Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human plasma samples
2.2. Cell culture
2.3. Virus
2.4. Reagents
2.5. Bio-plex multiplex immunoassay
2.6. Endothelial permeability assay
2.7. Data and statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient characteristics
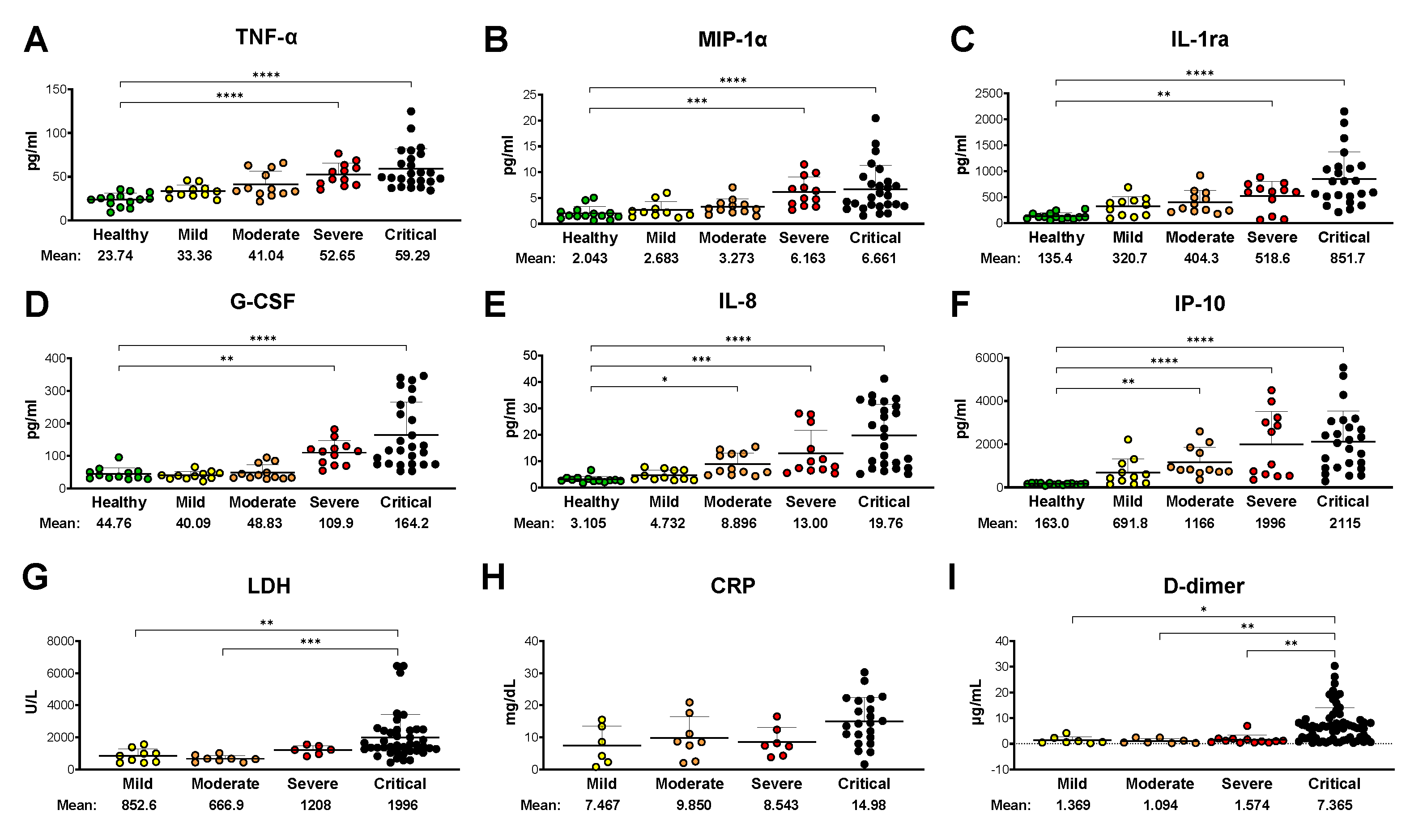
3.2. Plasma cytokine/chemokine levels show a strong correlation with disease severity
3.3. Clinical laboratory markers are elevated in COVID-19 patients’ blood
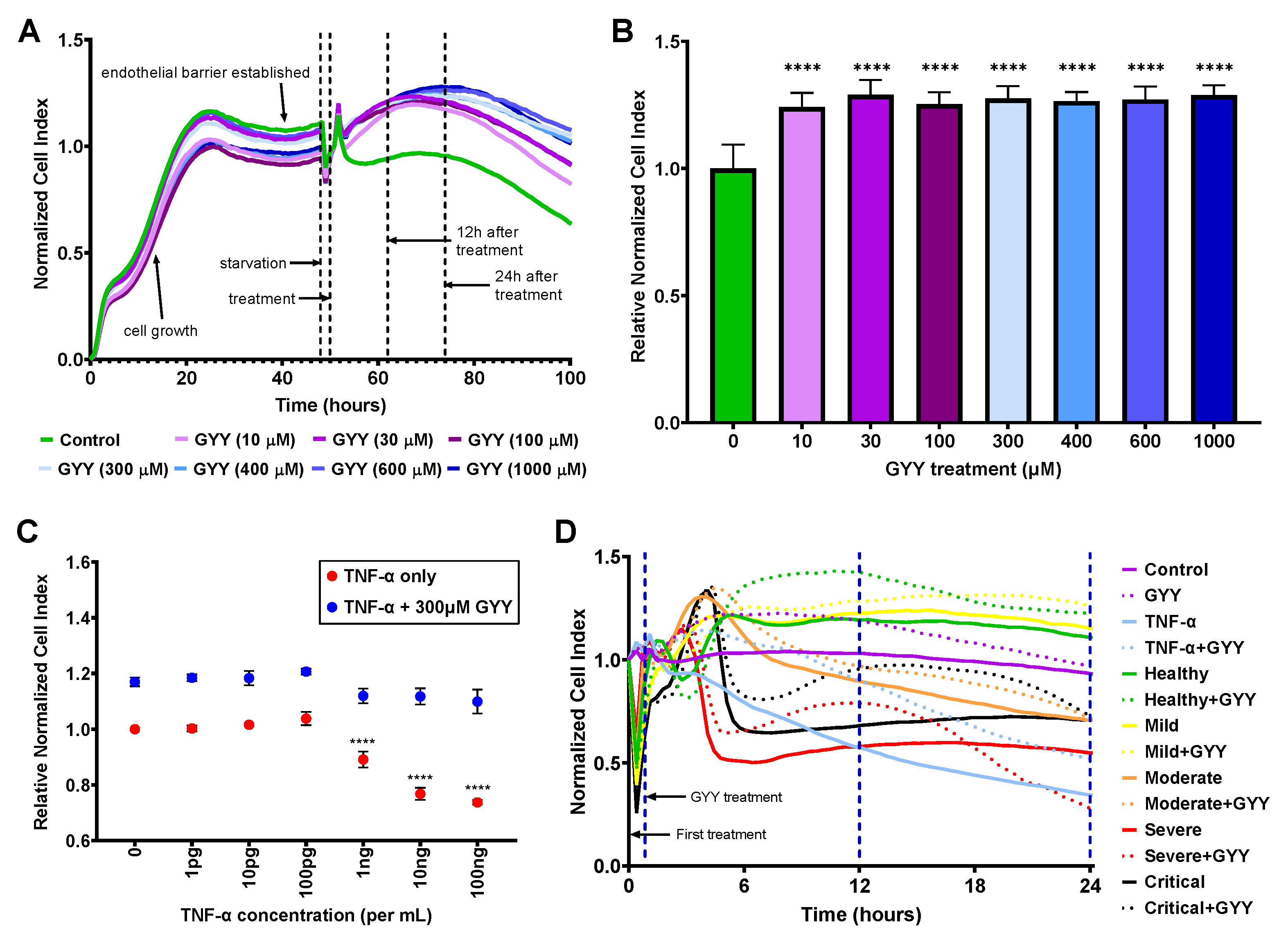
3.4. GYY4137 treatment improves endothelial barrier function
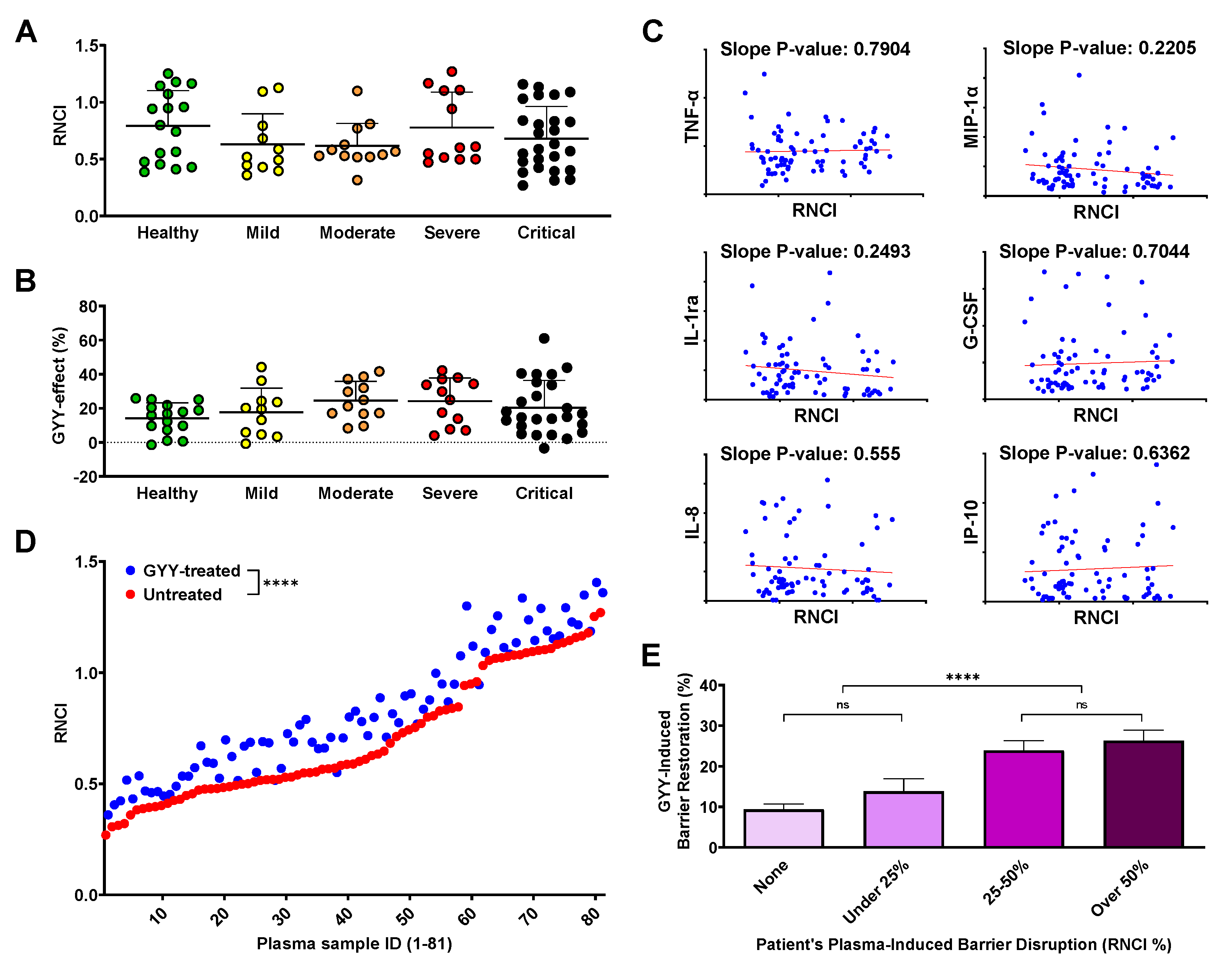
3.5. Human plasma treatment alters endothelial barrier function, and GYY4137 modifies these effects
3.6. Endothelial barrier disruption caused by plasma from COVID-19 patients does not correlate with disease severity or plasma cytokine/chemokine levels
3.7. GYY4137 increases endothelial barrier function in a disruption-dependent manner
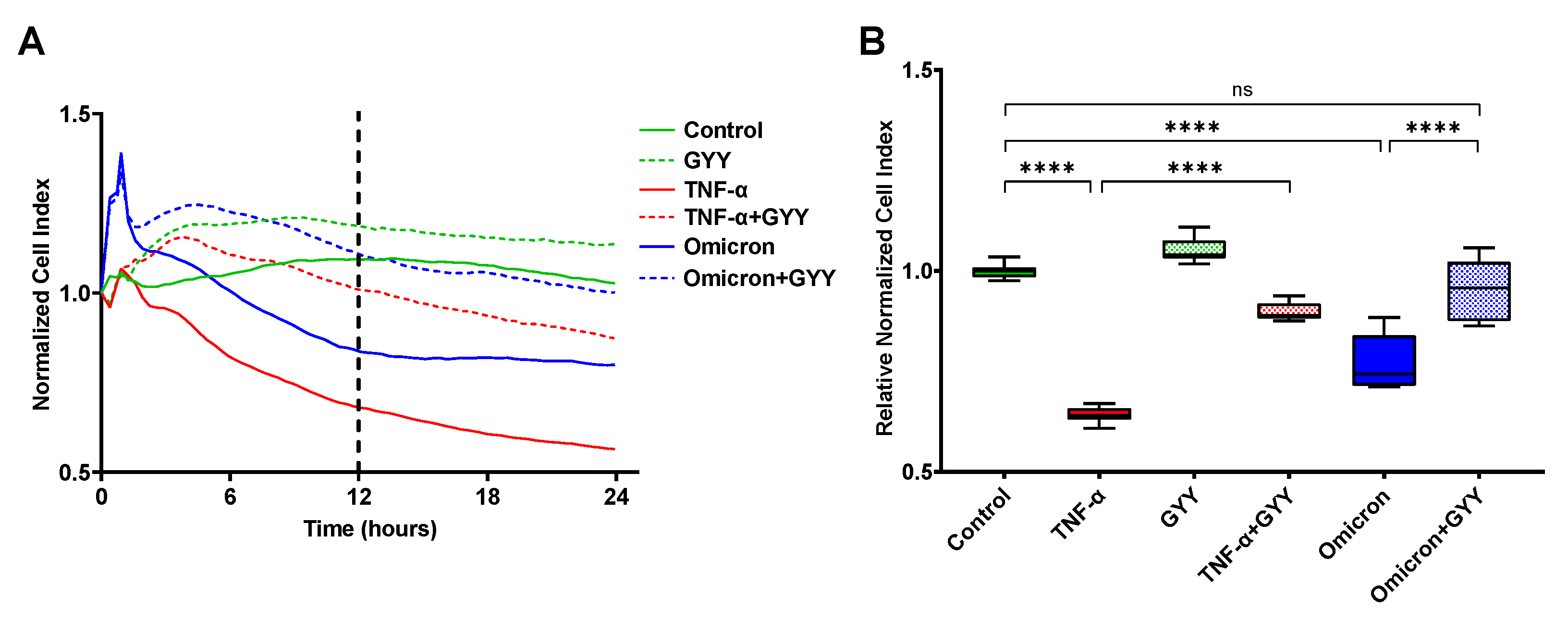
3.8. Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.1 increases endothelial barrier permeability, which can be prevented by GYY4137 treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO) Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Accessed on 18 May 2023, https://covid19.who.int.
- 2. Gebo KA, Heath SL, Fukuta Y, Zhu X, Baksh S, Abraham AG, Habtehyimer F, Shade D, Ruff J, Ram M, Laeyendecker O, Fernandez RE, Patel EU, Baker OR, Shoham S, Cachay ER, Currier JS, Gerber JM, Meisenberg B, Forthal DN, Hammitt LL, Huaman MA, Levine A, Mosnaim GS, Patel B, Paxton JH, Raval JS, Sutcliffe CG, Anjan S, Gniadek T, Kassaye S, Blair JE, Lane K, McBee NA, Gawad AL, Das P, Klein SL, Pekosz A, Casadevall A, Bloch EM, Hanley D, Tobian AAR, Sullivan DJ. Early Treatment, Inflammation and Post-COVID Conditions. medRxiv. 2023.
- Phillips S, Williams MA. Confronting Our Next National Health Disaster - Long-Haul Covid. N Engl J Med. 2021, 385, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Long COVID or Post-COVID Conditions. Accessed on 18 May 2023, https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html.
- 5. Ahamed J, Laurence J. Long COVID endotheliopathy: Hypothesized mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132.
- Chen W, Pan JY. Anatomical and Pathological Observation and Analysis of SARS and COVID-19: Microthrombosis Is the Main Cause of Death. Biol Proced Online. 2021, 23, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Halawa S, Pullamsetti SS, Bangham CRM, Stenmark KR, Dorfmuller P, Frid MG, Butrous G, Morrell NW, de Jesus Perez VA, Stuart DI, O'Gallagher K, Shah AM, Aguib Y, Yacoub MH. Potential long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the pulmonary vasculature: A global perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2022, 19, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby P, Luscher T. COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease. Eur Heart J. 2020, 41, 3038–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan MV, McGroder C, Stevens JS, Cook JR, Nordvig AS, Shalev D, Sehrawat TS, Ahluwalia N, Bikdeli B, Dietz D, Der-Nigoghossian C, Liyanage-Don N, Rosner GF, Bernstein EJ, Mohan S, Beckley AA, Seres DS, Choueiri TK, Uriel N, Ausiello JC, Accili D, Freedberg DE, Baldwin M, Schwartz A, Brodie D, Garcia CK, Elkind MSV, Connors JM, Bilezikian JP, Landry DW, Wan EY. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgonje AR, Abdulle AE, Timens W, Hillebrands JL, Navis GJ, Gordijn SJ, Bolling MC, Dijkstra G, Voors AA, Osterhaus AD, van der Voort PH, Mulder DJ, van Goor H. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Pathol. 2020, 251, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh V, Motwani R, Kumar A, Kumari C, Raza K. Histopathological observations in COVID-19: A systematic review. J Clin Pathol. 2021, 74, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia RF, Ligresti G, Caporarello N, Akilesh S, Ribatti D. COVID-19 Vasculopathy: Mounting Evidence for an Indirect Mechanism of Endothelial Injury. Am J Pathol. 2021, 191, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian Y, Lei T, Patel PS, Lee CH, Monaghan-Nichols P, Xin HB, Qiu J, Fu M. Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin. J Virol. 2021, 95, e0139621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 14. Barilli A, Visigalli R, Ferrari F, Bianchi MG, Dall'Asta V, Rotoli BM. Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Responses of Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Implications for COVID-19 Lung Pathology. Biomedicines. 2022; 10.
- Fajgenbaum DC, June CH. Cytokine Storm. N Engl J Med. 2020, 383, 2255–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch A, Dupont A, Goutay J, Caplan M, Staessens S, Moussa M, Jeanpierre E, Corseaux D, Lefevre G, Lassalle F, Faure K, Lambert M, Duhamel A, Labreuche J, Garrigue D, De Meyer SF, Staels B, Van Belle E, Vincent F, Kipnis E, Lenting PJ, Poissy J, Susen S, Lille CRN, Members of the LSC. Endotheliopathy Is Induced by Plasma From Critically Ill Patients and Associated With Organ Failure in Severe COVID-19. Circulation. 2020, 142, 1881–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura A, Vecchie A, Dagna L, Martinod K, Dixon DL, Van Tassell BW, Dentali F, Montecucco F, Massberg S, Levi M, Abbate A. Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canzano P, Brambilla M, Porro B, Cosentino N, Tortorici E, Vicini S, Poggio P, Cascella A, Pengo MF, Veglia F, Fiorelli S, Bonomi A, Cavalca V, Trabattoni D, Andreini D, Omodeo Sale E, Parati G, Tremoli E, Camera M. Platelet and Endothelial Activation as Potential Mechanisms Behind the Thrombotic Complications of COVID-19 Patients. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021, 6, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biering SB, Gomes de Sousa FT, Tjang LV, Pahmeier F, Zhu C, Ruan R, Blanc SF, Patel TS, Worthington CM, Glasner DR, Castillo-Rojas B, Servellita V, Lo NTN, Wong MP, Warnes CM, Sandoval DR, Clausen TM, Santos YA, Fox DM, Ortega V, Naar AM, Baric RS, Stanley SA, Aguilar HC, Esko JD, Chiu CY, Pak JE, Beatty PR, Harris E. SARS-CoV-2 Spike triggers barrier dysfunction and vascular leak via integrins and TGF-beta signaling. Nat Commun. 2022, 13, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colunga Biancatelli RML, Solopov PA, Sharlow ER, Lazo JS, Marik PE, Catravas JD. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunit S1 induces COVID-19-like acute lung injury in Kappa18-hACE2 transgenic mice and barrier dysfunction in human endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2021, 321, L477–L484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 21. Rotoli BM, Barilli A, Visigalli R, Ferrari F, Dall'Asta V. Endothelial Cell Activation by SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 Protein: A Crosstalk between Endothelium and Innate Immune Cells. Biomedicines. 2021; 9.
- Wagner JUG, Bojkova D, Shumliakivska M, Luxan G, Nicin L, Aslan GS, Milting H, Kandler JD, Dendorfer A, Heumueller AW, Fleming I, Bibli SI, Jakobi T, Dieterich C, Zeiher AM, Ciesek S, Cinatl J, Dimmeler S. Increased susceptibility of human endothelial cells to infections by SARS-CoV-2 variants. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021, 116, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 23. Bordoni V, Mariotti D, Matusali G, Colavita F, Cimini E, Ippolito G, Agrati C. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Airway Epithelium Triggers Pulmonary Endothelial Cell Activation and Senescence Associated with Type I IFN Production. Cells. 2022; 11.
- Muhl L, He L, Sun Y, Andaloussi Mae M, Pietila R, Liu J, Genove G, Zhang L, Xie Y, Leptidis S, Mocci G, Stritt S, Osman A, Anisimov A, Hemanthakumar KA, Rasanen M, Hansson EM, Bjorkegren J, Vanlandewijck M, Blomgren K, Makinen T, Peng XR, Hu Y, Ernfors P, Arnold TD, Alitalo K, Lendahl U, Betsholtz C. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is expressed in mouse pericytes but not endothelial cells: Implications for COVID-19 vascular research. Stem Cell Reports. 2022, 17, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmel L, Chew KY, Stocks CJ, Yordanov TE, Essebier P, Kulasinghe A, Monkman J, Dos Santos Miggiolaro AFR, Cooper C, de Noronha L, Schroder K, Lagendijk AK, Labzin LI, Short KR, Gordon EJ. Endothelial cells are not productively infected by SARS-CoV-2. Clin Transl Immunology. 2021, 10, e1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas R, Verin AD, Black SM, Catravas JD. Regulators of endothelial and epithelial barrier integrity and function in acute lung injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke E, Mehta D, Minshall R, Malik AB. Regulation of endothelial junctional permeability. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008, 1123, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lum H, Malik AB. Regulation of vascular endothelial barrier function. Am J Physiol. 1994, 267, L223–L241. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, Vanstapel A, Werlein C, Stark H, Tzankov A, Li WW, Li VW, Mentzer SJ, Jonigk D. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020, 383, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirino G, Szabo C, Papapetropoulos A. Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells, tissues, and organs. Physiol Rev. 2023, 103, 31–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson KR, DeLeon ER, Liu F. Controversies and conundrums in hydrogen sulfide biology. Nitric Oxide. 2014, 41, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi Govar A, Toro G, Szaniszlo P, Pavlidou A, Bibli SI, Thanki K, Resto VA, Chao C, Hellmich MR, Szabo C, Papapetropoulos A, Modis K. 3-Mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase supports endothelial cell angiogenesis and bioenergetics. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 866–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagy NL, Szabo C, Papapetropoulos A. Vascular biology of hydrogen sulfide. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C537–C549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola PJ, Naik JS, Gonzalez Bosc LV, Gardiner AS, Birg A, Kanagy NL. Hydrogen Sulfide Actions in the Vasculature. Compr Physiol. 2021, 11, 2467–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Pan LL, Liu XH, Gong QH, Wu D, Zhu YZ. Hydrogen sulfide attenuated tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced inflammatory signaling and dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e19766. [Google Scholar]
- Geng Y, Li E, Mu Q, Zhang Y, Wei X, Li H, Cheng L, Zhang B. Hydrogen sulfide inhalation decreases early blood-brain barrier permeability and brain edema induced by cardiac arrest and resuscitation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li H, Zhu L, Feng J, Hu X, Li C, Zhang B. Hydrogen Sulfide Decreases Blood-Brain Barrier Damage via Regulating Protein Kinase C and Tight Junction After Cardiac Arrest in Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018, 47, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 38. Bourque C, Zhang Y, Fu M, Racine M, Greasley A, Pei Y, Wu L, Wang R, Yang G. H2S protects lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by blocking NFkappaB transactivation in endothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018; 338, 20–29.
- Faller S, Hausler F, Goeft A, von Itter MA, Gyllenram V, Hoetzel A, Spassov SG. Hydrogen sulfide limits neutrophil transmigration, inflammation, and oxidative burst in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 14676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 40. Jiang L, Jiang Q, Yang S, Huang S, Han X, Duan J, Pan S, Zhao M, Guo S. GYY4137 attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via heme oxygenase-1 modulation. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019; 54, 77–86.
- Wang T, Wang L, Zaidi SR, Sammani S, Siegler J, Moreno-Vinasco L, Mathew B, Natarajan V, Garcia JG. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates particulate matter-induced human lung endothelial barrier disruption via combined reactive oxygen species scavenging and Akt activation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012, 47, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 42. Santos BM, Garattini EG, Branco LGS, Leite-Panissi CRA, Nascimento GC. The therapeutic potential of cystathionine gamma-lyase in temporomandibular inflammation-induced orofacial hypernociception. Physiol Behav. 2018; 188, 128–133.
- Yuan S, Pardue S, Shen X, Alexander JS, Orr AW, Kevil CG. Hydrogen sulfide metabolism regulates endothelial solute barrier function. Redox Biol. 2016, 9, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citi V, Martelli A, Brancaleone V, Brogi S, Gojon G, Montanaro R, Morales G, Testai L, Calderone V. Anti-inflammatory and antiviral roles of hydrogen sulfide: Rationale for considering H(2) S donors in COVID-19 therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4931–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G. H2S as a potential defense against COVID-19? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C244–C249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhanov N, Escaffre O, Freiberg AN, Garofalo RP, Casola A. Broad-Range Antiviral Activity of Hydrogen Sulfide Against Highly Pathogenic RNA Viruses. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 41029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li H, Ma Y, Escaffre O, Ivanciuc T, Komaravelli N, Kelley JP, Coletta C, Szabo C, Rockx B, Garofalo RP, Casola A. Role of hydrogen sulfide in paramyxovirus infections. J Virol. 2015, 89, 5557–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani S, Li H, Untereiner A, Wu L, Yang G, Austin RC, Dickhout JG, Lhotak S, Meng QH, Wang R. Decreased endogenous production of hydrogen sulfide accelerates atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2013, 127, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain SK, Bull R, Rains JL, Bass PF, Levine SN, Reddy S, McVie R, Bocchini JA. Low levels of hydrogen sulfide in the blood of diabetes patients and streptozotocin-treated rats causes vascular inflammation? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang P, Wu L, Ju Y, Fu M, Shuang T, Qian Z, Wang R. Age-Dependent Allergic Asthma Development and Cystathionine Gamma-Lyase Deficiency. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominic P, Ahmad J, Bhandari R, Pardue S, Solorzano J, Jaisingh K, Watts M, Bailey SR, Orr AW, Kevil CG, Kolluru GK. Decreased availability of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide is a hallmark of COVID-19. Redox Biol. 2021, 43, 101982. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Oza PP, Kashfi K. Utility of NO and H2S donating platforms in managing COVID-19: Rationale and promise. Nitric Oxide. 2022; 128, 72–102.
- Renieris G, Katrini K, Damoulari C, Akinosoglou K, Psarrakis C, Kyriakopoulou M, Dimopoulos G, Lada M, Koufargyris P, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ. Serum Hydrogen Sulfide and Outcome Association in Pneumonia by the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Shock. 2020, 54, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 54. Onikienko S, Vinokurov M, Yurinskaya M, Zemlyanoi A, Abkin S, Shaykhutdinova E, Palikov V, Ivanov A, Smirnova O, Fedyakina I, Bychkova N, Zatsepina O, Garbuz D, Evgen'ev M. The Effects of H(2)S and Recombinant Human Hsp70 on Inflammation Induced by SARS and Other Agents In Vitro and In Vivo. Biomedicines. 2022; 10.
- Escaffre O, Freiberg AN. Polyphenylene carboxymethylene (PPCM) microbicide repurposed as antiviral against SARS-CoV-2. Proof of concept in primary human undifferentiated epithelial cells. Antiviral Res. 2021, 194, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez E, Peng Z, Kozar RA, Cao Y, Ko TC, Wade CE, Cardenas JC. Antithrombin III Contributes to the Protective Effects of Fresh Frozen Plasma Following Hemorrhagic Shock by Preventing Syndecan-1 Shedding and Endothelial Barrier Disruption. Shock. 2020, 53, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez E, Fukuda S, Modis K, Fujiwara O, Enkhtaivan B, Trujillo-Abarca R, Ihara K, Lima-Lopez F, Perez-Bello D, Szabo C, Prough DS, Enkhbaatar P. Arginine vasopressin receptor 2 activation promotes microvascular permeability in sepsis. Pharmacol Res. 2021, 163, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 58. Tufa A, Gebremariam TH, Manyazewal T, Getinet T, Webb DL, Hellstrom PM, Genet S. Inflammatory mediators profile in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: A comparative study. Front Immunol. 2022; 13, 964179.
- Chen G, Wu D, Guo W, Cao Y, Huang D, Wang H, Wang T, Zhang X, Chen H, Yu H, Zhang X, Zhang M, Wu S, Song J, Chen T, Han M, Li S, Luo X, Zhao J, Ning Q. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen Y, Wang J, Liu C, Su L, Zhang D, Fan J, Yang Y, Xiao M, Xie J, Xu Y, Li Y, Zhang S. IP-10 and MCP-1 as biomarkers associated with disease severity of COVID-19. Mol Med. 2020, 26, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li L, Li J, Gao M, Fan H, Wang Y, Xu X, Chen C, Liu J, Kim J, Aliyari R, Zhang J, Jin Y, Li X, Ma F, Shi M, Cheng G, Yang H. Interleukin-8 as a Biomarker for Disease Prognosis of Coronavirus Disease-2019 Patients. Front Immunol. 2020, 11, 602395. [Google Scholar]
- Farhana A, Lappin SL: Biochemistry, Lactate Dehydrogenase. In: StatPearls. edn. Treasure Island (FL); 2023.
- Nehring SM, Goyal A, Patel BC: C Reactive Protein. In: StatPearls. edn. Treasure Island (FL); 2023.
- Bounds EJ, Kok SJ: D Dimer. In: StatPearls. edn. Treasure Island (FL); 2023.
- 65. Untereiner AA, Olah G, Modis K, Hellmich MR, Szabo C. H2S-induced S-sulfhydration of lactate dehydrogenase a (LDHA) stimulates cellular bioenergetics in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017; 136, 86–98.
- Liu P, Bian Y, Fan Y, Zhong J, Liu Z. Protective Effect of Naringin on In Vitro Gut-Vascular Barrier Disruption of Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells Induced by TNF-alpha. J Agric Food Chem. 2020, 68, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort KD, Collins LE, McLoughlin A, Cummins PM. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-mediated disruption of cerebrovascular endothelial barrier integrity in vitro involves the production of proinflammatory interleukin-6. J Neurochem. 2016, 136, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu J, Ma Z, Shetty S, Ma M, Fu J. Selective HDAC6 inhibition prevents TNF-alpha-induced lung endothelial cell barrier disruption and endotoxin-induced pulmonary edema. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016, 311, L39–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffre J, Rodriguez L, Matthay ZA, Lloyd E, Fields AT, Bainton RJ, Kurien P, Sil A, Calfee CS, Woodruff PG, Erle DJ, Hendrickson C, Krummel MF, Langelier CR, Matthay MA, Kornblith LZ, Hellman J, Consortium C-M-PfET, Covid-19 Associated Coagulopathy I, Thrombosis Study G. COVID-19-associated Lung Microvascular Endotheliopathy: A "From the Bench" Perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022, 206, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otifi HM, Adiga BK. Endothelial Dysfunction in Covid-19 Infection. Am J Med Sci. 2022, 363, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. Elevated level of C-reactive protein may be an early marker to predict risk for severity of COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2020, 92, 2409–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry BM, Aggarwal G, Wong J, Benoit S, Vikse J, Plebani M, Lippi G. Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2020, 38, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi G, Favaloro EJ. D-dimer is Associated with Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Pooled Analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2020, 120, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore S, Hill EM, Dyson L, Tildesley MJ, Keeling MJ. Retrospectively modeling the effects of increased global vaccine sharing on the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat Med. 2022, 28, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson OJ, Barnsley G, Toor J, Hogan AB, Winskill P, Ghani AC. Global impact of the first year of COVID-19 vaccination: A mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022, 22, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver JC, Silva EN, Soares LM, Scodeler GC, Santos AS, Corsetti PP, Prudencio CR, de Almeida LA. Different drug approaches to COVID-19 treatment worldwide: An update of new drugs and drugs repositioning to fight against the novel coronavirus. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 10, 25151355221144845. [Google Scholar]
- Usher, AD. The global COVID-19 treatment divide. Lancet. 2022, 399, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan S, Kenchappa DB, Leo MD. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Degradation of Junctional Proteins That Maintain Endothelial Barrier Integrity. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021, 8, 687783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu X, Xiang M, Jing H, Wang C, Novakovic VA, Shi J. Damage to endothelial barriers and its contribution to long COVID. Angiogenesis. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y, Han J, Wu X, Zeng H, Liu J, Zhang H. VEGF-D: A novel biomarker for detection of COVID-19 progression. Crit Care. 2020, 24, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pine AB, Meizlish ML, Goshua G, Chang CH, Zhang H, Bishai J, Bahel P, Patel A, Gbyli R, Kwan JM, Won CH, Price C, Dela Cruz CS, Halene S, van Dijk D, Hwa J, Lee AI, Chun HJ. Circulating markers of angiogenesis and endotheliopathy in COVID-19. Pulm Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020966547. [Google Scholar]
- Gadotti AC, de Castro Deus M, Telles JP, Wind R, Goes M, Garcia Charello Ossoski R, de Padua AM, de Noronha L, Moreno-Amaral A, Baena CP, Tuon FF. IFN-gamma is an independent risk factor associated with mortality in patients with moderate and severe COVID-19 infection. Virus Res. 2020, 289, 198171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev S, Gottesman T, Sahaf Levin G, Lederfein D, Berkov E, Diker D, Zaidman A, Nutman A, Ilan Ber T, Angel A, Kellerman L, Barash E, Navon R, Boico O, Israeli Y, Rosenberg M, Gelman A, Kalfon R, Simon E, Avni N, Hainrichson M, Zarchin O, Gottlieb TM, Oved K, Eden E, Tadmor B. Observational cohort study of IP-10's potential as a biomarker to aid in inflammation regulation within a clinical decision support protocol for patients with severe COVID-19. PLoS ONE. 2021, 16, e0245296. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs-Kasa A, Zaied AA, Leanhart S, Koseoglu M, Sridhar S, Lucas R, Fulton DJ, Vazquez JA, Annex BH. Elevated Cytokine Levels in Plasma of Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Do Not Contribute to Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Permeability. Microbiol Spectr. 2022, 10, e0167121. [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y, Ji W, Yang H, Chen S, Zhang W, Duan G. Endothelial activation and dysfunction in COVID-19: From basic mechanisms to potential therapeutic approaches. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei Y, Zhang J, Schiavon CR, He M, Chen L, Shen H, Zhang Y, Yin Q, Cho Y, Andrade L, Shadel GS, Hepokoski M, Lei T, Wang H, Zhang J, Yuan JX, Malhotra A, Manor U, Wang S, Yuan ZY, Shyy JY. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2. Circ Res. 2021, 128, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos KI, Papadopoulou A, Aw TC. Beauty and the beast: Host microRNA-155 versus SARS-CoV-2. Hum Cell. 2023, 36, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouros D, Alexandrakis MG, Antoniou KM, Agouridakis P, Pneumatikos I, Anevlavis S, Pataka A, Patlakas G, Karkavitsas N, Kyriakou D. The clinical significance of serum and bronchoalveolar lavage inflammatory cytokines in patients at risk for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. BMC Pulm Med. 2004, 4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Szabo PA, Dogra P, Gray JI, Wells SB, Connors TJ, Weisberg SP, Krupska I, Matsumoto R, Poon MML, Idzikowski E, Morris SE, Pasin C, Yates AJ, Ku A, Chait M, Davis-Porada J, Guo XV, Zhou J, Steinle M, Mackay S, Saqi A, Baldwin MR, Sims PA, Farber DL. Longitudinal profiling of respiratory and systemic immune responses reveals myeloid cell-driven lung inflammation in severe COVID-19. Immunity. 2021, 54, 797–814 e796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 90. Rauti R, Shahoha M, Leichtmann-Bardoogo Y, Nasser R, Paz E, Tamir R, Miller V, Babich T, Shaked K, Ehrlich A, Ioannidis K, Nahmias Y, Sharan R, Ashery U, Maoz BM. Effect of SARS-CoV-2 proteins on vascular permeability. Elife. 2021; 10.
- Behrens GMN, Cossmann A, Hoffmann M. Omicron spike protein: A clue for viral entry and immune evasion. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou J, Lan W, Wu X, Zhao T, Duan B, Yang P, Ren Y, Quan L, Zhao W, Seto D, Chodosh J, Luo Z, Wu J, Zhang Q. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Omicron diverse spike gene mutations identifies multiple inter-variant recombination events. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed AM, Ciling A, Taha TY, Chen IP, Khalid MM, Sreekumar B, Chen PY, Kumar GR, Suryawanshi R, Silva I, Milbes B, Kojima N, Hess V, Shacreaw M, Lopez L, Brobeck M, Turner F, Spraggon L, Tabata T, Ott M, Doudna JA. Omicron mutations enhance infectivity and reduce antibody neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022, 119, e2200592119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu B, Chan JF, Liu H, Liu Y, Chai Y, Shi J, Shuai H, Hou Y, Huang X, Yuen TT, Yoon C, Zhu T, Zhang J, Li W, Zhang AJ, Zhou J, Yuan S, Zhang BZ, Yuen KY, Chu H. Spike mutations contributing to the altered entry preference of SARS-CoV-2 omicron BA.1 and BA.2. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng B, Abdullahi A, Ferreira I, Goonawardane N, Saito A, Kimura I, Yamasoba D, Gerber PP, Fatihi S, Rathore S, Zepeda SK, Papa G, Kemp SA, Ikeda T, Toyoda M, Tan TS, Kuramochi J, Mitsunaga S, Ueno T, Shirakawa K, Takaori-Kondo A, Brevini T, Mallery DL, Charles OJ, Collaboration C-NBC-, Genotype to Phenotype Japan C, Ecuador CC, Bowen JE, Joshi A, Walls AC, Jackson L, Martin D, Smith KGC, Bradley J, Briggs JAG, Choi J, Madissoon E, Meyer KB, Mlcochova P, Ceron-Gutierrez L, Doffinger R, Teichmann SA, Fisher AJ, Pizzuto MS, de Marco A, Corti D, Hosmillo M, Lee JH, James LC, Thukral L, Veesler D, Sigal A, Sampaziotis F, Goodfellow IG, Matheson NJ, Sato K, Gupta RK. Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity. Nature. 2022, 603, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo C, Papapetropoulos A. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CII: Pharmacological Modulation of H2S Levels: H2S Donors and H2S Biosynthesis Inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev. 2017, 69, 497–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease Severity | Mild (n=7) | Moderate (n=6) | Severe (n=4) | Critical (n=9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room aira (%) | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Nasal cannulaa (%) | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Non-invasive ventilationa (%) | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% | 0.0% |
| Invasive ventilationa (%) | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 100.0% |
| Male (%) | 57.1% | 33.3% | 75.0% | 66.7% |
| Age at Admission, median (years) | 55 | 59 | 54 | 55 |
| Hispanic ethnicity (%) | 28.6% | 33.3% | 0.0% | 33.3% |
| White race (%) | 57.1% | 83.3% | 75.0% | 55.6% |
| Black race (%) | 42.9% | 16.7% | 25.0% | 44.4% |
| Days admitted, median (days) | 5 | 7 | 21 | 36 |
| On dexamethasone (%) | 14.3% | 50.0% | 75.0% | 100.0% |
| Taking remdesivir (%) | 57.1% | 83.3% | 100.0% | 100.0% |
| No antiviral used (%) | 42.9% | 16.7% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| COVID vaccinated (%) | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Discharged alive (%) | 100.0% | 100.0% | 75.0% | 11.1% |
| Transferred to another facility (%) | 0.0% | 0.0% | 25.0% | 33.3% |
| Death (%) | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 55.6% |
| Clinical characteristics at admission (mean ± SD) | ||||
| BMI | 34.80 ± 6.41 | 31.34 ± 4.50 | 39.53 ± 15.30 | 37.8 ± 9.24 |
| Body weight (kg) | 99.07 ± 19.04 | 85.98 ± 9.45 | 112.71 ± 22.38 | 113.42 ± 32.73 |
| Temperature (Degrees, ᵒC) | 37.10 ± 0.43 | 37.46 ± 1.13 | 38.00 ± 0.69 | 37.35 ± 1.00 |
| Oxygen saturation (%) | 96.14 ± 2.96 | 95.16 ± 2.22 | 90.75 ± 14.08 | 89.33 ± 4.35 |
| Respiration rate (breaths/minute) | 21.85 ± 5.04 | 21.50 ± 3.56 | 27.75 ± 17.63 | 26.77 ± 8.65 |
| LDH (U/L) | 750.45 ± 466.14 | 785.25 ± 204.77 | 1167.33 ± 322.76 | 1065.5 ± 389.10 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 8.50 ± 6.14 | 13.67 ± 6.59 | 10.36 ± 5.31 | 14.49 ± 5.77 |
| D-dimer (µg/mL) | 1.31 ± 1.48 | 0.57 ± 0.52 | 0.78 ± 0.36 | 1.63 ± 1.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





