1. Introduction
The Internet is widely adopted as a consumer technology and has become an essential means for individuals to engage in global communication and interaction. (Chou C, 2001) The digital world, particularly the Internet, holds considerable influence over the daily lives and activities of university students, facilitating not only their academic endeavors but also their day-to-day tasks and worldwide social engagement. While many people harness the power of the Internet for beneficial and creative purposes, there is a segment of the student population that shows signs of unhealthy or obsessive Internet use. (Chou C, et al., 2000)
The widespread availability of internet access through portable devices such as smartphones and tablets is the primary cause of excessive internet usage. It is now an essential component of contemporary lifestyles. The study conducted by Bischof-Kastner et al. in 2014. College students are at a higher risk of problematic internet usage due to the combination of free internet access and limited parental supervision. Excessive internet usage among university students leads to psychological and physical issues. Li et al. (2016)
Adolescents are at a higher risk of internet addiction due to their ongoing psychological and emotional development, lower self-regulation abilities, susceptibility to media influence, and propensity towards addictive behaviours. This study was conducted by Wu CY et al. in 2015. The phenomenon of internet addiction has resulted in the creation of a specific term, known as internet addiction disorder (IAD), due to the overindulgence and pathological use of this medium. (Naseri et al., 2015)
Internet addiction disorder, or pathological Internet use, is a compulsive–impulsive spectrum disorder that involves online and/or offline computer usage. (Block JJ, 2008) It is defined as an impulse-control disorder that does not involve an intoxicant and it is characterized by the failure to resist one’s temptation, an urge or an impulse to engage in a particular behavior despite serious personal consequences, and is considered pleasurable and is seldom resisted (Shaw M et al. 2008). College students are a population of special concern, vulnerable to Internet addiction. (Kandell JJ, 2009) Any activity can be considered an addiction when turned into an obligation. Internet addiction is one’s inability to control internet use, which interferes with normal living and may cause psychological, academic, family, social, and work difficulties or dysfunction. (Cao F et al. 2007)
It exhibits features akin to substance dependence, including fixation, mood alterations, tolerance, withdrawal, distress, and functional impairment. (Yoon HJ et al. 2014). Excessive internet use can displace valuable time and cause behavioral narrowing, leading to dramatic psychosocial outcomes. This phenomenon is called “pathological internet use” (PIU). (Petersen KU, 2009) The younger generation is likelier to use the internet for entertainment and communicating with friends and family. (Fu KW et al., 2010). Similarly, to substance abuse such as drugs or alcohol, they develop a full-fledged addiction to the Internet. (Young KS-1996) Internet addicts become virtual and fantasy world members, cutting their presence from the real world. They use the internet as a substitute for real-life human connection, which they cannot achieve normally (Patricia Wallace 2014).
IAD sufferers’ exhibit increased solitary behaviour, which negatively impacts their social functioning. In severe instances, patients may encounter physical discomfort or medical issues such as carpal tunnel syndrome, dry eyes, back pain, intense headaches, eating irregularities, and disrupted sleep. The source cited is Beard KW (2005).
The use of smartphones and related technologies is detrimental to cognitive abilities such as attention, memory, emotional regulation, and thinking. Some argue that contemporary connectivity is altering our neural pathways to constantly seek immediate satisfaction, and that this menace to our civilization is nearly as significant as climate change. This is a citation and does not require rewriting.
Moods are typically less intense than emotions and may not always be associated with a specific contextual stimulus. According to a study, the negative consequences of prolonged online activity on mood are that they sometimes feel excited or euphoric when online, admit to going online to escape other problems to some degree and socialize online more than in person (Rotunda RJ et al. 2003). Internet addiction can have an adverse effect on the mood of individuals, leading to increased internet usage as a coping mechanism to alleviate low mood (Roman M et al. 2013).
Physical activity is defined as daily activity that lasts for at least an hour and involves the use of skeletal muscles, such as walking, running, and playing sports (Taylor D, 2014). Physical exercise enhances physical health and well-being and mitigates the likelihood and consequences of physical and mental ailments (Bouchard et al., 1994).
Technological advancements, such as the internet, have contributed to decreased physical activity among humans (Mistry SK 2015). The substitution of outdoor activities with indoor ones has resulted in a sedentary lifestyle (Warbrick I et al., 2016). The decline in physical activity is significantly linked to an increasing incidence of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mental illness. This trend is exacerbated by the decreasing reliance on physical activity in contemporary lifestyles (McAuley E et al. 1994).
Many adolescents frequently deal with bodily discomforts like migraines and musculoskeletal discomfort, which can be linked to insufficient muscle engagement and a deficit of physical activities. These conditions can arise from spending extensive periods online, a behavior common among this age group (Hakala PT et al. 2006)
Extended computer use may lead to higher body fat and an increased risk of obesity (Matusitz J et al., 2012). Similarly, they exhibit sedentary behaviour and lack engagement in physical pursuits. Obesity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between increased body mass index (BMI) in adolescents and excessive internet use, which may lead to a lack of physical activity and sports engagement (Kautiainen S et al. 2005).
Consequently, the objective of this research was to establish the correlation between excessive internet usage and its potential addictive nature and college students’ cognition, mood, and physical activity level. The study hypothesized a significant association between internet addition and college students’ cognition, mood, and physical activity. The study will bring out the internet addiction awareness so that the adequate duration of the internet use might be practiced to improve cognition, mood, and physical activities among college students.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study design
This research was based on a correlational observational based on the interpretation of a self-administered questionnaire addressing the cognition, mood, and physical activity level among college students.
2.2. Study settings
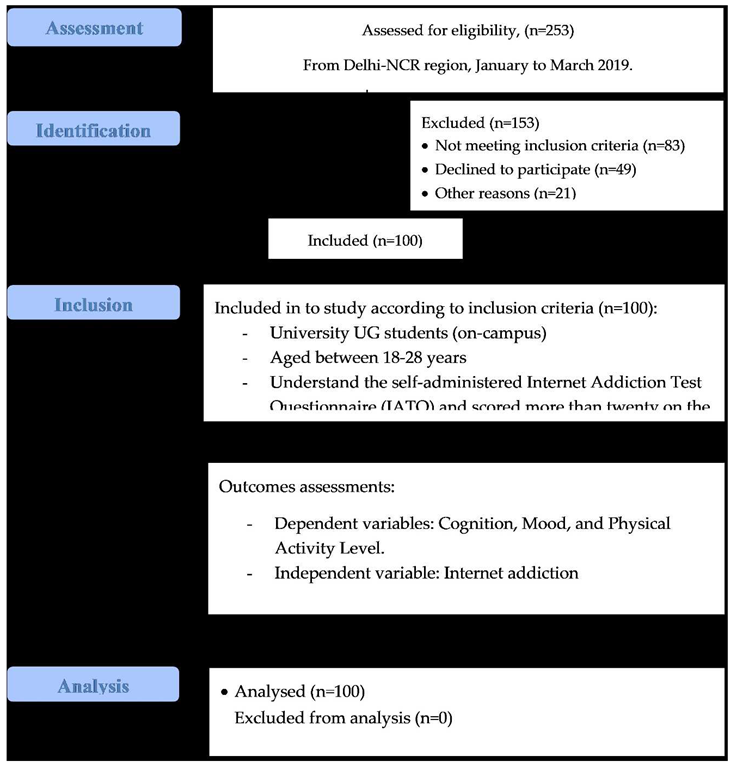
The study was conducted at the Manav Rachna University campus, comprising almost five thousand students of different academic levels. The study targeted mainly college undergraduate (UG) students, who were eighty percent of the total students. The study’s participants were approached through in-campus banners, pamphlets, and stalls/counters for study recruitment. The study data collection was completed within two months, starting in January 2019 and completing at the end of February 2019.
2.3. Study participants
One hundred university UG students were recruited based on the study’s eligibility criteria. The participants who were university UG students studying on campus, both females and males aged between 18–28 years, could understand the self-administered internet addiction test questionnaire (IATQ), and scored twenty or above on the IATQ, were included in this study (Lee K et al. 2013). However, the participants who had diagnosed cases of neurological, mental, psychiatric, and substance use disorders, post-surgery hampered their physical activities, did not have computers or devices like smartphones, laptops, etc., and showed non-cooperation or unwillingness to take part, were excluded from this study. An easily accessible option approach was used for selecting the study location, i.e., university; however, a simple random sampling method was used to avoid biasing, utilizing a number board/chart to choose odd and even counting numbers for the participant to be recruited. The participant who chose an odd and even number was accepted and denied, respectively, for the study screening.
2.4. Study variables
Impact of pathologic use of the internet was evaluated on multi-facets covering the participants’ level/status of cognition, mood, and physical activity, using a self-administered internet addiction test questionnaire (IATQ), cognitive failure questionnaire (CFQ) (Ekici G et al. 2016), the profile of mood state questionnaire (POMSQ) (Terry PC et al. 2001), and international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ) (Craig CL et al., 2003), respectively. The IATQ score of twenty or above was set to diagnose the participants’ internet addiction.
2.5. Variables assessments
2.5.1. Internet addiction test questionnaire (IATQ)
Dr. Kimberly Young created the Internet Addiction Test Questionnaire (IATQ) in 1998, consisting of 20 items. The scale employs a five-point Likert scale, ranging from 1 to 5, to evaluate the impact of internet usage on an individual’s daily life, social interactions, productivity, sleep, and emotional state. The test scores range from 20 to 100, with higher scores indicating greater susceptibility to internet addiction. Young’s classification categorizes internet users as minimal (20–49), moderate (50–79), and excessive (80–100) based on their scores (Lee K et al., 2013).
2.5.2. Cognitive Failures Questionnaire (CFQ)
The CFQ is a self-reported measure of deficits in attention, memory perception, and motor function while performing a simple task that an individual should typically complete without error. The score is obtained by summing the ratings of the 25 items, resulting in a range of scores from 0 to 100. A positive correlation exists between higher scores and increased cognitive failure. Ekici et al. (2016)
2.5.3. Profile of mood states questionnaire (PMOSQ)
The initial version of the Profile of Mood States Questionnaire (PMOSQ) comprises 65 self-evaluated items, scored on a five-point Likert Scale, with responses varying from 0 (“not at all”) to 4 (“extremely”). The Total Mood Disturbance (TMD) score is computed by adding up the scores for the negative dimensions (such as tension, depression, fatigue, confusion, anger) and then deducting the total scores for the positive aspects (including vigor and self-esteem related affect). Higher scores are indicative of a more unstable mood state. This measure has been validated and proven to be reliable (Terry PC et al. 2001).
2.5.4. The International Physical Activity Questionnaires (IPAQ)
To gauge the physical activity levels of the participants, the abbreviated version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) was implemented. This tool sets a standard that any physical activity should be carried out for a minimum duration of 10 minutes. A score, denoted in “MET-minute/week,” is achieved by multiplying the time spent, days, and MET values (equivalent to resting oxygen consumption). Based on this score, physical activity levels were categorized as physically inactive (<600 MET/week), low physical activity (600–3000 MET-min/week), or sufficient physical activity (>3000 MET-min/week). Energy expenditure from physical activities was estimated by multiplying each activity’s weekly duration (in minutes) by the corresponding MET energy values from the IPAQ, thus deriving energy expenses associated with intense, moderate, walking, sitting, and overall physical activities, expressed in MET-min/week. (Craig CL et al., 2003)
2.6. Study procedures
Using a convenience sampling method, i.e., a first-come-first-serve, one hundred college students, including females and males, were recruited in this study after screening based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Before starting the study, participants were asked to read, understand, and sign the informed consent form detailing the study’s background, problem, purpose, and potential harms and benefits. The participants’ demographic characteristics were documented before asked to complete the questionnaires, including IATQ, CFQ, POMSQ, and IPAQ. A STROBE (2010) flow diagram shows the study procedures, including participants’ enrollment, randomization/sampling, and data analysis, as presented in Figure 1.
2.7. Sample size estimation
The study’s effective sample size estimation was done using Raosoft- a sample size calculator available online (
http://www.raosoft.com/samplesize.html). For a study’s population of university UG students, i.e., almost 4000, keeping the margin of error at 8.96%, the confidence level at 95%, and the response distribution at 69%, a sample of hundred students were required to justify the sample power.
2.8. Statistical methods
A statistical tool—IBM SPSS v.28 (IBM SPSS, Inc. Armonk, USA), was used to analyze the participant’s data. Based on their internet addiction scores, participants were categorically identified as average, moderate, and excessive internet users. The mean scores for the outcomes, including IAT, CF, POMS, and IPA questionnaires, were analyzed. Pearson’s correlation coefficient was applied to determine the correlation among outcomes variables (IAT, CF, POMS, and IPA).
3. Results
With a response rate of 59%, one-hundred undergraduate students were recruited in this study. The descriptive statistics are presented in
Table 1.
The number of participants was categorized into average, moderate, and severe internet users according to the IAT mean scores, as presented in
Table 2.
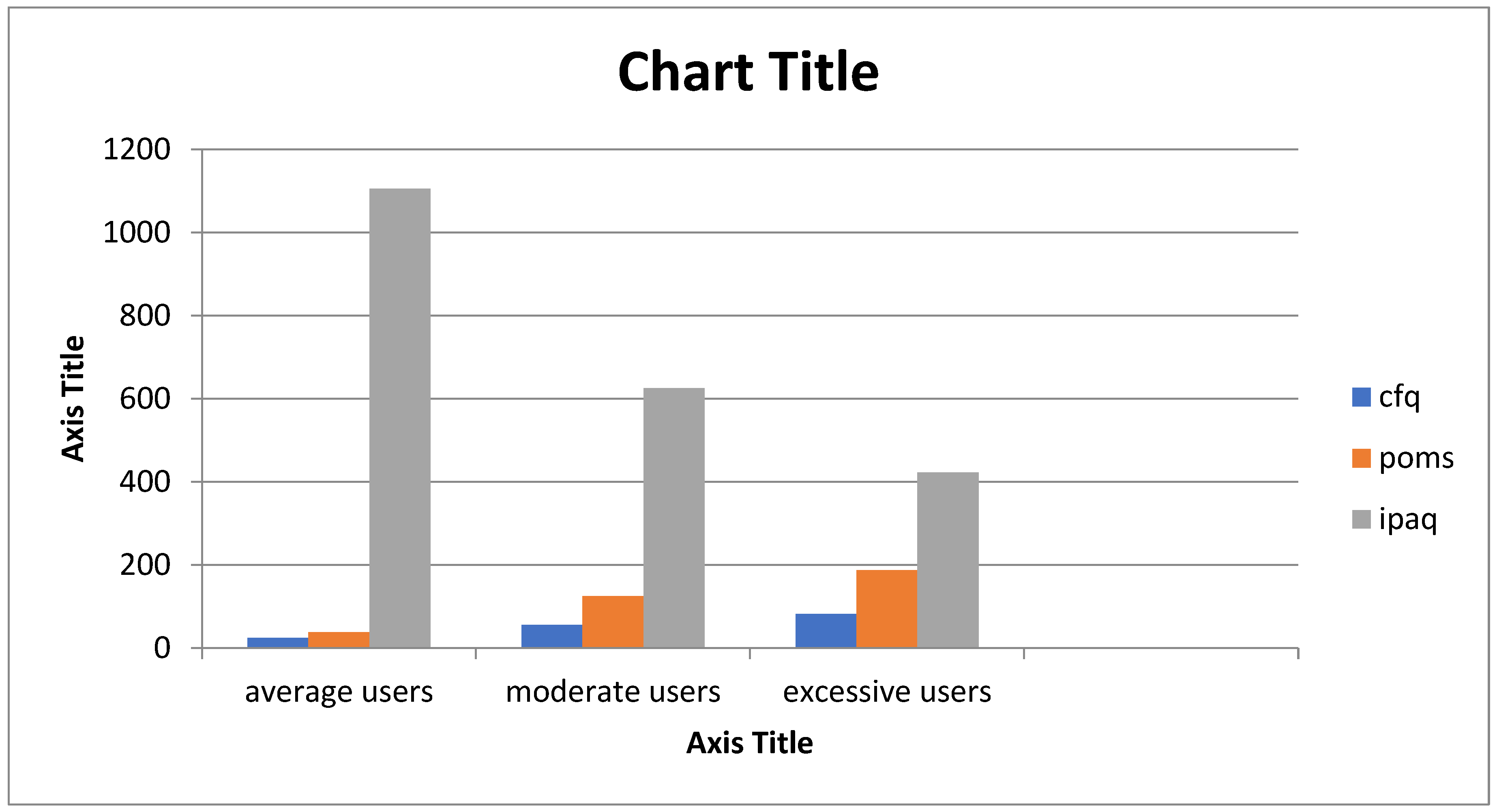
The categorized internet users among collegiate UG students obtained different mean scores for the variables IAT, CF, POMS, and IPA questionnaires, as presented in
Table 3 and
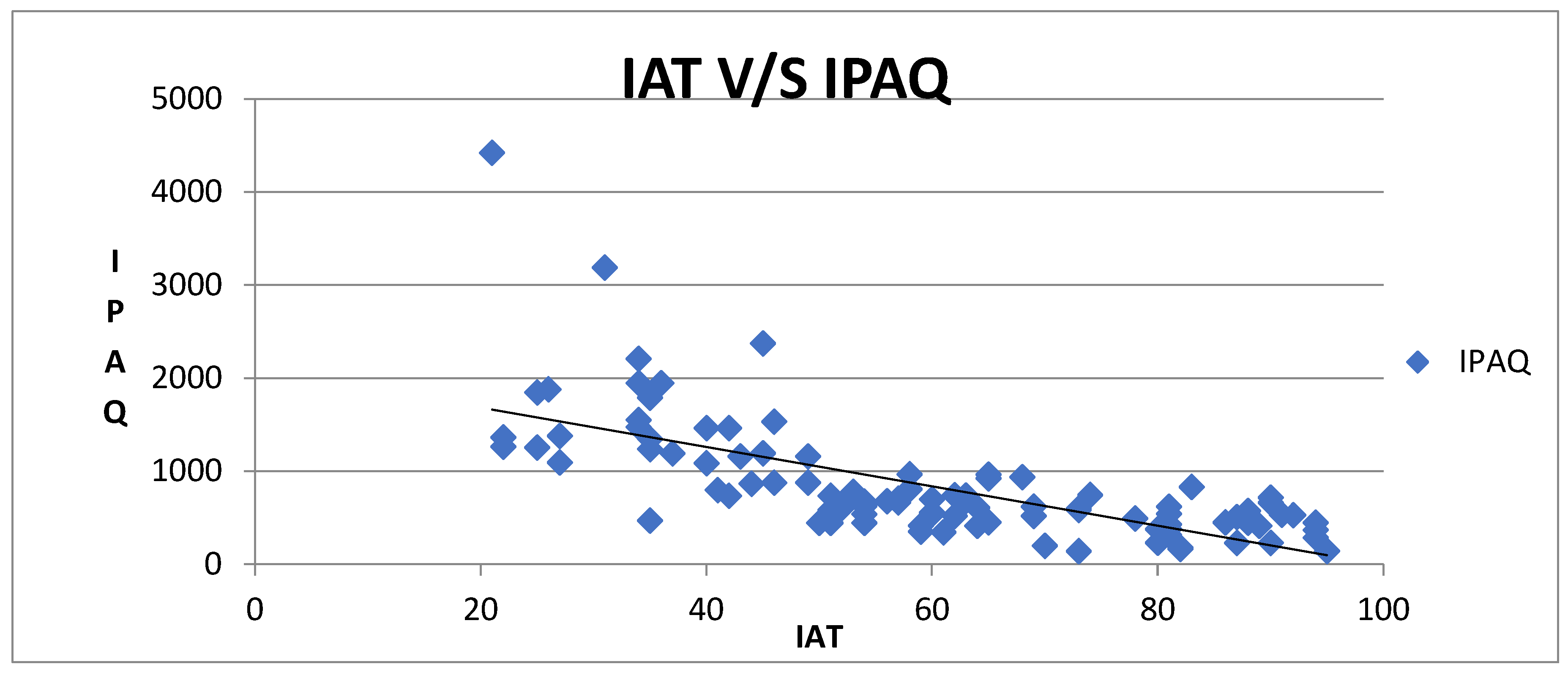
Figure 2.
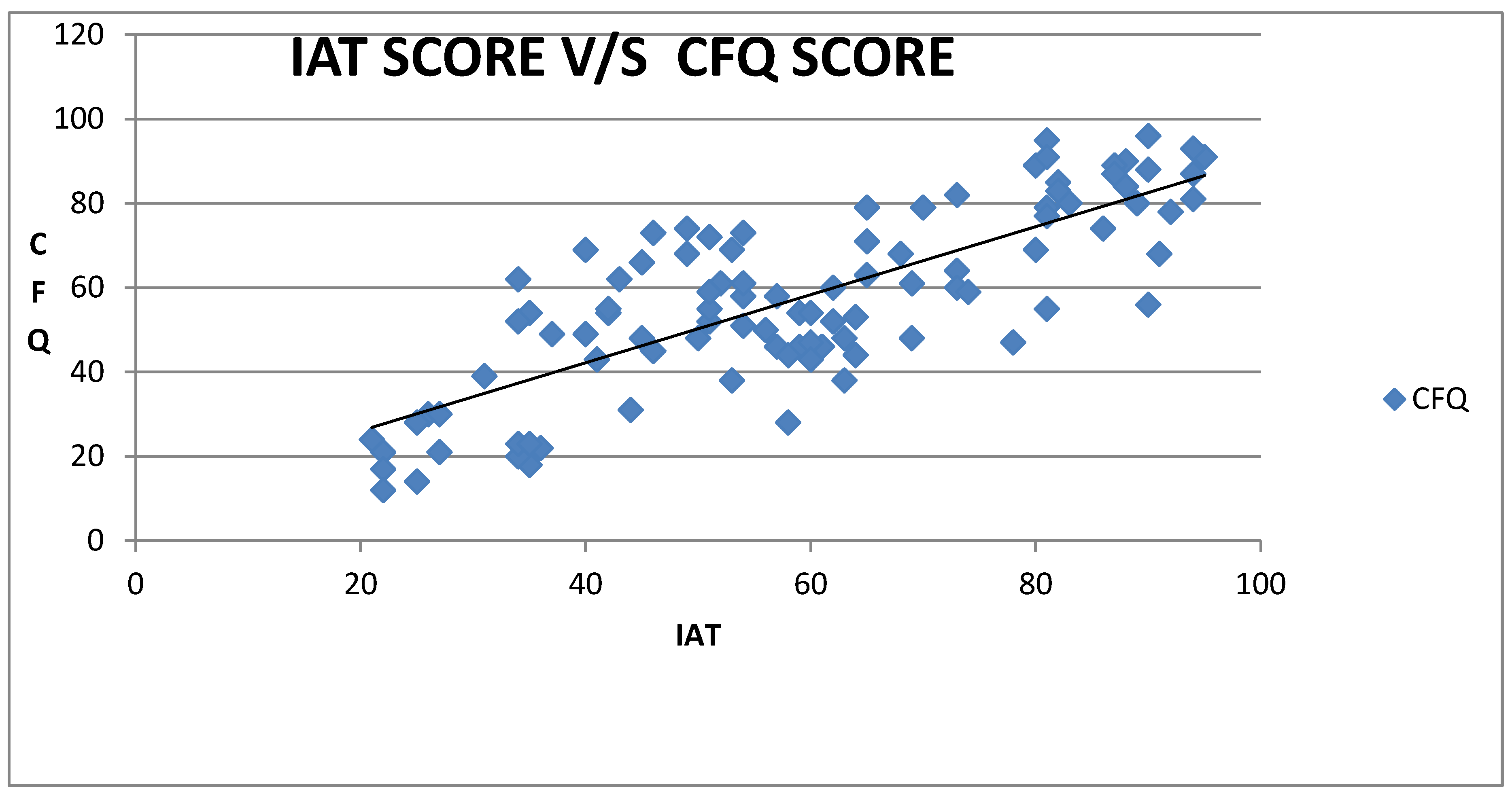
Pearson’s correlation coefficient test revealed that Internet addiction (IATQ) exhibited a moderate positive correlation with cognition (r = 0.79,
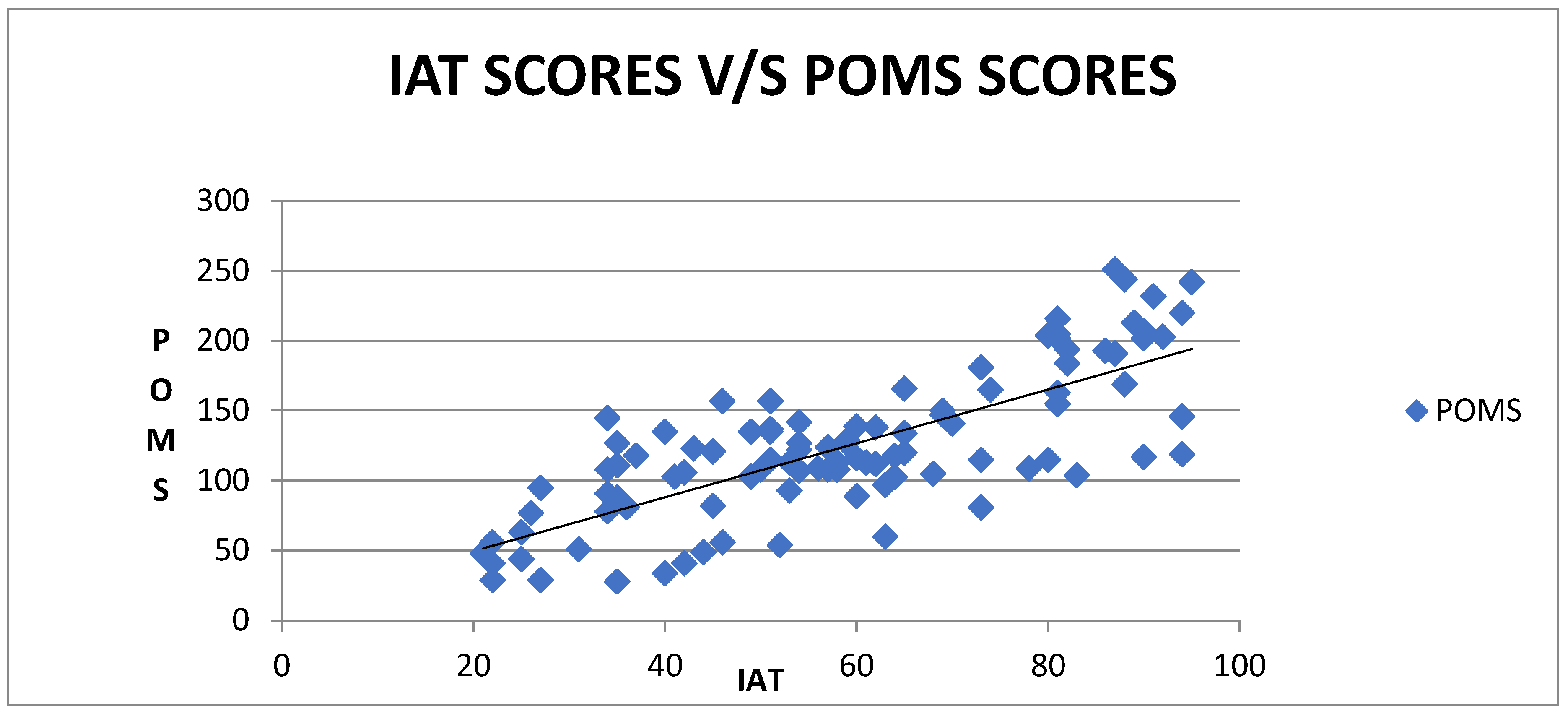
p < 0.05) and mood (r = 0.70,
p < 0.05); however, a moderate negative correlation with physical activities (r = −0.68,
p < 0.05), as presented in
Table 3 and
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5.
Table 3.
Correlation of Internet addiction (IAT) with cognition (CFQ), mood (POMSQ), and physical activity (IPAQ), using Pearson’s correlation coefficient tests (N = 100).
Table 3.
Correlation of Internet addiction (IAT) with cognition (CFQ), mood (POMSQ), and physical activity (IPAQ), using Pearson’s correlation coefficient tests (N = 100).
Pearson Correlation (2-tailed), N = 100
Variable 1 vs. Variable 2 |
Correlation
(r-value) |
Statistics
(95% CI, 2-tailed) |
| Variable 1 |
Variables 2 |
Lower CI |
Upper CI |
| Internet Addiction (IATQ) |
Cognition (CFQ) |
0.793** |
0.707 |
0.856 |
| Mood (POMSQ) |
0.703** |
0.588 |
0.791 |
| Physical Activity (IPAQ) |
−0.681** |
−0.774 |
−0.560 |
4. Discussion
The present research aimed to explore the correlation between internet addiction and cognitive function, mood state, and the level of physical activity among university students
A positive degree of correlation existed between internet addiction and cognition (r = 0.793) and mood (0.703), negative degree of correlation existed between internet addiction and physical activity (r = −0.681).
The mean cognition score in average users is 24.5 ± 19.09, in moderate users is 56.17 ± 11.92, and in severe users is 81.8 ± 10.80. The result of the current study showed that the increased usage of the internet greatly impacts the cognitive ability of students. With an increase in IAT scores, there was a significant increase in cognitive failure which was evaluated by the CFQ scores. Thus, a positive degree of correlation exists between internet addiction and cognition.
Mills KL’s 2016 study indicates that cognitive changes may be present in teenagers and young adults, but these changes do not necessarily impede their ability to effectively participate in our interconnected society. Sparrow et al. (2011) found that students who expected to have access to information in the future had lower recall of specific details but higher recall of the information’s location. This cognitive shift can be seen as an adaptation to the present environment, as it is more efficient to recall how to retrieve information when it is readily available rather than to remember numerous specific facts. Accessing the Internet’s collective memory may lead to decreased retention of specific facts, but increased proficiency in information retrieval. Fitton et al. (2013) found that the majority of adolescents held favourable opinions regarding the influence of technology on their cognitive and social development. Cognitive changes resulting from Internet use may be advantageous adaptations to a changing environment.
The current study also analyzed the correlation between internet addiction and mood to determine their relationship. It was seen that a positive degree of relationship existed between internet addiction and mood. The mean mood score in average users is 38.5 ± 36.56; in moderate users, it is 119.9 ± 25.58; and in severe users, it is 187.64 ± 41.84. Excessive use of the internet may disrupt their mood stability. In this current study, it is estimated that as internet addiction scores increased, scores for their mood also increased. The findings align with Romano et al.’s (2013) study, which investigated the varying effects of internet exposure on the positive mood of individuals with internet addiction. The study revealed a significant adverse effect of internet exposure on the positive affect of individuals with internet addiction. The study indicates that excessive internet use may be self-perpetuating and maintained as a means of escape, similar to other problematic behaviors. This is due to the fact that engaging in the behavior leads to a decrease in mood, which then prompts further engagement in order to alleviate the negative mood state.
Whang LS et al. (2003) found a significant correlation between the severity of Internet addiction and negative psychological outcomes such as loneliness, depression, and obsessive behaviour. Individuals with internet addiction exhibited elevated levels of loneliness and depression in comparison to those without such addiction. In contrast, the group not exhibiting internet addiction showed lower levels of loneliness, depression, and compulsive behaviour, indicating better psychological well-being.
Orzack et al. (1999) found that individuals with tendencies towards boredom, solitude, shyness, depression, and addiction may be at a greater risk for developing internet addiction.
A study by Akin et al. (2011) investigated the association between internet addiction and symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. The study highlighted significant correlations among these variables. Students with high levels of internet addiction are more prone to experiencing depression, anxiety, and stress. The study’s results indicate a positive correlation between addiction severity and elevated levels of stress, anxiety, and depression among individuals.
In 2017, Gholamian B et al. conducted a study to determine the prevalence of Internet addiction and its association with anxiety, stress, and depression among high-school students in Shahr-e Kord, Iran. Their findings were consistent with previous research. The study revealed that 69.5% of the participants were typical internet users, 27.6% demonstrated mild internet addiction, and 2.9% displayed severe addiction. The study found that individuals with Internet addiction had significantly higher average scores for anxiety, depression, and stress compared to regular Internet users.
In the current study, the relationship of internet addiction with physical activity is correlated negatively. The mean value of physical activity in MET in Average users is 1105.25 ± 745.85 MET-min/week; in moderate users, it is 625.10 ± 192.14 MET-min/week, and in excessive users, it is 422.92 ± 179.13 MET-min/week. Excessive users are inactive, whereas average and moderate users are minimally active. Thus, there was a statistically significant difference in internet addiction and physical activity levels in college students. In 2015, Kim SE et al. conducted a study examining the relationship between smartphone addiction and physical activity levels. The findings indicate that smartphone addiction may have negative impacts on physical health by reducing engagement in physical activities such as walking. Reduced physical activity can result in increased fat mass and decreased muscle mass, which are associated with adverse health consequences.
The results are consistent with Khan et al.’s (2017) study on medical college students, indicating a negative correlation between internet addiction and physical activity. The authors observed a correlation between physical inactivity in students and increased lethargy, as well as a potential for excessive use of internet devices. Inactive students had a significantly higher average score for Internet Addiction compared to physically active students.
Warbarick et al. (2016) conducted a study to examine the factors associated with reduced physical activity among indigenous New Zealanders. The study identified technology as a significant distraction. Zhou R et al. (2014) discovered a negative correlation between internet usage and engagement in physical activities such as sports and exercise. Heavy internet users exhibit lower park visitation rates relative to non-heavy users.
Park S (2014) found a negative correlation between physical activity and problematic Internet use in adolescents, with sleep satisfaction and stress serving as mediators.
This study is limited by a small sample size and a restricted geographical scope, which precludes generalisation of the findings to a larger population. Additionally, the study did not investigate the association between internet addiction and other factors such as sleep quality, academic performance, or behaviour. Future research should increase the sample size and geographical coverage, and explore the correlation between IAT outcomes and variables such as sleep quality, student conduct, and academic achievement.
5. Conclusion
The study concluded that in college UG students, Internet Addiction exhibits a acceptable positive correlation with Cognition and Mood and a acceptable negative correlation with physical activity. After analyzing the determinant, the study revealed that cognitive failure was higher in excessive internet users in relation to average and moderate internet users. The mood level was low (stable) in average online users and very high (unstable) in moderate and excessive users. College students’ heavy internet usage results in declining physical activity levels. As the level of addiction increases, the physical activity level decreases.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the study’s conception, design, methodology, data curation, data analysis, manuscript initial drafting, manuscript final drafting, reviewing, and editing. All authors read, understood, and approved the manuscript’s final version to be submitted.
Funding
Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R382), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R382), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia for funding this research.
Conflicts of Interests
The study’s authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
References
- Chou C (2001). Internet heavy use and addiction among Taiwanese college students: an online interview study. CyberPsychology & Behavior 4:573-585. [CrossRef]
- Chou C Hsiao M.C. (2000). Internet addiction, usage, gratification, and pleasure experience: the Taiwan college students’ case. Computers & Education 35(1):65-80. [CrossRef]
- Christina B K, Kuntsche E, Wolstein J (2014). Identifying problematic Internet users: development and validation of the Internet Motive Questionnaire for Adolescents (IMQ-A). Journal of medical interest research 16(10): e230. [CrossRef]
- Li W., O ‘Brien, J.E., Snyder SM, Howard M.O. (2016). Diagnostic Criteria for Problematic Internet Use among U.S. University Students: A Mixed-Methods Evaluation. PLoS One 11(1): e0145981. [CrossRef]
- Wu CY, Lee MB, Liao SC, Chang LR. (2015). Risk Factors of Internet Addiction among Internet Users: An Online Questionnaire Survey. PLoS One 10(10):e0137506. [CrossRef]
- Naseri L, Mohamadi J, Sayehmiri K, Azizpoor Y (2016). Perceived Social Support, Self-Esteem, and Internet Addiction Among Students of Al-Zahra University, Tehran, Iran Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Behavorial Sciences 9(3): e421. [CrossRef]
- Block JJ (2008). Issues for DSM-V: Internet Addiction. The American journal of psychiatry 165(3): 306-307. [CrossRef]
- Shaw M, Black DW (2008). Internet addiction: definition, assessment, epidemiology and clinical management CNS Drugs 22(5):353-65. [CrossRef]
- Kandell JJ (2009). Internet Addiction on Campus: The Vulnerability of College Students. CyberPsychology & Behavior1(1): 11-17. [CrossRef]
- Cao F, Su L, Liu TQ, Gao X (2007). The relationship between impulsivity and Internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents. European Psychiatry 22 466-471. [CrossRef]
- Yoo HJ, Cho SC, Ha J, Yune SK, Kim SJ, Hwang J, Chung A, Sung YH, Lyoo IK (2014). The association between internet addiction and psychiatric co-morbidity: a meta-analysis BMC Psychiatry; 14: 183. [CrossRef]
- Petersen KU (1), Weymann N, Schelb Y, Thiel R, Thomasius R (2009). Pathological Internet use--epidemiology, diagnostics, co-occurring disorders, and treatment Fortschritte der Neurologie-Psychiatrie 77(5):263-271. [CrossRef]
- Fu, K. W., Chan, W. S., Wong, P. W., & Yip, P. S. (2010). Internet addiction: prevalence, discriminant validity and correlates among adolescents in Hong Kong. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 196(6), 486-492. [CrossRef]
- Young KS (1996). Psychology of Computer Use: XL. Addictive Use of the Internet: A Case That Breaks the Stereotype Psychological Report 79(3 Pt 1):899-902. [CrossRef]
- Patricia Wallace (2014). Internet addiction disorder and youth. EMBO reports 15(1):12-16. [CrossRef]
- Beard KW (2005). Internet Addiction: A Review of Current Assessment Techniques and Potential Assessment Questions CyberPsychology & Behavior 8(1): 7-14. [CrossRef]
- Wilmer H. H., Sherman, L. E., & Chein, J. M. (2017). Smartphones and cognition: A review of research exploring the links between mobile technology habits and cognitive functioning. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 605. [CrossRef]
- Rotunda R. J., Kass, S. J., Sutton, M. A., & Leon, D. T. (2003). Internet use and misuse: Preliminary findings from a new assessment instrument. Behavior Modification, 27(4), 484-504. [CrossRef]
- Romano M, Osborne LA, Truzoli R, Reed P (2013). Differential Psychological Impact of Internet Exposure on Internet Addicts. Plos One 8(2): e55162. [CrossRef]
- Taylor D (2014). Physical activity is medicine for older adults Postgraduate Medical Journal 90(1059):26-32. [CrossRef]
- Mistry S. K., Puthussery S. (2015). Risk factors of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence in South Asian countries: a systematic review of the evidence. Public Health, 129(3), 200-209. [CrossRef]
- Warbrick I, Wilson D, & Boulton A (2016). Provider, father, and bro–Sedentary Māori men and their thoughts on physical activity. International Journal for Equity in Health, 1(15):1-11. [CrossRef]
- McAuley E., Courneya K. S., Rudolph D. L., Lox, C. L. (1994). Enhancing exercise adherence in middle-aged males and females. Preventive medicine, 23(4), 498-506. [CrossRef]
- Hakala, P. T., Rimpelä, A. H., Saarni, L. A., & Salminen, J. J. (2006). Frequent computer-related activities increase the risk of neck–shoulder and low back pain in adolescents. The European Journal of Public Health, 16(5), 536-541. [CrossRef]
- Matusitz J., McCormick J. (2012). Sedentarism: The effects of Internet use on human obesity in the United States. Social work in public health, 27(3):250-269. [CrossRef]
- Kautiainen S., Koivusilta, L., Lintonen, T., Virtanen, S. M., & Rimpelä, A. (2005). Use of information and communication technology and prevalence of overweight and obesity among adolescents. International Journal of Obesity 29(8), 925. [CrossRef]
- Lee K., Lee, H. K., Gyeong, H., Yu, B., Song, Y. M., & Kim, D. (2013). Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Internet Addiction Test among college students. Journal of Korean medical science, 28(5), 763-768. [CrossRef]
- Ekici, G., Uysal, S. A., & Altuntas, O. (2016). The validity and reliability of cognitive failure questionnaire in university students. Türk. Fizyoterapi ve Rehabilitasyon Dergisi, 27(2), 55-60.
- Terry P. C., Lane, A. M., Fogarty, G. J. (2003). Construct validity of the Profile of Mood States—Adolescents for use with adults. Psychology of sport and exercise, 4(2): 125-139. [CrossRef]
- Mills, K. L. (2016). Possible effects of Internet use on cognitive development in adolescence. Media and Communication, 4(3): 4-12. [CrossRef]
- Sparrow B., Liu, J., Wegner, D. M. (2011). Google effects on memory: Cognitive consequences of having information at our fingertips. science, 1207745. [CrossRef]
- Fitton, V. A., Ahmedani, B. K., Harold, R. D., & Shifflet, E. D. (2013). The role of technology on young adolescent development: Implications for policy, research and practice. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, 30(5), 399-413. [CrossRef]
- Romano M, Osborne LA, Truzoli R, Reed P (2013). Differential Psychological Impact of Internet Exposure on Internet Addicts. Plos One 8(2): e55162. [CrossRef]
- Whang L.S. M., Lee S., Chang G. (2003). Internet over users psychological profiles: a behavior sampling analysis on internet addiction. Cyberpsychology & behavior, 6(2): 143-150. [CrossRef]
- Orzack, Hecht M., January (1999). Computer Addiction: Is it Real or Virtual? Harvard Medical School, 15(7): p. i7.
- Akin A, Iskender M. (2011). Internet addiction and depression, anxiety and stress. International online journal of educational sciences, 3(1), 138-148.
- Gholamian B., Shahnazi H., & Hassanzadeh, A. (2017). The Prevalence of Internet Addiction and its Association with Depression, Anxiety, and Stress, among High-School Students. International Journal of Pediatrics, 5(4), 4763-4770.
- Kim, S. E., Kim, J. W., & Jee, Y. S. (2015). Relationship between smartphone addiction and physical activity in Chinese international students in Korea. Journal of behavioral addictions, 4(3), 200-205. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. A., Shabbir, F., & Rajput, T. A. (2017). Effect of Gender and Physical Activity on Internet Addiction in Medical Students. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences, 33(1), 191. [CrossRef]
- Zhou R., Fong, P. S., Tan P. (2014). Internet use and its impact on engagement in leisure activities in China. PloS one, 9(2), e89598. [CrossRef]
- Park, S. (2014). Associations of physical activity with sleep satisfaction, perceived stress, and problematic Internet use in Korean adolescents. BMC public health, 14(1):1143. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).