Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular docking preparation
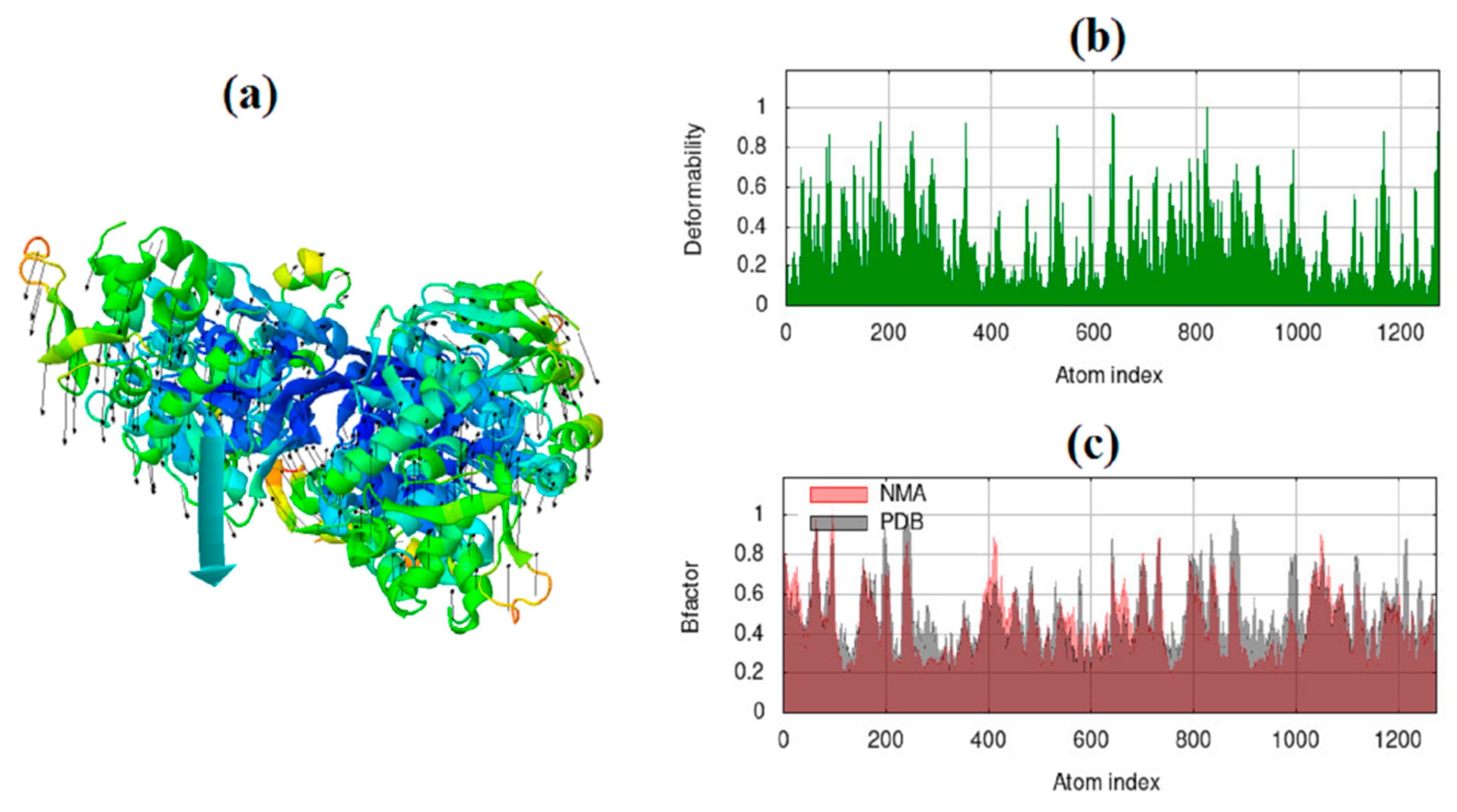
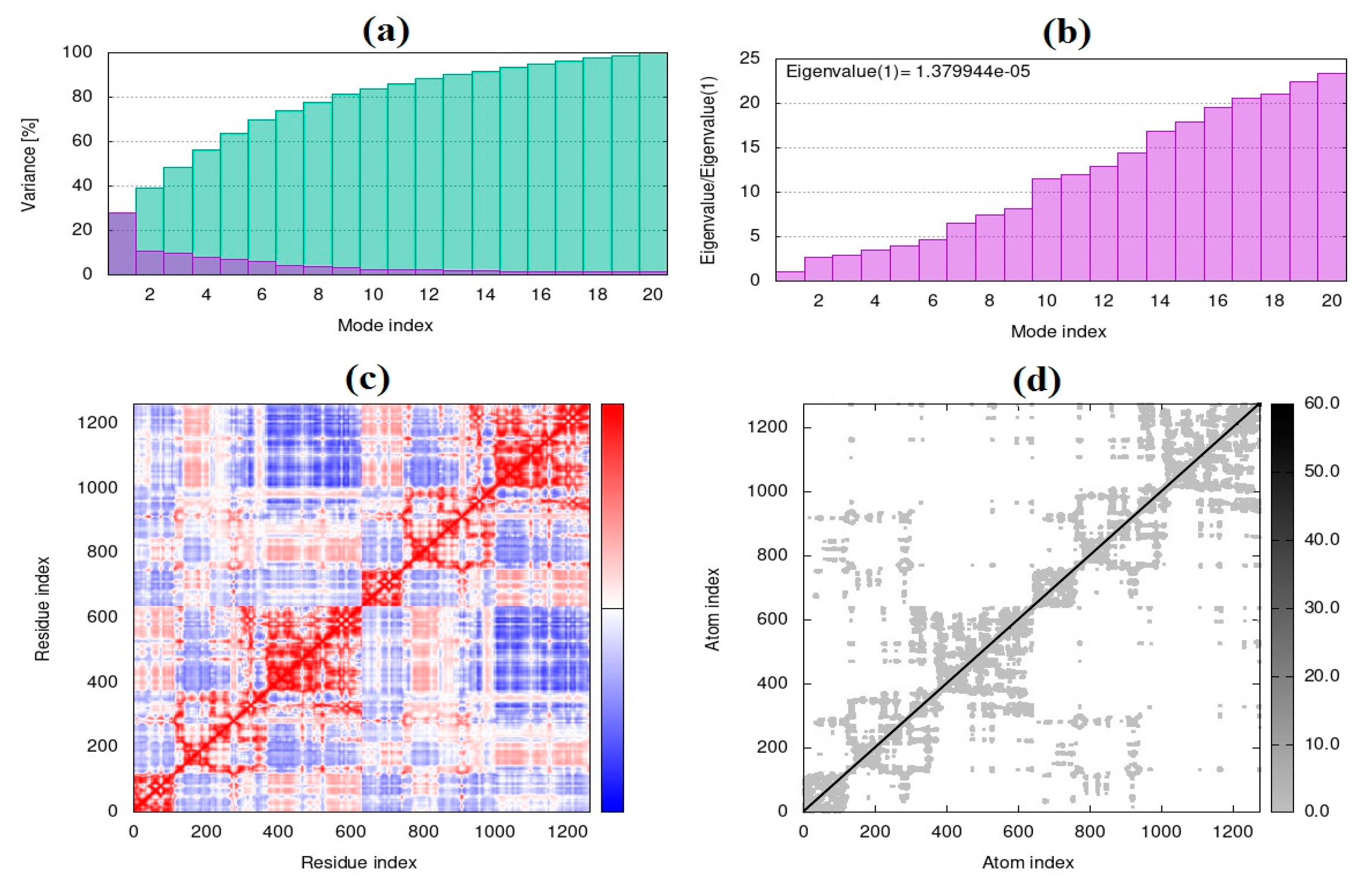
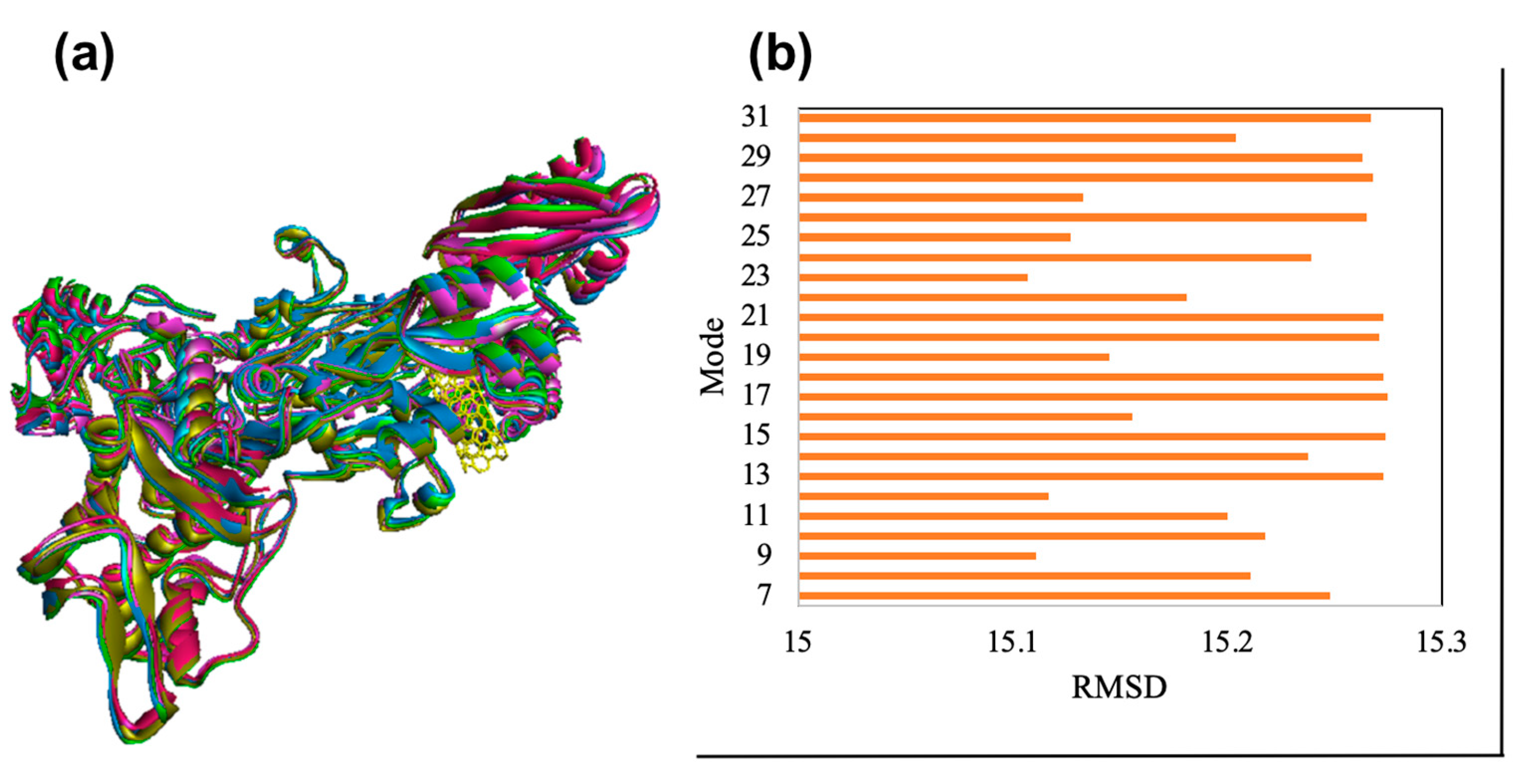
2.2. The normal mode analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular docking
3.2. The normal mode analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amraei, S.; Eslami, G.; Taherpour, A.; Hashemi, A. , Relationship between MOX genes and antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in nosocomial infections. Micro Nano Bio Aspects 2022, 1, (2), 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Amraei, S.; Eslami, G.; Taherpour, A.; Hashemi, A. , The role of ACT and FOX genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from hospitalized patients. Micro Nano Bio Aspects 2022, 1, (2), 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Amraei, S.; Ahmadi, S. , Recent studies on antimicrobial and anticancer activities of saponins: a mini-review. Nano Micro Biosystems 2022, 1, (1), 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, M.; Jabari, E.; Jabbari, E. , Functionalized carbon-based nanomaterials and quantum dots with antibacterial activity: a review. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, (1), 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riha, S. M.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M. B. , Synergistic Effect of Biomaterial and Stem Cell for Skin Tissue Engineering in Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Concise Review. Polymers 2021, 13, (10), 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J. J.; Im, H.; Kim, S. H.; Park, J. W.; Jung, Y. , Toward Biomimetic Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: 3D Printing Techniques in Regenerative Medicine. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Libanori, A.; Jiang, X.; Xu, W.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Q.; Sun, W.; Khademhosseini, A. , Multi-Dimensional Printing for Bone Tissue Engineering. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2021, 10, (11), 2001986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrubudin, N.; Lee, T. C.; Ramlan, R. , An Overview on 3D Printing Technology: Technological, Materials, and Applications. Procedia Manufacturing 2019, 35, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-Q.; Yang, J.-H.; Ding, X.; Ding, X.; Duan, S.; Xu, F.-J. , Polycaprolactone/polysaccharide functional composites for low-temperature fused deposition modelling. Bioactive Materials 2020, 5, (2), 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserfall, F.; Hendrich, N.; Ahlers, D.; Zhang, J. , Topology-aware routing of 3D-printed circuits. Additive Manufacturing 2020, 36, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Pan, H.; Su, Y.; Fang, D.; Qiao, S.; Ding, P.; Pan, W. , Opportunities and challenges of three-dimensional printing technology in pharmaceutical formulation development. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2021, 11, (8), 2488–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshana, B.; Jani, U.; Patel, A. , Influence of Bending Angle on Mechanical Performance of SWCNTs and DWCNTs Based on Molecular Mechanics: FE Approach. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies 2022.
- Nadeem, M. F.; Azeem, M.; Farman, I. , Comparative study of topological indices for capped and uncapped carbon nanotubes. Polycyc. Aromatic Compounds 2022, 42, (7), 4666–4683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Ruan, J.; Wu, Z.; Qian, J.; Yin, J. , Direct 3D printing of a tough hydrogel incorporated with carbon nanotubes for bone regeneration. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2019, 7, (45), 7207–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, S.; Peng, J.; Chen, A.; Nie, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, K. , Engineering gelatin-based alginate/carbon nanotubes blend bioink for direct 3D printing of vessel constructs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Kourinou, M.; Velidakis, E.; Mountakis, N.; Fischer-Griffiths, P. E.; Grammatikos, S.; Tzounis, L. , Additive manufacturing of multifunctional polylactic acid (PLA)—multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) nanocomposites. Nanocomposites 2021, 7, (1), 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Pinault, M.; Pfefferle, L. D.; Elimelech, M. , Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Exhibit Strong Antimicrobial Activity. Langmuir 2007, 23, (17), 8670–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Shi, G.; Wu, S.; Mo, J.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y. , Application of Fullerenes as Photosensitizers for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, S. M.; Abd El-Baky, R. M.; Abourehab, M. A. S.; Fadl, G. F. M.; Gamil, N. G. F. M. , Prevalence of Quorum Sensing and Virulence Factor Genes Among Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Patients Suffering from Different Infections and Their Association with Antimicrobial Resistance. Infection and drug resistance 2023, 16, 2371–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Gupta, R. K.; Harjai, K. , Multiple virulence factors regulated by quorum sensing may help in establishment and colonisation of urinary tract by Pseudomonas aeruginosa during experimental urinary tract infection. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 31, (1), 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seilie, E. S.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. , Staphylococcus aureus pore-forming toxins: The interface of pathogen and host complexity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishovitz, J.; Hermoso, J. A.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. , Penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. IUBMB life 2014, 66, (8), 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, V.; Okon, B. P.; Satsangi, A. T.; Das, S.; Waturuocha, U. W.; Vashist, A.; Clark-Curtiss, J. E.; Saini, D. K. , Mycobacterium tuberculosis PknK Substrate Profiling Reveals Essential Transcription Terminator Protein Rho and Two-Component Response Regulators PrrA and MtrA as Novel Targets for Phosphorylation. Microbiology Spectrum 2022, 10, (2), e01354–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsbers, A.; Vinciauskaite, V.; Siroy, A.; Gao, Y.; Tria, G.; Mathew, A.; Sánchez-Puig, N.; López-Iglesias, C.; Peters, P. J.; Ravelli, R. B. G. , Priming mycobacterial ESX-secreted protein B to form a channel-like structure. Current research in structural biology 2021, 3, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, A. N. , Emerging agents of gastroenteritis: Aeromonas, Plesiomonas, and the diarrheagenic pathotypes of Escherichia coli. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, (3), 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johura, F.-T.; Parveen, R.; Islam, A.; Sadique, A.; Rahim, M. N.; Monira, S.; Khan, A. R.; Ahsan, S.; Ohnishi, M.; Watanabe, H.; Chakraborty, S.; George, C. M.; Cravioto, A.; Navarro, A.; Hasan, B.; Alam, M. , Occurrence of Hybrid Escherichia coli Strains Carrying Shiga Toxin and Heat-Stable Toxin in Livestock of Bangladesh. Frontiers in Public Health 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Chen, C.; Lei, X.; Zhao, J.; Liang, J. , CASTp 3. 0: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, (W1), W363–W367. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, K.; Shin, H.; Cho, M. , Multiscale modeling of mechanical behaviors of Nano-SiC/epoxy nanocomposites with modified interphase model: Effect of nanoparticle clustering. Composites Sci. Technol. 2021, 203, 108572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A. J. , AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, (2), 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Blanco, J. R.; Aliaga, J. I.; Quintana-Ortí, E. S.; Chacón, P. , iMODS: internal coordinates normal mode analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, (Web Server issue), W271–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopéz-Blanco, J. R.; Garzón, J. I.; Chacón, P. , iMod: multipurpose normal mode analysis in internal coordinates. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, (20), 2843–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, J. A.; Chacón, P.; Abagyan, R. , Predictions of protein flexibility: first-order measures. Proteins 2004, 56, (4), 661–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Bhakta, S.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, A. R.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.-S.; Chakraborty, C. , A Novel Multi-Epitopic Peptide Vaccine Candidate Against Helicobacter pylori: In-Silico Identification, Design, Cloning and Validation Through Molecular Dynamics. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2021, 27, (2), 1149–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhre, K.; Sanejouand, Y.-H. , ElNémo: a normal mode web server for protein movement analysis and the generation of templates for molecular replacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, (suppl_2), W610–W614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Banerjee, M.; Mukherjee, A. , In silico designing of a novel polyvalent multi-subunit peptide vaccine leveraging cross-immunity against human visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis: an immunoinformatics-based approach. J. Mol. Model. 2023, 29, (4), 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J. A.; Pavlović, J.; Bauerová-Hlinková, V. , Normal Mode Analysis as a Routine Part of a Structural Investigation. In Molecules, 2019; Vol. 24.
- Al-Karmalawy, A. A.; Alnajjar, R.; Dahab, M.; Metwaly, A.; Eissa, I. , Molecular docking and dynamics simulations reveal the potential of anti-HCV drugs to inhibit COVID-19 main protease. Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021, 27, (Covid 19)–S109–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhou, C.; Pu, Q.; Deng, X.; Lan, L.; Liang, H.; Song, X.; Wu, M. , Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2022, 7, (1), 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Platig, J.; Cheng, T.-Y.; Ahmed, S.; Skaf, Y.; Potluri, L.-P.; Schwartz, D.; Steen, H.; Moody, D. B.; Husson, R. N. , Protein kinases PknA and PknB independently and coordinately regulate essential Mycobacterium tuberculosis physiologies and antimicrobial susceptibility. PLoS Path. 2020, 16, (4), e1008452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupetic, J.; Peñaloza, H. F.; Bain, W.; Hulver, M.; Mettus, R.; Jorth, P.; Doi, Y.; Bomberger, J.; Pilewski, J.; Nouraie, M.; Lee, J. S. , Elastase Activity From Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Isolates and ICU Mortality. Chest 2021, 160, (5), 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, J.; Harjai, K.; Chhibber, S. , Revisiting the virulence hallmarks of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a chronicle through the perspective of quorum sensing. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, (6), 2630–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacius, A.; Goldmann, O.; Floess, S.; Holtfreter, S.; Robert, P. A.; Nordengrün, M.; Kruse, F.; Lochner, M.; Falk, C. S.; Schmitz, I.; Bröker, B. M.; Medina, E.; Huehn, J. , Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Limits Type 1 While Fostering Type 3 Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramstad, S. N.; Wasteson, Y.; Lindstedt, B.-A.; Taxt, A. M.; Bjørnholt, J. V.; Brandal, L. T.; Bohlin, J. , Characterization of Shiga Toxin 2a Encoding Bacteriophages Isolated From High-Virulent O145:H25 Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skariyachan, S.; Parveen, A.; Garka, S. , Nanoparticle Fullerene (C60) demonstrated stable binding with antibacterial potential towards probable targets of drug resistant Salmonella typhi – a computational perspective and in vitro investigation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, (16), 3449–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, L.; Rasulev, B.; Turabekova, M.; Leszczynska, D.; Leszczynski, J. , Receptor- and ligand-based study of fullerene analogues: comprehensive computational approach including quantum-chemical, QSAR and molecular docking simulations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, (35), 5798–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, D.; Skariyachan, S.; Melappa, G. , Chapter 8 - Molecular interaction modeling of carbon nanotubes and fullerene toward prioritized targets of SARS-CoV-2 by computer-aided screening and docking studies. In Functionalized Carbon Nanomaterials for Theranostic Applications, Mallakpour, S.; Hussain, C. M., Eds. Elsevier: 2023; pp 157-179.
- Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, M.; Gomes, L. C.; Mergulhão, F. J. , Antimicrobial and anti-adhesive properties of carbon nanotube-based surfaces for medical applications: a systematic review. iScience 2021, 24, (1), 102001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardini, H. Z.; Amiri, A.; Shanbedi, M.; Maghrebi, M.; Baniadam, M. , Enhanced antibacterial activity of amino acids-functionalized multi walled carbon nanotubes by a simple method. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V. K.; McDonald, T. J.; Kim, H.; Garg, V. K. , Magnetic graphene–carbon nanotube iron nanocomposites as adsorbents and antibacterial agents for water purification. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 225, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Ma, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C. , Bioinspired and biocompatible carbon nanotube-Ag nanohybrid coatings for robust antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, M.; Tahghighi, A.; Rohani, M.; Hekmati, M.; Ahmadian, M.; Ahmadvand, H. , Robust antibacterial activity of functionalized carbon nanotube- levofloxacine conjugate based on in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, (1), 10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Hamblin, M. R. , Interaction of copper oxide nanoparticles with bacterial nucleic acids: a mini-review. Micro Nano Bio Aspects 2023, 2, (1), 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Aljelehawy, Q.; Maroufi, Y.; Javid, H.; Mohammadi, M. R.; Raji Mal Allah, O.; Taheri, S. V.; Mohammadzade, H. , Anticancer, antineurodegenerative, antimicrobial, and antidiabetic activities of carvacrol: recent advances and limitations for effective formulations. Nano Micro Biosystems 2023, 2, (1), 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kostarelos, K.; Lacerda, L.; Pastorin, G.; Wu, W.; Wieckowski, S.; Luangsivilay, J.; Godefroy, S.; Pantarotto, D.; Briand, J.-P.; Muller, S.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A. , Cellular uptake of functionalized carbon nanotubes is independent of functional group and cell type. Nature Nanotechnology 2007, 2, (2), 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Ouyang, P.; Shi, M.; Li, Q.; Maimaiti, T.; Lan, S.; Yang, S.-T.; Chang, X.-L. , Surface modification mediates the interaction between fullerene and lysozyme: Protein structure and antibacterial activity. Environmental Science: Nano 2021, 8, (1), 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed Ansari, M.; Soltani, A.; Ramezanitaghartapeh, M.; Singla, P.; Aghaei, M.; Khandan Fadafan, H.; Ardalan Khales, S.; Shariati, M.; Shirzad-Aski, H.; Balakheyli, H.; Sarim Imam, S.; Zafar, A. , Improved antibacterial activity of sulfasalazine loaded fullerene derivative: computational and experimental studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 348, 118083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Pineda, C.; Srirussamee, K.; Palma, P.; Fuenzalida, V. M.; Cartmell, S. H.; Palza, H. , Electroactive 3D Printed Scaffolds Based on Percolated Composites of Polycaprolactone with Thermally Reduced Graphene Oxide for Antibacterial and Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, (3), 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Velidakis, E.; Tzounis, L.; Mountakis, N.; Boura, O.; Grammatikos, S. A. , Multi-functional polyamide 12 (PA12)/ multiwall carbon nanotube 3D printed nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties. Adv. Compos. Mater 2022, 31, (6), 630–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
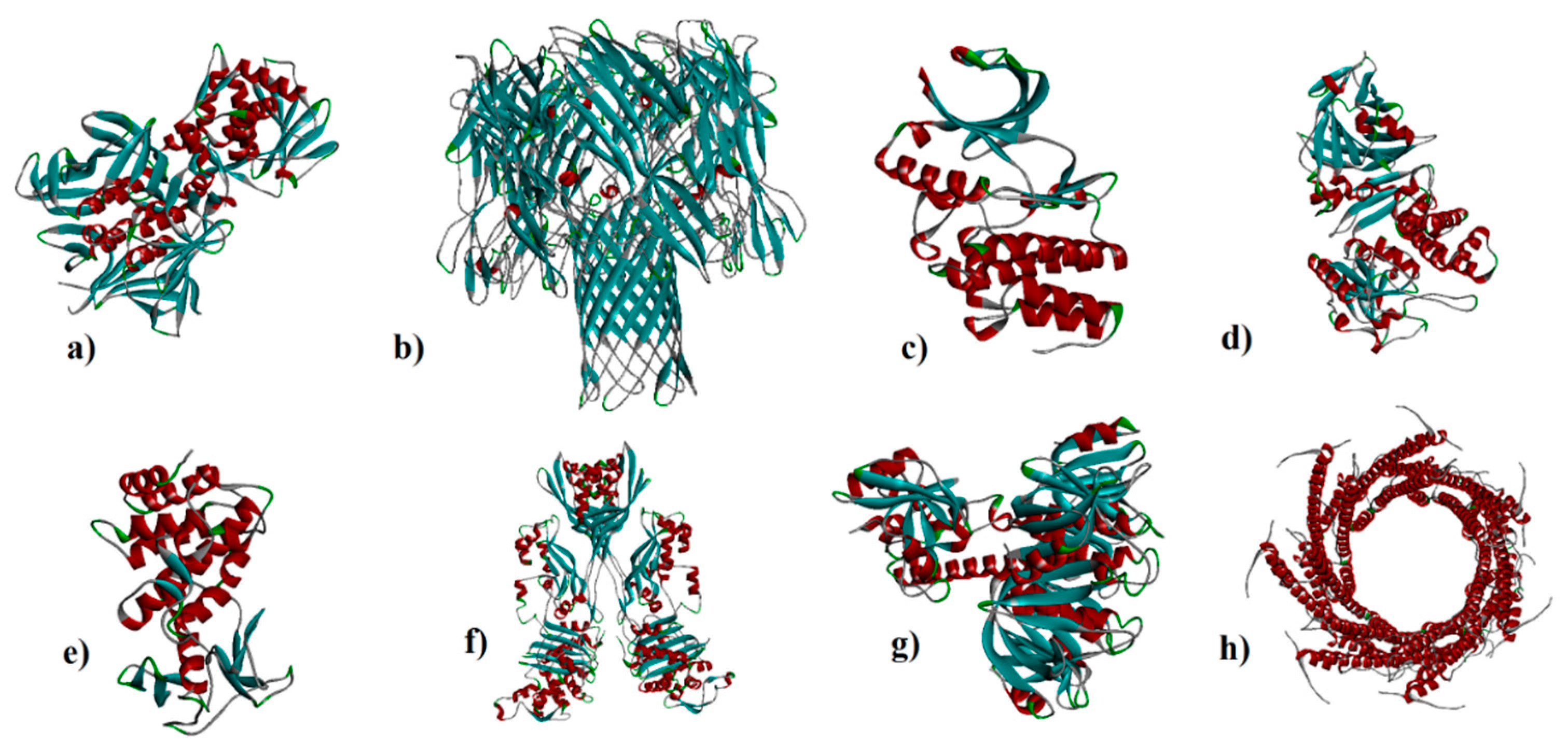
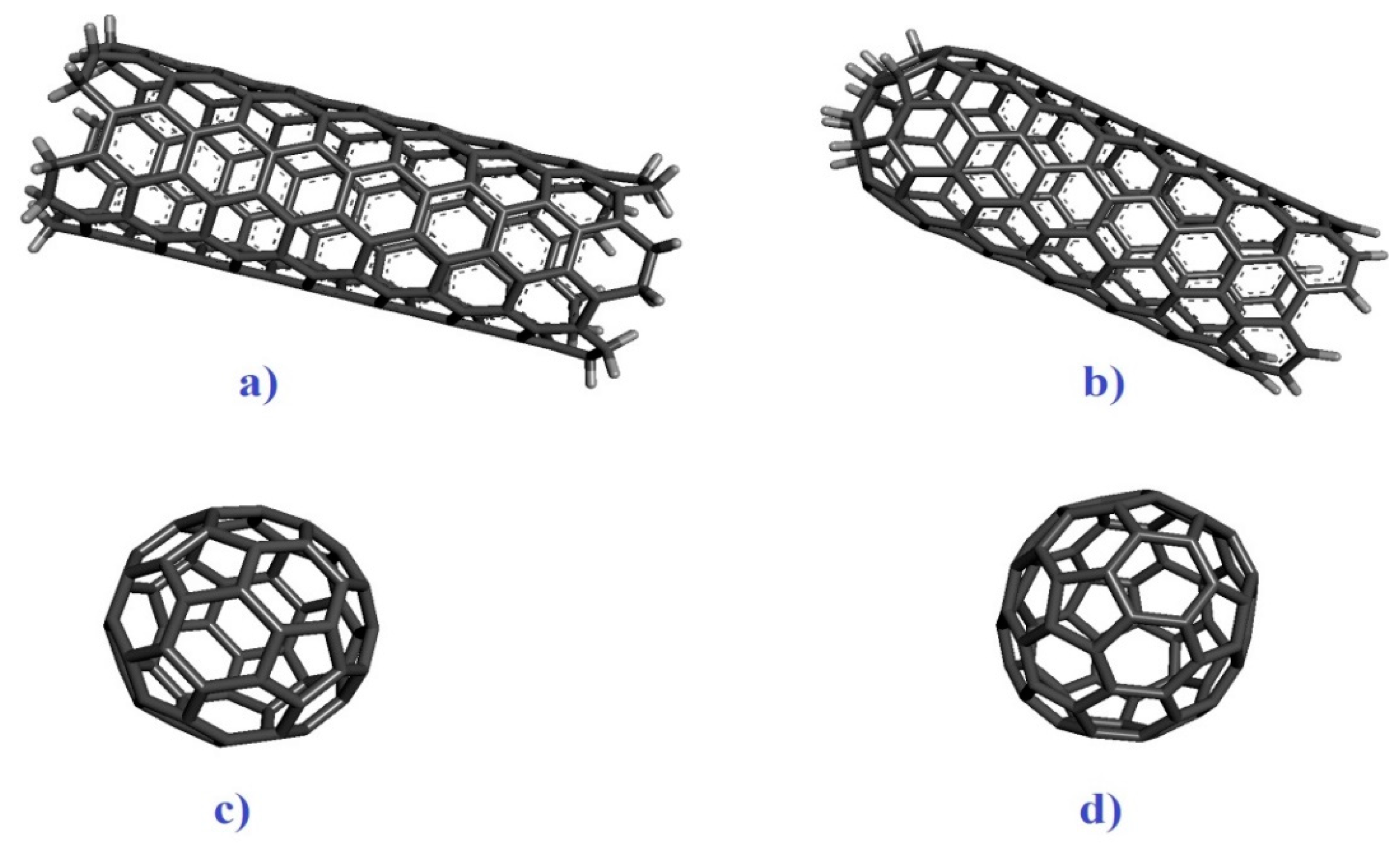
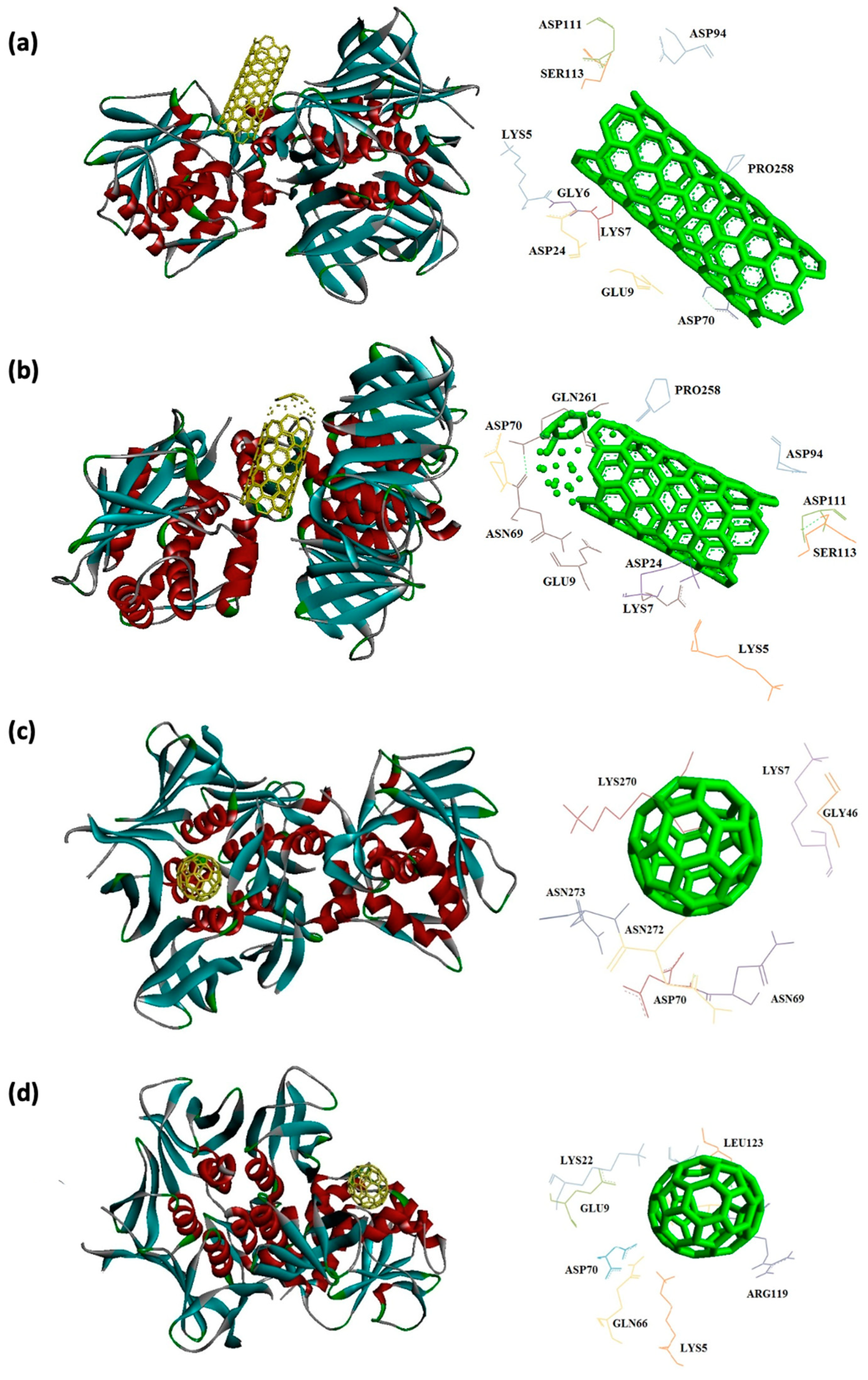
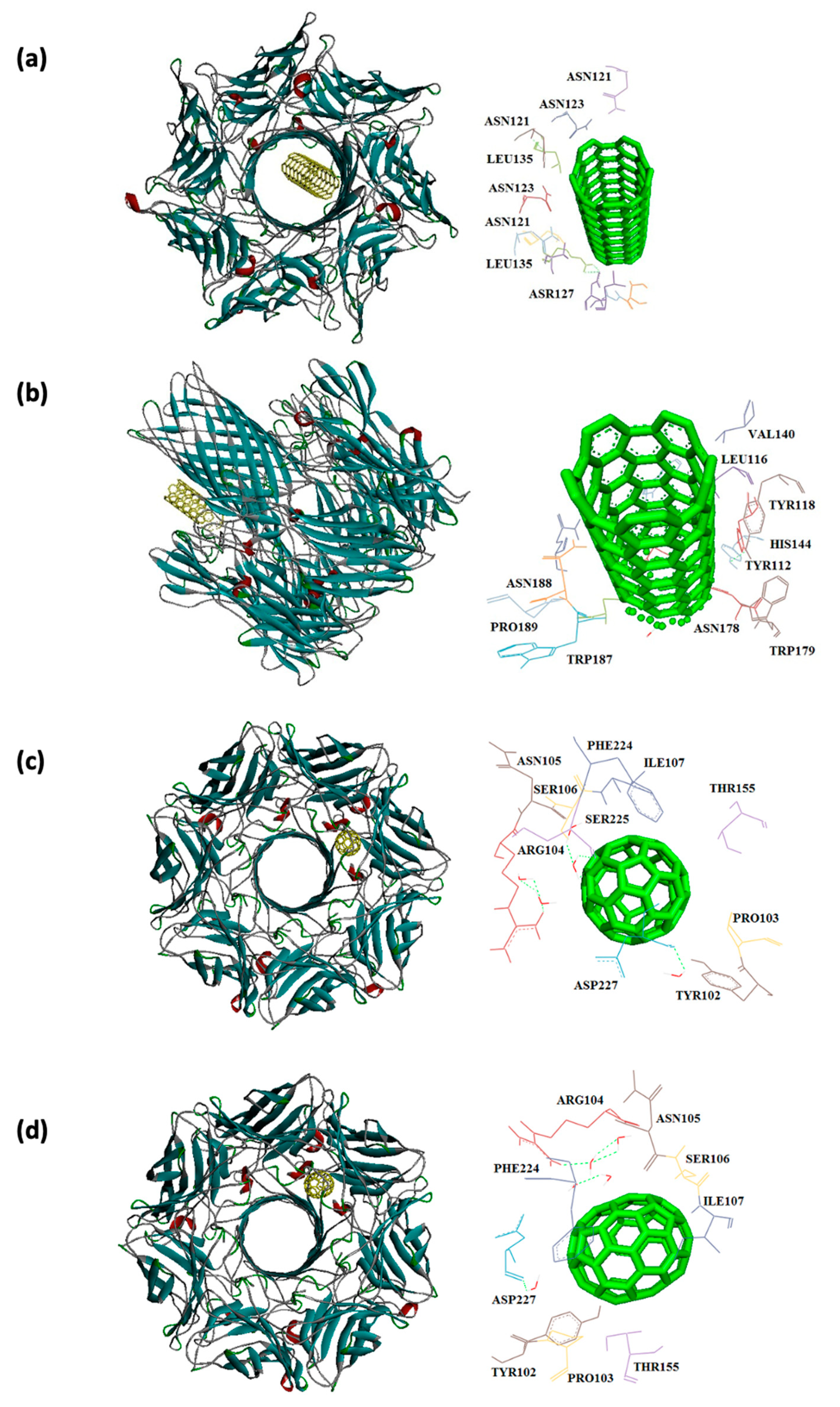
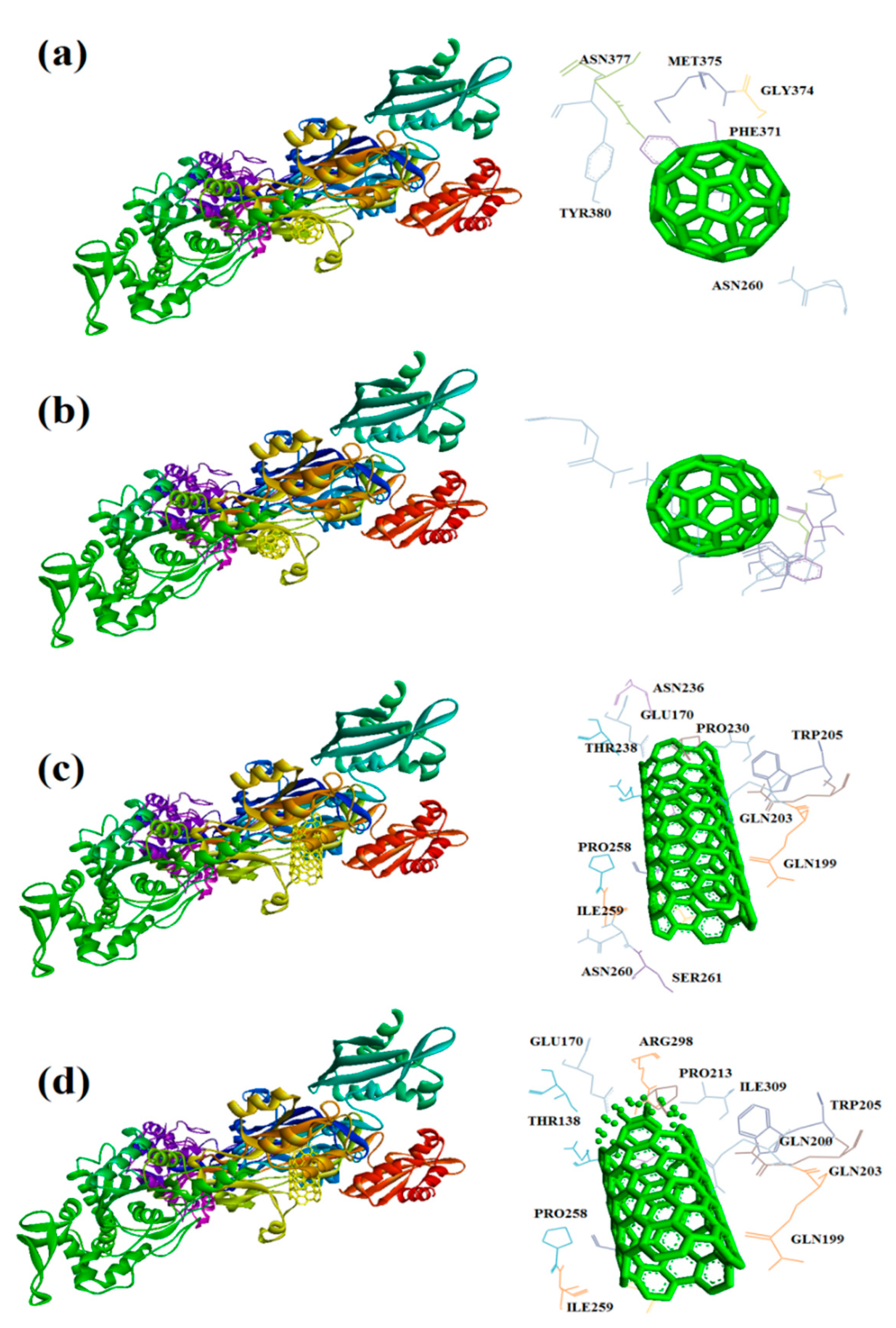
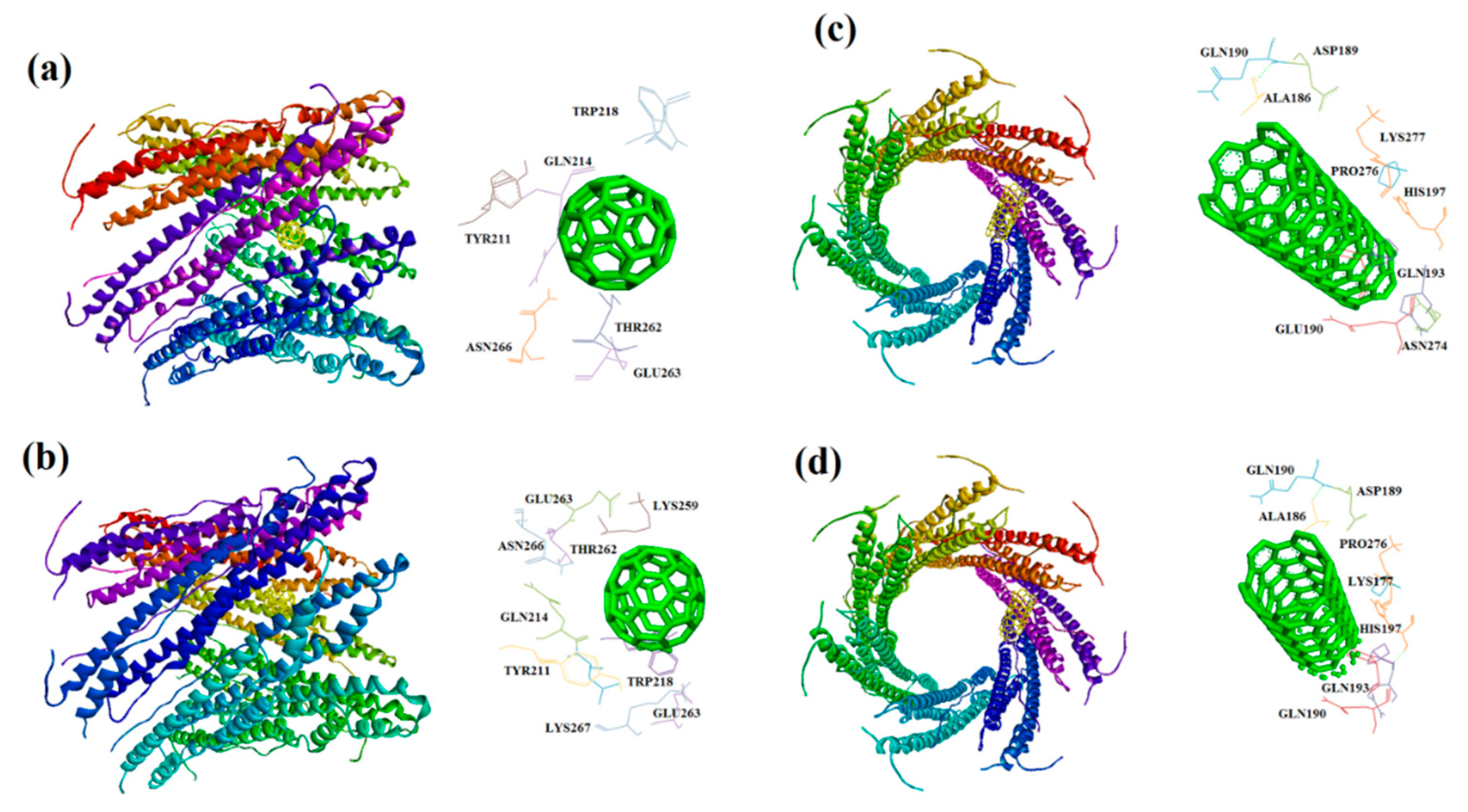
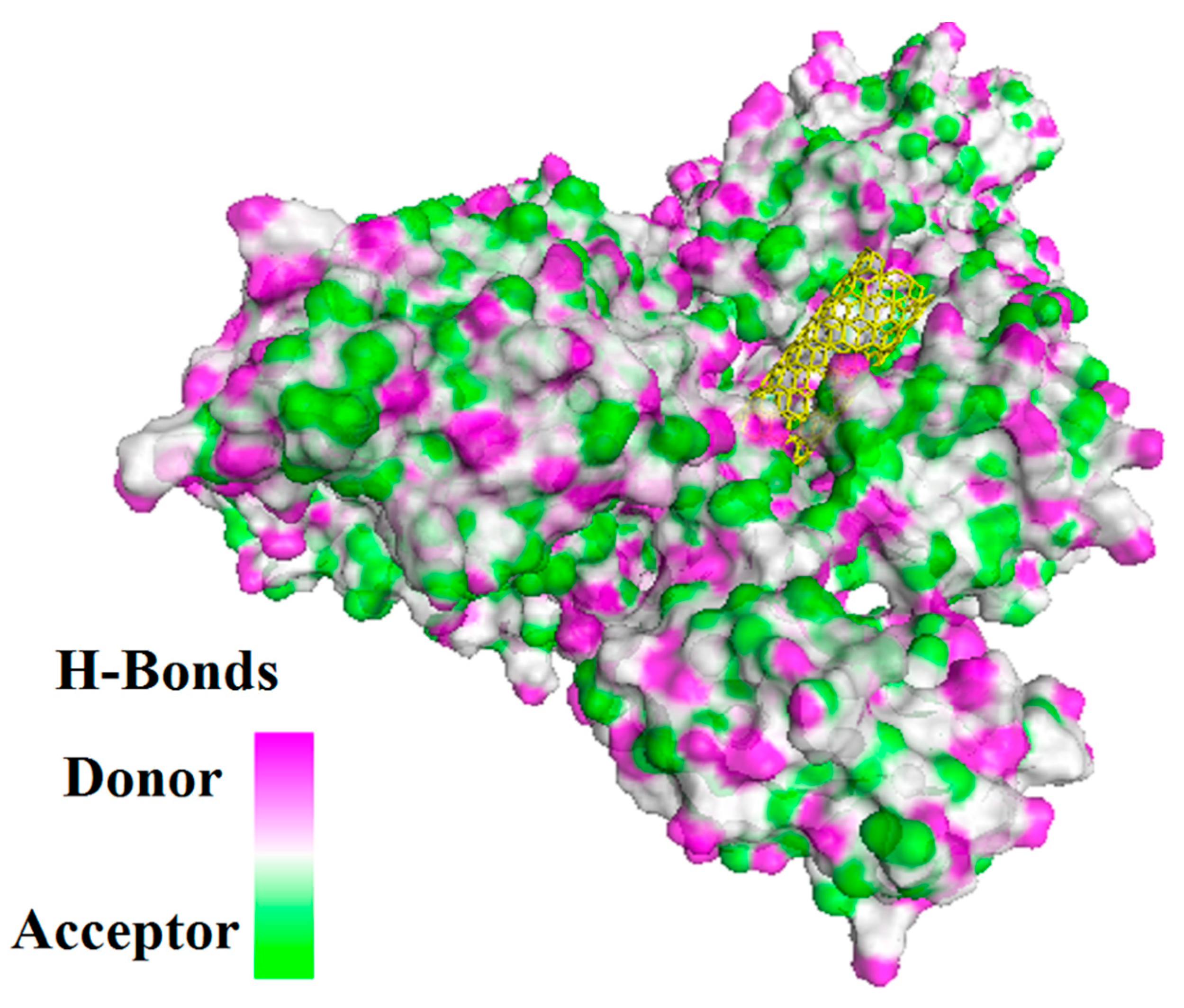
| Receptors | Binding affinity for CNT |
Interacting amino acids |
Binding affinity for capped CNT |
Interacting amino acids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7D6Q | -14.4 | ASP94, ASP111, SER113, PRO258, ASP70, LYS5, GLY6, LYS7, GLU9, and ASP24 | -16.1 | ASP94, ASP111, SER113, PRO258, GLN261, ASN69, ASP70, LYS5, LYS7, GLU9, and ASP24 |
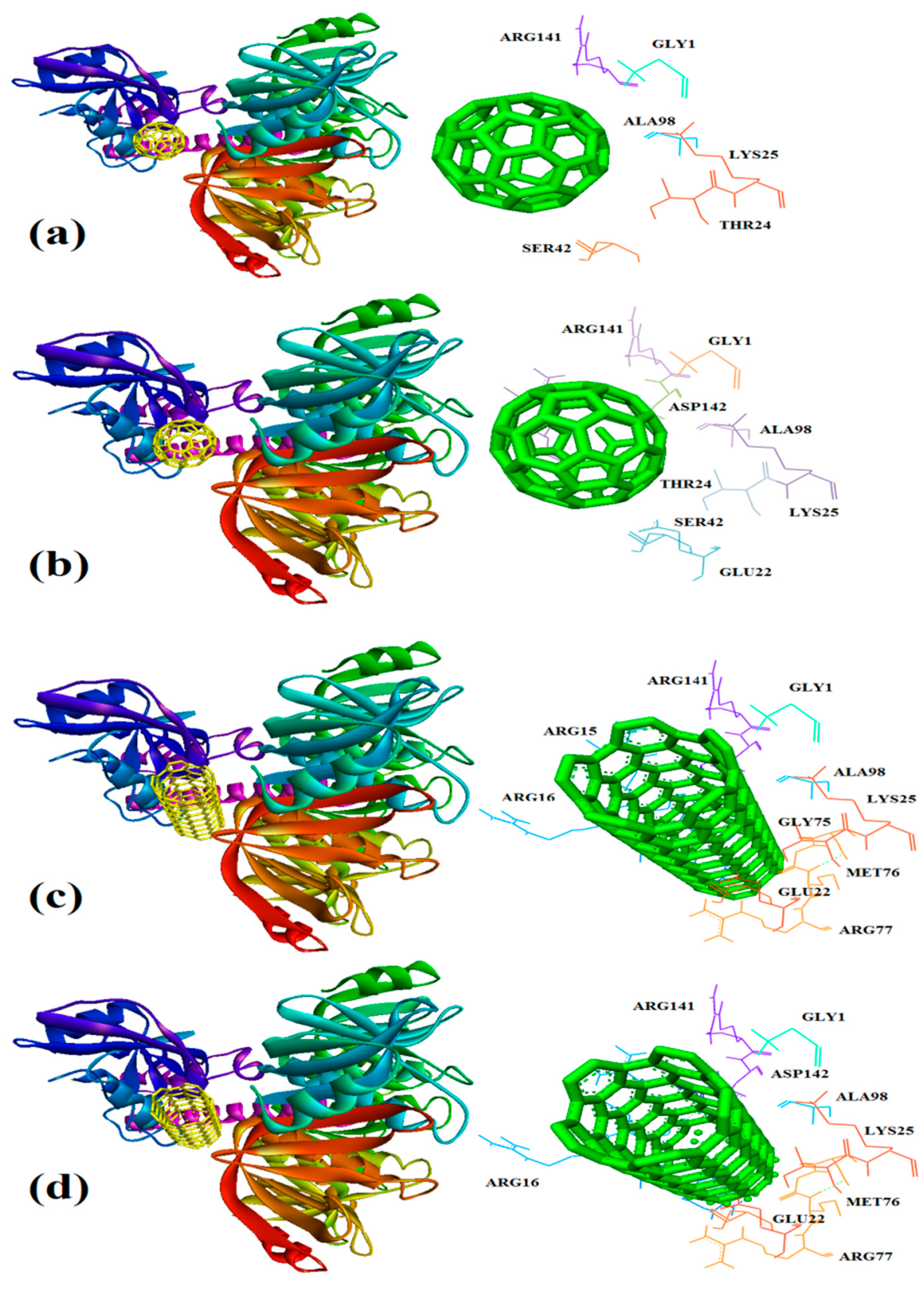
| 1TII | 97.4 | GLU22, THR24, LYS25, SER42, SER74, GLY75, MET76, ARG77, GLY1, ALA98, ARG15, ARG16, GLY18, ALA28, TYR29, GLU30, ARG31, LEU119, ARG141, ASP142 | 79 | GLU22, THR24, LYS25, SER42, SER74, GLY75, MET76, ARG77, GLY1 ALA98, ARG15 ARG16, GLY18 ALA28, GLU30 ARG31, LEU119 ARG141, ASP142 |
| 7AHL | -19.6 | THR125, LYS131, LEU135, ASN121, ASN123, LEU135, ASN121, ASN123, LEU135, ASN121, THR125, GLY126, and ASP127 |
-18.8 | LEU116, TYR118, VAL140, TYR112, HIS144, TRP179, PRO181, TYR182, SER186, TRP187, ASN188, PRO189, GLN194, ASN178, and TRP179 |
| 1MWT | -20.1 | ASN146, LYS148, GLU170, GLN199, GLN200, GLN203, TRP205, PRO213, ASN236, THR238, PRO258, ILE259, ASN260, SER261, ASP274, ASP275, ILE309 | -19.6 | ASN146, LYS148, GLU170, GLN199, GLN200 GLN203, TRP205 PRO213, THR238, PRO258 ILE259, ASP274, ASP275 ARG298, ILE309 |
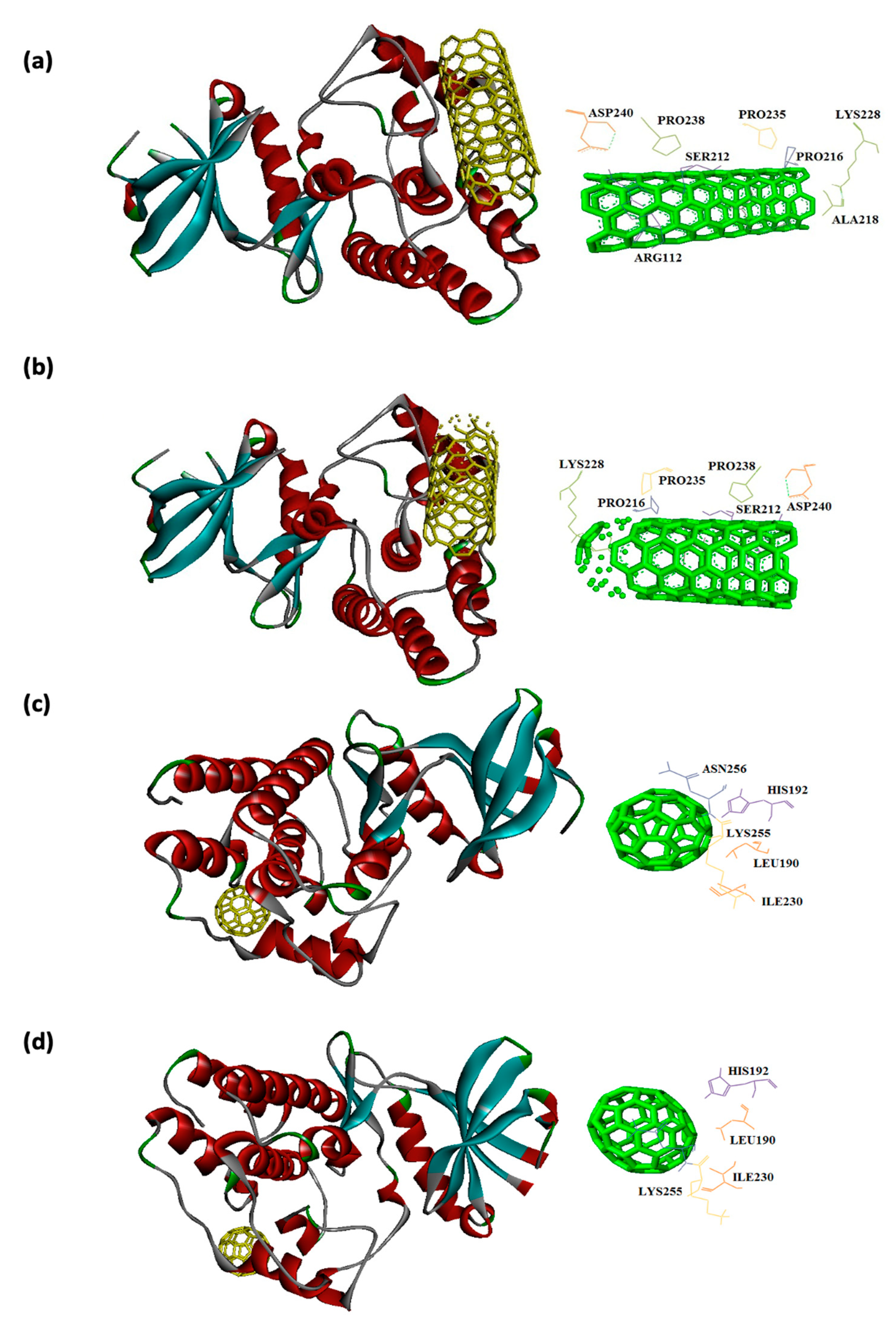
| 4OW8 | -13.0 | ARG112, SER212, LYS214, PRO216, ALA218, LYS228, PRO235, PRO238, and ASP240 |
-12.6 | ARG112, SER212, LYS214, PRO216, ALA218, LYS228, PRO235, PRO238, and ASP240 |
| 7P13 | -16.6 | ALA186, ASP189 GLN190, ASN274 GLN190, GLN193 HIS197, PRO276 LYS277, PRO279 PRO280 |
-16.3 | ALA186, ASP189 GLN190, GLN190 GLN193, HIS197 PRO276, LYS277 PRO279, PRO280 |
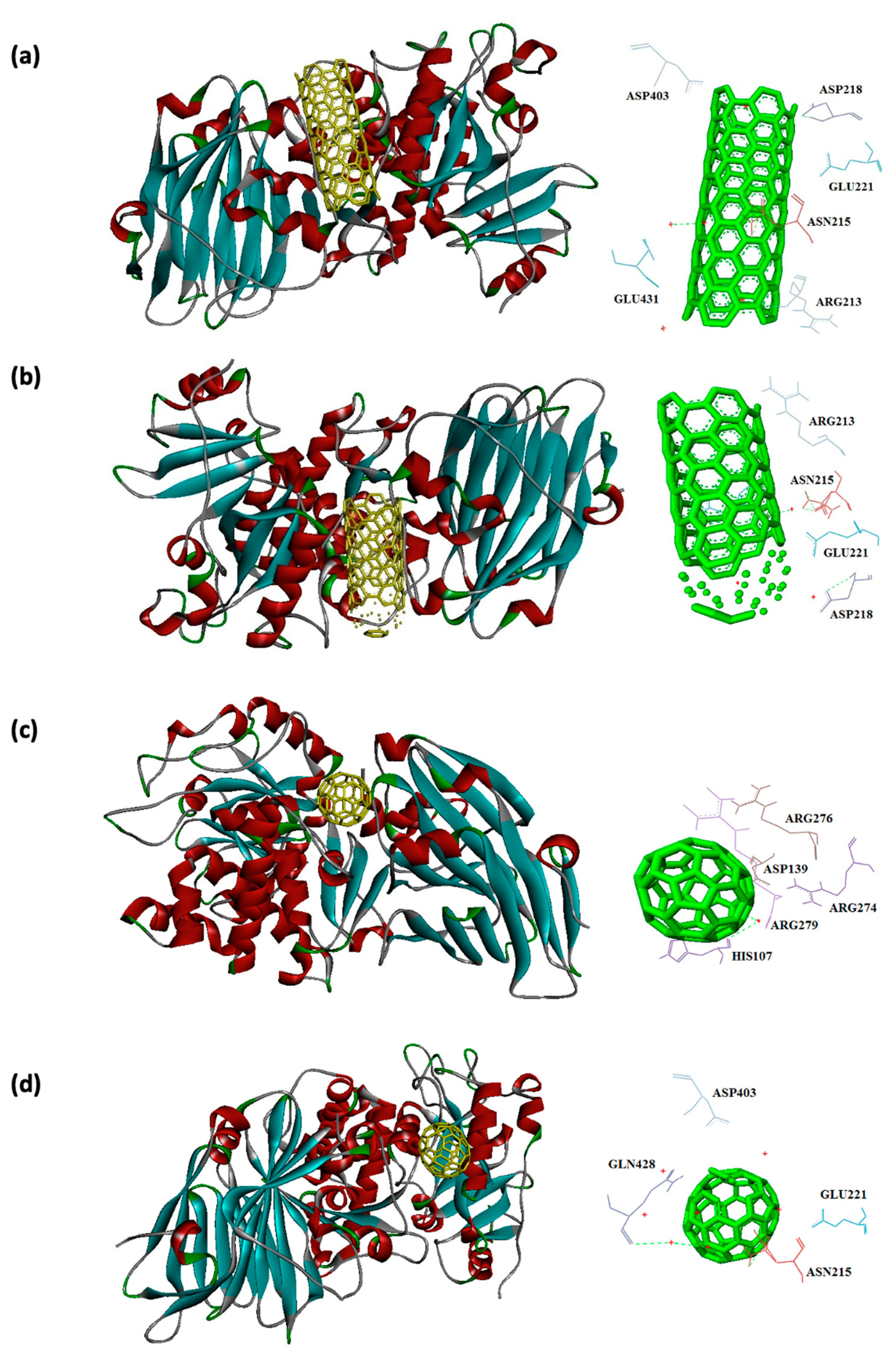
| 1IKQ | -12.9 | ARG213, ASN215, ASP218, GLU221, ASP403, and GLU431 |
-13.2 | ARG213, ASN215, ASP218, GLU221, and GLU431 |
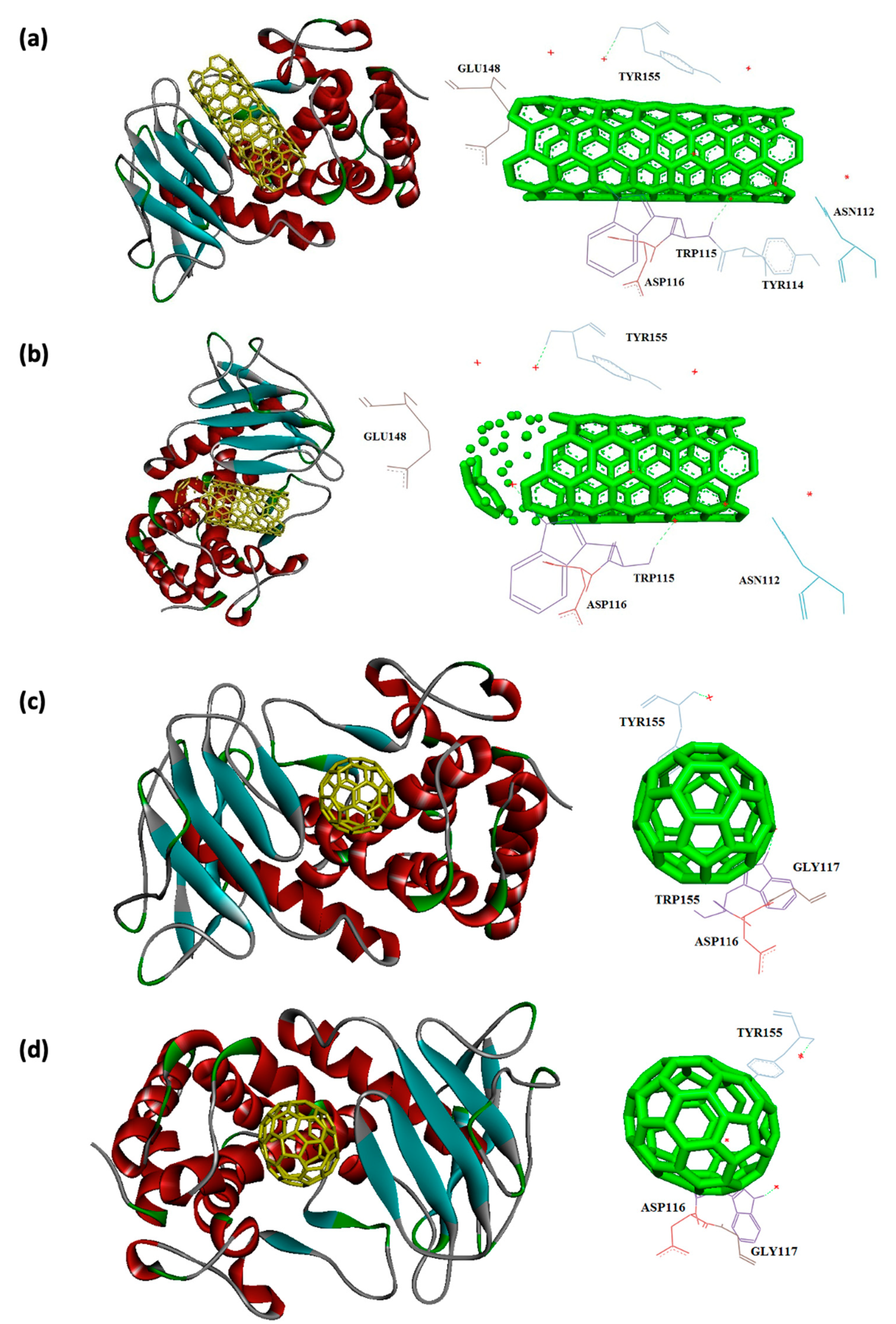
| 1EZM | -11.9 | ASN112, TYR114, TRP115, ASP116, ASP136, GLU148, TYR155, GLU172, GLU175, ASP183, and LEU185 |
-12.3 | ASN112, TRP115, ASP116, ASP136, GLU148, TYR155, GLU172, GLU175, ASP183, and LEU185 |
| Receptors | Binding affinity for C60 |
Interacting amino acids |
Binding affinity for C70 |
Interacting amino acids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7D6Q | -10.1 | LYS270, ASN272, ASN273, LYS7, GLY46, ASN69, ASP70 |
-10.0 | GLN118, ARG119, LEU123, GLU124, LYS5, GLN66, ASP70, GLU9, LYS22 |
| 1TII | -4.9 | THR24, LYS25, SER42, GLY1, ALA98, ARG141 | -2.5 | GLU22, THR24, LYS25, SER42, GLY1, ALA98 ARG15, ARG141, ASP142 |
| 7AHL | -12.8 | ARG104, ASN105, SER106, ILE107, TYR102, PRO103, THR155, PHE224, SER225, ASP227 |
-13.6 | ARG104, ASN105, SER106, ILE107, TYR102, PRO103, THR155, PHE224, SER225, ASP227 |
| 1MWT | -10.4 | TYR255, ASN260 PHE371, GLY374 MET375, ASN377 TYR380 |
-11.4 | TYR255, ASN260 LYS280, PHE371 GLY374, MET375 ASN377, TYR380 |
| 4OW8 | -8.3 | LEU190, HIS192, ILE230, LYS255, ASN256 |
-8.1 | LEU190, HIS192, ILE230, LYS255, ASN256 |
| 7P13 | -9.7 | THR262, GLU263 ASN266, TYR211 GLN214, TRP218 |
-10.5 | LYS259, THR262 GLU263, ASN266 TYR211, GLN214 LEU215, TRP218 GLU263, LYS267 |
| 1IKQ | -7.5 | HIS107, ASP139, ARG276, ARG279 | -7.6 | ASN215, GLU221, ASP403, GLN428 |
| 1EZM | -7.6 | TRP115, ASP116, GLY117, TYR155 | -7.7 | TRP115, ASP116, GLY117, TYR155 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





