1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cancer worldwide, with an estimated 1.9million incidence cases and 0.9 million global deaths in 2020 [
1] The burden is expected to reach approximately 3.3 million new cases in 2040 [
2]. CRC is primarily initiated in the mucosal lining of the colon and rectum by a series of genetic alterations affecting key signalling pathways, including WNT, MAPK and BMP, accompanied by defective DNA repair pathways or cell cycle checkpoints [
3,
4,
5]. Prognosis and treatment response are good for early stages, but remain poor for late-stage metastatic cancers.
Protein tyrosine kinases are central signalling components of many pathways involved in CRC and transmit signals though phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in target proteins. Aberrant protein tyrosine kinase signalling has frequently been linked with CRC pathogenesis [
6,
7]. There are two sub-families of Protein Tyrosine Kinases (PTKs) - Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) and Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (NRTKs) [
8]. RTKs activate numerous signalling pathways within cells and act both as transmembrane receptors and catalytic enzymes that contribute to regulating key cellular characteristics [
9]. Examples of critical RTKs in CRC include EGFR, VEGFR, PDGFR, IGFR and FGFRs, with both specific RTK inhibitors and multi-kinase inhibitors used to target them in patients with metastatic CRC (reviewed in [
10]).
NRTKs are intracellular proteins that can be membrane-bound or nuclear-specific [
7]. NRTKs are an integral component of most signal transduction cascades, regulating important cellular processes, including survival, cell division, regulation of gene expression, suppression of cell development, and regulation of cell adhesion and proliferation [
8]. The functions of NRTKs are highly dependent on intracellular localization and signalling by cell surface receptors and immune system receptors [
11]. NRTKS such as Src family kinases are already known to play a critical role in CRC [
12] along with FAK [
13] and JAK [
14] families. However, few specific NRTK inhibitors have been approved for CRC treatment to date.
1.1. Protein Tyrosine Kinase 6
Protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) also known as Breast Tumour Kinase (BRK) is an intracellular tyrosine kinases that belongs to the src sub-family of non-receptor family kinases [
8,
15,
16]. The full-length PTK6 isoform was originally detected in melanocytes and the sequence cloned from metastatic breast tumours [
15,
17]. Since then, PTK6 has been detected in several normal and tumour tissues at varying levels, where it activates a variety of oncoproteins that promote cell growth, survival and malignant transformation [
15,
18]. PTK6 phosphorylates both nuclear and cytoplasmic substrates such as β-catenin, PSF, Sam68, AKT, STATs, Paxillin and IRS4 as a phosphorylating kinase, which link PTK6 to signalling pathways that serve as direct regulators of gene expression [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27].
1.2. PTK6 transcript variants
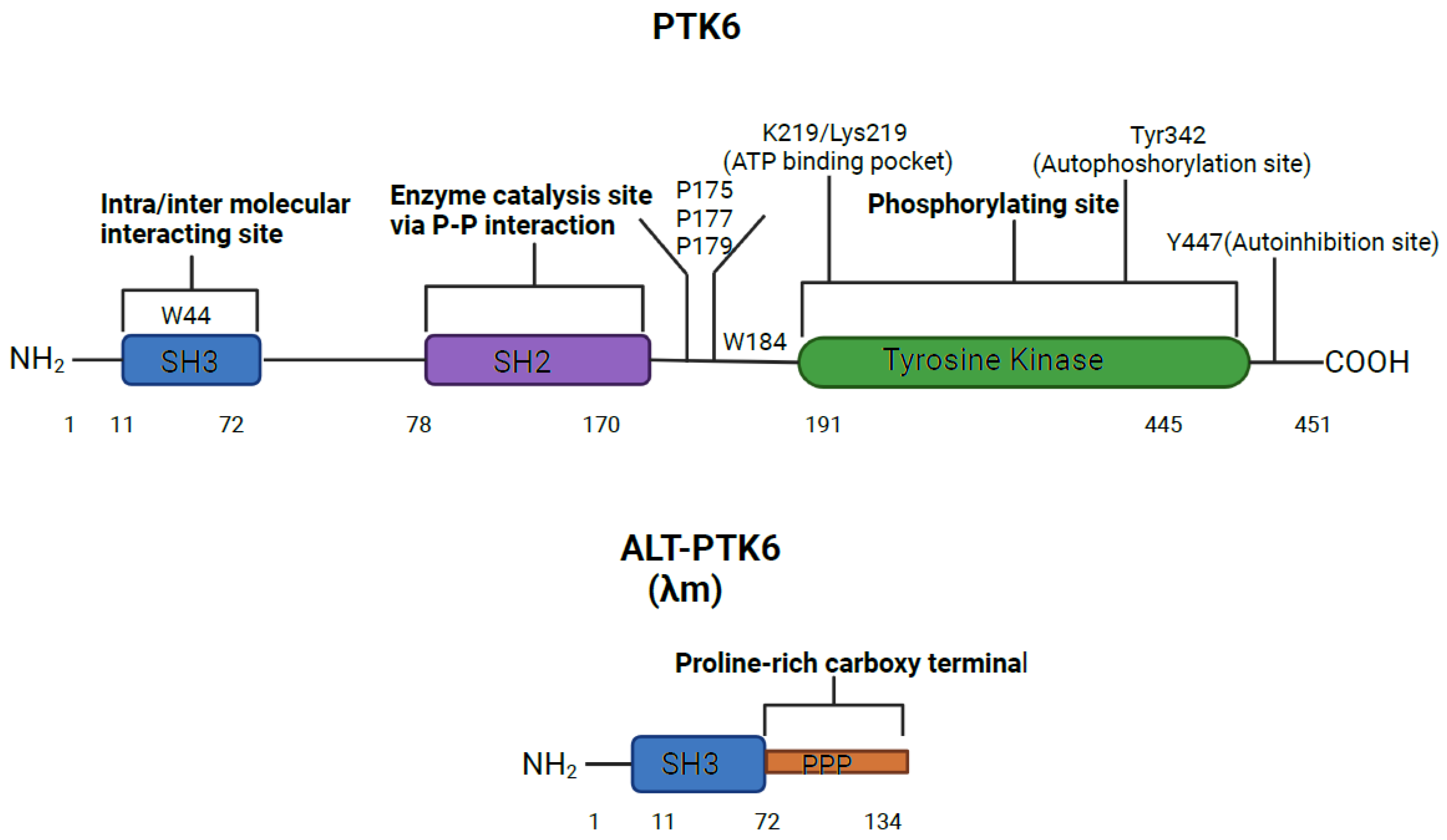
The human PTK6 gene lies on chromosome 20q13.33 and consists of 8 exons that span ten kilobases with a predicted molecular weight of 50kDa [
28,
29] (
Figure 1). It encodes approximately 451 amino acids and contains a unique kinase domain, joined by a linker region devoid of N-terminal myristylation sites, [
28] as well as two Src homology (SH) domains: phospho-tyrosine binding and protein-protein interaction domain SH2, linker interacting and substrate recognition domain SH3. Both SH2 and SH3 domains contribute to autoinhibition of PTK6 and to protein-protein interactions. However, the primary role of SH2 is likely to be regulation of catalytic activity of PTK6 [
30]. The SH3 domain primarily functions as a substrate recognition site, but also contibutes to enzyme control [
31,
32]. In response to changes in pH, the PTK6 SH3 domain undergoes conformational changes, indicating that its structure may impact substrate and protein interactions [
30,
32]. The tyrosine kinase domain of the PTK6 contains the ATP binding pocket, containing the key lysine residue 219, which needs to be phosphorylated to activate the kinase activity. Two further phosphorylation sites are important for activation status: tyrosine 342(Y342) and tyrosine 447(Y447). pY342 functions to increase PTK’s activity while pY447 supresses it [
32,
33].
The shorter isoform of PTK6 is called alternatively spliced variant of PTK6 (ALT-PTK6). ALT-PTK6, (also known as λm5) encodes a 134-amino-acid protein [
28]. It is 15 kilodaltons and shares the first 77 amino acids with the full-length version, but lacks exon 2, resulting in an early stop codon. ALT-PTK6 is missing the SH2 domain and contains a unique proline-rich carboxy-terminal sequence that differs structurally from the full-length PTK6 [
28]. It is reported that both PTK6 and ALT-PTK6 share a functioning substrate-recognition SH3 domain, making them competitive SH3 binding partner inhibitors [
28,
34]. It is therefore possible that ALT-PTK6 could act as a dominant negative version of PTK6 when they are co-expressed. Co-expression and altered localization of ALT-PTK6 and full-length PTK6 has been detected in human colon cancer cell lines [
34].
2. Regulation of PTK6 function
The function of PTK6 differs significantly depending on a number of factors: the expression level, intracellular location, phosphorylation status of PTK6 tyrosine residues, kinase activity and the interactions with alternative splice forms [
30,
31,
32,
34,
35].
2.1. PTK6 expression
PTK6 expression has been identified in normal intestinal epithelial cells, skin, the oral cavity, and the normal prostate and at a low or undetectable level in normal mammary glands, lung, and lymphoma cells [
15,
17,
18,
36,
37,
38]. PTK6 expression is highest in the epithelia of the intestine and skin [
39]. Recently, it has been discovered that PTK6 is highly expressed in non-tumorous larynx and esophagus tissues [
40,
41]. Elevated PTK6 expression has been detected in multiple cancers such as breast, cervical cancers, non-small cell lung cancer, high-grade ovarian cancer bladder cancer, pancreatic adenocarcinoma and colon cancer where it can promote malignant transformation and progression [
28,
33,
34,
42,
43,
44,
45].
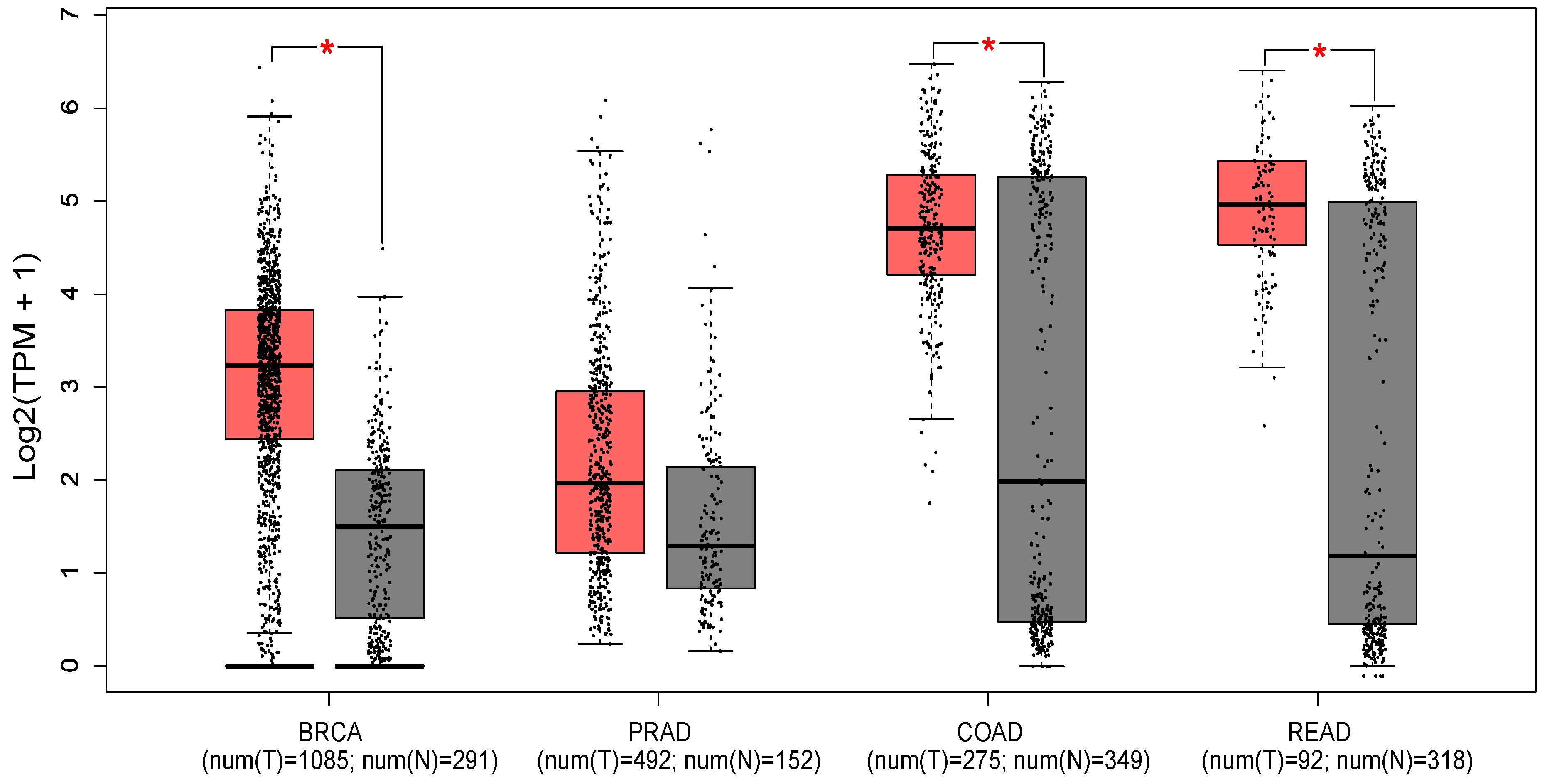
Figure 2 shows the expression profile of PTK6 across normal and cancerous tissues from the breast, prostate, colon and rectum using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas and the Genotype-tissue expression portal (GEPIA database -
http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/ [
46]). Significant differences in expression are evident in breast cancer, with PTK6 expressed more highly in tumors than normal tissue as expected, but not in prostate cancer despite evidence suggesting the importance of PTK6. Of relevance to this review, significant differences are observed in colon and rectal cancers although there is much greater variability in the normal tissue suggesting.
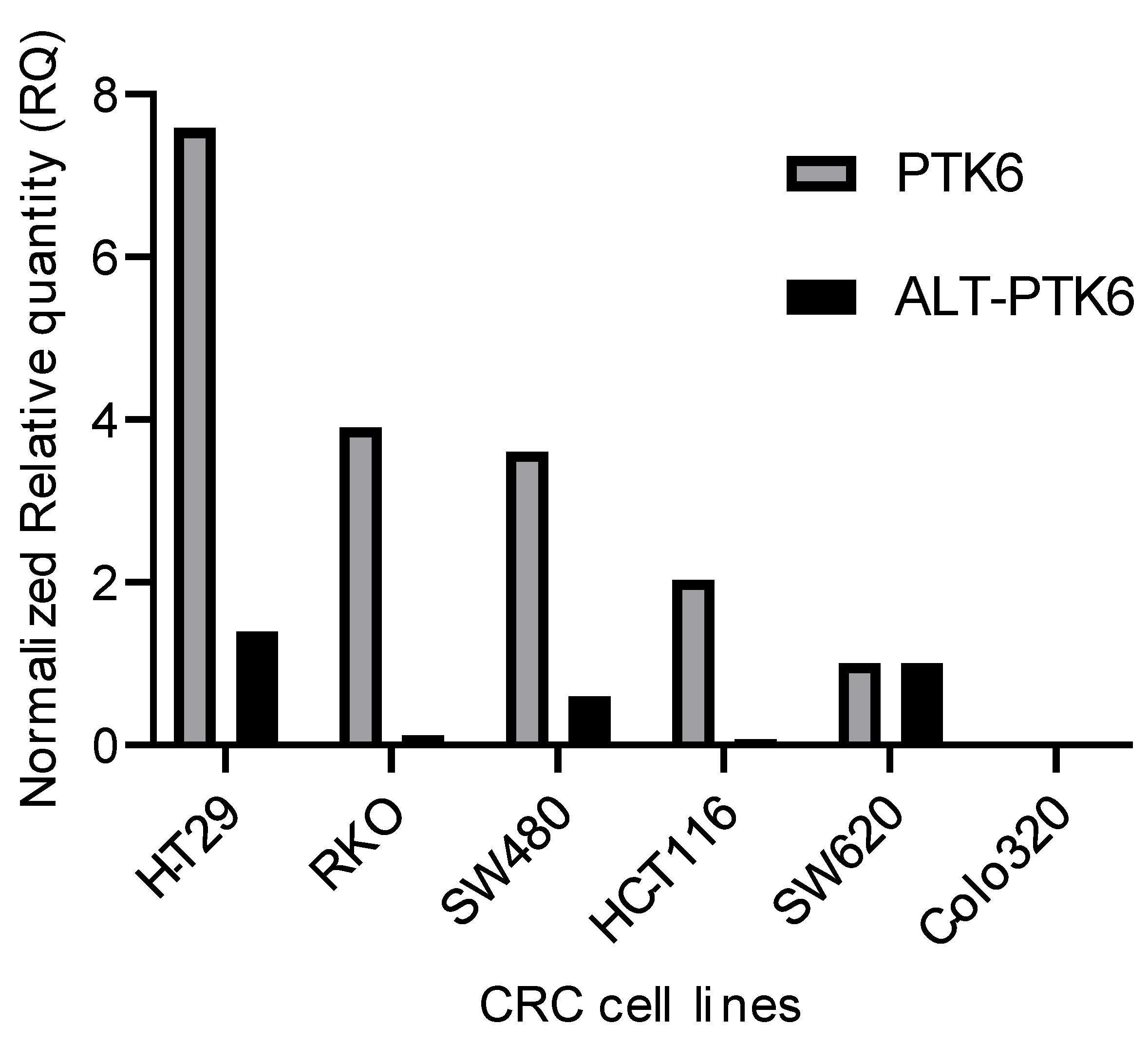
Figure 3 shows that PTK6 full length and ALT-PTK6 expression is variable across different colorectal cell lines indicating that its importance could be restricted to a subset of colorectal cancers.
2.2. PTK6 localization
Recent research indicates that the functions of PTK6 are context-dependent and vary by cell type, tumor status and intracellular location [
26,
47]. Localization of PTK6 isoforms are likely to play a key role in its function, as the range of available substrates will differ between the nucleus and cytoplasm [
48]. Due to the lack of myristylation/ palmitoylation sites or a nuclear localization sequence (NLS), the localization of PTK6 varies widely depending on tissue type and external stimulation. The localization pattern also differs between normal and tumor cells [
26,
47,
48].
Derry
et al. [
18] proposed that PTK6 is primarily a cytoplasmic kinase with the ability to relocalize to the nucleus under certain conditions, following their observations in prostrate tumor cells [
18]. A functional distinction between membrane and nuclear location has been reported in several studies. For instance, PTK6 is found to be expressed at the membrane in human breast, prostate, liver, and lung cancer tissues [
25,
33]. It is also detected in the cytoplasm and nucleus of normal colonic and prostate epithelia, respectively [
39,
49]. In addition, overexpression of PTK6 in prostate cancer cells causes re-localization to the nucleus from the cytoplasm [
18]. PTK6's oncogenic effects are largely mediated by its intracellular localization. For example, the membrane targeted PTK6 enhances cell proliferation, tumorigenicity, and invasiveness in breast, prostate, HEK239 human kidney, and SW620 CRC cell lines [
18,
22,
23,
48,
49]. At the cell membrane, PTK6 interacts with regulators of growth and migration such as the ErbB family transmembrane receptors, ADAM 15 A/B and IGF-1R receptors, as well as membrane translocated cytoplasmic proteins such as paxillin, Akt, FAK, p130Cas and IRS4 (see
Table 1). On the other hand, nuclear PTK6 phosphorylation causes a tumor suppressive role. One potential rationale for this role is that PTK6 nuclear targets retain the kinase in the nucleus, preventing it from enhancing growth and therefore exerting a tumor suppressive action.
2.3. PTK6 and substrate phosphorylation
PTK6 has a variety of direct targets which it phosphorylates at specific tyrosine residues (
Table 1). Qiu
et al. found that the PTK SH3 domain interactions are likely to govern the specificity of PTK6 substrate phosphorylation [
32]. To date more than 30 potential PTK6 substrates have been identified (
Table 1) These include the RNA-binding proteins: Sam68, SLM-1, SLM-2, and PSF ; transcription factors: STAT3 and STAT5a/b ; and a variety of signaling molecules: EGFR, p190RhoGAP, paxillin, Akt, IRS-4, BKS/STAP-2, and KAP3A.
Table 1.
PTK6 substrates and binding partners. •symbol represents direct substrates of PTK6; ‘+/-’ indicates activation or inhibition of substrates.
Table 1.
PTK6 substrates and binding partners. •symbol represents direct substrates of PTK6; ‘+/-’ indicates activation or inhibition of substrates.
| Substrates |
Tissues |
Localization |
Promotes |
Reference |
| ADAM-15A |
Breast |
Membrane |
Unknown |
[50] |
| ADAM-15B |
Breast |
Membrane |
Unknown |
[50] |
| •AKT + |
Prostrate Breast |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[25] |
| •ARAP1+ |
Breast |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[51] |
| BCAR1 (P130CAS)+ |
Prostrate |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[52] |
| •β-catenin± |
Colon |
Membrane/Cytoplasm
Nucleus |
Oncogenic
Differential |
[23] |
| c-CBL |
|
cytoplasm |
oncogenic |
[53] |
| Dok1 |
Breast |
Cytoplasm/Nucleus |
Oncogenic |
[54] |
| EGFR+ |
Breast |
Membrane |
Oncogenic |
[55] |
| ERBB2+ |
Breast |
Membrane |
Oncogenic |
[33,55] |
| ERBB3 |
Breast |
Membrane |
Unknown |
[56] |
| ERBB4 |
Breast |
Membrane |
Unknown |
[56] |
| ERK5 |
|
cytoplasm |
Cell migration |
[57] |
| FAK+ |
Prostrate |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[52] |
| •FLJ39441 |
Breast |
Cytoplasm |
Unknown |
[58] |
| GAPA p65 |
|
Cytoplasm |
Differentiation |
[59] |
| •GNAS |
|
cytoplasm |
Cell migration |
[58] |
| HSP70 |
|
Cytoplasm |
Protein stability |
[60] |
| HSP90 |
|
Cytoplasm |
Protein stability |
[60] |
| IGF-1R+ |
Breast |
Membrane |
|
[61] |
| •IRS-4+ |
Breast |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[24] |
| •KAP3A+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm/Nucleus |
Oncogenic |
[58] |
| P38 MAPK+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[56] |
| •p190RhoGAP+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[62] |
| P27Kip1+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm/Nucleus |
Oncogenic |
[63] |
| •Paxillin+ |
breast |
Membrane/Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[19] |
| PSF+ |
Breast |
Nucleus |
Cell cycle arrest |
[22] |
| •PTEN |
Breast |
Cytoplasm |
Unknown |
[56] |
| P130 CAS |
|
|
Migration |
|
| •SAM68± |
Breast/Colon |
Nucleus |
Differential |
[20,22] |
| •SLM1± |
Mammary gland |
Nucleus |
Differential |
[39] |
| •SLM2± |
Mammary gland |
Nucleus |
Differential |
[39] |
| •STAP2+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm |
Oncogenic |
[15] |
| STAP3+ |
|
Cytoplasm |
|
|
| •STAT3 |
Breast/Colon |
Cytoplasm/Nucleus |
Oncogenic |
[21] |
| •STAT5a/b+ |
Breast |
Cytoplasm/Nucleus |
Oncogenic |
[64] |
2.3. PTK6 and signalling molecule interaction
PTK6 functions downstream of ERBB2 (HER2) and other receptor tyrosine kinases, such as EGFR and MET [
55,
65,
66,
67]. Since ERBB2 forms heterodimers with EGFR, and MET can heterodimerize with both ERBB2 and EGFR [
68], it is not clear if MET and EGFR activate PTK6 directly or act through ERBB2. However, activated PTK6 was found to directly phosphorylate tyrosine 845 in the EGFR kinase domain suggesting a feedback loop involving the two proteins [
69]. PTK6 has also been found to bind to and phosphorylate the tyrosine residue on ARAP1. PTK6 enhances EGFR signaling via ARAP1 by inhibiting EGFR internalization and degradation [
51,
53,
69]. Clinically, the interaction between PTK6 and EGFR has wide implications, as PTK6 may potentially be a factor for the low efficacy of anti-EGFR drugs in breast cancer treatment. Indeed, depletion of PTK6 was found to sensitize cells to Cetuximab [
69]. Furthermore, EGFR is overexpressed in CRC with anti-EGFR therapies given to patients with metastatic CRC [
70]. Therefore PTK6 could also be explored as a predictive biomarker for efficacy of EGFR inhibitors in CFC. Serine/threonine kinase AKT is another direct substrate of PTK6, although studies conflict as to whether it has a repressive or activating role [
25,
55,
71,
72,
73]. Again, AKT is a key pathway and potential therapeutic target in CRC [
74]. PTK6 directly phosphorylates a number of other key signal transduction proteins including paxillin which activates Rac1 GTPase [
19] and insulin receptor substrate 4 (IRS-4) downstream of IGF-1 [
24].
2.4. PTK6 and RNA binding proteins interaction
PTK6 binds and phosphorylates several nuclear RNA-binding proteins, including Sam68, which was one of the first PTK6 substrates identified and the most extensively studied [
20]. PTK6 expression negatively regulates Sam68 by direct phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues [
20]. Sam68 is important in CRC due to its regulation of the DNA damage response [
75]. Similar to Sam68, the Sam68-like mammalian proteins SLM-1 and SLM-2 are phosphorylated by PTK6
in vitro, negatively regulating their RNA-binding function [
39]. PTK6 was shown to phosphorylate and yield a cytoplasmic re-localization of the PTB-associated splicing factor (PSF) from the nucleus, resulting in cell cycle arrest, a function consistent with reports of pro-tumor suppressive role of PTK6 within the nucleus [
22].
2.5. PTK6 and transcription factors interaction
PTK6 has been involved in activating the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) family of proteins [
21,
26]. STAT3 activation has been associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer due to higher cell proliferation, migration, and survival [
21]; [
76,
77] [
78]). PTK6 activates STAT3-mediated transcription [
26,
79,
80]) and may also activate STAT5-mediated transcription [
81]. Both transcription factors are directly phosphorylated by PTK6, and STAT3, when activated, promotes proliferation and migration, and impairs apoptosis in colon cancer cell lines, mouse models and breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and T47D [
21,
26].
2.6. Kinase activity of PTK6
In addition to localization, oncogenic functions of PTK6 depend on the phosphorylation status of its two tyrosine residues. Phosphorylation of the Y342 residue activates PTK6, with active PTK6 being detected in breast tumors but not in normal breast tissues [
33]. Conversely, in ovarian cancer, PTK6 de-phosphorylation of Y342 occurs due to tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) activity [
82]. Similarly,
in vitro studies on prostate cancer demonstrate that PTK6 is also dephosphorylated at Y342 by the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) [
83] On the other hand, Y447 phosphorylation inhibits kinase activity [
32,
35], suggesting that specific tyrosine kinase residue phosphorylation states could play a vital, but tissue specific, role in cancer development and progression. Further regulation of kinase activity occurs in the linker region via conserved trytophan W184 [
32] PTK6 autophosphorylation and kinase activity has been shown to be activated by EGF, heregulin-β1, and IGF1 [
61,
84,
85]. The kinase activity of PTK6 is negatively regulated by PTPN1 phosphatase [
82] and SRMS kinase [
86], as well as the STAT3 target SOCS3 [
87].
In several instances, activities of PTK6 have been shown to be kinase-independent and may be attributed to adaptor/scaffolding functions mediated by its SH3 and SH2 domains. Indeed, mouse xenografts of breast cancer cells carrying a kinase-inactive PTK6 (due to K219M mutation) still developed into tumors at a similar rate to those with wildtype PTK6 [
88]. Kinase-inactive PTK6 was also shown to promote proliferation of the T47D breast cancer cell line. PTK6 kinase activity was not required for PTK6-dependent HGF induced cell migration or for PTK6-ERK5 interaction and ERK5 activation [
65]. Similarly, PTK6 was able to promote epithelial characteristics in colon cancer cell lines independent of kinase activity [
35]. These data suggest that PTK6 has both kinase dependent and independent functions in normal and cancer tissue. Some kinase independent functions of PTK6 may play a role in oncogenesis and specific inhibitors may not yield any anticancer efficacy [
89].
Importantly though, two studies have shown that in triple negative breast cancer cell lines, the inhibition of PTK6 kinase activity augmented the cytotoxic effects of both doxorubicin or paclitaxel. Therefore, it is likely that kinase inhibition of PTK6, in combination with chemotherapies, would still be effective therapeutically but may depend on tumor context [
35,
88].
2.7. Isoform interaction
It is reported that both PTK6 and ALT-PTK6 share a functioning SH3 domain, making them competitive SH3 binding partner inhibitors [
28,
34]. This functional relationship is likely to be critical for the functional roles of PTK6 and ALT-PTK6 in cells when they are co-expressed. Co-expression and altered localization of ALT-PTK6 and full-length PTK6 has been detected in human colon and prostate cancer cell lines [
34]. Although role of ALT-PTK6 has been broadly explored in prostate cancer cells; its expression pattern, involvement in regulating signalling, and mechanisms of action in CRCs have yet to be determined.
In a co-transfection experiments with full length PTK6 and ALT-PTK6, Brauer
et al. demonstrated the inhibitory effects of ALT-PTK6 on the phosphorylation of PTK6 in prostate cancer cell lines [
34]. They suggest that ALT-PTK6 inhibits the transcriptional activities of TCF/β-catenin, thereby inhibiting cell growth and proliferation. In addition, increasing levels of ALT-PTK6 are associated with decreased phosphorylation of PTK6 and enhanced nuclear localization in prostate cancer [
34]. This study revealed that ALT-PTK6 has a functional role in PTK6 signalling in prostate cancer by negatively regulating PTK6 activity and subcellular localization. This information implies that ALT-PTK6 inhibits the full-length form of PTK6 as well as its cytoplasmic and membrane-associated substrate-binding ability [
34]. Recently the ratio of ALT-PTK6 to full-length PTK6 expression was shown to have significant prognostic value in predicating patient outcomes in breast cancer [
88]. Therefore, further detailed investigation of ALT-PTK6 and PTK6 interactions in cancers may be a fruitful avenue of research to develop a highly-specific PTK6 inhibitor.
3. PTK6 expression and activation in colon cancer
3.1. Normal intestine
PTK6 is present throughout the normal human gastrointestinal tract, in the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, and colon. PTK6 expression is primarily found in the non-dividing epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract that are undergoing terminal differentiation [
90]. The highest level of PTK6 mRNA and protein is found in the middle and upper colonic crypts. Disruption of PTK6 promotes growth arrest and maturation of columnar epithelial cells in the normal mouse small intestine [
36]. In fact, PTK6 directly regulates β-catenin transcriptional activity, repressing the WNT pathway, to promote enterocyte differentiation in the mouse intestine [
36]. PTK6 may also play a role in driving differentiation in cancer cells since increased PTK6 expression is also evident in differentiating Caco-2 colon cancer cells [
90].
3.2. PTK6 in colon cancer
PTK6 has been implicated in modulating cell signaling in numerous tissues. However, it is becoming clear that there are functional distinctions between its role in normal and tumor cell types. In normal epithelial tissues, PTK6 expression supports cell differentiation and tissue homeostasis reviewed in [
49]. However, in cancers such as breast and ovarian, PTK6 is involved in cellular proliferation, migration, and survival activities [
42,
43,
61].
Nevertheless, there is still some uncertainty surrounding the role of PTK6 in colon cancer. Llor et al. demonstrated that PTK6 mRNA expression is low in normal tissues compared to the adjacent tumor tissues at different stages, with tumor tissues showing 2-3.5 times higher PTK6 expression than the normal tissues [
90]. In addition, it is reported that the PTK6 gene is amplified in colon cancer [
35]. Conversely, Palka-Hamblin et al [
23] showed that nuclear targeted PTK6 mediated phosphorylation of β-catenin inhibited β-catenin/TCF driven transcription and WNT pathway activity in SW620 colon cancer cells. However, membrane targeted PTK6 positively regulated β-catenin/TCF transcriptional activity suggesting that membrane localization enhances PTK6 oncogenic activity [
23]. Similar conclusions were drawn by Mathur et al., [
35] who reported decreased PTK6 expression in colon carcinoma samples relative to normal differentiated epithelial cells but elevated PTK6 in the membrane of the metastatic colon cancer cells. They also showed that PTK6 knockdown increased SW480 xenograft tumor development, indicating tumor suppressor activities. However, the same study reported that TCGA Colorectal Cancer dataset analysis, comparing tumor with paired normal tissue, clearly demonstrated PTK6 overexpression in colon adenocarcinomas relative to adjacent normal tissue. [
35] which is similar to the unpaired TCGA/GTex comparison (
Figure 1). It must be noted that the studies above combine analysis at both the mRNA and protein level, which may contribute to some of the conflicting observations. However, it is clear that importance of PTK6 activation status and localization are also key factors in mediating its pro or anti-tumorigenic effects.
In vivo experiments by Haegebarth A et al. suggested that disruption of the PTK6 gene has no effect on intestinal tumorigenesis in mouse models [
36]. Interestingly, also in mouse models, loss of PTK6 conferred resistance to tumor development following treatment with the colon carcinogen azomethane (AOM), [
26]. Similarly, when DNA damaging agents such as radiation and chemotherapy drugs (e.g. 5-fluorouracil) were used in colon cancer cells, PTK6 expression promoted survival of these cells, again suggesting an important role for PTK6 following treatment with DNA damaging agents [
91]. Furthermore, it was found that γ-Irradiation induces PTK6 expression in the intestinal crypts of proliferating progenitor cells, where it is implicated in DNA-damage-induced apoptosis [
47]. Thus, PTK6 expression appears to be induced in response to DNA damage and in some cases promotes survival but others apoptosis.
PTK6 actively regulates cell cycle properties in breast and colon via activating the STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) family proteins [
21,
91]. In the HCT116 colon cells, PTK6 stimulated STAT3, and the disruption of PTK6 in mice induced STAT3 activation, indicating that this substrate is a key mediator for PTK6’s role in normal and cancerous intestinal cells [
26].
The above data indicate a complex and context dependent mode of PTK6 function in CRC. Additional research is required to clarify the precise functions of PTK6 in normal intestine and colon tumor including levels of expression, cellular localization and response to cellular and DNA damaging stresses.
4. Tyrosine kinase targeted therapy in cancer
Since aberrant tyrosine kinases activities are directly linked with the poor clinical outcomes and survival rates for cancer patients, they have become one of the most extensive class of therapeutic targets under development. Already, there are good range of clinically approved therapeutic tyrosine kinase inhibitors available, which are usually used in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and surgery (
http://www.brimr.org/PKI/PKIs.htm). Plenty of others are in the drug discovery and clinical trials pipeline.
There are two main types of protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors, reviewed in [
92]. Type 1 inhibitors competitively target the ATP binding pocket in active kinases, however, they often exhibit low selectivity, which increases the potential for adverse side effects. Type 2 inhibitors are more selective and target the inactive conformation of kinases to stabilize the enzyme in the inactive state. More recently, allosteric and covalent type kinase inhibitors have shown even greater target selectivity [
93,
94].
Understanding the critical role of tyrosine kinases in the development of CRC has created a platform to identify, characterize and test a plethora of therapeutic kinases inhibitor molecules. Of these, monoclonal antibody inhibitors of EGFR (e.g. Cetuximab) and VEGFR (e.g. Bevacizumab) are the most widely used globally, while the multi kinase inhibitor regorafenib is also FDA approved [
10]
4.1. PTK6 inhibitors
Despite the growing evidence of PTK6's oncogenic function in cancers, there have been few conclusive studies on the clinical benefits of targeted PTK6 inhibitors. Here we summarize the available inhibitors and current progress towards clinical utility.
4.1.1. Biological inhibitors
The suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) protein has been identified as the first potent biological inhibitor of PTK6, showing a tumor suppressive effect in T47D and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines [
87]. Gao
et al show that inhibition of PTK6 activity by SOCS3 is mediated by binding to the kinase domain, causing PTK6 ubiquitination and protein degradation. Since PTK6 activates STAT3 and STAT3 induces SOCS3 expression, this results in a negative feedback mechanism to control PTK6 activity [
87]. A very recent study on uveal melanoma cells demonstrates that, overexpression of SOCS3 can partially inhibit the PTK6 driven uveal melanoma cell proliferation [
95].
4.1.2. Chemical inhibitors
To date, some of the most potent PTK6 inhibitors, causing significant repression of breast cancer cell migration and invasion, are marine natural products such as the derivatives of the marine Triterpene Sipholenols: 4β-O-benzyl sipholenol A and 4β-O-benzyl-19,20-anhydrosipholenol A [
96]. The compounds were identified through a semi-synthetic optimization of the triterpene sipholenols and were found to have anti-migratory and anti-invasive effects on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells while remaining non-toxic to the normal breast epithelial cells. These two derivatives exhibited inhibition of PTK6 phosphorylation in vitro. Oleanolic acid is another common therapeutic triterpene, derived from Terminalia bentzoe L. [
97]. Again, semi-synthetic optimization of oleanolic acid identified two potent analogues: 3-O-[N-(3′-chlorobenzenesulfonyl)-carbamoyl]-oleanolic acid and 3-O-[N-(5′-fluorobenzenesulfonyl)-carbamoyl]-oleanolic acid. Significantly reduced phosphorylation of PTK6 and its substrates was observed accompanied by reduced invasiveness and migration of breast cancer cells. Further natural marine products have been identified using similar technologies, and are also proposed to exert their anti-proliferative and anti-migratory effects via PTK6 and paxillin. These include: derivatives of phenylmethylene hydantoins, and Z-4-hydroxyphenylmethylene hydantoin [
98].
Perhaps surprisingly, Geldanamycin, a known suppressor of Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) has also be shown to mediate its effects by targeting PTK6 for proteasomal degradation [
60]. The inhibitor is thought to decrease Hsp90/PTK6 interactions and therefore increase PTK6 interactions with E3 ligase components of the proteasome.
Chemical inhibitors of the PTK6 ATP binding pocket show some of the highest selectivity for PTK6. Tilfrinib (4f) 4-anilino α-carbolines mediated PTK6 inhibition shows anti-proliferative effects on MCF7, HS-578/T, and BT-549 breast cancer cell lines [
99]. Mahmoud
et al. demonstrated that 4f significantly reduces the phosphorylation of PTK6 substrate STAT3 and induces cell death of non-adherent breast cancer cells. MK138 and MK150, the two most potent derivatives of Tilfrinib, selectively inhibit PTK6 and suppress STAT3 activity in T47D breast cancer cell lines [
100]. Similarly, the compound Imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-8-amines is highly selective at attenuating the phosphorylation of PTK6 substrate SAM68, thereby inhibiting PTK6 activity [
101]. Shim
et al [
102] reported derivatives of (E)-5-(benzylideneamino)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2 (3H)- one) that showed 20-fold higher selectivity than similar NRTK’s. These compounds effectively decreased the phosphorylation of PTK6 substrates Paxillin and STAT3 [
102]. Findings from Qiu
et al demonstrated very low selectivity of type 1 inhibitors, compounds 21a and 21c, with the type 2 inhibitors, PF-6683324 and PF-6689840 showing superior selectivity [
89].
Small molecule inhibitor XMU-MP-2 also binds to the ATP binding site of the PTK6 and acts as a potent PTK6 inhibitor with low cytotoxicity [
103]. The drug suppressed growth of tumors induced by PTK6 transformed cells in xenograft models and suppressed both STAT3 and STAT5 activity. XMU-MP-2 also displayed strong synergy with HER2 and ER inhibitors. This is encouraging since PTK6 inhibitors, like many tyrosine kinase inhibitors, are likely to be most effective as part of combination therapies [
103].
Further attempts to design direct PTK6 inhibitors which high specificity have led to the identification of Pyrazolopyrimidine PP1 and PP2 [
102] and PF-6683324 and PF-6689840 which were designed specifically to bind to unphosphorylated PTK6 [
89]. However, despite growth inhibition of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, the direct inhibition of PTK6 could not be demonstrated and off target effects were evident.
Table 2.
Compounds that target PTK6 activity.
Table 2.
Compounds that target PTK6 activity.
| Name of the inhibitor |
Type of inhibitor |
References |
| SOCS3(The suppressor of cytokine signalling 3) |
Biological |
[87,95] |
| 4β-O-benzyl sipholenol A and 4β-O-benzyl-19,20-anhydrosipholenol A |
Marine natural products |
[96] |
| Oleanolic acid |
Marine natural products |
[97] |
| Phenylmethylene hydantoins, and Z-4-hydroxyphenylmethylene hydantoin |
Marine natural products |
[98] |
| Geldanamycin (an inhibitor of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) |
Natural product |
[60] |
| Tilfrinib (4f) |
Chemical |
[99] |
| Imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-8-amines |
Chemical |
[101] |
| (E)-5-(benzylideneamino)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2 (3H)- one) |
Chemical |
[102] |
| XMU-MP-2 |
Chemical |
[103] |
| Pyrazolopyrimidine PP1 and PP2 |
Chemical |
[102] |
| PF-6683324, PF-6689840, 21a, 21c |
Chemical |
[89] |
| Dasatinib |
Chemical |
[104,105] |
| Vemurafenib |
Chemical |
[106] |
Beyond these novel and newly synthesized compounds, two drugs already used widely in the clinic also appear to target PTK6. Dasatinib is a small molecule inhibitor of BCR-ABL and SRC family tyrosine kinases that has been widely used for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia [
104,
105]. Dasatinib has been described as an “off-target” tyrosine kinase inhibitor of PTK6, as the drug also significantly reduces PTK6 activity [
107]. Unfortunately, the mode of action of Dasatinib against PTK6 has not been explored. It is important to note that Dasatinib is also highly effective against other kinases such as Bone Marrow kinase on chromosome X (BMX), and Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK), and therefore quite general off-target effects can be observed in clinical settings [
108]. Vemurafenib, designed as an inhibitor of BRAFV600E, was also shown to selectively inhibit PTK6 through binding to its active site [
106]. Both Vemurafenib and the related compound PLX4720 inhibit PTK6 via off-target effects and Vemurafenib targeting of PTK6 in prostate cancer xenograft models was able to reduce tumor growth. While, Vemurafenib inhibition of PTK6 has only been exhibited in the prostate cancer model, it presents an interesting avenue for follow up studies since BRAF activating mutations occur in several cancer types including CRC.
5. Future perspectives: The potential of PTK6 inhibitory therapy in CRC
The role of PTK6 in CRC remains context dependent and complex. Here, we have summarized and discussed the, often conflicting, literature on PTK6 in colon cancer. A number of lines of evidence combine to provide a compelling argument for investigating PTK6 as a potential therapeutic target in CRC. Publicly available data suggest that PTK6 is overexpressed in tumors compared with normal tissue. When located at the membrane (but not the nucleus), PTK6 has been shown to increase WNT pathway activity, where WNT is the most frequently upregulated CRC pathway and best characterized driver of CRC. This membrane localization is more apparent in metastatic colon cancer cells. What is particularly interesting is that PTK6 expression promotes survival of cells in DNA damaging conditions. This suggests that repressing PTK6 expression in combination with chemo and radio therapies could enhance their efficacy.
As with all tyrosine kinase inhibitors, PTK6 inhibitors exhibit a range of potencies and selectivities. One of the most selective chemical inhibitors is tilfrinib (4f). Tilfrinib’s effects are mediated through a reduction in phosphorylation and activity of the transcription factor STAT3. STAT3 is overexpressed in about 70% of human cancers and has been shown to be important for survival of CRC stem-cell like cells [
109].
CRC cancer cell lines show a wide range of PTK6 expression levels. In our laboratory we have begun experiments to measure the effects of PTK6 inhibitors, including tilfrinib, on CRC cell line proliferation and survival. Preliminary evidence suggests that PTK6 inhibitors are cytotoxic to cell lines with high PTK6 levels when used alone and also act in synergy with chemotherapy drugs such as 5-FU. Further experiments are underway to explore the levels and localization of PTK6 and ATL-PTK6 in these cells, how these relate to PTK6 inhibitor sensitivity, and whether PTK6 expression levels are modulated during treatment with chemo and radio therapies.
6. Conclusion
PTK6 has long been known as a prognostic biomarker in breast cancer but its importance in other cancers is less clear and the available data is complex and sometimes conflicting. Despite this, we argue here that it is worth exploring PTK6 as a therapeutic target in CRC and making use of the plethora of CRC model systems to test some of the available PTK6 inhibitors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J. and A.L.; writing-original draft preparation, S.J; writing-reviewing and editing, A.L. and A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Translational Oncology 2021, 14, 101174–101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearnhead, N.S.; Britton, M.P.; Bodmer, W.F. The ABC of APC. Hum Mol Genet 2001, 10, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R.; Vogelstein, B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, J.C.; Kodach, L.L.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Van Den Brink, G.R. Bone morphogenetic protein signalling in colorectal cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 2008, 8, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, M.A.; Kutuk, O.; Basaga, H. Protein Kinases as Drug Targets in Cancer. Current Cancer Drug Targets 2006, 6, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Tyrosine kinase-Role and significance in Cancer Review; 2004; pp. 101-115.
- Gocek, E.; Moulas, A.N.; Studzinski, G.P. Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinases signaling pathways in normal and cancer cells. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2014, 51, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhesh Dev, S.; Zainal Abidin, S.A.; Farghadani, R.; Othman, I.; Naidu, R. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Their Signaling Pathways as Therapeutic Targets of Curcumin in Cancer. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 772510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Aranda, M.; Redondo, M. Targeting Receptor Kinases in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiry, P.; Torkamani, A.; Schork, N.J.; Hegele, R.A. Kinase mutations in human disease: Interpreting genotype-phenotype relationships. Nature Reviews Genetics 2010, 11, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W. Regulation of Src Family Kinases during Colorectal Cancer Development and Its Clinical Implications. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, K.Y. Inhibiting focal adhesion kinase: A potential target for enhancing therapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer therapy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2018, 10, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, C.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, J.S. The JAK2/STAT3/CCND2 Axis promotes colorectal Cancer stem cell persistence and radioresistance. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2019, 38, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Barker, K.T.; Martindale, J.E.; Kamalati, T.; Lowe, P.N.; Page, M.J.; Gusterson, B.A.; Crompton, M.R. Cloning and characterisation of cDNAs encoding a novel non-receptor tyrosine kinase, brk, expressed in human breast tumours. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ostrander, J.H.; Daniel, A.R.; Lange, C.A. Brk/PTK6 signaling in normal and cancer cell models. Current Opinion in Pharmacology 2010, 10, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.T.; Strunk, K.M.; Spritz, R.A. A survey of protein tyrosine kinase mRNAs expressed in normal human melanocytes. Oncogene 1993, 8, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derry, J.J.; Prins, G.S.; Ray, V.; Tyner, A.L. Altered localization and activity of the intracellular tyrosine kinase BRK/Sik in prostate tumor cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 4212–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Shen, C.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lin, F.C.; Huang, Y.P.; Chen, R.H. Brk activates rac1 and promotes cell migration and invasion by phosphorylating paxillin. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 10558–10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derry, J.J.; Richard, S.; Valderrama Carvajal, H.; Ye, X.; Vasioukhin, V.; Cochrane, A.W.; Chen, T.; Tyner, A.L. Sik (BRK) phosphorylates Sam68 in the nucleus and negatively regulates its RNA binding ability. Mol Cell Biol 2000, 20, 6114–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, H.; Miller, W.T.; Poli, V.; Reich, N.C. Identification of STAT3 as a specific substrate of breast tumor kinase. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4904–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukong, K.E.; Huot, M.E.; Richard, S. BRK phosphorylates PSF promoting its cytoplasmic localization and cell cycle arrest. Cell Signal 2009, 21, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palka-Hamblin, H.L.; Gierut, J.J.; Bie, W.; Brauer, P.M.; Zheng, Y.; Asara, J.M.; Tyner, A.L. Identification of beta-catenin as a target of the intracellular tyrosine kinase PTK6. J Cell Sci 2010, 123, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Zappacosta, F.; Su, W.; Annan, R.S.; Miller, W.T. Interaction between Brk kinase and insulin receptor substrate-4. Oncogene 2005, 24, 5656–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tyner, A.L. Context-specific protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) signalling in prostate cancer. Eur J Clin Invest 2013, 43, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierut, J.; Zheng, Y.; Bie, W.; Carroll, R.E.; Ball-Kell, S.; Haegebarth, A.; Tyner, A.L. Disruption of the mouse protein tyrosine kinase 6 gene prevents STAT3 activation and confers resistance to azoxymethane. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Sara, E.A.; Crompton, M.R. A novel adaptor-like protein which is a substrate for the non-receptor tyrosine kinase, BRK. Oncogene 2000, 19, 4273–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Barker, K.T.; Shipley, J.; Crompton, M.R. Characterisation and chromosome mapping of the human non receptor tyrosine kinase gene, brk. Oncogene 1997, 15, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.T. Assignment of the human PTK6 gene encoding a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase to 20q13.3 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 1997, 77, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, T.; Schlessingert, J. SH2 and SH3 domains. Curr Biol 1993, 3, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jung, J.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, W.; Lee, S.T. Molecular dissection of the interaction between the SH3 domain and the SH2-Kinase Linker region in PTK6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2007, 362, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Miller, W.T. Role of the Brk SH3 domain in substrate recognition. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Emmadi, R.; Wang, Z.; Wiley, E.L.; Gann, P.H.; Khan, S.A.; Banerji, N.; McDonald, W.; Asztalos, S.; Pham, T.N.; et al. PTK6/BRK is expressed in the normal mammary gland and activated at the plasma membrane in breast tumors. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6038–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, P.M.; Zheng, Y.; Evans, M.D.; Dominguez-Brauer, C.; Peehl, D.M.; Tyner, A.L. The alternative splice variant of protein tyrosine kinase 6 negatively regulates growth and enhances PTK6-mediated inhibition of beta-catenin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, P.S.; Gierut, J.J.; Guzman, G.; Xie, H.; Xicola, R.M.; Llor, X.; Chastkofsky, M.I.; Perekatt, A.O.; Tyner, A.L. Kinase-Dependent and -Independent Roles for PTK6 in Colon Cancer. Mol Cancer Res 2016, 14, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegebarth, A.; Bie, W.; Yang, R.; Crawford, S.E.; Vasioukhin, V.; Fuchs, E.; Tyner, A.L. Protein tyrosine kinase 6 negatively regulates growth and promotes enterocyte differentiation in the small intestine. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 4949–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petro, B.J.; Tan, R.C.; Tyner, A.L.; Lingen, M.W.; Watanabe, K. Differential expression of the non-receptor tyrosine kinase BRK in oral squamous cell carcinoma and normal oral epithelium. Oral Oncol 2004, 40, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasioukhin, V.; Serfas, M.S.; Siyanova, E.Y.; Polonskaia, M.; Costigan, V.J.; Liu, B.; Thomason, A.; Tyner, A.L. A novel intracellular epithelial cell tyrosine kinase is expressed in the skin and gastrointestinal tract. Oncogene 1995, 10, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Haegebarth, A.; Heap, D.; Bie, W.; Derry, J.J.; Richard, S.; Tyner, A.L. The nuclear tyrosine kinase BRK/Sik phosphorylates and inhibits the RNA-binding activities of the Sam68-like mammalian proteins SLM-1 and SLM-2. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 54398–54404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.K.; Zhang, X.R.; Zhong, Q.; Li, M.Z.; Liu, Z.M.; Lin, Z.R.; Wu, D.; Zeng, M.S. Low expression of PTK6/Brk predicts poor prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med 2013, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Bao, J.Y.J.; Kwan, P.S.; Chan, Y.P.; Tong, C.M.; Fu, L.; Zhang, N.; Tong, A.H.Y.; Qin, Y.R.; Tsao, S.W.; et al. Identification of PTK6, via RNA sequencing analysis, as a suppressor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.T.; Jackson, L.E.; Crompton, M.R. BRK tyrosine kinase expression in a high proportion of human breast carcinomas. Oncogene 1997, 15, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmandt, R.E.; Bennett, M.; Clifford, S.; Thornton, A.; Jiang, F.; Broaddus, R.R.; Sun, C.C.; Lu, K.H.; Sood, A.K.; Gershenson, D.M. The BRK tyrosine kinase is expressed in high-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary. Cancer Biol Ther 2006, 5, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.L.; Ye, Y.L.; Wu, Z.M.; He, Q.M.; Tan, L.; Xiao, K.H.; Wu, R.Y.; Yu, Y.; Mai, J.; Li, Z.L.; et al. Overexpression of PTK6 predicts poor prognosis in bladder cancer patients. J Cancer 2017, 8, 3464–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Deng, A. Expression of protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) in nonsmall cell lung cancer and their clinical and prognostic significance. Onco Targets Ther 2013, 6, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegebarth, A.; Perekatt, A.O.; Bie, W.; Gierut, J.J.; Tyner, A.L. Induction of protein tyrosine kinase 6 in mouse intestinal crypt epithelial cells promotes DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ie Kim, H.; Lee, S.T. Oncogenic functions of PTK6 are enhanced by its targeting to plasma membrane but abolished by its targeting to nucleus. J Biochem 2009, 146, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, P.M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Tyner, A.L. Cytoplasmic retention of protein tyrosine kinase 6 promotes growth of prostate tumor cells. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4190–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.L.; Poghosyan, Z.; Pennington, C.J.; Scott, X.; Handsley, M.M.; Warn, A.; Gavrilovic, J.; Honert, K.; Kruger, A.; Span, P.N.; et al. Distinct functions of natural ADAM-15 cytoplasmic domain variants in human mammary carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res 2008, 6, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.A.; Lee, E.S.; Yoon, H.Y.; Randazzo, P.A.; Lee, S.T. PTK6 inhibits down-regulation of EGF receptor through phosphorylation of ARAP1. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 26013–26021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Miller, D.J.; Guibao, C.D.; Donato, D.M.; Hanks, S.K.; Zheng, J.J. Structural and functional insights into the interaction between the Cas family scaffolding protein p130Cas and the focal adhesion-associated protein paxillin. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 18281–18289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.A.; Lee, S.T. PTK6 promotes degradation of c-Cbl through PTK6-mediated phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013, 431, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah, S.; Goel, R.K.; Dai, C.; Kalra, N.; Beaton-Brown, E.; Bagu, E.T.; Bonham, K.; Lukong, K.E. BRK targets Dok1 for ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation to promote cell proliferation and migration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalati, T.; Jolin, H.E.; Fry, M.J.; Crompton, M.R. Expression of the BRK tyrosine kinase in mammary epithelial cells enhances the coupling of EGF signalling to PI 3-kinase and Akt, via erbB3 phosphorylation. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5471–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubele, M.; Walch, A.K.; Ludyga, N.; Braselmann, H.; Atkinson, M.J.; Luber, B.; Auer, G.; Tapio, S.; Cooke, T.; Bartlett, J.M. Prognostic value of protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) for long-term survival of breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 2008, 99, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Basson, M.D.; Ito, H. PTK6 promotes cancer migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer cells dependent on ERK signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukong, K.E.; Richard, S. Sam68, the KH domain-containing superSTAR. Biochim Biophys Acta 2003, 1653, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasioukhin, V.; Tyner, A.L. A role for the epithelial-cell-specific tyrosine kinase Sik during keratinocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1997, 94, 14477–14482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.A.; Cho, H.S.; Yoon, J.B.; Chung, I.K.; Lee, S.T. Hsp90 rescues PTK6 from proteasomal degradation in breast cancer cells. Biochem J 2012, 447, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, H.Y.; Shrestha, Y.; Selfors, L.M.; Frye, F.; Iida, N.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L.; Yao, J.; Lu, Y.; Epstein, C.B.; et al. PTK6 regulates IGF-1-induced anchorage-independent survival. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, M.S.; Li, F.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Kuo, M.L.; Settleman, J.; Chen, R.H. Breast tumor kinase phosphorylates p190RhoGAP to regulate rho and ras and promote breast carcinoma growth, migration, and invasion. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 7779–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Asbach, B.; Shteyn, E.; Gomez, C.; Coltoff, A.; Bhuyan, S.; Tyner, A.L.; Wagner, R.; Blain, S.W. Brk/Protein tyrosine kinase 6 phosphorylates p27KIP1, regulating the activity of cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Mol Cell Biol 2015, 35, 1506–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, A.M.; Silva, C.M. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b: A new target of breast tumor kinase/protein tyrosine kinase 6. Breast Cancer Res 2007, 9, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, N.E.; Lange, C.A. Breast tumor kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 mediate Met receptor signaling to cell migration in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 2010, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Ball-Kell, S.M.; Tyner, A.L. Protein tyrosine kinase 6 promotes ERBB2-induced mammary gland tumorigenesis in the mouse. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Chatti, K.; Qiu, H.; Lakshmi, B.; Krasnitz, A.; Hicks, J.; Yu, M.; Miller, W.T.; Muthuswamy, S.K. Brk is coamplified with ErbB2 to promote proliferation in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 12463–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanizaki, J.; Okamoto, I.; Sakai, K.; Nakagawa, K. Differential roles of trans-phosphorylated EGFR, HER2, HER3, and RET as heterodimerisation partners of MET in lung cancer with MET amplification. Br J Cancer 2011, 105, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Liang, K.; Hsu, J.M.; Albarracin, C.; Mills, G.B.; Hung, M.C.; Fan, Z. Brk/PTK6 sustains activated EGFR signaling through inhibiting EGFR degradation and transactivating EGFR. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4372–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, B.; Vijayakumar, M.; Priya, K.; Kim, J.H.; Prabakaran, D.S.; Shahid, M.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Alsaidan, M.; Othman Bahakim, N.; Hassan Abdelzaher, M.; et al. EGFR-Based Targeted Therapy for Colorectal Cancer-Promises and Challenges. Vaccines (Basel) 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ostrander, J.H.; Faivre, E.J.; Olsen, A.; Fitzsimmons, D.; Lange, C.A. Regulated association of protein kinase B/Akt with breast tumor kinase. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 1982–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bie, W.; Brauer, P.M.; Perez White, B.E.; Li, J.; Nogueira, V.; Raychaudhuri, P.; Hay, N.; Tonetti, D.A.; et al. PTK6 activation at the membrane regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 5426–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Peng, M.; Wang, Z.; Asara, J.M.; Tyner, A.L. Protein tyrosine kinase 6 directly phosphorylates AKT and promotes AKT activation in response to epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 4280–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanankutty, A. PI3K/ Akt/ mTOR Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence. Curr Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Sun, X.; Wier, E.M.; Hodgson, A.; Liu, Y.; Sears, C.L.; Wan, F. Sam68/KHDRBS1 is critical for colon tumorigenesis by regulating genotoxic stress-induced NF-kappaB activation. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.M.; Jin, X.; Lin, H.J.; Huang, M.; Liu, R.; Reynolds, R.K.; Lin, J. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses growth of human ovarian and breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7925–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.Z.; Zhang, W.Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, Q.; Coppola, D.; Mansour, M.; Xu, L.M.; Costanzo, C.; Cheng, J.Q.; Wang, L.H. Twist is transcriptionally induced by activation of STAT3 and mediates STAT3 oncogenic function. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 14665–14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, J.J.; Levy, D.E.; Shahalizadeh, S.; Hallett, M.; Muller, W.J. Identification of a Stat3-dependent transcription regulatory network involved in metastatic progression. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 6823–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, O.; Miyasaka, Y.; Sekine, Y.; Mizushima, A.; Muromoto, R.; Nanbo, A.; Yoshimura, A.; Matsuda, T. STAP-2 is phosphorylated at tyrosine-250 by Brk and modulates Brk-mediated STAT3 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 384, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, O.; Sekine, Y.; Mizushima, A.; Nakasuji, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Muromoto, R.; Nanbo, A.; Oritani, K.; Yoshimura, A.; et al. Interactions of STAP-2 with Brk and STAT3 participate in cell growth of human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 38093–38103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, O.; Mizushima, A.; Sekine, Y.; Yamamoto, C.; Muromoto, R.; Nanbo, A.; Oritani, K.; Yoshimura, A.; Matsuda, T. Involvement of STAP-2 in Brk-mediated phosphorylation and activation of STAT5 in breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci 2011, 102, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Lin, G.; Lucito, R.; Tonks, N.K. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B antagonized signaling by insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and kinase BRK/PTK6 in ovarian cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 24923–24934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, D.J.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Macias, V.; Ball-Kell, S.; Zenner, M.L.; Bie, W.; Tyner, A.L. PTEN is a protein phosphatase that targets active PTK6 and inhibits PTK6 oncogenic signaling in prostate cancer. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, G.; Jain, S.; Kundu, G.C. Osteopontin promotes vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent breast tumor growth and angiogenesis via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Klein, E.A.; Assoian, R.K.; Kazanietz, M.G. Heregulin beta1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through Rac/ERK-dependent induction of cyclin D1 and p21Cip1. Biochem J 2008, 410, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Aleem, S.; Yang, M.; Miller, W.T.; Tonks, N.K. Protein-tyrosine Phosphatase and Kinase Specificity in Regulation of SRC and Breast Tumor Kinase. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 15934–15947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cimica, V.; Reich, N.C. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 inhibits breast tumor kinase activation of STAT3. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 20904–20912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmi, R.S.; Box, G.M.; Wazir, U.; Hussain, H.A.; Davies, J.A.; Court, W.J.; Eccles, S.A.; Jiang, W.G.; Mokbel, K.; Harvey, A.J. Breast Tumour Kinase (Brk/PTK6) Contributes to Breast Tumour Xenograft Growth and Modulates Chemotherapeutic Responses In Vitro. Genes 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Levine, K.; Gajiwala, K.S.; Cronin, C.N.; Nagata, A.; Johnson, E.; Kraus, M.; Tatlock, J.; Kania, R.; Foley, T.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors reveal PTK6 kinase is not an oncogenic driver in breast cancers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, X.; Serfas, M.S.; Bie, W.; Vasioukhin, V.; Polonskaia, M.; Derry, J.; Abbott, C.M.; Tyner, A.L. BRK/Sik expression in the gastrointestinal tract and in colon tumors. Clin Cancer Res 1999, 5, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Gierut, J.J.; Mathur, P.S.; Bie, W.; Han, J.; Tyner, A.L. Targeting protein tyrosine kinase 6 enhances apoptosis of colon cancer cells following DNA damage. Mol Cancer Ther 2012, 11, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.L.; Gray, N.S. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisner, J.; Gontla, R.; van der Westhuizen, L.; Oeck, S.; Ketzer, J.; Janning, P.; Richters, A.; Muhlenberg, T.; Fang, Z.; Taher, A.; et al. Covalent-Allosteric Kinase Inhibitors. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2015, 54, 10313–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Clausen, M.H.; Nielsen, T.E. Allosteric small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 2015, 156, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yao, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, L.; Huang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, D.; Wu, W. PTK6 inhibits autophagy to promote uveal melanoma tumorigenesis by binding to SOCS3 and regulating mTOR phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudah, A.I.; Jain, S.; Busnena, B.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Optimization of marine triterpene sipholenols as inhibitors of breast cancer migration and invasion. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.E.; Akl, M.R.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Sallam, A.A.; Haggag, E.G.; Kamal, A.M.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery, optimization, and pharmacophore modeling of oleanolic acid and analogues as breast cancer cell migration and invasion inhibitors through targeting Brk/Paxillin/Rac1 axis. Chem Biol Drug Des 2015, 85, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.A.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Foudah, A.I.; Akl, M.R.; Nazzal, S.; Meyer, S.A.; Liu, Y.Y.; El Sayed, K.A. Marine natural products-inspired phenylmethylene hydantoins with potent in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities via suppression of Brk and FAK signaling. Org Biomol Chem 2014, 12, 5295–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.A.; Krug, M.; Wersig, T.; Slynko, I.; Schächtele, C.; Totzke, F.; Sippl, W.; Hilgeroth, A. Discovery of 4-anilino α-carbolines as novel Brk inhibitors. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2014, 24, 1948–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelze, M.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Sippl, W.; Wersig, T.; Hilgeroth, A.; Ritter, C.A. Novel 4-anilino-alpha-carboline derivatives induce cell death in nonadhesive breast cancer cells through inhibition of Brk activity. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2015, 53, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Belanger, D.B.; Curran, P.J.; Shipps, G.W., Jr.; Miao, H.; Bracken, J.B.; Arshad Siddiqui, M.; Malkowski, M.; Wang, Y. Discovery of novel imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-8-amines as Brk/PTK6 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011, 21, 5870–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.J.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, S.T. The associated pyrazolopyrimidines PP1 and PP2 inhibit protein tyrosine kinase 6 activity and suppress breast cancer cell proliferation. Oncol Lett 2017, 13, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gui, F.; He, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Deng, Z.; Sun, X.; Huang, X.; et al. Targeting BRK-positive breast cancers with small-molecule kinase inhibitors. Cancer Research 2017, 77, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Chen, B. The role of dasatinib in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia. Drug Des Devel Ther 2015, 9, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rix, U.; Hantschel, O.; Durnberger, G.; Remsing Rix, L.L.; Planyavsky, M.; Fernbach, N.V.; Kaupe, I.; Bennett, K.L.; Valent, P.; Colinge, J.; et al. Chemical proteomic profiles of the BCR-ABL inhibitors imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib reveal novel kinase and nonkinase targets. Blood 2007, 110, 4055–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, D.J.; Hitchinson, B.; Gilic, M.B.; Bie, W.; Gaponenko, V.; Tyner, A.L. Vemurafenib Inhibits Active PTK6 in PTEN-null Prostate Tumor Cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2019, 18, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.K.; Birudukota, S.; Swaminathan, S.; Battula, S.K.; Vadivelu, S.; Tyagi, R.; Gosu, R. Co-crystal structures of PTK6: With Dasatinib at 2.24 A, with novel imidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-8-amine derivative inhibitor at 1.70 A resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017, 482, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantschel, O.; Rix, U.; Schmidt, U.; Burckstummer, T.; Kneidinger, M.; Schutze, G.; Colinge, J.; Bennett, K.L.; Ellmeier, W.; Valent, P.; et al. The Btk tyrosine kinase is a major target of the Bcr-Abl inhibitor dasatinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 13283–13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Fuchs, J.; Li, C.; Olson, V.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Lin, J. STAT3 signaling pathway is necessary for cell survival and tumorsphere forming capacity in ALDH(+)/CD133(+) stem cell-like human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011, 416, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).