Submitted:
23 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- *
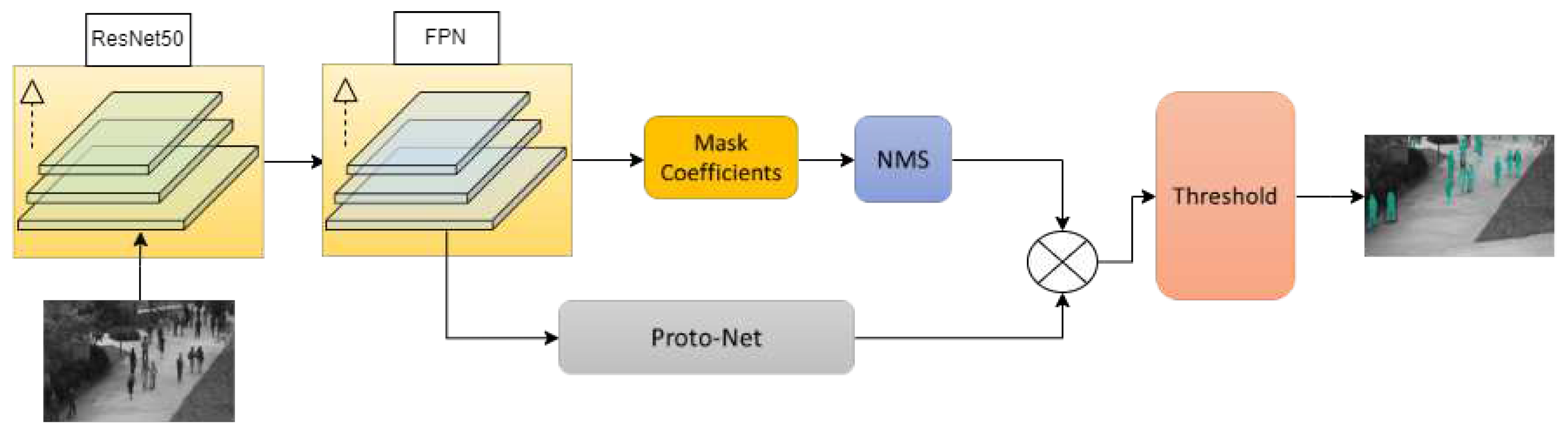
- This paper fine-tunes the YOLACT network and introduces a mask generation module to meet the requirements of the proposed method.
- *
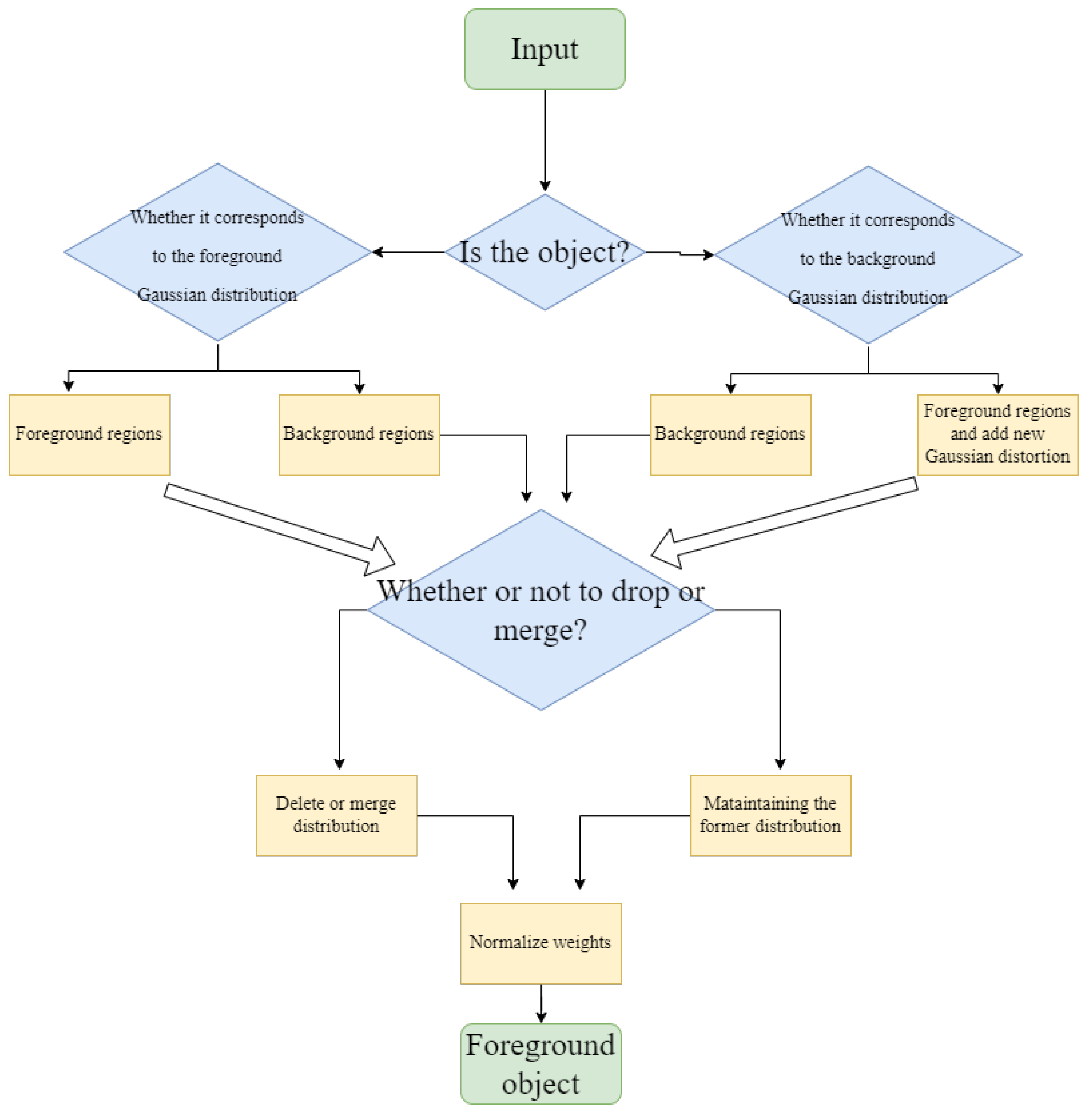
- This paper combines traditional methods with deep learning networks to extract foreground mask images from video frames, thereby enhancing the richness and accuracy of the foreground masks.
- *
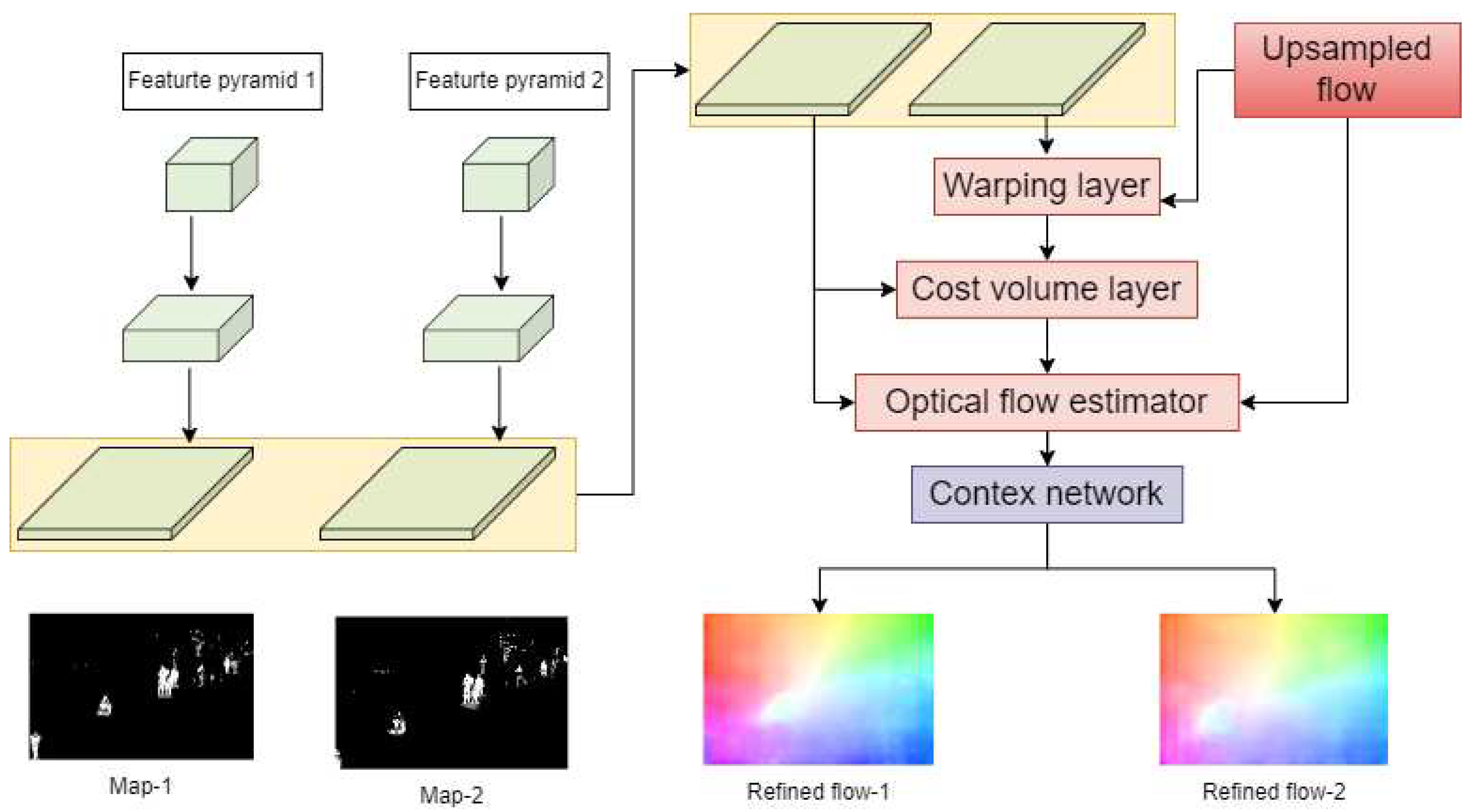
- In this paper, PWC-Net is used to extract foreground object features and these features are used to train the anomaly detection classifier, resulting in improved accuracy of anomaly detection classification.
- *
- The method proposed in this paper consists of two stages. The first stage involves detecting and locating anomalies in video frames, while the second stage focuses on tracking the objects in the video frames to facilitate better understanding and analysis.
- *
- This paper adopts a hybrid methods to detect and locate anomalous video frames. Specifically, we use deep features to construct the feature space instead of handcrafted features, and then use traditional machine learning methods to detect anomalies. By leveraging the strengths of these two approaches, we improve the performance of the method.
2. Related works
2.1. Anomaly Detection Analysis
2.2. The Learning Paradigms for Video Anomaly Detection
2.3. Object Detection
2.4. Feature Extraction
2.5. Detection Based Tracking
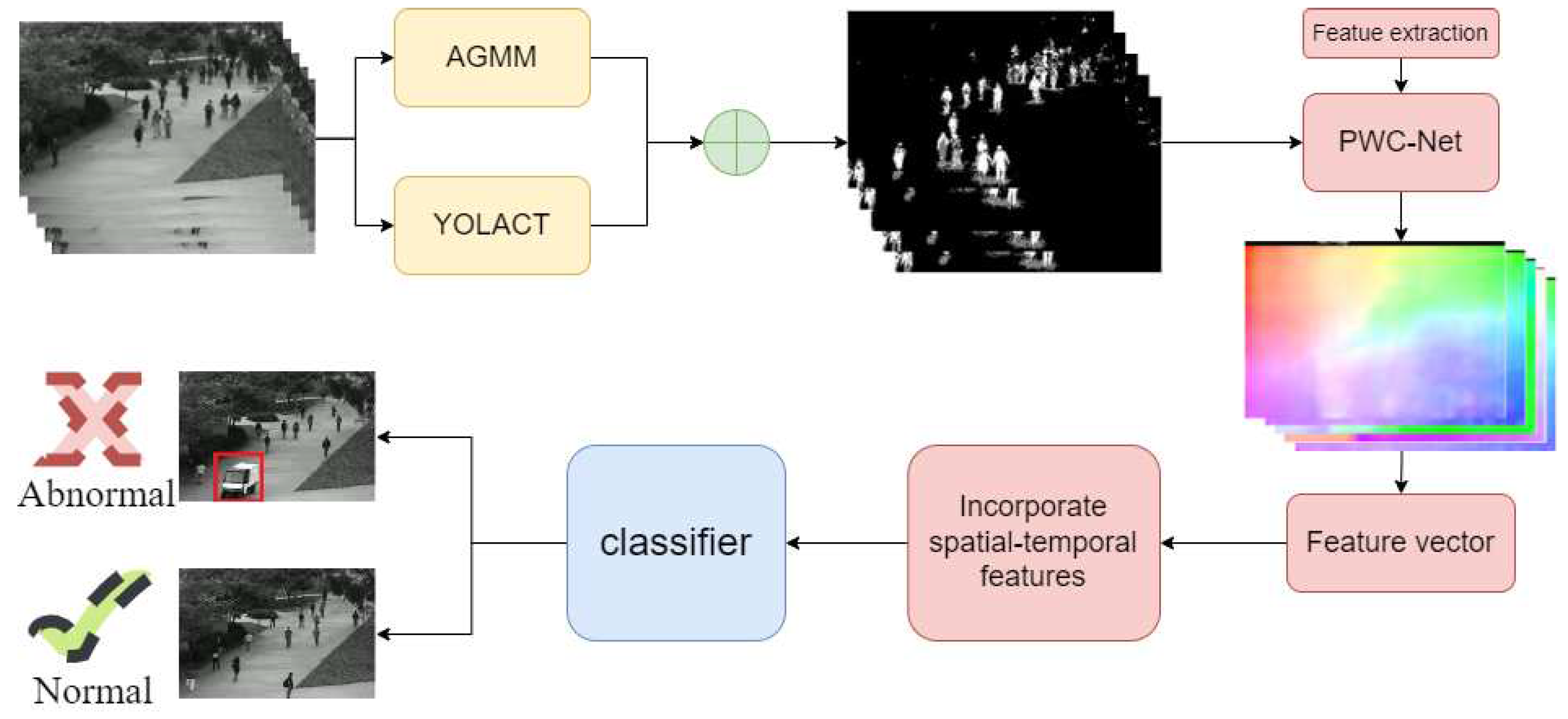
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Object Detection
3.2. Feature Learning
3.3. Abnormal Behavior Detection
3.4. Tracking
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental basis
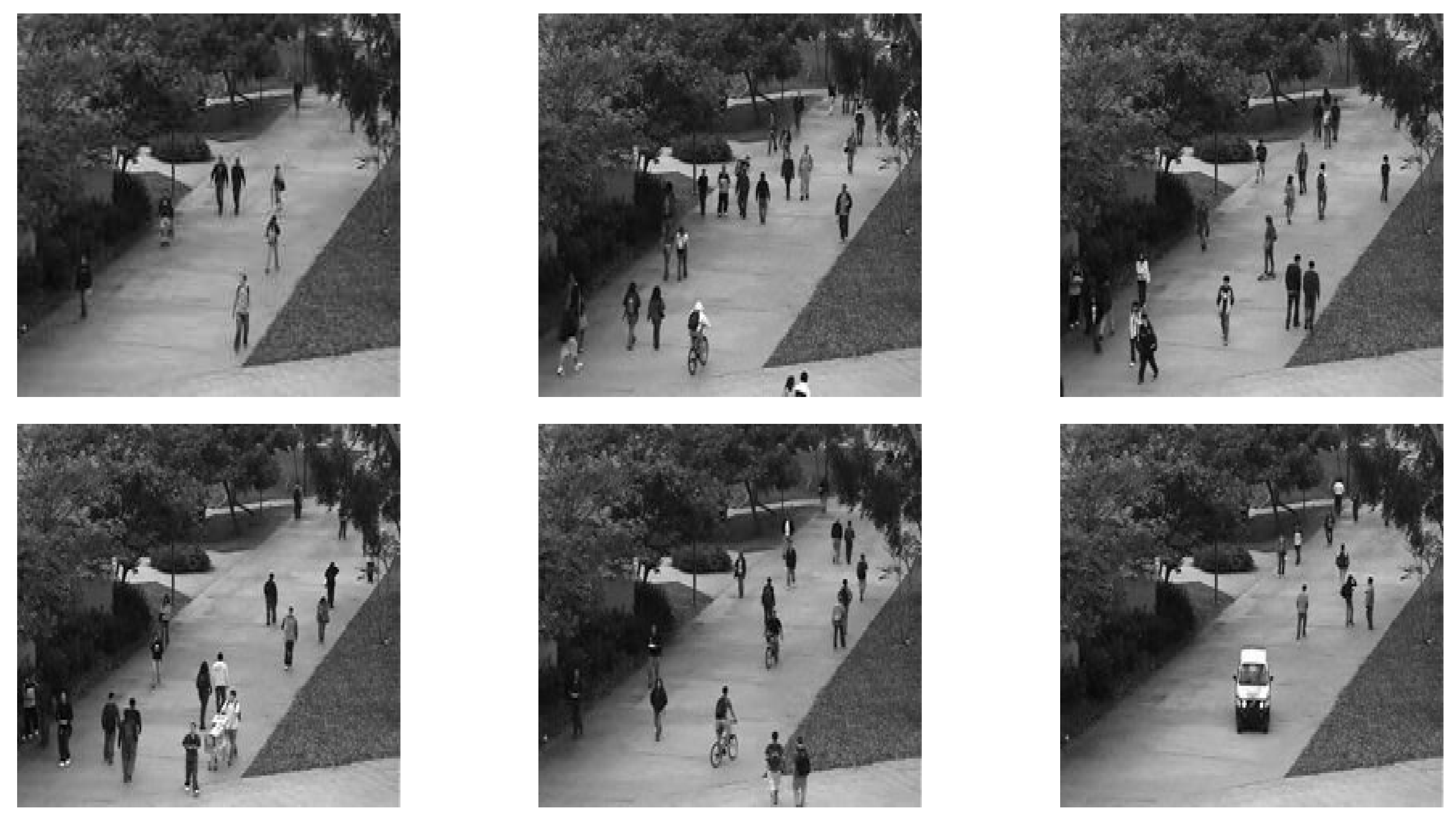
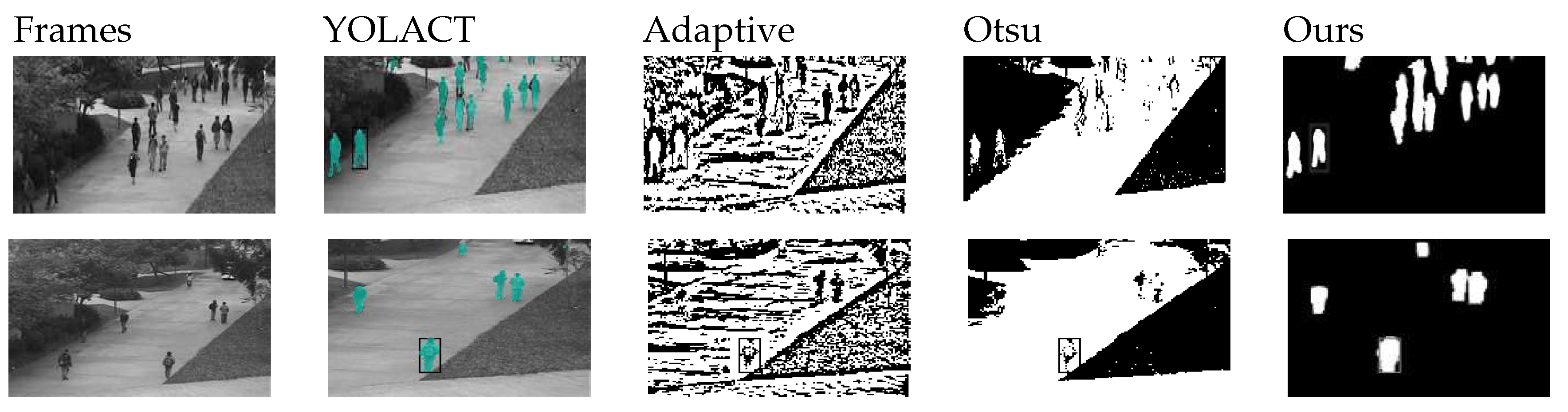
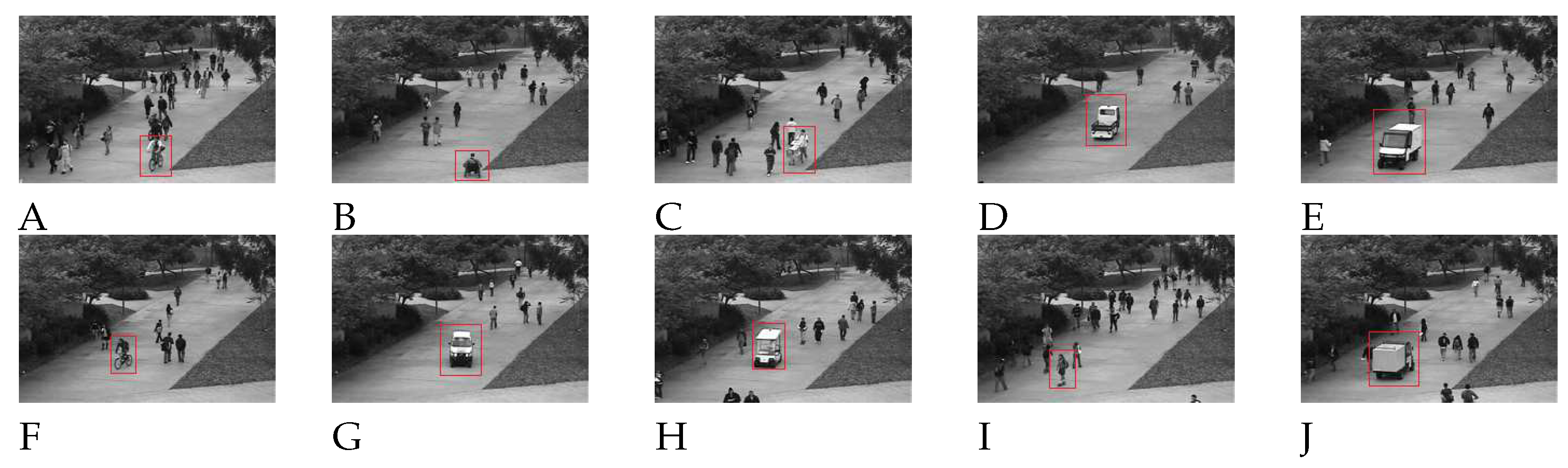
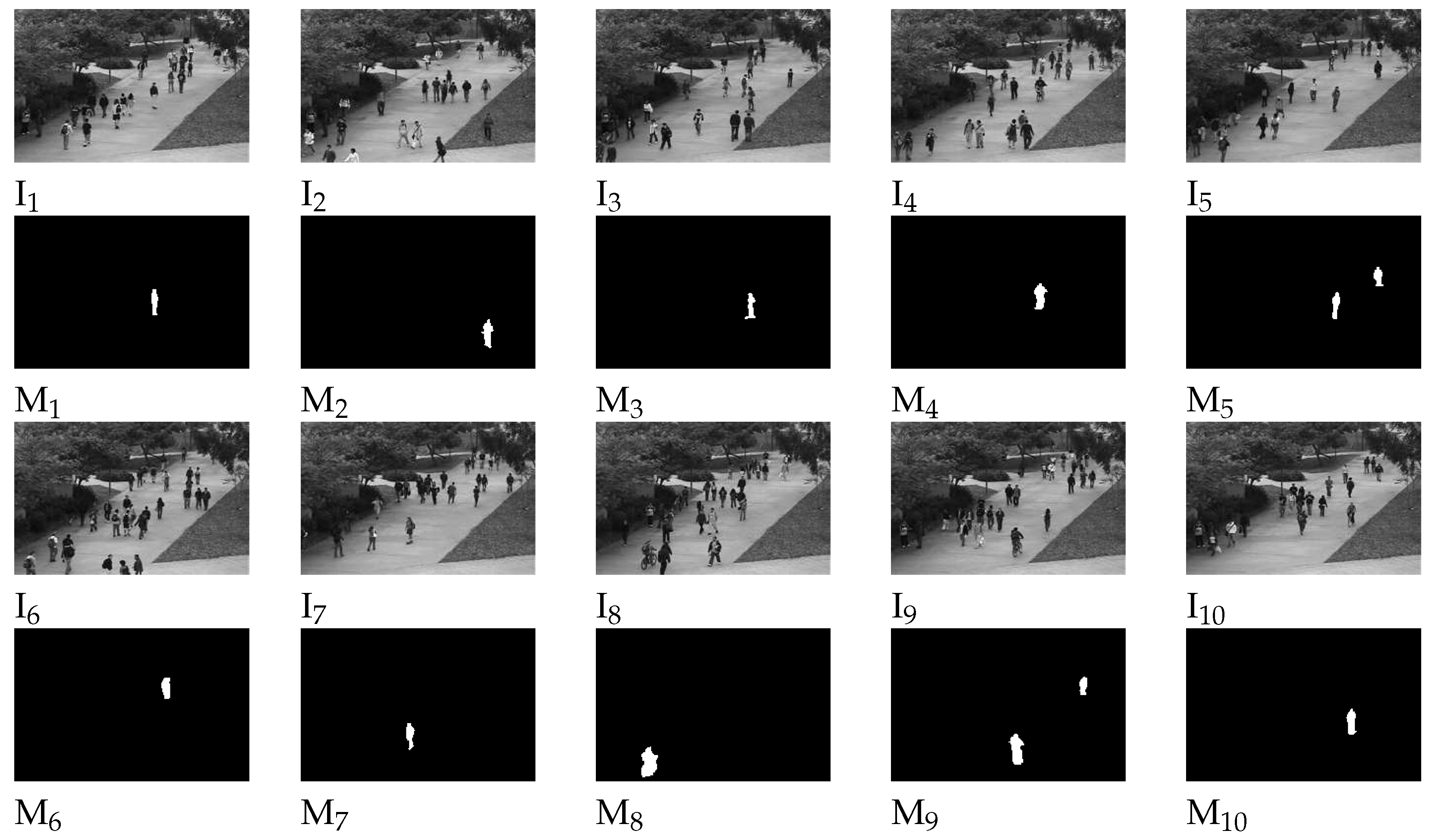
4.2. Moving target detection and analysis
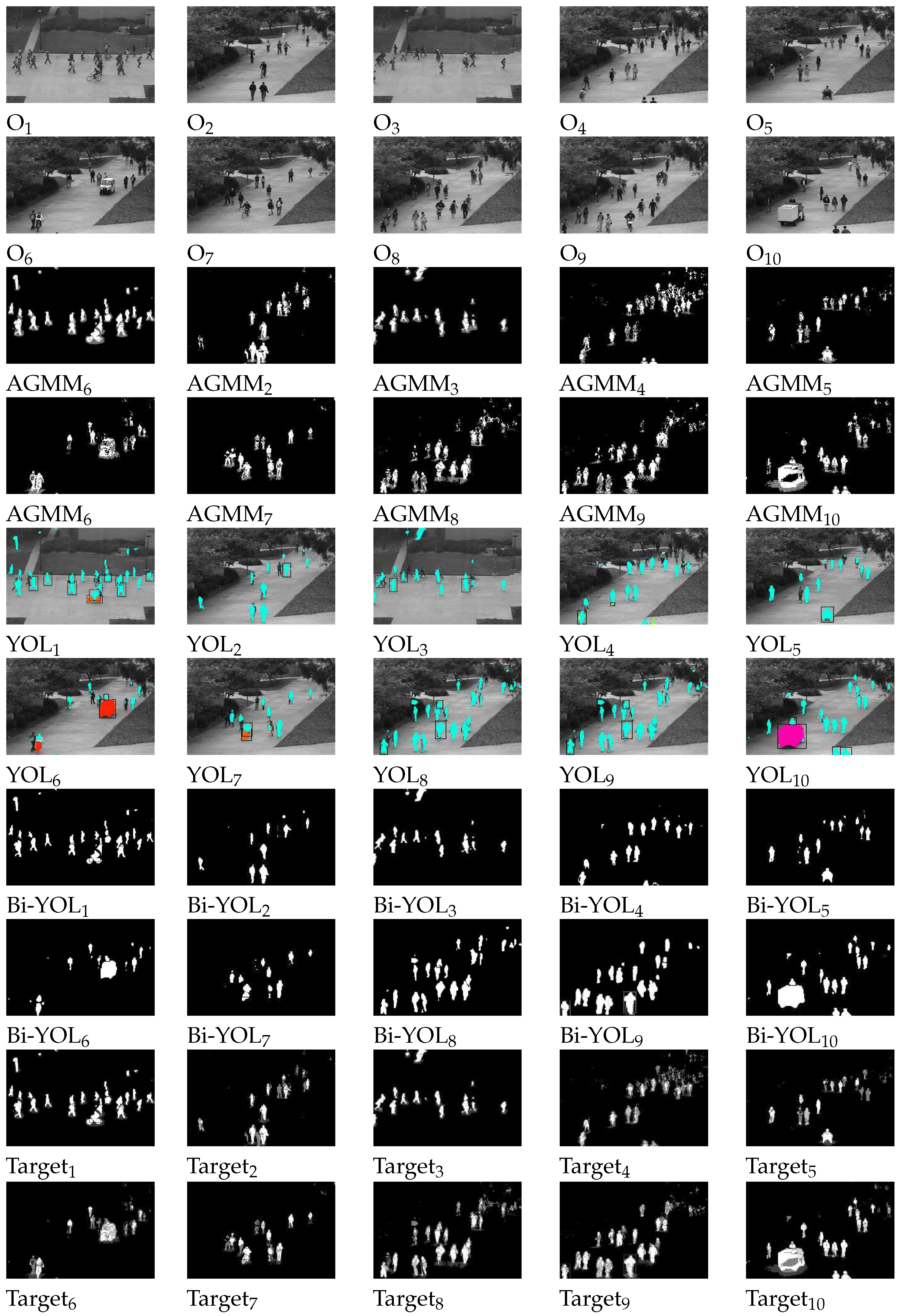
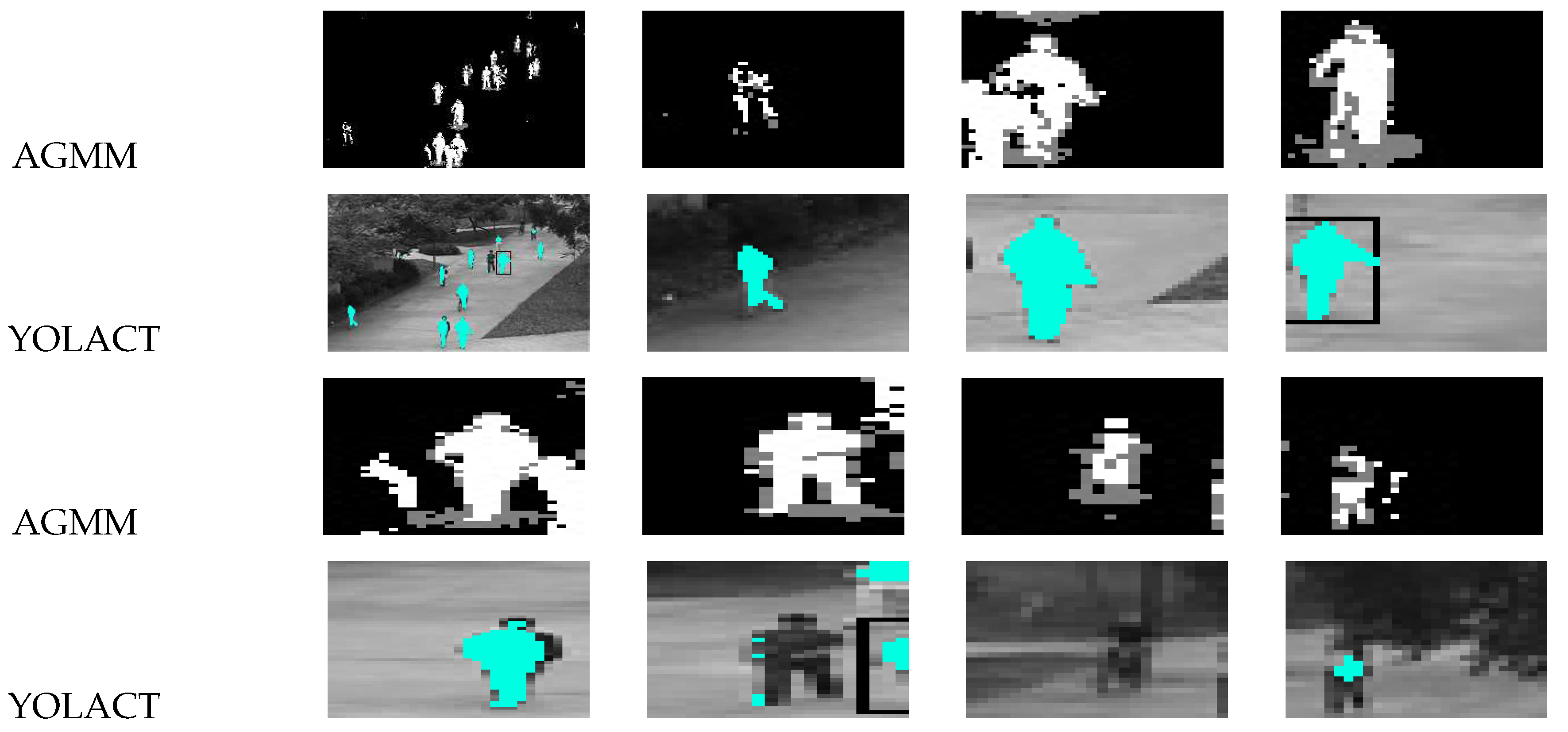
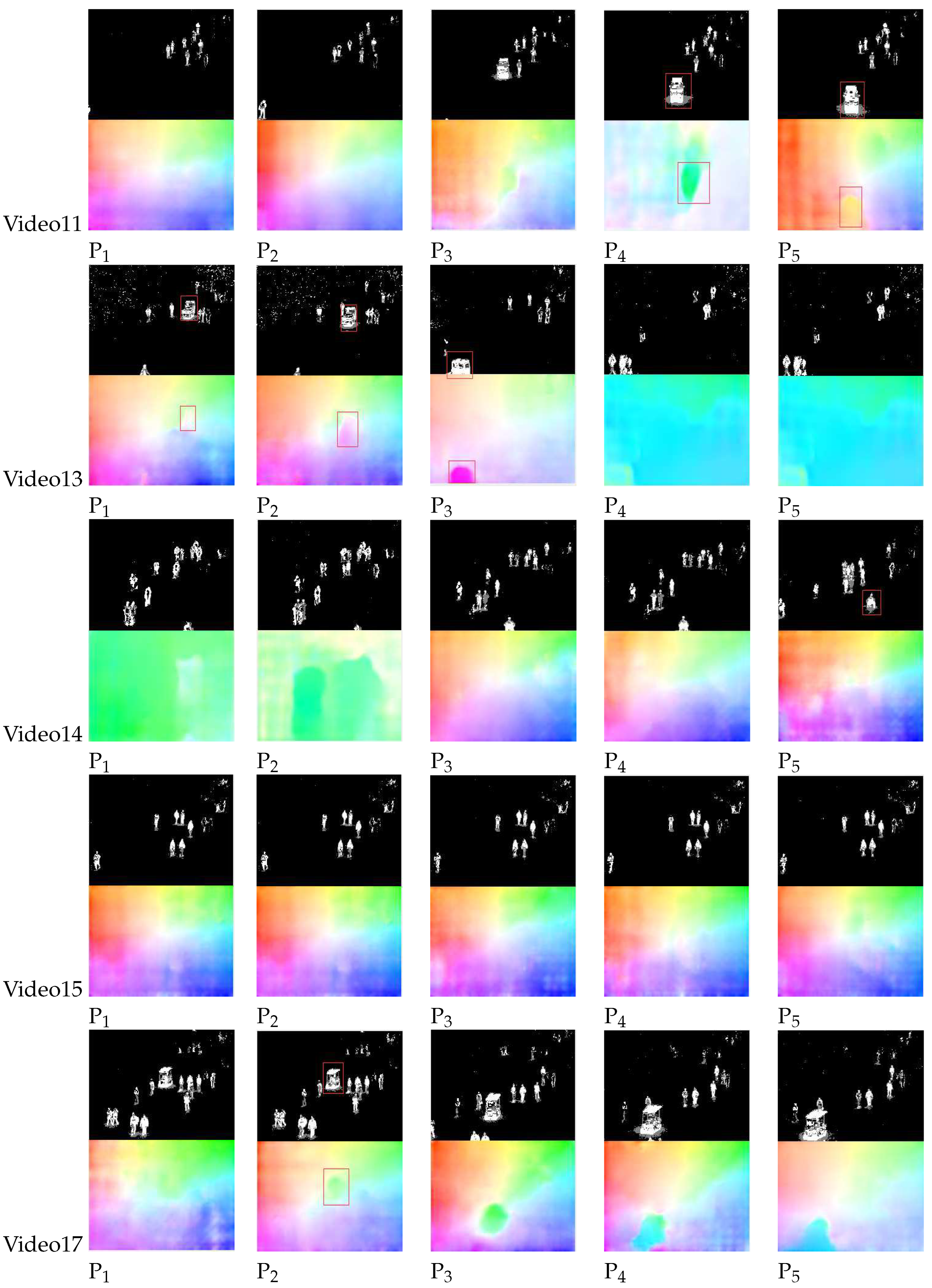
4.3. Target Feature Analysis
4.4. Anomaly Detection analysis
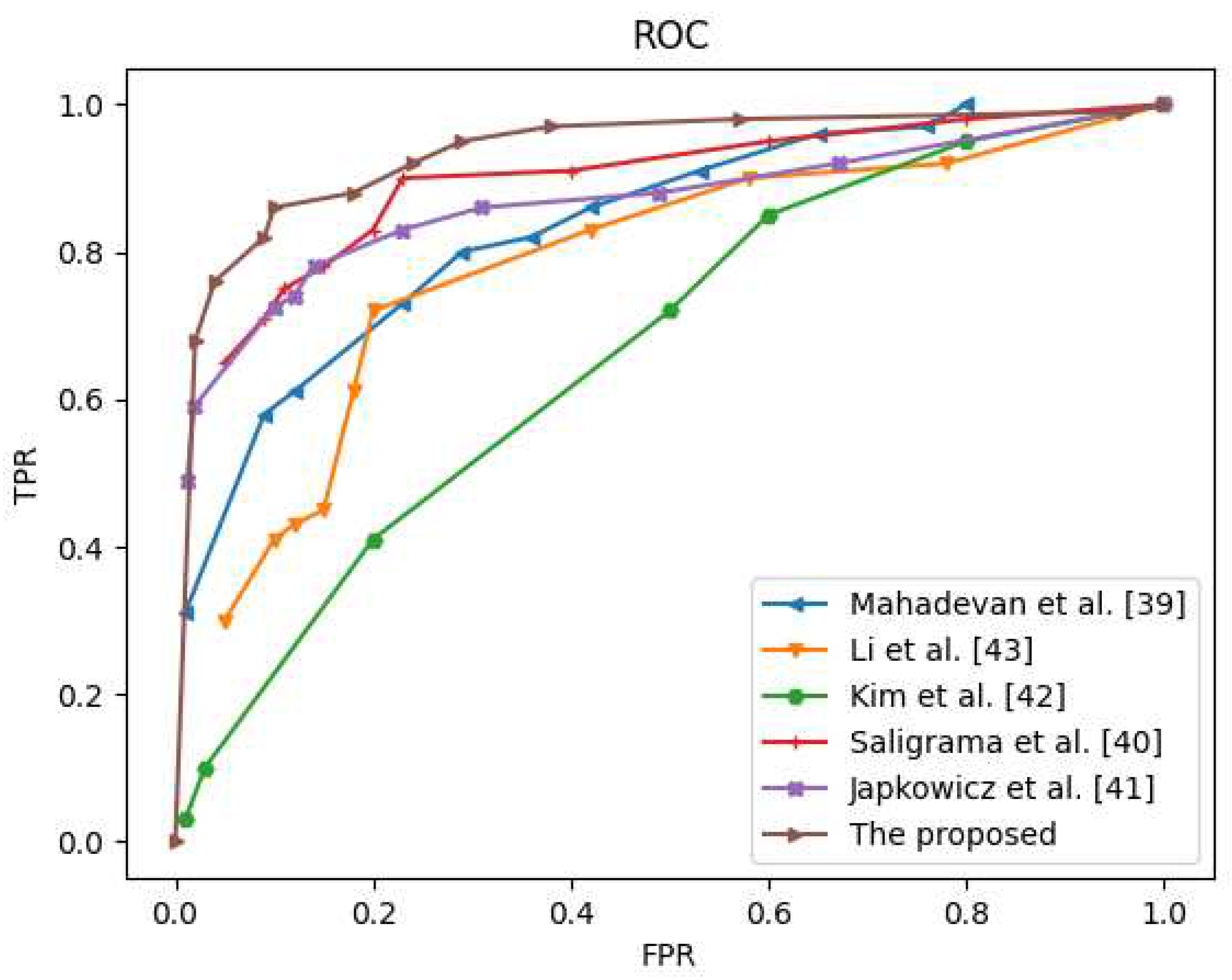
4.5. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis
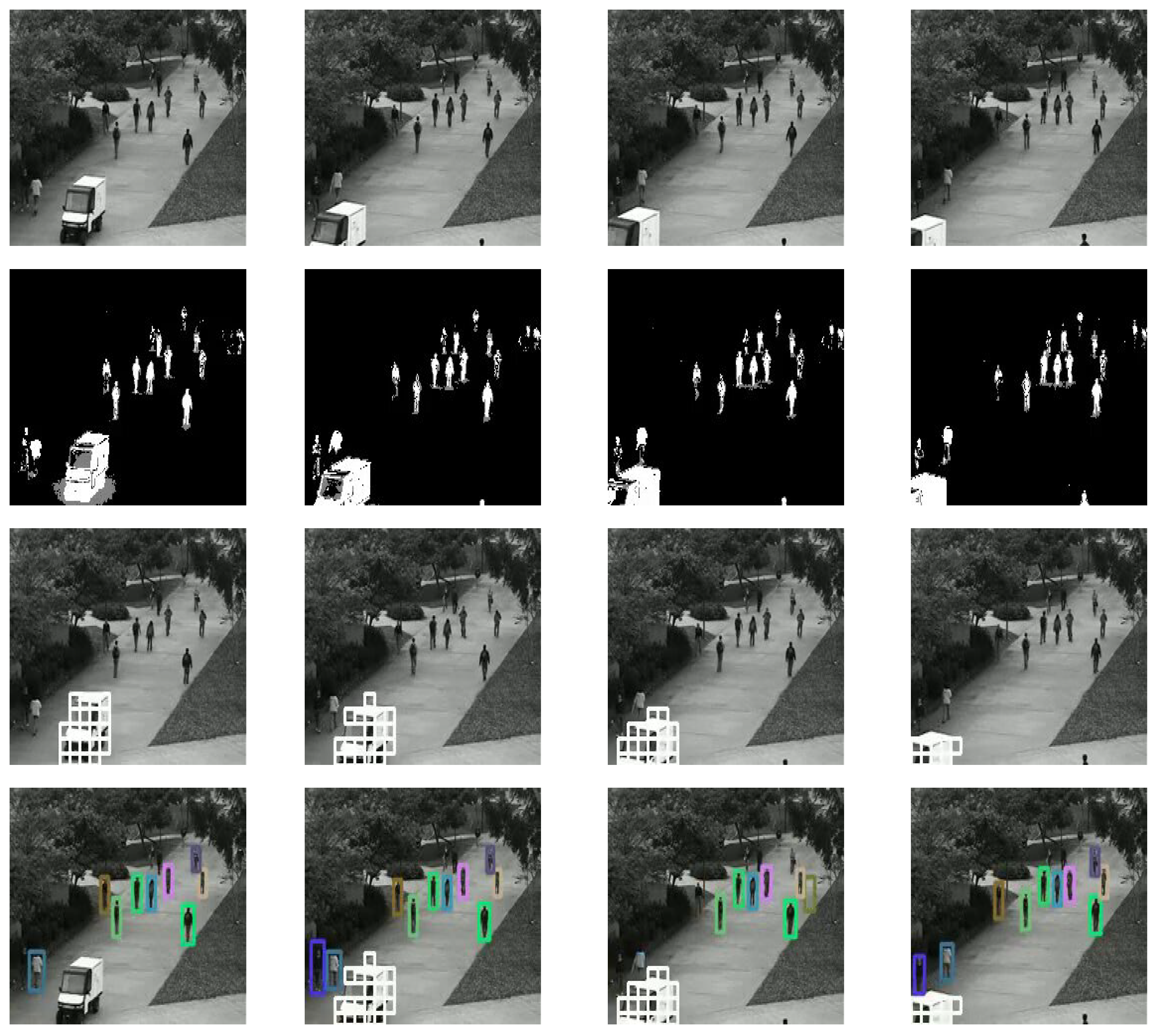
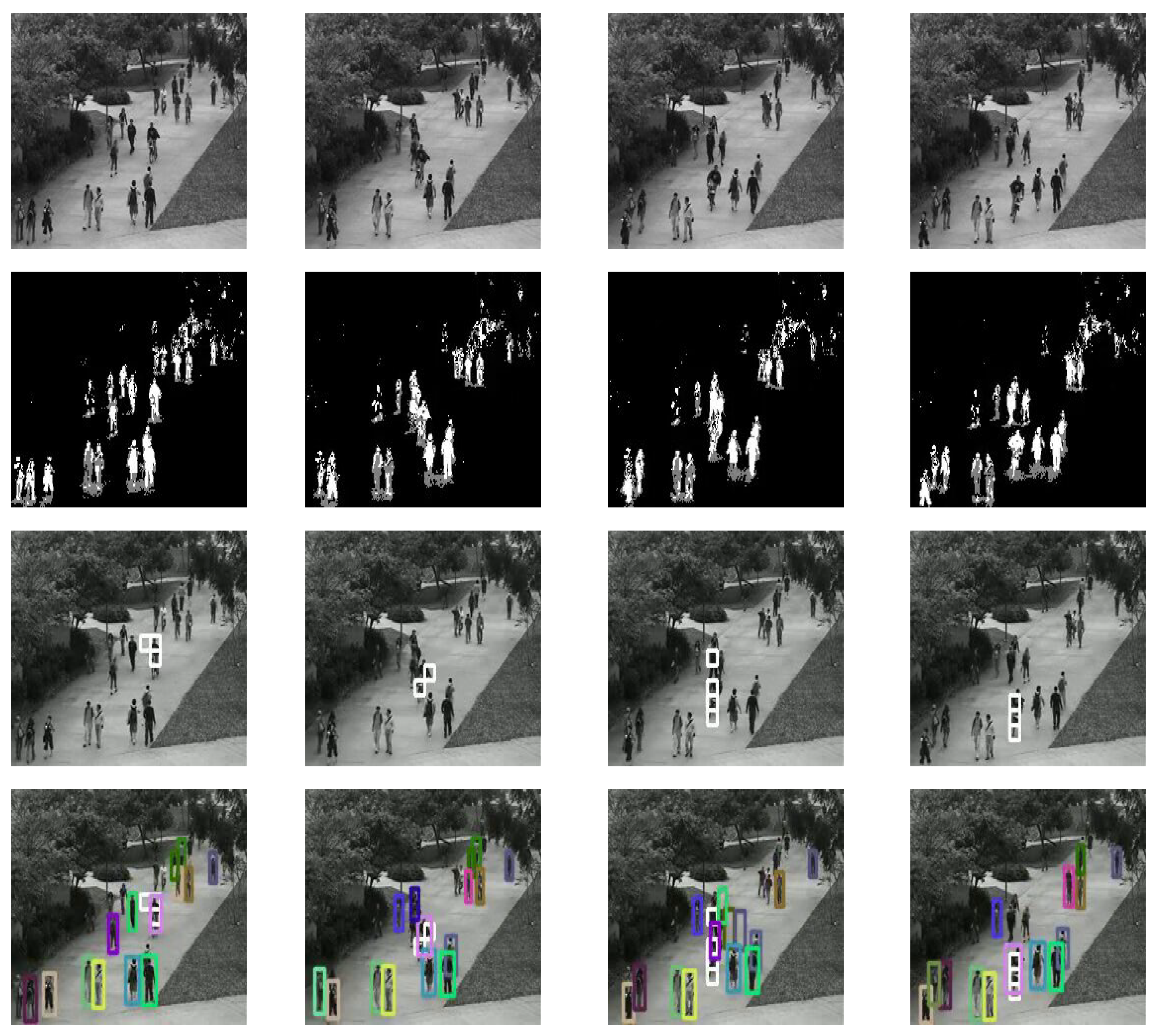
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| YOLOv5 | You only look once version 5 |
| GMM | Gaussian mixture model |
| OP | Optical flow |
| STT | Spatio-temporal technique |
| CNN | Convolutional neural networks |
| BoW | Bag-of-words |
| MRF | Markov random field |
| HMOFP | Histogram of maximal optical flow projection |
| AGMM | Adaptive gaussian mixture mode |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| DeepSORT | Deep simple online and realtime tracking |
| MOT | Multiple object tracking |
| R-CNN | Region-based CNN |
| SSD | Single shot multiBox detector |
| ReID | Person Re-identification |
| FG | Foreground |
| BG | Background |
| UCSD | University of California San Diego |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| EER | Equal error rate |
| FPS | Frame per second |
| TPR | True positive rate |
| FPR | False positive rate |
| TP | True positive |
| TN | True negative |
| FN | False negative |
| FP | False positive |
| PWC | Pyramid, Warping, and Cost Volume |
| YOLACT | You Only Look At CoefficienTs |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| HOG | Histogram of oriented gradients |
| S-CNN | Slicing CNN |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| ST-CNN | Spatial-temporal convolutional neural network |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
| MoSIFT | Motion scale invariant feature transform |
| DBT | detection-based tracking |
| COCO dataset | Microsoft Common Objects in Context |
| S-CNN | Slicing-convolutional neural networks |
References
- Ren, J.; Xia, F.; Liu, Y.; I, Lee. Deep Video Anomaly Detection: Opportunities and Challenges. 2021 International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW) 2021, 959—966.
- L, Wan.; Y, Sun.; I, Lee.; W, Zhao.; F, Xia. Industrial pollution areas detection and location via satellite-based IIoT. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2020, vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 1785–1794.
- Xu, S.; Zhao, M.; Huang, K. Real-time Video Anomaly Detection with Region Proposal Network and YOLO-Act. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2021, 17 (9), 6446-6454. [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, M. Y.; Kautz, J. PWC-Net: CNNs for optical flow using pyramid, warping, and cost volume. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition 2018, pp. 8934-8943.
- Wu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, J. Real-Time Video Anomaly Detection Using PWC-Net and Frame Difference. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 64281-64289.
- Peng, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, X. Real-time video anomaly detection based on improved PWC-Net. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 2020, 11 (1), 177-184.
- S, Varadarajan.; H, Wang.; P, Miller.; H, Zhou. Fast convergence of regularized Region-based Mixture of Gaussians for dynamic background modelling. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 2015, 136 : 45–58.
- R, Azzam.; M.S, Kemouche.; N, Aouf.; M, Richardson. Efficient visual object detection with spatially global Gaussian mixture models and uncertainties. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 2016, 36 : 90–106. [CrossRef]
- Z, Ji.; Y, Huang.; Y, Xia.; Y, Zheng. A robust modified Gaussian mixture model with rough set for image segmentation. Neurocomputing 2017, 266 : 550–565.
- M, Sabokrou.; M, Fathy.; M, Hoseini.; R, Klette. Real-time anomaly detection and localization in crowded scenes. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Hynes Convention Center in Boston, Massachusetts 2015, 56–62.
- R, Leyva.;, V. Sanchez, C.T. Li. Video anomaly detection with compact feature sets for online performance. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2017, 26(7):3463–3478. [CrossRef]
- T, Lu.; L, Wu.; X, Ma.; P, Shivakumara.; C.L, Tan. Anomaly detection through spatio-temporal context modeling in crowded scenes. 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2014, 2203–2208.
- M, Marsden.; K, McGuinness.; S, Little.; N.E.O., Connor. Holistic features for real time crowd behaviour anomaly detection. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Phoenix, 2016, 918–922.
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. Acm 2017, 60, 84–90.
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014, pp. 580–587. [CrossRef]
- Afiq, A.A.; Zakariya, M.A.; Saad, M.N.; Nurfarzana, A.A.; Khir, M.H.M.; Fadzil, A.F.; Jale, A.; Gunawan, W.; Izuddin, Z.A.A.; Faizari, M. A review on classifying abnormal behavior in crowd scene. Vis. Commun. Image Represent 2019, 58, 285–303. [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yan, Y.;Ricci, E. Detecting anomalous events in videos by learning deep representations ofappearance and motion. Computer Vision andImage Understanding 2017, 156: 117-127.
- Tran, H.; Hogg, D. Anomaly detection using a convolu-tional winner-take-all autoencoder. Proc of the BritishMachine Vision Conference 2017: 1-13.
- Li, J.; Chang,L. Video anomaly detection andlocalization via multivariate Gaussian fully convolution adversarial auto encoder. Neuro computing 2019, 369: 92-105.
- Ribeiro, M.; Lazzaretti, A.; E, Lopes H S. A study of deep convolutional auto-encoders for anomaly detection in videos. Pattern Recognition Letters 2018, 105: 13-22. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.;Qiao, M N.; Lin, Z W. Generative neural networks for anomaly detection in crowded scenes. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2019, 14 (5) : 1390-1399. [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, M.; Nabi, M.; Sangineto, E. Abnormal event detection in videos using generative adversarial nets. 2017 IEEE InternationalConference on Image Processing (ICIP) 2017, 2017: 1577-1581.
- Li, Y Y.; Cai, Y H.; Liu, J Q. Spatio-temporal unity networking for video anomaly detection. 2017 IEEE Access 2019, 7: 172425-172432. [CrossRef]
- Y, Hu.; H, Chang.; F, Nian.; Y, Wang.; T, Li. Dense crowd counting from still images with convolutional neural networks. Journal of Visual Communication & Image Representation 2016, 38 (C): 530-539.
- J, Shao.; C.C., Loy.; K, Kang.; X, Wang. Slicing convolutional neural network for crowd video understanding. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas 2016: 5620–5628.
- A, D.; Chevrolet, J. C.; Chevret, S. et al. Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2014, 1 (4): 568-576.
- C, Feichtenhofer.; Pinz, A.; Zisserman, A. Convolutional Two-stream Network Fusion for Video Action Recognition. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016: 1933-1941.
- S, Yi.; H, Li.; X, Wang. Pedestrian behavior understanding and prediction with deep neural networks. European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 263–279.
- Luo et al. Crowd abnormal behavior recognition based on deep learning and sparse optical flow. Computer Engineering 2020, 46 (4): 287-293, 300.
- Gong, M G.; Zeng, H M.; Xie, Y. et al. Local distinguish ability aggrandizing network for human anomaly detection. Neural Net works 2020, 122: 364-373.
- Zou, Y F. Recognition and research about abnormalbehavior of human based on video. Kunming :Yunnan University 2019.
- D, Fortun.; P, Bouthemy.; C, Kervrann. Optical flow modeling and computation: a survey. rComputer Vision and Image Understanding 2015, 134: 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Y, Yuan.; Y, Feng.; X, Lu. Statistical hypothesis detector for abnormal event detection in crowded scenes. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 2016, 99: 1-12.
- Q, Wang.; Q, Ma.; C.H., Luo.; H.Y., Liu.; C.L., Zhang. Hybrid histogram of oriented optical flow for abnormal behavior detection in crowd scenes. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 2016, 30 (02): 14.
- Li, A.; Miao, Z.; Cen, Y.; Wang, T.; Voronin, V. Histogram of maximal optical flow projection for abnormal events detection in crowded scenes. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2015, 11 (11): 406941. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.L.; Schönhuber, M. Identification and Characterization of an Anomaly in Two-Dimensional Video Disdrometer Data. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 315. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, A.; Bahuguna, A. D-CAD: Deep and crowded anomaly detection. Proceedings of the 7th international conference on computer and communication technology 2017: 100-105.
- T, Lu.; L, Wu.; X, Ma.; P, Shivakumara.; C.L., Tan. Anomaly detection through spatio-temporal context modeling in crowded scenes[C]. 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2014, 2203–2208.
- Zhou, S F.; Shen, W.; Zeng, D. et al. Spatial-temporal convolu tional neural networks for anomaly detection and localization in crowded scenes. Signal Processing:Image Communication 2016, 47 (9): 358-368.
- Sabokrou, M.; Fayyaz, M.; Fathy, M. et al. Deep-cascade: cascading 3D deep neural networks for fast anomaly detection and localization in crowded scenes. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2017, 26 (4): 1992-2004. [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y Y.; Song, J X.; Abnormal event detection based on SVM in video surveillance. IEEE Workshop on Advanced Research and Technology in Industry Applications, Ottawa, Canada 2014, 1379-1383.
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple Online and Realtime Tracking with a Deep Association Metric. arXiv e-prints, 2017.
- Ciaparrone, Gioele. et al. Deep learning in video multi-object tracking: A survey. Neurocomputing 2020: 61-88. [CrossRef]
- Piccardi, M. Background subtraction techniques: a review. Systems, Man and Cybernetics. IEEE 2004.
- Zoran, Zivkovic.; Ferdinand, van der Heijden. Efficient adaptive density estimation per image pixel for the task of background subtraction. Pattern recognition letters 2006 27 (7): 773–780.
- Zoran, Zivkovic. Improved adaptive gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. Pattern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference 2004, volume 2, pages 28–31.
- O’donovan, Peter J. Optical Flow : Techniques and Applications. 2005.
- Guizilini, V.; Lee, K. H.; Ambrus, R. et al. Learning Optical Flow, Depth, and Scene Flow without Real-World Labels. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sebastian Bullinger, Christoph Bodensteiner.; Michael, Arens. Instance flow based online multiple object tracking. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) 2017, pages: 785–789.
- Gunnar, Farnebäck. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. Scandinavian conference on Image analysis. Springer 2003, pages; 363–370. [CrossRef]
- Jerome, Revaud.; Philippe, Weinzaepfel.; Zaid, Harchaoui.; Cordelia, Schmid. Deepmatching: Hierarchical deformable dense matching. International Journal of Computer Vision 2016, 120 (3): 300–323.
- Yinlin, Hu.; Rui, Song.; Yunsong, Li. Efficient coarse-to-fine patchmatch for large displacement optical flow. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2016, pages: 5704–5712.
- G, Farneback. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. Image Analysis. Springer 2003, pages: 363–370.
- D, Sun.; X, Yang.; M, Y Liu.; J, Kautz. PWC-Net: CNNs for Optical Flow Using Pyramid, Warping, and Cost Volume. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA 2018, pp. 8934-8943, doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00931.
- Z, Zivkovic. Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition ICPR 2004, pp. 28-31 Vol.2, doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2004.1333992.
- Mahadevan, V.; Li, W.; Bhalodia, V.; V, asconcelos, N. Anomaly detection in crowded scenes. CVPR 2010, pp. 1975–1981.
- W, Li.; V, Mahadevan.; N, Vasconcelos. Anomaly detection and localization in crowded scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36 (1): 18– 32, jan. [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, V.; Li, W.; Bhalodia, V.; Vasconcelos, N. Anomaly detection in crowded scenes. Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2010, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18, pp. 1975–1981.
- Japkowicz, N.; Myers, C.; Gluck, M. A. A Novelty Detection Approach to Classification. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-95) 1995, pp. 518–523.
- J, Kim.; K, Grauman. Observe locally, infer globally: A space-time mrf for detecting abnormal activities with incremental updates. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2009, 1, 2,4, 8, 9.
- Sikdar, A.; Chowdhury, A. S. An adaptive training-less system for anomaly detection in crowd scenes. ArXiv preprint arXiv:1906.00705, 2019, 36 (1): 18-32.



| DeepSORT parameters | Weight |
|---|---|
| MAX-DIST | 0.2 |
| MIN-CONFIDENCE | 0.3 |
| NMS-MAX-OVERLAP | 0.5 |
| MAX-IOU-DISTANCE | 0.7 |
| MAX-AGE | 70 |
| N-INIT | 3 |
| NN-BUDGET | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




