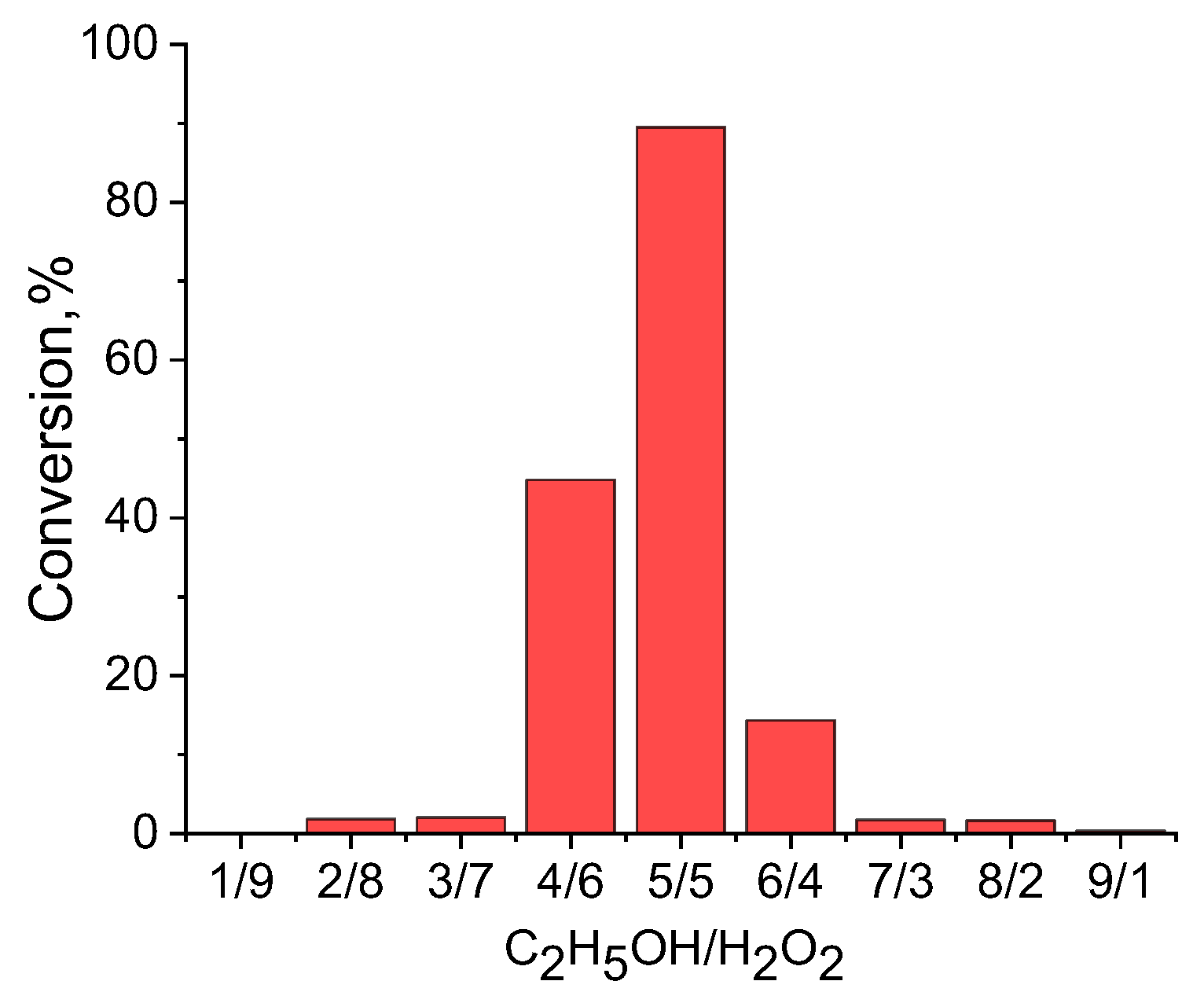1. Introduction
Acetaldehyde can be synthesized by various methods including partial oxidation of ethanol or ethylene, hydration of acetylene and ethanol dehydrogenation [
1]. The use of molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide as green, inexpensive, and readily available oxidants in combination with metal catalysts has practical advantages due to the favorable economics associated with O
2 and the formation of environmentally benign by-products (water and hydrogen peroxide) [
2,
3,
4]. Noble metals such as platinum [
5,
6], palladium [
7], ruthenium [
8], iridium [
9], and gold [
10,
11] anchored on the surface various supports has been demonstrated the high activity in partial oxidation of ethanol.
Nowadays biocatalytic oxidation offers practical solutions for the oxidation of alcohols. According to the classification of biocatalytic processes immobilized-enzyme catalysis has been attracting attention from many industries and researchers, mainly because of their high selectivity, specificity and activity under environmental benign conditions [
12]. Entrapment methods can be used to immobilize isolated enzymes and render them more stable, and easier to separate and recycle [
13].
Keilin and Hartree [
14] firstly showed that catalase was also capable of oxidizing a wide variety of compounds including ethanol in the presence of a hydrogen peroxide-generating system. Later the selective oxidation of primary alcohols to the aldehyde level with non-immobilized [
15,
16] and with immobilized enzymes [
17,
18] was successfully realized.
Last year the great attention is paid to macroporous cryogels that can be obtained by conventional radical copolymerization in cryoconditions [
19]. On a microscopic level, moderately frozen molecular solutions can be represented as heterophase systems containing the polycrystals of frozen solvent (for instance, water crystals) and some unfrozen fraction called “unfrozen liquid microphase”, where the monomers are concentrated. The reaction occurs inside of unfrozen regions due to extremely high local monomer concentration while the crystals of frozen solvent play the role of porogens after defrosting. The pore size of cryogels can vary from several microns to several hundred microns. Due to porous structure, cryogels can retain up to 74% of water molecules in large pores, and such big pores, can be used as monolithic (stationary) or flow-through catalytic reactor.
The achievements in the creating polymeric cryogels, mainly for needs of biotechnology and biomedicine have been described in reviews and book chapters [
20,
21,
22]. For instance, the anionic and cationic cryogels were used for nanoparticles immobilization into superporous cryogels matrix for sodium borohydride decomposition [
23,
24,
25]. Recently, Demirci et al. [
26,
27] studied the enzymatic activity of alpha-Glucosidase entrapped within various cryogels, including neutral, anionic, and cationic superporous cryogels, obtained in situ under polymerization conditions. Cryogels with tunable porosity, pore sizes, and functionality for the entrapment of enzymes have been concluded to be effective tools in development of novel biotechnological processes [
26,
27,
28].
Reactions performed by immobilized enzymes can be made in reactors of different configurations. The most used enzymatic reactors are packed-bed and fluidized-bed reactors, which can be operated continuously. The types of reactors used for immobilized enzymes were summarized in [
29]. Basically, the same principles as for other processes using heterogeneous catalysis are valid, resulting in well-known reactor configurations.
The present work was inspired by our previous research reports on the aerobic oxidation of alcohols mediated by biocatalyst composed of catalase immobilized within polyampholyte cryogel p(APTAC-
co-AMPS) [
30]. The one-stage immobilization of metal nanoparticles into matrix of amphoteric cryogels was developed by our research group [
31,
32,
33] and further was successfully used for selective hydrogenation of various substrates in flow-through reactor. The traditional batch type laboratory reactor was widely used for the liquid-phase oxidative catalysis in reaction coupling of low-valent phosphorus compounds with alcohols, yellow phosphorus, and octene-1 [
34,
35,
36,
37].
The present manuscript deals with the study of the biocatalyst composed of catalase immobilized within polyampholyte cryogel in ethanol oxidation, because the previous article [
30] was focused on the study of iso-propanol and n-butanol oxidation in flow-through catalytic reactor. The aim of this work is comparative study of the catalytic properties of catalase immobilized within monolithic polyampholyte cryogel in oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde under mild conditions (ambient temperature, atmospheric pressure) using the flow-through and batch catalytic reactors.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and characterization of biocatalyst
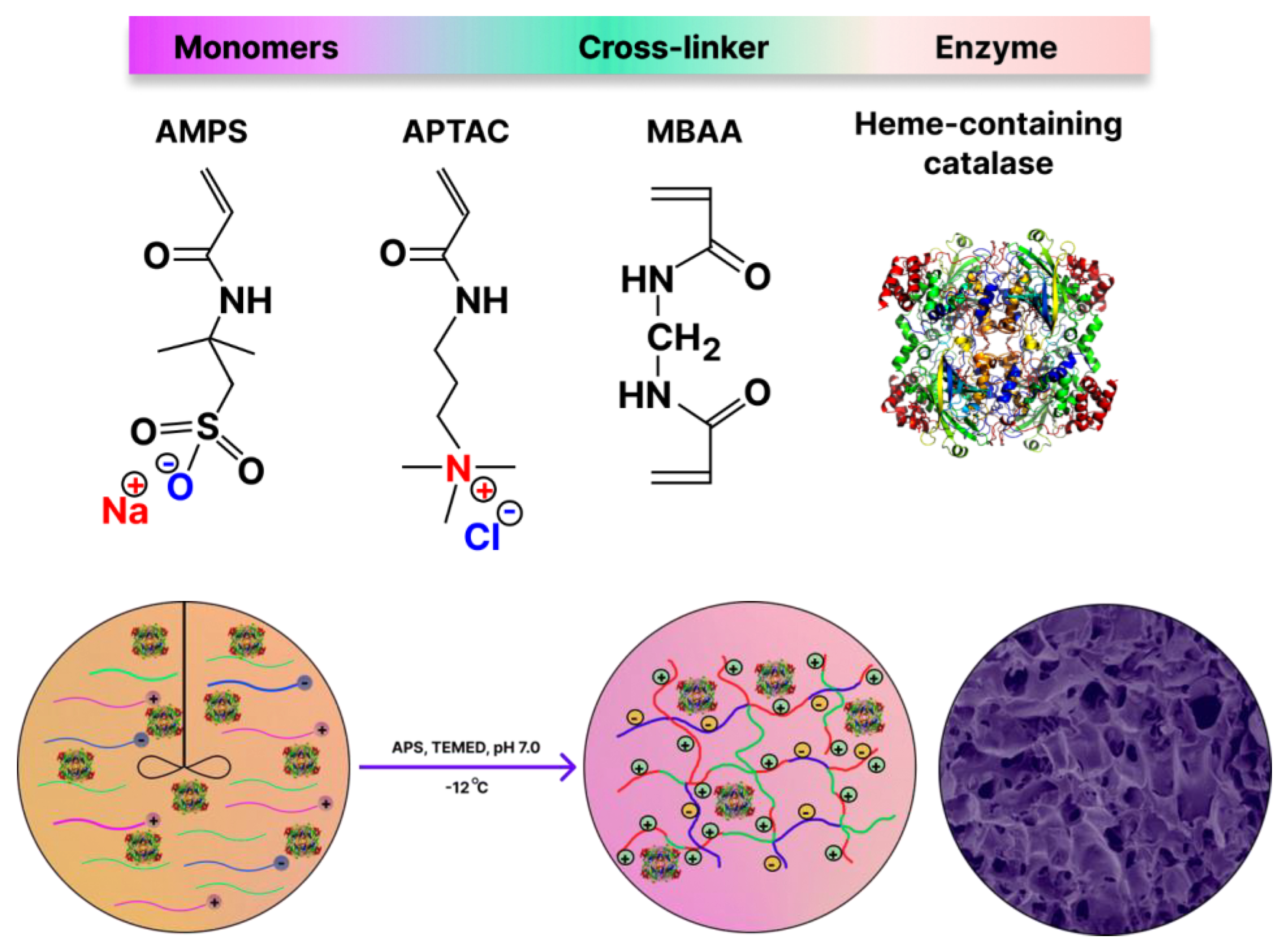
The monolithic p(APTAC-
co-AMPS) cryogel containing various amounts of catalase were synthesized under cryoconditions (T = -12°C) at an initial molar ratio of monomers [APTAC]:[AMPS] = 75:25 mol.% in the presence of 10 mol.% MBAA, ammonium persulfate (APS), used as an initiator, and N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED), as an accelerator (
Figure 1) [
30].
Stabilization of catalase in the matrix of p(AMPS-
co-APTAC) cryogel occurs due to electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged protein and the excess of cationic groups [
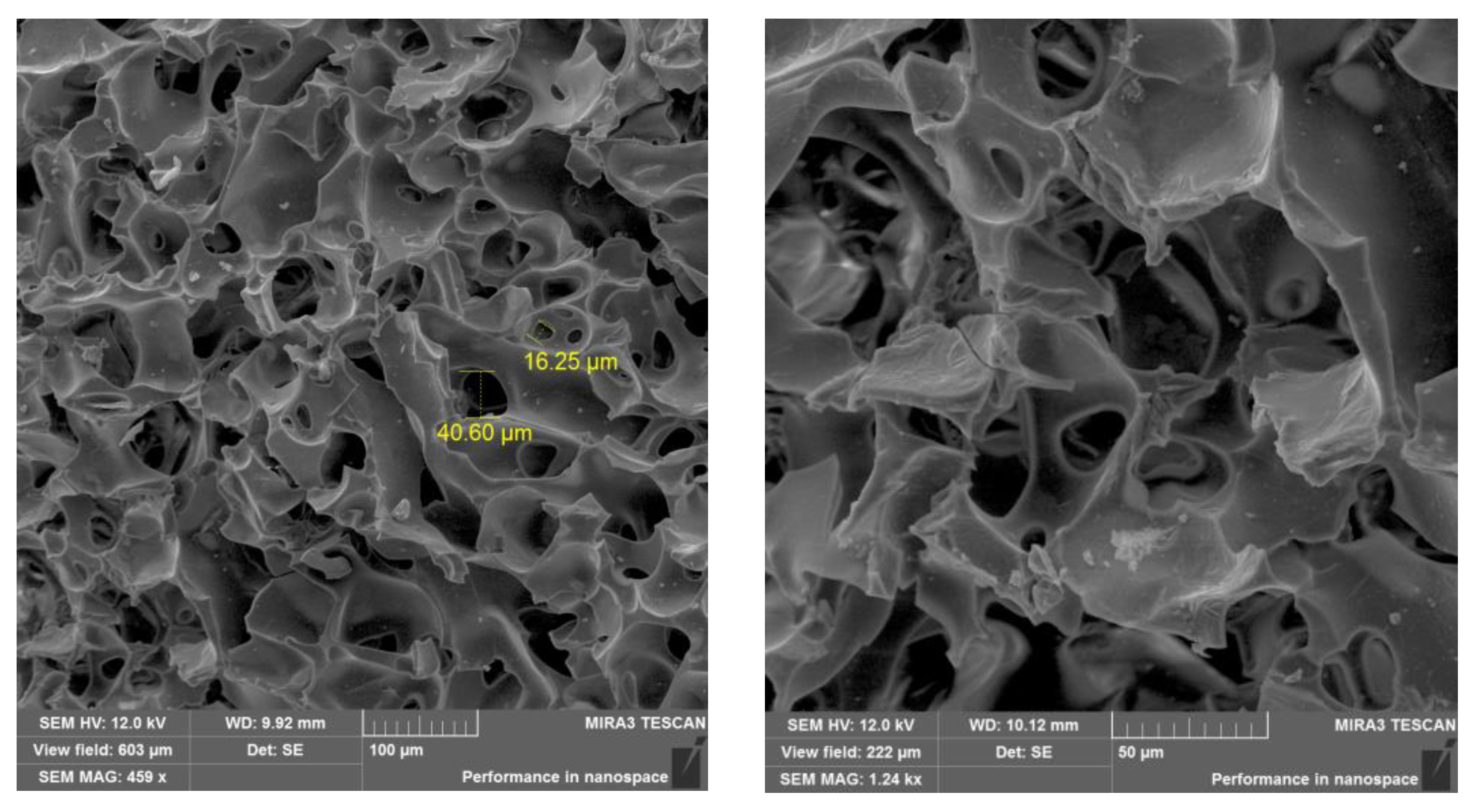
38]. As seen from the SEM images, the average pore size of p(AMPS-
co-APTAC) cryogel sample with immobilized catalase varies from 15 to 55 μm (see
Figure 2). Such large pores provide for the free flow of liquid substrate and oxidation agent under gravity and at hydrostatic pressure.
The activity of cryogel-immobilized catalase in the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide was evaluated previously [
30]. The initial activities of catalase immobilized in cryogel samples (diameter, 10 mm and height, 10 mm) are 89.6, 200 and 221 U⋅mL
-1, which correspond to the amount of immobilized catalase of 1, 5 and 10 mg, or an immobilization yield of 40.32%, 90.0%, and 99.45%. The best catalytic activity was exhibited by the catalase sample with an immobilization yield 99.45%, because it becomes inactivated only after the decomposition of 50 mL of hydrogen peroxide, and was thus selected for oxidation of ethanol.
2.2. Catalytic oxidation of ethanol using catalase immobilized within monolithic cryogel p(APTAC-co-AMPS) in flow-through catalytic reactor
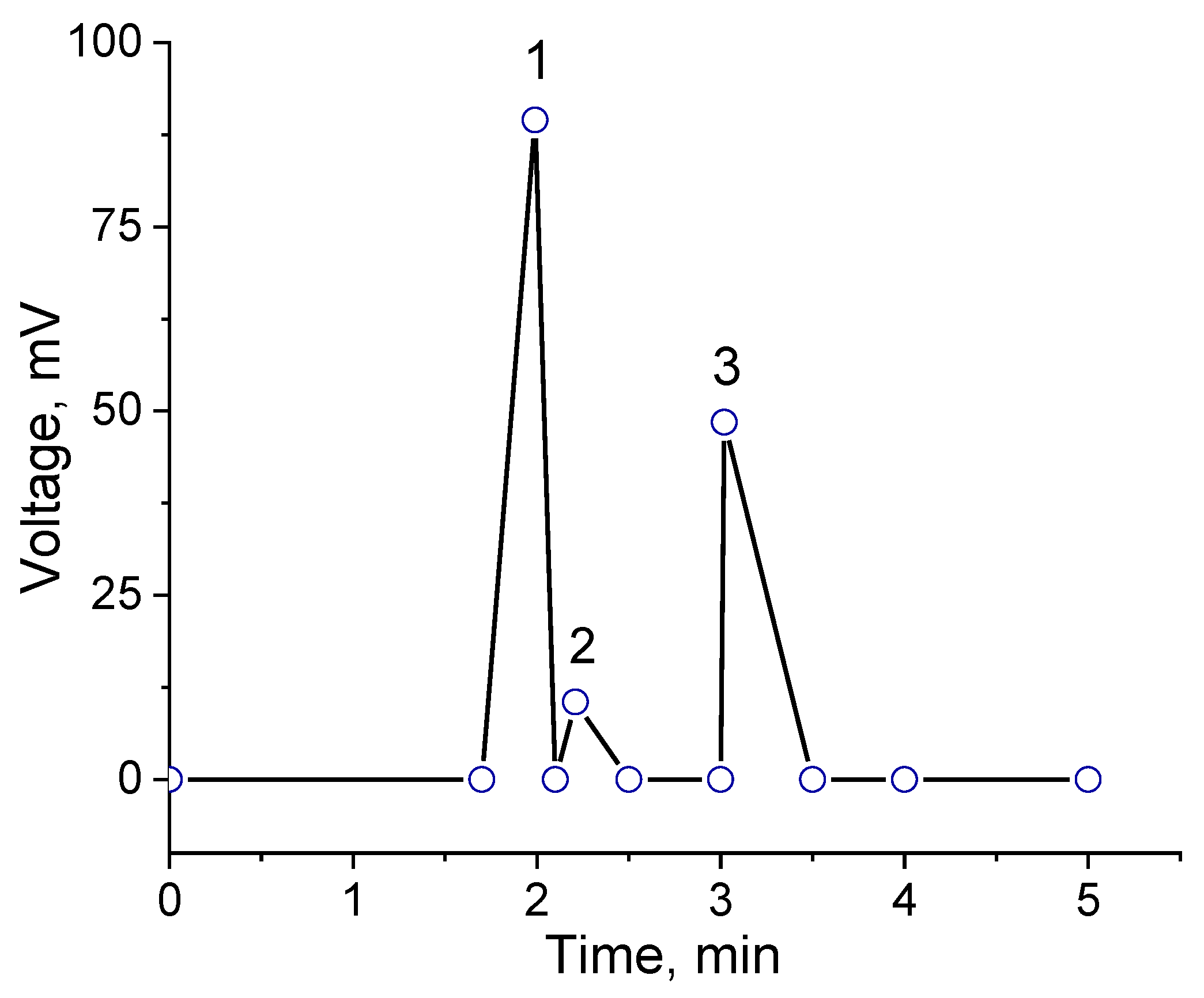
Figure 3 shows the results of chromatographic analysis of the products after the first pass of the mixture of ethanol and hydrogen peroxide through the flow-through catalytic reactor at 20
°C. The optimal mixture of alcohol to hydrogen peroxide passed through the monolithic cryogel samples was found to be 1:1 by volume, because an excess of either ethanol or hydrogen peroxide produces low yields of the acetaldehyde. For this reason, all further experiments were carried out at a 1:1 volume ratio of substrate to oxidizing agent. The chromatographic peak 3 in chromatogram, which appear at t = 3.5 min corresponds to ethyl acetate. Peak 1 at t = 1.99 min belongs to acetaldehyde, whereas peak 2 at t = 3.0 min matches ethanol itself (
Figure 3). Oxidation of the mixture of ethanol-hydrogen peroxide was found to produce acetaldehyde at a yield of 91.8%. Successive oxidation of the ethanol/hydrogen peroxide mixture leads to decreasing yields of acetaldehyde up to 85.2% (2nd cycle) and 14.5% (3rd cycle). This loss in the effectiveness is probably connected with the shrinking of the amphoteric cryogel p(APTAC-
co-AMPS) matrix in water-organic solvent mixture or leaching out of catalase.
The influence of pH, temperature and volume ratios of the substrate to oxidizing agent on the conversion degree of ethanol was evaluated.
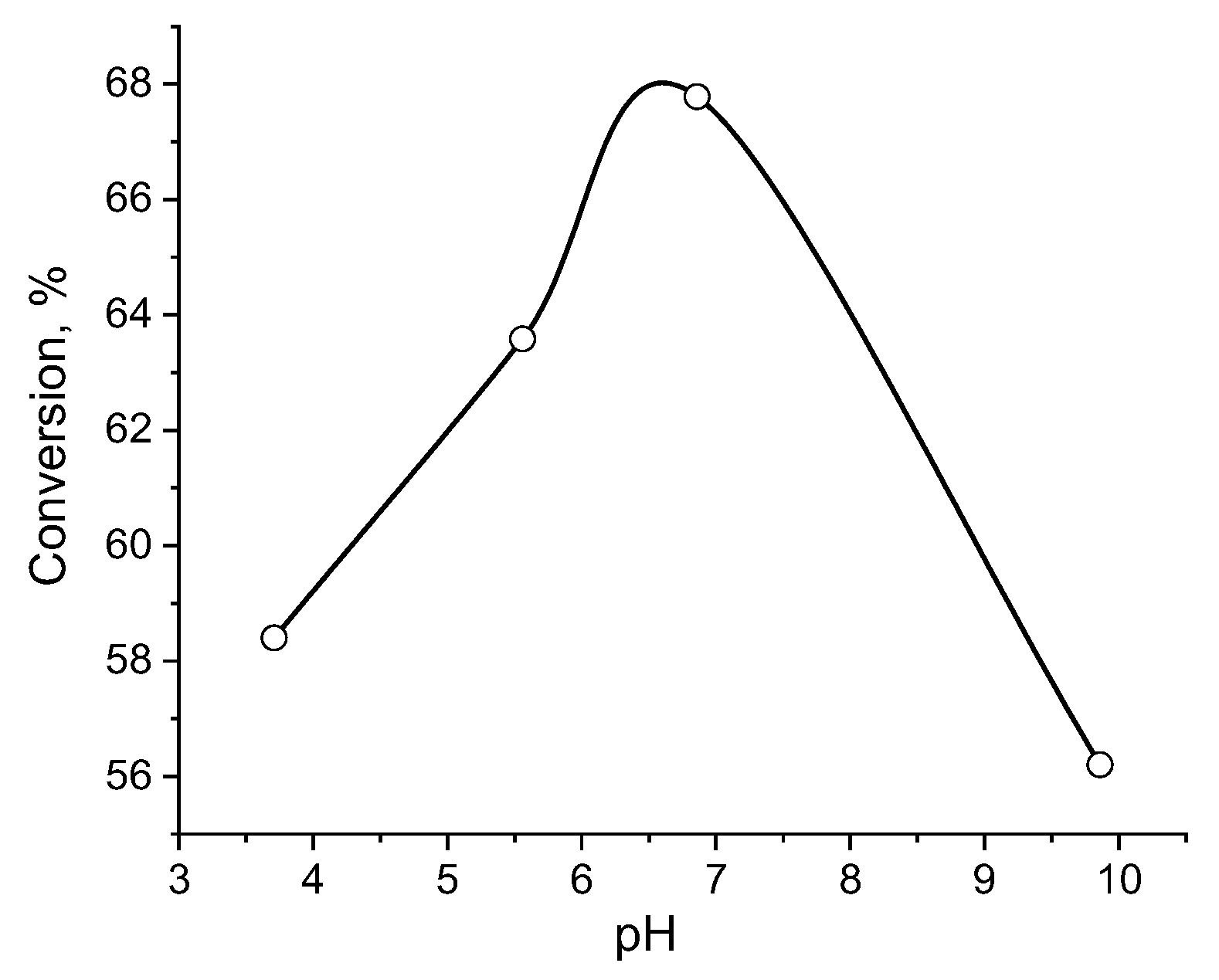
The maximum conversion of ethanol using p(APTAC-
co-AMPS) cryogel containing immobilized catalase is observed at a pH 6.9, which corresponds to the initial pH value of the ethanol-hydrogen peroxide mixture (
Figure 4). This is close to a pH 6.4, where the maximal decomposition of hydrogen peroxide takes place when utilizing a p(APTAC-
co-AMPS) cryogel-immobilized catalase [
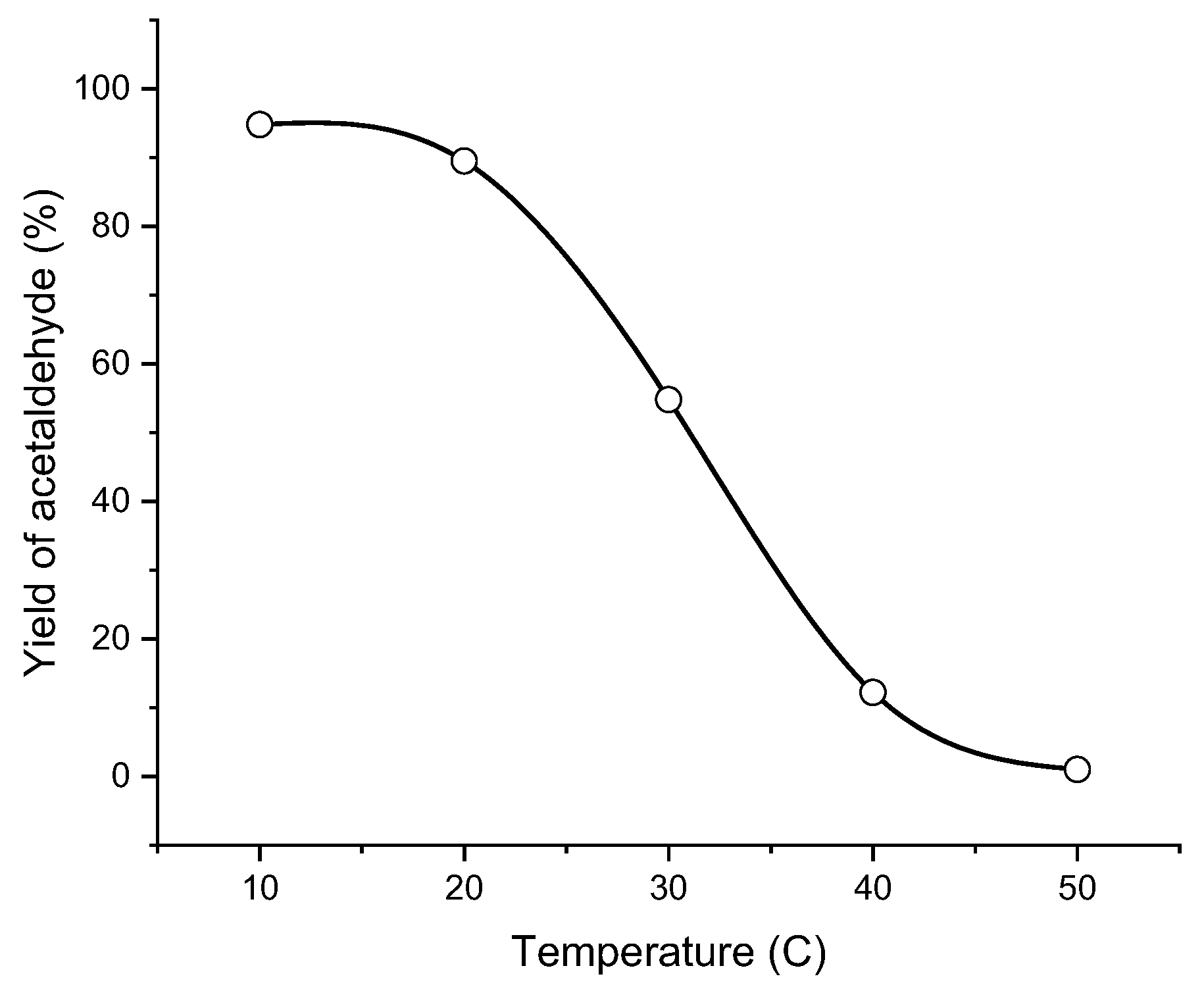
30]. It was observed that the oxidative activity of amphoteric cryogel-immobilized catalase is higher at low temperatures, but is lower at high temperatures as in the case of iso-propanol oxidation [
30], which can probably be accounted for by the exothermic character of the oxidation of alcohols.
It is noticeable that the maximum activity of gellan gel-immobilized catalase [
39] have demonstrated at a pH 6.5. For hydrogen peroxide degradation the p(NIPAM-
co-HEMA) hydrogel-immobilized catalase has the same optimum as the free enzyme (around pH 7.0) [
40].
The optimal ratio of the ethanol-hydrogen peroxide mixture passed through the sample of monolithic cryogel with a flow rate of 6-7.5 mL⋅min
-1 was equal to 50:50 vol.%. Under these conditions, the yield of acetaldehyde reached up to 89.5% (
Figure 5).
The activity of cryogel-encapsulated catalase is higher at low temperature (
Figure 6). Probably at low temperature, the cryogel is preferentially in the swollen state and the pores are more accessible for substrate and peroxide [
40]. Increasing of temperature can cause shrinking of cryogel matrix retarding the effective diffusion coefficient of substrate to surface area due to lower internal mass transfer resistance. Another reason may be the exothermic character of ethanol oxidation by hydrogen peroxide.
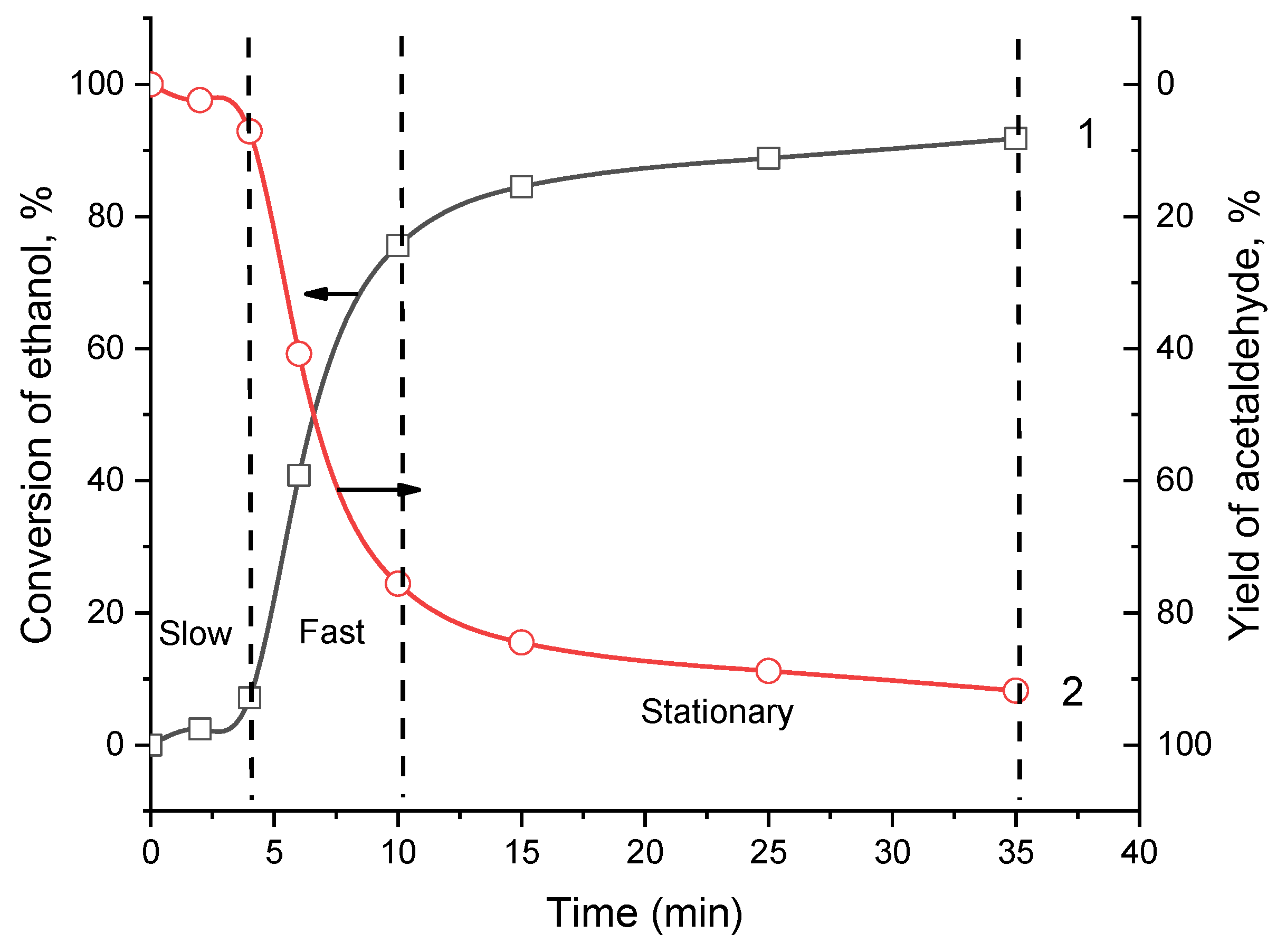
In the course of ethanol oxidation, the time-dependent consumption of ethanol and accumulation of acetaldehyde changes antibatically (
Figure 7). The oxidation of ethanol can conditionally be divided into 3 stages. The first stage is up to 4 min where the process is slow (induction period). The second stage is lasted between 4-10 min where fast oxidation of ethanol takes place. The third stage in the range of 15-35 min is related to stationary state where the conversion degree is gradually stabilized.
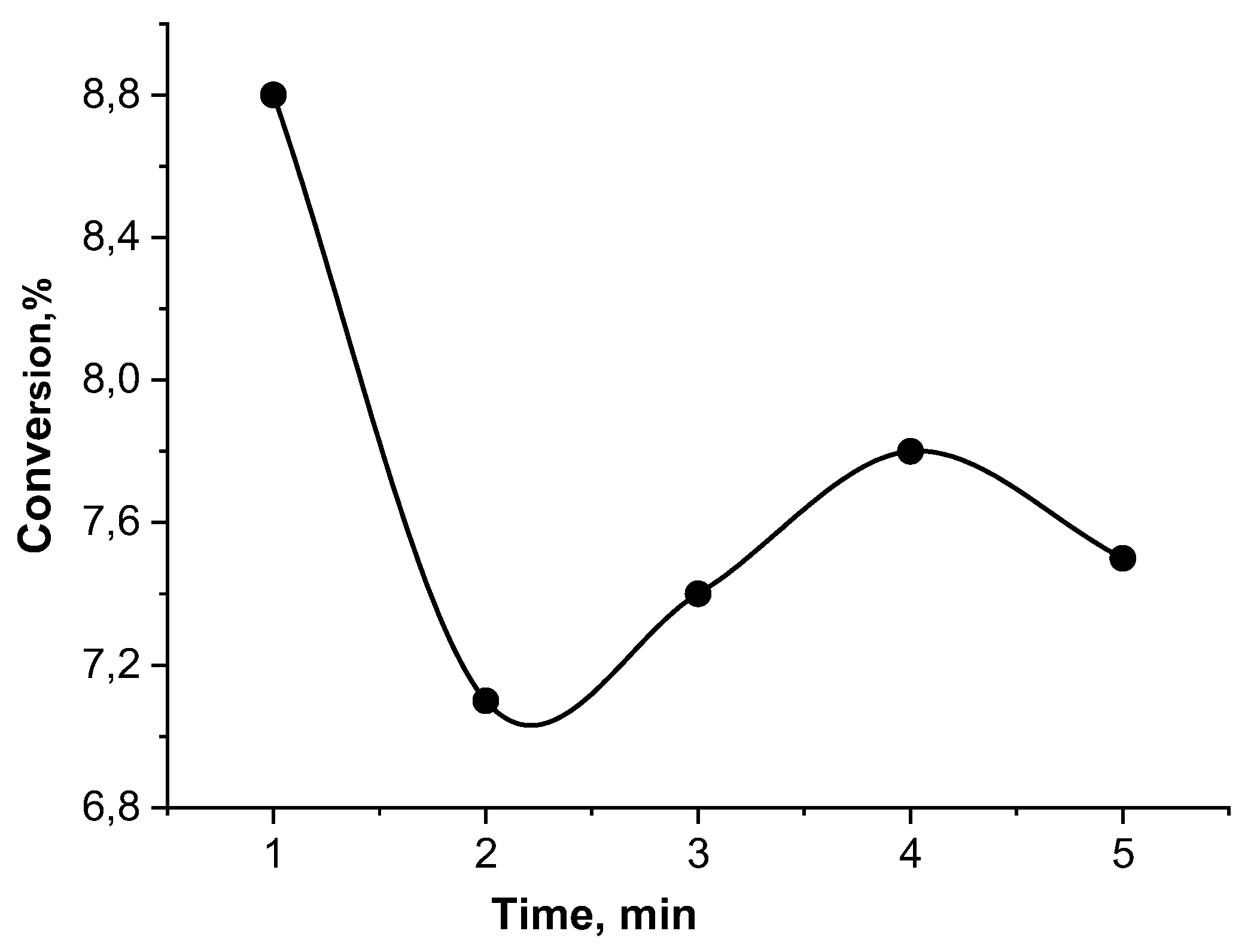
Oxidation of ethanol by hydrogen peroxide was performed by cryogels themselves without immobilized catalase (
Table 1) and free catalase (
Figure 8). In both cases the conversion is rather low and does not exceed 7.0±0.3 %. The conclusion is that the anionic, cationic and amphoteric cryogels without immobilized catalase are not active in oxidation of ethanol. At the same time the pristine catalase without cryogel matrix is also inactive.
The reusability of cryogel-immobilized catalase was evaluated using the same cryogel sample in 5 times successive oxidation reactions, with cryogel samples being rinsed out with distilled water before every use (
Table 2). The conversion degree of ethanol to acetaldehyde sharply decreases over successive runs, and after the 5 times becomes extremely low (0.3%). For explanation of this phenomenon we make several assumptions. The first assumption is connected with shrinking of cryogel samples in the mixture of ethanol-hydrogen peroxide (reactant) or acetaldehyde-water (product) that can retard the accessibility of active centers with respect to substrate. Moreover, the presence of organic substances within cryogel matrix can deactivate or even poison the heme structure of catalase that is responsible for generation of active radicals. The leaching out of catalase due to destruction of cryogel samples should also be taken into account.
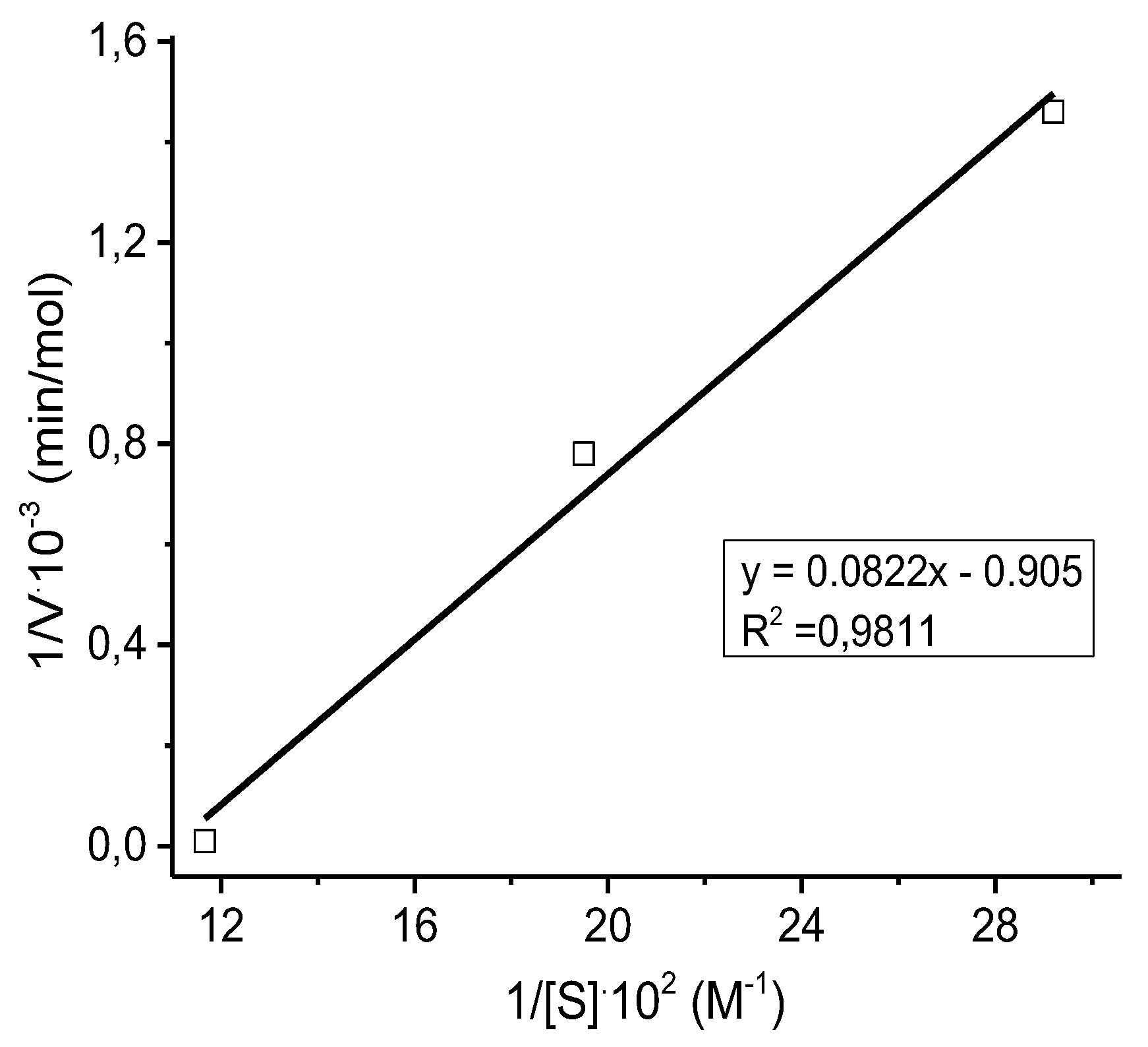
The kinetic parameters of ethanol oxidation were determined from the Michaelis-Menten plots in the concentrations range of ethanol 0.0343-0.0857 moles. The Lineweaver-Burk plots were also constructed according to Eq. (1) [
41].
where V
0 is the initial rate (μmol⋅min
-1), [S] is the ethanol concentration (mM), K
m is the Michaelis constant (mM), and V
max is the maximum enzymatic rate (μmol⋅min
-1).
The value of the coefficient of determination (R
2 = 0.9811) indicates good regression, which can be used to explain 98.11% of the total variation in the response (
Figure 9).
The value of the Michaelis constant for immobilized catalase was equal to K
m = 4.0 M. The maximum rate of the enzymatic process is V
max = 5⋅10
-2 mol⋅L
-1⋅min
-1. The catalytic constant (or number of conversions) can be considered as the number of moles of product formed per unit time by one mole of pure enzyme saturated with the substrate and it was equal to k
2 = 1.1⋅10
6 min
-1. It is known that the conversion number for catalase is 5⋅10
6 min
-1 [
29].
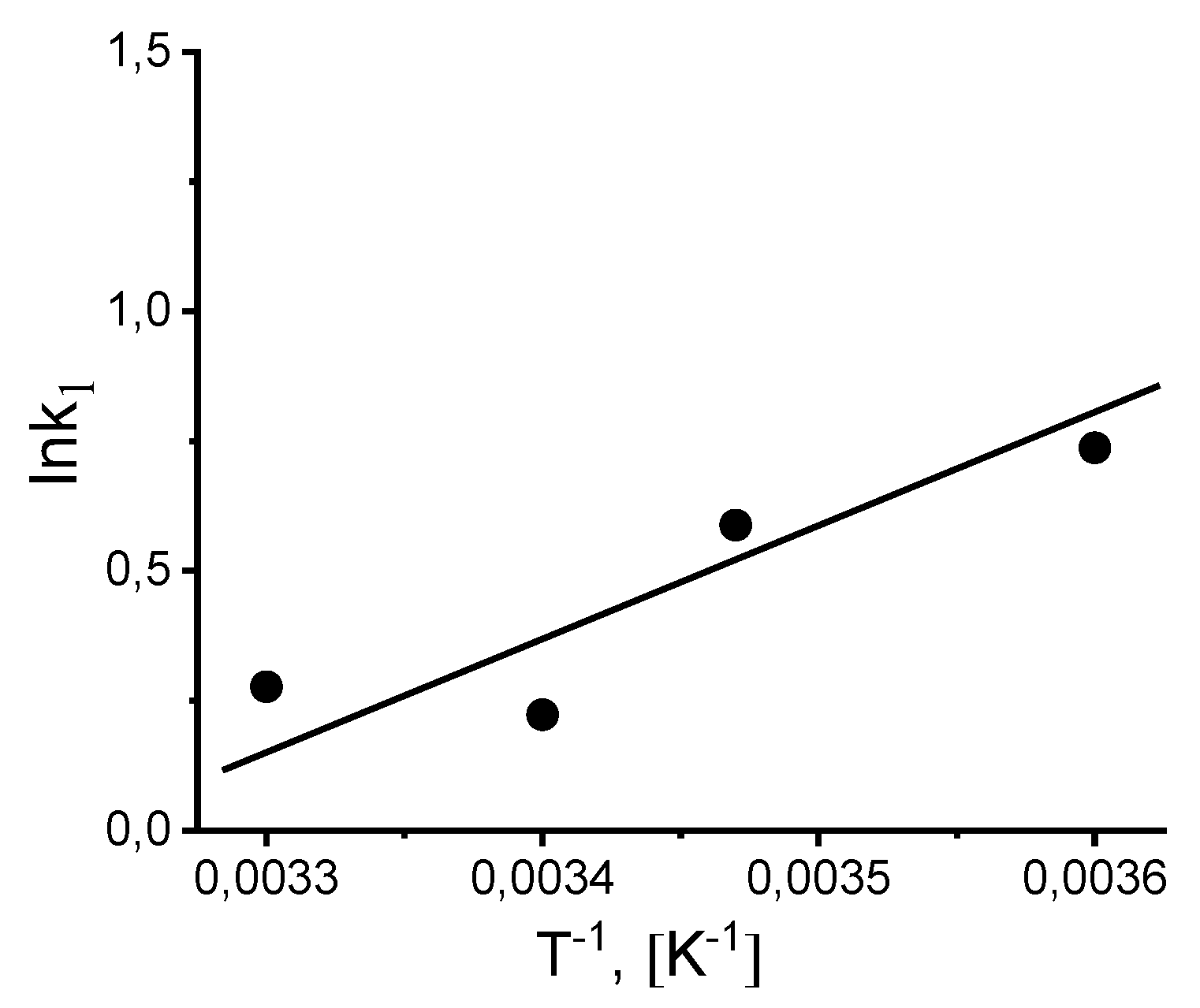
The activation energy (Е
a, kJ⋅mol
-1) was calculated from the slope of the straight line in Arrhenius coordinates lgk-1/T at temperature interval of 5-20 °C (
Figure 10).
The activation energy was equal to Е
a = 7.31 kJ⋅mol
-1 that is two times less than the value for the activation energy calculated for the decomposition of H
2O
2 (E
a = 14 kJ⋅mol
-1) [
41]. The change in the entropy of activation (ΔS
‡) in the temperature range of 5-20 °C lies in the limit of ΔS
‡ = -250.0-(-246.01) J⋅mol
-1⋅grad
-1). Negative values for ΔS‡ indicate that entropy decreases on forming the transition state, which often indicates an associative mechanism in which two reaction compounds form a single activated complex.
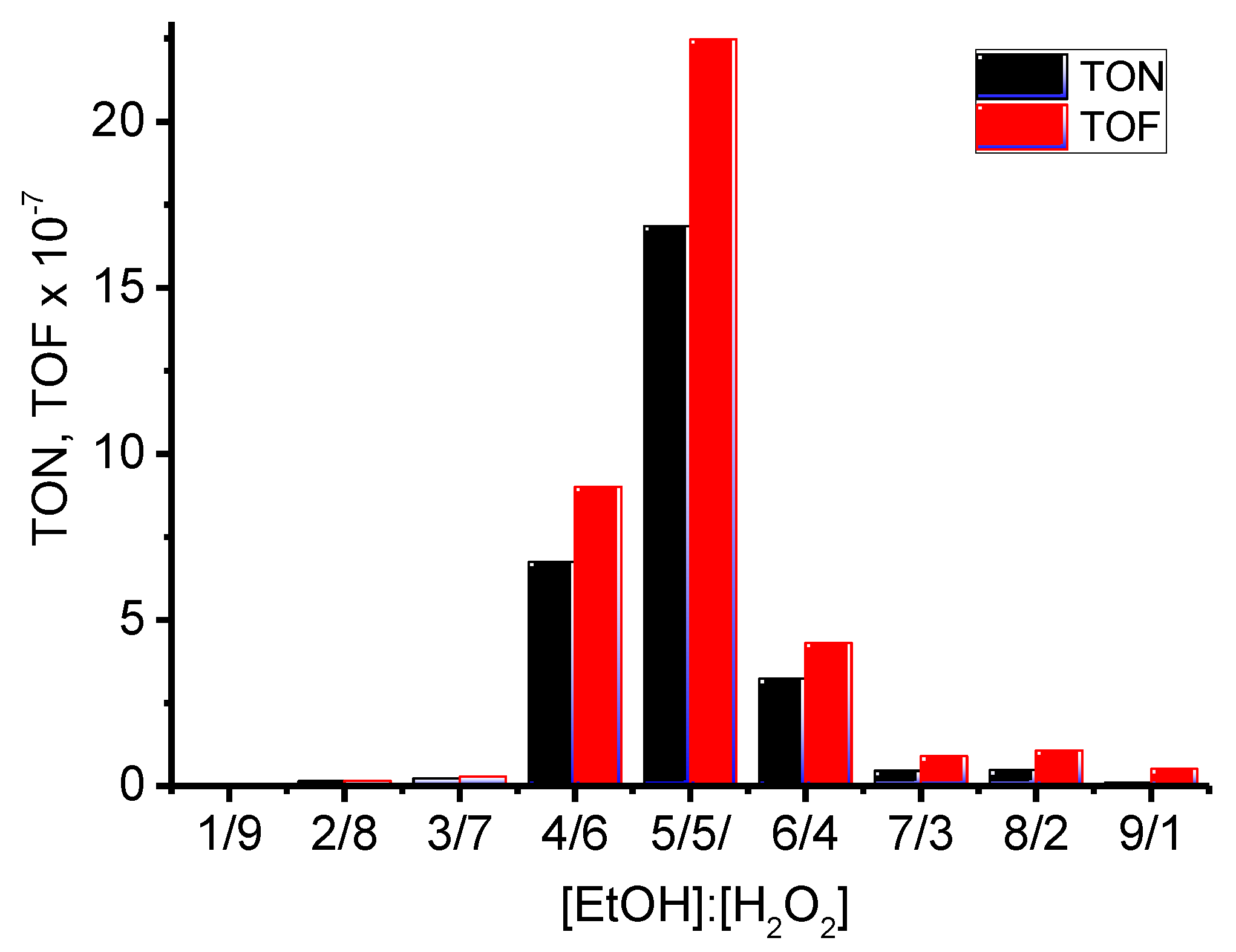
The calculated values of turnover number (TON) and turnover frequency (TOF) in oxidation of ethanol are rather high (
Figure 11,
Table 3).
2.3. Oxidation of ethanol by cryogel-immobilized enzyme – catalase in batch type catalytic reactor
The oxidation of ethanol by catalase entrapped in a cryogel matrix of macroporous polyampholyte was studied in batch type reactor at 20 °C with hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen (100%) and air (
Table 4).
Oxidation of ethanol was carried out in the kinetic mode with intensive shaking, which significantly reduced diffusion inhibition and improved heat and mass transfer. When ethanol was oxidized by molecular oxygen during 5-30 min the yield of acetaldehyde was equal to 97-98% regardless of the form of the used cryogel as a monolith or powder. The volume of oxygen absorbed during ethanol oxidation was equal to 11.8 mL in case of powdered cryogel with immobilized catalase and 13.0 mL in the case of monolithic cryogel (
Table 4). The yield of acetaldehyde, according to GC analysis, was high for both powdered cryogel (96.7%) and monolithic cryogel (97.7%). However, the yield and conversion of ethanol decreased by 1.6 times when the experiments were performed in air.
The reusability of cryogel-immobilized catalase was evaluated using the same cryogel sample in 5 times successive oxidation reactions without rinsing out with distilled water before every use (
Table 5). The conversion degree of ethanol to acetaldehyde insignificantly decreases over successive five runs, and after the 5 runs becomes 57.3%.
The calculated TON and TOF values for oxidation of ethanol are given in
Table 6.
The comparative analysis of advantages and disadvantages of flow-through and batch type reactors for oxidation of ethanol given in
Table 7.
2.4. Mechanistic aspects of ethanol oxidation
Catalase is an antioxidant enzyme found in most aerobic organisms. It catalyzes the dismutation of H
2O
2 into water and oxygen. Most of these enzymes are homotetramers with a heme group on each subunit. In the catalase reaction, a two-electron transfer occurs between two hydrogen peroxide molecules, one acting as an electron donor and the other as an electron acceptor. The reaction mechanism proceeds in two steps (
Figure S12). In the first step, catalase is oxidized by a peroxide molecule to form an intermediate called compound I. Compound I is characterized by a ferroxyl group containing FeIV and a porphyrin cation radical. In this reaction, a water molecule is formed (reaction 1). In the second step of the reaction, compound I is reduced by another peroxide molecule, returning the catalase to its initial state and producing water and dioxygen (reaction 2), (
Figure S12) [
42].
The use of oxidases has the advantage that the cheapest and environmentally most “friendly” oxidant such as molecular oxygen can be used. Alcohol oxidases [1.1.3.x] catalyse a two- or four-electron transfer onto molecular oxygen, giving hydrogen peroxide (2 e
-) or water (4 e
-) as by-product, respectively (
Figure S13) [
43].
A simplified mechanism of oxidation of alcohols by free catalase in the presence of pure oxygen and air oxygen instead of hydrogen peroxide follows a similar mechanism, which is shown in
Figure S14 [
44]. The use of molecular oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor is attractive from a thermodynamic driving force point of view, as well as from an ecological point of view, since only water is formed as a byproduct.
According to the proposed simplified mechanism, the initial alcohol binds to the active center of the enzyme, namely, the iron(III) ion, and is oxidized by deprotonation/hydride transfer to form hydrogen peroxide. Next, hydrogen peroxide H
2O
2 protonates B: and converts it to BH
⊕ [
45]. Then there is coordination with the heme HOO
Ɵ, Fe(III) iron, and its oxidation to the Fe(IV) state with a π-cationic porphyrin radical and a water molecule. Regeneration B: for the next cycle occurs after oxidation of Fe(III) to Fe(IV) and deprotonation BH
⊕. The porphyrin radical generates active hydroxyl radicals •OH, which attack hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl groups of alcohols, turning them into either ketones or aldehydes.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
Anionic and cationic monomers, including 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid sodium salt (AMPS, 98 wt.%) and(3-acrylamidopropyl)trimethylammonium chloride (APTAC, 75 wt.% in water), crosslinking agent N,N’-methylenbisacrylamide (MBAA, >99% purity), ammonium persulfate (APS, >99% purity), and N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED, >99% purity) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. (Milwaukee, WI), and used without further purification. Catalase from bovine liver with catalytic activity of 2000 U⋅ml-1 was also acquired from Sigma-Aldrich (USA). Potassium permanganate (KMnO4, >99% purity), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 0.07 M), H2SO4 (20 wt.%) and phosphate buffer with pH 7.0 were used for determination of the activity of catalase utilizing the permanganometric method. Finally, reagent grade ethanol of 99.5–99.9% purity (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was distilled and used as substrate.
Gas–liquid chromatographic analysis was carried out on a DANI Master GC (Italy). A gas chromatograph mass spectrometer Agilent 6890 N/5973 N (USA) was used for the identification of the products. Morphology of cryogels was observed utilizing a SEM JSM-6390 LV (JEOL, Japan).
3.2. Synthesis of catalase-encapsulated monolithic p(APTAC-co-AMPS) cryogel
Synthetic protocol of encapsulation of catalase within APTAC-
co-AMPS cryogel matrix has been already published [
30]. The cationic monomer APTAC (0.9 g, 3.27 mmol) and anionic monomer APMS (0.5 g, 1.09 mmol) were first dissolved in 8 mL of deionized water. Afterwards, 10 mg of catalase and 67.1 mg of MBAA (0.435 mmol) were added to the solution and stirred for 20 min. Following the addition of 10 mg of APS, the solution was stirred and then purged with argon over a period of 20 min. Further, 0.1 mL TEMED solution was added, and the mixture vigorously stirred for several minutes. Finally, the resulting solution was placed into a pre-cooled (-12
oC) glass tube with a diameter of 10 mm and height of 10 mm, and placed into cryostat for 24 h. The cryogel sample obtained, having the shape of the reaction vessel, was washed out using deionized water over a time of 72 h, then air dried at room temperature overnight, and finally placed in a vacuum oven set at room temperature in order to reach a constant mass.
3.3. Determination of the enzymatic activity of catalase
The enzymatic activity of catalase was determined by permanganatometric method that is proportional to the difference of the volumes of 0.025M KMnO
4 solution used for titration of control (V
control), e.g., without enzyme, and tested (V
tested) probes and calculated by the formula:
where n is dilution number of initial solution of catalase, 4.17 is conversion coefficient of catalase to arbitrary unit [
46].
3.4. Calculation of the immobilization yield of catalase in cryogel samples
The immobilization yield of catalase entrapped into cryogel samples with diameter 10 mm and height 10 mm was determined by the procedure described in [
47] and calculated according to formula:
3.5. Oxidation of ethanol in flow-through and batch type catalytic reactor
3.5.1. Flow-through reactor
Oxidation of ethanol was carried out on a flow-through catalytic reactor composed of a glass tube with an inner diameter of 10 mm and height of 40 mm, containing the monolithic cryogel sample (
Figure S15). The reactor was equipped with a thermostatic jacket to maintain a constant temperature. A dried cylindrical piece of cryogel with a diameter of 10 mm and height of 10 mm was placed inside of the reactor. Then, 2 mL of deionized water was passed through the cryogel sample. Due to quick swelling of the cryogel, a tight seal formed between the inner wall of the glass tube and swollen sample. Such simple construction allows the mixture of substrate (alcohol) and oxidizing agent (hydrogen peroxide) to flow freely under gravity through the cryogel pores, and creates enough contact between the catalase and reaction mixture. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide used in all experiments was equal to 0.06 mol⋅L
-1. The mixture of alcohol and hydrogen peroxide in 10 mL (1:1 by volume) was passed through the catalytic reactor containing cryogel-immobilized catalase, resulting in an immobilization yield of 99.45%. The total volume of the solution poured into the reactor creates enough hydrostatic pressure of the liquid to flow out through the cryogel [
48]. The collected product was extracted utilizing ethyl acetate/ or hexane, and then was analyzed using gas-liquid chromatography and gas chromatograph mass spectrometry.
3.5.2. Batch type reactor
Oxidation of ethanol in thermostated glass batch reactor with entire volume 150 mL was carried out (so called as catalytic “duck”) by hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen and air in anaerobic and aerobic conditions (
Figure S16). The kinetic reaction regime was reached by shaking the reactor with frequency of about 250–300 swingings/min. A dried cylindrical piece of cryogel with immobilized catalase as monolith with weight 89.6-98.8 mg or powder with weight 86.0-93.2 mg was placed inside of the reactor. Then the hexane (5 mL) was added. The 5 mL of ethanol was added to the reactor in this order and the resulting solution was thoroughly purged with argon/or oxygen/or air during 5 min. The mixture of ethanol and hydrogen peroxide was 10 mL (1:1 by volume). Then, the hydrogen peroxide (0.06 mol⋅L
-1) was added into the reactor against a brisk argon/or oxygen/or air current through the dropping funnel. The total time of the experiment was 5 and 30 minutes. The product accumulation was monitored by checking their composition by GC analysis.
4. Conclusions
Thus, flow-through and batch type catalytic reactors in laboratory conditions are suitable for selective oxidation of ethanol into acetaldehyde in good-to-excellent yields under mild conditions using a biocatalytic system based on cryogel-entrapped catalase. The conversion of ethanol into acetaldehyde in flow-through catalytic reactor reaches up to 91.8%. The influence of temperature, pH and volume ratios of the substrate to oxidizing agent on the conversion degree of ethanol was evaluated. The following optimal conditions for ethanol oxidation with hydrogen peroxide were found: T = 10-20 °C, pH = 6.9-7.1, [C2H5OH]:[H2O2] = 50:50 vol.%. The catalytic activities of anionic, cationic and amphoteric cryogels without immobilized catalase and free catalase were extremely low and did not exceed 6-9%.
The reusability of cryogel-immobilized catalase was evaluated in the course of 5 successive ethanol oxidation. Sharp decrease of the catalytic activity of monolith cryogel-immobilized catalase between 3-5 cycles was explained by shrinking of cryogel samples in the mixture of water-organic solvent, partly deactivation of the heme structure of catalase and leaching out of catalase from cryogel matrix. Kinetic parameters such as the Michaelis constant (Km) and Vmax for the immobilized catalase on the p(APTAC-co-AMPS) monolith cryogel were determined by Lineweaver–Burk plots using ethanol as substrate. The activation energy of ethanol oxidation was ∼2 times lower than that of H2O2 decomposition.
The oxidation of ethanol by catalase entrapped in a cryogel matrix of macroporous polyampholyte was studied in batch type reactor with the help of hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen and air. The acetaldehyde yields irrespective to cryogel forms, monolith or powder were in the range of ~ 60-98%. In batch type reactor oxidation of ethanol by hydrogen peroxide and molecular oxygen yields up to ~ 97-98% of acetaldehyde. The oxidation degree of ethanol by air is lower (~ 60%). The reusability of cryogel-entrapped catalase in batch rector was evaluated. It was found that the conversion degree of ethanol to acetaldehyde insignificantly decreases over successive five runs, and after the fifth runs becomes 57.3%. TOF value for flow-through catalytic reactor was 6 times higher than that of batch laboratory reactor.
Thus, the suggested methods might be useful for the oxidation of aliphatic alcohols into their corresponding carbonyl compounds. The advantages of enzyme-entrapped cryogel samples are minimal volume of catalyst, high surface to volume ratio, energy saving and “green chemistry” aspects, high selectivity and productivity. The major drawback of cryogel microreactors is weak mechanical properties. A serious problem represents the chemical destruction of cryogel matrix and leaching out of enzyme from the 3D-network that can cause contamination of final products.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Figure S12, Catalase mechanism of hydrogen peroxide dismutation to water and oxygen.; Figure S13, Removal of H2O2 from the reaction mixture employing catalase.; Figure S14, Simplified mechanism of ethanol oxidation by catalase-immobilized cryogel matrix in the presence of oxygen and air.; Figure S15, Schematic view of the cryogel-based flow-through catalytic reactor setup, with immobilized catalase for the catalytic oxidation of ethanol and hydrogen peroxide.; Figure S16, Schematic view of batch type catalytic reactor setup for the catalytic oxidation of ethanol by hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen and air. 1 – catalytic “duck”, 2 – valve for catalyst insertion, 3 – thermostated burette, 4 – thermostat, 5 – electric motor, 6 – shaker, 7 – laboratory autotransformer, 8 – Berzelius laboratory gasholder.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.N.A. and S.E.K.; Methodology, D.N.A., I.A.S., K.S.M., N.A.T., B.S.B., G.S.T., A.V.S. and S.E.K.; Validation, I.A.S.., B.S.B., G.S.T., A.V.S. and S.E.K.; Investigation, I.A.S., K.S.M., N.A.T., B.S.B., G.S.T., A.V.S. and S.E.K.; Writing—original draft preparation, D.N.A.; Writing—review and editing, D.N.A.; Supervision, D.N.A., G.S.T., A.V.S. and S.E.K.; Project administration, D.N.A. and S.E.K.; Funding acquisition, D.N.A. and S.E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan, grant number IRN AP14869287.
Data Availability Statement
All data created is provided in this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Nurlan Bakranov (Laboratory of Engineering Profile, Satbayev University) for carrying out the SEM analyses.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Neramittagapong, A.; Attaphaiboon, W.; Neramittagapong, S. Acetaldehyde production from ethanol over Ni-based catalysts. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2008, 35, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Arends, I.W.C.E.; Sheldon, R.A. Modern oxidation of alcohols using environmentally benign oxidants. In Modern oxidation methods; J.-E. Bäckvall, Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Green oxidation in water. In Handbook of green chemistry; Volume 5, Ch.-J. Li, Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Martins, N.M.R.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Catalytic oxidation of alcohols: recent advances. Сh. 3. In Advances in Organometallic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, Volume 63; 2015, 1-157. [CrossRef]
- Sapi, A.; Liu, F.; Cai, X.; Thompson, Ch.M.; Wang, H.; An, K.; Krier, J.M.; Somorjai, G.A. Comparing the catalytic oxidation of ethanol at the solid-gas and solid-liquid interfaces over size-controlled Pt nanoparticles: striking differences in kinetics and mechanism. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6727–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrollahi, R.; Wenderich, K.; Mul, G. Room temperature oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde over Pt/WO3. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 160026(1-7). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, R.; Zhu, F.-Ch.; Sun, Sh.-G.; Villullas, H.M. New understandings of ethanol oxidation reaction mechanism on Pd/C and Pd2Ru/C catalysts in alkaline direct ethanol fuel cells. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 224, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, D.; Vaiano, V.; Ciambelli, P. Photocatalytic synthesis of acetaldehyde by selective oxidation of ethanol on RuOx-VOx/TiO2. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Hensen, E.J.M. Selective oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde by Au-Ir catalysts. J. Catal. 2013, 305, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hensen, E.J.M. Highly efficient and robust Au/MgCuCr2O4 catalyst for gas-phase oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14032–14035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redina, E.A.; Greish, A.A.; Mishin, I.V.; Kapustin, G.I.; Tkachenko, O.P.; Kirichenko, O.A.; Kustov, L.M. Selective oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde over Au-Cu catalysts prepared by a redox method. Catal. Today 2014, 241, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A.; Woodley, J.M. Role of biocatalysis in sustainable chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 801–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.T.; Marr, P.C.; Marr, A.C. Enzyme entrapment, biocatalyst immobilization without covalent attachment. Green Chem., 2021, 23, 4980–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilin, D.; Hartree, E.F. Catalase, peroxidase and metmyoglobin as catalysts of coupled peroxidatic reactions. Biochem. J. 1955, 60, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, R.; Ferrara, N.; Molinari, F. An easy and efficient method for the production of carboxylic acids and aldehydes by microbial oxidation of primary alcohols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 513–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, R.; Romano, A.; Gandolfi, R.; Sinisterra Gago, J.V.; Molinari, F. Chemoselective oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes with Gluconobacter oxydans. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6059–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukeda, H.; Ishii, T.; Sawamura, M.; Isobe, K. Glycolaldehyde production from ethylene glycol with immobilized alcohol oxidase and catalase. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, M.; Galli, C.; Gentili, P.; Macchitella, D. An oxidation of alcohols by oxygen with the enzyme laccase and mediation by TEMPO. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 7551–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Das, B. Introduction to polymeric gels. Ch. 1. In Polymeric Gels. Characterization, Properties and Biomedical Applications. Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–27. [CrossRef]
- Lozinsky, V.I. Cryogels based on natural and synthetic polymers: Preparation, properties and applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2002, 71, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macroporous polymers: Production, properties and biotechnological/biomedical applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017, рр. 530, Eds. Mattiasson B., Kumar A., Galaev I.
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Savina, I.N.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. Cryogels: morphological, structural and adsorption characterization. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 187–188, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Seven, F. The use of superporous p(AAc (acrylic acid)) cryogels as support for Co and Ni nanoparticle preparation and as reactor in H2 production from sodium borohydride hydrolysis. Energy 2014, 71, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Yildiz, S. Preparation of superporous poly(4-vinyl pyridine) cryogel and their templated metal nanoparticle composites for H2 production via hydrolysis reactions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 126, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Seven, F. Energy and environmental usage of super porous poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propan sulfonic acid) cryogel support. RSC Advances 2014, 4, 23886–23897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, S.; Sahiner, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Karadag, E.; Sahiner, N. Enhanced enzymatic activity and stability by in situ entrapment of α-Glucosidase within super porous p(HEMA) cryogels during synthesis. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00534(1-12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, S.; Sahiner, N. Superporous neutral, anionic, and cationic cryogel reactors to improved enzymatic activity and stability of α-Glucosidase enzyme via entrapment method. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 128233(1-12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunbas, C.; Aslan, A.; Kusat, K.; Sahiner, M.; Akgöl, S.; Sahiner, N. Synthesis and characterization of a new cryogel matrix for covalent immobilization of catalase. Gels 2022, 8, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, A.; Kumar, S.; Liese, A.; Kragl, U. Reactions on immobilized biocatalysts. In Handbook of heterogeneous catalysis; Ch. 16, G. Ertl, H. Knozinger, F. Schuth, J. Weitkamp Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagulova, I.; Tatykhanova, G.; Shakhvorostov, A.; Akbayeva, D.; Kudaibergenov, S. Oxidation of iso-propanol and n-butanol by catalase encapsulated within macroporous polyampholyte cryogel matrix. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudaibergenov, S.E. Physicochemical complexation and catalytic properties of polyampholyte cryogels. Gels 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudaibergenov, S.E.; Dzhardimalieva, G.I. Flow-through catalytic reactors based on metal nanoparticles immobilized within porous polymeric gels and surfaces/hollows of polymeric membranes. Polymers 2020, 12, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhardimalieva, G.I.; Zharmagambetova, A.K.; Kudaibergenov, S.E.; Uflyand, I.E. Polymer-immobilized clusters and metal nanoparticles in catalysis. Kinet. Catal. 2020, 61, 198–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfman, Ya.A.; Abdreimova, R.R. Oxidative alkoxylation of tetraphosphorus. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 1993, 63, 289–303. [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman, Ya.A.; Abdreimova, R.R.; Akbayeva, D.N. Kinetics and mechanism of oxidative alkoxylation of tetraphosphorus in the presence of Cu(II) sulfates and carboxylates. Kinet. Catal. 1995, 36, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Akbayeva, D.N.; Faizova, F.Ch.; Abdreimova, R.R.; Peruzzini, М. Oxidation of white phosphorus by peroxides in aqueous and alcoholic solutions: mechanistic aspects and catalytic studies. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2007, 267, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayeva, D.N.; Bakirova, B.S.; Seilkhanova, G.A.; Sitzmann, H. Oxidation of octene-1 in the presence of palladium-polyvinylpyrrolidone complex. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2018, 13, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektenova, G.A.; Kudaibergenov, S.E.; Bekturov, E.A. Interaction of catalase with cationic hydrogels: influence of pH, kinetics of process and isotherms of adsorption. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1999, 10, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, M.; Bajan, N.; Popa, A.A.; Verestiuc, L. The preparation, characterization and properties of catalase immobilized on crosslinked gellan. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A: Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 43, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arıca, M.Y. , Öktem, H.A., Öktem, Z., Tuncel, S.A. Immobilization of catalase in poly(isopropylacrylamide-co-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) thermally reversible hydrogels. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trawczynska, I. New method of determining kinetic parameters for decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. Catalysts 2020, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curieses Andrés, C.M.; Pérez de la Lastra, J. M.; Juan, C.A.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Chemistry of hydrogen peroxide formation and elimination in mammalian cells, and its role in various pathologies. Stresses 2022, 2, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroutil, W.; Mang, H.; Edegger, K.; Faber, K. Biocatalytic oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puetz, H.; Puchlova, E.; Vrankova, K.; Hollmann, F. Biocatalytic oxidation of alcohols. Catalysts 2020, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, P.; Fita, I.; Loewen, P.C. Enzymology and structure of catalases. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 51, 51–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatiani, V.S. Fermentative methods of analysis. Moscow: Nauka, 1969, рр. 740.
- Sheldon, R.A.; van Pelt, S. Enzyme immobilisation in biocatalysis: why, what and how. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6223–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, A.G. Catalase immobilization—A review. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Synthetic protocol for the encapsulation of catalase within the monolithic p(APTAC-co-AMPS) cryogel matrix (75:25 mol.%), which bears the excess of positive charges.
Figure 1.
Synthetic protocol for the encapsulation of catalase within the monolithic p(APTAC-co-AMPS) cryogel matrix (75:25 mol.%), which bears the excess of positive charges.
Figure 2.
Catalase-immobilized macroporous cryogel matrix for oxidation of ethanol. Bar scale is 100 (left) and 50 μm (right).
Figure 2.
Catalase-immobilized macroporous cryogel matrix for oxidation of ethanol. Bar scale is 100 (left) and 50 μm (right).
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of oxidized ethanol. Peak 1 belongs to acetylaldehyde, peak 2 belongs to ethanol. Peak 3 corresponds to solvent – ethyl acetate used for extraction.
Figure 3.
Chromatogram of oxidized ethanol. Peak 1 belongs to acetylaldehyde, peak 2 belongs to ethanol. Peak 3 corresponds to solvent – ethyl acetate used for extraction.
Figure 4.
pH-dependent conversion of ethanol using amphoteric cryogel-immobilized catalase at 25 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg.
Figure 4.
pH-dependent conversion of ethanol using amphoteric cryogel-immobilized catalase at 25 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg.
Figure 5.
Ethanol conversion versus EtOH-hydrogen peroxide volume ratio.
Figure 5.
Ethanol conversion versus EtOH-hydrogen peroxide volume ratio.
Figure 6.
Temperature-dependent activity of cryogel-entrapped catalase in ethanol oxidation.
Figure 6.
Temperature-dependent activity of cryogel-entrapped catalase in ethanol oxidation.
Figure 7.
Dependence ethanol conversion (1) and yield of acetaldehyde (2) on time at 20 °С.
Figure 7.
Dependence ethanol conversion (1) and yield of acetaldehyde (2) on time at 20 °С.
Figure 8.
Oxidation of ethanol by pure catalase at 20 °C. [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, [сatalase] = 10 mg, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, stirring time 5 min.
Figure 8.
Oxidation of ethanol by pure catalase at 20 °C. [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, [сatalase] = 10 mg, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, stirring time 5 min.
Figure 9.
Lineweaver-Burk plot of immobilized catalase.
Figure 9.
Lineweaver-Burk plot of immobilized catalase.
Figure 10.
Arrhenius plot for calculating the activation energy Еact of catalase decomposition during H2O2 decomposition.
Figure 10.
Arrhenius plot for calculating the activation energy Еact of catalase decomposition during H2O2 decomposition.
Figure 11.
Dependence of TON and TOF from volume ratio EtOH-Н2О2.
Figure 11.
Dependence of TON and TOF from volume ratio EtOH-Н2О2.
Table 1.
Oxidation of ethanol by anionic, cationic, and amphoteric monolithic macroporous cryogels at 20 °C, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, [Catalase] = 10 mg, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL.
Table 1.
Oxidation of ethanol by anionic, cationic, and amphoteric monolithic macroporous cryogels at 20 °C, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, [Catalase] = 10 mg, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL.
| Cryogels |
p(APTAC) |
p(AMPS) |
p(APTAC-co-AMPS) |
p(APTAC-co-AMPS) |
| Composition (mol. %) |
100 |
100 |
50:50 |
25:75 |
| Ethanol conversion (%) |
6.7 |
7.0 |
7.3 |
7.4 |
Table 2.
Reusability of cryogel-encapsulated catalase in oxidation of ethanol at 20 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, pH = 7.1.
Table 2.
Reusability of cryogel-encapsulated catalase in oxidation of ethanol at 20 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, pH = 7.1.
| Runs |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
| Throughput rate, mL⋅min-1
|
5.0 |
5.0 |
3.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
| Contact time, min |
2.0 |
4.0 |
9.0 |
20.0 |
25.0 |
| Conversion, % |
91.8 |
85.2 |
14.5 |
0.7 |
0.3 |
Table 3.
Calculated values of TON and TOF.
Table 3.
Calculated values of TON and TOF.
| [EtOH]:[H2O2], mL |
1:9 |
2:8 |
3:7 |
4:6 |
5:5 |
6:4 |
7:3 |
8:2 |
9:1 |
| TON⋅10-7 [a]
|
0 |
0.14 |
0.23 |
6.75 |
16.86 |
3.23 |
0.45 |
0.48 |
0.10 |
| TOF⋅10-7 [b] |
0 |
0.15 |
0.28 |
9.00 |
22.48 |
4.31 |
0.89 |
1.07 |
0.51 |
Table 4.
Oxidation of ethanol by catalase, entrapped in a cryogel matrix, on a catalytic “duck” at 20 °C with hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen and air [a].
Table 4.
Oxidation of ethanol by catalase, entrapped in a cryogel matrix, on a catalytic “duck” at 20 °C with hydrogen peroxide, molecular oxygen and air [a].
| Reaction time, min (volume of absorbed O2) |
Yield of acetaldehyde, % |
Mass of sample, mg |
| Cryogel monolith |
Cryogel powder |
Cryogelmonolith |
Cryogelpowder |
| H2O2
|
O2
|
Air |
H2O2
|
O2
|
Air |
| 30 |
97.0 |
- |
- |
95.2 |
- |
- |
98.8 |
86.0 |
| 30 (13 mL) |
- |
97.7 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
95.2 |
- |
| 30 (11.8 mL) |
- |
- |
- |
- |
96.7 |
- |
- |
95.6 |
| 30 |
- |
- |
59.8 |
- |
- |
60.5 |
95.2 |
93.2 |
| 5 |
96.7 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
89.6 |
- |
Table 5.
Reusability of cryogel-encapsulated catalase in oxidation of ethanol at 25 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, pH = 6.9.
Table 5.
Reusability of cryogel-encapsulated catalase in oxidation of ethanol at 25 °C. [catalase] = 10 mg, [H2O2] = 0.06 mol⋅L-1, VEtOH = 5 mL, VH2O2 = 5 mL, pH = 6.9.
| Runs |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
| Contact time, min |
40.0 |
30.0 |
30.0 |
20.0 |
15.0 |
| Conversion, % |
65.8 |
63.8 |
60.4 |
57.9 |
57.3 |
Table 6.
Calculated values of TON and TOF.
Table 6.
Calculated values of TON and TOF.
| Oxidant |
Н2О2
|
О2
|
air |
| TON⋅10-7 [b]
|
18.3 |
17.9 |
18.2 |
18.4 |
18.2 |
11.3 |
11.4 |
| TOF⋅10-7 [c] |
0.6 |
0.6 |
3.7 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
0.4 |
0.4 |
Table 7.
Comparison of oxidation processes using flow-through and batch type reactors.
Table 7.
Comparison of oxidation processes using flow-through and batch type reactors.
| Type of reactor |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Flow-through reactor |
- high acetaldehyde yield and high ethanol conversion,
- high reaction rate,
- short contact time,
- possibility of conducting experiments at low temperatures (5-15 oC),
- high TON and TOF. |
- sharp drop in the product yield when repeated stability tests were performed,
- using only the liquid-phase oxidizers such as hydrogen peroxide, impossibility of oxidation with gaseous oxidizers as molecular oxygen and air. |
| Batch type reactor |
- high yield of acetaldehyde and high conversion of ethanol,
- possibility to carry out oxidation processes with different oxidizing agents both in the liquid state and with gases (O2, air),
- possibility to measure the amount of oxygen absorbed and monitor the oxygen absorption rate,
- reduction of diffusion inhibition by intensive shaking,
- good stability of the biocatalyst. |
- accumulation of the reaction product in the solution leading to inevitable catalyst deactivation,
- limited volume of reactor,
- impossibility to conduct experiments at low temperatures (5-15 °C). |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).