Submitted:
21 May 2023
Posted:
22 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
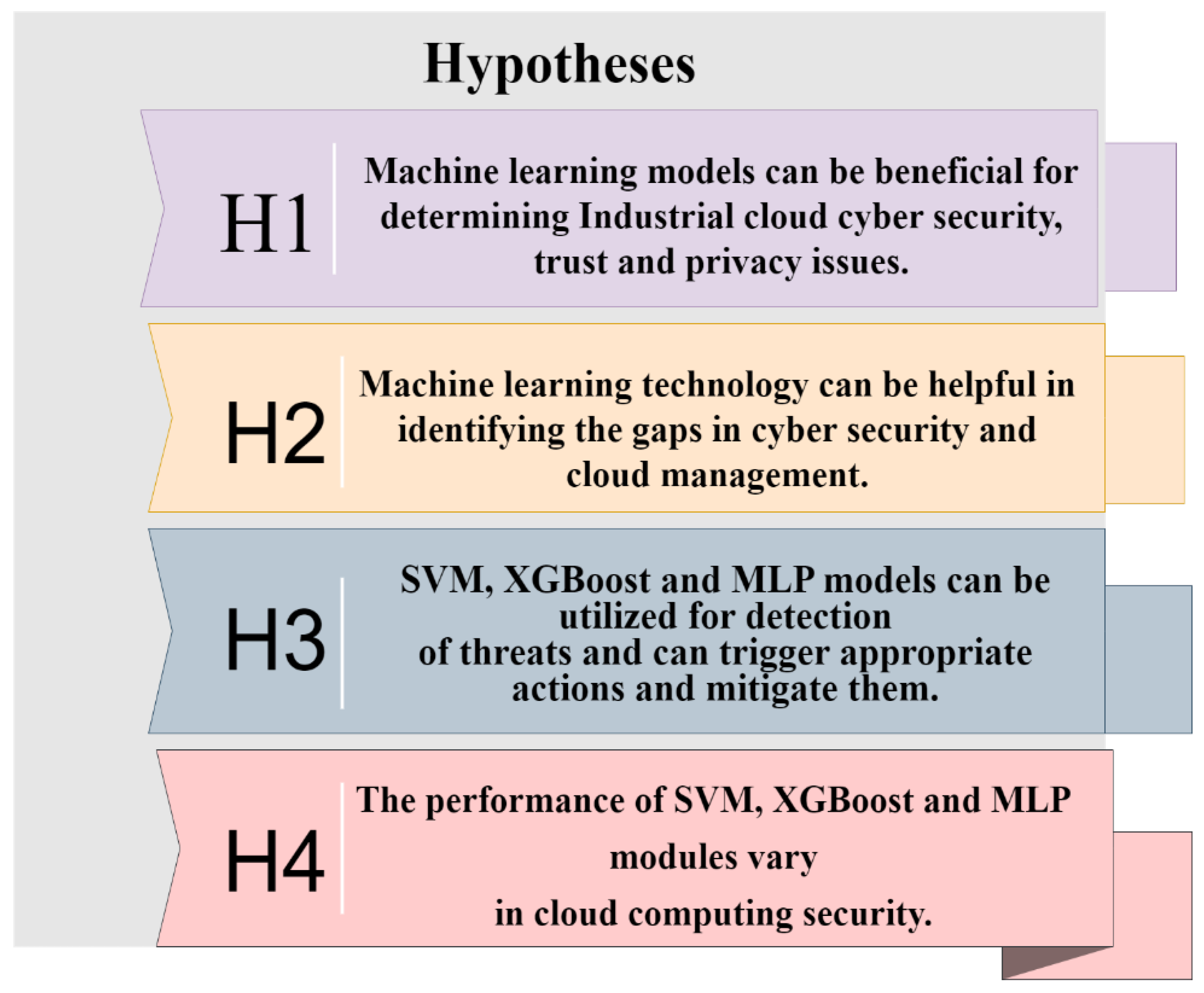
- Use ML models to sermonize industrial cloud cyber security, trust, and privacy issues.
- Identification of gaps in utilizing the ML approach for cloud security.
- Detection and mitigation of security threats.
- Triggering appropriate security actions.
- Comparison of the performance of SVM, X.G.B., and ANN models in cloud computing security.
| Year | Study | Focus | Key Findings and Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Kaur et al. [32] | Data classification In cloud |
Analyze the security issues at authentication and storage. Development of data classification model. Author does not suggest any framework to solve the security concerns. |
| 2017 | Salman et al. [33] | Anomaly detection and classification | Detection of attacks and their classification by LR and RF. 99 % detection and 93.6 % classification accuracy by RF. Fail to categorize some attacks. |
| 2018 | Marwan et al. [34] | Healthcare cloud data security | Prevent unauthorized asses to healthcare cloud data. Use of SVM and FCM for image pixel classification to ensure security. Only focus on image segmentation for security and privacy and does not mention future challenges. |
| 2019 | Subramanian et al. [35] | Cloud cyber security | Avoid static nature for security verification of cloud. Used CNN model for automatic response to threats and save enterprise data. Does not mention type of threats, privacy, trust issues and future challenges in cyber cloud |
| 2020 | Praveena et al. [36] | Hybrid cloud security | Reduction of security risks to hybrid cloud by enhanced C4.5 algorithm. Determine the level of security during storing and authorizing the data. Author does not discuss threats and trust issues and future concerns of hybrid cloud. |
| 2020 | Wang et al. [37] | DDOS attack detection | MLP based model to detect the DDOS attacks. Detection based on the feature selection and feedback mechanism to for detection error. Model not able to find global optimized feature, feedback mechanism can generate false response. |
| 2020 | Chkirbene et al. [27] | Anomalies detection | Classify scheme to protect network from unwanted nodes. Reduce incorrect data issues and differentiate attacks. Author does not discuss trust concerns, industrial cyber issues, and insufficient models' comparison. |
| 2021 | Haseeb et al. [38] | Health industrial IoT security | Avoid uncertainty in data management of health sector. Data protection by EDM-ML approach and ensures trust between networks. Does not compare performance of Models and not mention future prospects. |
| 2021 | Alsharif et al. [39] | IoT security | ML-IDS are used to take account of traffic defects. Offloading heavy tasks from cloud. Does not studied industrial cyber cloud concerns, issues regarding using ML approach for cloud. |
| 2022 | Tabassum et al. [33] | QoS security | Neuro-fuzzy approach to study cloud security, reliability, and efficiency. Discuss threats, security, and trust issues. No comparison of model's performance. |
| 2022 | Bangui et al. [40] | Threat detection in Vehicular Ad-hoc Network (VANET) | Detection and Prevention of Intrusion in VANET. Use of RF and coresets detection for increasing detection efficacy. Does not provide proper solution to the different types of threats. Lack of performance comparison and trust or privacy factors. |
3. Methodology
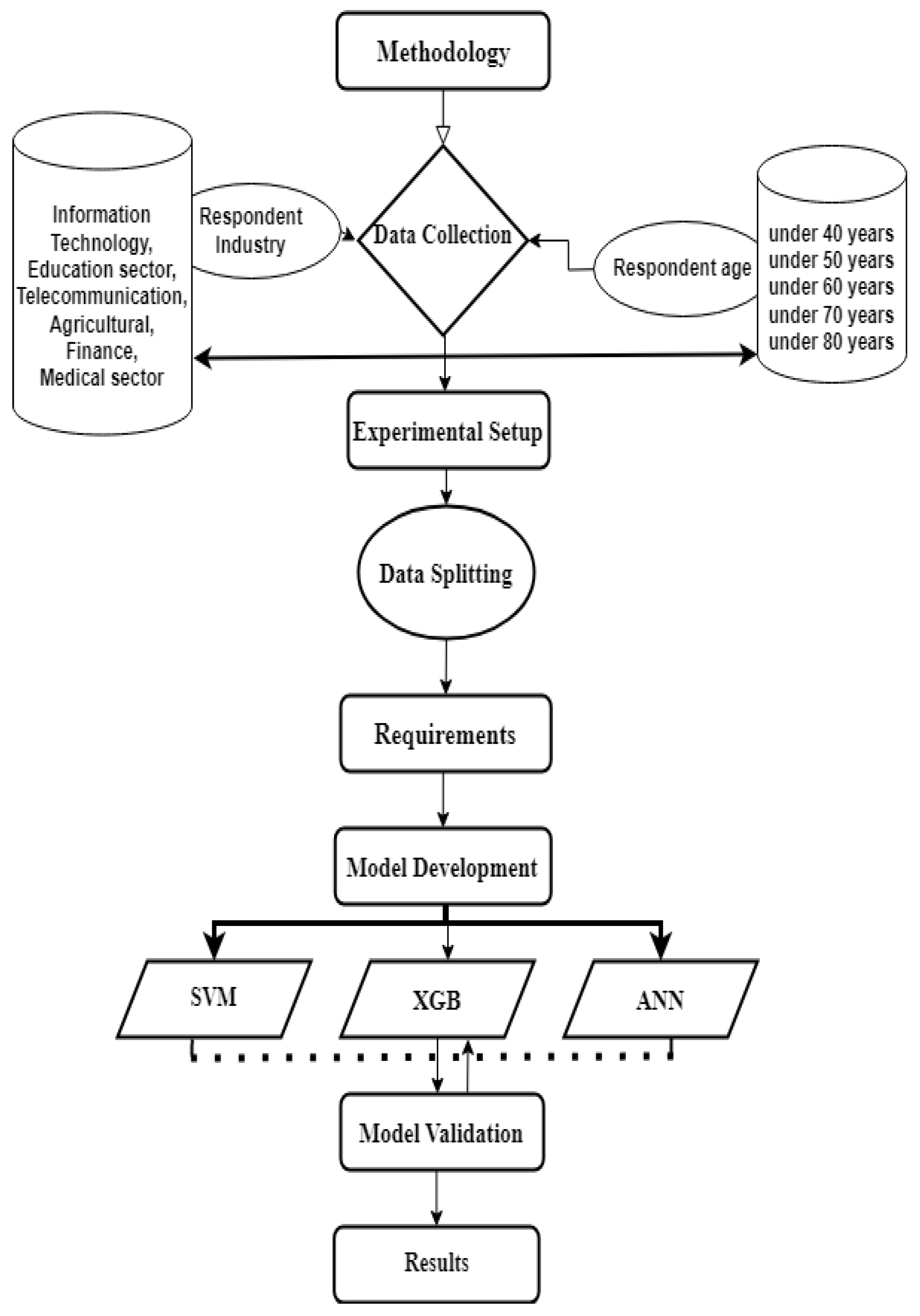
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Data Splitting
3.4. Requirements
3.5. Model's Architecture
3.5.1. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
3.5.2. Gradient Boosting Model
3.5.3. Artificial Neural Networks
3.6. Evaluation Matrices
4. Results and Discussion:
4.1. Features Selection
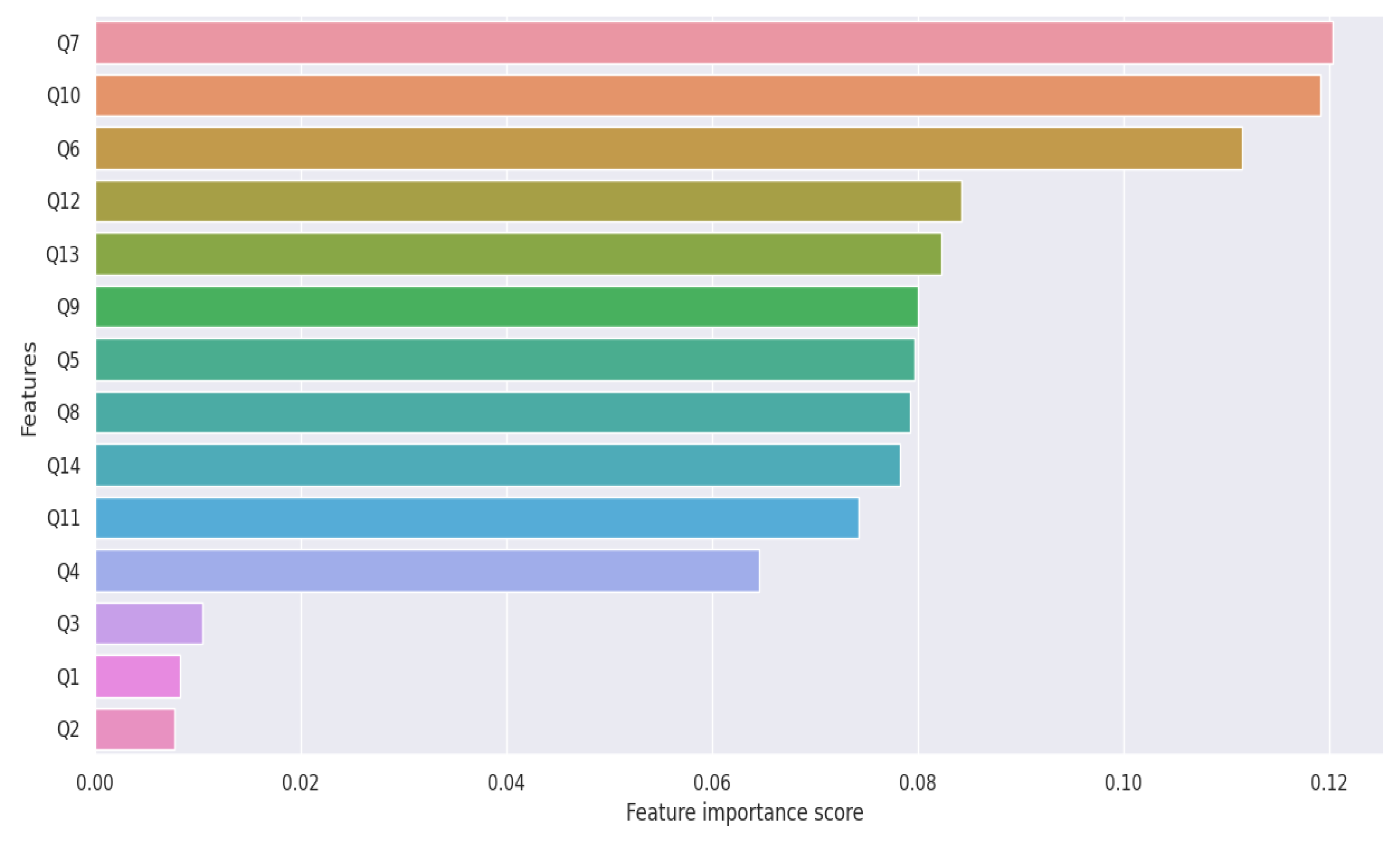
4.2. ML Analysis:
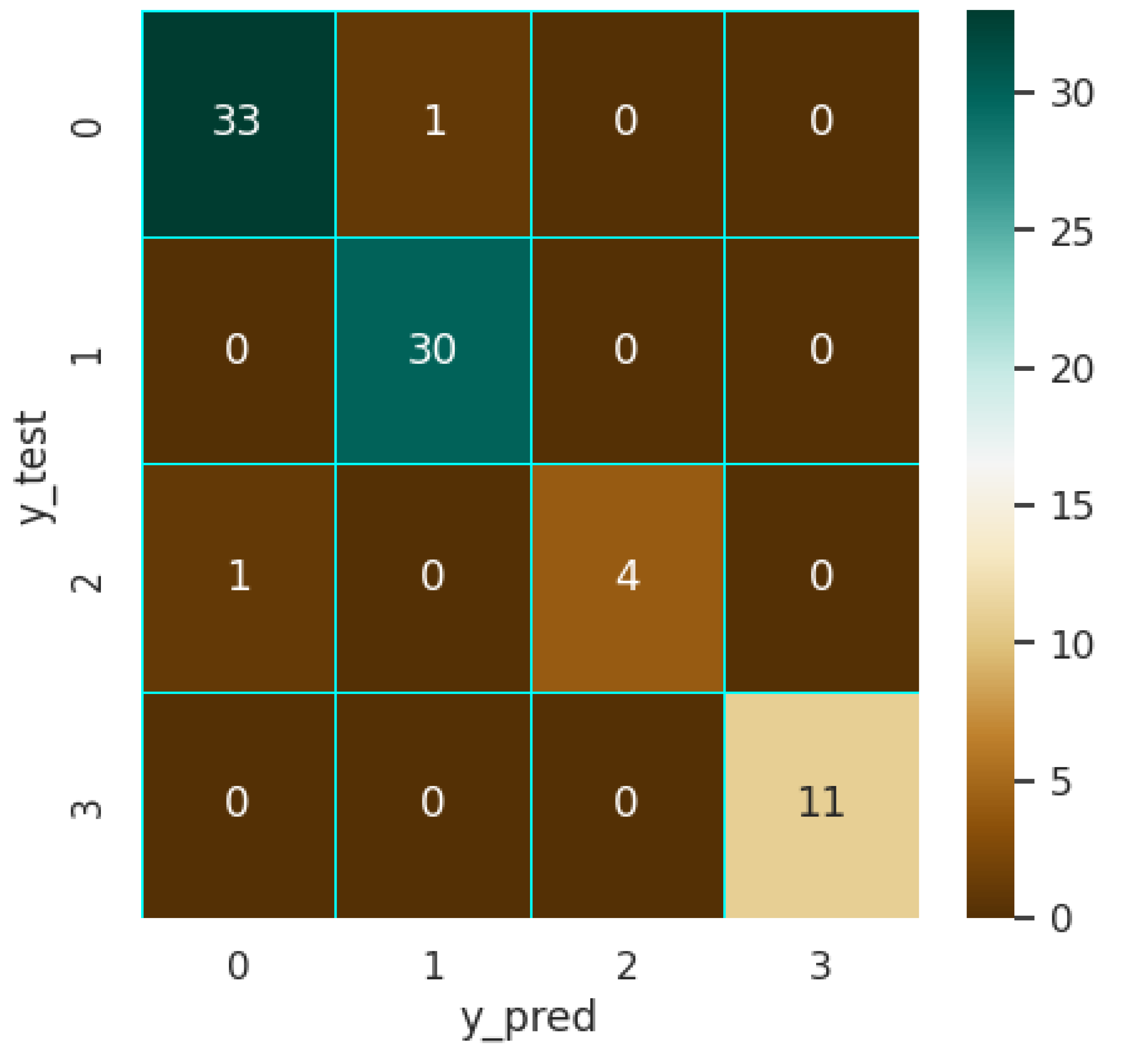
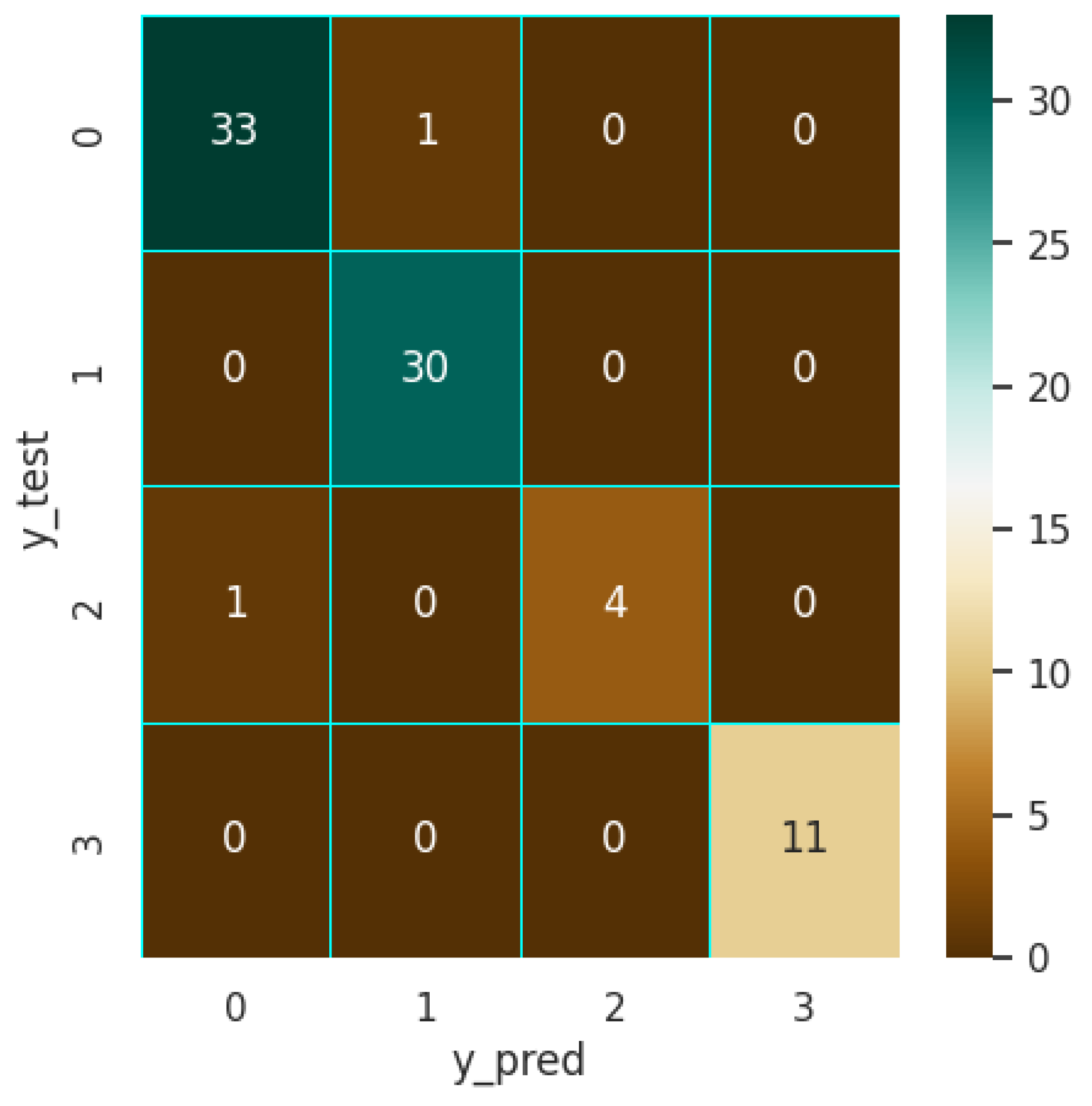
4.2.1. XGB Model
4.2.2. SVM Model
4.2.3. MLP Model
5. Conclusion and Suggestion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassif, A.B.; et al. Machine learning for cloud security: A systematic review. 2021, 9, 20717–20735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, U.A.; et al. A review of machine learning algorithms for cloud computing security. 2020, 9, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A.; et al. Securing machine learning in the cloud: A systematic review of cloud machine learning security. 2020, 3, 587139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhamare, D.; et al. Feasibility of supervised machine learning for cloud security. In 2016 International Conference on Information Science and Security (I.C.I.S.S.). 2016. IEEE.
- O'Donovan, P.; et al. A comparison of fog and cloud computing cyber-physical interfaces for Industry 4.0 real-time embedded machine learning engineering applications. 2019, 110, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, A. Emerging security challenges in cloud computing: An insight into cloud security challenges and their mitigation. In 2011 World Congress on Information and Communication Technologies. 2011. IEEE.
- Hassan, W.; et al. Cloud computing survey on services, enhancements, and challenges in the era of machine learning and data science. 2020, 9, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Goyal, R.J.C.S.R. On cloud security requirements, threats, vulnerabilities, and countermeasures: A survey. 2019, 33, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ige, T.; Sikiru, A. Implementation of data mining on secure cloud computing over a web API using a supervised machine learning algorithm. In Artificial Intelligence Trends in Systems: Proceedings of 11th Computer Science On-line Conference 2022, Vol. 2. 2022. Springer.
- Khalid, A.; et al. Understanding vulnerabilities in cyber-physical production systems. 2022, 35, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.-P.A.; et al. Robotics cyber security: Vulnerabilities, attacks, countermeasures, and recommendations. 2022: P. 1-44.
- Achar, S.J.I.J.o.C.; Engineering, S. Cloud Computing Security for Multi-Cloud Service Providers: Controls and Techniques in our Modern Threat Landscape. 2022, 16, 379–384. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth, S.; et al. Application of cloud computing in banking and e-commerce and related security threats. 51 2022, 51, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsmadi, I.; et al. Vulnerability assessment of industrial systems using Shodan. 2022, 25, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahariev, P.; et al. A review of the main characteristics and security vulnerabilities of the wireless communication technologies in the Industry 4.0 domain. In 2022 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media, and Technology with E.C.T.I. Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering (ECTI DAMT & N.C.O.N.). 2022. IEEE.
- Karunasingha, D.S.K.J.I.S. Root mean square error or mean absolute error? Use their ratio as well. 2022, 585, 609–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, Z.J.S.; Networks, C. Hierarchical network security measurement and optimal proactive defense in cloud computing environments. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwandu, E.; et al. Cyber-security challenges in the aviation industry: A review of current and future trends. 2022, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, H.; et al. Security and privacy challenges in cloud computing environments. 2010, 8, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, E., L.J.S.O.C. Tamilselvan, and Applications. A focus on the future cloud: Machine learning-based cloud security. 2019, 13, 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; et al. Design of network threat detection and classification based on machine learning on cloud computing. 2019, 22, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V., Verma, V.; Sharma, A. Detection of DDoS attacks using machine learning in cloud computing. In Advanced Informatics for Computing Research: Third International Conference, I.C.A.I.C.R. 2019, Shimla, India, June 15–16, 2019, Revised Selected Papers, Part II 3. 2019. Springer.
- Kwabena, O.-A.; et al. Mscryptonet: Multi-scheme privacy-preserving deep learning in cloud computing. 2019, 7, 29344–29354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; et al. M.L.P.A.M.: A machine learning and probabilistic analysis based model for preserving security and privacy in a cloud environment. 2020, 15, 4248–4259. [Google Scholar]
- Thakkar, A. R.J.A.o.C.M.i.E. Lohiya, A review on machine learning and deep learning perspectives of I.D.S. for IoT: Recent updates, security issues, and challenges. 2021, 28, 3211–3243. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.S.S., Wicker, A.; Swann, M. Practical machine learning for cloud intrusion detection: Challenges and the way forward. In Proceedings of the 10th A.C.M. Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security. 2017.
- Chkirbene, Z.; et al. Machine learning based cloud computing anomalies detection. 2020, 34, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; et al. A Static Machine Learning Based Evaluation Method for Usability and Security Analysis in E-Commerce website. 2023.
- Kandi, P.; et al. A Review: Data Security in Cloud Computing Using Machine Learning. in 2022 5th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I). 2022. IEEE.
- Mohammad, A.S. , Pradhan, M. R.J.C.; Engineering, E., Machine learning with big data analytics for cloud security. 2021, 96, 107527. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon, R.L. Psaltis, A., The future of cloud computing in financial services: A machine learning and artificial intelligence perspective, in The Essentials of Machine Learning in Finance and Accounting. 2021, Routledge. p. 123-138.
- Kaur, K.; Zandu, V. , A secure data classification model in cloud computing using machine learning approach. International Journal of Grid and Distributed Computing, 2016, 9, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, T.; et al. Machine learning for anomaly detection and categorization in multi-cloud environments. in 2017 IEEE 4th international conference on cyber security and cloud computing (CSCloud). 2017. IEEE.
- Marwan, M.; Kartit, A.; Ouahmane, H. Security enhancement in healthcare cloud using machine learning. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 127, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian; Tamilselvan, L. A focus on the future cloud: Machine learning-based cloud security. Service Oriented Computing and Applications, 2019, 13, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena; Rangarajan, P. A machine learning application for reducing the security risks in hybrid cloud networks. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2020, 79, 5161–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang; Lu, Y.; Qin, J. A dynamic MLP-based DDoS attack detection method using feature selection and feedback. Computers & Security, 2020, 88, 101645. [Google Scholar]
- Haseeb, K.; et al. Efficient data uncertainty management for industrial health internet of things using machine learning. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2021, 34, e4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharif, M.; Rawat, D.B. Study of machine learning for cloud-assisted iot security as a service. Sensors, 2021, 21, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangui, H.; Ge, M.; Buhnova, B. A hybrid machine learning model for intrusion detection in V.A.N.E.T. Computing, 2022, 104, 503–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; et al. A Bayesian Q-learning game for dependable task offloading against DDoS attacks in sensor edge cloud. 2020, 8, 7546–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; et al. Privacy-preserving federated deep learning for cooperative hierarchical caching in fog computing. 2021, 9, 22246–22255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.S.; Pradhan, M.R. Machine learning with big data analytics for cloud security. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2021, 96, 107527. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, N.; et al. Qos-based cloud security evaluation using the neuro-fuzzy model. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2022, 70, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Bagaa, M.; et al. A machine learning security framework for IoT systems. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 114066–114077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetic, Z. , Hajdarevic, K.; Dogru, N. Cloud computing threats classification model based on the detection feasibility of machine learning algorithms. In 2017 40th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (M.I.P.R.O.). 2017. IEEE.
- Vora, U.; et al. Machine Learning–Based Security in Cloud Database—A Survey. Machine Learning Techniques and Analytics for Cloud Security, 2021: P. 239-269.
- Fontaine, J.; et al. Log-based intrusion detection for cloud web applications using machine learning. In Advances on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing (3PGCIC-2019) 14. 2020. Springer.
- Aboueata, N.; et al. Supervised machine learning techniques for efficient network intrusion detection. In 2019 28th International Conference on Computer Communication and Networks (I.C.C.C.N.). 2019. IEEE.
- Auria, L.; Moro, R.A. , Support vector machines (SVM) as a technique for solvency analysis. 2008.
- Xinfeng, Z.; Yan, Z. , Application of support vector machine to reliability analysis of engine systems. TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2013, 11, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, R.S., Carbonell, J.G.; Mitchell, T.M., Machine learning an artificial intelligence approach. 1984: Springer.
- Pandeeswari, N.; Kumar, G. Anomaly detection system in cloud environment using fuzzy clustering based ANN. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2016, 21, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, S.A.; Muniyandi, A.P. Secure authentication schemes in cloud computing with a glimpse of artificial neural networks: A review. Cyber Security and Applications, 2023, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.J.; De, T. MLP-GA based algorithm to detect application layer DDoS attack. Journal of information security and applications, 2017, 36, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahakonye, L.A.C.; et al. Efficient classification of enciphered SCADA network traffic in a smart factory using decision tree algorithm. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 154892–154901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, T.; Moon, J. , A hybrid machine learning approach to network anomaly detection. Information Sciences, 2007, 177, 3799–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, M.; et al. A hybrid machine learning approach for malicious behavior detection and recognition in cloud computing. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 151, 102507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddabachigari, S.; Abraham, A.; Thomas, J. Intrusion detection systems using decision trees and support vector machines. International Journal of Applied Science and Computations, U.S.A., 2004, 11, 118–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zimba, A.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Bayesian network-based weighted A.P.T. attack paths modeling in cloud computing. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2019, 96, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Jiang, D.; Lv, Z. Modeling network traffic for traffic matrix estimation and anomaly detection based on Bayesian network in cloud computing networks. Annals of Telecommunications, 2017, 72, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Leisch, F.; Hornik, K. The support vector machine under test. Neurocomputing 2003, 55, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussila, S. , Worksite data analysis using cloud services for machine learning. 2019.
- Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. , Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. 7 (December). 2013. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree-boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd A.C.M. signed international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. 2016.
- Nielsen, D.J.N.U.o.S. , and Technology, Tree boosting with XGBoost. 2016.
- Bellafqira, R.; et al. Secure multilayer perceptron based on homomorphic encryption. In Digital Forensics and Watermarking: 17th International Workshop, I.W.D.W. 2018, Jeju Island, Korea, October 22-24, 2018, Proceedings 17. 2019. Springer.
- Guezzaz, A.; et al. A distributed intrusion detection approach based on machine learning techniques for cloud security, in Intelligent Systems in Big Data, Semantic Web and Machine Learning. 2021, Springer. p. 85-94.
- Rai, A.K.; Dwivedi, R.K. Fraud detection in credit card data using machine learning techniques. In Machine Learning, Image Processing, Network Security and Data Sciences: Second International Conference, MIND 2020, Silchar, India, July 30-31, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 2. 2020. Springer.
- Jupalle, H.; et al. Automation of human behaviors and its prediction using machine learning. Microsystem Technologies, 2022, 28, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sr No. | Survey Questions |
|---|---|
| 1. | How familiar are you with cloud computing security and machine learning? |
| 2. | Have you or your organization implemented any cloud computing security measures in your operations? |
| 3. | What are the biggest security concerns you have about cloud computing? |
| 4. | How do you think ML can be used to improve cloud computing security? |
| 5. | How confident are you in the effectiveness of current cloud computing security measures? |
| 6. | In your opinion, what are the biggest challenges in implementing effective cloud computing security? |
| 7. | How often do you or your organization conduct security assessments or audits for cloud computing systems? |
| 8. | What role do you think human factors play in cloud computing security? |
| 9. | What measures do you think cloud service providers should take to improve the security of their offerings? |
| 10. | How do you think regulations and compliance requirements affect cloud computing security? |
| 11. | How can organizations ensure their cloud service providers comply with security standards and regulations? |
| 12. | How do you think increasing Internet of Things (IoT) devices affect cloud computing security? |
| 13. | How effective do you believe machine learning has improved the security of your industry's cloud computing operations? |
| 14. | How important is security in your industry's cloud computing operations? |
| 15. | What are your future plans for using machine learning in cloud computing security in your industry? |
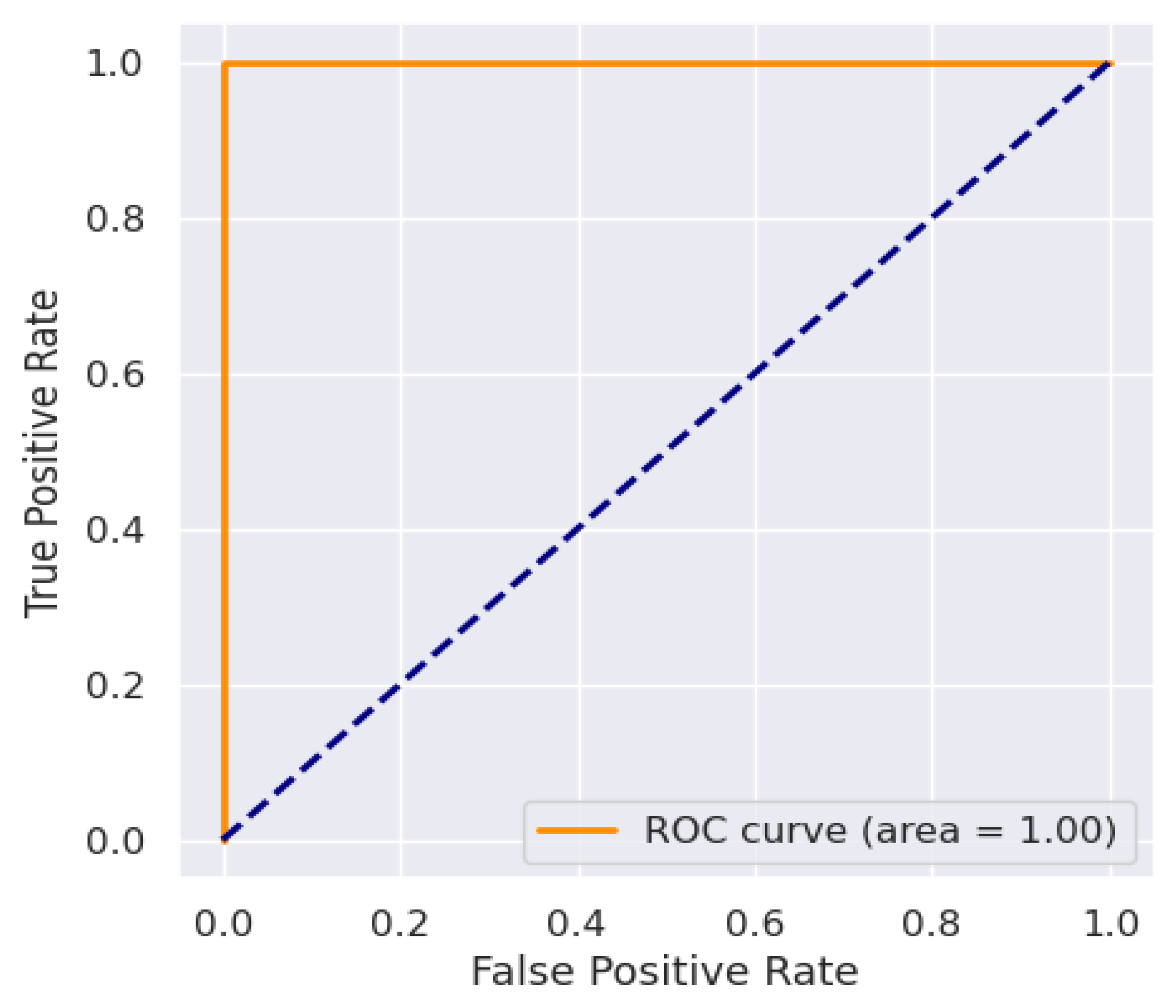
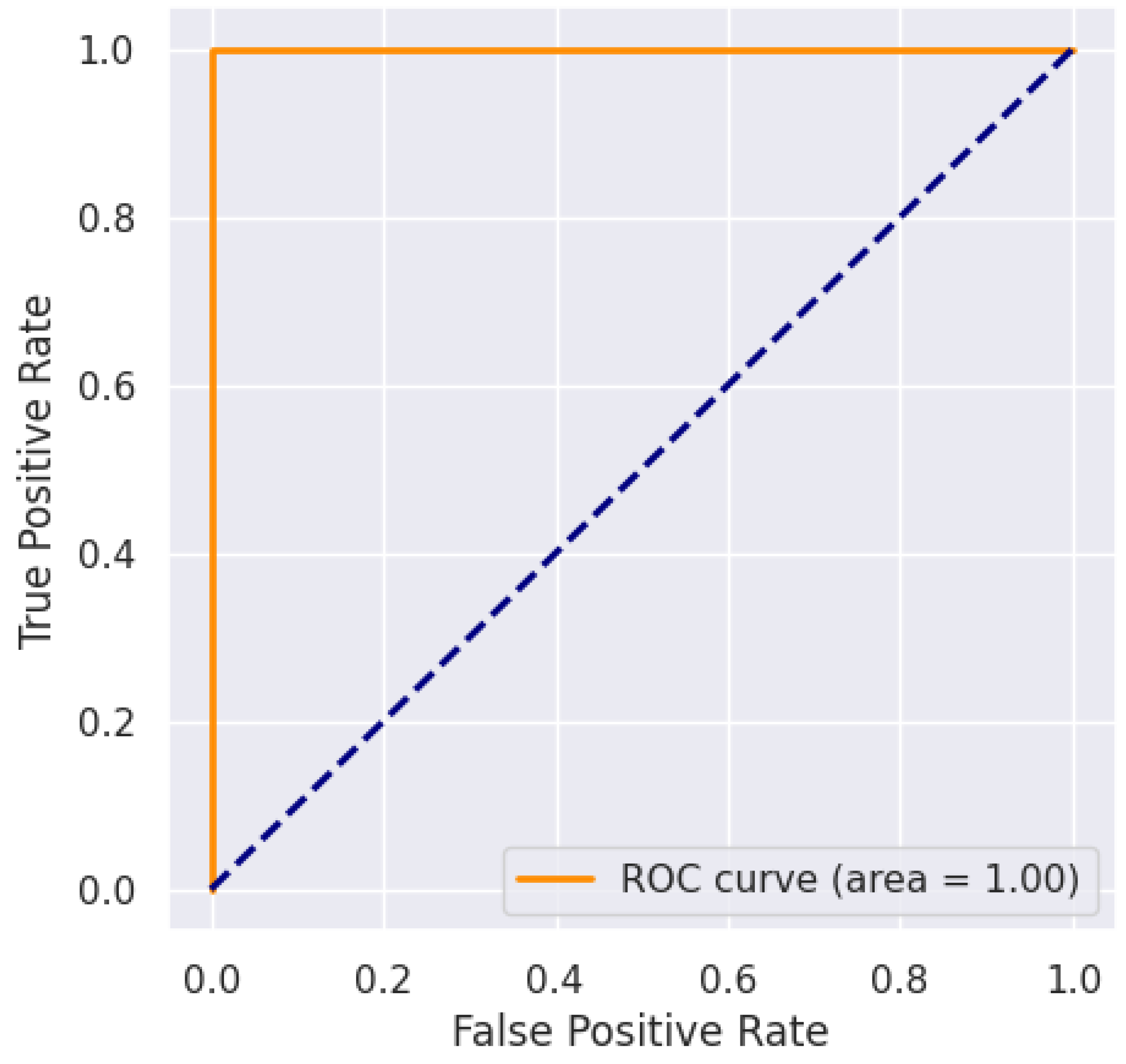
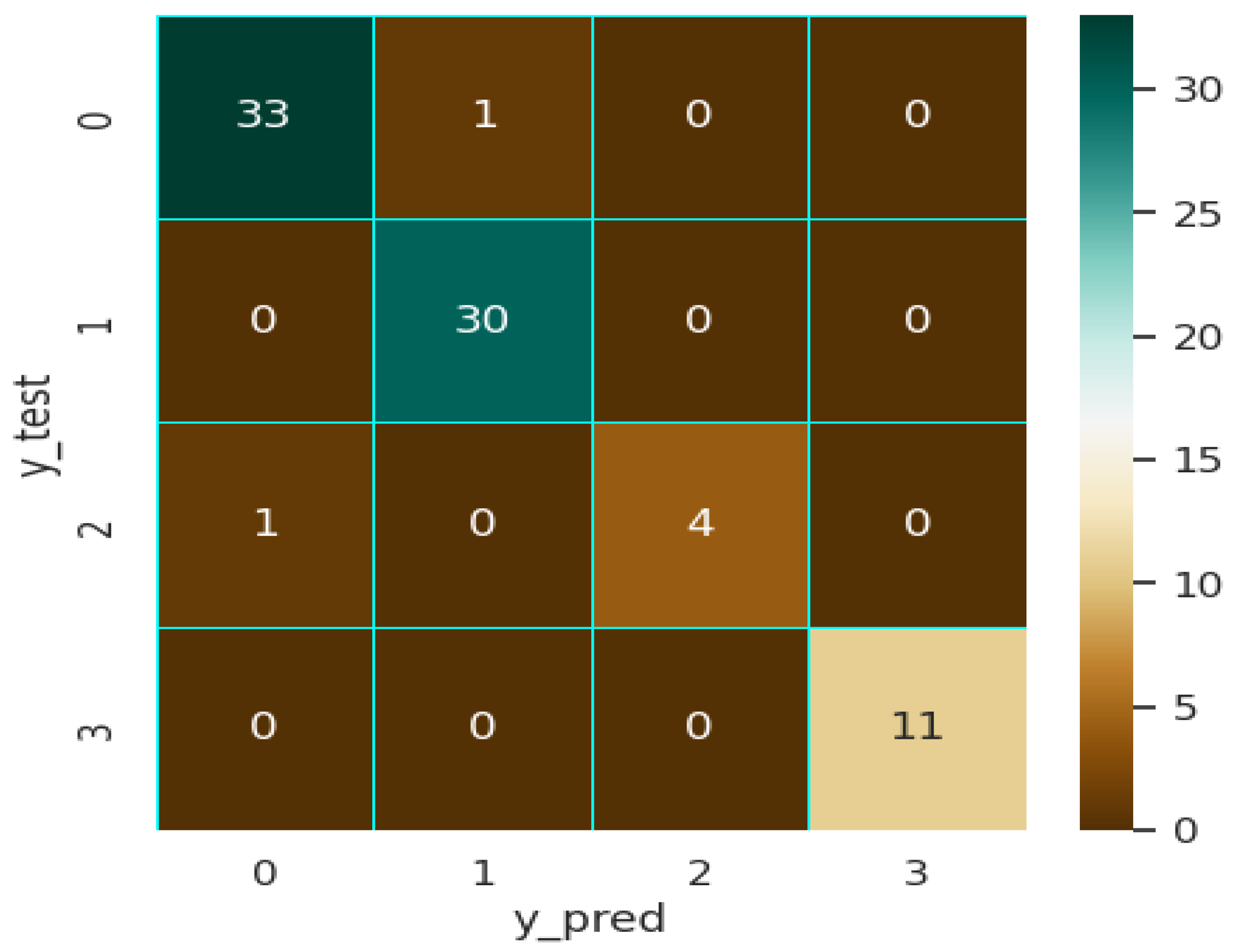
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-score | ROC-AUC |
| XGB | 97.50 | 97.60 | 97.60 | 97.50 | 1 |
| SVM | 97.35 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 97.30 | 1 |
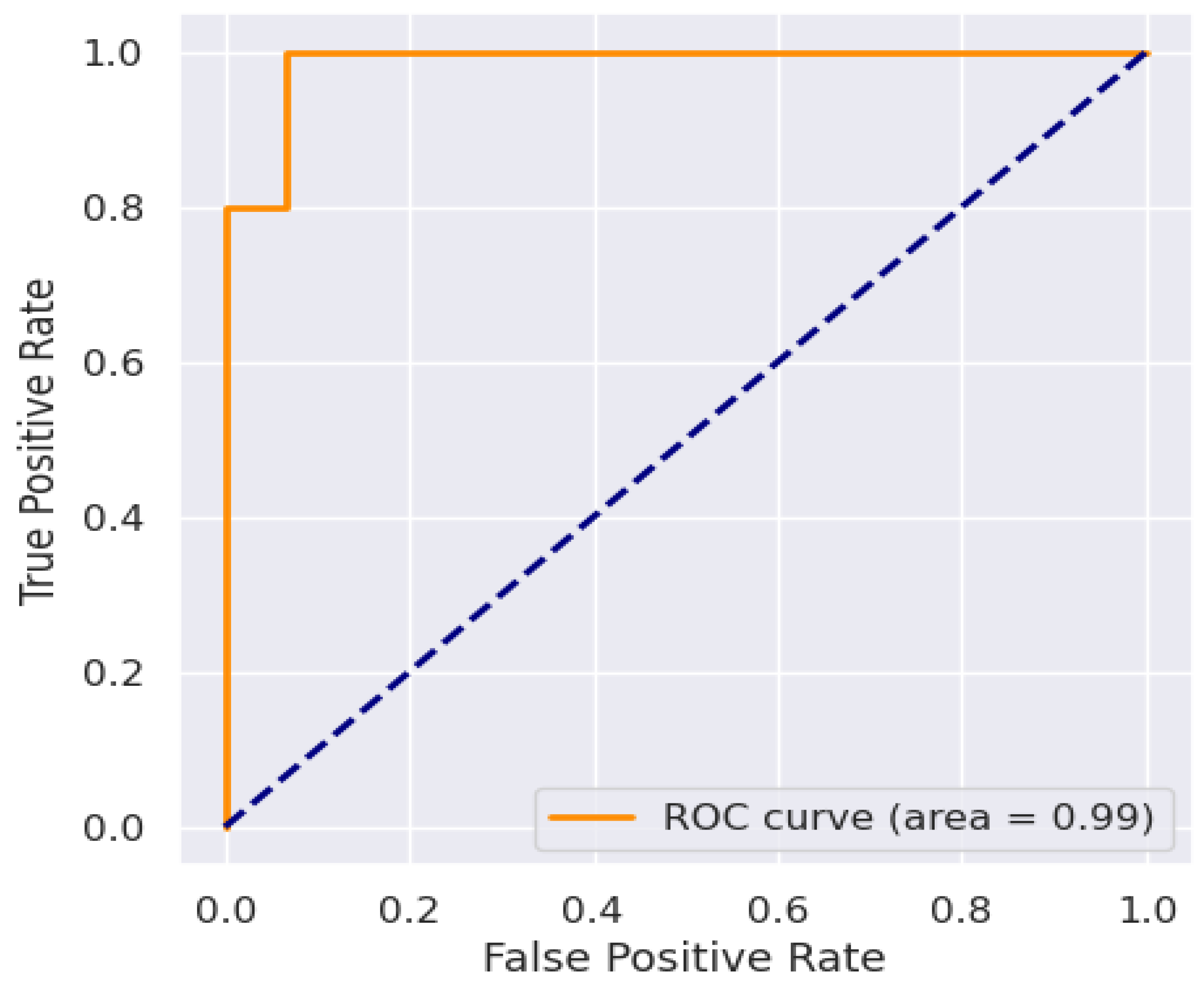
| MLP | 96.20 | 96.21 | 96.20 | 96.20 | 99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





