1. Introduction
Rice blast is a major disease caused by
Magnaporthe oryzae in rice-growing regions worldwide. Rice panicle blast is of particular concern because it is directly correlated with yield loss and quality decline. In Japan, rice production focuses on high-eating-quality varieties, such as ‘Koshihikari’, ‘Hitomebore’, ‘Hinohikari’, ‘Akitakomachi’, and ‘Nanatsuboshi’; however, these varieties have poor resistance to blast, which contributes to disease occurrence and increases the difficulty of controlling the disease [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Despite the use of fungicides as prophylactics to prevent damage, panicle blast damage persists (
Figure 1A). Breeding resistant varieties is an effective, economical, and environmentally friendly integrated pest management (IPM) technology that can reduce rice blast damage and pesticide use, contributing to the achievement of the sustainable development goals (SDGs) [
5,
6,
7]. In Japan, two methods have been used for rice blast-resistant breeding: introducing true resistance, which is a type of qualitative resistance expressed by a major gene from foreign rice varieties, and introducing field resistance, which is a type of quantitative resistance expressed by a minor gene or polygene from upland rice varieties. Although true resistance is relatively easy to introduce, it is unstable because resistance often collapses within a few years after the dissemination of true-resistant varieties. Moreover, field resistance is generally more stable and less susceptible to resistance collapse; however, it is challenging to introduce and integrate all field resistance genes into one commercial variety while eliminating defective traits, such as poor eating quality associated with upland rice, using conventional breeding techniques [
8,
9,
10].
The discovery of genes that express quantitative resistance (herein referred to as ‘field resistance’) and development of DNA markers closely linked to these genes are carried out since the 1990s. [
11,
12,
13]. DNA marker-assisted selection (MAS) of genes that express high-field resistance, such as
Pb1 (
panicle blast resistance 1),
pi21,
Pi35, and
Pi39, has been increasingly utilised in breeding [
14,
15,
16,
17]. A recent example is the ‘Mineasahi SBL’ variety, which is highly resistant to rice blast and contains both the
Pb1 and
Pi39 genes, which is widely distributed in the mid-mountainous areas of Aichi Prefecture (
Figure 2) [
18]. In this review, we discuss the long-term durability of high field resistance to rice blast expressed by the
Pb1 gene, which has remained effective in a wide range of rice paddy fields in Japan for over 40 years. This discussion is based on findings from breeding, genetics, molecular genetics, and epidemiological studies. We summarise the results obtained from these fields of study and discuss the sustainable use of major genes expressing high field resistance to rice blast.
2. Classification of Rice Resistance to Blast Disease: True Resistance and Field Resistance
Rice blast resistance can be classified into two types: true/complete/qualitative resistance, which is race-specific and expressed by a major resistance (R) gene; and field resistance, which is race-non-specific and expressed by multiple microgenes. True resistance shows a hypersensitive response (HR) accompanied by hypersensitive cell death, whereas field resistance does not show this HR [
19,
20]. Although true resistance is highly effective against blast disease, it is unstable owing to the potential for resistance breakdown. In contrast, field resistance involving multiple polygenes is generally more stable and less prone to collapse. This type of resistance is called horizontal resistance [
21,
22,
23], and it has been extensively studied in upland rice.
3. True Resistance and Its Breeding Application in Rice Blast Disease Management
The NBS-LRR and R genes, which encode proteins with similar structures, exhibit specificity for the blast race [
24,
25,
26], which exerts strong ‘selection pressure’ on the blast population that does not have an affinity for the true resistance gene. This pressure results in the development of ‘complete resistance’, which means that susceptible lesions do not occur on rice leaves in areas where true resistance varieties are cultivated. However, true resistance is limited to a specific blast race [
6,
27,
28]. Thus, the emergence of a blast race compatible with true resistance may lead to the proliferation and rapid spread of the blast race in the blast population. This phenomenon is known as ‘resistance collapse’ or ‘breakdown of resistance’, and it has been observed repeatedly in rice varieties carrying true blast resistance genes, where a blast race with an affinity for the true resistance gene spreads in a rice-growing region only a few years after its dissemination, resulting in severe damage from rice blast [
29,
30,
31].
Several attempts have been made to accumulate multiple true blast-resistance genes in one variety to avoid resistance collapse [
32,
33,
34]. However, a severe outbreak of panicle blast was observed in ‘Hama-Asahi, ’ a rice cultivar which integrates four true resistance genes (
Pib,
Pik,
Pii, and
Pia), in the first year after its introduction in the panicle blast test plot at the Mountainous Region Agricultural Institute, Aichi Prefectural Agricultural Research Centre (
Figure 1B), which provided an experimental field suitable for the growth of the blast fungus (Fujii, personal communication). The ‘Unification’ series of Japonica-Indica varieties that were jointly developed by Korea and IRRI accumulated multiple true blast resistance genes, had high yields, and were initially popular in South Korea [
35]. However, these varieties were severely damaged by rice blast years after their dissemination, and their cultivation was ceased [
35].
In Niigata and other prefectures, efforts are being made to use multiline varieties with true blast resistance to avoid the breakdown of blast resistance when the true resistance gene is expressed [
36,
37]. The ‘Koshihikari Niigata BL’ group of Koshihikari homologous multilines includes the
Pia, Pii, Pita-2, Piz, Pik, Pik-m, Piz-t, Pib, Pib+Pia, Pib+Pii, Piz-t+Pii, Piz-t+Pik, and
Pit lines [
37,
38,
39]. This multiline is produced by mixing two susceptible (30%) and two resistant lines (70%), and it is grown throughout Niigata Prefecture since 2005. Further to being extremely successful in reducing blast damage, it has reduced the application of blast control chemicals by 70% and avoided the breakdown of true resistance [
38].
Multiline rice varieties have been proposed as a solution for blast control. However, to effectively utilise multiline varieties, a substantial number of homogeneous rice blast resistance genes must be generated and strict management of the maintenance and breeding of multiple homogeneous lines is required. This includes confirming the true resistance genotypes using DNA markers and purity tests. Furthermore, the continuous and systematic monitoring of race distribution within the blast fungus population in areas where multiline cultivars are grown is necessary. The production of multiline varieties also incurs significant labour and operational costs, particularly for seed production and monitoring during dissemination. Therefore, these issues must be addressed to fully realise the potential of multiline varieties for blast control. Additionally, integrating blast field resistance into multiline varieties remains a challenge to be addressed.
4. Field Resistance and Its Use in Breeding for Rice Blast Resistance
Field resistance in rice is controlled by multiple microgenes expressing quantitative resistance as a ‘polygene’ [
40], and it is generally non-specific to various blast races and has been considered a durable resistance type [
41,
42] that does not collapse over time due to the absence of specificity to a blast race/strain/isolate that attacks field resistance [
22]. However, owing to the complexity of multiple micro-acting genes (quantitative trait loci: QTLs) that express field resistance, it is challenging to identify individual QTLs through differences in disease severity in field tests. To effectively breed rice for blast resistance using field resistance, it is necessary to identify the major gene that controls high field resistance and exerts strong suppressive effects against rice blast, develop a DNA marker closely linked to the high field resistance gene, and establish a breeding method using MAS. Until these advancements are made, breeding efforts for rice blast resistance using field resistance will be limited to a few specialized institutes, such as the Tohoku Agricultural Research Centre of the National Agricultural Research Organization and the Mountainous Regional Agricultural Institute of Aichi Prefectural Agricultural Research Centre, which have favourable weather conditions for leaf and panicle blast development [
43,
44].
5. Paradigm Shift in the Concept of Blast Field Resistance
Blast field resistance has traditionally been considered quantitative resistance, in which multiple microgenes are expressed as polygenes. However, recent progress in rice genome research has led to the identification of individual rice QTLs that express quantitative resistance with strong disease-suppressive effects, such as
Pb1, pi21, Pi34, Pi35, Pi39, and
Pi63, among blast field resistance genes [
14,
15,
16,
17,
45,
46]. Notably,
pi21, Pb1, and
Pi63 have been isolated, and their protein structures have been determined [
47,
48,
49].
Consequently, a single major gene has been shown to express strong quantitative resistance (field resistance) to blast. Advances in molecular genetics have demonstrated the existence of quantitative resistance governed by these major genes, and the traditional definition of field resistance as that ‘expressed by the combined action of multiple microgene sets’ no longer explains the whole picture of field resistance. In other words, a paradigm shift in the concept of field resistance has occurred due to advances in genome research. Therefore, it is necessary to reconstruct the concept of field resistance.
In practical breeding, the use of MAS for rice blast resistance breeding based on quantitative blast resistance governed by major genes is rapidly progressing in Japan [
50,
51,
52,
53]. However, to ensure specificity to the blast fungus race/strain/isolate and the stability and persistence of resistance expression, it is necessary to distinguish between conventional field resistance and highly potent type of quantitative resistance expressed by a major gene. The latter is considered a quantitative resistance, in which a major gene is expressed with high potency.
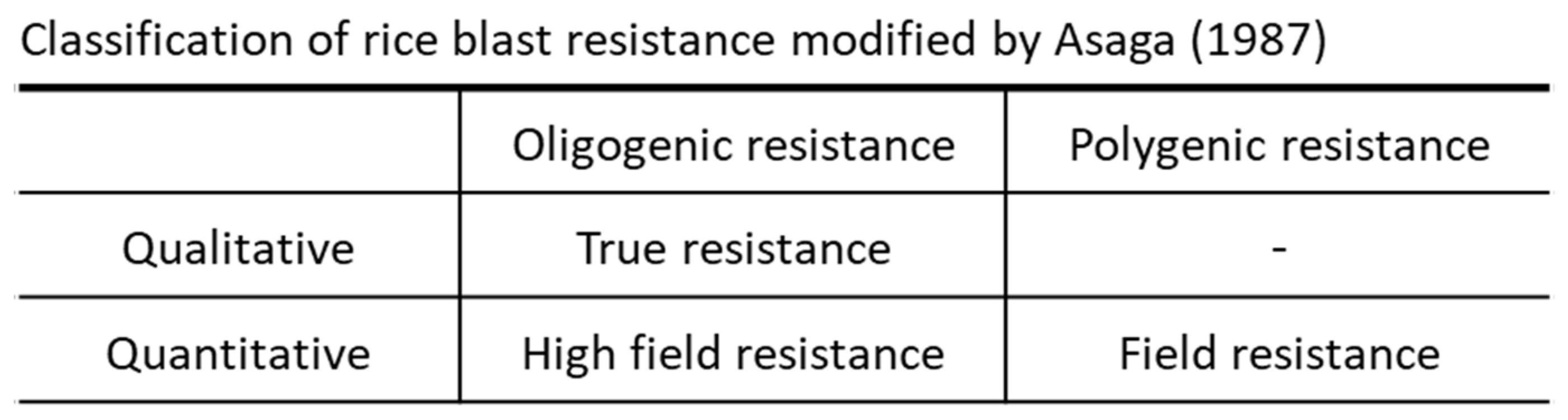
In 1989, Shindo and Asaga proposed a redefinition of quantitative resistance to blast disease based on the discovery of
Pif, a major gene that expresses strong quantitative resistance [
54]. They divided quantitative resistance into two types: one dominated by major acting genes and the other dominated by minor acting genes. The new definition for quantitative resistance dominated by the major acting gene was termed ‘highly potent field resistance’ or ‘high field resistance’, whereas conventional field resistance, which is a quantitative resistance expressed by multiple micro-acting genes, was redefined as 'field resistance in a narrow sense’. Asaga proposed that both types of quantitative resistance be defined together as 'field resistance in a broad sense' (
Table 1).
Although Shindo and Asaga's (1989) redefinition of field resistance to blast disease is a tentative definition that should be re-evaluated in light of the rapid developments in resistance gene research, this review considers quantitative resistance expressed by a major gene with a strong suppressive effect on blast disease development as a type of field resistance known as 'high field resistance'[
54]. This paper reviews the durability of ‘high field resistance’ to rice blast disease conferred by a major gene based on previous findings and discusses the sustainable use of this resistance.
6. Durability of Field Resistance Conferred by Major Gene, which is Highly Effective against Rice Blast Disease
It has been reported that strain specificity occurs during
Pif gene-mediated high field resistance to blast in the
indica rice variety Modan as well as during the leaf blast field resistance of 'Chubu 32' derived from upland rice. In the case of ‘Chubu 32’, the major gene expressing high field resistance to blast
Pi34 has been shown to have obvious strain specificity and establishes a gene-for-gene relationship with the Avr gene of the blast fungus, which is similar to the R gene expressing true resistance [
55,
56,
57]. These findings suggest that resistance genes expressing quantitative resistance may also establish a gene-for-gene relationship with respect to strain specificity if they are specific to individual field resistance genes. In addition, it has been reported that field resistance is also strain-specific for ‘Koganenishiki’ and ‘Yamabiko’, which are Japanese rice varieties [
58]. Furthermore, the high field resistance gene
Pi63 carried by the upland rice variety 'Jiapei' encodes a CC-NBS-LRR protein and has clear strain specificity. There are further reports on rice cultivars, QTLs, or R genes conferring field resistance (partial resistance) with specificity to the blast fungus [
59,
60,
61]. These results suggest that field resistance alone does not guarantee non-specificity for various blast strains or durability of the expressed resistance, even for highly potent field resistance genes. Similar reports on race specificity have been published for several resistance genes that quantitatively express resistance to rust in wheat [
41,
44,
57,
58,
62].
7. Pb1 Gene: A Partially Mutated R Gene Structure Conferring Durable Resistance to Panicle Blast in Rice
The
Pb1 gene, which was derived from the
indica rice variety 'Modan' and introduced into Japanese rice cultivars via the rice stripe virus resistant intermediate maternal line 'St No. 1', confers strong field resistance to panicle blast but only moderate field resistance to leaf blast [
63,
64]. The
Pb1 gene is located on the long arm of rice chromosome 11, which is also the location of the rice stripe virus resistance gene
Stvb-i, and the two genes are linked with a recombination value of 5.2% [
14,
64,
65].
Hayashi
et al. revealed that the
Pb1 gene encodes a partial structural variant of R gene with an 'atypical' CC-NBS-LRR structural protein [
48]. The P-loop in NBS is missing, and other structures have been reported to be partially altered. Surprisingly, the
Pb1 gene was found to have a partially mutated R gene structure, making it the principal active gene. The molecular genetic mechanism by which
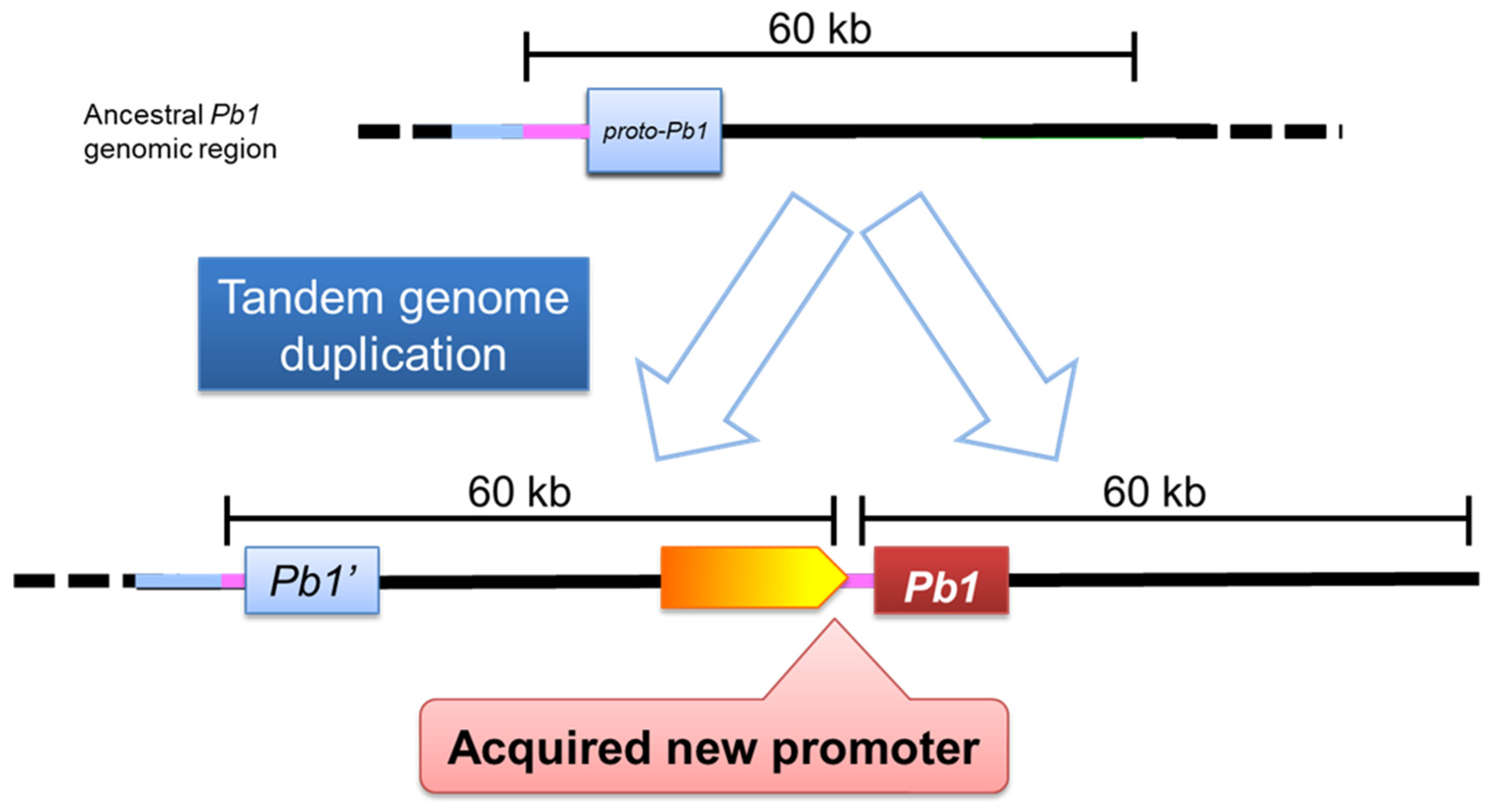
Pb1, originally a ‘non-expressed gene’, led to blast resistance has been revealed to be the duplication of a specific genomic region (
Figure 3) [
48]. The duplication of a 60-kb region resulted in two
Pb1 genes being placed in series, and the
Pb1 gene copied backwards became an 'expressed gene' by the action of a promoter present behind the forward
Pb1 gene, which led to the development of high field resistance to blast (
Figure 4). This study elucidated the 'gene evolution' associated with field resistance [
48].
8. Mechanism of Non-Specific Blast Resistance in the Pb1 Gene and Involvement of WRKY45
As mentioned above,
Pb1 has been identified as a major gene that exhibits an altered R gene structure, and its expression is known to confer resistance to rice blast disease. However, a unique property of
Pb1 is its ability to confer broad-spectrum resistance, which is largely characterised by its non-specificity towards different blast races and strains. Studies have shown that
Pb1-conferred strong field resistance to panicle blast is not only non-specific to different blast races but also exhibits a high level of non-specificity to various strains, including foreign strains [
48]. This broad-spectrum resistance is a major feature of the
Pb1 gene and likely due to the ability of the gene to target a conserved component of the pathogen, which is present in all blast races and strains. The non-specificity of
Pb1 is a highly desirable trait for rice breeders because it provides durable resistance against a wide range of blast races and strains.
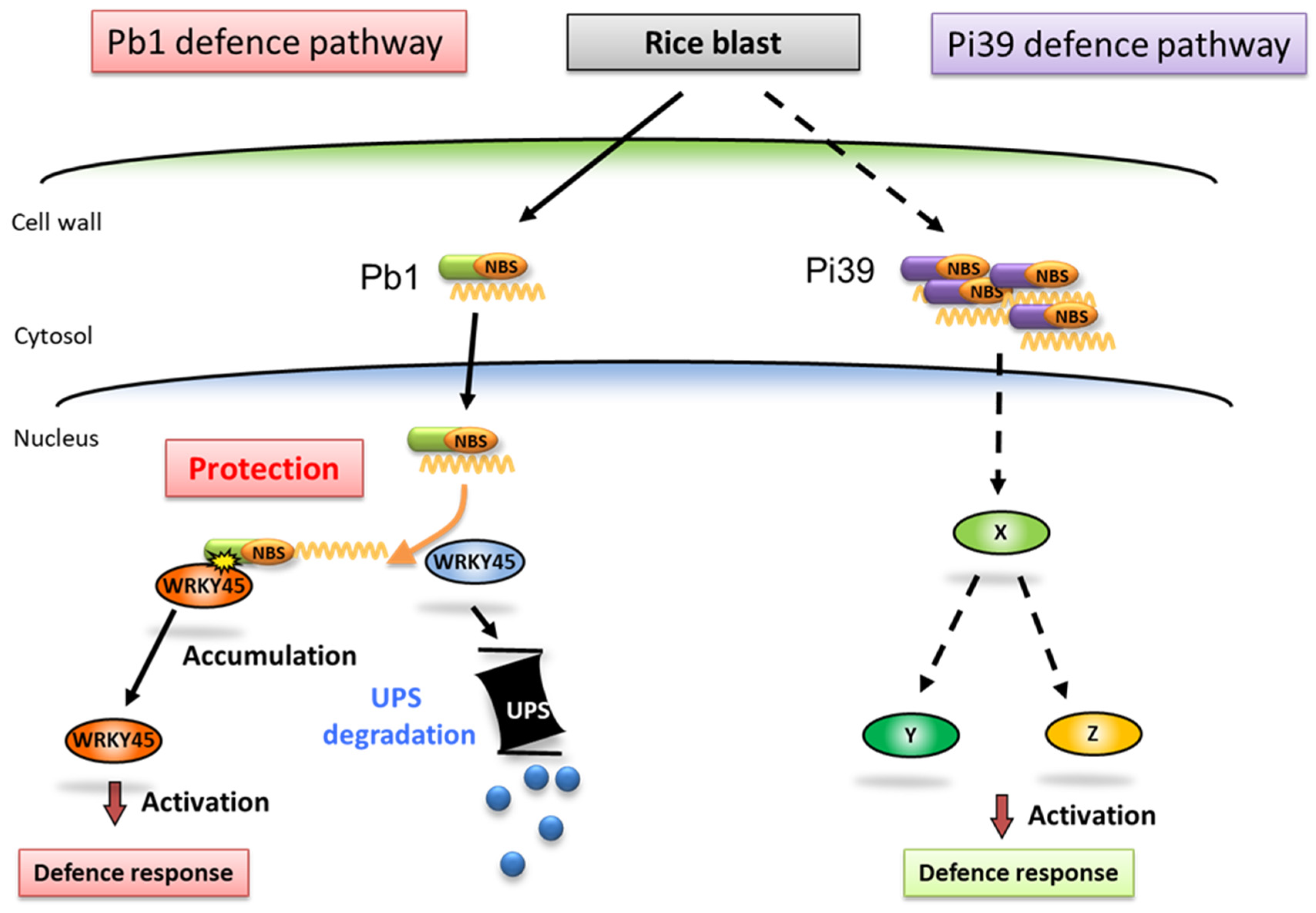
Inoue
et al. (2013) demonstrated that the transcription factor WRKY45 plays a critical role in the regulation of blast resistance by the
Pb1 gene [
66]. They found that Pb1 protein interacts with WRKY45 in the coiled coil (CC) region to suppress the regulatory degradation of WRKY45 by the ubiquitin proteasome [
67], which in turn increases the accumulation of WRKY45 in the cell and enhances blast resistance (
Figure 5). In addition, WRKY45 knockdown significantly weakens the blast resistance of
Pb1-possessing varieties and
Pb1-overexpressing transformants [
68]. While proteins with the CC-NBS-LRR structure derived from the five true blast resistance genes
Pi36,
Pib,
Pita,
Pit, and
Piz-t also bind to WRKY45 in the CC region, the effector-triggered immunity of each of these five genes was reported to be unaffected by WRKY45 [
69], indicating that resistance responses mediated by WRKY45 are highly specific.
The
Pb1 gene exhibits a modified R gene structure, and its protein has a CC-NBS-LRR structure lacking the R gene-like P-loop without showing a typical HR response [
63,
64,
70], indicating that
Pb1 is a true resistance gene that has lost its intrinsic R gene function. The interaction between the Pb1 protein and WRKY45 amplifies blast resistance by suppressing the regulatory degradation of WRKY45, and overexpression of
Pb1 and WRKY45 results in pre-invasion resistance and shows similar resistance responses, supporting the idea that
Pb1 does not act as an R gene [66,68]. These findings strongly suggest that the non-specificity of blast-resistant varieties carrying
Pb1 to various blast strains may be attributed to the indirect expression of blast resistance of the
Pb1 gene via WRKY45.
A detailed look at the difference in the degree of panicle blast disease development between susceptible cultivar ‘Aichinokaori’ without
Pb1 and resistant cultivar NIL ‘Aichinokaori SBL’ with
Pb1 revealed that the differences in disease severity were relatively small in some rice blast strains [
48], indicating that other factors may also play a role in the blast resistance of rice. Therefore, in addition to studying
Pb1 and its interaction with WRKY45, careful observations of affinitive strains that specifically attack
Pb1 are necessary to better understand the complex mechanisms underlying rice blast resistance. Furthermore, it has been reported that 'Matsuribare' [
71], which possesses
Pb1 and exhibits strong field resistance to panicle blast, does not show resistance to bacterial leaf blight, which is caused by a different pathogen, and may develop resistance through the accumulation of WRKY45. Interestingly, 'Matsuribare' shows a 'weak' disease susceptibility response, suggesting that the
Pb1-mediated blast resistance may also involve other defence mechanisms in addition to WRKY45-mediated pathways. This important issue requires further clarification to fully understand the complex interplay between the different defence mechanisms and their contributions to blast resistance in rice.
The complex interactions between the genetic makeup of rice plants and the specific strains of blast fungi encountered in the field can lead to variations in resistance among varieties carrying the same resistance gene. For instance, although the
Pb1 gene has been identified as a key resistance gene against rice panicle blast, some
Pb1-carrying varieties have been found to exhibit weak field resistance to panicle blast. To better understand the mechanisms underlying these differences in resistance, several studies have identified the QTLs associated with the expression of
Pb1. Inoue
et al. (2017) identified four QTLs on chromosomes 7, 8, 9, and 11 that regulate the expression of the
Pb1 gene and proposed a set of expression-regulated QTLs that can stably and strongly express
Pb1. These QTLs were found to differ between the
Pb1-carrying varieties ‘Satojiman’, which has weaker field resistance to panicle blast, and ‘Koshihikari Aichi SBL’ [
72], which has strong field resistance to panicle blast. Similarly, the NRI-bred variety ‘Niji-no -kirameki’, which carries the
Pb1 gene from the weaker-resistant variety ‘Satojiman’, has been found to exhibit significantly stronger field resistance to panicle blast compared with ‘Satojiman’. Nagaoka
et al. (2020) hypothesised that the improved resistance of ‘Niji-no-kirameki’ may be due to recombination of the QTLs identified by Inoue
et al. (2017) in the genetic background of the
Pb1 donor variety. These findings suggest that a better understanding of the genetic factors underlying resistance to rice blast and careful observations of the occurrence of affinitive strains that specifically attack
Pb1 are crucial for developing rice varieties with robust resistance to this devastating disease.
9. Exploring the Mechanisms of Adult Plant Resistance in Rice with the Pb1 Gene
The identification of genes that contribute to rice blast resistance has been a major focus of research. The
WRKY45 gene was found to be involved in the regulation of defence genes in response to blast fungus infection [
73]. A study of the genetic basis of resistance to rice blast found that resistance to leaf blast was associated with the accumulation of WRKY45 [
68].
Although the Pb1 gene was shown to confer strong field resistance to panicle blast, it does not confer strong resistance to leaf blast, suggesting that different types of resistance mechanisms are involved in both cases [48,63]. Field tests using rice NILs for Pb1 and RNA expression studies during different developmental stages of rice plants have shown that Pb1 confers adult plant resistance (APR) to rice blast [1,48]. Recent studies have shown that the field resistance of the glutinous rice variety 'Miyazakimochi' to rice blast is also associated with APR, which is similar to Pb1-bearing varieties. However, the qPbm11 QTL, which is responsible for the resistance of 'Miyazaki Mochi' to panicle blast, is different from Pb1 and acts in a WRKY45-independent manner [74,75]. These findings suggest that different genetic mechanisms are involved in resistance to panicle blast and leaf blast in rice, and that the regulation of WRKY45 and QTLs may play important roles in the expression of blast resistance.
10. Sustainability of Pb1-Mediated Field Resistance to Panicle Blast
Durable resistance, as defined by Johnson (1981, 1984), is characterised by the ability to maintain disease suppression effects under disease-favourable conditions and observation in a wide range of resistant varieties over an extended period of time. To assess whether the resistance conferred by a disease resistance gene qualifies as durable resistance, it is necessary to evaluate the stability of resistance expression, including the occurrence of resistance breakdown, through demonstration trials conducted over a prolonged period on large plots in farmers' fields in different regions [
42]. Although this criterion is time consuming, it remains a fundamental principle that is still relevant today and has been cited extensively.
A CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF DURABLE RESISTANCE: Durable resistance is a resistance that remains effective during its prolonged and widespread use in an environment favorable to the disease. The test for durable resistance must include two elements, time (long) and area (large). Resistance in a cultivar cannot justifiably be described as durable if the cultivar has been grown only in small-scale experiments, even if such tests are repeated at many locations and over several or many years. Experience shows that resistance that survives such tests may nevertheless not survive widespread use under agricultural conditions. Nor can resistance be described as durable if it has only been used briefly, even though on a large area [
42].
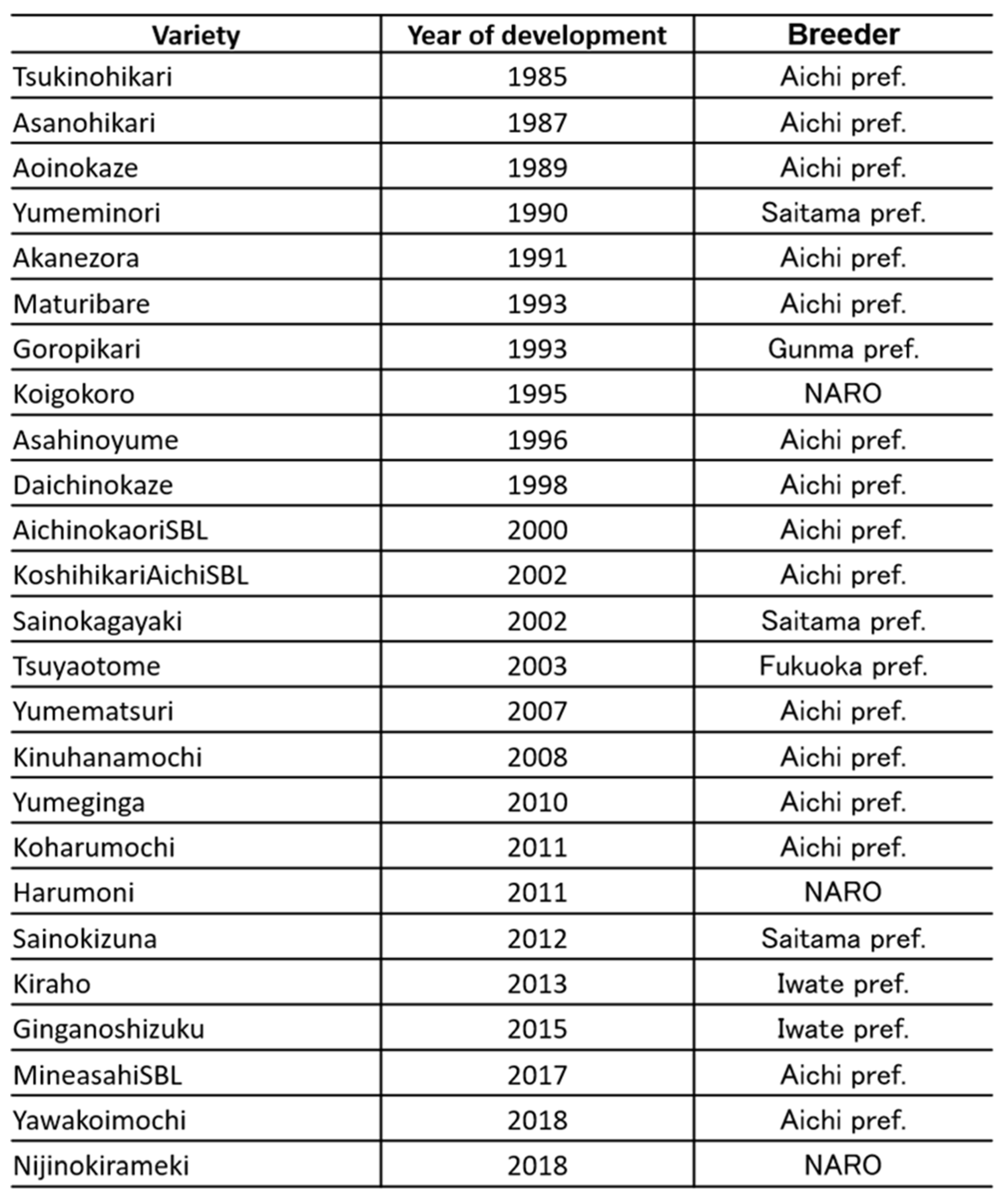
A series of rice varieties with high field resistance to panicle blast conferred by the
Pb1 gene, including ‘Hoshinohikari’, ‘Aoisora’, ‘Tsukinohikari’, ‘Asanohikari’, ‘Matsuribare’, ‘Akanezora’, ‘Asahinoyume’, ‘Aoinokaze’, ‘Daichinokaze’, ‘Aichinokaori SBL’, ‘Sainokagayaki’, ‘Goropikari’, ‘Yumematsuri’, ‘Sainokizuna’, ‘Koshihikari Aichi SBL’ and ‘Niji-no-kirameki’, has been cultivated in farmers' paddy fields in the Kanto and Tokai regions of Japan for over 40 years [1,63]. These varieties have been expressing strong and continuous field resistance to panicle blast for more than 40 years and have been used as parent materials for breeding rice varieties with blast resistance in many rice breeding institutions in Japan (
Table 2) [50,51]. Furthermore, blast strains with high affinity for the
Pb1 gene have not resulted in the breakdown of resistance in farmers’ fields to date, leading to the recognition of durable resistance of this gene in Japan based on Johnson's criteria. Recently, the
Pb1 gene has also been used for blast-resistance breeding in Korea, where it has expressed strong field resistance to panicle blast in the southern part of the country [
76].
The durability of the resistance expressed by the Pb1 gene and the occurrence of resistance breakdown in countries other than Japan and Korea have yet to be explored. The worldwide stability and persistence of high-field resistance to panicle blast mediated by Pb1 also requires further investigation. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct studies that evaluate the durability of Pb1-mediated resistance in other global regions. This research will enhance our understanding of the stability of Pb1 gene-mediated resistance to panicle blast, which is essential for the development of sustainable strategies for blast disease management.
11. Uncovering the Epidemiological Mechanisms for the Persistent Resistance of Pb1-Conferred High Field Resistance to Panicle Blast
APR has been proposed to be the epidemiological mechanism responsible for the lack of breakdown of the highly potent field resistance to panicle blast expression of the Pb1 gene. The Pb1 gene provides only moderate quantitative resistance to leaf blast and exerts low selection pressure on the blast fungus population at the leaf blast stage. Consequently, the selective growth and spread of blast strains with a specific affinity for the Pb1 gene are hindered because of the low selective pressure for the affinitive strain that specifically attacks Pb1 at the leaf blast stage. This mechanism has resulted in the long-standing non-collapse of resistance to panicle blast conferred by the Pb1 gene over the past 40 years [1,63]. This hypothesis is supported by subsequent studies conducted by other investigators [45,48].
In a recent study, Zenbayashi (2007) reported that the number of times the blast fungus can change generations before rice harvest is limited after the panicle emergence stage, which is when the
Pb1 gene develops strong quantitative resistance to rice panicle blast. This insufficient number of generations is not conducive to the selective multiplication and spread of affinitive strains that specifically attack
Pb1, thus leading to a bottleneck effect. This bottleneck effect, in which the number of
Pb1-compatible strains is drastically reduced by seed disinfection the following year, is another epidemiological mechanism underlying the lack of selection and spread of
Pb1-specific affinitive strains. Similarly, the wheat disease resistance gene
Lr34, which encodes an ABC transporter with a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) in the plasma membrane, has shown stable and durable resistance against rust and powdery mildew in wheat cultivars worldwide, with no breakdown observed for more than 50 years.
Lr34-carrying wheat cultivars have been reported to express APR against these diseases, which is similar to the expression of APR by
Pb1, indicating that high-level field resistance without long-term collapse is a common feature of APR expressed by differently structured major genes [
77,
78,
79].
Probenazole, an agrochemical used in rice cultivation for over 45 years, has not caused any rice blast resistance outbreaks to date [
80,
81,
82,
83]. Despite having no fungicidal activity against the blast fungus, probenazole acts as a plant activator [
66] by inducing the biosynthesis of salicylic acid in rice plants, which then induces the expression of WRKY45 and OsNPR1 [84, 85]. The
Pb1 gene plays a role in suppressing the regulatory degradation of WRKY45 in rice and promoting its accumulation, which results in high field resistance to blast disease [66, 68, 86]. WRKY45 also regulates the expression of 260 defence genes encoding PR proteins and ABC transporters [
87]. The activation of WRKY45 is regulated by the cooperation between MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation [
88]. Therefore, the long-term absence of the breakdown of
Pb1-mediated high-field resistance may also be attributed to the indirect mechanism of blast resistance via WRKY45. This
Pb1 strategy for indirect control of rice blast is similar to that of probenazole [
82]. In conclusion, we confirmed the importance of maintaining the race and strain diversity of rice blast fungus populations, especially during the leaf blast stage, to avoid the breakdown of resistance when using resistance gene(s) for blast disease management in rice cultivation.
12. Challenges in Demonstrating the Durability of High Field Resistance Genes other than Pb1 Against Blast
Several high field resistance genes to blast have been identified in rice, including
Pif derived from the
indica rice variety ‘Modan’;
Pi34,
Pi63, and
pi21 derived from upland rice; and
Pi39 derived from a Chinese rice landrace [17,44,47,49,57,89]. Although
Pif,
Pi34, and
Pi63 exhibit blast strain specificity,
pi21 and
Pi39 are non-specific to the blast race. Paddy rice cultivars harbouring
pi21 or
Pi39 alone have been reported to exhibit high field resistance to blast fungus races in rice paddies in various regions of Japan. However, the total cultivated area with these resistance genes remains limited and does not meet the criteria for durable resistance, which requires extensive and continuous cultivation of rice varieties possessing only resistance genes [
42]. Additionally, while
pi21 and
Pi39 showed significantly stronger quantitative resistance to leaf blast than
Pb1, the higher selection pressure on the blast population at the leaf blast stage increased the possibility of selection and spread of a strain with a specific affinity for the resistance gene in the blast fungus population, which may eventually compromise the durability of resistance. Therefore, large-scale cultivation of rice varieties possessing these genes alone and cultivation over a long period in various parts of the country are necessary for the future verification of their resistance durability [
42]. Recently, the two novel genes
Pb2 and
Pb3, which are located on rice chromosome 11 and encode NLR proteins that express panicle blast resistance, were identified by Chinese researchers [90,91]. Therefore, it is important to elucidate the mechanisms of panicle blast resistance conferred by these genes. Furthermore, it is crucial to clarify whether these genes confer durable resistance to rice blast.
13. Pyramiding of Major Genes Conferring High Field Resistance for Sustainable Use
Rather than relying solely on the innate durability of individual genes, multiple high-potential field-resistance genes with distinct resistance mechanisms can be incorporated in a single cultivar to improve the stability and sustainability of blast resistance expressed by driver genes [35,92]. These gene combinations include
Pb1+pi21, Pb1+Pi39, and
Pb1+pi21+Pi39 [
93]. The pyramiding of multiple high-field resistance genes is anticipated to increase the degree, stability, and persistence of quantitative resistance exhibited by blast high-field resistance varieties.
Pb1-carrying varieties with high field resistance to panicle blast have been widely cultivated in various regions of Japan for over 40 years without experiencing any breakdown in panicle blast resistance. The high field resistance of
Pb1 varieties meets the criteria for durable resistance.
Pb1-expressing high-field resistance to panicle blast is the only high-field resistance to blast that has been demonstrated to be durable in a large area over a long period of time; thus,
Pb1 is a promising candidate key gene for the accumulation of blast resistance genes, as highlighted by Johnson (1981). To this end, rice blast resistant varieties such as ‘Tachiharuka’ [
94], ‘Minenohoshi (Chubu 134)’ [
95], and ‘Yawakoimochi (Aichi 126)’ [
96] carrying both
Pb1 and
Pi39 high field resistance genes have already been developed. Furthermore, ‘Chubu-mochi 136’ containing three high field resistance genes to rice blast (
Pb1,
pi21 and
Pi39) was bred at the Mountains Regional Agriculture Research Institute of Aichi Prefectural Agricultural Research Centre. These varieties also possess the rice stripe virus resistance gene
Stvb-i [
65].
The new rice variety ‘Mineasahi SBL’ was developed by introducing two high field resistance genes to blast (
Pb1 and
Pi39) and a rice stripe virus resistance gene (
Stvb-i) into the original susceptible variety ‘Mineasahi’ using the MAS breeding method, and it has shown promising results in controlling panicle blast (
Table 2). The variety was fully updated in 2021 and has been widely grown on 1, 500 ha of land in the mid-mountainous areas of Aichi Prefecture. The effectiveness of ‘Mineasahi SBL’ in controlling panicle blast has been observed in farmers' fields, and it received the highest disease preventive value of 100 for its efficacy in suppressing panicle blast. Chemical pesticides for rice blast have been excluded from rice cultivation in response to the high control efficacy of ‘Mineasahi SBL’. Furthermore, the variety has received a ‘Special A’ rating for its eating quality, indicating that the chromosomal regions carrying the
Pb1,
Pi39, and
Stvb-i genes are free from QTLs associated with poor eating quality.
Continuous large-scale cultivation of highly field-resistant genotypes in an environment conducive to blast fungi, as observed in the case of true resistance-accumulated varieties, is yet to be investigated. Whether it will result in the selection and spread of super-blast isolates with a strong affinity for all high-field resistance genes, which would potentially lead to the collapse of resistance in varieties with high field resistance is a matter of interest. To increase the durability of resistant varieties, high-field resistance genes (groups) and conventional microarray genes that express field resistance may be accumulated. Zenbayashi (2007) suggested that high-field resistance genes, such as Pi34, which has confirmed strain specificity in a multiline approach, could be applied to continuously suppress blast disease similar to true resistance genes. Although the breeding costs and labour requirements for multiline use remain a challenge, it is considered an effective strategy for preventing the collapse of resistance in strain-specific high field resistance genes.
14. Towards Sustainable Management with Highly Potent Field Resistance Genes
To achieve sustainable and environmental friendly rice cultivation, it is crucial to recognise the value of field resistance genes, which have high potential as a ‘common treasure’ bestowed by nature on humankind. A major challenge for the future is to ensure long-term and sustainable use of these genes in controlling rice blast disease while avoiding the collapse of resistance. This achievement is expected to contribute towards achieving an SDG for rice blast disease control [8,97,98]. While utilising high field resistance genes for controlling rice blast, it is important to consider not only their high disease suppression effect and inherent durability but also their limited lifespan as ‘disposable’ consumables. This entails addressing bottlenecks in seed disinfection, utilising pest forecasting information, and re-establishing control levels for resistant varieties.
To conclude, it is imperative that researchers from diverse fields, such as plant pathology, epidemiology, ecology, molecular genetics, and breeding, collaborate with responsible breeders for advancements in interdisciplinary research and practical breeding.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, K. F. Y. K. and H.I.; methodology, T.S., M. N., T. Y. and N. H; writing—review and editing, Y.U. and H. S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 17K07678 and Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research(B) 20H02953.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support and contributions of several individuals who contributed to this review. First, we are grateful to the late Dr. Mabito Iwasaki's encouragement in writing this review on the persistence of field resistance to blast disease. We also thank Dr. Yuriko Hayano-Saito, Senior Research Scientist at the Disease Research Laboratory, Central Agricultural Research Centre, and Dr. Kaoru Zenbayashi-Sawata, Director of the Planning Office, Tohoku Agricultural Research Centre, National Agricultural Research Organization, for their helpful discussions, valuable suggestions, and advice during the compilation of this review. Additionally, Dr. Makoto Sakai, Director of the Centre for Food and Agricultural Business Promotion, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, provided a list of recent Pb1 rice varieties, whereas Dr. Akihiro Ikeda, former Director of the Rice Crop Research Laboratory, Mountainous Region Agricultural Institute, Aichi Prefectural Agricultural Research Centre, shared a list of Pb1-possessing rice varieties.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Fujii, K.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Sugiura, N.; Hayashi, N.; Izawa, T.; Iwasaki, M. Quantitative evaluation of protective effect of Pb1 gene, conferring field resistance to rice panicle blast, using near-isogenic lines. Breed. Sci. 2005, 7, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Hori, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Yano, M. Koshihikari: a premium short-grain rice cultivar–its expansion and breeding in Japan. Rice 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigusa, M.; Hossain, M.Z.; Sato, T.; Shibuya, K. Establishment of cultivation method of Hitomebore rice in cold regions. Tohoku Journal of Crop Science 1995, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Tanno, H.; Sugawara, K.; Munekata, S.; Taberi, K.; Aikawa, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Satoh, T.; Maeda, H.; Honma, A. A new rice [Oryza sativa] variety"" Nanatsuboshi"". Bulletin of Hokkaido Prefectural Agricultural Experiment Stations (Japan) 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosawa, S. Identification of blast-resistance genes in some rice varieties. Japanese Journal of Breeding 1978, 28, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S. Pathogen variability and host resistance in rice blast disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol 1980, 18, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, A.; Khan, S. Increasing rice grain yield under biotic stresses: mutagenesis, transgenics and genomics approaches. Rice Research for Quality Improvement: Genomics and Genetic Engineering: Volume 2: Nutrient Biofortification and Herbicide and Biotic Stress Resistance in Rice 2020, 149–178. [CrossRef]
- Miah, G.; Rafii, M.; Ismail, M.; Puteh, A.; Rahim, H.; Asfaliza, R.; Latif, M. Blast resistance in rice: a review of conventional breeding to molecular approaches. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2369–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, A.; Fakheri, B.; Hassan, F.S.C.; Noroozi, M. Blast resistance in rice: a review of breeding and biotechnology. Int. J. Agric. Sci. (IJACS) 2014, 7, 329–333. [Google Scholar]
- Tanweer, F.A.; Rafii, M.Y.; Sijam, K.; Rahim, H.A.; Ahmed, F.; Latif, M.A. Current advance methods for the identification of blast resistance genes in rice. C R Biol 2015, 338, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, M.; Sasaki, T. Genetic and molecular dissection of quantitative traits in rice. Oryza: from molecule to plant 1997, 145–153.
- Koide, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Xu, D.; Fukuta, Y. Resistance genes and selection DNA markers for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. : JARQ 2009, 43, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yonemaru, J.; Yano, M. Towards the understanding of complex traits in rice: substantially or superficially? DNA Res. 2009, 16, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1Fujii, K.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Saito, K.; Sugiura, N.; Hayashi, N.; Tsuji, T.; Izawa, T.; Iwasaki, M. Identification of a RFLP marker tightly linked to the panicle blast resistance gene, Pb1, in rice. Breed. Sci. 2000, 50, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Okuno, K. QTL analysis and mapping of pi21, a recessive gene for field resistance to rice blast in Japanese upland rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Koizumi, S.; La, T.; Zenbayashi, K.; Ashizawa, T.; Yasuda, N.; Imazaki, I.; Miyasaka, A. Pi35 (t), a new gene conferring partial resistance to leaf blast in the rice cultivar Hokkai 188. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, T.; Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Kudo, S. Mapping of a blast field resistance gene Pi39 (t) of elite rice strain Chubu 111. Plant Breed. 2008, 127, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T., Nakamura, M., Saka Norikuni, Ikeda Akihiro, ; Terashima Takehiko, M.Y., Nonoyama Toshihiro, ; Yoshida Tomofumi, ShirodaM. and KatoT. Breeding of a New Rice Variety "Chubu 138", a Near-isogenic Line of "Mineasahi, " with Blast and Rice Stripe Disease Resistance. Research bulletin of the Aichi Agricultural Research Center 2017, 49, 93–102.
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic acquired resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriyama, A.E.K. Vulnerability of Field Resistance to Blast in Rice. J. Agric. Sci. 1987, 42, 337–340. [Google Scholar]
- Bonman, J.; Leung, H. In Breeding for durable resistance to rice blast disease dream or reality? Phytopathology, 2004; American Phytopathological Society Annual Meeting: Phytopathology, 2004.
- Vanderplank, J.E. Disease resistance in plants. Elsevier: 2012; 0323161987.
- Meyers, B.C.; Kozik, A.; Griego, A.; Kuang, H.; Michelmore, R.W. Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 809–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, L.; Tan, X.; Koehl, P.; Michelmore, R.W. Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhadir, Y.; Subramaniam, R.; Dangl, J.L. Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS–LRR proteins and their partners. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kiyosawa, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hirano, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kushibuchi, K.; Watanabe, S. Proposal of a new method for differentiating races of Pyricularia oryzae Cavara in Japan. Japanese Journal of Phytopathology 1976, 42, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriyama, K.; Ezuka, A.; Asaga, K.; Yokoo, M. A method of estimating true resistance genes to blast in rice varieties by testing their backcrossed progenies for race-specific reactions. Japanese Journal of Breeding 1983, 33, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyosawa, S. Genetics and epidemiological modeling of breakdown of plant disease resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1982, 20, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasaprasad, S.; Johnson, R.; Kiyosawa, S.; Ling, Z. Genetic studies on rice blast relationships. Major Fungal Diseases of Rice: Recent Advances 2001, 145–162. [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S.; Jena, K. Current status and future prospects for research on blast resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Advances in genetics, genomics and control of rice blast disease 2009, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Michelmore, R. Molecular approaches to manipulation of disease resistance genes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1995, 33, 393–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, N. QTL mapping and quantitative disease resistance in plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 479–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ashikawa, I. Development of PCR-based allele-specific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonman, J.; Estrada, B.; Kim, C.; Ra, D.; Lee, E. Assessment of blast disease and yield loss in susceptible and partially resistant rice cultivars in two irrigated lowland environments. Plant Dis. 1991, 75, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasahara, M.; Koizumi, S. In Rice blast control with Sasanishiki multilines in Miyagi Prefecture, Rice Blast: Interaction with Rice and Control: Proceedings of the 3rd International Rice Blast Conference, 2004; Springer: 2004; pp 201–207.
- Shinzo, A. Breeding of a blast resistant multiline variety of rice, Sasanishiki BL. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q.: JARQ 2004, 38, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, K. In Breeding and practical application of blast-resistant isogenic lines in rice [Oryza sativa] cultivar Koshihikari in Niigata [Japan] Prefecture, Gamma Field Symposia (Japan), 2010; 2010.
- Ishizaki, K.; Hashimoto, N.; Matsui, T.; Nabata, K.; Kanbe, T.; Nara, E.; Hoshi, T.; Abe, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Kasaneyama, H. Blast resistant isogenic line in rice cultivar Koshihikari'Koshihikari Niigata BL No. 13'. Journal of the Niigata Agricultural Research Institute 2015, 13, 47–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Endo, I.; Yano, M.; Sasaki, T.; Inoue, M.; Kudo, S. Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Fr Field Resistance to Rice Blast in Upland Rice, 'Sensho'. Breed. Res. 2002, 4, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. Durable resistance: definition of, genetic control, and attainment in plant breeding. Phytopathology 1981, 71, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. A critical analysis of durable resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1984, 22, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Morimoto, T.; Tanabe, K.; Shumiya, A.; Fujii, K. Method of selection for field resistance to rice blast disease [caused by Pyricularia oryzae] by means of the shortening of breeding cycle in rice, 2: Optimum condition for identifying field resistance and the effect of plant selection. Research Bulletin of the Aichi-ken Agricultural Research Center (Japan) 1983.
- Saka, N.A. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) breeding for field resistance to blast disease (Pyricularia oryzae) in Mountainous Region Agricultural Research Institute, Aichi Agricultural Research Center of Japan. Plant Prod. Sci. 2006, 9, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenbayashi-Sawata, K.; Fukuoka, S.; Katagiri, S.; Fujisawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Ashizawa, T.; Koizumi, S. Genetic and physical mapping of the partial resistance gene, Pi34, to blast in rice. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, H.; Fujimura, T.; Kawasaki, S. Fine mapping of a strong QTL of field resistance against rice blast, Pikahei-1 (t), from upland rice Kahei, utilizing a novel resistance evaluation system in the greenhouse. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Koga, H.; Ono, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ebana, K.; Hayashi, N.; Takahashi, A.; Hirochika, H.; Okuno, K. Loss of function of a proline-containing protein confers durable disease resistance in rice. Science 2009, 325, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Inoue, H.; Kato, T.; Funao, T.; Shirota, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, H.; Yamane, H.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication. Plant J. 2010, 64, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hayashi, N.; Wang, C.-T.; Fukuoka, S.; Kawasaki, S.; Takatsuji, H.; Jiang, C.-J. Rice blast resistance gene Pikahei-1 (t), a member of a resistance gene cluster on chromosome 4, encodes a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat protein. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K. Establishment of marker-assisted selection (MAS) system for rice stripe virus and panicle blast resistance in rice breeding. Breeding Research 2008, 10, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, M.; Oda, N.; Minoda, T.; Saito, K.; Ishii, H.; Ueno, T.; Okada, T.; Takei, Y.; Shigematsu, O.; Yagasaki, K.; et al. Breeding of a new rice cultivar “SAINOKIZUNA”. Bulletin of the Saitama Prefectural Agriculture and Forestry Research Center 2013, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nagaoka, I.; Sasahara, H.; Matsushita, K.; Maeda, H.; Shigemune, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Goto, A.; Miura, K. “Nijino-no-kirameki”, a new rice cultivar with high-yielding and resistance to high temperature, lodging and rice stripe disease. Breed. Res. 2020, 22, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, T.; Okamura, M.; Nagaoka, I.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ohdaira, Y. Quantitative assessment on the grain appearance of a new Japanese rice cultivar ‘Niji-no-kirameki’with a novel heat-avoidance mechanism during ripening. Plant Stress 2022, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, K.; Asaga, K. Studies on a new method to evaluate panicle resistance of rice varieties to rice blast. Bull. Tohoku Natl. Agric. Exp. Stn 1989, 80, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hirabayashi, H.; Nemoto, H.; Hirayama, M.; Kato, H.; Imbe, T.; Ando, I. Mapping QTLs for field resistance to rice blast in the Japanese upland rice variety Norin 12. Breed. Sci. 2006, 56, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballini, E.; Morel, J.-B.; Droc, G.; Price, A.; Courtois, B.; Notteghem, J.-L.; Tharreau, D. A genome-wide meta-analysis of rice blast resistance genes and quantitative trait loci provides new insights into partial and complete resistance. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenbayashi-Sawata, K.; Ashizawa, T.; Koizumi, S. Pi34-AVRPi34: a new gene-for-gene interaction for partial resistance in rice to blast caused by Magnaporthe grisea. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2005, 71, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehashi, H.; Kiyosawa, S. Strain-specific reaction of field resistance of Japanese rice varieties revealed with Philippine strains of rice blast fungus, Pyricularia oryzae Cav. Japanese Journal of Breeding 1981, 31, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, Z.I.; Tharreau, D.; Price, A.H. Quantitative trait loci analysis suggests that partial resistance to rice blast is mostly determined by race–specific interactions. New Phytologist 2004, 162, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, D. Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi49 in the durably resistant rice cultivar Mowanggu. Euphytica 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lei, C.; Xu, X.; Hao, K.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X. Pi64, encoding a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to leaf and neck blast in rice. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, S.; Fujii, S. Variation of field resistance to leaf blast in a rice strain, Chubu 32, due to isolates of the pathogen. Research Bulletin of the Aichi-ken Agricultural Research Center (Japan) 1995, 27, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Tooyama, T.; Sugiura, N.; Saka, N.; Izawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Shumiya, A. Characteristics and genealogical analysis of panicle blast resistance in a RSV-resistant japonica rice cultivar Tsukinohikari and related cultivars. Breed. Res. 1999, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Naoki. S.; Nagao, H.; Norikuni, S.; Takamichi, T.; Toshihiko, I.; Akio, S. Gene analysis of panicle blast resistance in rice cultivars with rice stripe resistance. Breed. Res. 1, 203–210. [CrossRef]
- Hayano-Saito, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Fujii, K.; Saito, K.; Iwasaki, M.; Saito, A. Localization of the rice stripe disease resistance gene, Stv-bi, by graphical genotyping and linkage analyses with molecular markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 96, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, M.; Koga, H.; Akagi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Goto, S.; Sawada, M.; Kurihara, T.; Matsushita, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J.; et al. Rice WRKY45 plays important roles in fungal and bacterial disease resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, A.; Inoue, H.; Goto, S.; Nakayama, A.; Sugano, S.; Hayashi, N.; Takatsuji, H. Nuclear ubiquitin proteasome degradation affects WRKY 45 function in the rice defense program. Plant, J. 2013, 73, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N.; Matsushita, A.; Xinqiong, L.; Nakayama, A.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.J.; Takatsuji, H. Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 through protein-protein interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9577–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N.; Jiang, C.-J.; Takatsuji, H. CC-NBS-LRR-type R proteins for rice blast commonly interact with specific WRKY transcription factors. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Kato, S. Studies on Field Resistance of Rice. Research bulletin of the Aichi Agricultural Research Center 1993, 25, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shumiya, A.; Ito, T.; Kudo, S.; Fujii, K.; Kato, T.; Saka, N.; Touyama, T.; Shaku, I. A new stripe-resistant rice variety" Matsuribare". Research Bulletin of the Aichi-ken Agricultural Research Center 1994, 1–16.
- Sugiura, N.; Tsuji, T.; Fujii, K.; Kato, T.; Saka, N.; Touyama, T.; Hayano Saito, Y.; Izawa, T. Molecular marker-assisted selection in a recurrent backcross breeding for the incorporation of resistance to rice stripe virus and panicle blast in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Res. (Japan) 2004, 6, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Nakayama, A.; Jiang, C.J.; Ono, K.; Toki, S.; Takatsuji, H. Rice WRKY45 plays a crucial role in benzothiadiazole-inducible blast resistance. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Oide, S.; Ebana, K.; La, N.T.; Hayashi, K.; Ashizawa, T.; Suzuki, F.; Koizumi, S. Quantitative trait locus analysis of resistance to panicle blast in the rice cultivar Miyazakimochi. Rice 2014, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Hayashi, N. The panicle blast resistance mechanism of qPbm11 in the rice cultivar Miyazaki-mochi is independent from that of Pb1. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q.: JARQ 2019, 53, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-N.; Kim, S.-Y.; Hur, Y.-J.; Yeo, U.-S.; Sohn, Y.-B.; Song, Y.-C.; Park, D.-S.; Nam, M.-H. Enhancement of panicle blast resistance in Korean rice cultivar ‘Saeilmi’by marker assisted backcross breeding. Plant Breed. Biotech. 2015, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drijepondt, S.; Pretorius, Z. Greenhouse evaluation of adult-plant resistance conferred by the gene Lr34 to leaf rust of wheat. Plant Dis. 1989, 73, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Genetic association of leaf rust resistance gene Lr34 with adult plant resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat. Phytopathology (USA) 1992, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Krattinger, S.G.; Lagudah, E.S.; Spielmeyer, W.; Singh, R.P.; Huerta-Espino, J.; McFadden, H.; Bossolini, E.; Selter, L.L.; Keller, B. A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 2009, 323, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Mase, S.; Sekizawa, Y. Effect of probenazole on the activities of enzymes related to the resistant reaction in rice plant. Japanese Journal of Phytopathology 1980, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashita, H.; Yoshioka, K.; Takayama, M.; Kuga, R.; Midoh, N.; Usami, R.; Horikoshi, K.; Yoneyama, K.; Yamaguchi, I. Characterization of PBZ1, a probenazole-inducible gene, in suspension-cultured rice cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Seo, S.; Mitsuhara, I.; Ohashi, Y. Probenazole-induced accumulation of salicylic acid confers resistance to Magnaporthe grisea in adult rice plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007, 48, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimono, M.; Yazaki, J.; Nakamura, K.; Kishimoto, N.; Kikuchi, S.; Iwano, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Sakata, K.; Sasaki, T.; Nishiguchi, M. cDNA microarray analysis of gene expression in rice plants treated with probenazole, a chemical inducer of disease resistance. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2003, 69, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.-J.; Miyazawa, S.-I.; Masumoto, C.; Yazawa, K.; Hayashi, N.; Shimono, M.; Nakayama, A.; Miyao, M.; Takatsuji, H. Role of OsNPR1 in rice defense program as revealed by genome-wide expression analysis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Duan, C.-J.; Luo, X.-M.; Le, N.; Wei, H.; Liang, S.; Chu, C.; Pan, Q. Involvement of OsNPR1/NH1 in rice basal resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 131, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vleesschauwer, D.; Gheysen, G.; Höfte, M. Hormone defense networking in rice: tales from a different world. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Fukushima, S.; Goto, S.; Matsushita, A.; Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Jiang, C.-J.; Akagi, A.; Yamazaki, M.; Inoue, H. Genome-wide identification of WRKY45-regulated genes that mediate benzothiadiazole-induced defense responses in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimaru, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Harada, K.; Nishio, Y.; Hori, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Inoue, H.; Shigeta, S.; Inoue, K.; Shimada, K. Cooperative regulation of PBI1 and MAPKs controls WRKY45 transcription factor in rice immunity. Nat. Comm. 2022, 13, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norikuni, S.; Shuichi, F.; Takehiko, T.; Satoru, K.; Masaki, S.; Ikuo, A.; Kazuhiko, S.; Hiroyuki, S.; Hideo, M.; Ikuma, E.; Hiromi, K.a.I.M. Breeding of a new rice variety "Chubu 125" with high field resistance for blast and excellent eating quality. Research bulletin of the Aichi Agricultural Research Center 2010, 42, 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, P.; Liu, K.; Ma, W.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Jiang, T.; et al. Genome-wide association sudy identifies a rice panicle blast resistance gene Pb3 encoding NLR protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Jiang, T.; Xiong, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a rice panicle blast resistance gene, Pb2, encoding NLR protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundt, C. Probability of mutation to multiple virulence and durability of resistance gene pyramids. Phytopathology 1990, 80, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, S.; Saka, N.; Mizukami, Y.; Koga, H.; Yamanouchi, U.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Ebana, K.; Mizobuchi, R.; Yano, M. Gene pyramiding enhances durable blast disease resistance in rice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makoto Sakai, K.T.; Kaji, R.; Tamura, Y.; Kataoka, T. “Tachiharuka” a high yielding rice variety suitable for direct seeding with excellent palatability, resistances to blast and stripe virus. Breed. Res. 2014, 16, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida Tomofumi, S.N.; Mitsuru, N.; Takehiko, T.; Yuko, M.; Hiromi, K.; Yasunori, N.; Toshihiro, N.; Kudo Satoru, S.M.; Satoru, K.; Akihiro, I. Breeding of a new rice variety, Chubu 134, with two genes, Pi39 and Pb1, for field resistance to blast disease. Research bulletin of the Aichi Agricultural Research Center 2014, 46, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Taro, N.M. , Takayuki, U.; Akihiro, I.; Takahiro, K. Breeding of a low hardening speed glutinous rice variety “Aichimochi 126” which lacks starch branching enzyme 1 activity. Breed. Res. 2019, 21, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.; Wiesner-Hanks, T.; Wisser, R.; Balint-Kurti, P. Navigating complexity to breed disease-resistant crops. Nat. Rev. Gen. 2018, 19, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkani, S.; Rafii, M.Y.; Shabanimofrad, M.; Miah, G.; Sahebi, M.; Azizi, P.; Tanweer, F.A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Nasehi, A. Molecular breeding strategy and challenges towards improvement of blast disease resistance in rice crop. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
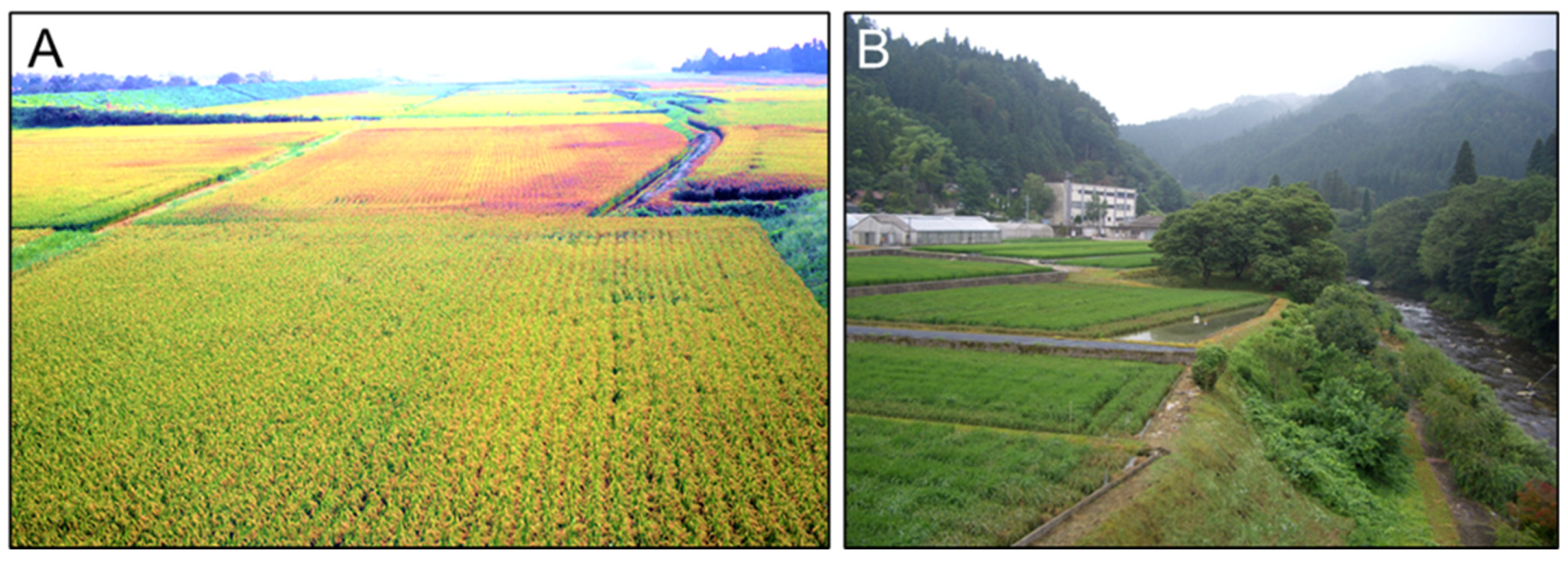
Figure 1.
In 2003, rice blast was spread in Japan, and the impact of rice production due to blast. This picture was taken in a paddy field, Miyagi prefecture in Japan. The red part of rice was damaged by the rice blast (A). Mountainous Region Agricultural Institute, Aichi Agricultural Research Centre, Japan, which is developing rice blast resistance breeding (B). The institute was located in the mountaneous region at higher altitute of 505 meters.
Figure 1.
In 2003, rice blast was spread in Japan, and the impact of rice production due to blast. This picture was taken in a paddy field, Miyagi prefecture in Japan. The red part of rice was damaged by the rice blast (A). Mountainous Region Agricultural Institute, Aichi Agricultural Research Centre, Japan, which is developing rice blast resistance breeding (B). The institute was located in the mountaneous region at higher altitute of 505 meters.
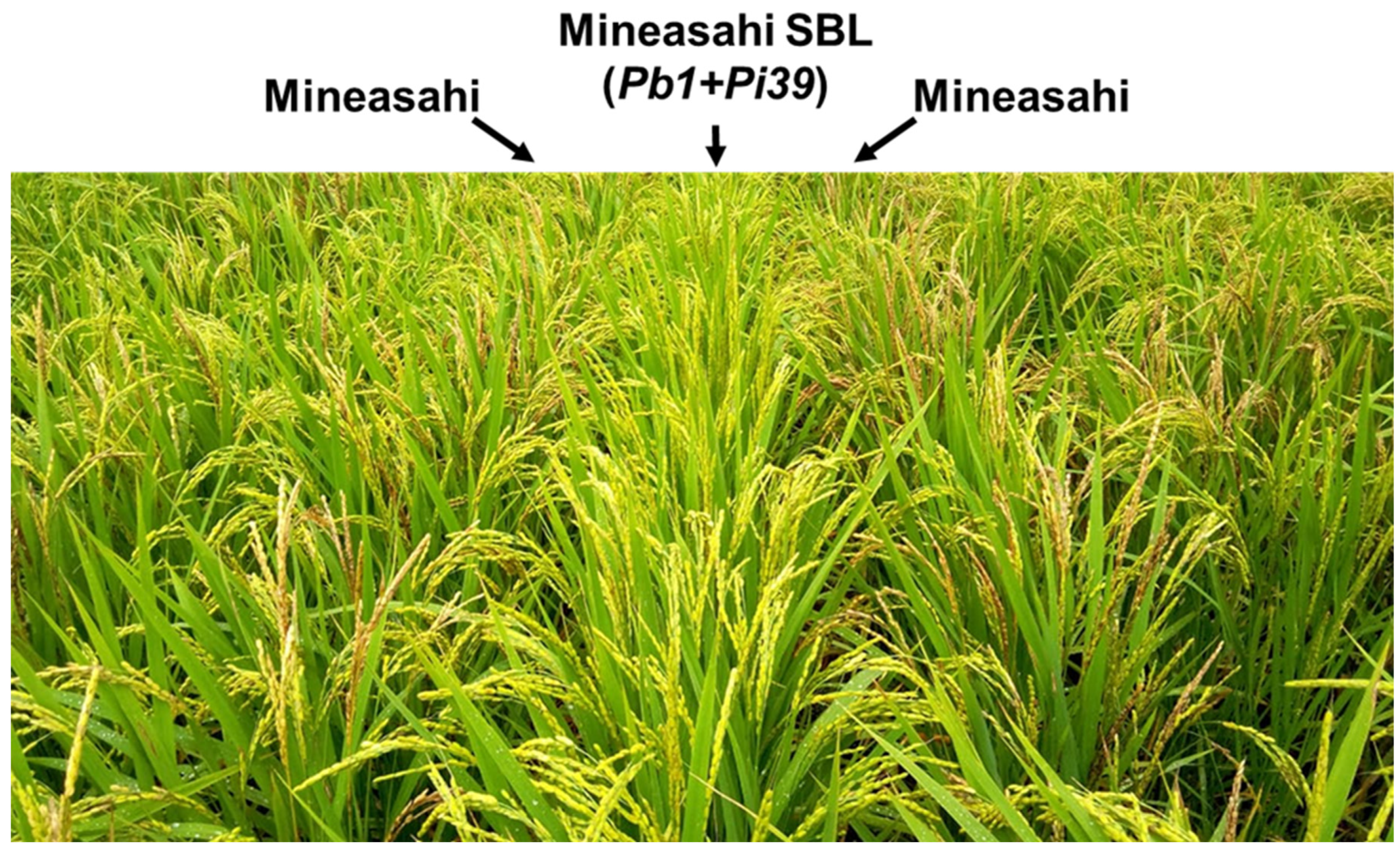
Figure 2.
Mineasahi SBL harbours two quantitative resistance genes: Pb1 and Pi39. Disease symptoms of Mineasahi SBL (Pb1+Pi39) and near-isogenic Mineasahi (Pb1-, Pi39-) cultivars grown in a rice field in Tsukude, Shinshiro, Aichi, Japan. The altitude was 500 m. The picture was taken approximately two weeks after the full heading stage in 2021. Mineasahi SBL did not show any disease symptoms of panicle blast, whereas Mineasahi did show symptoms.
Figure 2.
Mineasahi SBL harbours two quantitative resistance genes: Pb1 and Pi39. Disease symptoms of Mineasahi SBL (Pb1+Pi39) and near-isogenic Mineasahi (Pb1-, Pi39-) cultivars grown in a rice field in Tsukude, Shinshiro, Aichi, Japan. The altitude was 500 m. The picture was taken approximately two weeks after the full heading stage in 2021. Mineasahi SBL did not show any disease symptoms of panicle blast, whereas Mineasahi did show symptoms.
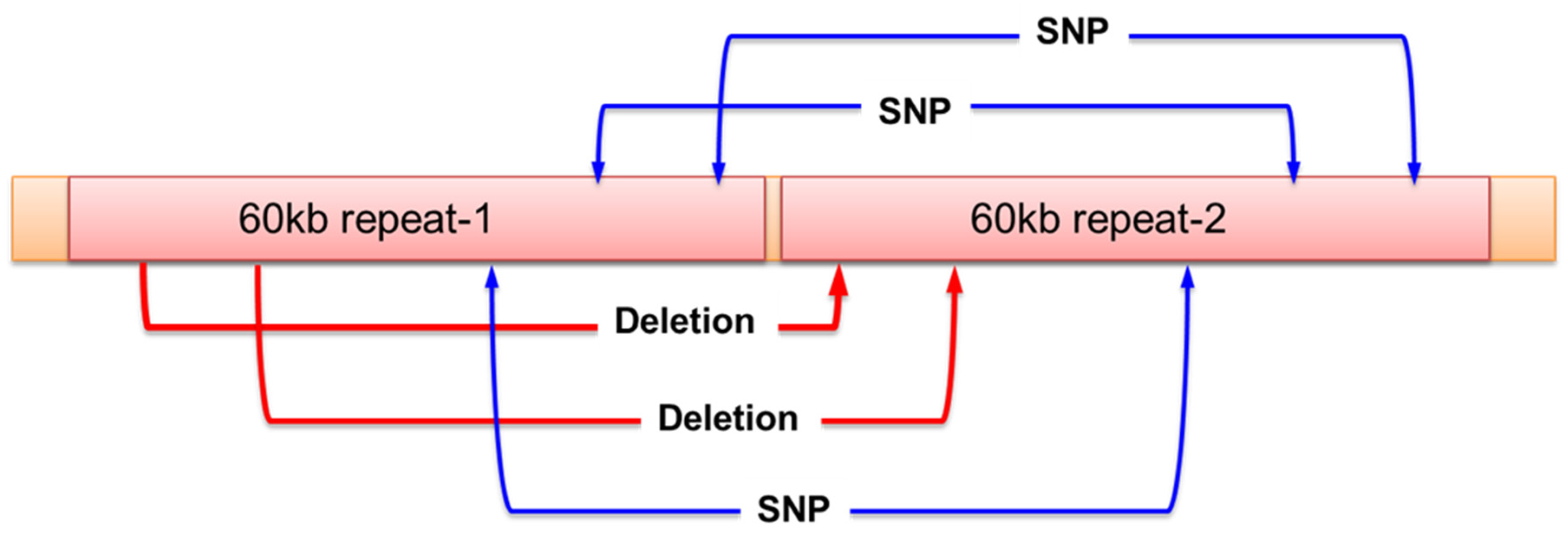
Figure 3.
The sequence of Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone including Pb1 resistance gene. The BAC clone (clone name: St-h-49J11) contained two fragments of 60kb sequence with tandemly repeat. The clone had only two deletion sites and three SNPs even over 150kb sequence.
Figure 3.
The sequence of Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone including Pb1 resistance gene. The BAC clone (clone name: St-h-49J11) contained two fragments of 60kb sequence with tandemly repeat. The clone had only two deletion sites and three SNPs even over 150kb sequence.
Figure 4.
A model: Tandem genome duplication confer the active promoter for Pb1 resistance gene expression. An ancestral Pb1 genomic region was thought to be exist, and the region was duplicated as a tandem genome. Although the proto-Pb1 doesn’t have a strong expression activity, Pb1 acquires new promoter, which enable to resist against the rice blast through tandem genome dupulication.
Figure 4.
A model: Tandem genome duplication confer the active promoter for Pb1 resistance gene expression. An ancestral Pb1 genomic region was thought to be exist, and the region was duplicated as a tandem genome. Although the proto-Pb1 doesn’t have a strong expression activity, Pb1 acquires new promoter, which enable to resist against the rice blast through tandem genome dupulication.
Figure 5.
Predicted mechanisms of resistance against rice blast in varieties with both the Pb1 and Pi39 resistance genes. In rice, the accumulation level of WRKY45 protein increases in response to blast infection. However, that level is considered insufficient to confer blast resistance. In Pb1-possessing rice varieties, Pb1 protein protects WRKY45 from proteasome-dependent degradation, resulting in enhanced accumulation of WRKY45 and resistance to rice blast. Pi39 confers resistance through unidentified pathway(s). UPS, ubiquitin-proteasome system; X, Y, and Z, unknown signaling factors.
Figure 5.
Predicted mechanisms of resistance against rice blast in varieties with both the Pb1 and Pi39 resistance genes. In rice, the accumulation level of WRKY45 protein increases in response to blast infection. However, that level is considered insufficient to confer blast resistance. In Pb1-possessing rice varieties, Pb1 protein protects WRKY45 from proteasome-dependent degradation, resulting in enhanced accumulation of WRKY45 and resistance to rice blast. Pi39 confers resistance through unidentified pathway(s). UPS, ubiquitin-proteasome system; X, Y, and Z, unknown signaling factors.
Table 2.
Rice cultivars have the panicle blast resistance gene, Pb1 wide spreads in all over Japan. Each prefectural Agricultural institutes and National Agriculture and Food Research, NARO breeds Pb1 including cultivars since 1985.
Table 2.
Rice cultivars have the panicle blast resistance gene, Pb1 wide spreads in all over Japan. Each prefectural Agricultural institutes and National Agriculture and Food Research, NARO breeds Pb1 including cultivars since 1985.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).