Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.4. Lipids Extration and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
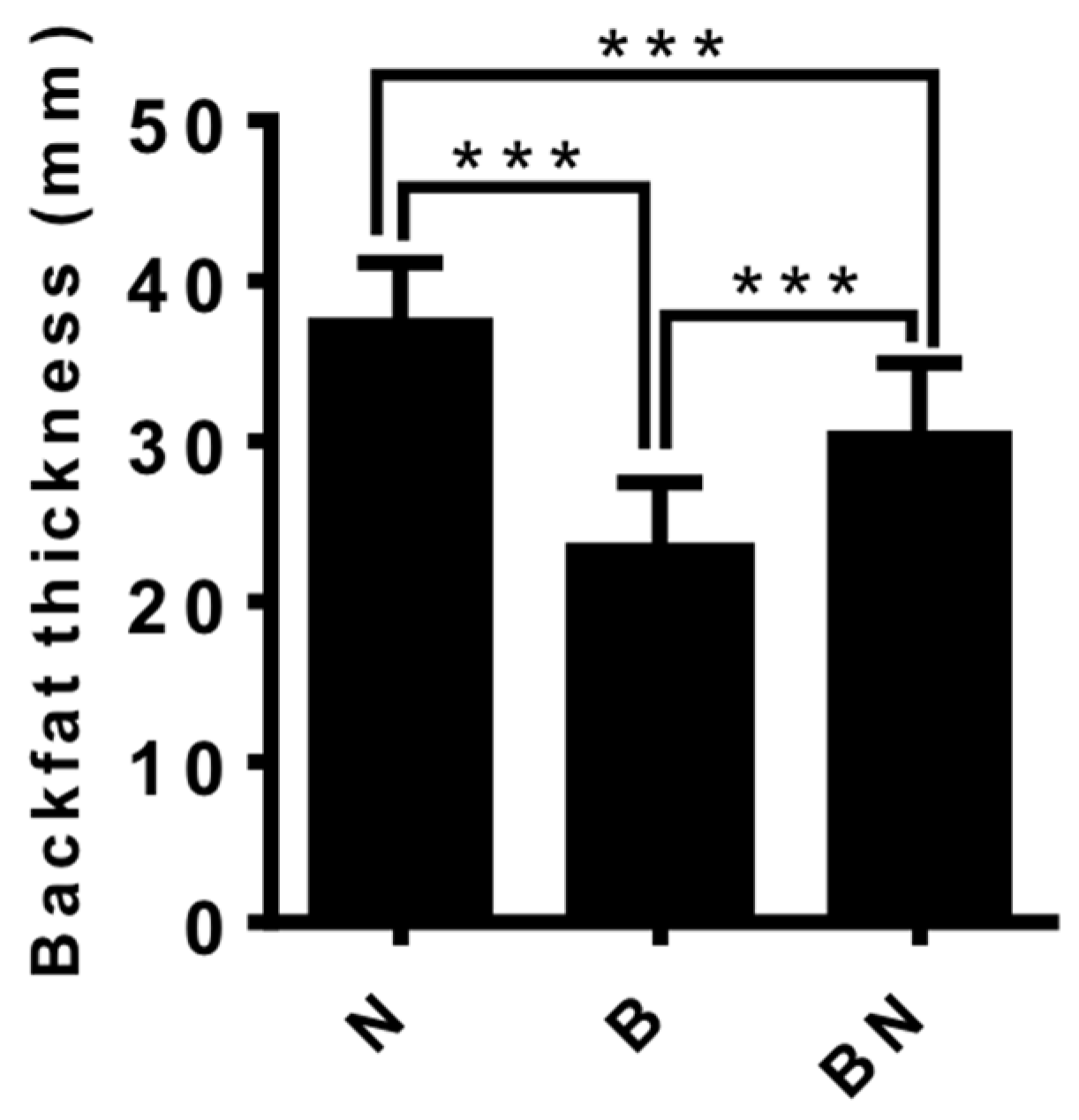
3.1. The Backfat Thickness of Ningxiang pigs, Berkshire pigs and F1 Pigs
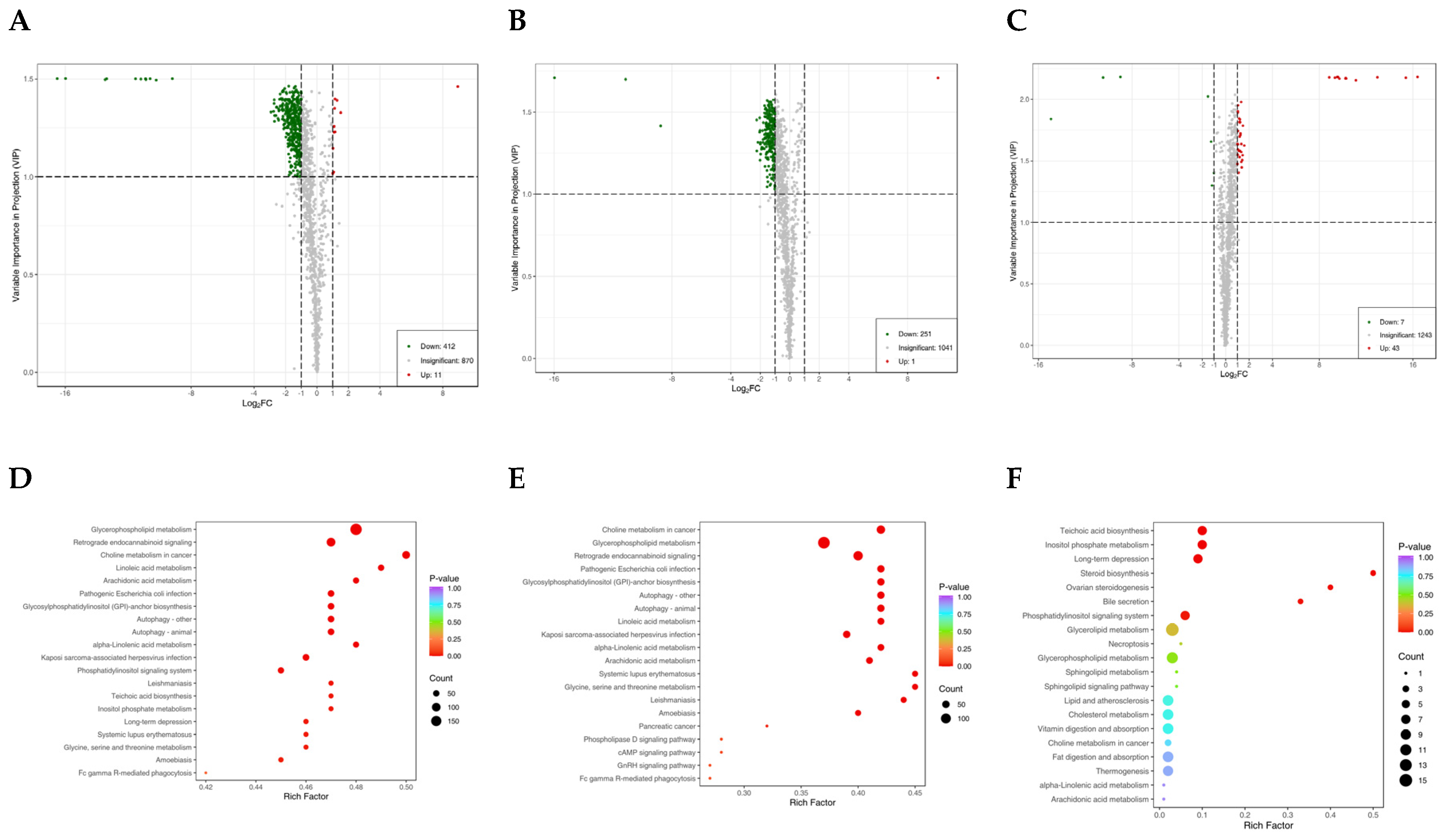
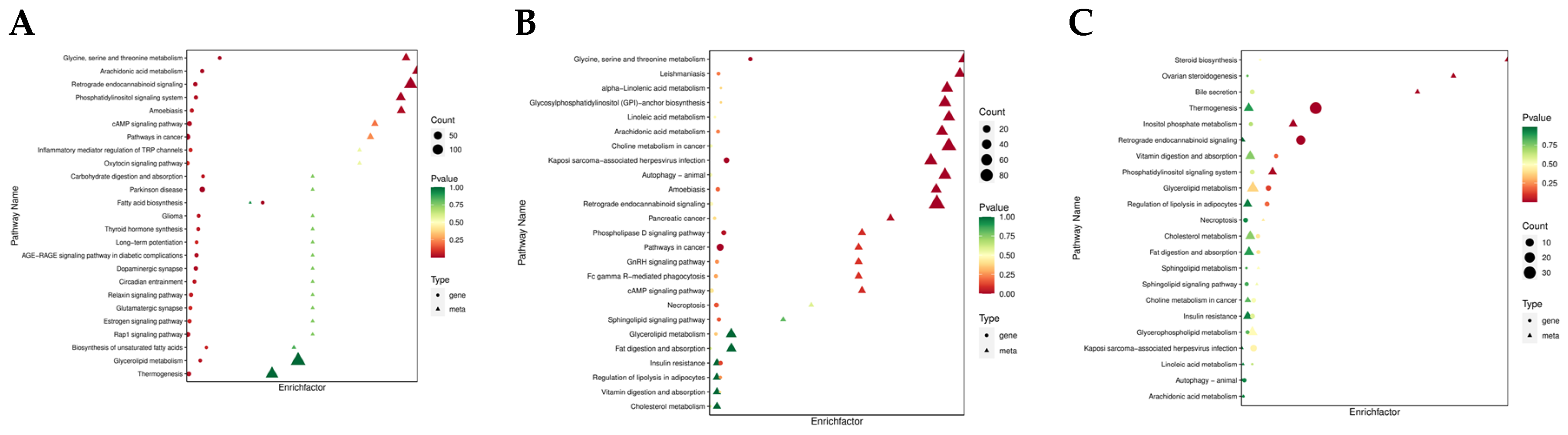
3.2. Lipidomic Data Analysis
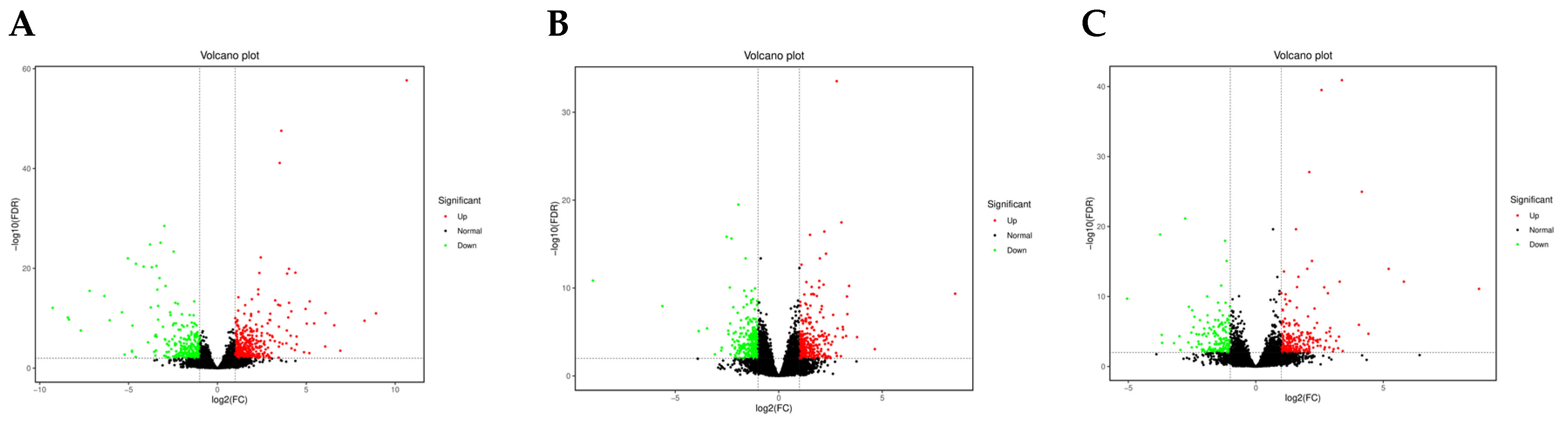
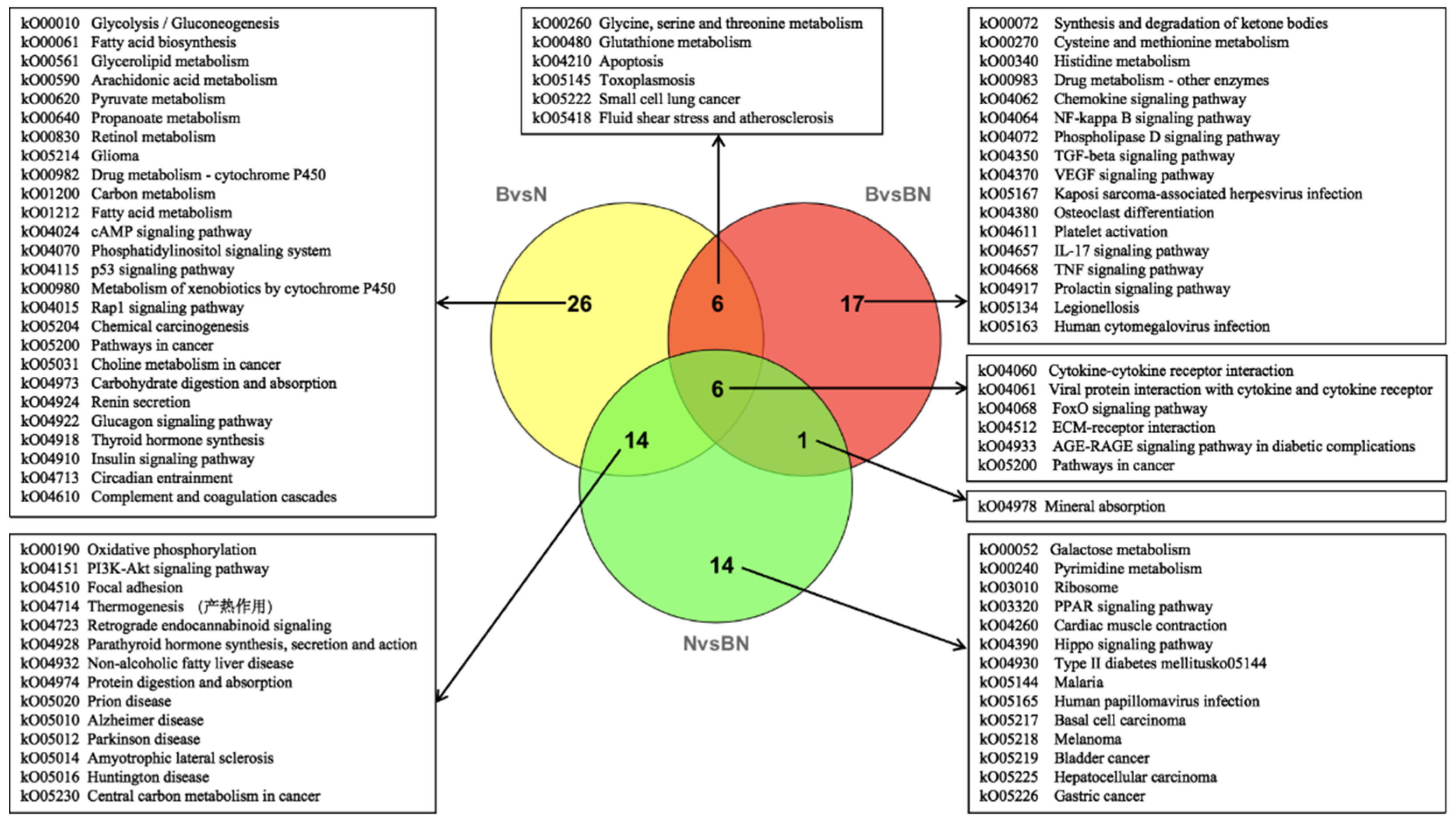
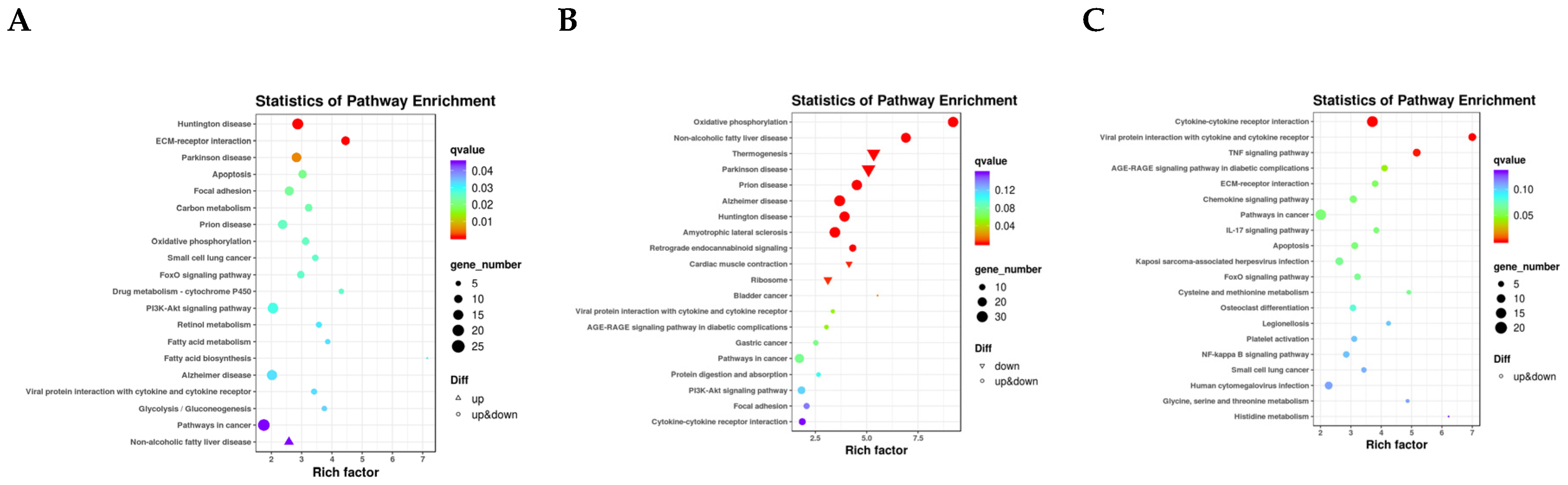
3.3. Transcriptome Data Analysis
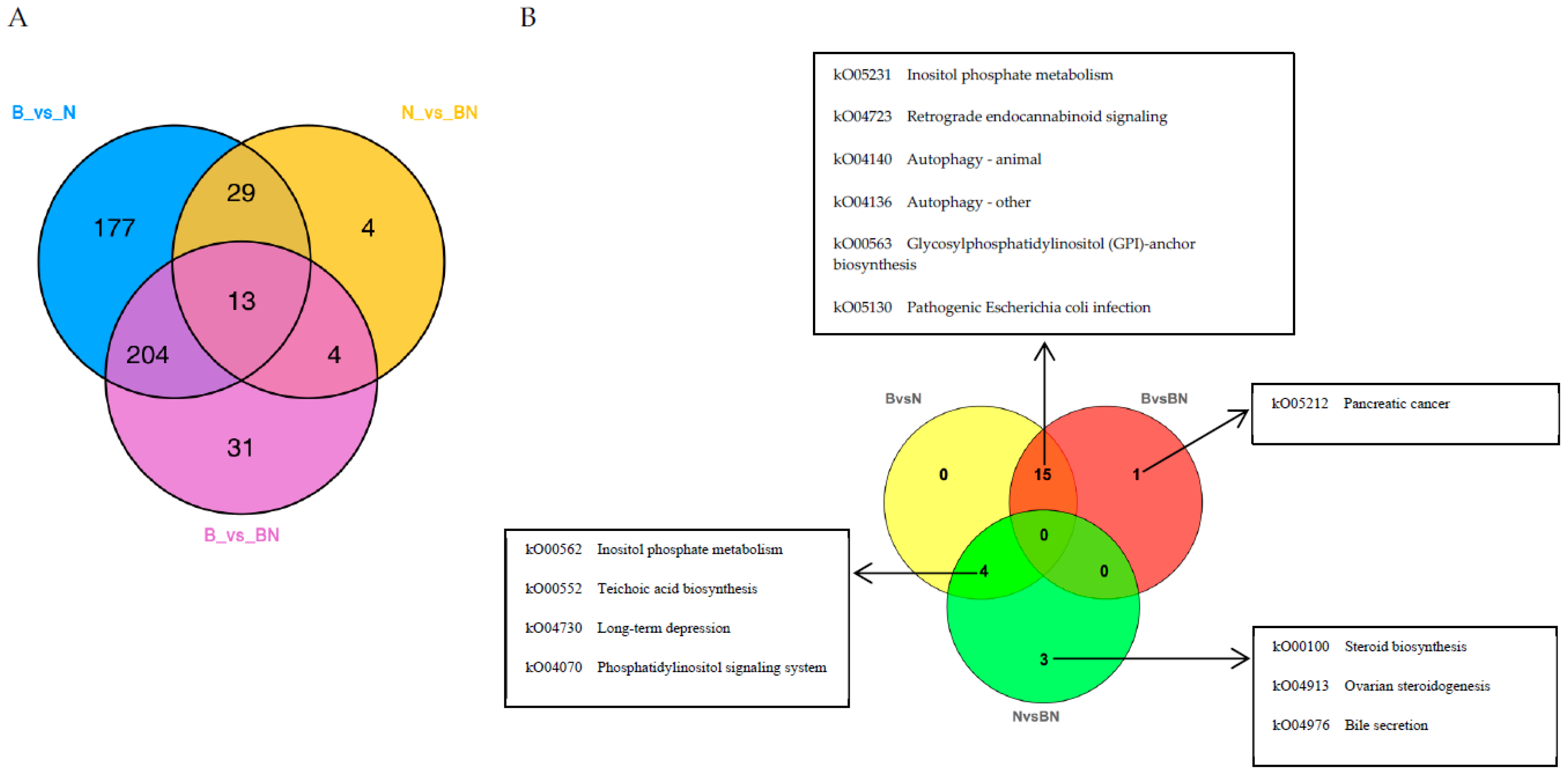
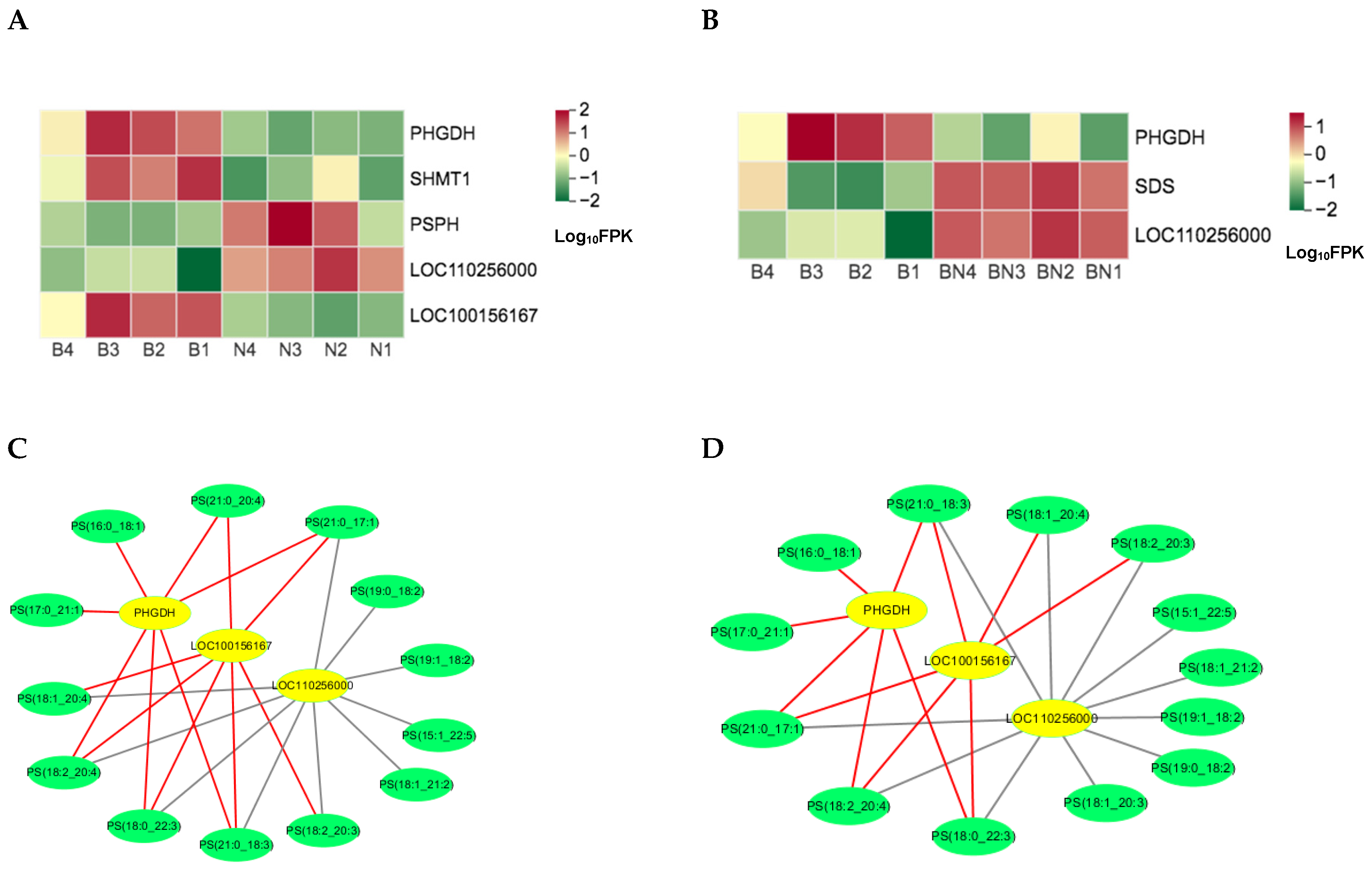
3.4. Joint Analysis of the Transcriptome and Lipidome Data
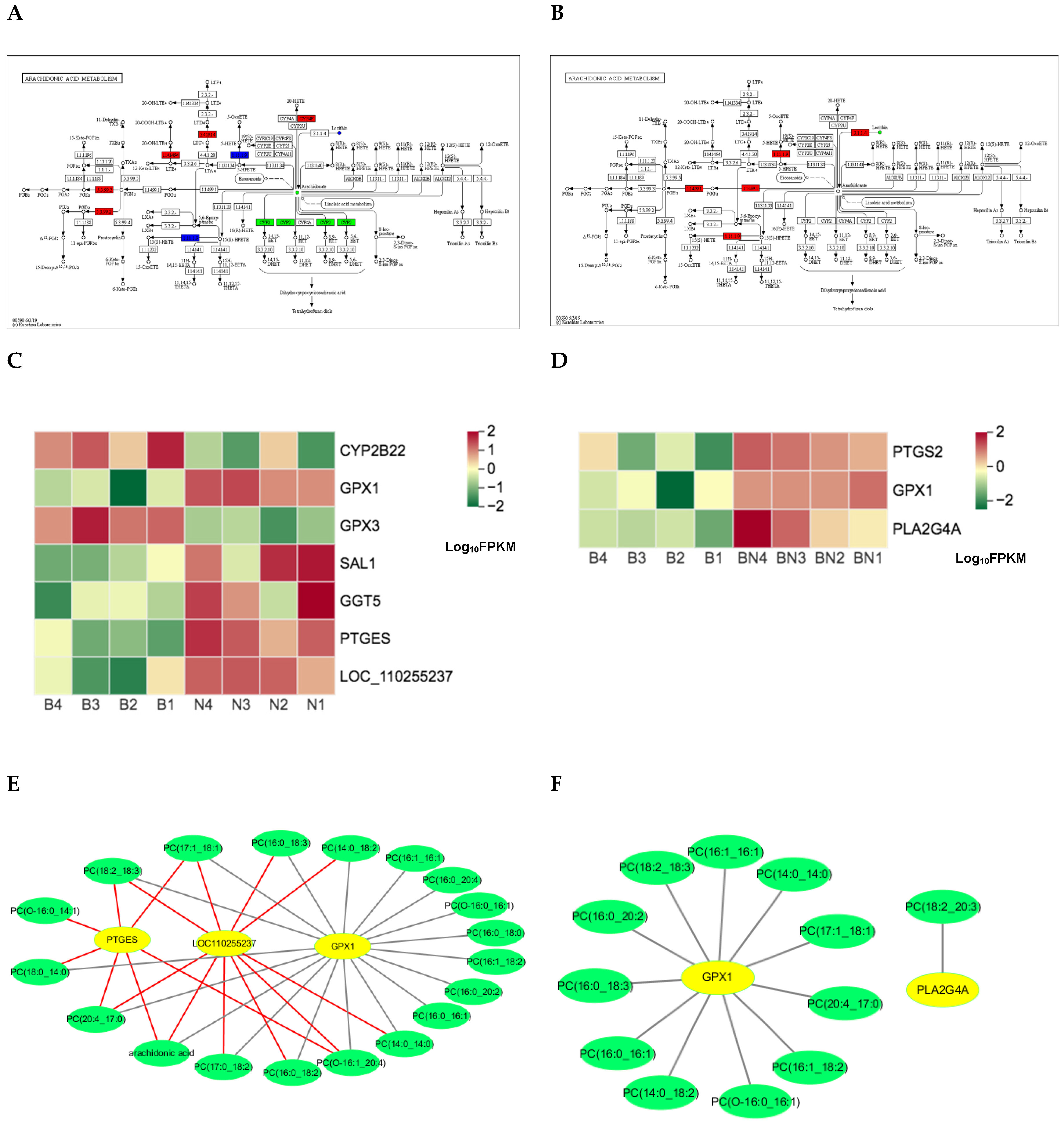
3.5. Candidate genes and Lipids Screening with the Combined Transcriptome and Lipidome Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Huge Difference Existed in the Lipid Composition of the Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue among Ningxiang pigs, Berkshire pigs and F1 Pigs
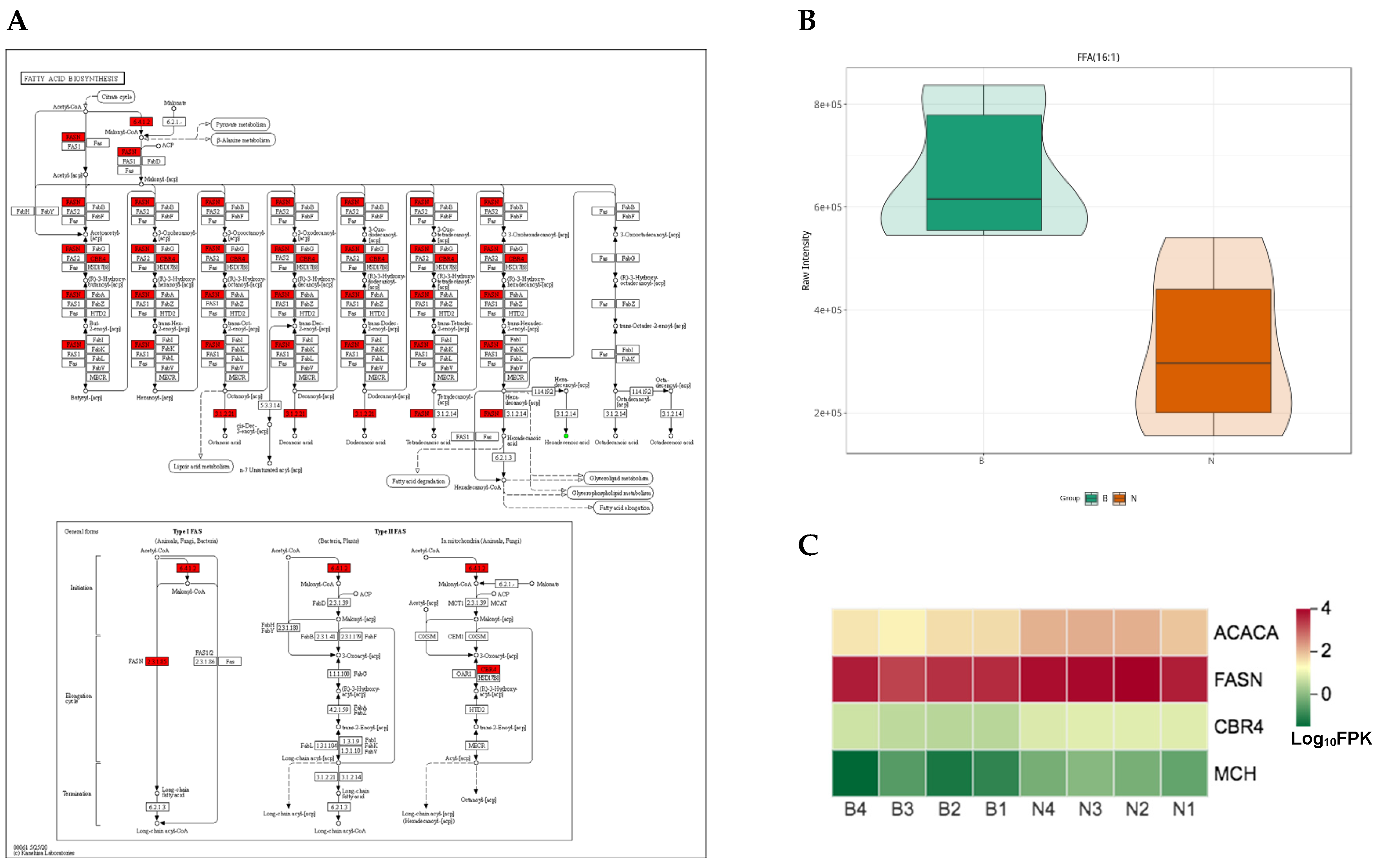
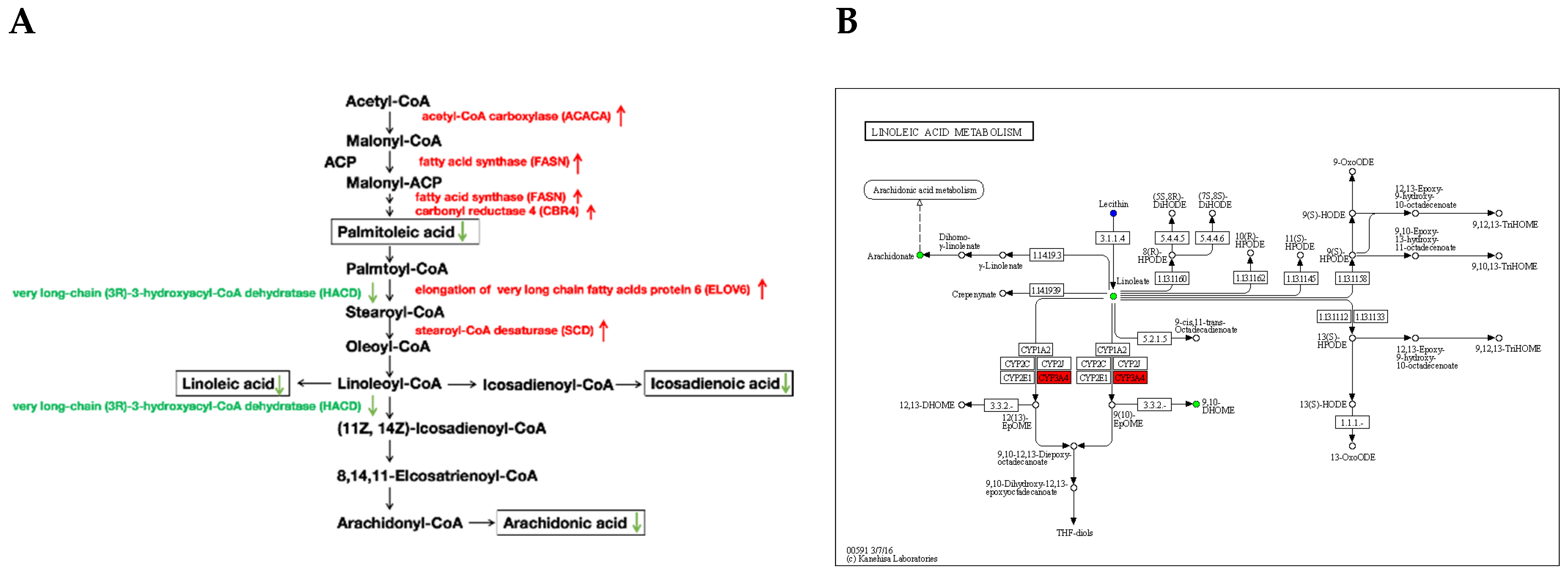
4.2. The KEGG Pathways Belonging to Fatty Acids Biosynthesis and Metabolism Related DEGs and SCLs Contribute to the Difference of Fatty Acids Composition of Adipose Tissue and Fat Deposition among Ningxiang, Berkshire and F1 Pigs
4.3. Some of the KEGG Pathways Related genes screened by Muti-Omics Association Analysis were Probably Overlapped with Artificial Selected Genes
4.4. Application of Multi-Omics Data to Pig Breeding for Improvement the Backfat Thickness and Fatty Acids Composition of Adipose Tissue
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barea R, Nieto R, Aguilera JF. Effects of the dietary protein content and the feeding level on protein and energy metabolism in Iberian pigs growing from 50 to 100 kg body weight. Animal. 2007, 1, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood JD, Enser M, Fisher AV, Nute GR, Sheard PR, Richardson RI, Hughes SI, Whittington FM. Fat deposition, fatty acid composition and meat quality: A review. Meat Science. 2008, 78, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barea R, Isabel B, Nieto R, López-Bote C, Aguilera JF. Evolution of the fatty acid profile of subcutaneous back-fat adipose tissue in growing Iberian and Landrace × Large White pigs. Animal. 2013, 7, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang ZW, Liao QC, Sun Y, Pan TL, Liu SQ, Miao WW, Li YX, Zhou L, Xu GX. Lipidomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of the Longissimus Muscle of Luchuan and Duroc Pigs. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2021, 8, 667622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang YN, Ao QW, Jiang QY, Guo YF, Lan GQ, Jiang HS. Comparisons of different myosin heavy chain types, AMPK, and PGC-1α gene expression in the longissimus dorsi muscles in Bama Xiang and Landrace pigs. Genetics and Molecular Research. 2016, 15, 15028379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poklukar K, Čandek-Potokar M, Batorek Lukač N, Tomažin U, Škrlep M. Lipid Deposition and Metabolism in Local and Modern Pig Breeds: A Review. Animals. 2020, 10, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian I, Verma S, Kumar S, Jere A, Anamika K. Multi-omics data integration, interpretation, and its application. Bioinformatics and Biology Insights. 2020, 14, 1177932219899051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang LY, Zhang YW, Zhang B, Zhong HA, Lu YF, Zhang H. Candidate gene screening for lipid deposition using combined transcriptomic and proteomic data from Nanyang black pigs. BMC Genomics. 2021, 22, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebret B, Dourmad JY, Mourot J, Pollet PY, Gondret F. Production performance, carcass composition, and adipose tissue traits of heavy pigs: influence of breed and production system. Journal of Animal Science. 2014, 92, 3543–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Granados P, Seiquer I, Benítez R, Óvilo C, Nieto R. Effects of lysine deficiency on carcass composition and activity and gene expression of lipogenic enzymes in muscles and backfat adipose tissue of fatty and lean piglets. Animal. 2019, 13, 2406–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouba M, Mourot J, Peiniau P. Stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity in adipose tissues and liver of growing Large White and Meishan pigs. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 1997, 118, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Peng YL, Li SC, Sun JB, Liu XL, Yang SL. Study on genetic resources and germplasm characteristics of Ningxiang pigs. Journal of Hunan Agriculture University (Natural Sciencess). 2008, 34, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan HW, Xiong YC, Wang ZC, Dong WJ, Zhou QC, Xie SS, Li XY, Zhao SH, Ma YL. Integrative analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic profiles reveal the complex molecular regulatory network of meat quality in Enshi black pigs. Meat Science. 2022, 183, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandekeere S, Dubois C, Kalucka J, Sullivan MR, García-Caballero M, Goveia J, Chen R, Diehl FF, Bar-Lev L, Souffreau J, Pricher A, Kumar S, Vinckier S, Hirabayashi Y, Furuya S, Schoonjans, Eelen G, Ghesquiere B, Keshet E, Li XR, Heiden MGV, Dewerchin M, Carmeliet P. Serine Synthesis via PHGDH Is Essential for Heme Production in Endothelial Cells. Cell Metabolism. 2018, 28, 573–587.e513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li MZ, Tian SL, Yeung CKL, Meng XH, Tang QZ, Niu LL, Wang X, Jin L, Ma JD, Long KR, Zhou CW, Cao YC, Zhu L, Bai L, Tang GQ, Gu YR, Jiang AA, Li XW, Li RQ. Whole-genome sequencing of Berkshire (European native pig) provides insights into its origin and domestication. Scientific Reports. 2014, 4, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenker, S. UK recommendations for dietary fat: should they be reassessed in light of the recent joint FAO/WHO recommendations? Nutrition Bulletin. 2012, 37, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira MS, Pires VM, Alfaia CM, Costa AS, Luxton R, Doran O, Bessa RJ, Prates JA. Differential effects of reduced protein diets on fatty acid composition and gene expression in muscle and subcutaneous adipose tissue of Alentejana purebred and Large White × Landrace × Pietrain crossbred pigs. The British Journal of Nutrition. 2013, 110, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo D, Quintanilla R, Varona L, Díaz I, Ramírez O, Pena RN, Amills M: Polymorphism of the pig acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase alpha gene is associated with fatty acid composition in a Duroc commercial line. Animal genetics. 2009, 40, 410–417. [CrossRef]
- Crespo-Piazuelo D, Criado-Mesas L, Revilla M, Castelló A, Noguera JL, Fernández AI, Ballester M, Folch JM. Identification of strong candidate genes for backfat and intramuscular fatty acid composition in three crosses based on the Iberian pig. Scientific Reports. 2020, 10, 13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ros-Freixedes R, Gol S, Pena RN, Tor M, Ibáñez-Escriche N, Dekkers JC, Estany J. Genome-wide association study singles out SCD and LEPR as the two main loci influencing intramuscular fat content and fatty acid composition in duroc pigs. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0152496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire JP, Mourot J, Cunha LF, Almeida JA, Aumaitre A. Effect of the source of dietary fat on postweaning lipogenesis in lean and fat pigs. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. 1998, 42, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon M, Wyszynska-Koko J, Vincent A, Hérault F, Lebret B. Comparison of muscle transcriptome between pigs with divergent meat quality phenotypes identifies genes related to muscle metabolism and structure. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e33763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao SM, Ren LJ, Chen L, Zhang X, Cheng ML, Li WZ, Zhang YY, Gao SZ. Differential expression of lipid metabolism related genes in porcine muscle tissue leading to different intramuscular fat deposition. Lipids. 2009, 44, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang ZX, Li QG, Chamba YZ, Zhang B, Shang P, Zhang H, Wu CX. Identification of Genes Related to Growth and Lipid Deposition from Transcriptome Profiles of Pig Muscle Tissue. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0141138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan YH, Zheng CB, Zheng J, Ma L, Ma XR, Zhong YZ, Zhao XC, Li FN, Guo QP, Yin YL. Profiles of muscular amino acids, fatty acids, and metabolites in Shaziling pigs of different ages and relation to meat quality. Science China Life Sciences. 2022, 65, 2227–22246. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaka T, Shimano H. Elovl6: a new player in fatty acid metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2009, 87, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John LC, Lunt DK, Smith SB. Fatty acid elongation and desaturation enzyme activities of bovine liver and subcutaneous adipose tissue microsomes. Journal of Animal Science. 1991, 69, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Xiao Q, Zhang QQ, Sun H, Chen JC, Li ZC, Xue M, Ma PP, Yang HJ, Xu NY, Wang QS, Pan YC. Genomic analysis reveals genes affecting distinct phenotypes among different Chinese and western pig breeds. Scientific Reports. 2018, 8, 13352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang SB, Li XL, Li K, Fan B, Tang ZL. A genome-wide scan for signatures of selection in Chinese indigenous and commercial pig breeds. BMC Genetics. 2014, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang WJ, Liu Z, Zhao QQ, Du H, Yu J, Wang HW, Liu XC, Liu H, Jing XT, Yang HP, Shi GH, Zhou L, Liu JF. Population Genetic Structure and Selection Signature Analysis of Beijing Black Pig. Frontiers in genetics. 2022, 13, 860669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang W, Li XJ, Jiang Y, Zhou M, Liu LQ, Su SG, Xu CL, Li XT, Wang CL. Genetic architecture and selection of Anhui autochthonous pig population revealed by whole genome resequencing. Frontiers in Genetics. 2022, 13, 1022261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang XY, Ran XQ, Niu X, Huang SH, Li S, Wang JF. Whole-genome sequence analysis reveals selection signatures for important economic traits in Xiang pigs. Scitific Reports. 2022, 12, 11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Yang M, Zhou M, Wang YL, Wu XD, Zhang XD, Ding YY, Zhao GY, Yin ZJ, Wang CL. Identification of signatures of selection by whole-genome resequencing of a chinese native pig. Frontiers in genetics. 2020, 11, 566255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosse M, Lopes MS, Madsen O, Megens HJ, Crooijmans RP, Frantz LA, Harlizius B, Bastiaansen JW, Groenen MA. Artificial selection on introduced Asian haplotypes shaped the genetic architecture in European commercial pigs. Proceedings Biological Sciences. 2015, 282, 20152019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang K, Wu PX, Yang Q, Chen DJ, Zhou J, Jiang AA, Ma JD, Tang QZ, Xiao WH, Jiang YZ, Zhu L, Li XW, Tang GQ. Detection of Selection Signatures in Chinese Landrace and Yorkshire Pigs Based on Genotyping-by-Sequencing Data. Frontiers in genetics. 2018, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizuka D, Lyon BE. Coots use hatch order to learn to recognize and reject conspecific brood parasitic chicks. Nature. 2010, 463, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estany J, Ros-Freixedes R, Tor M, Pena RN. A functional variant in the stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene promoter enhances fatty acid desaturation in pork. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e86177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piórkowska K, Małopolska M, Ropka-Molik K, Szyndler-Nędza M, Wiechniak A, Żukowski K, Lambert B, Tyra M. Evaluation of SCD, ACACA and FASN mutations: effects on pork quality and other production traits in pigs selected based on RNA-Seq results. Animals. 2020, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love MI, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biology. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biology. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics. 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




