Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Multiple daily injections (MDI) – A long-acting insulin administered one time daily (morning or evening) - and a rapid-acting one before meals (its dose is calculated considering the amount of carbohydrate and the blood glucose level) [35];
- Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) – A rapid-acting insulin administered 24 hours/day using an insulin pump. [36].
2. Materials and Methods
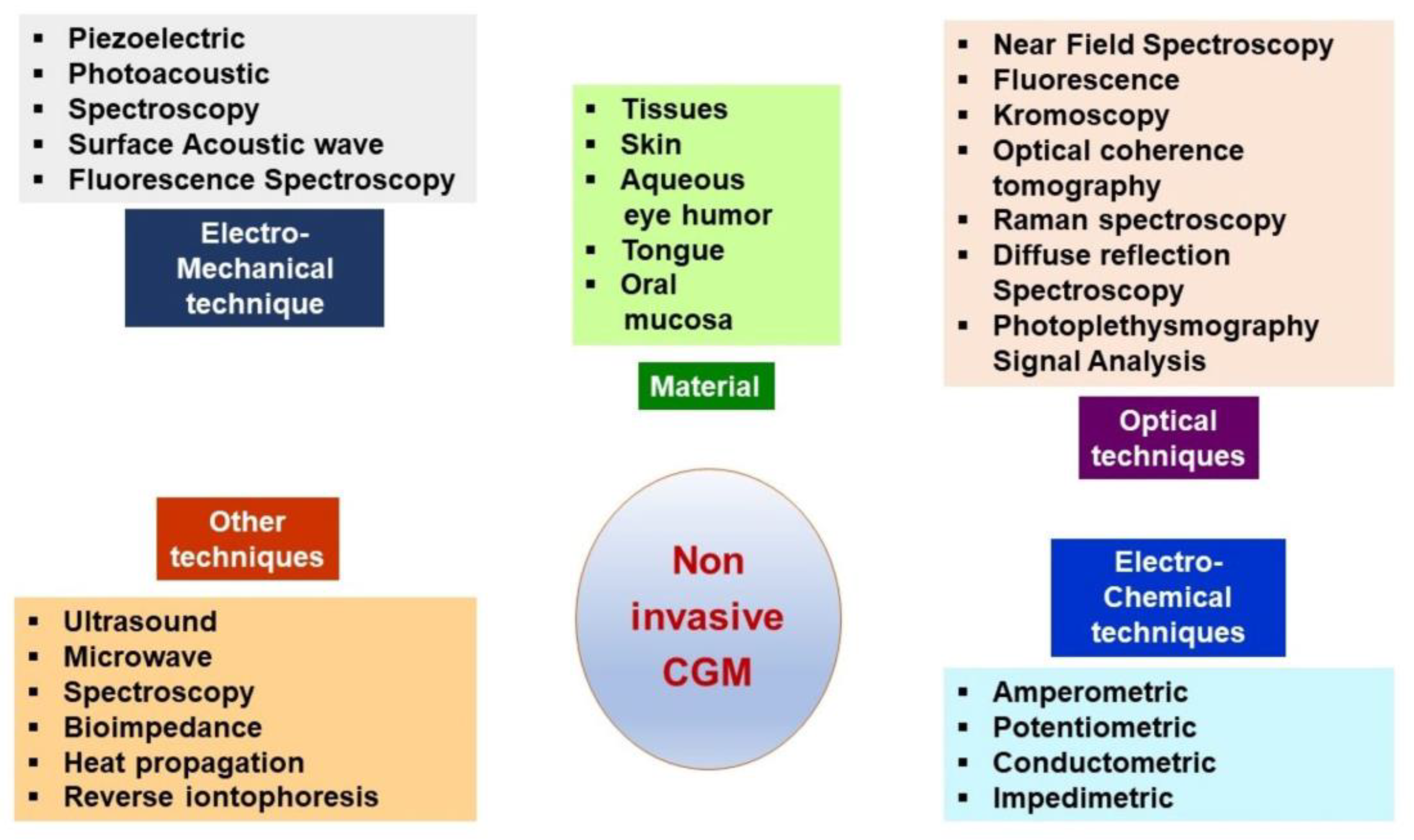
3. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
3.1. Description
- ▪ Maintaining a constant glycemic level daily.
- ▪ Diminishing hypoglycemia emergencies.
- ▪ Reducing finger pricks number.
- ▪ Decreasing BG and HbA1c levels variability.
3.2. Limits
- ▪ CGM systems are more expensive than standard glucometers.
- ▪ The finger prick glucose test is needed twice daily for some CGM to check the accuracy.
- ▪ Readings are not trusted, and too much time is needed to use them [90].
- ▪ Invasiveness.
- ▪ Short lifespan.
- ▪ Biocompatibility.
- ▪ Calibration and prediction.
3.3. Potential adverse effects related to the insertion, removal, and wear of the sensor
- ▪ Allergies to adhesives
- ▪ Bleeding and bruising
- ▪ Infection, pain, or discomfort
- ▪ Sensor destruction during extraction
- ▪ Skin inflammation, scarring, thinning, discoloration, or redness.
- ▪ Excessive insulin administration could increase the risk of hypoglycemia
- ▪ Inappropriate administration of carbohydrates increases the risk of hyperglycemia and acute diabetic ketoacidosis. Moreover, there could appear long-term microvascular complications of diabetes.
- ▪ Inaccurate calculation of the glucose change rate could increase the incidence of hypo or hyperglycemia.
4. Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Delivery Systems (CSII)
- ▪ A continuous infusion of rapid-acting insulin throughout the day and night (basal),
- ▪ The user gives a discreet, one-time dose of rapid-acting insulin for meals or high blood glucose correction (bolus).
- People with T1DM or insulin-dependent T2DM.
- Persons with multiple-day injections of Insulin and a similar number of BG tests.
- Individuals - able to assess appropriate blood glucose control.
- Capable of performing insulin pump therapy initiation and maintenance.
- Able to maintain frequent contact with the healthcare team.
- Able to consider insulin pumps as a tool to improve diabetes care.
- Capable of accurately calculating carbohydrates and insulin bolus.
- Patients with critical clinical conditions have serious difficulties controlling glycemic targets despite intensive treatment and monitoring.
- With substantially decompensated diabetes (frequent severe hypoglycemia and/or hypoglycemia).
- Other associated conditions: extreme insulin sensitivity, gastroparesis, pregnancy, variable schedules or work shifts, significant "dawn phenomenon," high insulin doses therapy, or severe insulin resistance.
4.1. Conventional Insulin Pumps
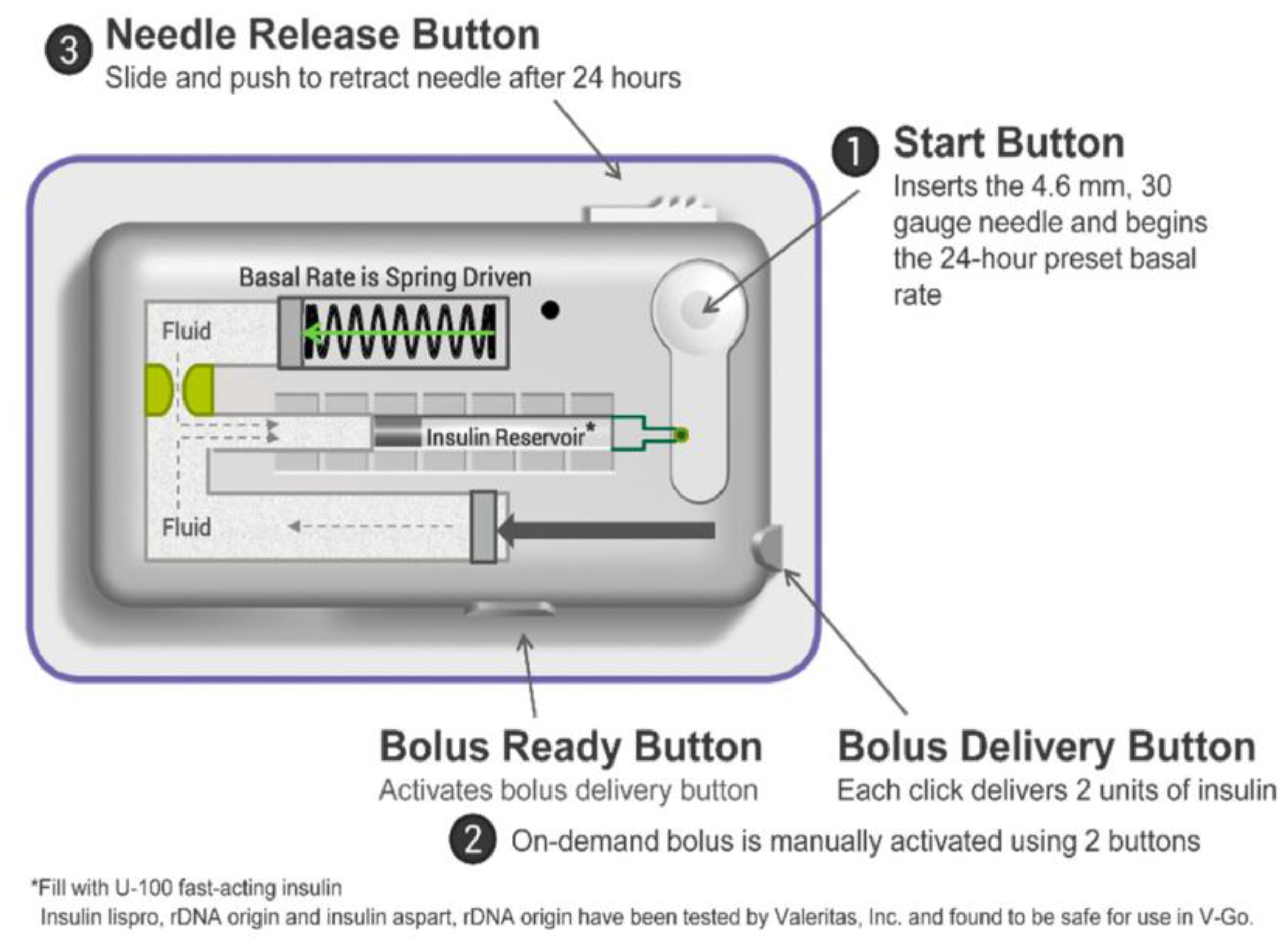
4.2. Insulin Patch Pumps (PP)
4.2.1. Simple insulin PPs devices
4.2.2. Full-Featured Electromechanical Patch Pumps
4.2.3. PPs suitable for AID systems
4.3. Sensor Augmented Pump Therapy (SAPT)
- ▪ With low-glucose suspend (SAPT-LGS)
- ▪ With predictive low-glucose management (SAPT-PLGM).
| SAPT-LGS | SAPT-PLGM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | |||
| When the pump users did not recognize the warning sounds, the SAPT-LGS automatically stops the basal insulin infusion (for up to 2 h) as a response to hypoglycemia detected by a sensor. Then, the basal insulin infusion is released at the rate previously programmed. | Basal insulin delivery is usually stopped when the sensor indicates a glucose level below 70 mg/dL. When the users do not exert an action, the insulin infusion returns at the last regulated rate after two hours of suspending. |
||
| SAPT-LGS system can diminish moderate-to-severe hypoglycemia, especially during nighttime. | SAPT-PLGS system reduces more effectively the frequency of hypoglycemia and the risk of developing this condition in a severe form in T1DM patients. | ||
| Devices | |||
|
RT-Paradigm® Veo™* (Medtronic, Northridge, CA, USA) |
RT-MiniMed 640G (Medtronic, Northridge, CA, USA) |
||
| MARD% | 13.6% | MARD% | 14.2% |
| Calibration | 3 days | Calibration | 3 days |
| Life of sensor | 6 days | Life of sensor | 6 days |
| Clinical studies | |||
| Studies using SAPT-LGS demonstrated a diminishing in hypoglycemic events (with 40–50%), without an A1C increase, compared to SAPT alone [112,113]. | Under real-life conditions, SAPT-PLGM decreases hypoglycemic events in patients previously treated with MDI and SAPT-LGS. It occurs without deteriorating glycemic control in SAPT-LGS patients and improves A1C in those treated with MDI [114,115]. | ||
| Ideal user | |||
| Able to permanently wear a device on the body and manage CGM data. | Able to comfortably wear an automatic device. | ||
| Able to check BG when needed. | Able to regulate the carbohydrate amount. | ||
| Able to respond and manage CGM alerts | |||
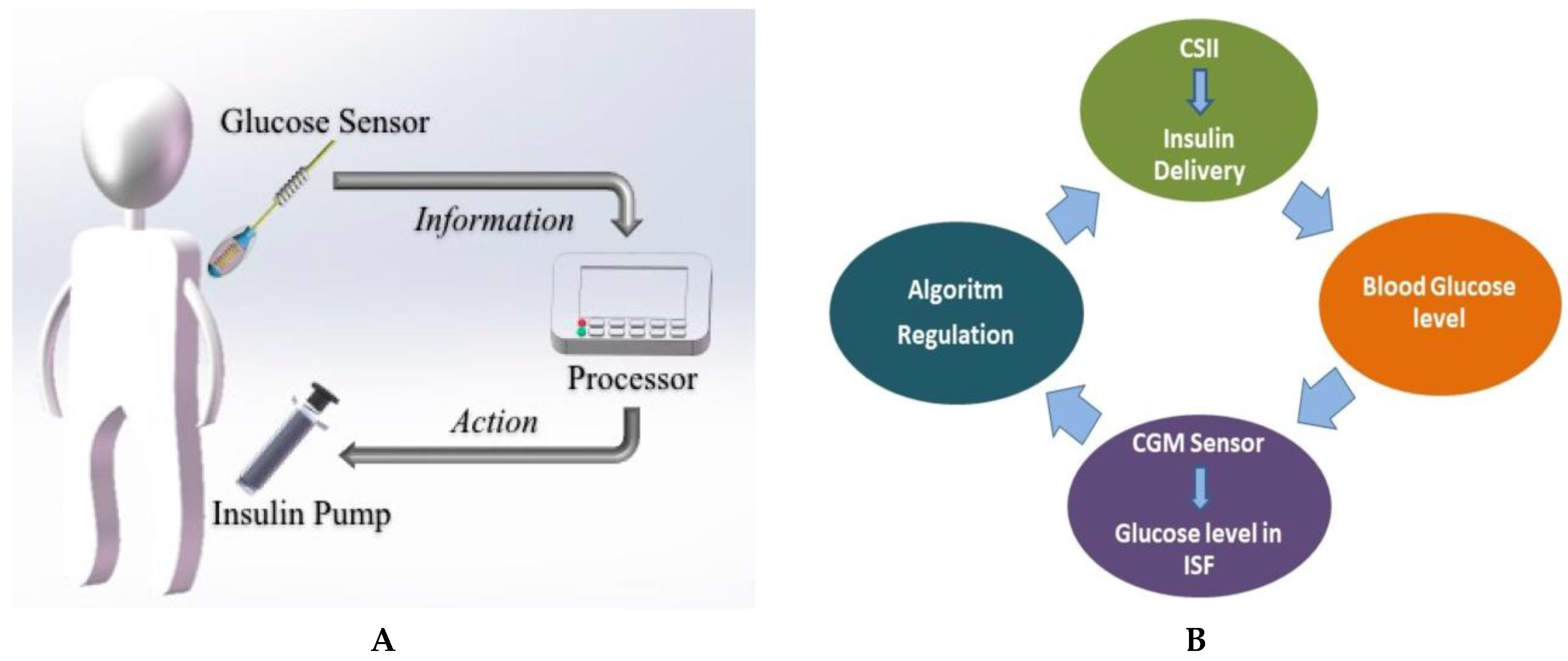
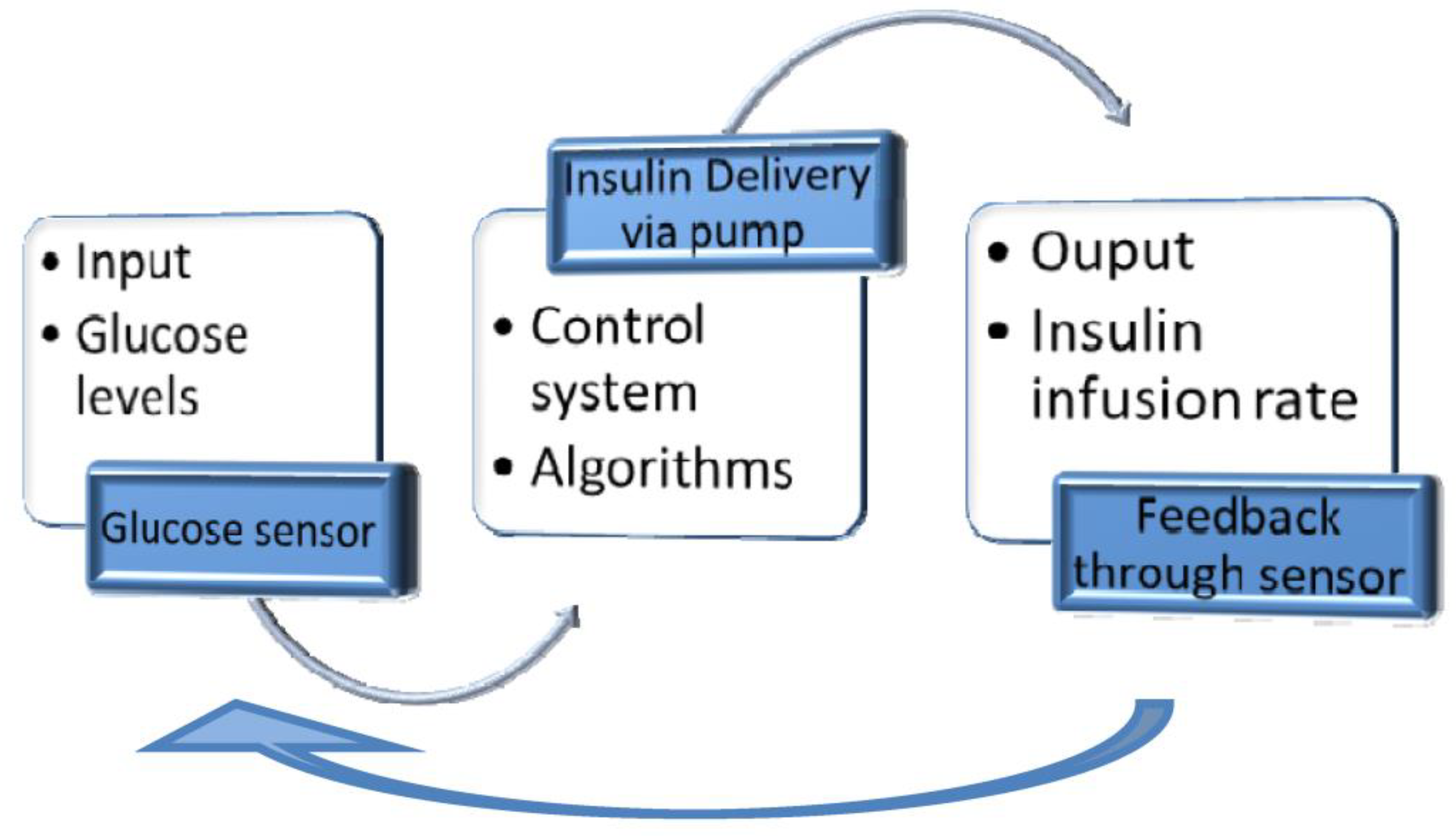
4.4. Closed-loop Insulin Systems (Artificial Pancreas)
- ▪ Glucose measuring device (CGM)
- ▪ Control device for BG analysis and insulin dosing regulation (computer/microprocessor)
- ▪ Insulin infusion device (insulin pump)
4.4.1. Benefits
- ▪ The glucose levels could be continuously monitored.
- ▪ The control algorithms improve BG control, automatically regulating the amount of insulin.
- ▪ The System helps the T1DM user avoid emerging events (hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia).
4.4.2. Limits
- ▪ The T1DM patient regularly verifies the devices to ensure that they function correctly.
- ▪ The user must continuously verify the CGM and infusion pump catheter, ensuring they are in a suitable place, and change them when needed.
- ▪ The CGM accuracy should be verified, and the CGM sensor must be regularly replaced.
- ▪ The patient must count the mealtime carbohydrates and enter them into the System.
- ▪ The control software settings must be verified to ensure that the insulin infusion has a suitable amount.
- ▪ The extreme BG levels should be regulated if the System is unable.
- ▪ The adhesive patches used with these systems may cause skin redness or irritation.
- ▪ Other medicines might also interfere with the glucose monitor.
4.4.3. Complications
- ▪ Hypoglycemia occurs when a significant basal rate of insulin is delivered due to a human error in insulin pump programming or a device malfunction.
- ▪ Hyperglycemia is caused by programming error or device malfunction, leading to a low insulin delivery rate (battery depletion or malposition, cannula occlusion, total pump failure).
- ▪ If the infusion set is not changed regularly, at 3-4 days, there is irritation and infections at the place of cannula insertion.
- ▪ Insulin pump therapy discontinuation (18-50%) is the T1DM patient choice for various reasons: unwanted interference with the lifestyle, missing improvements in glycemic control, and infection at the insertion place. It occurs with high incidence in women, younger patients, pregnancy, and when the patient has psychological comorbidities.
5. The impact of new technologies on T1DM people’s Quality of Life
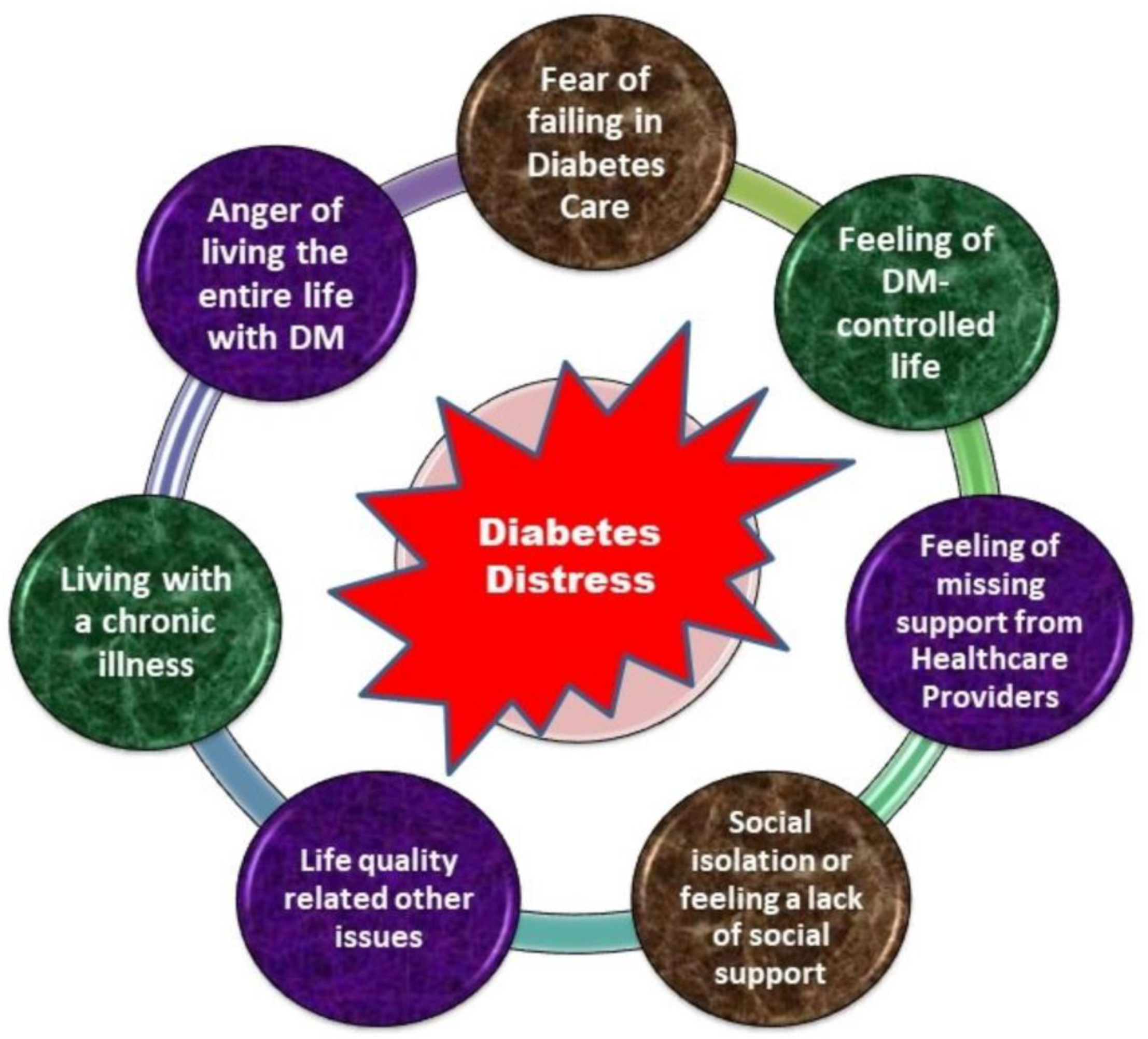
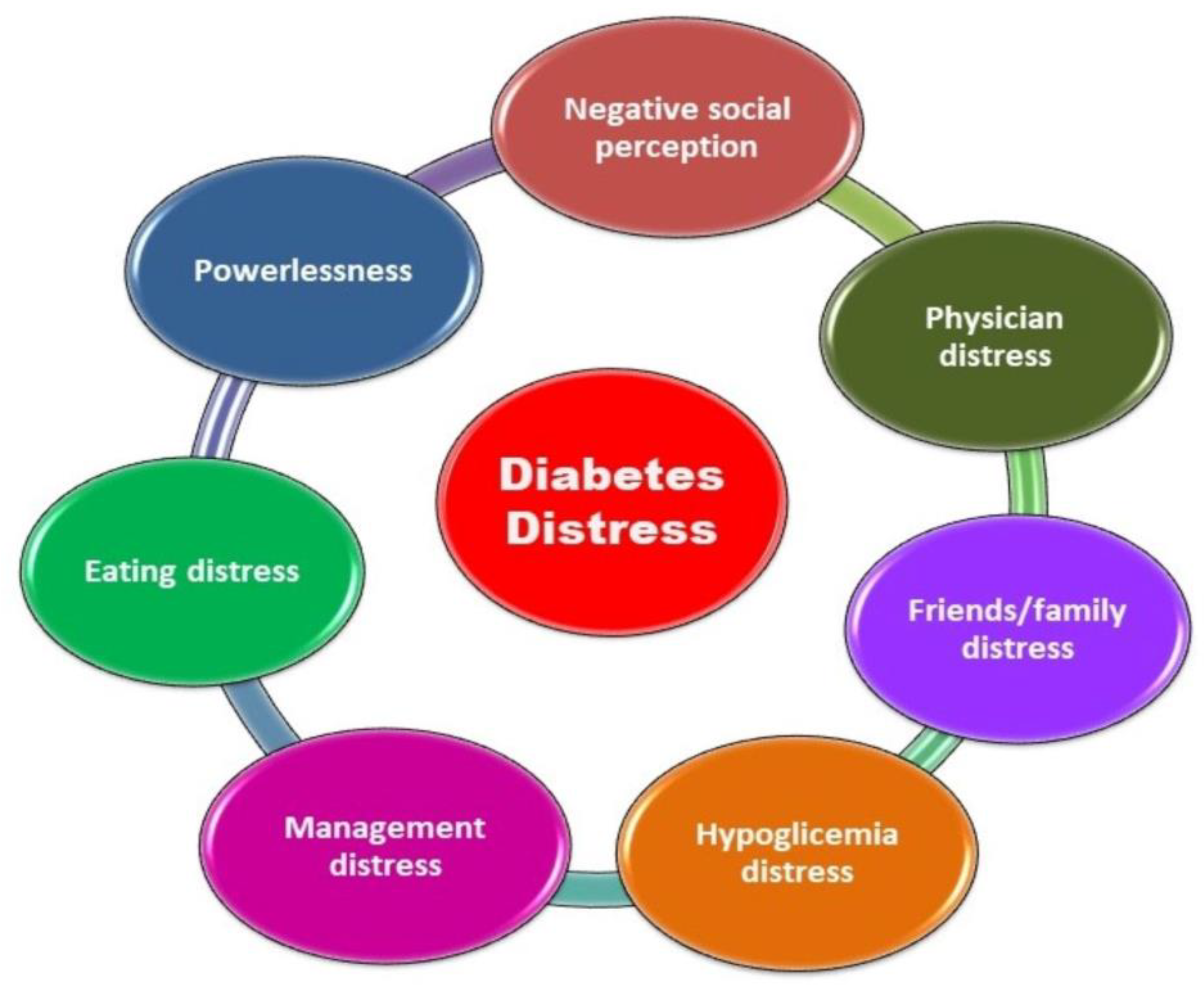
5.1. Evaluation of Diabetes Distress
5.2. Satisfaction Survey for Diabetes Technology Users
- ▪ Openness.
- ▪ Emotional and behavioral burdens.
- ▪ Trust.
- ▪ Effectiveness.
- ▪ Burdensomeness.
- ▪ Inconvenience.
5.3. Quality of Life Evaluation
- ▪ Reducing their fear of hypoglycemia,
- ▪ Decreasing their sense of regimen burden,
- ▪ Diminishing their worries about out-of-range blood sugar levels,
- ▪ Improving their overall freedom to engage in activities that they enjoyed.
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Alam, S.; Hasan, M.K.; Neaz, S.; Hussain, N.; Hossain, M.F.; Rahman, T. Diabetes Mellitus: Insights from Epidemiology, Biochemistry, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Complications, and Comprehensive Management. Diabetology 2021, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.M. Highlighting Diabetes Mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Thomaidou, S.; van Tienhoven, R.; Zaldumbide, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus as a disease of the β-cell (do not blame the immune system?). Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pozzilli, P.; Maddaloni, E.; Buzzetti, R. Combination immunotherapies for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, R.N.; Evans-Molina, C. Combination Immunotherapy for Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2017, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Carballido, J.M.; Wesley, J.D.; Ahmed, S.T. Overcoming Obstacles in the Development of Antigen-Specific Immunotherapies for Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730414. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- von Scholten, B.J.; Kreiner, F.F.; Gough, S.C.L.; von Herrath, M. Current and future therapies for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, J.L. Timing of Immunotherapy in Type 1 Diabetes: The Earlier, the Better? ImmunoHorizons 2021, 5, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P.; Wołącewicz, M.; Cywoniuk, P.; Klak, M.; Wszoła, M. Crosstalk Between Immunity System Cells and Pancreas. Transformation of Stem Cells Used in the 3D Bioprinting Process as a Personalized Treatment Method for Type 1 Diabetes. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz). 2020, 68, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, E.K.; Bundy, B.N.; Stier, K.; Serti, E.; Lim, N.; Long, S.A.; Geyer, S.M.; Moran, A.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Evans-Molina, C.; et al. Teplizumab improves and stabilizes beta cell function in antibody-positive high-risk individuals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc8980. [Google Scholar]
- Frontino, G.; Guercio Nuzio, S.; Scaramuzza, A.; D’Annunzio, G.; Toni, S.; Citriniti, F.; Bonfanti, R. Prevention of type 1 diabetes: where we are and where we are going. Minerva Pediatr. 2021, 73, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigoto, A.L.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Clark, P.; Long, S.A.; Linsley, P.S.; Harris, K.M.; Gitelman, S.E.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Gottlieb, P.A.; Hagopian, W.; et al. Treatment of type 1 diabetes with teplizumab: clinical and immunological follow-up after 7 years from diagnosis. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwong, S.P.; Wang, C. Review: Usnic acid-induced hepatotoxicity and cell death. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Ren, S.; Pan, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhao, X. Versatile Oral Insulin Delivery Nanosystems: From Materials to Nanostructures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahameed, M.; Xue, S.; Stefanov, B.A.; Hamri, G.C. El; Fussenegger, M. Engineering a Rapid Insulin Release System Controlled By Oral Drug Administration. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105619. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Canett-Romero, R.; Prakash, S.; Rascón-Chu, A.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Micard, V. Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; He, S.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.; Cai, Q.; Zhou, W. Multivesicular liposomes for glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadi, S.; Moosavian, S.A.; Mashreghi, M.; Rahiman, N.; Golmohamadzadeh, S.; Tafaghodi, M.; Sadri, K.; Chamani, J.; Jaafari, M.R. B12-functionalized PEGylated liposomes for the oral delivery of insulin: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 69, 103141. [Google Scholar]
- Bahman, F.; Taurin, S.; Altayeb, D.; Taha, S.; Bakhiet, M.; Greish, K. Oral insulin delivery using poly (Styrene co-Maleic acid) micelles in a diabetic mouse model. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, E.; Zhu, H.; Du, H.; Wang, K.; Song, B.; Yang, C.; Shi, Y.; et al. Zwitterionic micelles efficiently deliver oral insulin without opening tight junctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 605–614. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Guo, T.; Nan, J.; Yang, L.; Liao, G.; Park, H.J.; Li, J. Hyaluronic-Acid-Coated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Insulin Oral Delivery: Fabrication, Characterization, and Hypoglycemic Ability. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, e2100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiang, H.; Yang, W.; Xu, Y.; Feng, T.; Cai, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Oral insulin delivery by epithelium microenvironment-adaptive nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2022, 341, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhatib, M.M.; Ali, A.I.; Al-Badrawy, A.S. In vitro and in vivo comparative study of oral nanoparticles and gut iontophoresis as oral delivery systems for insulin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Wong, J.; Gogoi, R.; Brown, T.; Mitragotri, S. Intestinal micropatches for oral insulin delivery. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, N.; Nazari, M.; Fahanik-Babaei, J.; Eliassi, A. Long-term administration of intranasal insulin improves peripheral glucose concentration in diabetic male rats. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 24, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roque, P.; Nakadate, Y.; Sato, H.; Sato, T.; Wykes, L.; Kawakami, A.; Yokomichi, H.; Matsukawa, T.; Schricker, T. Intranasal administration of 40 and 80 units of insulin does not cause hypoglycemia during cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Can. J. Anesth. 2021, 68, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Tu, R.; Zhang, X.; He, W.W.; Hou, C.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Yu, J.M.; Jiang, G.H. Intranasal insulin ameliorates neurological impairment after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, D.D.; Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X.D. Insulin delivery systems combined with microneedle technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Moro-Oka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Miyahara, Y.; Suganami, T.; Matsumoto, A. Temperature-Stable Boronate Gel-Based Microneedle Technology for Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 2781–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, C.Y.; Lu, W.L.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Huang, Y.B.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Sublingual delivery of insulin: Effects of enhancers on the mucosal lipid fluidity and protein conformation, transport, and in Vivo hypoglycemic activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzengin, S.; Guler, E.; Eser, E.; Polat, E.B.; Gunduz, O.; Cam, M.E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of 3D printed sodium alginate/polyethylene glycol scaffolds for sublingual delivery of insulin: Preparation, characterization, and pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 204, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hermansen, K.; Fontaine, P.; Kukolja, K.K.; Peterkova, V.; Leth, G.; Gall, M.A. Insulin analogues (insulin detemir and insulin aspart) versus traditional human insulins (NPH insulin and regular human insulin) in basal-bolus therapy for patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucidi, P.; Porcellati, F.; Andreoli, A.M.; Carriero, I.; Candeloro, P.; Cioli, P.; Bolli, G.B.; Fanelli, C.G. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of NPH insulin in type 1 diabetes: The Importance of appropriate resuspension before subcutaneous injection. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorino, M.I.; Petrizzo, M.; Bellastella, G.; Esposito, K. Continuous glucose monitoring for patients with type 1 diabetes on multiple daily injections of insulin: pros and cons. Endocrine 2018, 59, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, L.J.; Neville, K.A. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections for type 1 diabetes. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2019, 55, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savu, O.; Elian, V.; Steriade, O.; Teodoru, I.; Mihut, S.; Tacu, C.; Covic, A.; Serafinceanu, C. The impact of basal insulin analogues on glucose variability in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing renal replacement therapy for end-stage renal disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Georgi, J.; Chhabra, H.; Vigersky, R.A. The Rising Cost of Insulin for Pump Users: How Policy Drives Prices. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 1177–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Lawton, J.; Kirkham, J.; Rankin, D.; White, D.A.; Elliott, J.; Jaap, A.; Smithson, W.H.; Heller, S.; Gianfrancesco, C.; Gordon, V.; et al. Who gains clinical benefit from using insulin pump therapy? A qualitative study of the perceptions and views of health professionals involved in the Relative Effectiveness of Pumps over MDI and Structured Education (REPOSE) trial. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkert, D.; Vijayakumar, P.; Luo, J.; Schwartz, J.I.; Rabin, T.L.; Defilippo, E.; Lipska, K.J. Cost-Related Insulin Underuse Among Patients With Diabetes. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroșan, E.; Popovici, V.; Elian, V.; Dărăban, A.M.; Rusu, A.I.; Licu, M.; Mititelu, M.; Karampelas, O. The Impact of Medical Nutrition Intervention on the Management of Hyperphosphatemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease: A Case Series. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elian, V.; Ditu, G.; Bodnarescu, M.; Calin, A.; Serafinceanu, C.; Cioca, G.; Pantea-Stoian, A. Protein-Energy Wasting and Survival in Diabetes Mellitus Hemodialysis Patients. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Management of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications, Bucharest, Romania, 3–5 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson, B.; Lyngfelt, L.; Strömblad, S.O.; Franzén, S.; Eeg-Olofsson, K. The significance of chronic kidney disease, heart failure and cardiovascular disease for mortality in type 1 diabetes: nationwide observational study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuth, S. Insights from the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study on the use of intensive glycemic treatment to reduce the risk of complications of type 1 diabetes. In Proceedings of the Endocrine Practice; 2006; Vol. 12, pp. 34–41.
- Niazi, A.K.; Kalra, S. Diabetes and tuberculosis: A review of the role of optimal glycemic control. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2012, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva de Sousa, G.G.; Yamamura, M.; de Araújo, M.F.M.; Ramos, A.C.V.; Arcêncio, R.A.; de Jesus Costa, A.C.P.; Pascoal, L.M.; Santos, F.S.; de Oliveira Serra, M.A.A.; Fontoura, I.G.; et al. Vulnerable territories to tuberculosis-diabetes mellitus comorbidity in a northeastern Brazilian scenario. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Bhadada, S.K.; Minz, R.W.; Dayal, D.; Kochhar, R. Interplay between type 1 diabetes mellitus and celiac disease: Implications in treatment. Dig. Dis. 2018, 36, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogut, M.D.; Brinegar, C.H. Addison’s disease and diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatr. 1972, 81, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingley, M.; Quebedeaux, P.; Schmidbauer, K.; Amghaiab, I.A.; Chan, J. PMON315 Hyperglycemia Dilemma: Concomitant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Cushing’s disease. J. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 6, A624–A625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, I.; Ciubotaru, V.; Tulin, A.; Hortopan, D.; Caragheorgheopol, A.; Purice, M.; Neamtu, C.; Elian, V.I.; Banica, A.; Oprea, L.; et al. The multifarious cushing’s – Lessons from a case series. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh). 2019, 15, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Wardian, J.L.; True, M.W.; Folaron, I.; Colburn, J.; Tate, J.M.; Beckman, D.J. The Choice Should Be Yours: Diabetes-Related Distress by Insulin Delivery Method for People with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tareen, R.S.; Tareen, K. Psychosocial aspects of diabetes management: Dilemma of diabetes distress. Transl. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 383–396. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, K.; Crabtree, V.; Adolfsson, P.; Davies, M.; Kerr, D.; Kraus, A.; Gianferante, D.; Bevilacqua, E.; Serbedzija, G. Impact of Type 1 Diabetes Technology on Family Members/Significant Others of People with Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, M. Psychological aspects of diabetes management. Med. (United Kingdom) 2022, 50, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mianowska, B.; Fedorczak, A.; Michalak, A.; Pokora, W.; Barańska-Nowicka, I.; Wilczyńska, M.; Szadkowska, A. Diabetes related distress in children with type 1 diabetes before and during the covid-19 lockdown in spring 2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Valimaki, M.; Whittemore, R.; Grey, M.; Guo, J. Factors associated with diabetes distress among adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Nurs. 2021, 30, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.B.; Voorhorst, I.; Van De Gaar, V.H.W.; Keukens, A.; Potter Van Loon, B.J.; Snoek, F.J.; Honig, A. Diabetes distress is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with gestational diabetes: A prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, T.C.; Joensen, L.; Parkin, T. Twenty-five years of diabetes distress research. Diabet. Med. 2020, 37, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, M.; Pouwer, F.; Snoek, F.J. How to identify clinically significant diabetes distress using the Problem Areas in Diabetes (PAID) scale in adults with diabetes treated in primary or secondary care? Evidence for new cut points based on latent class analyses. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e056304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Earles, J.; Dudl, R.J.; Lees, J.; Mullan, J.; Jackson, R.A. Assessing psychosocial distress in diabetes: Development of the Diabetes Distress Scale. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.R.; Peyrot, M. Health-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in the sensor-augmented pump therapy for A1C reduction 3 (STAR 3) trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Klamann, M.; Majkowska, L. New technologies and metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Diabetol. 2017, 6, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbell, B.; Lawton, J.; Boughton, C.; Hovorka, R.; Rankin, D. Parents’ experiences of caring for a young child with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and synthesis of qualitative evidence. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Pauley, M.E.; Berget, C.; Messer, L.H.; Forlenza, G.P. Barriers to uptake of insulin technologies and novel solutions. Med. Devices Evid. Res. 2021, 14, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pease, A.; Zomer, E.; Liew, D.; Lo, C.; Earnest, A.; Zoungas, S. Cost-effectiveness of health technologies in adults with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prahalad, P.; Tanenbaum, M.; Hood, K.; Maahs, D.M. Diabetes technology: improving care, improving patient-reported outcomes and preventing complications in young people with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2018, 35, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Gonder-Frederick, L.A.; Shepard, J.A.; Grabman, J.H.; Ritterband, L.M. Psychology, technology, and diabetes management. Am. Psychol. 2016, 71, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umpierrez, G.E.; Klonoff, D.C. Diabetes technology update: Use of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring in the hospital. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.; Yeung, M.; Mendelsohn Curanaj, F.A. Managing Patients with Insulin Pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitors in the Hospital: to Wear or Not to Wear. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2021, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.; Boyle, E.; Delaney, C.; Shaw, J. A comparison of blood glucose meters in Australia. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 71, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos, A.; Apostolopoulou, D.; Tsoubeli, A. Application of health informatics in the education of diabetic patients for the improvement of self-management and reporting to specialists. J. Inf. Technol. Healthc. 2007, 5, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Olczuk, D.; Priefer, R. A history of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2018, 12, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi, R.; Micheli, F.; Mozzillo, E.; Cauvin, V.; Liguori, A.; Soffiati, M.; Giani, E. Intermittently Scanned and Continuous Glucose Monitor Systems: A Systematic Review on Psychological Outcomes in Pediatric Patients. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 660173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.M.; Charleer, S.; Fieuws, S.; De Block, C.; Hilbrands, R.; Van Huffel, L.; Maes, T.; Vanhaverbeke, G.; Dirinck, E.; Myngheer, N.; et al. Comparing real-time and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes (ALERTT1): a 6-month, prospective, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2275–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staal, O.M.; Hansen, H.M.U.; Christiansen, S.C.; Fougner, A.L.; Carlsen, S.M.; Stavdahl, Ø. Differences between flash glucose monitor and fingerprick measurements. Biosensors 2018, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkert, M.; Van Dijk, P.R.; Edens, M.A.; Díez Hernández, A.; Slingerland, R.; Gans, R.; Delgado Álvarez, E.; Bilo, H. Performance of the Eversense versus the Free Style Libre Flash glucose monitor during exercise and normal daily activities in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Jiang, N.; Shao, X.; Elsherif, M.; Alam, F.; Salih, A.; Butt, H.; Yetisen, A.K. Recent advances in optical sensors for continuous glucose monitoring. Sensors & Diagnostics 2022, 1, 1098–1125. [Google Scholar]
- Gaynanova, I.; Punjabi, N.; Crainiceanu, C. Modeling continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data during sleep. Biostatistics 2022, 23, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakami, T. The Advanced Diabetes Technologies for Reduction of the Frequency of Hypoglycemia and Minimizing the Occurrence of Severe Hypoglycemia in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropff, J.; DeVries, J.H. Continuous Glucose Monitoring, Future Products, and Update on Worldwide Artificial Pancreas Projects. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18, S253–S263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappon, G.; Acciaroli, G.; Vettoretti, M.; Facchinetti, A.; Sparacino, G. Wearable continuous glucose monitoring sensors: A revolution in diabetes treatment. Electron. 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Channa, A.; Jeoti, V.; Stojanović, G.M. Comprehensive Review on Wearable Sweat-Glucose Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sensors 2022, 22, 638. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.T.; Segovia, D.E.; Lee, C.C.; Nguyen, K.L. Consistency of continuous ambulatory interstitial glucose monitoring sensors. Biosensors 2018, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensh, B.D.; Wisniewski, N.A.; Neil, B.M.; Burnett, D.R. Susceptibility of interstitial continuous glucose monitor performance to sleeping position. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J. , El-Khatib, F.H., Sinha, M., Magyar, K.L., Mckeon, K., Goergen, L.G., Hillard, M.A., Nathan, D.M. and Damiano, E.R. Multiday outpatient glycemic control in adolescents with type 1 diabetes using a bihormonal bionic pancreas: The barton center summer camp study. Diabetes 2014, 63, A62. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, R.W.; Riddlesworth, T.D.; Ruedy, K.; Ahmann, A.; Haller, S.; Kruger, D.; McGill, J.B.; Polonsky, W.; Price, D.; Aronoff, S.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettoretti, M.; Cappon, G.; Facchinetti, A.; Sparacino, G. Advanced diabetes management using artificial intelligence and continuous glucose monitoring sensors. Sensors (Switzerland) 2020, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagougui, S.; Taleb, N.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. The benefits and limits of technological advances in glucose management around physical activity in patients type 1 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2019, 10, 818. [Google Scholar]
- Von Dem Berge, T.; Biester, S.; Biester, T.; Buchmann, A.K.; Datz, N.; Grosser, U.; Kapitzke, K.; Klusmeier, B.; Remus, K.; Reschke, F.; et al. Recommendations for Diabetes Treatment with Systems for Automated Insulin Delivery. Diabetol. und Stoffwechsel 2022, 17, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.R. Nonadjunctive Use of Continuous Glucose Monitors for Insulin Dosing: Is It Safe? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed NA.; Aleppo G.; Aroda VR.; Bannuru RR.; Brown FM.; Bruemmer D.; Collins BS.; Hilliard ME.; Isaacs D.; Johnson EL.; Kahan S.; Khunti K.; Leon J.; Lyons SK.; Murdock L.; Perry ML.; Prahalad P.; Pratley RE.; Seley JJ.; Stanton RC.; Woodward CC.; Gabbay RA. on behalf of the American Diabetes Association. 17. Diabetes Advocacy: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S279-S280.
- https://www.diabetesnet.com/diabetes-technology/meters-monitors/compare-current-monitors/ accessed on March 14, 2023.
- Helton, K.L.; Ratner, B.D.; Wisniewski, N.A. Biomechanics of the sensor-tissue interface - Effects of motion, pressure, and design on sensor performance and foreign body response - Part II: Examples and application. In Proceedings of the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology; 2011; Vol. 5, pp. 647–656.
- Petrofsky, J.S.; McLellan, K.; Prowse, M.; Bains, G.; Berk, L.; Lee, S. The effect of body fat, aging, and diabetes on vertical and shear pressure in and under a waist belt and its effect on skin blood flow. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2010, 12, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardilouze, J.L.; Karpe, F.; Currie, J.M.; Frayn, K.N.; Fielding, B.A. Subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow varies between superior and inferior levels of the anterior abdominal wall. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, E.; Tamborlane, W. V. A tale of two compartments: Interstitial versus blood glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2009, 11, S11–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.L.; Schwartz, S.L.; Brazg, R.L.; Bugler, J.R.; Peyser, T. a; McGarraugh, G. V Accuracy of the 5-Day FreeStyle Navigator Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoss, U.; Budiman, E.S.; Liu, H.; Christiansen, M.P. Continuous glucose monitoring in the subcutaneous tissue over a 14-day sensor wear period. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borazan, A.; Binici, D.N. Relationship between insulin resistance and inflammation markers in hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerritsen, M.; Jansen, J.A.; Kros, A.; Vriezema, D.M.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Lutterman, J.A.; Van Hvell, S.W.F.M.; Van Der Gaag, A. Influence of inflammatory cells and serum on the performance of implantable glucose sensors. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.C.; Spokane, R.B.; Homan, M.M.; Sudan, R.; Miller, M. Long-term stability of electro-enzymatic glucose sensors implanted in mice. An update. ASAIO Trans. 1988, 34, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.diabetes.co.uk/news/2023/feb/non-invasive-blood-glucose-monitoring-wearable-launch-date-revealed.html accessed on March 14, 2023.
- Alsaleh, F.M.; Smith, F.J.; Keady, S.; Taylor, K.M.G. Insulin pumps: From inception to the present and toward the future. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkhadra, K.; Alahdab, F.; Tamhane, S.U.; McCoy, R.G.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections in individuals with type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 2017, 55, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.diabetes.co.uk/insulin-pumps/pros-cons-of-insulin-pumps.html, accessed on March 14, 2023.
- Kulzer, B.; Freckmann, G.; Heinemann, L.; Schnell, O.; Hinzmann, R.; Ziegler, R. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice Patch Pumps : What are the advantages for people with diabetes ? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 187, 109858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidan, T.; Nikkel, C.; Dziengelewski, B.; Wu, S.; Chen, A.M.H. Clinical Evaluation of Basal-Bolus Therapy Delivered by the V-Go® Wearable Insulin Delivery Device in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Analysis. Pharmacy 2020, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.; Cook, C.B. Insulin Pumping Patches: Emerging Insulin Delivery Systems. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Berget, C.; Messer, L.H.; Forlenza, G.P. A clinical overview of insulin pump therapy for the management of diabetes: Past, present, and future of intensive therapy. Diabetes Spectr. 2019, 32, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohar, S.L. Subcutaneous open-loop insulin delivery for type 1 diabetes: Paradigm Real-Time System. Issues Emerg. Health Technol. 2007, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mastrototaro, J.; Lee, S. The integrated MiniMed Paradigm real-time insulin pump and glucose monitoring system: Implications for improved patient outcomes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2009, 11, S37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Danne, T.; Kordonouri, O.; Holder, M.; Haberland, H.; Golembowski, S.; Remus, K.; Bläsig, S.; Wadien, T.; Zierow, S.; Hartmann, R.; et al. Prevention of hypoglycemia by using low glucose suspend function in sensor-augmented pump therapy. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergenstal, R.M.; Klonoff, D.C.; Garg, S.K.; Bode, B.W.; Meredith, M.; Slover, R.H.; Ahmann, A.J.; Welsh, J.B.; Lee, S.W.; Kaufman, F.R. Threshold-Based Insulin-Pump Interruption for Reduction of Hypoglycemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.B.; Nicholas, J.A.; Smith, G.J.; Fairchild, J.M.; King, B.R.; Ambler, G.R.; Cameron, F.J.; Davis, E.A.; Jones, T.W. Reduction in hypoglycemia with the predictive low-Glucose management system: A long-term randomized controlled trial in adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Forlenza, G.P.; Li, Z.; Buckingham, B.A.; Pinsker, J.E.; Cengiz, E.; Paul Wadwa, R.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Church, M.M.; Weinzimer, S.A.; Jost, E.; et al. Predictive low-glucose suspend reduces hypoglycemia in adults, adolescents, and children with type 1 diabetes in an at-home randomized crossover study: Results of the PROLOG trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughton, C.K.; Hovorka, R. New closed-loop insulin systems. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, X.L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhu, Z.G.; Qian, S.H.; Flewitt, A.J. Current and emerging technology for continuous glucose monitoring. Sensors (Switzerland) 2017, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Youssef, J.; Castle, J.; Ward, W.K. A review of closed-loop algorithms for glycemic control in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Algorithms 2009, 2, 518–532. [Google Scholar]
- Quiroz, G. The evolution of control algorithms in artificial Pancreas: A historical perspective. Annu. Rev. Control 2019, 48, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigersky, R.A.; Huang, S.; Cordero, T.L.; Shin, J.; Lee, S.W.; Chhabra, H.; Kaufman, F.R.; Cohen, O. Improved HBA1C, total daily insulin dose, and treatment satisfaction with insulin pump therapy compared to multiple daily insulin injections in patients with type 2 diabetes irrespective of baseline C-peptide levels. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Abuin, P.; Rivadeneira, P.S.; Ferramosca, A.; González, A.H. Artificial pancreas under stable pulsatile MPC: Improving the closed-loop performance. J. Process Control 2020, 92, 246–260. [Google Scholar]
- Incremona, G.P.; Messori, M.; Toffanin, C.; Cobelli, C.; Magni, L. Model predictive control with integral action for artificial Pancreas. Control Eng. Pract. 2018, 77, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Karpelyev, V.A.; Philippov, Y.I.; Averin, A. V.; Boyarskiy, M.D.; Gavrilov, D.A. Development and in silico validation of the pid-algorithm for the artificial Pancreas with intraperitoneal insulin delivery. Diabetes Mellit. 2018, 21, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Gregory, J.M.; Moore, L.M.; Williams, P.E.; Farmer, B.; Cherrington, A.D.; Lord, P.; Shelton, B.; Cohen, D.; Zisser, H.C.; et al. A new animal model of insulin-glucose dynamics in the intraperitoneal space enhances closed-loop control performance. J. Process Control 2019, 76, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, S.; Danisman, K. In silico testing of optimized Fuzzy P+D controller for artificial Pancreas. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ahmad, I.; Arif, H.; Ammara, U.E.; Majeed, A. Artificial pancreas control strategies used for type 1 diabetes control and treatment: A comprehensive analysis. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2020, 3, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Peyser, T.; Dassau, E.; Breton, M.; Skyler, J.S. The artificial Pancreas: Current status and future prospects in the management of diabetes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1311, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybrid Closed-Loop Insulin Delivery Systems for People with Type 1 Diabetes, available online at https://www.cadth.ca/hybrid-closed-loop-insulin-delivery-systems-people-type-1-diabetes, accessed on March 14, 2023.
- De Bock, M.; Dart, J.; Roy, A.; Davey, R.; Soon, W.; Berthold, C.; Retterath, A.; Grosman, B.; Kurtz, N.; Davis, E.; et al. Exploration of the Performance of a Hybrid Closed Loop Insulin Delivery Algorithm That Includes Insulin Delivery Limits Designed to Protect Against Hypoglycemia. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khatib, F.H.; Russell, S.J.; Magyar, K.L.; Sinha, M.; McKeon, K.; Nathan, D.M.; Damiano, E.R. Autonomous and continuous adaptation of a bihormonal bionic pancreas in adults and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhatib, F.; Buckingham, B.A.; Buse, J.B.; Harlan, D.M.; Magyar, K.; Ly, T.T.; Kirkman, M.S.; Malkani, S.; Thompson, M.J.; Lock, J.P.; et al. Home use of a bihormonal bionic pancreas vs. Conventional insulin pump therapy in adults with type 1 diabetes: A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. Diabetes 2016, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Rayannavar, A.; Mitteer, L.M.; Balliro, C.A.; El-Khatib, F.H.; Lord, K.L.; Hawkes, C.P.; Ballester, L.S.; Damiano, E.R.; Russell, S.J.; De Leon, D.D. The bihormonal bionic Pancreas improves glycemic control in individuals with hyperinsulinism and postpancreatectomy diabetes: A pilot study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2582–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.W.; Russell, S.J.; Damiano, E.R.; El-Khatib, F.H.; Ruedy, K.J.; Balliro, C.; Li, Z.; Calhoun, P. A Multicenter Randomized Trial Evaluating Fast-Acting Insulin Aspart in the Bionic Pancreas in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2022, 24, 681–696. [Google Scholar]
- Wszola, M.; Klak, M.; Kosowska, A.; Olkowska-Truchanowicz, J.; Tymicki, G.; Berman, A.; Bryniarski, T.; Kołodziejska, M.; Uchrynowska-Tyszkiewicz, I.; Kamiński, A. Bionic Pancreas: the first results of functionality bionic tissue model with pancreatic islets. Korean J. Transplant. 2021, 35, S44–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Balliro, C.; Sherwood, J.; Jafri, R.; Hillard, M.; Sullivan, M.; Greaux, E.; Selagamsetty, R.; El-Khatib, F.; Damiano, E. Home use of the iLet bionic Pancreas in the bihormonal configuration using glucagon versus the insulin-only configuration in adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, S97. [Google Scholar]
- NCT03565666 The Insulin-Only Bionic Pancreas Bridging Study 2018, available at https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03565666 , accessed on March 10, 2023. 10 March.
- Fisher, L.; Polonsky, W.H.; Hessler, D.M.; Masharani, U.; Blumer, I.; Peters, A.L.; Strycker, L.A.; Bowyer, V. Understanding the sources of diabetes distress in adults with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complications 2015, 29, 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Hessler, D.; Fisher, L.; Polonsky, W.; Johnson, N. Understanding the areas and correlates of diabetes-related distress in parents of teens with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2016, 41, 750–758. [Google Scholar]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Hessler, D.; Johnson, N. Emotional distress in the partners of type 1 diabetes adults: Worries about hypoglycemia and other key concerns. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Hessler, D.; Edelman, S. V. Development of a New Measure for Assessing Glucose Monitoring Device-Related Treatment Satisfaction and Quality of Life. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L.; Hessler, D.; Edelman, S. V. Development of a New Measure for Assessing Insulin Delivery Device Satisfaction in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, L.E.; Andersen, M.M.; Jensen, S.; Nørgaard, K.; Willaing, I. The effect of peer support in adults with insulin pump-treated type 1 diabetes: A pilot study of a flexible and participatory intervention. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2017, 11, 1879–1890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elian, V.; Musat, M.; Radulian, G.; Negoita, O. A model of efficiency on introducing technology in T1DM management process for patients with 30+year’s duration of diabetes - a single-center interventional study. Diabetes Technology and Therapeutics 2020, 22, A225–A225. [Google Scholar]
- Fanzola, V.; Riboni, S.; Cannalire, G.; Metti, M.; Bensi, G.; Granata, C.; Biasucci, G. The impact of new continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices versus self-management of blood glucose (SMBG) on the daily life of parents and children affected by type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2022, 11, e110111. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, S.R.; Clements, M.A. Psychological Reactions Associated with Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Youth. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, J.T.; Pratt, K.; Aggarwal, J.; Volkening, L.K.; Laffel, L.M.B. Psychosocial correlates of continuous glucose monitoring use in youth and adults with type 1 diabetes and parents of youth. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landau Z, Rachmiel M, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Boaz M, Bar-Dayan Y, Wainstein J, T.R. Parental sleep quality and continuous glucose monitoring system use in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2015, 17, S18–S19.
- Rusak, E.; Ogarek, N.; Wolicka, K.; Mrówka, A.; Seget, S.; Kuźnik, M.; Jarosz-Chobot, P. The quality of life and satisfaction with continuous glucose monitoring therapy in children under 7 years of age with T1D using the rTCGM system integrated with insulin pump—a caregivers point of view. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, W.H.; Hessler, D.; Ruedy, K.J.; Beck, R.W. The impact of continuous glucose monitoring on markers of quality of life in adults with type 1 diabetes: Further findings from the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlenza, G.P.; Messer, L.H.; Berget, C.; Wadwa, R.P.; Driscoll, K.A. Biopsychosocial Factors Associated With Satisfaction and Sustained Use of Artificial Pancreas Technology and Its Components: a Call to the Technology Field. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissberg-Benchell, J.; Hessler, D.; Polonsky, W.H.; Fisher, L. Psychosocial Impact of the Bionic Pancreas during Summer Camp. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 840–844. [Google Scholar]
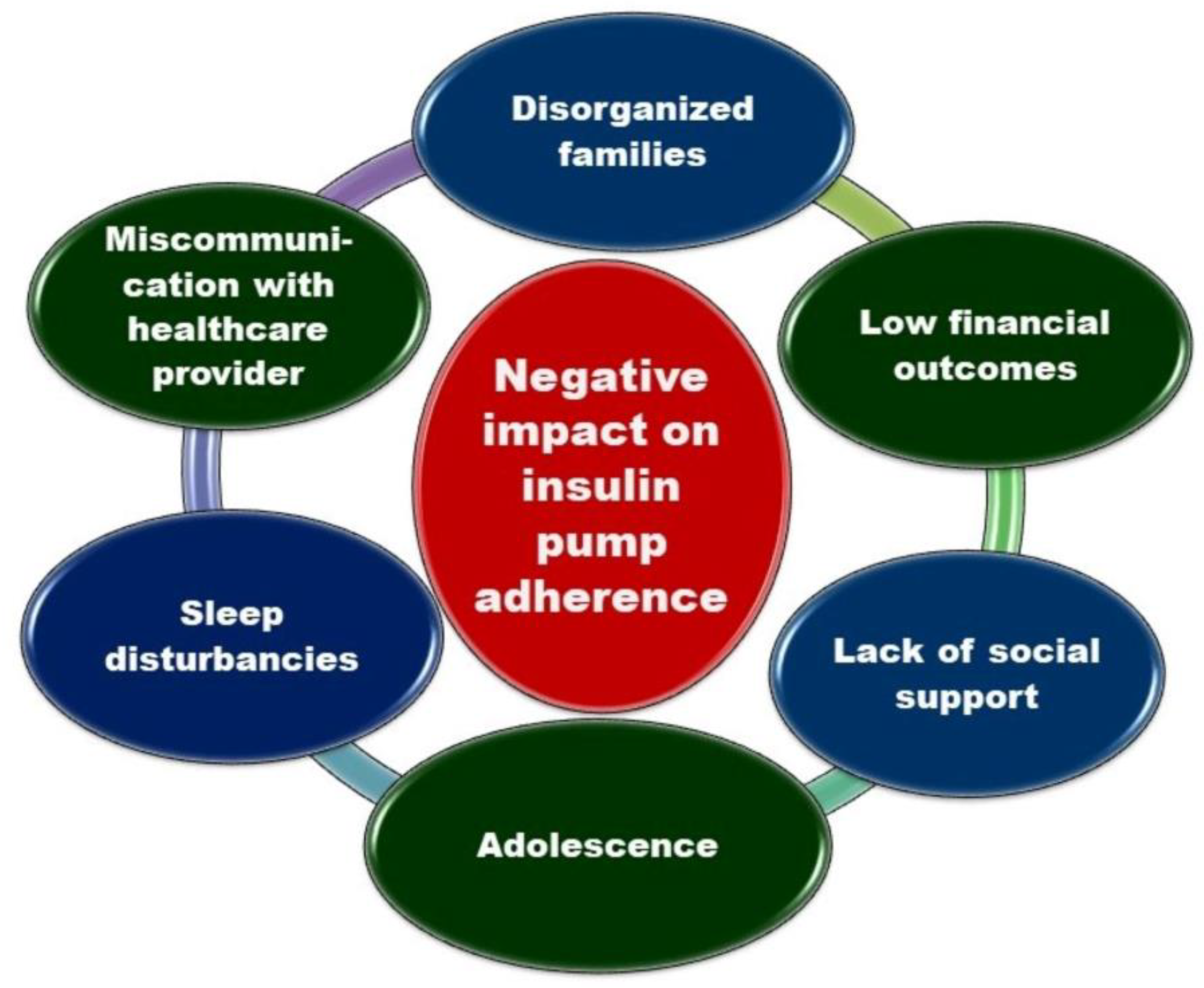
- Vidal Florc, M.; Jansà Morató, M.; Galindo Rubio, M.; Penalba Martínez, M. Factors associated to adherence to blood glucose self-monitoring in patients with diabetes treated with insulin. The dapa study. Endocrinol. Diabetes y Nutr. 2018, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Peralta, F.; Menéndez, E.; Conde, S.; Conget, I.; Novials, A. Clinical characteristics and management of type 1 diabetes in Spain. The SED1 study. Endocrinol. Diabetes y Nutr. 2021, 68, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaans, E.A.J.M.; Kleefstra, N.; Groenier, K.H.; Bilo, H.J.G.; Brand, P.L.P. Adherence to insulin pump treatment declines with increasing age in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 2020, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giani, E.; Snelgrove, R.; Volkening, L.K.; Laffel, L.M. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Adherence in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes: Associations with Biomedical and Psychosocial Variables. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafir, L.M.; Moisa, S.M.; Vlaiculescu, M.V.; Butnariu, L.I.; Boca, L.O.; Constantin, M.M.L.; Lupu, P.M.; Brinza, C.; Temneanu, O.R.; Burlacu, A. Insulin Pump Therapy Efficacy and Key Factors Influencing Adherence in Pediatric Population-A Narrative Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022, 58, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, M.; Cooper, M.; Retterath, A.; Nicholas, J.; Ly, T.; Jones, T.; Davis, E. Continuous Glucose Monitoring Adherence: Lessons from a Clinical Trial to Predict Outpatient Behavior. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanenbaum, M.L.; Adams, R.N.; Hanes, S.J.; Barley, R.C.; Miller, K.M.; Mulvaney, S.A.; Hood, K.K. Optimal Use of Diabetes Devices: Clinician Perspectives on Barriers and Adherence to Device Use. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, A. IDF21-0043 Technology Trio: Continuous Glucose Monitoring, Telehealth, and Electronic Messaging for Insulin-Treated Patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 186, 109605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, D.C.; Barry, S.; Wagner, D. V.; Speight, J.; Choudhary, P.; Harris, M.A. Distal technologies and type 1 diabetes management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Jung, I.; Park, C.Y. Current advances of artificial pancreas systems: A comprehensive review of the clinical evidence. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 813–839. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Varughese, B.; Li, Z.; Kushner, P.R. Healthcare resource waste associated with patient nonadherence and early discontinuation of traditional continuous glucose monitoring in real-world settings: A multicountry analysis. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2018, 20, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravaine, V.; Ancla, C.; Catargi, B. Chemically controlled closed-loop insulin delivery. J. Control. Release 2008, 132, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpatti, L.R.; Matranga, M.A.; Cortinas, A.B.; Delcassian, D.; Daniel, K.B.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Glucose-Responsive Nanoparticles for Rapid and Extended Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; He, J.; Bai, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.M.; Zhang, W. Engineering synthetic artificial pancreas using chitosan hydrogels integrated with glucose-responsive microspheres for insulin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Bioartificial Organ Manufacturing Technologies. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Parvaneh, S.; Kemény, L.; Ghaffarinia, A.; Yarani, R.; Veréb, Z. Three-dimensional bioprinting of functional β-islet-like constructs. Int. J. Bioprinting 2022, 9, 256–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Dexcom G6 | Guardian 3 | Libre 2 | Eversense E3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer [77] | DexCom, Inc, San Diego, California, USA | Medtronic, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA |
Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, Illinois, USA |
Senseonics Holdings, Maryland, USA |
| FDA Approval [77] | March 2018 | September 2016 | September 2017 | February 2022 |
| Users [77] | Adults and children over 2 years | Adults and children over 7 years | Adults and children over 4 years | Adults over 18 years |
| Days of Sensor Wear (RT) [77] | 10 | 7 | 14 | 180 |
| Sensing molecule [77] |
Glucose-oxidase | Glucose-oxidase | Glucose-oxidase | Boronic-acid derivative |
| Technique Category [77] |
Electrochemical | Electrochemical | Electrochemical | Optique |
| Components [77] | Sensor, transmitter, app | Sensor, Transmitter, app |
Sensor, reader |
Sensor, Transmitter, app, insertion tool |
| Sensor size [77] | Unavailable | 9.5 mm long | Height: 5 mmDiameter: 35 mm | 15 mm long |
| Approved areas of sure [77] | 2-13 years - abdomen and buttocks over 14 years – abdomen and arm |
Abdomen, buttocks, and upper arm |
Back of upper arm |
Upper arm |
| Accuracy (MARD%) [77] |
9% | 10.55% | 9.7% | 8.5% |
| Daily calibration Frequency [77] |
0 (factory calibration) |
2-4 | 0 (factory calibration) |
2 (at 12 h) |
| Integration with an insulin pump [77] | Tandem t:slim Control-IQ (and older Basal-IQ) | Medtronic MiniMed 740G, 780G etc. | No | No |
| Cost [92] | - Transmitter: $300 / 3 months. - Sensors: $420 for 1 month supply. - Receiver: $380 (it is unnecessary if the patient uses a smartphone application). |
- Rechargeable Transmitter: $1100 (12 months warranty, or longer). - Sensors: $450 for a set with 5 sensors (35-day supply). |
- Sensors: $135 for 1 month (28 days supply). - Reader: $175 (it is not necessary if the patient has a smartphone application). |
- $1400 for the Sensor, Transmitter, and supplies, - In addition, the price of insertion in the doctor’s office. - Limited time Eversense Bridge program globally diminishes the price to $99 plus insertion’s cost. |
| Smartphone integration [92] | Android, iOs, Apple Watch |
Android, iOs |
Android, iOs |
Android, iOs, Apple Watch |
| Data-sharing [92] |
≤ 10 people | ≤ 4 people | ≤ 20 people | ≤ 5 people |
| A separate receiver is available [92] | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Water Resistance [92] | 2.75 m, ≥ 24 hours | 2.5 m, 10 min | 1 m, 30 min | 1 m, 30 min |
| Skin complications | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Insulin Pump Therapy Benefits | Insulin Pump Therapy Limits |
|---|---|
| Better diabetes control. Fewer injections. |
The need to understand the functioning and proper management of the device. |
| Improved quality of life. | High costs, if not covered by the insurance company. |
| The flexibility of basal insulin delivery during the day and night. The flexibility of food intake and exercises. |
A device that should be worn on the body with tubing that can be caught on objects. |
| Diminished risk of hypoglycemia. | Skin allergies or infections. |
| Diminished risk of complications. | Multiple alerts. |
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| The devices are tubeless, without request for an insulin infusion system | Waste of insulin when PPs are replaced |
| The needle could be automatically inserted; thus, their application could be less painful. | The infusion place is poorly visible, and regular inspection is complex. |
| The needle is not visible. More convenient than conventional pumps in numerous activities (showering, swimming, sweating or making exercises). |
The accuracy of insulin delivery of some PPs is often lower than that of conventional pumps, particularly at low basal doses. |
| Smaller and lighter than conventional pumps. PPs can be attached to various body parts and discreetly carried, offering more effortless movement. Technical properties are often specifically adapted to T1DM patients’ needs. Simple education and training are requested for their use. |
Its have a poor ecological balance due to waste from plastic material and batteries. Risk of infections. |
| Diminished price if certain PPs compared to conventional pumps. | Higher price than MDI. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





