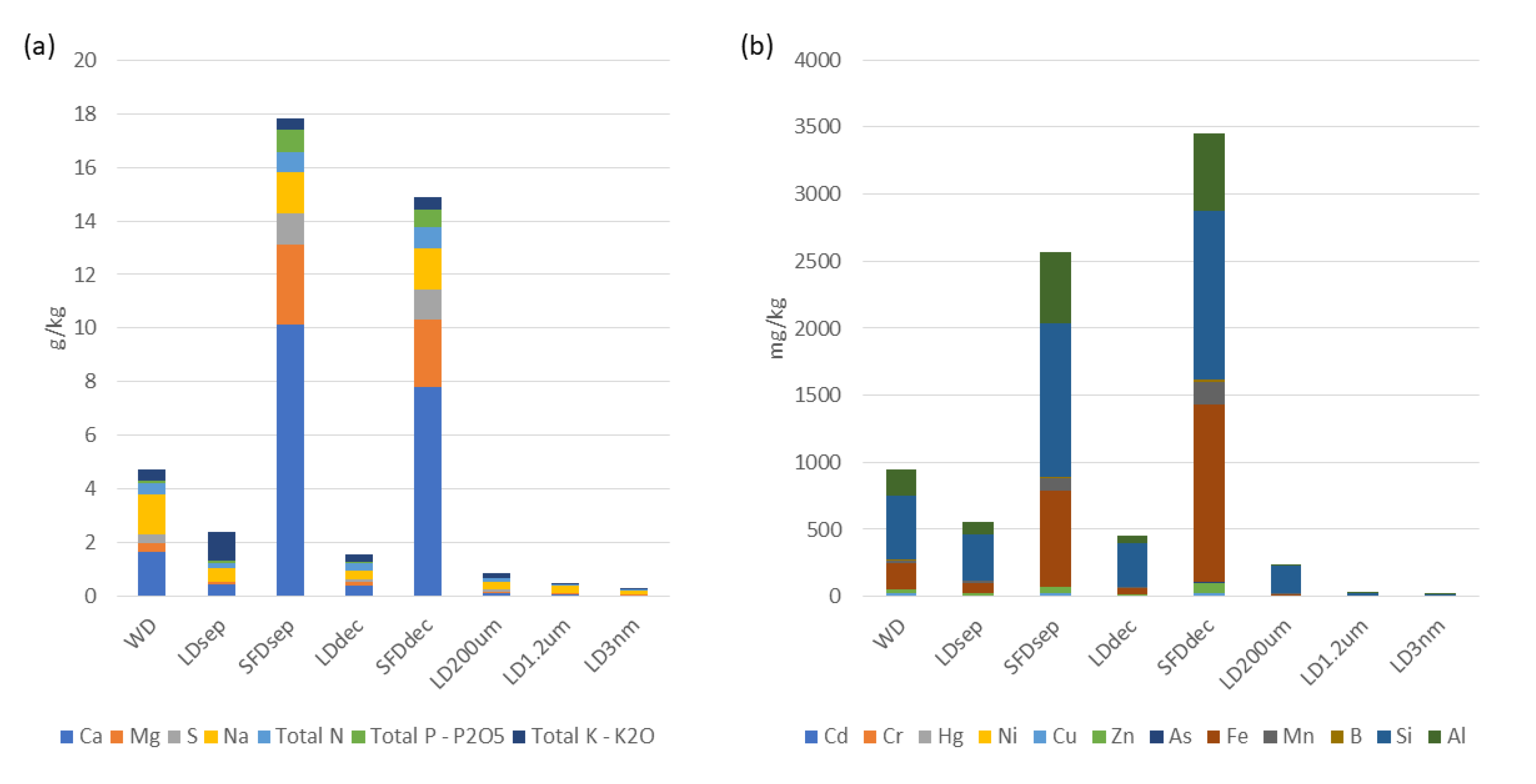
General observations derived from Tables 2 and 3 and Figure 4 revealed that the solid digestate exhibits a higher abundance of nutrients, minerals, and macronutrients in comparison to all liquid digestates. Furthermore, it is worth mentioning that the type of separation affected the accumulation of macromolecules and metals or micronutrients. Mechanical separation with sieves (SFDsep) was more effective for macromolecules in contrast to centrifugal separation (SFDdec), especially for calcium content. Concerning trace elements and heavy metals a reverse phenomenon was observed, while metals were found in higher amounts in the solid phase of SFDdec than SFDsep. Especially, in the case of Cr, Ni, and Fe the amounts were almost two times higher than SFDsep.
Table 1.
Physicochemical characterization of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
Table 1.
Physicochemical characterization of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
| Parameter |
WD |
Mechanical Separation |
Centrifugation |
Filtration |
uFiltration |
NF |
| (unit) |
WD |
LDsep |
SFDsep |
LDdec |
SFDdec |
LD200um |
LD1.2um |
LD3nm |
| Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
| pH |
7.8 |
0.09 |
8.2 |
0.10 |
8.6 |
0.11 |
8.3 |
0.10 |
8.5 |
0.10 |
8.3 |
0.10 |
8.3 |
0.10 |
8.3 |
0.00 |
|
Conductivity 25°C (μS/cm)
|
24200 |
729 |
2830 |
311 |
2450 |
625 |
1874 |
150 |
1653 |
635 |
1400 |
49 |
340 |
32 |
281 |
14 |
|
Total Solids (TS) (%)
|
5.23 |
0.20 |
2.66 |
0.10 |
29.03 |
1.12 |
1.91 |
0.07 |
20.41 |
0.79 |
0.77 |
0.02 |
0.23 |
0.01 |
0.16 |
0.01 |
|
Volatile Solids (VS) (%)
|
3.82 |
0.00 |
1.61 |
0.00 |
23.97 |
0.00 |
1.29 |
0.00 |
13.96 |
0.00 |
0.59 |
0.00 |
<0.05 |
n.a.* |
<0.05 |
n.a. |
|
Total Suspended Solids (TSS) (mg/kg)
|
_ |
_ |
8226 |
1192 |
_ |
_ |
6133 |
889 |
_ |
_ |
4760 |
690 |
15 |
2.2 |
5.50 |
2.50 |
Volatile Suspended Solids (VSS)
(mg/kg)
|
_ |
_ |
984.5 |
n.a. |
_ |
_ |
51 |
n.a. |
_ |
_ |
33 |
n.a. |
11 |
n.a. |
6.00 |
0.00 |
COD
(mgO2/kg)
|
21800 |
2108 |
18400 |
1779 |
35840 |
n.a. |
16200 |
1567 |
33900 |
3278 |
7100 |
687 |
522 |
50.5 |
242 |
41.4 |
Turbidity
(NTU)
|
40365 |
n.a. |
12372 |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
7646 |
n.a. |
n.a. |
n.a. |
953 |
n.a. |
264 |
n.a. |
15.3 |
3.58 |
ΝO3-
(mg/kg)
|
12.3 |
2.09 |
9.81 |
n.a. |
7.82 |
1.33 |
8.64 |
1.47 |
12.1 |
2.06 |
3.1 |
0.53 |
0.522 |
0.09 |
1.49 |
0.66 |
Table 2.
Macro-nutrient content of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
Table 2.
Macro-nutrient content of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
| Parameter |
WD |
Mechanical Separation |
Centrifugation |
Filtration |
uFiltration |
NF |
| (unit) |
WD |
LDsep |
SFDsep |
LDdec |
SFDdec |
LD200um |
LD1.2um |
LD3nm |
| Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
|
Ca(g/kg)
|
1.63 |
0.14 |
0.43 |
0.04 |
10.11 |
0.87 |
0.39 |
0.03 |
7.81 |
0.67 |
0.12 |
0.01 |
0.06 |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.01 |
|
Mg (g/kg)
|
0.33 |
0.03 |
0.09 |
0.01 |
3.01 |
0.27 |
0.12 |
0.01 |
2.49 |
0.22 |
0.04 |
0.00 |
0.03 |
0.00 |
0.02 |
0.00 |
|
S (g/kg)
|
0.32 |
n.a.* |
<0.05 |
n.a. |
1.14 |
n.a. |
0.12 |
n.a. |
1.13 |
n.a. |
0.07 |
n.a. |
0.03 |
n.a. |
0.02 |
0.00 |
|
Na (g/kg)
|
1.5 |
0.18 |
0.51 |
0.06 |
1.57 |
0.19 |
0.32 |
0.04 |
1.53 |
0.18 |
0.29 |
0.04 |
0.27 |
0.03 |
0.14 |
0.08 |
|
Total N (g/kg)
|
0.43 |
0.01 |
0.2 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.01 |
0.28 |
0.01 |
0.82 |
0.02 |
0.13 |
0.00 |
0.03 |
0.00 |
0.02 |
0.00 |
|
Total P - P2O5 (g/kg)
|
0.09 |
0.00 |
0.11 |
0.00 |
0.83 |
0.03 |
0.03 |
0.00 |
0.66 |
0.03 |
0.02 |
0.00 |
0.001 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
|
Total K - K2O (g/kg)
|
0.42 |
0.04 |
1.04 |
0.10 |
0.43 |
0.04 |
0.29 |
0.03 |
0.44 |
0.04 |
0.17 |
0.02 |
0.05 |
0.00 |
0.03 |
0.00 |
Table 3.
Micro- nutrient content of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
Table 3.
Micro- nutrient content of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
| Parameter |
WD |
Mechanical Separation |
Centrifugation |
Filtration |
uFiltration |
NF |
| (unit) |
WD |
LDsep |
SFDsep |
LDdec |
SFDdec |
LD200um |
LD1.2um |
LD3nm |
| Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
|
Cd (mg/kg) |
0.031 |
0.00 |
0.016 |
0.00 |
0.031 |
0.00 |
0.006 |
0.00 |
0.041 |
0.00 |
<0.001 |
n.a.* |
<0.001 |
n.a. |
<0.001 |
n.a. |
|
Cr (mg/kg) |
0.55 |
0.09 |
0.39 |
0.06 |
1.91 |
0.31 |
0.21 |
0.03 |
4.14 |
0.68 |
0.13 |
0.02 |
<0.02 |
n.a. |
<0.02 |
n.a. |
|
Hg (mg/kg) |
0.025 |
0.00 |
0.017 |
0.00 |
0.074 |
0.01 |
0.007 |
0.00 |
0.017 |
0.00 |
<0.001 |
n.a. |
<0.001 |
n.a. |
<0.001 |
n.a. |
|
Ni (mg/kg) |
1.01 |
0.14 |
0.62 |
0.09 |
3.17 |
0.44 |
0.44 |
0.06 |
5.81 |
0.81 |
0.21 |
0.03 |
0.073 |
0.01 |
0.14 |
0.03 |
|
Cu (mg/kg) |
20.8 |
1.90 |
1.83 |
0.17 |
17 |
1.55 |
2.74 |
0.25 |
16.7 |
1.52 |
0.9 |
0.08 |
0.06 |
0.01 |
0.05 |
0.01 |
|
Zn (mg/kg) |
32.1 |
8.66 |
18.3 |
4.94 |
51.2 |
13.82 |
12.3 |
3.32 |
77.2 |
20.84 |
3.6 |
0.97 |
0.49 |
0.13 |
0.19 |
0.00 |
|
As (mg/kg) |
0.29 |
0.04 |
0.12 |
0.02 |
0.23 |
0.03 |
0.04 |
0.01 |
0.23 |
0.03 |
<0.005 |
n.a. |
<0.005 |
n.a. |
<0.005 |
n.a. |
|
Fe (mg/kg) |
189 |
45.98 |
78.5 |
19.10 |
713 |
173.47 |
46.9 |
11.41 |
1331 |
323.83 |
13.8 |
3.36 |
1.79 |
0.44 |
0.27 |
0.09 |
|
Mn (mg/kg) |
24.8 |
2.38 |
14.4 |
1.38 |
91.9 |
8.81 |
7.3 |
0.70 |
167 |
16.02 |
4.6 |
0.44 |
0.066 |
0.01 |
<0.025 |
n.a. |
|
Β (mg/kg) |
5.56 |
0.99 |
3.59 |
0.64 |
15.9 |
2.84 |
3.61 |
0.64 |
13.3 |
2.38 |
1.85 |
0.33 |
1.17 |
0.21 |
1.54 |
0.16 |
|
Si (mg/kg) |
475 |
n.a. |
349 |
n.a. |
1139 |
n.a. |
327 |
n.a. |
1260 |
n.a. |
203 |
n.a. |
20 |
n.a. |
12.54 |
3.68 |
|
Al (mg/kg) |
199 |
43.48 |
86.4 |
18.88 |
538 |
117.55 |
54.6 |
11.93 |
573 |
275.31 |
6.55 |
1.43 |
0.36 |
0.08 |
0.14 |
0.07 |
Table 4.
Detection and quantification of indicator pathogen of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
Table 4.
Detection and quantification of indicator pathogen of retrieved fractions in each stage of treatment of the developed sanitation pilot unit.
| Parameter |
Unit |
WD |
Separator |
Decanted |
Bag Filter |
uFiltration |
NF |
| |
|
WD |
LDsep |
SFDsep |
LDdec |
SFDdec |
LD200um |
LD1.2um |
LD3nm |
| Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
Average |
SD |
| Salmonella spp. |
/25 g |
N.D.* |
n.a.** |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
N.D. |
n.a. |
| Escherichia coli |
cfu/g |
480 |
15 |
160 |
n.a. |
310 |
11 |
120 |
n.a. |
350 |
20 |
<40 |
n.a. |
<9.1 |
n.a. |
<9.1 |
n.a. |
| Enterococcus faecalis |
cfu/g |
830 |
29 |
650 |
31 |
770 |
25 |
390 |
13 |
620 |
19 |
<40 |
n.a. |
<40 |
n.a. |
<9.1 |
n.a. |
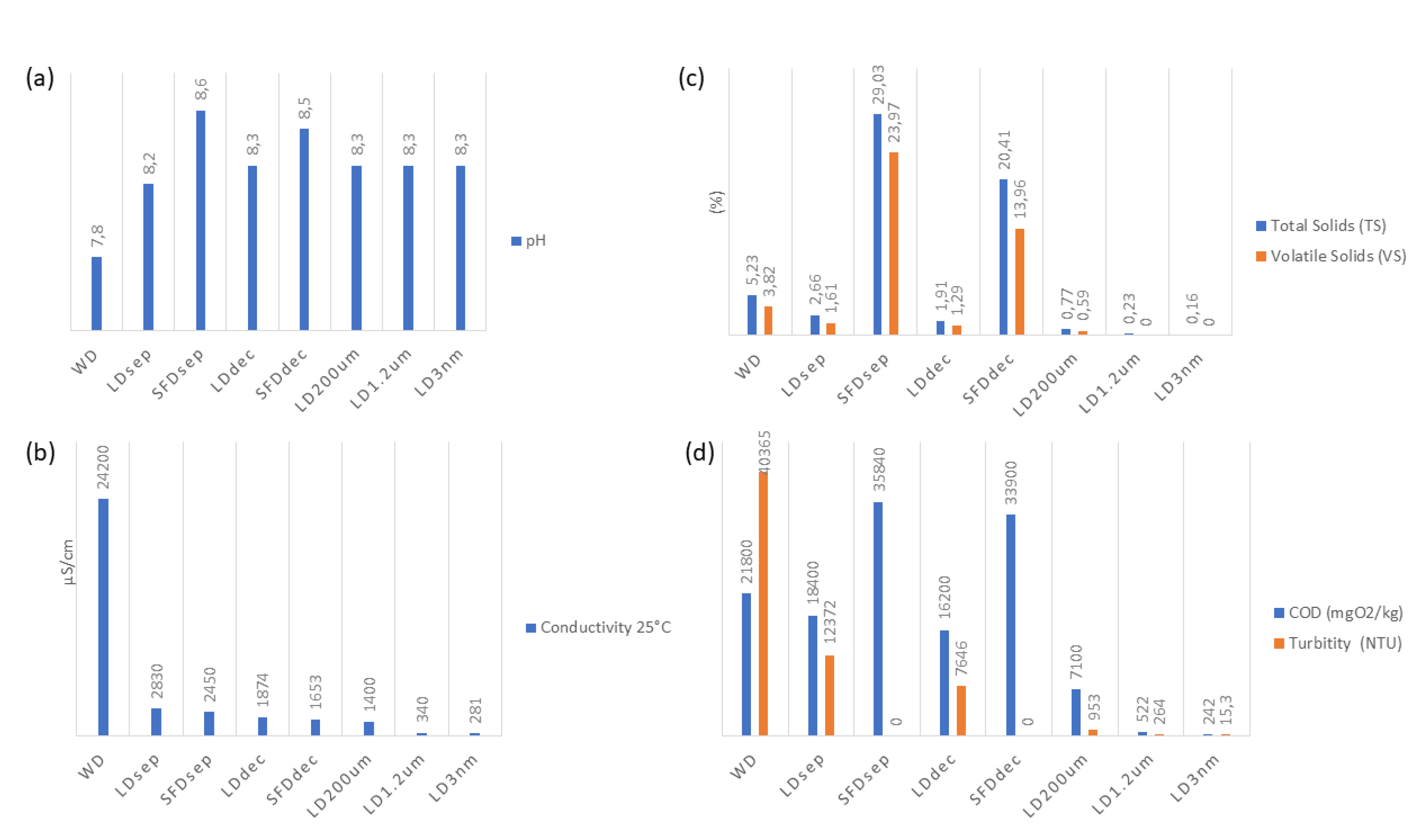
As anticipated, the solids present in the liquid digestate are approximately 85% lower than those observed in the SFD. The microbial population is more pronounced in the whole digestate compared to the liquid fraction, as bacteria adhere to the solids, forming aggregates that provide protection against thermal and chemical alterations. However, it should be noted that the whole digestate exhibits significantly higher contamination levels than the solid digestate, indicating that the separation step contributes to microbial reduction. Regarding the microbiological characteristics of the digestate, it has been observed that potentially pathogenic aerobic microorganisms were present. Throughout the process, all pathogens demonstrated a reduction of 3 to 4 logarithmic units without the addition of spiked material.
The pH values remain consistent across all treatment processes, averaging at 8.3, indicating a stable pH level throughout all filtration and separation procedures. The conductivity values exhibit a significant decrease as the treatment processes progress from LDdec to LDNF. This suggests the effective reduction of influent conductivity by the treatment processes. The percentage of total solids (TS) gradually decreases from LDdec to LDNF, indicating successful removal of solid particles during the treatment processes. The volatile solids (VS) percentage remains consistently low and falls below the detectable limit (<0.05), indicating efficient removal of volatile solids during the treatment processes. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) values exhibit a decreasing trend from LDdec to LDNF 8 min, demonstrating the effectiveness of the treatment processes in reducing organic pollutants. Turbidity values decrease as the treatment processes advance, indicating the removal of suspended particles and improved water clarity. Notably, TSS values demonstrate a significant decrease from LDdec to LDNF, indicating effective removal of suspended solids during the treatment processes. Similarly, the VSS values remain consistently low and fall below the detectable limit. Salmonella spp., Escherichia coli, and Enterococcus faecalis show values below the detection limit (<9.1 or N.D.), indicating successful microbial removal during the process.
The concentrations of elements, such as Ca, Mg, S, Na, Total N, Total P – P2O5, Total K – K2O, ΝO3-, Cd, Cr, Hg, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Fe, Mn, Β, Si, and Al, exhibit varying levels across the different treatment processes. Further analysis and comparison are required to assess the effectiveness of the treatment processes in reducing or removing these elements.
Regarding the SFDsep and SFDdec, collectively, the parameters presented in Table 3 demonstrate that they represent concentrated fractions of the initial WD. The concentrations of various elements in the SFDsep and SFDdec fractions exhibit elevated levels in comparison to the WD. Similarly, the total solids (TS) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) values also display increased concentrations in the SFDsep and SFDdec fractions when compared to the WD. Graphical representations of these observations are given in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Process physicochemical parameters variation. (a) pH; (b) Conductivity 25 °C; (c) Total Solids (TS) and Volatile Solids (VS); (d) Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Turbidity.
Figure 3.
Process physicochemical parameters variation. (a) pH; (b) Conductivity 25 °C; (c) Total Solids (TS) and Volatile Solids (VS); (d) Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) and Turbidity.
Figure 4.
Process parameters variation. (a) Nutrient composition; (b) Metal composition.
Figure 4.
Process parameters variation. (a) Nutrient composition; (b) Metal composition.
4. Conclusions
The effective management of organic waste can be achieved through the utilization of anaerobic digestion (AD) systems, a sustainability and circular economy strategy, which converts waste into value-added products such as energy, organic fertilizers, and minimize its impact on the environment. It is essential to implement proper disinfection procedures to prevent the spread of pathogens through the food chain. Pathogenic microorganisms can survive the digestion process in animal waste, making disinfection crucial. Several methods, such as pasteurization, chlorine treatment, UV-light exposure, ozone treatment, and high-pressure treatment, can be employed to reduce the presence of pathogens in the final digestate effluent. However, the appropriate handling of digestion residue for soil improvement or organic fertilizer should adhere to regulations concerning animal by-products and limits for microorganisms, such as Escherichia coli, Enterococcaceae, and Salmonella. Innovative approaches are currently being developed to decrease microbial contamination in digestate, ensuring its safe application as a soil amendment or fertilizer.
In this study, we have designed and tested a pilot sanitation unit utilizing centrifugation and subsequent steps of filtration with decreasing porosity (micro-, nanofiltration). The results demonstrate promising outcomes in purifying liquid digestate for purposes such as irrigation and industrial use, taking into account design and engineering aspects. Treatment processes including centrifugation, microfiltration, and nanofiltration effectively reduced organic pollutants, eliminated suspended solids, and eliminated potentially pathogenic microorganisms. Physicochemical analysis revealed stable pH levels, reduced conductivity, decreased total solids (TS) and volatile solids (VS), and improved water clarity throughout the treatment processes. Further analysis is necessary to evaluate the efficacy of the treatment process in reducing specific elements and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
These findings emphasize the potential of a sustainable alternative disinfection method and innovative technologies like nanofiltration reactors in the management of organic waste. Such approaches contribute to pollution reduction, safeguard agricultural practices, and promote public health and safety. The usage of treated and sanitized liquid digestate residue can boost sustainability on many fronts. Treated liquid digestate can be utilized for irrigation, disposable cooling water, and as soil conditioners or organic liquid fertilizers, while the recovery of nutrients and water can be achieved leading to low carbon emissions and a circular economy. Future studies should concentrate on improving existing methods and developing new procedures to help overcome the current difficulties associated with the high diversity of the matrix.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.; methodology, T.S., and V.T.; software, T.S., A.G.C., and G.R.; validation, T.S. and G.R.; formal analysis, T.S. and G.S.; investigation, T.S., A.G.C., G.S., and V.T.; resources, T.S.; data curation, T.S. and A.G.C.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S., T.S. and A.G.C.; writing—review and editing, T.S., G.S., G.R., and P.F.; visualization, T.S., A.C.G. and G.S.; supervision, T.S.; project administration, T.S.; funding acquisition, T.S., All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund of the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation, under the call RESEARCH - CREATE – INNOVATE (project code: T2EDK-04043).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available, upon request, from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge operational manager Stefanos Patsatzis of Biogas Lagada S.A. for the industrial tests and the provision of appropriate quantities of digestate. The authors also wish to acknowledge all staff members of Qlab P.C. for their individual roles that contributed to the implementation of this study, thank you Vasiliki Tsioni, Ioanna Dalla, Ifigeneia Grigoriadou, Ioanna Christoforidou and Panagiotis Pantazis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Doyeni, M.O.; Stulpinaite, U.; Baksinskaite, A.; Suproniene, S.; Tilvikiene, V. Greenhouse gas emissions in agricultural cultivated soils using animal waste-based digestates for crop fertilization. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 159, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez B, Álvarez-Rivera G, Valdés A, Ibáñez E, Cifuentes A. Food by-products and food wastes: are they safe enough for their valorization? Trends Food Sci Technol. 2021;114:133–47.
- PALMISANO, AC. Introduction to solid waste decomposition. IN: Microbiology of Solid Waste. Ed. Palmisano &Barlaz; Boca Roton, Florida. New York; 1996.
- Kovačić. ; Lončarić, Z.; Jović, J.; Samac, D.; Popović, B.; Tišma, M. Digestate Management and Processing Practices: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goberna, M.; Podmirseg, S.; Waldhuber, S.; Knapp, B.; García, C.; Insam, H. Pathogenic bacteria and mineral N in soils following the land spreading of biogas digestates and fresh manure. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 49, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Lü, F.; Hao, L.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; He, P. Digestate management for high-solid anaerobic digestion of organic wastes: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfetsas, T.; Patsatzis, S.; Chioti, A.; Kopteropoulos, A.; Dimitropoulou, G.; Tsioni, V.; Kotsopoulos, T. A review of advances in valorization and post-treatment of anaerobic digestion liquid fraction effluent. Waste Manag. Res. J. a Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2022, 40, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Ortega, Y.R.; MARILYN, C. ERICKSON* and YNES R. ORTEGACenter for Food Safety, Department of Food Science and Technology, University of Georgia, 1109 Experiment Street, Griffin, Georgia 30223-1797, USA; Hohweyer, J.; Dumètre, A.; Aubert, D.; Azas, N.; Villena, I.; Kniel, K.E.; Shearer, A.E.H.; et al. Inactivation of Protozoan Parasites in Food, Water, and Environmental Systems. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2786–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uggetti, E.; García, J.; Álvarez, J.A.; García-Galán, M.J. Start-up of a microalgae-based treatment system within the biorefinery concept: from wastewater to bioproducts. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bei, E.; Lens, P.N.; Thomas, O.; Hu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhan, X. In situ electrochemical oxidation in electrodialysis for antibiotics removal during nutrient recovery from pig manure digestate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 413, 127485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynaud G, Druilhe C, Jimenez J, Patureau D, Pourcher AM, Wéry N. Inactivation of pathogenic bacteria in digestates by competition with indigenous bacteria. Environnement, Risques & Santé. 2020;19(1):35–40.
- Xinjie, W.; Xin, N.; Qilu, C.; Ligen, X.; Yuhua, Z.; Qifa, Z. Vetiver and Dictyosphaerium sp. co-culture for the removal of nutrients and ecological inactivation of pathogens in swine wastewater. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 20, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziel, J.A.; Frana, T.S.; Ahn, H.; Glanville, T.D.; Nguyen, L.T.; van Leeuwen, J. (. Efficacy of NH3 as a secondary barrier treatment for inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in digestate of animal carcasses: Proof-of-concept. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0176825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- General Directorate of Sustainable Livestock Production and Veterinary Medicine. Management of livestock and slaughterhouses manure, and digestion residue from bi-ogas plants. 2016.
- Validation of alternative transformation parameters for biogas plants and composting plants. 2019.
- Falaras, P., G. Romanos and PA. Photocatalytic purification device. Application number. 2012;7:24.
- JMD 145116/02-02-2011 (Official Government Gazette B 354/2011). Determination of measures, terms and procedures for the reuse of treated liquid waste and other provisions. 2011.
- Andrew, D. Eaton EWRRBB, Bridgewater L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd Edition. Vol. 10. American Public Health Association Washington, DC; 2017.
- 2540 SOLIDS. In: Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd [Internet]. American Public Health Association; 2017. (Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater). [CrossRef]
- ISO 17294-1:2004 Water quality — Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) — Part 1: General guidelines. 2004; Available from: https://www.iso.org/standard/32957.html.
- ISO 17294-2:2016 Water quality — Application of inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) — Part 2: Determination of selected elements including uranium isotopes [Internet]. 2016. Available from: https://www.iso.org/standard/62962.html.
- Lipps WC BTBHE. 3125 Metals by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. In: Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater [Internet]. American Public Health Association; 2018. (Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater). [CrossRef]
- LCK 514 Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 May 23]. Available from: www.hach.com.
- LCK 314 Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) [Internet]. 2019. Available from: www.hach.com.
- Eaton AD, Rice EW, Baird RB. 5220 D chemical oxygen demand (COD), closed reflux, colorimetric method. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 1998.
- Clescerl LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD. 4500 NO3 nitrogen (nitrate). Standard Methods For Examination of Water and Wastewater 20th edn Amer Public Health Assn. 1999.
- Rice EW, Bridgewater L, Association APH. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Vol. 10. American public health association Washington, DC; 2012.
- Agrawal, P.; Wilkstein, K.; Guinn, E.; Mason, M.; Martinez, C.I.S.; Saylae, J. A Review of Tangential Flow Filtration: Process Development and Applications in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2023, 27, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).