1. Introduction
Graphene, a representative two-dimensional material, has been actively investigated for applications in viral biosensors, such as biosensors for detection of influenza and Cov19 viruses [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. To assess the quality of graphene films, Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and measurements of the concentration and mobility of charge carriers are widely used.
Currently it is not clear to what extent is it possible to preserve the quality of pristine graphene films in the process of chips fabrication and obtaining biosensors based on it. Recent publications [
9,
10,
11,
12] have shown that the quality of graphene films can be disturbed already at the initial stage of the chip formation of a given topology by photolithography (РLG) procedure. It is shown that photoresist interacts with graphene creating local regions with resist residues (LRRs) poorly removed from the graphene surface. This problem cannot be solved completely by selecting a specific photoresist, since the interaction proceeds at the level of benzene rings, presenting in all types of photoresists used, and graphene (regardless of the method of its production) [
11]. The traditional method of controlling the photoresist removal process in an optical microscope does not detect LRRs on graphene.
The presence of LRRs impairs graphene morphologies, enhances heterogeneous deformation distribution and non-reproducibility of biosensor parameters even until graphene functionalization, antibody immobilization and antigen (virus) sensing [
9,
10,
11,
12]. In particular, it has been shown that the resistance value of biosensors obtained from the same batch can vary from 2 to 10 times, and reproducible resistance values are observed only for 20% of biosensors [
9].
One of the methods to resolve the problem is to use a protective (sacrificial) layer between graphene film and a photoresist to limit the interaction between them [
12,
13,
14]. Other method is to control of graphene morphology after each PLG process by AFM methods with additional cleaning of the detected LRR in solvents. Encouraging results were obtained by both methods [
9,
12].
The effectiveness of the practical use of viral biosensors determines by reproducibility of the fabricated chips parameters and graphene quality. In this work, we report on assess the quality and reproducibility of graphene parameters in chips at the initial stage of their production not only AFM and Raman studies but with low-frequency noise studies.
As two-dimensional structure and widely tunable two-dimensional carrier concentration, monolayer graphene films offer unique opportunities for studying their 1/f noise [
15]. A smaller density of structural defects and higher material quality usually results in smaller noise spectral density. An independent investigation of 1/f noise in a wide selection of graphene devices (μ in the range 400 to 20,000 cm
2·V
–1·s
–1) concluded that in most of the devices examined the dominant contribution to 1/f noise was from the mobility fluctuations arising from the fluctuations in the scattering cross-section σ [
15,
16].
The low-frequency 1/f noise caused by mobility fluctuations can appear as a result of the superposition of elementary events in which the scattering cross-section, σ, of the scattering centers fluctuates from σ1 to σ2. For graphene films, the dependence of the spectral density of low- frequency current noise (S
I ) or voltage fluctuations (S
U) on frequency has the form S
U ~ 1/f
γ in the frequency range 1-100Hz. The nature of this noise is diverse and reflects fluctuation processes in the material, such as fluctuations in carrier mobility, carrier concentration, fluctuations in the height of barriers, charge fluctuations in surface states, as well as the charge state of defects with different activation energies [
15,
17]. Fluctuations in the population levels forming the tail of the density of states near the boundaries of the conduction band and the valence band. These fluctuations may be due to various imperfections of the crystal lattice: clusters, extended defects, local stresses, inhomogeneities of composition, non-ohmic contacts. The regions on the dependence S
U ~ 1/f
γ with a parameter γ other than 1 also suggests the presence of local areas with inhomogeneous deformation. Comparing the magnitude of low-frequency noise at a frequency of 1.22 Hz with the same geometry of the chips allows us to judge integrally the graphene quality and the reproducibility of the graphene properties in the chips.
2. Materials and Methods
The graphene films were formed on semi-insulating 4H-SiC substrates by thermal decomposition of the (0001) Si surface in a graphite crucible with induction heating [
18]. The method allows one to obtain high-quality graphene films on a high-resistance substrate of arbitrarily large areas, which is important to process graphene chips (dies) for sensing applications.
The ordinary photolithography process was applied to form a topological pattern of the graphene/SiC-based chips utilizing AZ1318 photoresist. The photoresist was removed in acetone and the graphene surface was examined by AFM followed by additional cleaning of the LRRs Details of graphene films processing and mounting of chips on holders can be found elsewhere [
18,
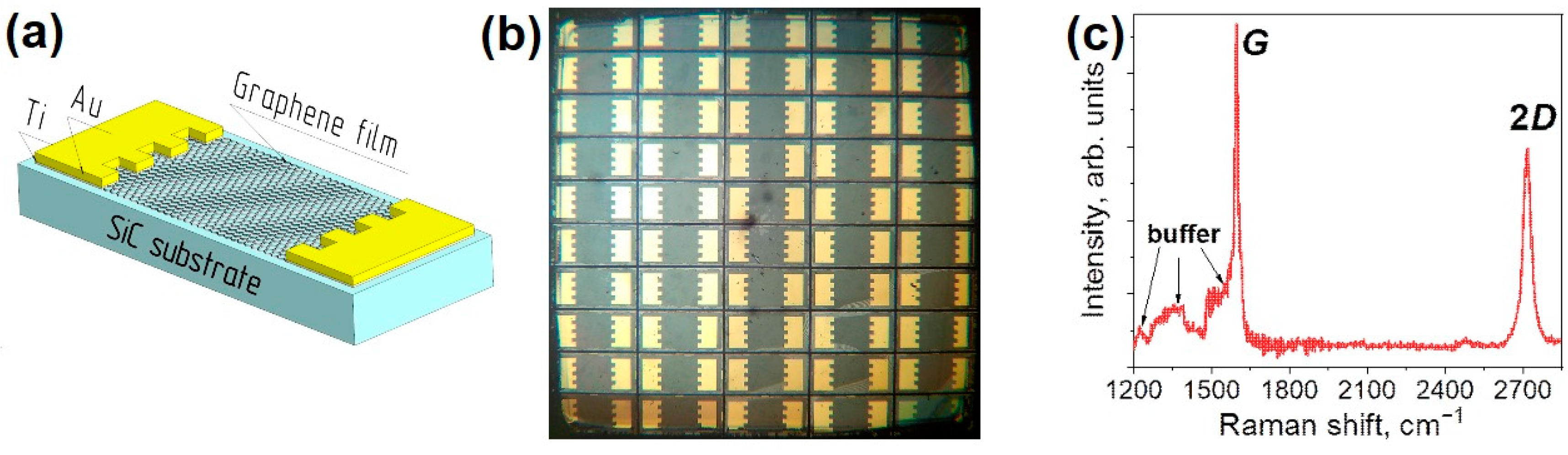
19]. Chips with two contact pads (graphene resistors- the base of biosensors) is shown
Figure 1a, b. The size of the sensing area (active surface of graphene in the chip) is about 0.8 × 0.8 mm
2 .
The presence of graphene films on the SiC surface was confirmed and their structure was characterized by Raman spectroscopy. Measurements were performed at room temperature in the backscattering geometry using a Horiba LabRAM HREvo UV-VIS-NIR-Open spectrometer (Horiba Jobin-Yvon, France) equipped with a confocal microscope. A YAG:Nd laser with a wavelength of 532 nm was used as an excitation source. The laser beam was focused in the area with ~ 1 µm diameter using an Olympus MPLN100x objective lens (NA = 0.9). The laser power nm was limited to 4.0 mW to prevent damaging and modification of graphene films.
AFM and Kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) measurements of the graphene surface morphology were carried out on an Ntegra AURA setup (NT-MDT, Russia). AFM studies were carried out using the HA_FM cantilever (
www.tipsnano.com) in a resonant mode of operation. The AFM probe knocks on the surface scanning frequency 0.6 Hz. The stiffness coefficient of such a cantilever is 3.5 N/m, the radius of curvature is less than 10 nm, the scanning field size is 256 × 256 points.
The power spectral density of voltage fluctuations was measured for the graphene chips mounted on a holder in a frequency range from 1 to 50 kHz. The studied chips were connected in series with a low-noise load resistor RL whose resistance varied from 100 Ω to 13 kΩ, depending on the current passing through the chip. The voltage fluctuations SU at the resistors RL were amplified by a low-noise preamplifier SR560 (Stanford Research Systems, USA) and subsequently measured by an SR 770 FET NETWORK Analyzer (Stanford Research Systems, USA). The background noise of the preamplifier did not exceed 4 nV/√Hz at 1 kHz, which is approximately equivalent to the Johnson–Nyquist noise of a 1000-Ω resistance. The I–U characteristics of the chip were measured using the KEITHLEY 6487 power source.
3. Results and Discussion
The Raman spectra of the as-grown graphene film consist of sharp G and 2D lines characteristic of monolayer graphene [
21] and several bands centered at approximately 1230, 1380 and 1550 cm
−1 corresponding to the buffer layer [
22] as shown in
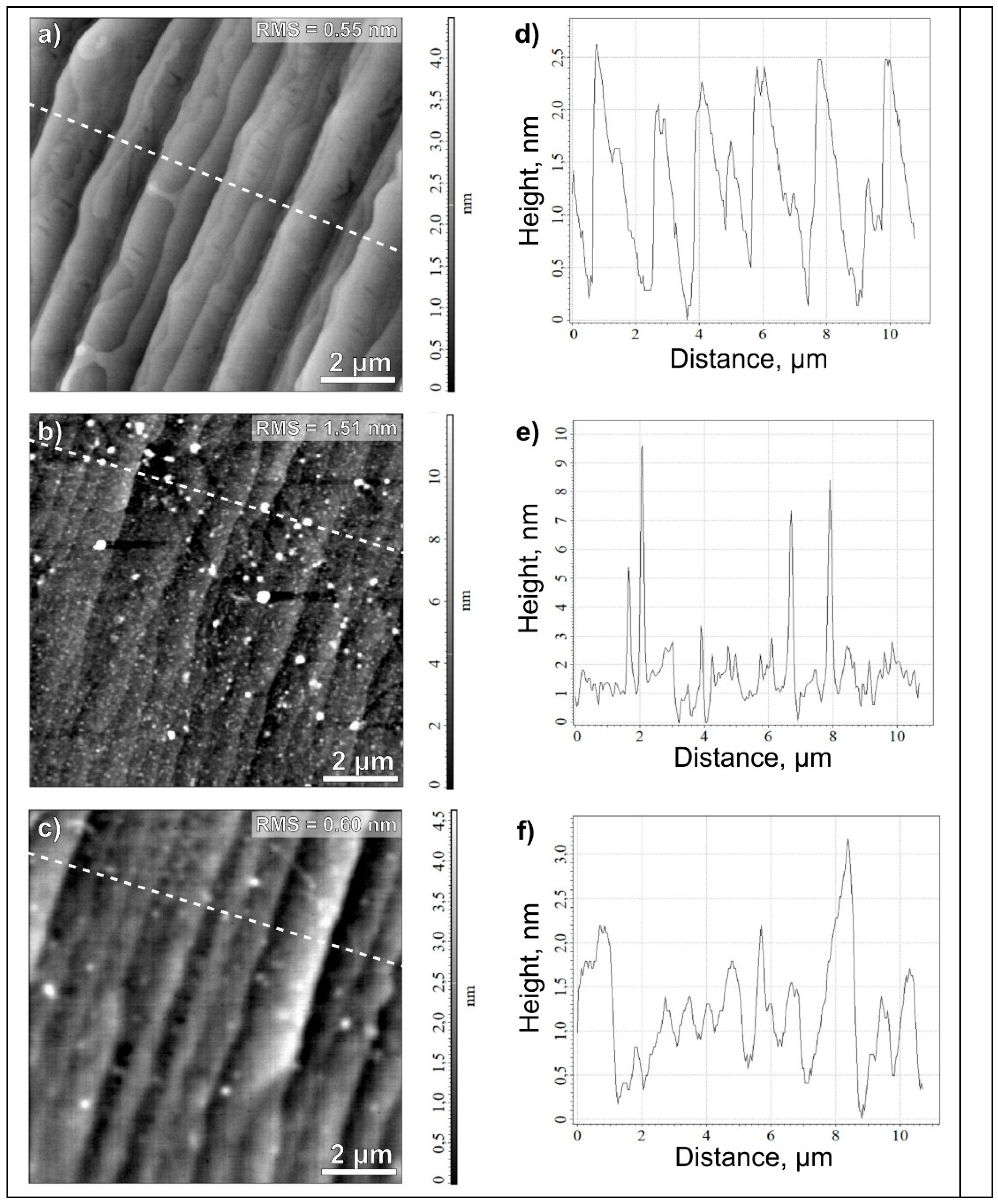
Figure 1c. High structural quality of the graphene film is indicated by the absence of the defect-related D line. The root mean square roughness (RMS) of as-grown (pristine) graphene films was 0.4 - 0.5 nm at AFM scan 10 µm × 10 µm.
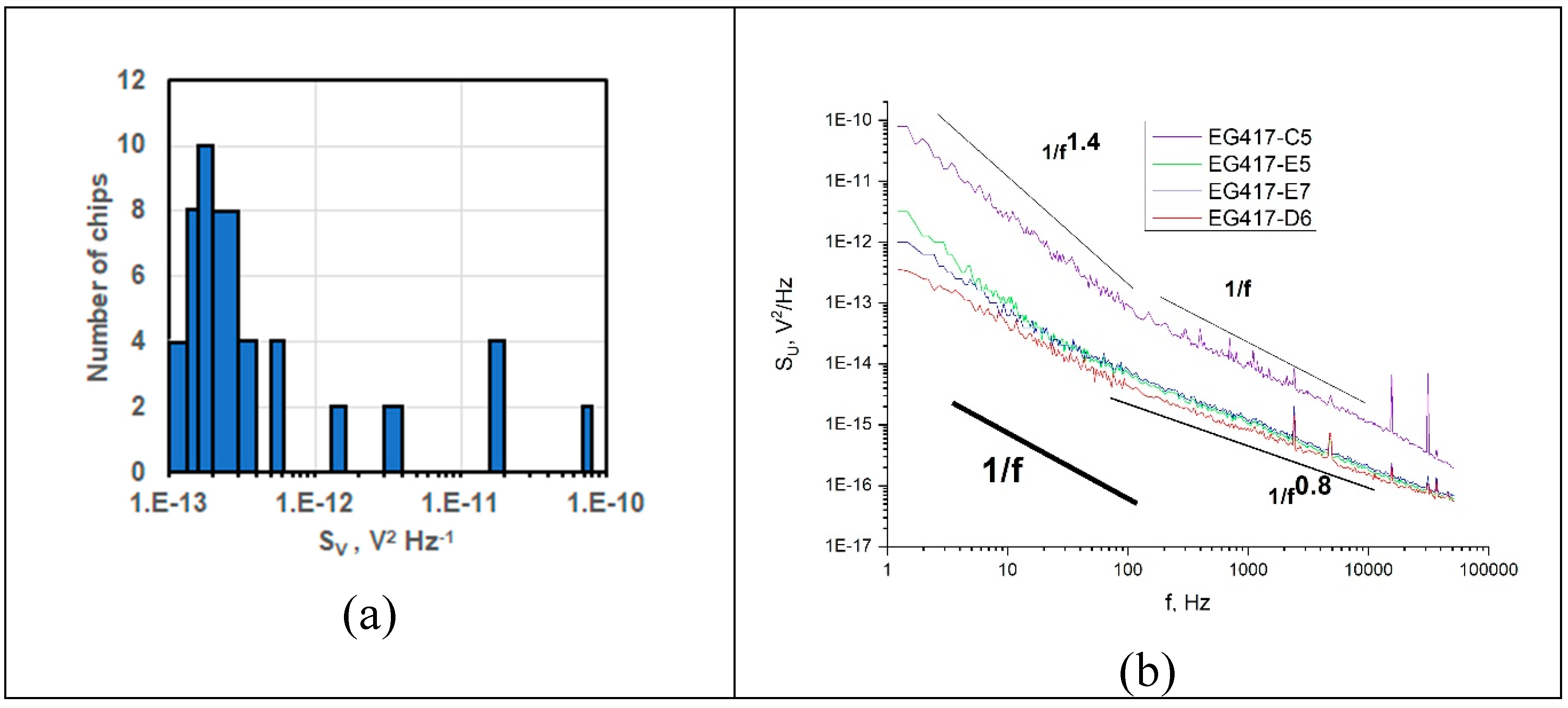
50 chips fabricated from the same graphene/SiC sample (EG417 series chips further in the text) were evaluated based on AFM characterization, the results of resistance measurement, the level of spectral density of low-frequency noise (SU) at a frequency of 1.22 Hz, as well as analyzing the shape of SU frequency dependencies.
In the earlier study [
9], the resistance value spread in as-fabricalueted chips was up to 1-10 kΩ without AFM control graphene topology after each stage of PLG. At the same time, only 20% of chips out of 50 ones had resistance values in the range of 1-1.6 kOhm and the RMS roughness is 0.5 - 1 nm at AFM scan of 10 µm × 10 µm
Figure 2a, as the same as on pristine graphene film before PLG. The terraces visible on the surface are typical of the graphene films on SiC substrates [
23]. Large values of resistance in chips, as a rule, were accompanied by a large RMS value of graphene surface roughness up to 1.5 - 10nm at AFM scan of 10 µm × 10 µm
Figure 2b. The LRRs (white regions in AFM view) are the cause of RMS increase.
In this work, an additional cleaning of the LRRs after the AFM control made it possible to significantly reduce the spread of resistance values down to 1-1.6 kΩ. No RMS values larger than 2 nm were observed on graphene in majority of chips. The most typical values are near 0.60 nm
Figure 2c., which coincides or is close to the initial RMS values of initial graphene/SiC surface (RMS = 0.55 nm)
To find out the reasons for the resistance spread in the range 1-1.6 kΩ , measurements of the spectral density of voltage fluctuations S
U at a frequency of 1.22Hz were carried out on all 50 chips. The histogram of the distribution of S
U values is shown in
Figure 3a. For 82% of chips, S
U values are as low as S
U =(1-4)×10
-13 V
2·Hz
-1 that indicates good quality graphene. The Rаman spectra for these chips are similar to those shown in
Figure 1c.
Figure 3 shows the frequency dependences of S
U for several chips from the same EG417 series. For the EG417-D6 chip in
Figure 3b, two regions are clearly visible. In the frequency range 1-100 Hz, the experimental data fit to the dependence S
U ~ 1/f. A weaker dependence S
U ~1/f
0.8 is observed for higher frequency f>100 Hz. We believe the S
U dependence at higher frequency might be due to a superposition of 1/f noise and generation-recombination (GR) noise. These features mean that, in addition to the system of defects typical of low-dimensional materials, there are single Shockley-Reed-Hall defects. It should be noted that this S
U behavior is observed on graphene in chips with RMS values close to those on the pristine graphene film before PLG
Figure 2a
For the remaining 18% of chips, the spread of S
U values was in the range from 6x10
-13 to 8x10
-11 V
2·Hz
-1. The S
U of these chips has different values of excess noise and the regions with frequency dependencies S
U ~1/f
γ having various values of γ up to 1.4 with a maximum S
U value at 1.22 Hz for the EG417-C5 chip in
Figure 3b.
According to theoretical concepts, this kind of dependence is due to the presence of inhomogeneous deformations in the material [
15]. We have observed earlier that the dependence S
U ~ 1/f
γ (γ >1) in graphene films and chips is consistent with Raman spectra data demonstrating an inhomogeneous distribution of compressive stresses in graphene [
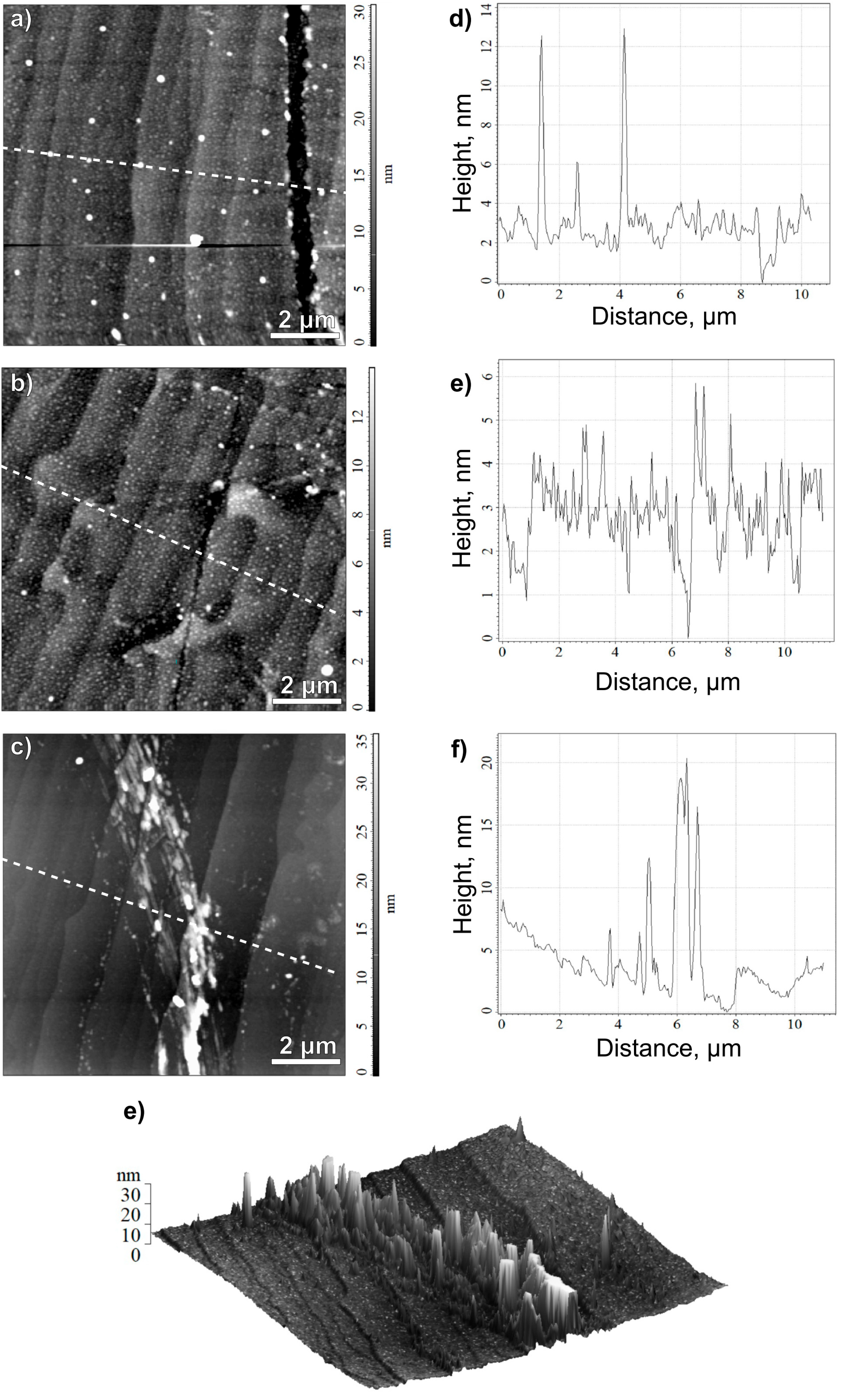
24]. Studying of graphene topography in these chips reveals cracks in graphene shown in
Figure 4a,b,c,d (EG417-Е7, - C5) and extended LRRs regions shown in
Figure 4e,g (EG417-E5) or a large number of heterogeneously spaced LRRs
Figure 2b and
Figure 4e.
Figure 3.
Frequency dependence of SU. The histogram of SU distribution at a frequency of 1.22Hz for 50 chips obtained with an additional cleaning of the LRRs (a), low-frequency noise spectra of the chips with different SU values (b). Dashed lines indicate a simulation of the1/fγ dependence with γ 0.8, 1, and 1.4 for references. The insert shows the chip numbers.
Figure 3.
Frequency dependence of SU. The histogram of SU distribution at a frequency of 1.22Hz for 50 chips obtained with an additional cleaning of the LRRs (a), low-frequency noise spectra of the chips with different SU values (b). Dashed lines indicate a simulation of the1/fγ dependence with γ 0.8, 1, and 1.4 for references. The insert shows the chip numbers.
The area of superposition of two types of noise is observed in the graphene of chips EG417-E7 and EG417-E5 in
Figure 3b., but judging by the slope of the S
U dependencies, the contribution of GR noise is less. In addition, the higher the noise level at a frequency of 1.22 Hz, and also at f<100 Hz, the slope of S
U dependence increases (S
U ~ 1/f
1.4), which, according to theoretical concepts, reveals the presence of inhomogeneously distributed deformations [
15].
As it was shown previously [
9], the heterogeneous distribution of deformations in the graphene chip used as a biosensor leads to non-uniform spread of the immobilized of antibodies. The attachment of viruses (antigens) occurs not only to antibodies in accordance with antibody-antigen immunoreaction but on the part of the graphene surface what gives an error when determining the concentration of viruses. The antibody-antigen immunoreaction on the graphene surface is a principal for operation of the graphene-based biosensors. The formation of cracks in graphene leads to additional inhomogeneous deformations. Cracks also form uncontrollable areas to attach antigen directly to the graphene surface besides antibody-antigen immunoreaction. It destroys the normal biosensor operation.
5. Conclusions
The results obtained revealed several reasons for the deterioration of graphene quality in chips for use in biosensors: the presence of randomly distributed local regions with resist residues LRRs and inhomogeneously distributed deformations, as well as the formation of cracks. It is shown that additional cleaning of LRRs identified by AFM makes it possible to restore the RMS roughness of graphene close to the roughness of the pristine graphene before PLG and to reduce the spread of chips resistance values. It was found out that monitoring of the spectral density of voltage fluctuations (SU) and the features of the type of frequency dependence SU make it possible to identify chips with inhomogeneously deformed graphene that may deteriorate the detecting properties of the biosensors made on the basis of these chips. Thus, the quality assessment of graphene by AFM and low-frequency noise methods and also Raman spectra in chips makes it possible to improve the reproducibility of the parameters of chips intended for use in biosensors of viral infections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. and A.U.; low-noise spectra acquisition, E.S.; graphene characterization by AFM, E.G. and V.P.; Raman spectra acquisition, I.E.; graphene samples fabrication, S.P.; graphene chips processing and cleaning, E.T., M.P., and A.R.; methodology, N.S.; writing—original draft preparation, N.S.; writing—review and editing, N.S. and A.U.; visualization, E.S., V.P., S.P., A.U.; funding acquisition and project administration, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Sergey P. Lebedev and Alexander A. Lebedev are grateful for the financial support from the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, grant number 075-15-2021-1349 ???
Acknowledgments
The authors express their acknowledgement to Dr. V. Davydov for help in Raman characterization of graphene films and Dr. Yu. Makarov for technical support of the investigations.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.” “The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results”.
References
- Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Lukas, H.; Tu, J.; Min, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Gao, W.; Gao, W. A Graphene-Based Multiplexed Telemedicine Platform for Rapid and Low-Cost COVID-19. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 217. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedev, A.A.; Davydov, S.Y.; Eliseyev, I.A. Graphene on SiC Substrate as Biosensor: Theoretical Background, Preparation, and Characterization. Materials 2021, 14, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsahi, S.; Lerner, M.B.; Goldstein, J.M.; Lee, J.; Tang, X.; Bagarozzi, D.A.; Pan, D.; Locascio, L.; Walker, A.; Barron, F.; Goldsmith, B.R. Novel graphene-based biosensor for early detection of Zika virus infection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Bahamonde, J.; Nguyen, H.N.; Fanourakis, S.K.; Rodrigues, D.F. Recent advances in graphene-based biosensor technology with applications in life sciences. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, T.J.M.; Carvalho, M.N.; Ghislandi, M.G.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A. Functionalized graphene-based materials as innovated adsorbents of organic pollutants: A consise overview. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X. Graphene-Based Biosensors for Detection of Biomarkers. Micromachines 2020, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmidt, N.M.; Usikov, A.S.; Shabunina, E.I.; Nashchekin, A.V.; Gushchina, E.V.; Eliseev, I.A.; Petrov, V.N.; Puzyk, M.V.; Avdeev, O.V.; Klotchenko, S.A.; Lebedev, S.P.; Tanklevskaya, E.M.; Makarov, Y.N.; Lebedev, A.A.; Vasin, A.V. Investigation of the morphology and electrical properties of graphene used in the development of biosensors for detection of influenza viruses. Biosensors 2022, 12, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, I.A.; Gushchina, E.A.; Klotchenko, S.A.; Lebedev, A.A.; Lebedeva, N.M.; Lebedev, S.P.; Nashchekin, A.V.; Petrov, V.N.; Puzyk, M.V.; Roenkov, A.D.; Smirnov, A.N.; Tanklevskaya, E.M.; Usikov, A.S.; Shabunina, E.I.; Shmidt, N.M. Modification in adsorption properties of graphene during the development of viral biosensors. Semiconductors 2022, 56, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Mitchell, J.J.; Burwell, G.; Rejnhard, K.; Jenkins, C.A.; Ahmadi, E.D.; Sharma, S.; Guy, O.J. Application of Molecular Vapour Deposited Al2O3 for Graphene-Based Biosensor Passivation and Improvements in Graphene Device Homogeneity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, E.H. The influence of thermal annealing to remove polymeric residue on the electronic doping and morphological characteristics of graphene. Carbon 2013, 65, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Muoth, M.; Helbling, T.; Mattmann, M.; Hierold, C. Suppression of resist contamination during photolithography on carbon nanomaterials by a sacrificial layer. Carbon 2014, 66, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Tuan Hoang, T.T.; Ngoc Van, B.; Shong, L.; Hu, K.Y.; Thai, J.-H. Ahn. Residue-free photolithographic patterning of graphene. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Y.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, J.; Jin, Z. Reducing metal/graphene contact resistance via N, N-dimethylacetamide-assisted clean fabrication process. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 315201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.A. Low-frequency 1/f noise in graphene devices. Nature Nanotechnology 2013, 8, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigal’skii, G.P. Fluctuation and noise in electron devices; Physmatlit: Moscow, Russia, 2012; p. 512. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Rumyantsev, S.; Shur, M.S.; Balandin, A.A. Origin of 1/f noise in graphene multilayers: Surface vs. volume. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 093111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.A.; Davydov, V.Y.; Usachov, D.Y. Study of Properties and Development of sensors based on graphene films grown on SiC (0001) by thermal destruction method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 951, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usikov, A.; Borodkin, K.; Novikov, S.; Roenkov, A.; Goryachkin, A.; Puzyk, M.; Barash, I.; Lebedev, S.; Zubov, S.A.; Makarov, Y. Graphene/SiC dies for electrochemical blood-type sensing. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2019, 68, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roth, S.; Geim, A.K. Raman Spectrum of Graphene and Graphene Layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Ahn, G.; Shim, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Ryu, S. Optical Separation of Mechanical Strain from Charge Doping in Graphene. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseyev, I.A.; Davydov, V.Y.; Smirnov, A.N.; Nestoklon, M.O.; Dementev, P.A.; Lebedev, S.P.; Lebedev, A.A.; Bokai, K.A.; Usachov, D.Y. Raman Spectroscopy Estimation of the Carrier Concentration and the Value of Strain in Monolayer Graphene Films Grown on 4H-SiC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1400, 055037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, S.P.; Amel’chuk, D.G.; Eliseyev, I.A.; Barash, I.S.; Dementev, P.A.; Zubov, A.V.; Lebedev, A.A. Surface morphology control of the SiC (0001) substrate during the graphene growth. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures 2019, 28, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseyev, I.A.; Usikov, A.S.; Lebedev, S.P.; Roenkov, A.D.; Puzyk, M.V.; Zubov, A.V.; Makarov, Y.N.; Lebedev, A.A.; Shabunina, E.I.; Dementev, P.A.; Smirnov, A.N.; Shmidt, N.M. Raman scattering and low-frequency noise in epitaxial graphene chips. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2020, 1697, 012130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).