Submitted:
22 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Traction Motor Stator ITSC Fault Diagnostic Condition Control
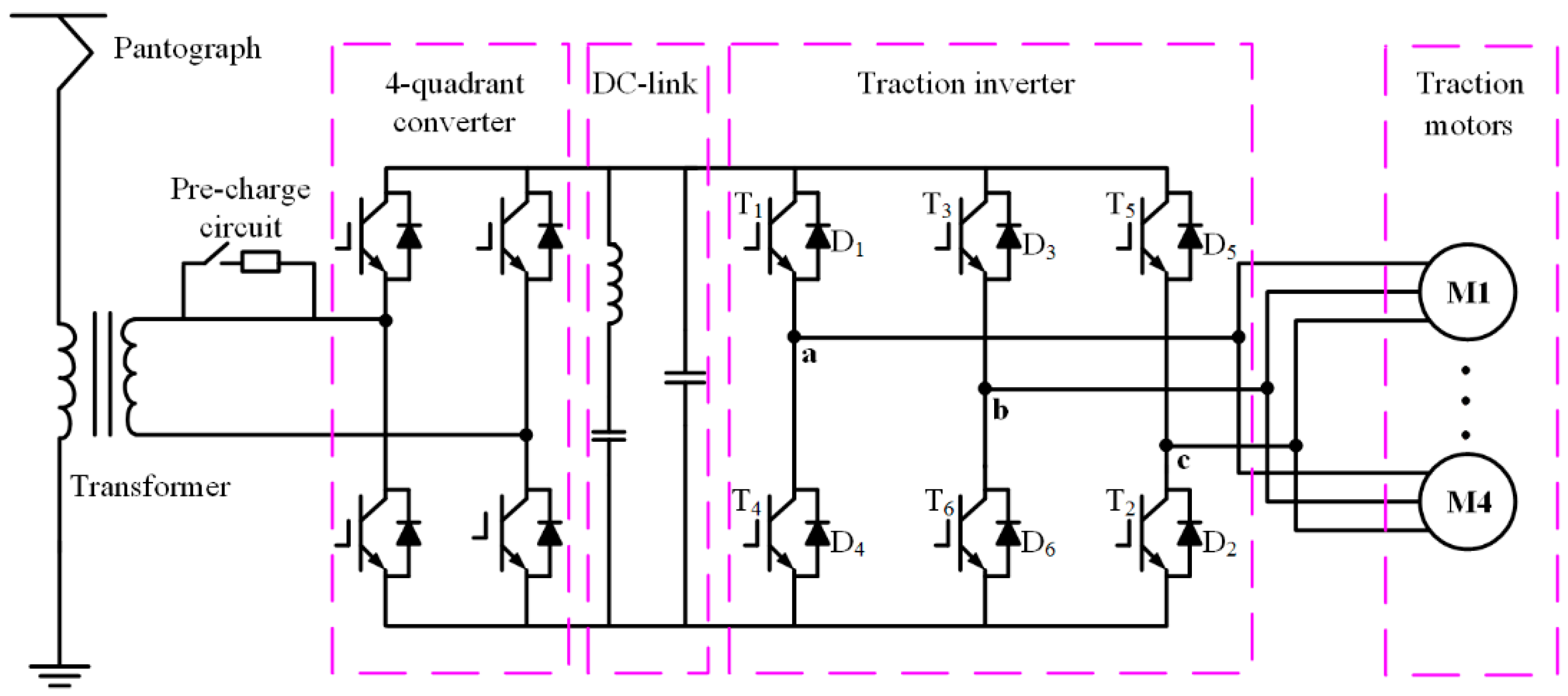
2.1. Working Status of Two-level Traction Inverter
| Mode | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| SB | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| SC | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Voltagevector |
2.2. ITSC Fault Diagnostic Condition Control
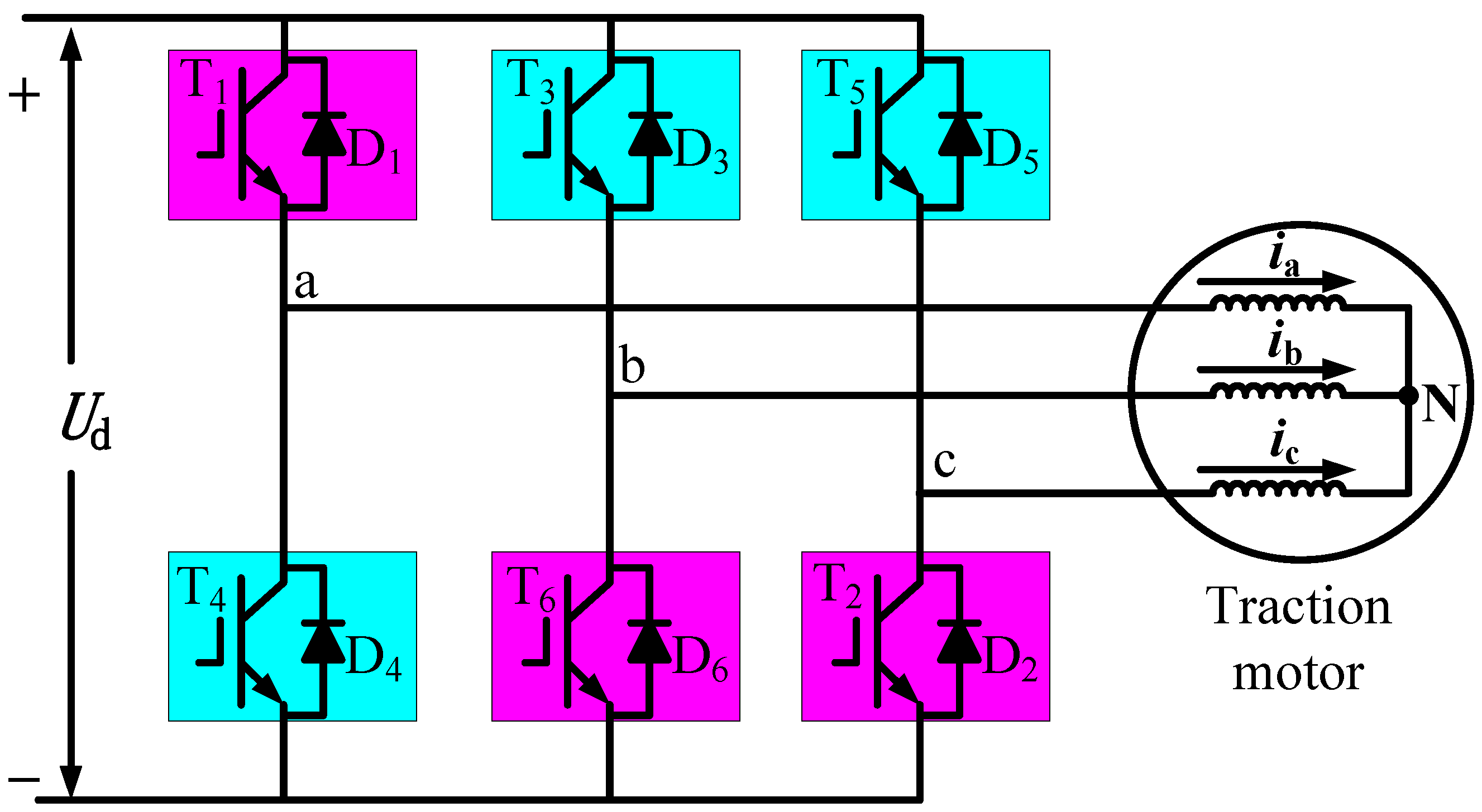
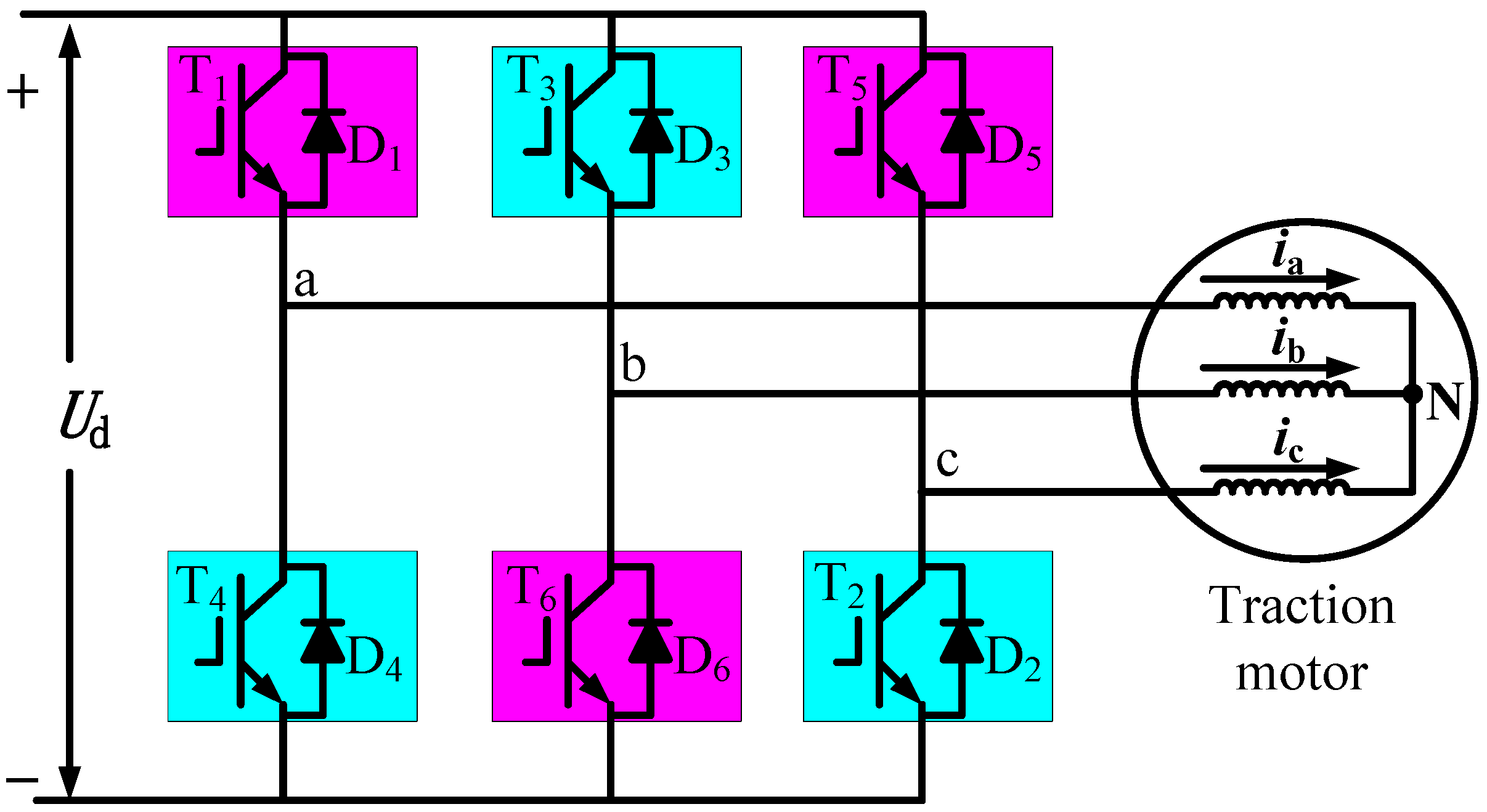
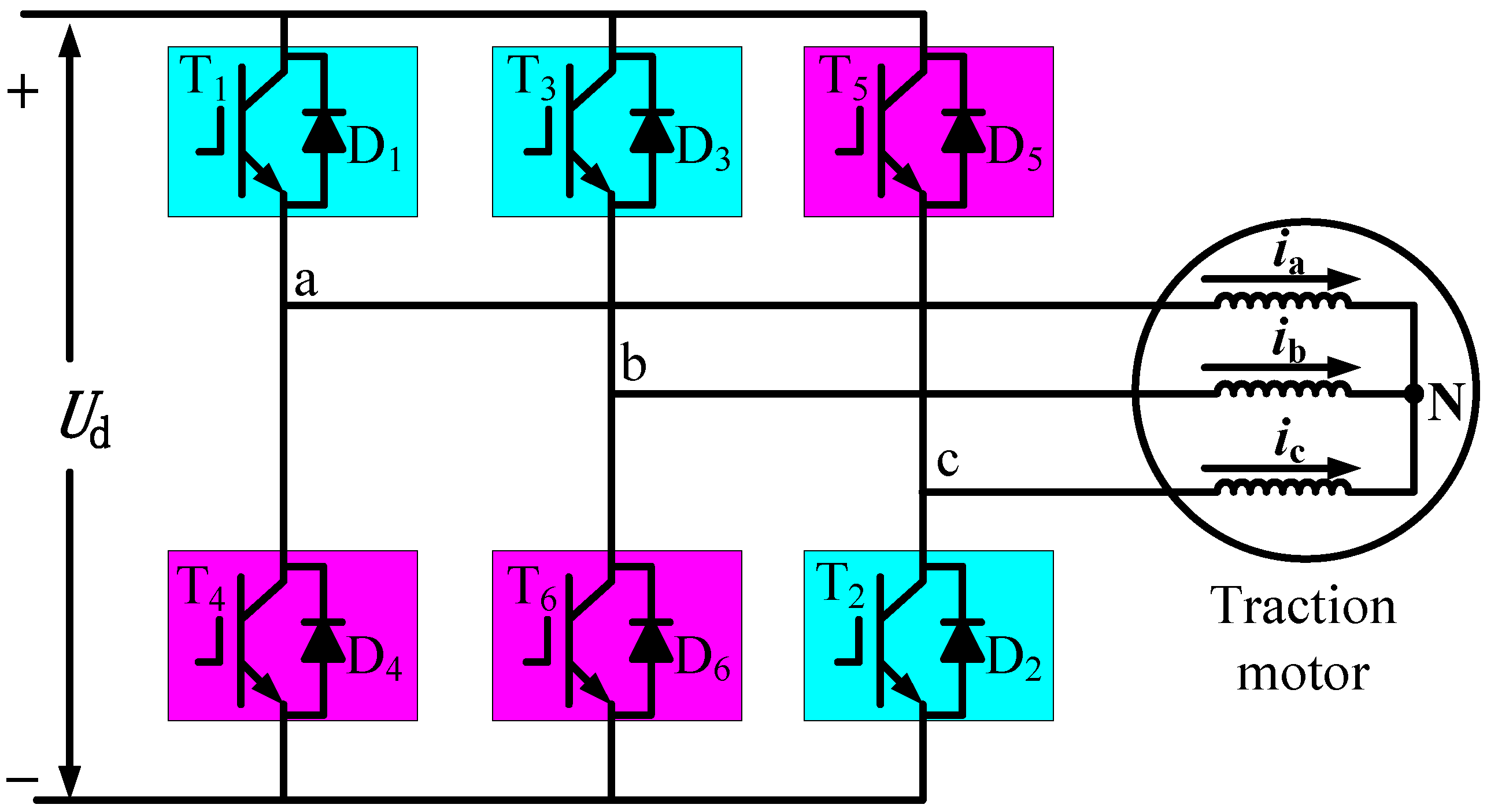
2.3. Traction Motor Magnetomotive Force Analysis under Diagnostic Condition
3. SPWM Excitation Voltage and Goertzel Algorithm
3.1. Traction Motor SPWM Excitation Voltage Control
3.2. Calculation of Current Fundamental Component Using Goertzel Algorithm
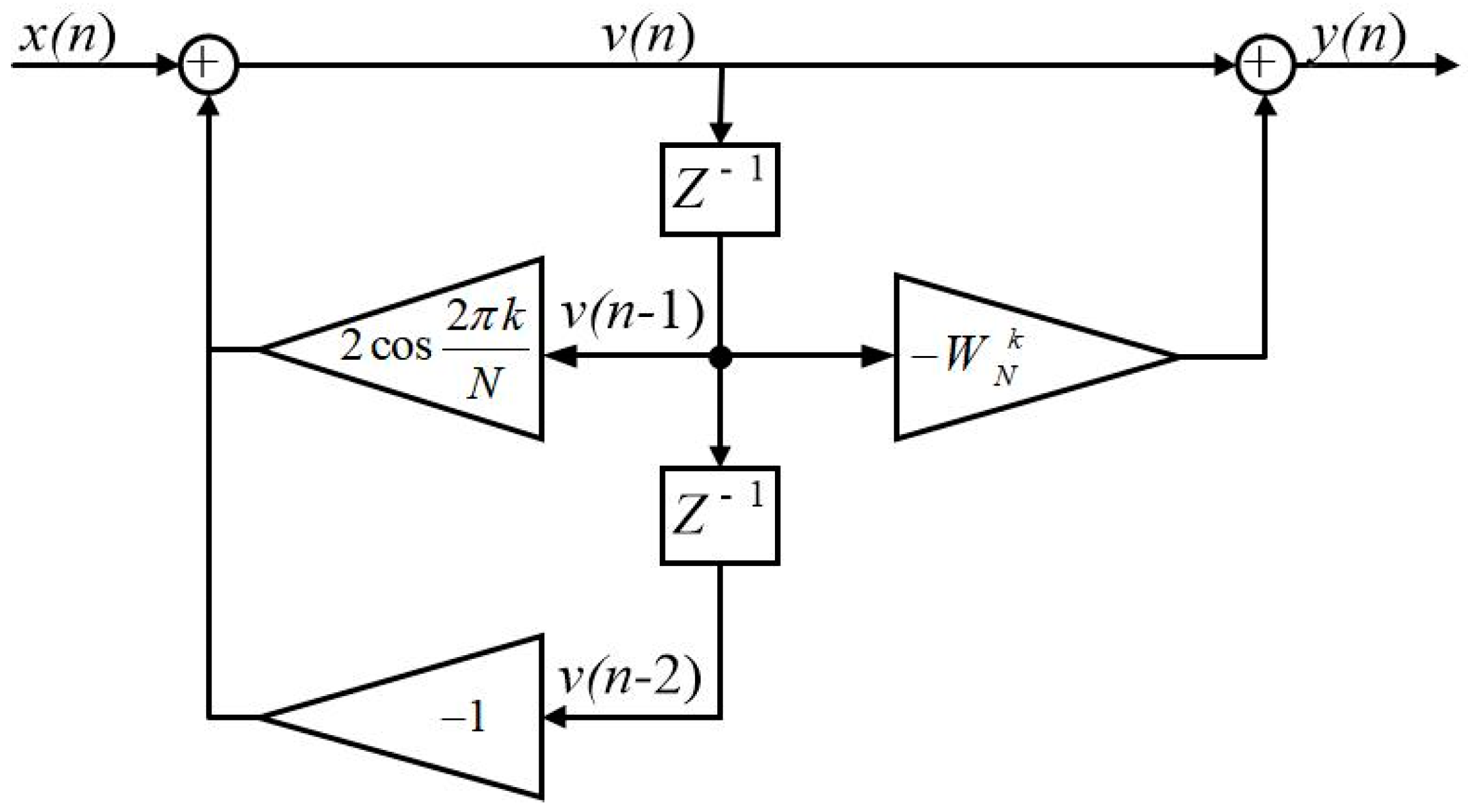
4. Fault Features and Diagnostic Model of Traction Motor ITSC Fault
4.1. Fault Features of Traction Motor ITSC Diagnostic Conditions
| Diagnostic condition I | Diagnostic condition II | Diagnostic condition III |
|---|---|---|
| Δibc=ibmax-icmax | Δica=icmax-iamax | Δiab=iamax-ibmax |
| Δθbc=θb-θc | Δθca=θc-θa | Δθab=θa-θb |
4.2. Random Forest Fault Diagnosis Model
4.3. Fault Diagnosis of Traction Motor ITSC Fault
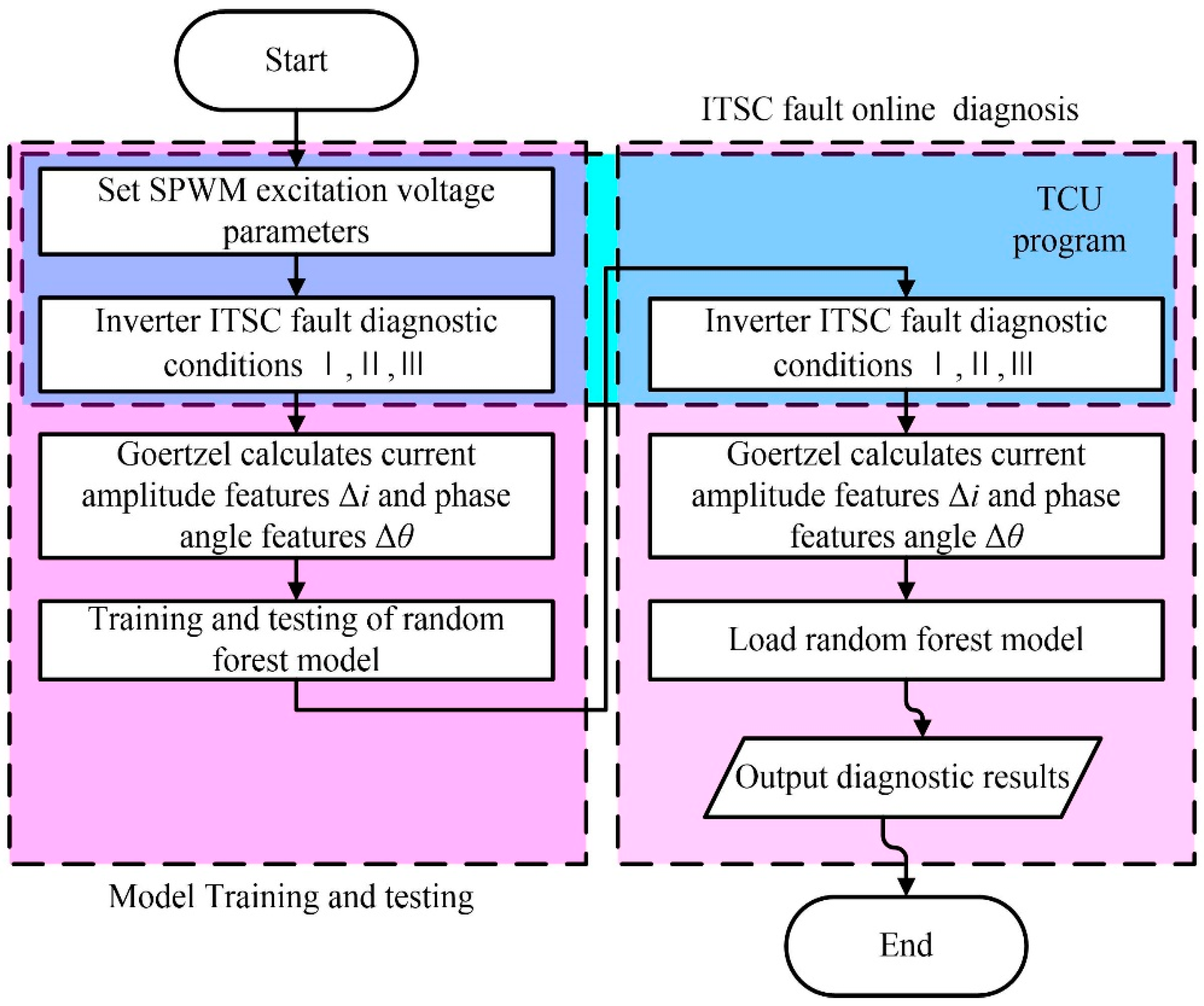
5. Diagnosis For Traction Motor ITSC Fault Simulation Experimental Platform
5.1. Traction Motor ITSC Fault Diagnosis Simulation Experimental Platform
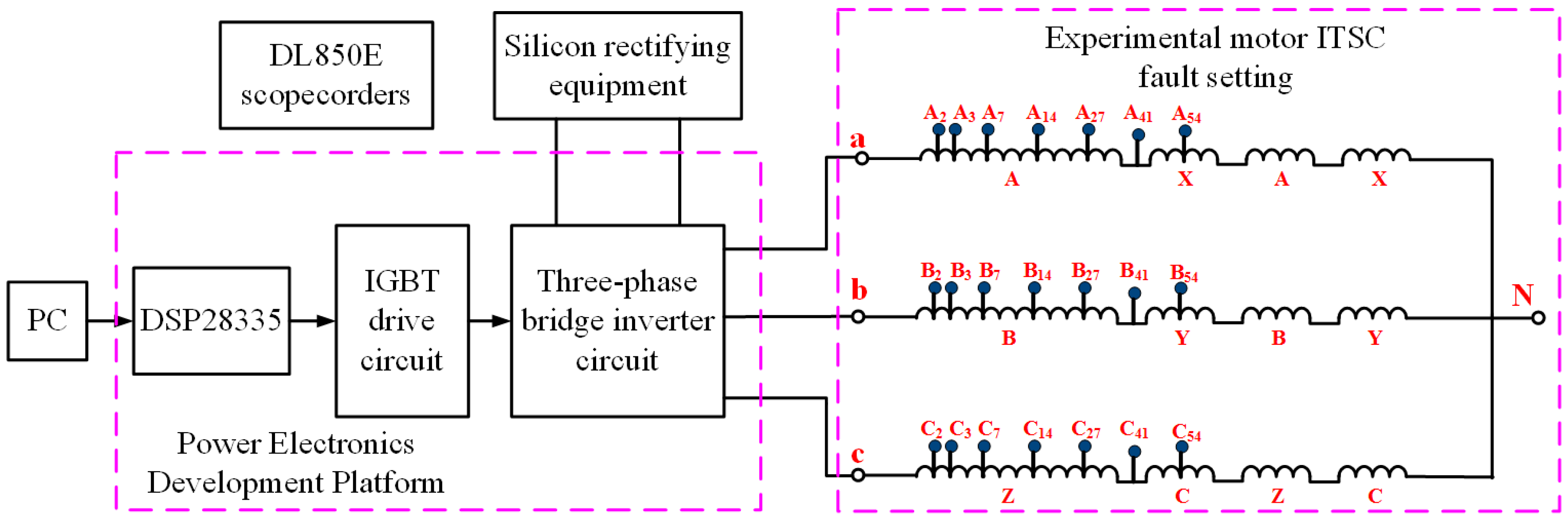
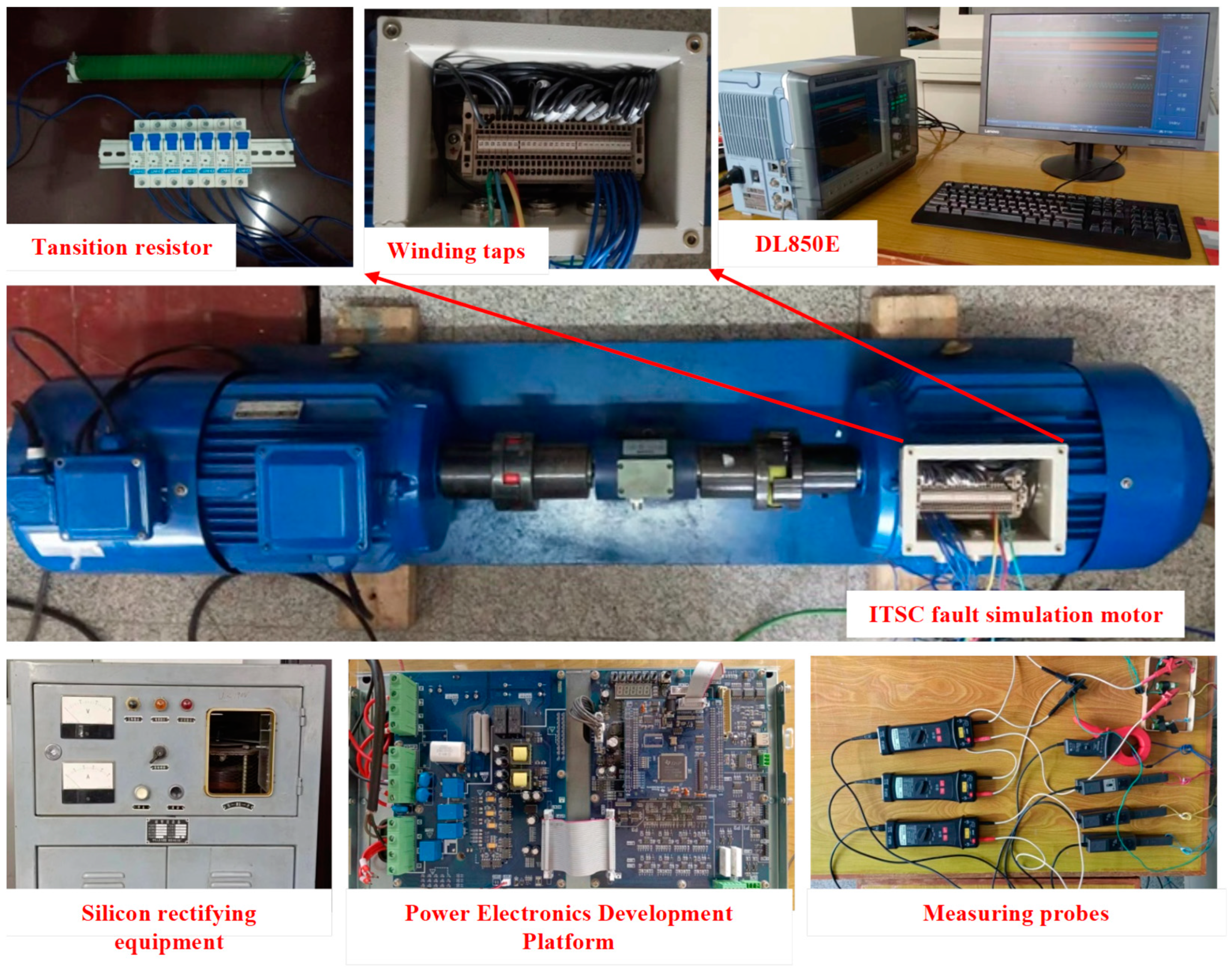
5.2. SPWM Excitation Voltage Parameters of Experimental Platform
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal power | 5.5kW | Nominal frequency | 50Hz |
| Nominal voltage | 380V | Connection mode | Y |
| Nominal current | 11.7A | Nominal speed | 1445rpm |
| Poles | 4 | Turns per phase | 164 |
| Modulation frequency | 100Hz | Modulation index | 0.4 |
| Carrier frequency | 5000Hz | DC-link voltage | 300V |
5.3. Analysis of ITSC Fault Diagnosis Signals
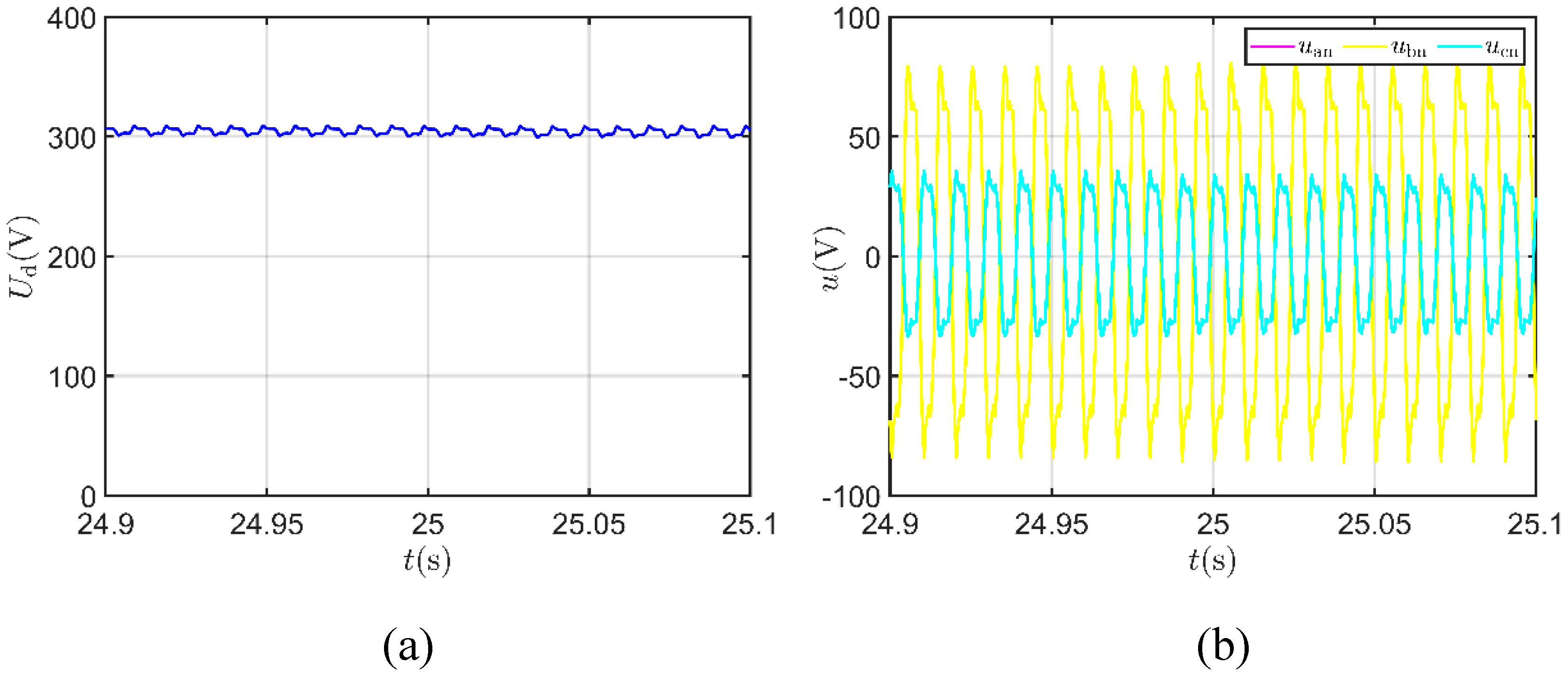
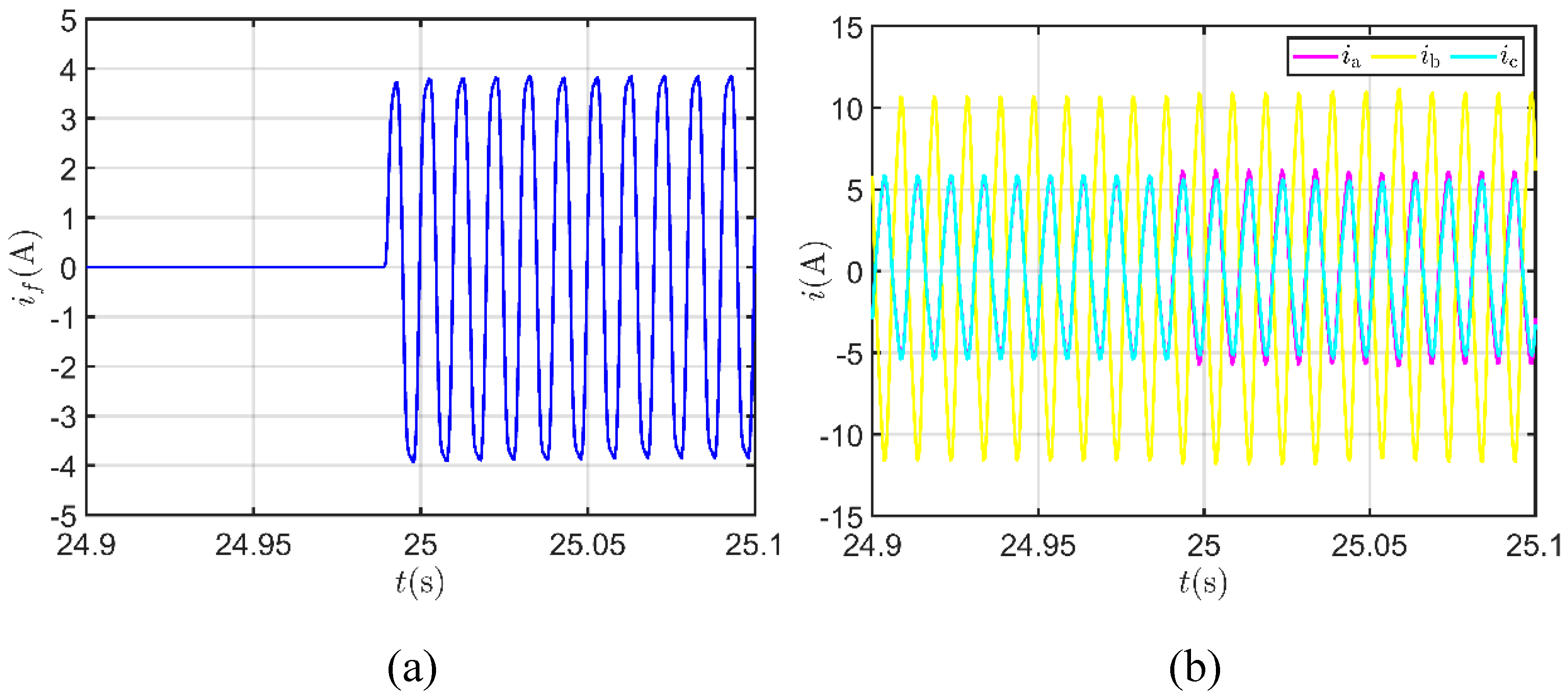
5.4. The Impact of ITSC Fault Extent on Features
| Parameters | values |
|---|---|
| Transition resistance (Ω) | 0, 1, 2, 4, 8 |
| Short-circuit turns | 5, 7, 12, 20, 25, 34, 39, 47, 52 |
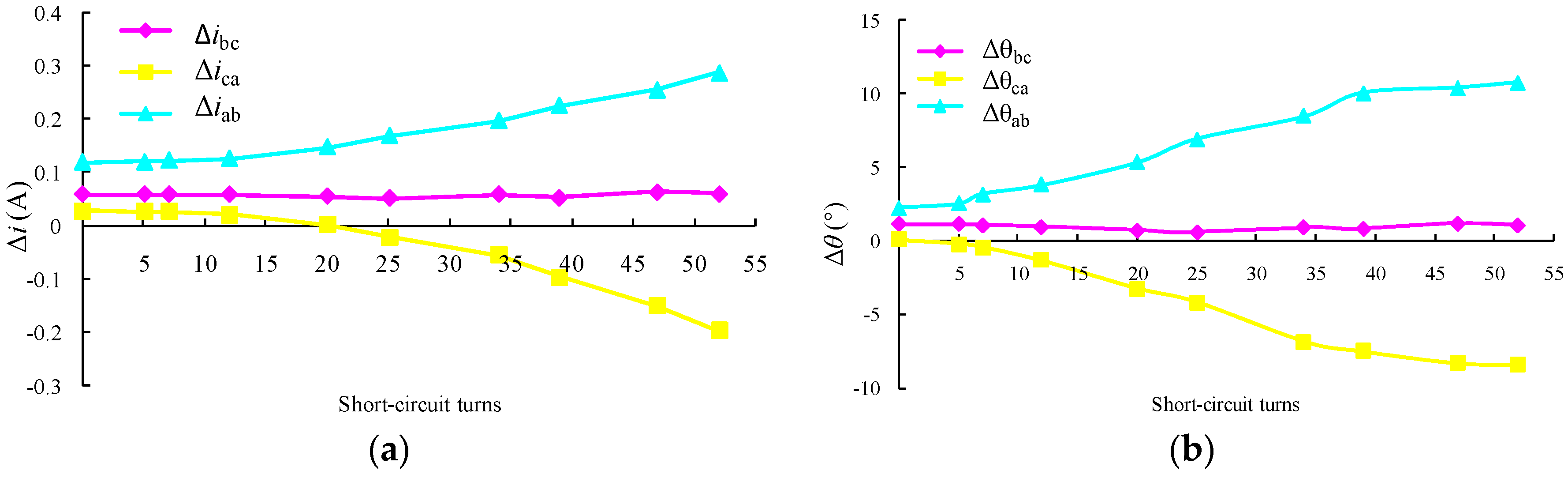
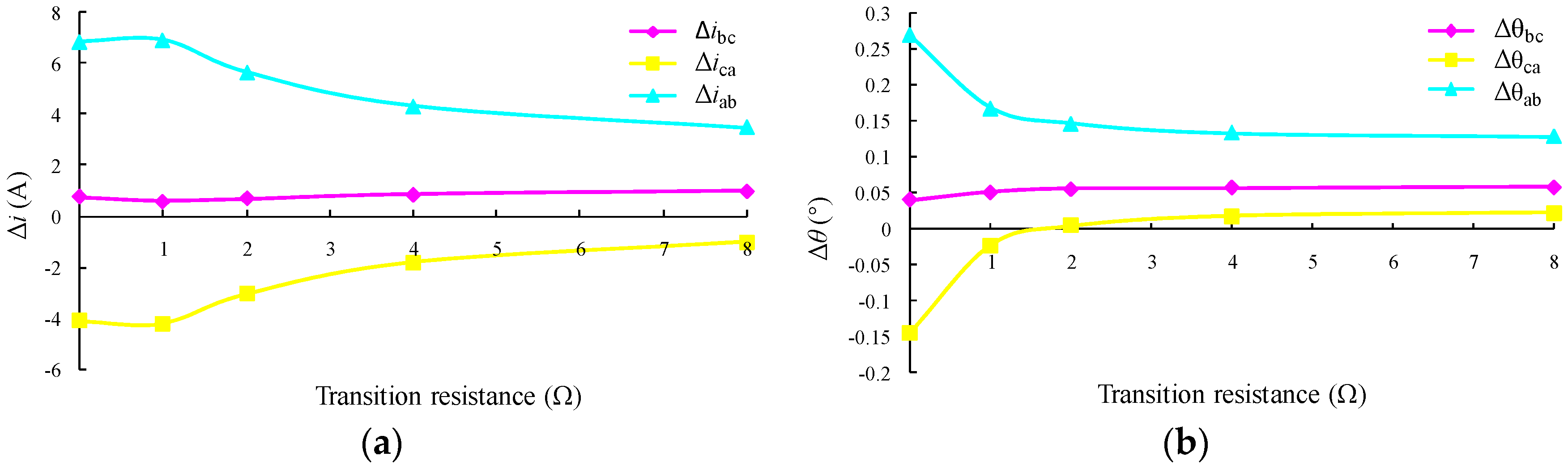
5.5. Fault Detection and Location Based on Random Forest Model
| Models | Accuracy of the train sets | Accuracy of the test sets |
|---|---|---|
| BP neural network | 97.86% | 97.5% |
| KNN | 98.57% | 100% |
| SVM | 95% | 97.5% |
| Naive Bayes | 99.29% | 100% |
| Rondom Forest | 100% | 100% |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S-G. A Study on Traction Motor Characteristic in EMU Train. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Gyeonggi-do, Korea, 22-25October 2014.
- Chen, Z.P.; Wang, Z.; Jia, L.M.; Cai, G.Q. Analysis and Comparison of Locomotive Traction Motor Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Methods. Appl. Mech. Mater.2011, 97–98, 994–1002. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.97-98.994. [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Shao, J.; Teng, W. Enhanced Fault Diagnosis Using Broad Learning for Traction Systems in High-Speed Trains. IEEE Trans. Power Electron.2020, 36, 7461–7469. doi:10.1109/TPEL.2020.3043741. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, J. FPGA-Based Hardware-in-the-Loop Real-Time Simulation Implementation for High-Speed Train Electrical Traction System. IET Electr. Power Appl.2020, 14,850-858.doi:10.1049/iet-epa.2019.0655. [CrossRef]
- Elbouchikhi,E.; Amirat, Y.; Feld, G.; Benbouzid, M. Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test Based Approach for Stator-Fault Detection in a PWM Inverter-Fed Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron.2019,66, 6343–6353.doi:10.1109/TIE.2018.2875665. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ameri, S.M.; Alawady, A.A.; Yousof, M.F.M.; Kamarudin, M.S.; Salem, A.A.; Abu-Siada, A.; Mosaad, M.I. Application of Frequency Response Analysis Method to Detect Short-Circuit Faults in Three-Phase Induction Motors. Appl. Sci.2022, 12, 2046. doi:10.3390/app12042046. [CrossRef]
- Tallam, R.M.; Habetler, T.G.; Harley, R.G. Transient Model for Induction Machines With Stator Winding Turn Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl.2002, 38, 632-637.
- Kallesoe, C.S.; Vadstrup, P.; Rasmussen, H.; Izadi-Zamanabadi, R. Observer Based Estimation of Stator Winding Faults in Delta-Connected Induction Motors, a LMI Approach. In Proceedings of the IAS Annual Meeting, FL, USA , 08-12October2006.doi:10.1109/IAS.2006.256880. [CrossRef]
- Angelo, C.; Bossio, G.R.; Gi Ac Cone, S.J.; Valla, M.I.; Garcia, G.O. Online Model-Based Stator-Fault Detection and Identification in Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron.2009, 56, 4671–4680. doi:10.1109/TIE.2009.2012468. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Wang, D.; Seshadrinath, J.; Ukil, A.; Krishna, M.S.; Nadarajan, S.; Vaiyapuri, V. A Method for Incipient Interturn Fault Detection and Severity Estimation of Induction Motors Under Inherent Asymmetry and Voltage Imbalance. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2017, 3, 703–715. doi:10.1109/TTE.2017.2726351. [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, H.; Benatman, K. Stator Winding Inter-turn Short-circuit Detection in Induction Motors by Parameter Identification. IET Electr. Power Appl.2017,11, 272–288. doi:10.1049/iet-epa.2016.0432. [CrossRef]
- Bachir, S.; Tnani, S.; Trigeassou, J.-C.; Champenois, G. Diagnosis by Parameter Estimation of Stator and Rotor Faults Occurring in Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 963–973. doi:10.1109/TIE.2006.874258. [CrossRef]
- Bazine, I.B.A.; Tnani, S.; Poinot, T.; Champenois, G.; Jelassi, K. On-Line Detection of Stator and Rotor Faults Occurring in Induction Machine Diagnosis by Parameters Estimation. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics & Drives; Bologna, Italy, 05-08September2011.doi:10.1109/DEMPED.2011.6063609. [CrossRef]
- Aswad, R.A.K.; Jassim, B.M.H. Detection and Localization of the Stator Winding Inter-Turn Fault in Induction Motors Based on Parameters Estimation Using Genetic Algorithm. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2022, 103, 405–414. doi:10.1007/s40031-021-00670-x. [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S. Stator Fault Detection in Induction Machines Using Triplen Harmonics at Motor Terminal Voltage after Switch-Off. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12-16 June 2005.
- Qing Wu; Nandi, S. Fast Single-Turn Sensitive Stator Interturn Fault Detection of Induction Machines Based on Positive- and Negative-Sequence Third Harmonic Components of Line Currents. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl.2010,46,974–983. doi:10.1109/TIA.2010.2045329. [CrossRef]
- El Bouchikhi, E.H.; Choqueuse, V.; Benbouzid, M. Induction Machine Faults Detection Using Stator Current Parametric Spectral Estimation. Mech Syst Signal Pr.2015, 52–53, 447–464. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2014.06.015. [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, T.; Samet, H. A Kalman Filter Based Technique for Stator Turn-Fault Detection of the Induction Motors. Int.J.Emerg.Electr.P.2017, 18,1-14. doi:10.1515/ijeeps-2017-0071. [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, M.H.; Gallehdar, D.; Haghjoo, F.; Cruz, S. A Secure and Sensitive Wavelet Transform Based Technique for Stator Fault Detection in the Cases of Line-connected and Inverter-fed Induction Machines. IET Electr. Power Appl.2021, 15, 1138–1153. doi:10.1049/elp2.12084. [CrossRef]
- Almounajjed, A.; Sahoo, A.K.; Kumar, M.K. Diagnosis of Stator Fault Severity in Induction Motor Based on Discrete Wavelet Analysis. Measurement. 2021, 182, 109780. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109780. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Wang, Y.; Song, J. Fourier and Wavelet Transformations Application to Fault Detection of Induction Motor with Stator Current. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2010, 17, 93–101. doi:10.1007/s11771-010-0016-4. [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, B.A.; Varma, S.; Jagadanand, G. Precise Wavelet Selection for Condition Monitoring of Inverter-Fed Induction Machine. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Informatics, Communication and Energy Systems (SPICES); Kollam, India, 08-10 August 2017.doi:10.1109/DEMPED.2011.6063609. [CrossRef]
- Seshadrinath, J.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Single-Turn Fault Detection in Induction Machine Using Complex-Wavelet-Based Method. IEEE Trans. on Ind. Applicat. 2012, 48, 1846–1854. doi:10.1109/TIA.2012.2222012. [CrossRef]
- Akhil Vinayak, B.; Anjali Anand, K.; Jagadanand, G. Wavelet-based Real-time Stator Fault Detection of Inverter-fed Induction Motor. IET Electr. Power Appl.2020, 14, 82–90. doi:10.1049/iet-epa.2019.0273. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, T. Diagnosis of Stator Faults in Induction Motor Based on Zero Sequence Voltage after Switch-Off. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A2008, 9, 165–172. doi:10.1631/jzus.A071297. [CrossRef]
- Dash, R. N.; B. Subudhi.; S. Das. A comparison between MLP NN and RBF NN techniques for the detection of stator inter-turn fault of an induction motor.2010 International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Control and Robotics; Rourkela, India,27-29 December 2010.doi:10.1109/IECR.2010.5720163. [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Barron, A.; Tapia-Tinoco, G.; Razo-Hernandez, J.R.; Valtierra-Rodriguez, M.; Granados-Lieberman, D. A Neural Network-Based Model for MCSA of Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Faults in Induction Motors and Its Power Hardware in the Loop Simulation. Comput.Electr.Eng.2021, 93, 107234. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107234. [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhao, J. A Novel Nonlinear Observer for Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor. J Algorithms.Comput. 2020, 14, 174830262092272, doi:10.1177/1748302620922723. [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Benakcha, A.; Laib, I.; Chehaidia, S.E.; Menacer, A.; Soudan, B.; Olabi, A.G. Early Detection and Localization of Stator Inter-Turn Faults Based on Discrete Wavelet Energy Ratio and Neural Networks in Induction Motor. Energy.2020, 212, 118684. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2020.118684. [CrossRef]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Incipient Interturn Fault Detection and Severity Evaluation in Electric Drive System Using Hybrid HCNN-SVM Based Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2022, 18, 1823–1832. doi:10.1109/TII.2021.3067321. [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Chen, F.; Dong, S. Compound Fault Diagnosis of Stator Interturn Short Circuit and Air Gap Eccentricity Based on Random Forest and XGBoost. Math. Probl. Eng.2021,42, 2149048. doi:10.1155/2021/2149048. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Chen, F. Multiple-Model-Based Diagnosis of Multiple Faults With High-Speed Train Applications Using Second-Level Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 6257–6266.doi:10.1109/TIE.2020.2994867. [CrossRef]
- Koodziejek, P.; D. Wachowiak. Fast Real-Time RDFT- and GDFT-Based Direct Fault Diagnosis of Induction Motor Drive.Energies.2022,15,1-7.
- Sundararajan P; Sathik M; Sasongko F; et al. Condition Monitoring of DC-Link Capacitors Using Goertzel Algorithm for Failure Precursor Parameter and Temperature Estimation. IEEE T.Power.Electr, 2020, 35(6),6386-6396.doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2019.2951859. [CrossRef]
- Papathanasopoulos, D.A.; Giannousakis, K.N.; Dermatas, E.S.; Mitronikas, E. D.Vibration monitoring for position sensor fault diagnosis in brushless dc motor drives. Energies, 14. Papathanasopoulos, D.A.;Giannousakis, K.N.; Dermatas, E.S.;Mitronikas, E.D. VibrationMonitoring for Position Sensor FaultDiagnosis in Brushless DC MotorDrives. Energies2021, 14, 2248.doi: 10.3390/en14082248. [CrossRef]
- Rafael Peña-Alzola; Michal Sztykiel; Catherine E. Jones; Patrick J. Norman; Gareth MooreJosep Pou; Graeme M. Bur. First-Fault Detection in DC Distribution With IT Grounding Based on Sliding Discrete Fourier-Transform. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021,36,3649-3654.doi:10.1109/TPEL.2020.3026985. [CrossRef]
- Prasetyo, Y.T. "The Big One"Earthquake PreparednessAssessment among Younger FilipinosUsing a Random Forest Classifier andan Artificial Neural Network.Sustainability2023, 15, 679. doi:10.3390/su15010679. [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Cui, X.; Du, B.Random-Forest Machine LearningApproach for High-Speed RailwayTrack Slab Deformation IdentificationUsing Track-Side VibrationMonitoring. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4756. doi:10.3390/app11114756. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Q. Y. Xu; W. S. Chen . Classification of Bird and Drone Targets Based on Motion Characteristics and Random Forest Model Using Surveillance Radar Data. IEEE Access2021,9,160135-160144. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3130231. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; R. Yang; M. Zhong. Graph-based semi-supervised random forest for rotating machinery gearbox fault diagnosis. Control.Eng.Pract.2021,117,104952.doi:10.1016/j.conengprac.2021.104952. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





