Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
31 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
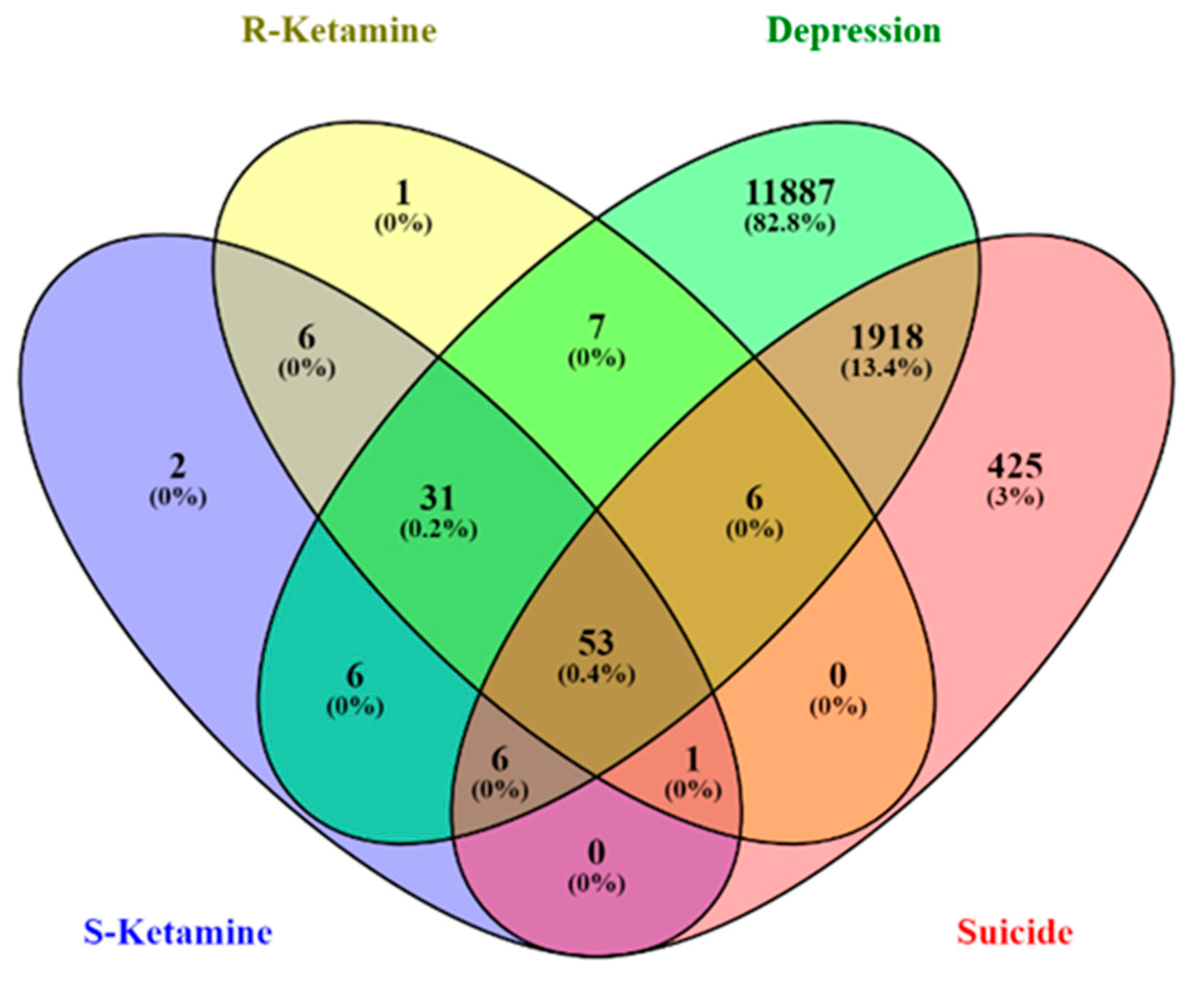
2.1. Identification of the ketamine enantiomers, suicide, and depression-overlapping genes
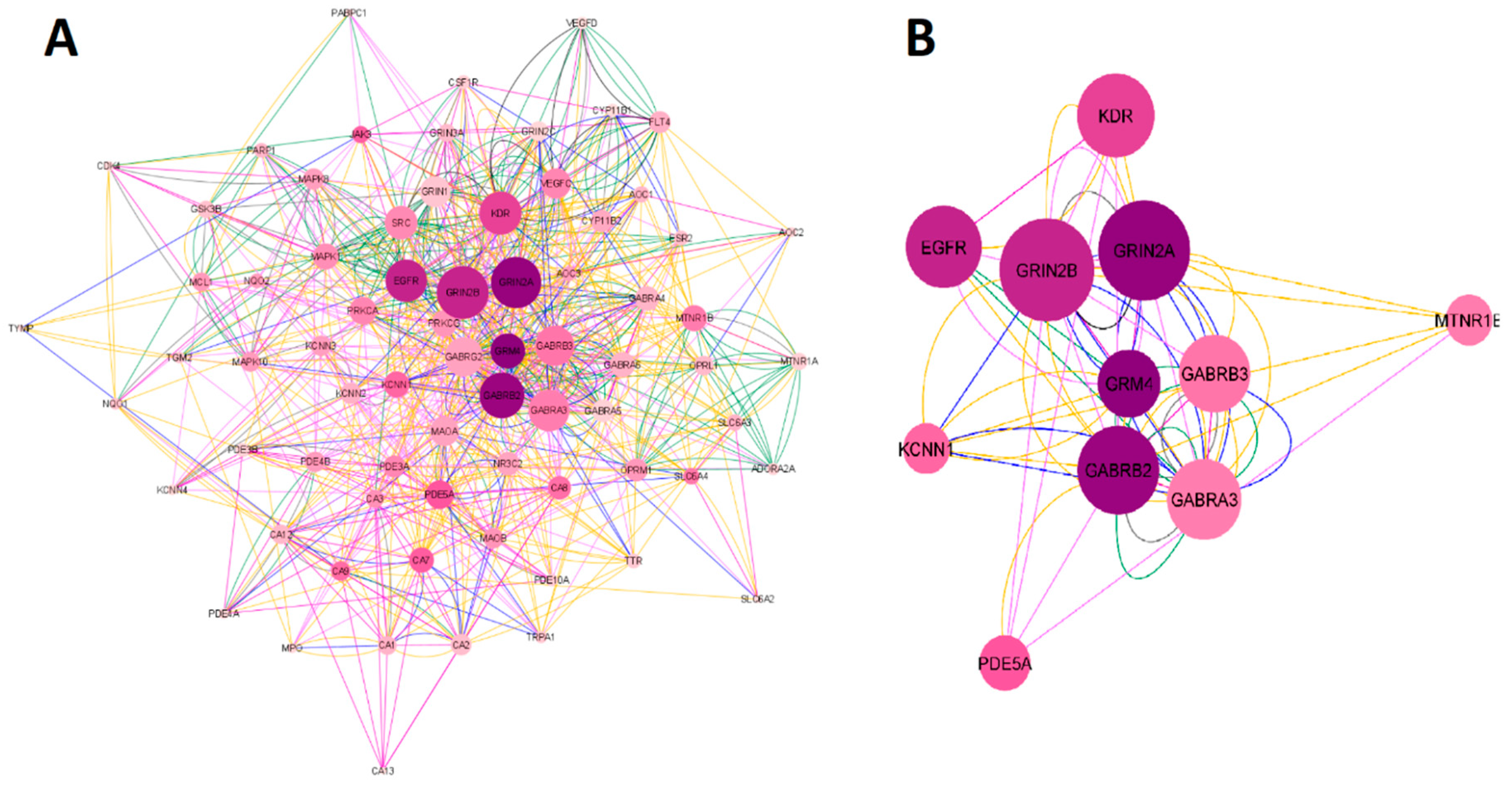
2.1.1. Network construction of ketamine enantiomers, suicide, and depression-overlapping genes
2.1.2. Network construction of esketamine, suicide and depression-overlapping genes
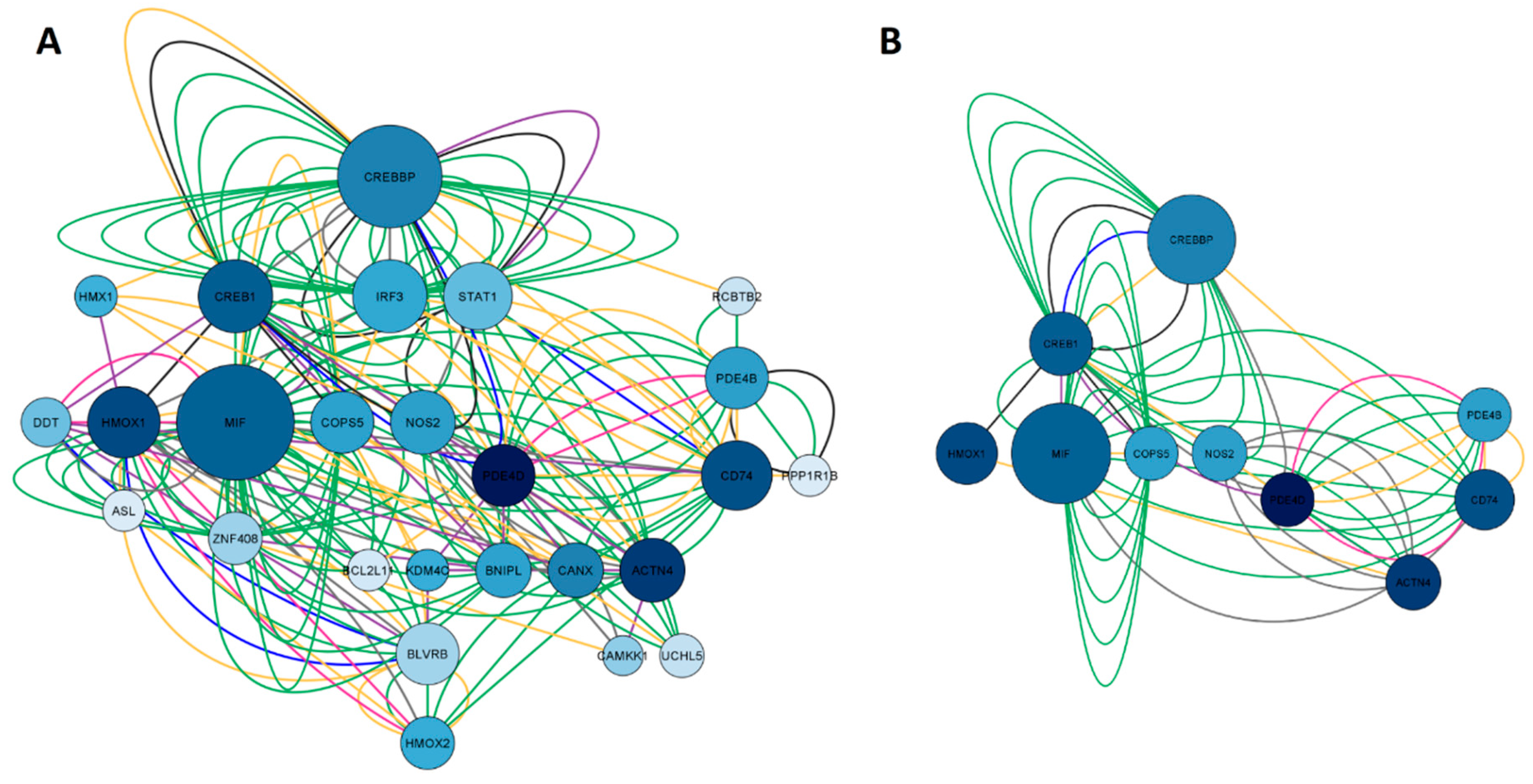
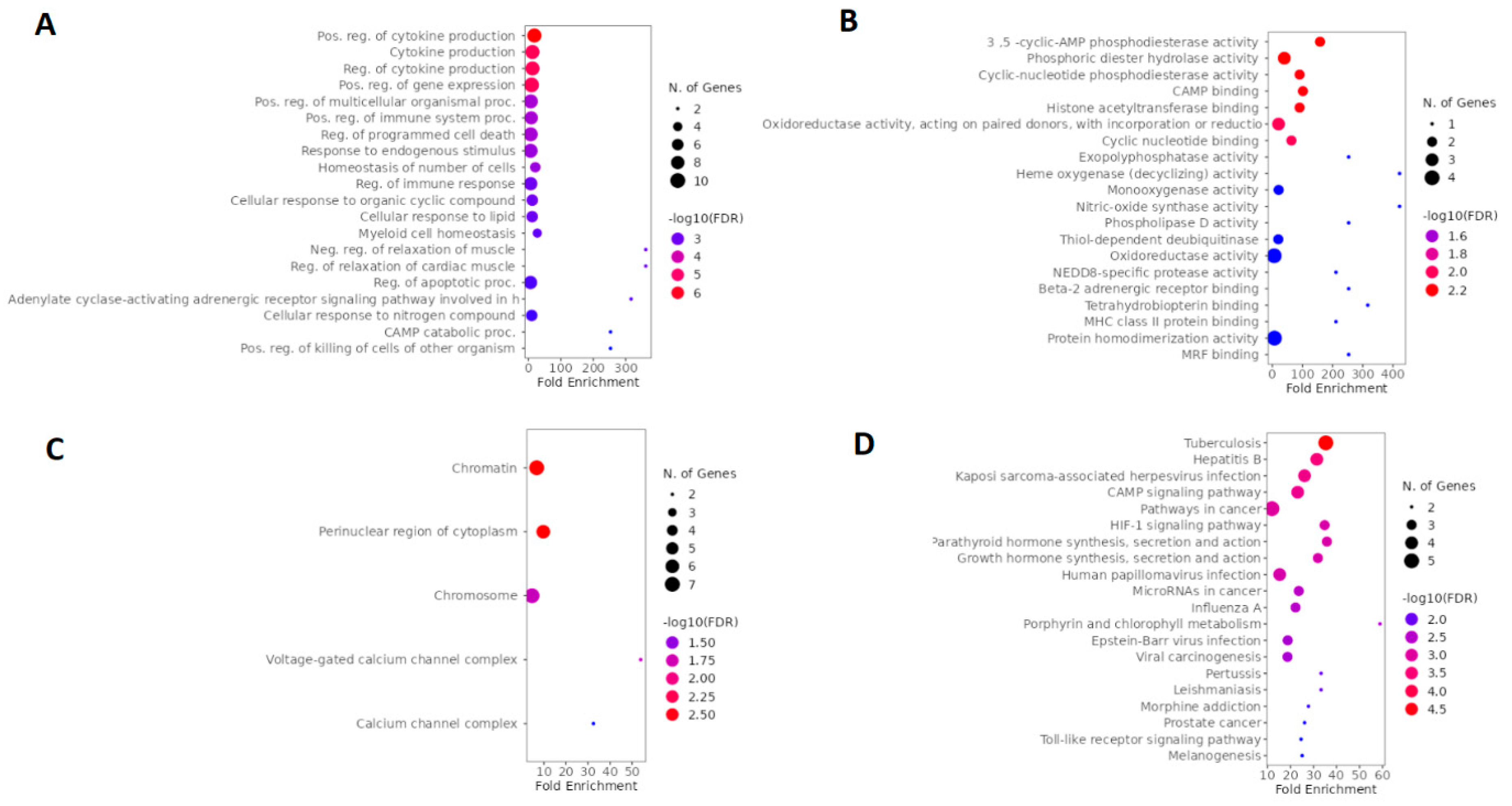
2.1.3. Network construction of arketamine, suicide and depression-overlapping genes
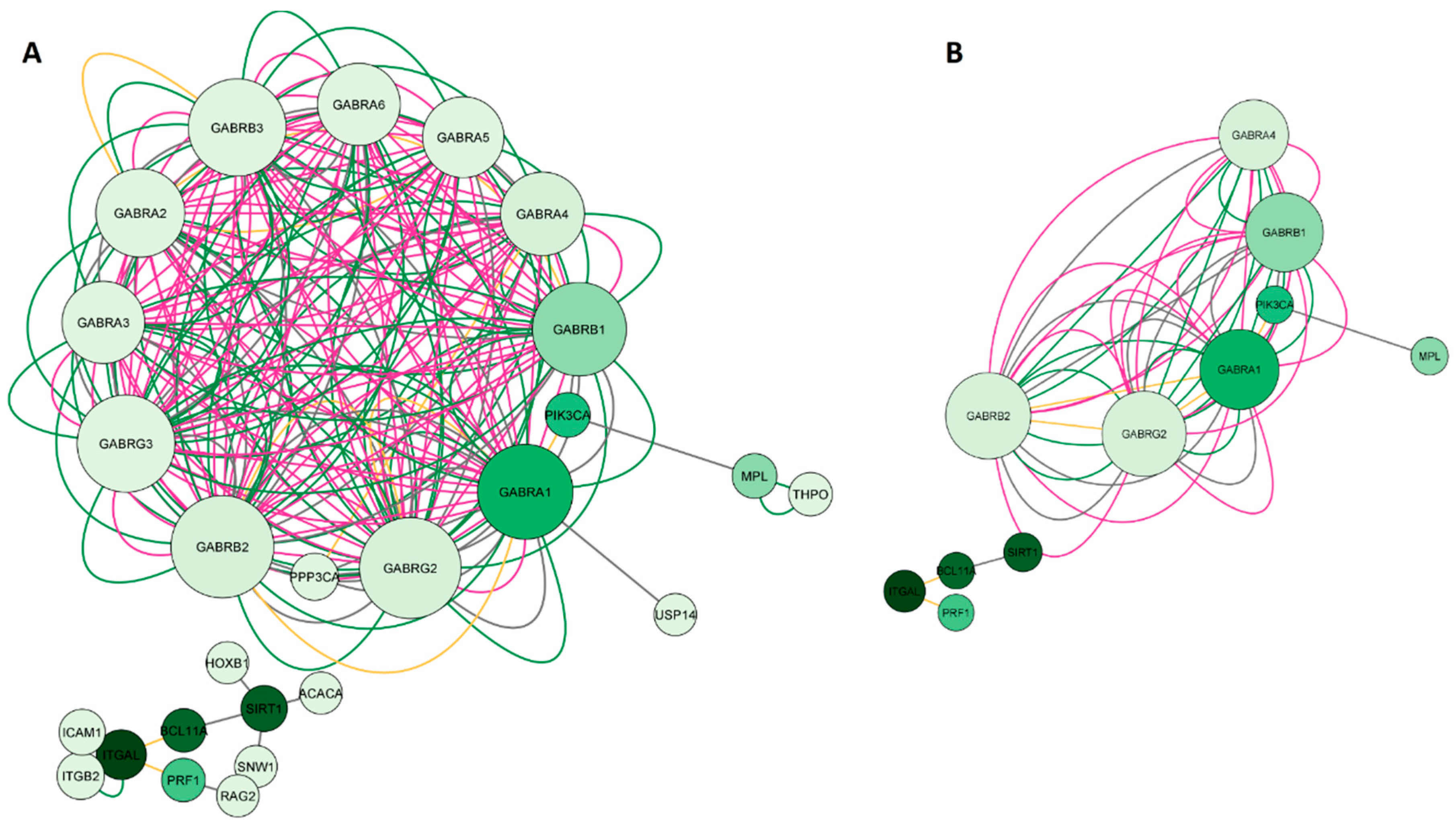
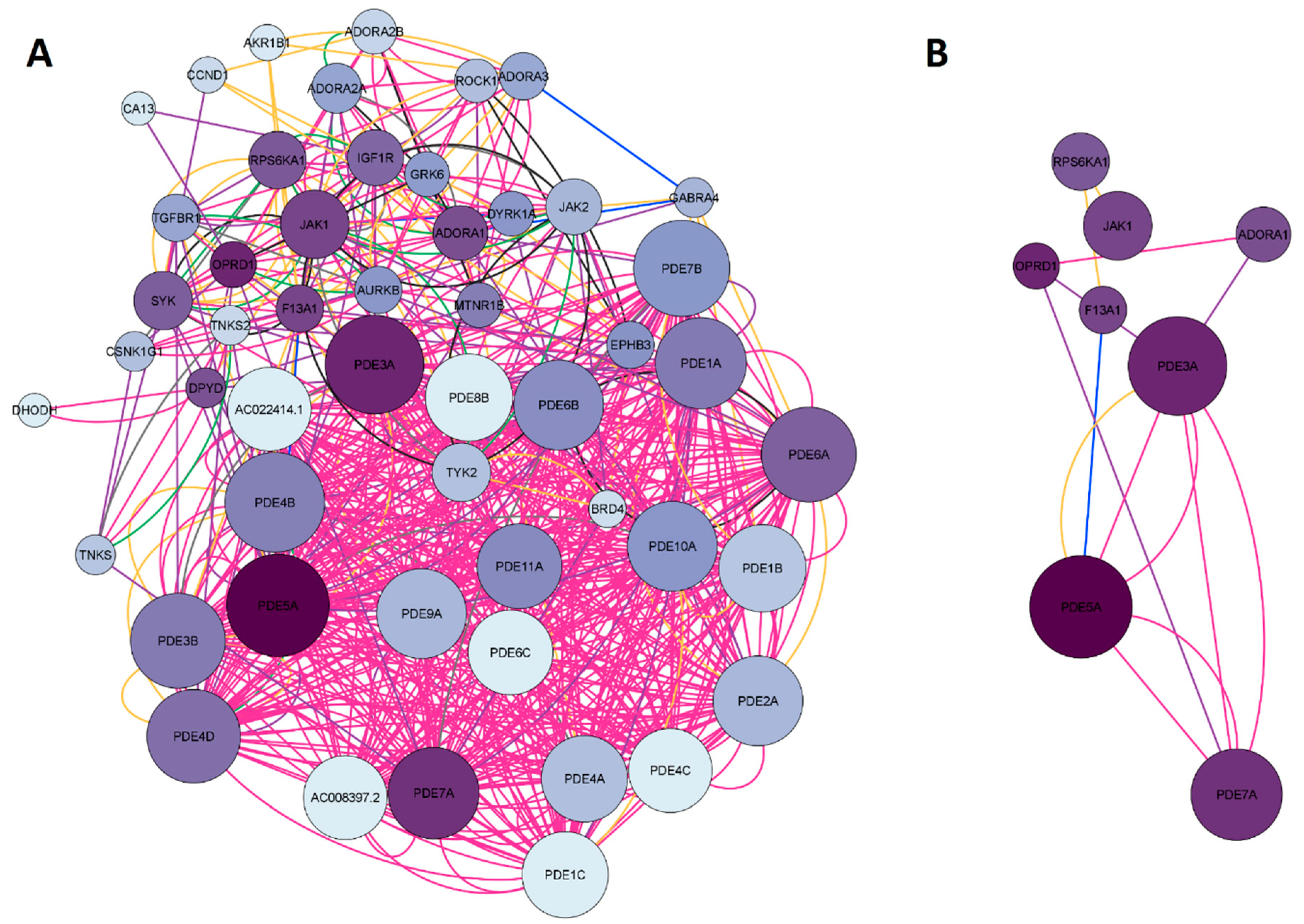
2.1.4. Network construction of ketamine enantiomers and depression-overlapping genes
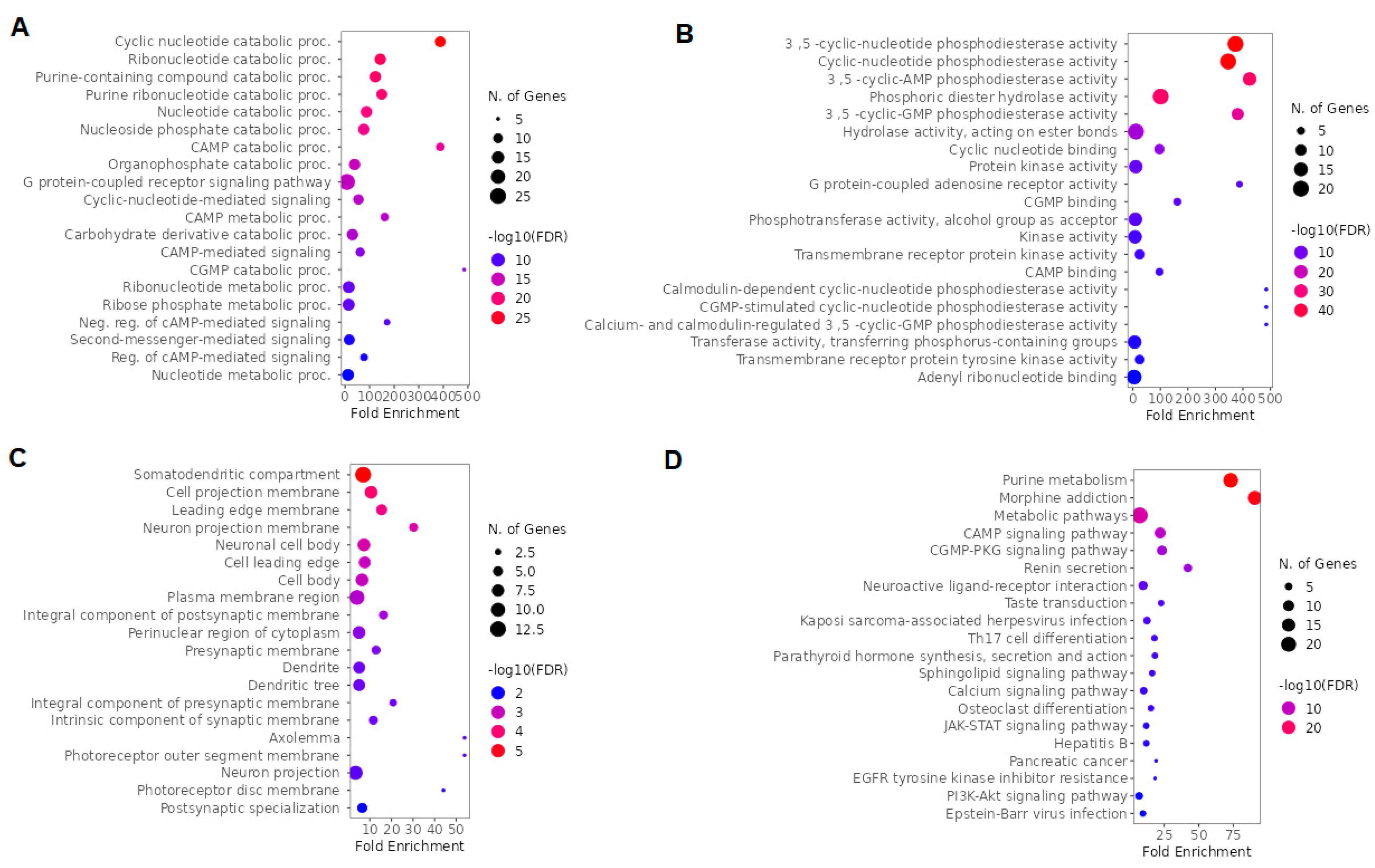
2.2. GO and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis of ketamine enantiomers, suicide, and depression-overlapping genes
2.3. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of esketamine, suicide and depression-overlapping genes
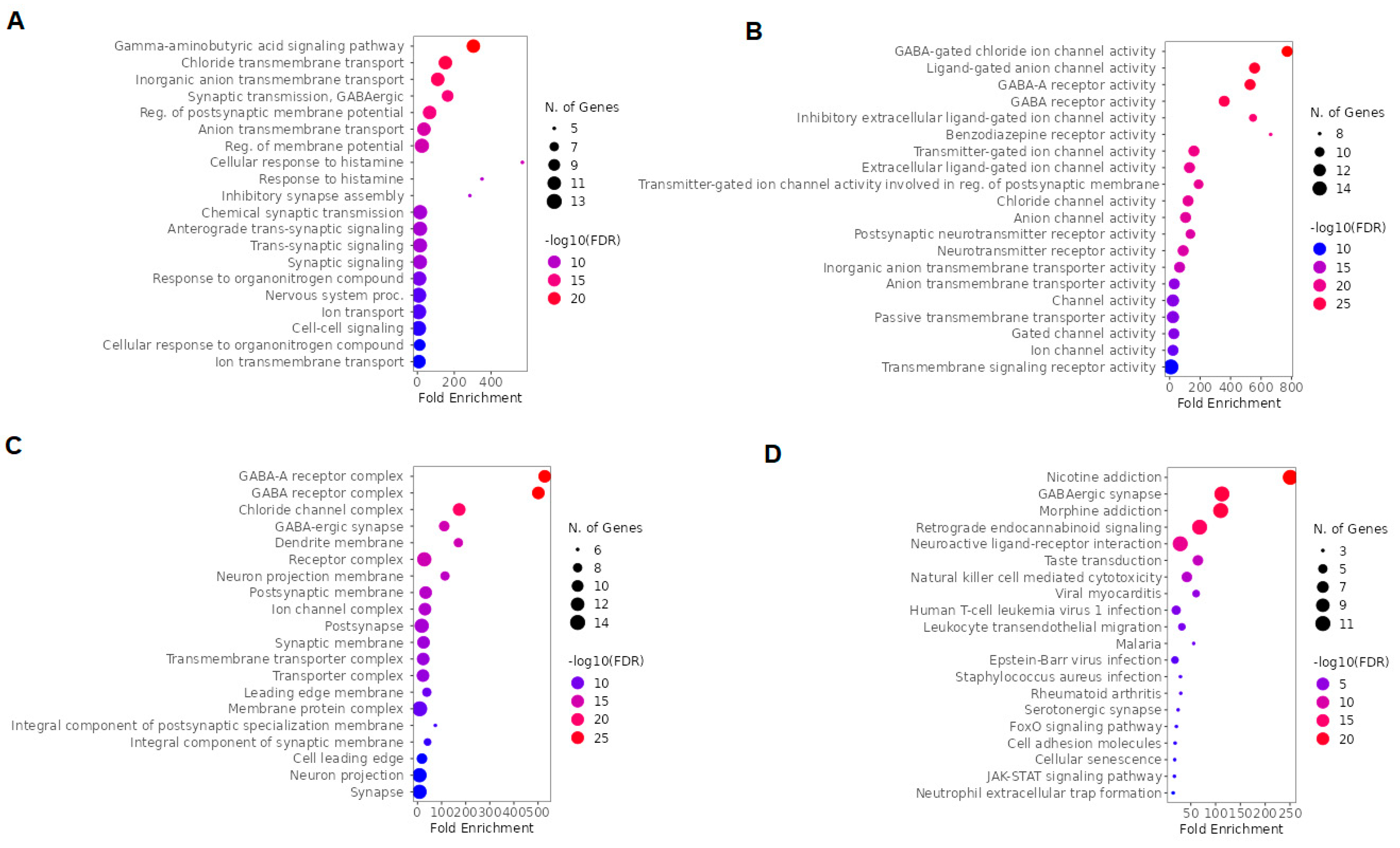
2.4. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of arketamine, suicide, and depression-overlapping genes
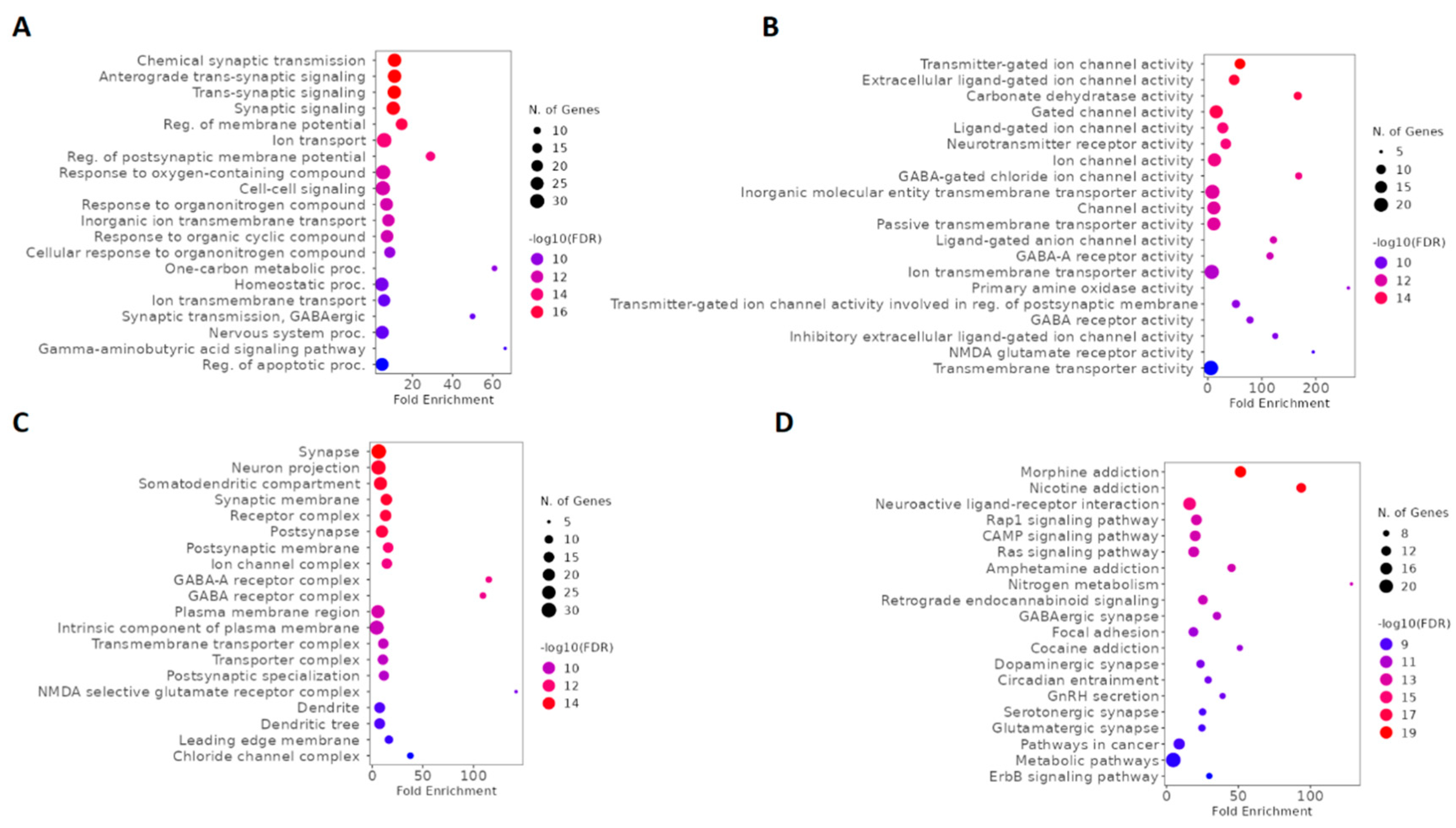
2.5. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of ketamine enantiomers and depression-overlapping genes
2.6. Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the potential target genes of ketamine enantiomers in suicide and depression
4.2. Gene-gene Interaction Network Construction and Analysis
4.3. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis
4.4. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO, W. H. O. , Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates. Geneva, 2017.
- WHO, W. H. O. ;., I. A. f. S. P., Preventing suicide: a resource for media professionals, 2017 update. Geneva, 2017.
- de Mello, A. J.; Moretti, M.; Rodrigues, A. L. S. , SARS-CoV-2 consequences for mental health: Neuroinflammatory pathways linking COVID-19 to anxiety and depression. World J Psychiatry 2022, 12(7), 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaster, M. P.; Moretti, M.; Cunha, M. P.; Rodrigues, A. L. , Novel approaches for the management of depressive disorders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villas Boas, G. R.; Boerngen de Lacerda, R.; Paes, M. M.; Gubert, P.; Almeida, W. L. D. C.; Rescia, V. C.; de Carvalho, P. M. G.; de Carvalho, A. A. V.; Oesterreich, S. A. , Molecular aspects of depression: A review from neurobiology to treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 851, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonsky, E. D.; May, A. M.; Saffer, B. Y. , Suicide, Suicide Attempts, and Suicidal Ideation. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 2016, 12, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, N.; Kang, J.; Campos, A. I.; Coleman, J. R. I.; Edwards, A. C.; Galfalvy, H.; Levey, D. F.; Lori, A.; Shabalin, A.; Starnawska, A.; et al. Dissecting the Shared Genetic Architecture of Suicide Attempt, Psychiatric Disorders, and Known Risk Factors. Biol Psychiatry 2022, 91(3), 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P. J.; Riggs, L. M.; Highland, J. N.; Georgiou, P.; Pereira, E. F. R.; Albuquerque, E. X.; Thomas, C. J.; Zarate, C. A.; Gould, T. D. , Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolite Pharmacology: Insights into Therapeutic Mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 2018, 70(3), 621–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Zhang, T.; Lv, S.; Zhou, L.; Du, D.; Lin, H.; Guo, F.; Luo, C.; Zhu, S. , Structural basis of ketamine action on human NMDA receptors. Nature 2021, 596(7871), 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R. S.; Li, N. , A neurotrophic hypothesis of depression: role of synaptogenesis in the actions of NMDA receptor antagonists. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012, 367(1601), 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.; Rodrigues, A. L. S. , Novel Targets for Fast Antidepressant Responses: Possible Role of Endogenous Neuromodulators. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks), 2019; 3, 2470547019858083. [Google Scholar]
- He, P. K.; Gao, Y. Y.; Lyu, F. J.; Chen, J. N.; Zhang, Y. H.; Nie, K.; Zhang, Q. X.; Huang, R.; Duan, Q. R.; Guo, M. L.; Liu, Z. H.; Huang, H. L.; Ma, G. X.; Wang, L. J.; Wang, L. M. , Idebenone-Activating Autophagic Degradation of. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021, 2021, 8548380. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, D.; Chen, K. , Bioinformatics Analysis of Potential Biomarkers and Pathway Identification for Major Depressive Disorder. Comput Math Methods Med 2021, 2021, 3036741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, S. , Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analyses Unveil the Mechanisms of Yiguanjian Decoction against Parkinson's Disease from Inner/Outer Brain Perspective. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 4758189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y. G.; Wu, H. B.; Chen, J. S.; Li, X.; Qiu, Z. K. , Exploring the Potential Antidepressant Mechanisms of Pinellia by Using the Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Metab Brain Dis 2022, 37(4), 1071–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, S.; Lin, N.; Hou, M.; Wei, M.; Li, T.; Shi, J. , Integration of Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology Reveals the Mechanism of the Therapeutic Effect of Xixin Decoction on Alzheimer's Disease. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2022, 25(10), 1785–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J. P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S. B.; Philpott, K. L. , Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162(6), 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muegge, I.; Bergner, A.; Kriegl, J. M. , Computer-aided drug design at Boehringer Ingelheim. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2017, 31(3), 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H. C. S.; Shan, H.; Dahoun, T.; Vogel, H.; Yuan, S. , Advancing Drug Discovery via Artificial Intelligence. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2019, 40(8), 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K. , Rapid-acting antidepressant ketamine, its metabolites and other candidates: A historical overview and future perspective. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2019, 73(10), 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chang, L.; Hashimoto, K. , A historical review of antidepressant effects of ketamine and its enantiomers. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 190, 172870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.; Yong, X. L. H.; Roche, K. W.; Anggono, V. , Regulation of NMDA glutamate receptor functions by the GluN2 subunits. J. Neurochem. 2020, 154(2), 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. , NMDA receptor subunit diversity: impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nature Rev.. Neurosci. 2013, 14(6), 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, O. H.; Yang, L.; Wang, C. C.; Hargroder, E. A.; Zhang, Y.; Delpire, E.; Hall, B. J. , GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors regulate depression-like behavior and are critical for the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine. eLife 2014, 3, e03581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sang, K.; Dong, Y.; Ni, Z.; Ma, S.; Hu, H. , Ketamine blocks bursting in the lateral habenula to rapidly relieve depression. Nature 2018, 554(7692), 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X. H.; Zhang, G. F.; Xu, N.; Duan, G. F.; Jia, M.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Z. Q.; Yang, J. J. , Extrasynaptic CaMKIIα is involved in the antidepressant effects of ketamine by downregulating GluN2B receptors in an LPS-induced depression model. J Neuroinflammation 2020, 17(1), 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanos, P.; Gould, T. D. , Mechanisms of ketamine action as an antidepressant. Mol. Psychiatry 2018, 23(4), 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorumski, C. F.; Izumi, Y.; Mennerick, S. , Ketamine: NMDA Receptors and Beyond. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36(44), 11158–11164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calandra, T.; Roger, T. , Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: a regulator of innate immunity. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3(10), 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conboy, L.; Varea, E.; Castro, J. E.; Sakouhi-Ouertatani, H.; Calandra, T.; Lashuel, H. A.; Sandi, C. , Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is critically involved in basal and fluoxetine-stimulated adult hippocampal cell proliferation and in anxiety, depression, and memory-related behaviors. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16(5), 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, M.; Meinhardt, A.; Lan, H. Y.; Dhabhar, F. S.; Mu, W.; Metz, C. N.; Chesney, J. A.; Gemsa, D.; Donnelly, T.; Atkins, R. C.; Bucala, R. , MIF expression in the rat brain: implications for neuronal function. Mol. Med. 1998, 4(4), 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Lee, J. P. W.; Elgass, K.; Pinar, A. A.; Tate, M. D.; Aitken, E. H.; Fan, H.; Creed, S. J.; Deen, N. S.; Traore, D. A. K.; Mueller, I.; Stanisic, D.; Baiwog, F. S.; Skene, C.; Wilce, M. C. J.; Mansell, A.; Morand, E. F.; Harris, J. , Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9(1), 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, R.; Schwarz, M. J.; Riedel, M.; Dehning, S.; Cerovecki, A.; Spellmann, I.; Arolt, V.; Müller, N. , Elevated macrophage migration inhibitory factor and decreased transforming growth factor-beta levels in major depression--no influence of celecoxib treatment. J Affect. Disord, 2011; 134, 1-3, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, K. M.; Bosch, J. A.; Engeland, C. G.; Cacioppo, J. T.; Marucha, P. T. , Elevated macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is associated with depressive symptoms, blunted cortisol reactivity to acute stress, and lowered morning cortisol. Brain Behav Immun. 2010, 24(7), 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Gennarelli, M.; Uher, R.; Breen, G.; Farmer, A.; Aitchison, K. J.; Craig, I. W.; Anacker, C.; Zunsztain, P. A.; McGuffin, P.; Pariante, C. M. , Candidate genes expression profile associated with antidepressants response in the GENDEP study: differentiating between baseline 'predictors' and longitudinal 'targets'. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38(3), 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Kumar, G.; Liao, Y.; Gk, P.; Fan, H. , Inhibition of phosphodiesterase: A novel therapeutic target for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 1019187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delhaye, S.; Bardoni, B. , Role of phosphodiesterases in the pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26(9), 4570–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H. T.; O'Donnell, J. M. , Phosphodiesterases in the central nervous system: implications in mood and cognitive disorders. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2011, (204), 447–485. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, Y. H.; Heo, Y. S.; Kim, C. M.; Hyun, Y. L.; Lee, T. G.; Ro, S.; Cho, J. M. , Phosphodiesterase: overview of protein structures, potential therapeutic applications and recent progress in drug development. Cell Mol Life Sci 2005, 62(11), 1198–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresele, P.; Momi, S.; Falcinelli, E. , Anti-platelet therapy: phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011, 72(4), 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, D. M.; Heinzmann, A. C. A.; Oggero, S.; Albers, H. J.; Nagy, M.; Hagué, P.; Kuijpers, M. J. E.; Vanderwinden, J. M.; van der Meer, A. D.; Perretti, M.; Koenen, R. R.; Cosemans, J. M. E. M. , Inhibition of Phosphodiesterase 3A by Cilostazol Dampens Proinflammatory Platelet Functions. Cells 2021, 10(8), 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, X.; Pérez-Torres, S.; Palacios, J. M.; Puigdomènech, P.; Mengod, G. , Differential distribution of cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase 7A mRNA in rat brain and peripheral organs. Synapse 2001, 40(3), 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.; Satała, G.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Bucki, A.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Świerczek, A.; Pociecha, K.; Partyka, A.; Jastrzębska-Więsek, M.; Lubelska, A.; Latacz, G.; Gawalska, A.; Bojarski, A. J.; Wyska, E.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G. , Novel anilide and benzylamide derivatives of arylpiperazinylalkanoic acids as 5-HT. Eur J Med Chem 2020, 201, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W. S.; Geethakumari, A. M.; Biswas, K. H. , Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5): Structure-function regulation and therapeutic applications of inhibitors. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 134, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M. L.; Whelan, F.; Deloukas, P.; Whittaker, P.; Delgado, M.; Cantor, R. M.; McCann, S. M.; Licinio, J. , Phosphodiesterase genes are associated with susceptibility to major depression and antidepressant treatment response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006, 103(41), 15124–15129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Lin, P.; Pan, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. T. , Antidepressant-like effects of the phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor etazolate and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor sildenafil via cyclic AMP or cyclic GMP signaling in mice. Metab Brain Dis 2014, 29(3), 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terunuma, M. , Diversity of structure and function of GABA. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2018, 94(10), 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallard, E.; Letourneur, D.; Legendre, P. , Electrophysiology of ionotropic GABA receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021, 78(13), 5341–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S. H.; Reddy, D. S. , Genetic and Molecular Regulation of Extrasynaptic GABA-A Receptors in the Brain: Therapeutic Insights for Epilepsy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2018, 364(2), 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.; Wiglusz, M. S.; Gałuszko-Wegielnik, M.; Włodarczyk, A.; Cubała, W. J. , Antianhedonic Effect of Repeated Ketamine Infusions in Patients With Treatment Resistant Depression. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12, 704330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogo, D.; Jasrai, A. K.; Kim, H.; Nasri, F.; Ceban, F.; Lui, L. M. W.; Rosenblat, J. D.; Vinberg, M.; Ho, R.; McIntyre, R. S. , The effect of ketamine on anhedonia: improvements in dimensions of anticipatory, consummatory, and motivation-related reward deficits. Psychopharmacology 2022, 239(7), 2011–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troppoli, T. A.; Zanos, P.; Georgiou, P.; Gould, T. D.; Rudolph, U.; Thompson, S. M. , Negative Allosteric Modulation of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid A Receptors at α5 Subunit-Containing Benzodiazepine Sites Reverses Stress-Induced Anhedonia and Weakened Synaptic Function in Mice. Biol Psychiatry. 2022, 92(3), 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R. S.; Del-Porto, J. A.; Surjan, J.; Magalhães, E.; Sant, L. C. D.; Lucchese, A. C.; Tuena, M. A.; Nakahira, C.; Fava, V. A. R.; Steglich, M. S.; Barbosa, M. G.; Sarin, L. M.; Lacerda, A. L. T. , Comparative effectiveness of esketamine in the treatment of anhedonia in bipolar and unipolar depression. J Affect Disord. 2021, 278, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugasawa, Y.; Cheng, W. W.; Bracamontes, J. R.; Chen, Z. W.; Wang, L.; Germann, A. L.; Pierce, S. R.; Senneff, T. C.; Krishnan, K.; Reichert, D. E.; Covey, D. F.; Akk, G.; Evers, A. S. , Site-specific effects of neurosteroids on GABA. eLife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Kanes, S.; Colquhoun, H.; Gunduz-Bruce, H.; Raines, S.; Arnold, R.; Schacterle, A.; Doherty, J.; Epperson, C. N.; Deligiannidis, K. M.; Riesenberg, R.; Hoffmann, E.; Rubinow, D.; Jonas, J.; Paul, S.; Meltzer-Brody, S. , Brexanolone (SAGE-547 injection) in post-partum depression: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390(10093), 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunduz-Bruce, H.; Silber, C.; Kaul, I.; Rothschild, A. J.; Riesenberg, R.; Sankoh, A. J.; Li, H.; Lasser, R.; Zorumski, C. F.; Rubinow, D. R.; Paul, S. M.; Jonas, J.; Doherty, J. J.; Kanes, S. J. , Trial of SAGE-217 in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. N Engl J Med 2019, 381(10), 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deligiannidis, K. M.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Gunduz-Bruce, H.; Doherty, J.; Jonas, J.; Li, S.; Sankoh, A. J.; Silber, C.; Campbell, A. D.; Werneburg, B.; Kanes, S. J.; Lasser, R. , Effect of Zuranolone vs Placebo in Postpartum Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78(9), 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. , Ketamine abuse potential and use disorder. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 126 Pt 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimatsu, Y.; Cash, D.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, K.; Bernanos, M.; Simmons, C.; Williams, S. C.; Kimura, H. , TAK-063, a phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor, modulates neuronal activity in various brain regions in phMRI and EEG studies with and without ketamine challenge. Neuroscience 2016, 339, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan Ezquerra-Romano, I.; Lawn, W.; Krupitsky, E.; Morgan, C. J. A. , Ketamine for the treatment of addiction: Evidence and potential mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. , SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47 (W1), W357–W364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B. A.; Thiessen, P. A.; Yu, B.; Zaslavsky, L.; Zhang, J.; Bolton, E. E. , PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49 (D1), D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T. I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; Kaplan, S.; Dahary, D.; Warshawsky, D.; Guan-Golan, Y.; Kohn, A.; Rappaport, N.; Safran, M.; Lancet, D. , The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016; 54, 1.30.1–1.30.33. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Lopes, C.; Zuberi, K.; Montojo, J.; Bader, G. D.; Morris, Q. , GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46 (W1), W60–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N. S.; Wang, J. T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. , Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13(11), 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S. X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. , ShinyGO: a graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36(8), 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, I. A.; Costa, L. S. C.; Dos Santos, K. B.; Karl, A. L. M.; Rocha, G. K.; Teixeira, I. M.; Galheigo, M. M.; Medeiros, V.; Krempser, E.; Custodio, F. L.; Barbosa, H. J. C.; Nicolas, M. F.; Dardenne, L. E. , Drug design and repurposing with DockThor-VS web server focusing on SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic targets and their non-synonym variants. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11(1), 5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.; Bettio, L. E. B.; Rosa, P. B.; Rosa, J. M.; Altê, G. A.; Rodrigues, A. L. S. , The antidepressant-like effect of guanosine involves the modulation of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors. Purinergic Signal. 2022, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burley, S. K.; Berman, H. M.; Kleywegt, G. J.; Markley, J. L.; Nakamura, H.; Velankar, S. , Protein Data Bank (PDB): The Single Global Macromolecular Structure Archive. Methods Mol Biol. 2017, 1607, 627–641. [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen, E. F.; Goddard, T. D.; Huang, C. C.; Meng, E. C.; Couch, G. S.; Croll, T. I.; Morris, J. H.; Ferrin, T. E. , UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30(1), 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
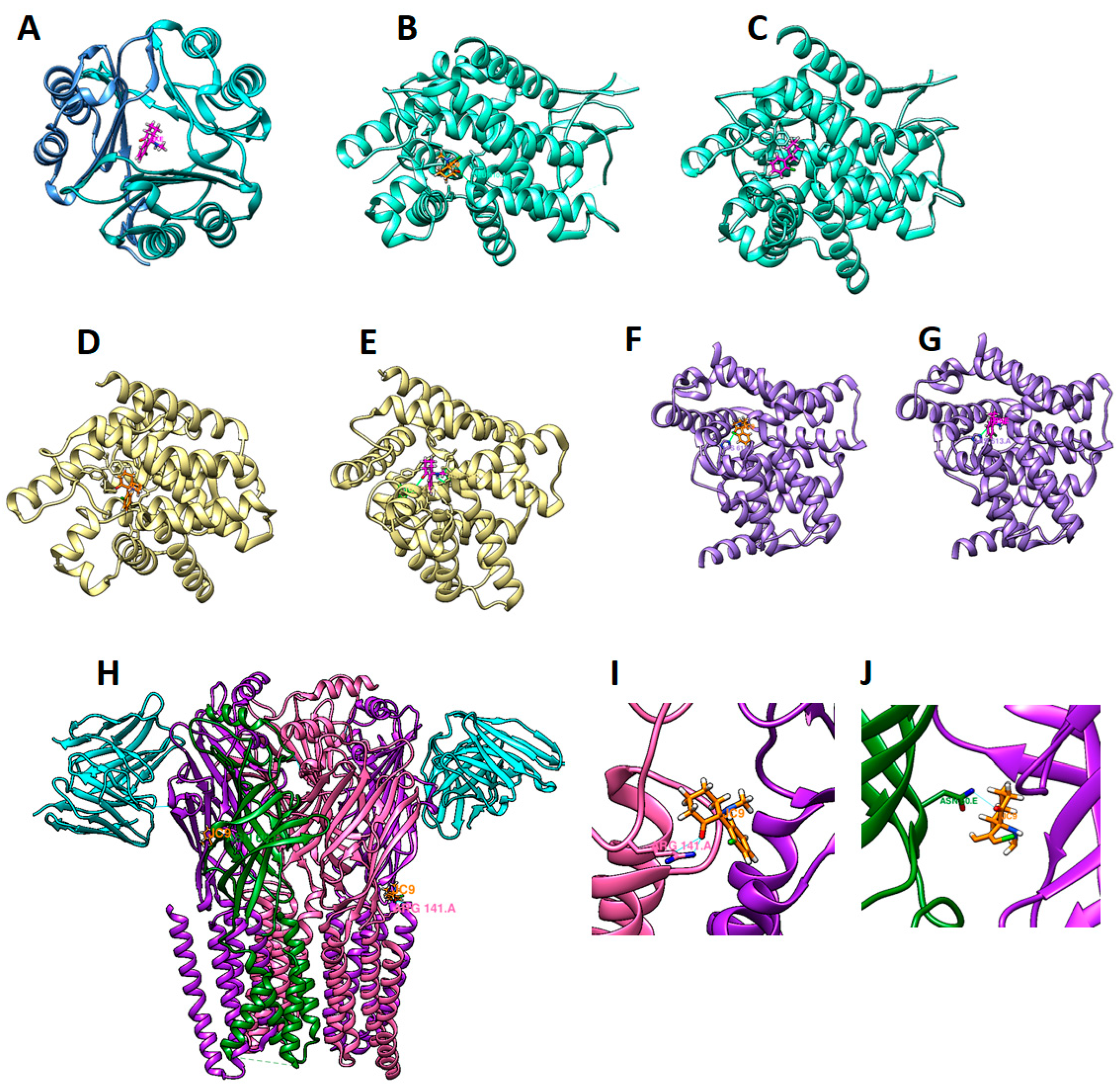
| Gene Symbol | PDB ID | Ligand ID (Binding Site) | Esketamine Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
Arketamine Docking Score (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRIN2B PDE3A MIF |
7EU8 | JC9 (ketamine) | -8.102 | -7.974 |
| 7KWE | X5M | -7.505 | -8.120 | |
| 1GCZ | center of protein | N.A. | -8.008 | |
| PDE7A | 1ZKL | IBM | -7.811 | -7.826 |
| PDE5A | 1T9S | 5GP | -7.629 | -7.740 |
| GABRB2 | 6D6T | Cl channel | N.A. | -7.747 |
| JAK1 | 4E4N | 0NL | -7.609 | -7.563 |
| GABRG2 | 6D6T | FYP (benzodiazepines) | -7.448 | N.A. |
| GRIN2A | 7EU7 | JC9 (ketamine) | -7.461 | -7.426 |
| GABRB2 | 6D6T | Y01 (neurosteroids) | -7.371 | -7.387 |
| PDE4D | 1OYN | ROL | N.A. | -7.347 |
| CREB1 | 5ZKO | center of protein | N.A. | -7.339 |
| EGFR | 7OXB | 35Z | -7.117 | -6.986 |
| CD74 | 5KSV | Between alpha helices and beta sheets | N.A. | -7.038 |
| F13A1 | 5MHL | MI0621 | -7.032 | -6.931 |
| GABRA4 | 7QNA | ABU (GABA) | -7.027 | N.A. |
| ACTN4 | 6OA6 | center of protein | N.A. | -7.004 |
| GABRB1 | 6DW1 | ABU (GABA) | -6.720 | N.A. |
| GABRA1 | 6D6T | ABU (GABA) | -6.608 | N.A. |
| GABRB2 | 6D6T | ABU (GABA) | -6.608 | -6.465 |
| GRM4 | 7E9H | SEP (phosphoserine) | -6.322 | -6.308 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





