Submitted:
17 May 2023
Posted:
18 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
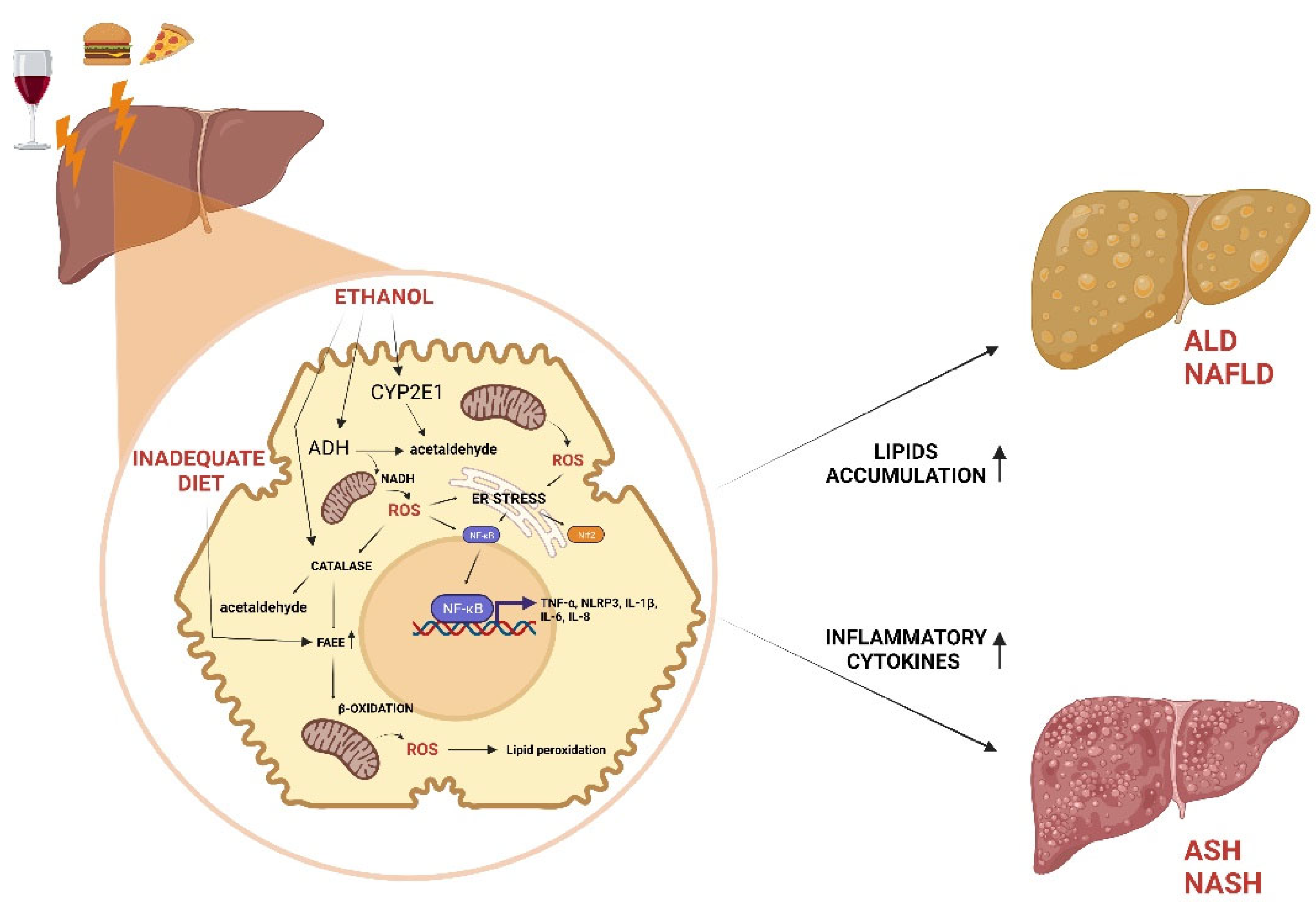
1.1. The Liver: Function and Diseases
1.1.1. ALD and NAFLD
1.1.2. ASH and NASH
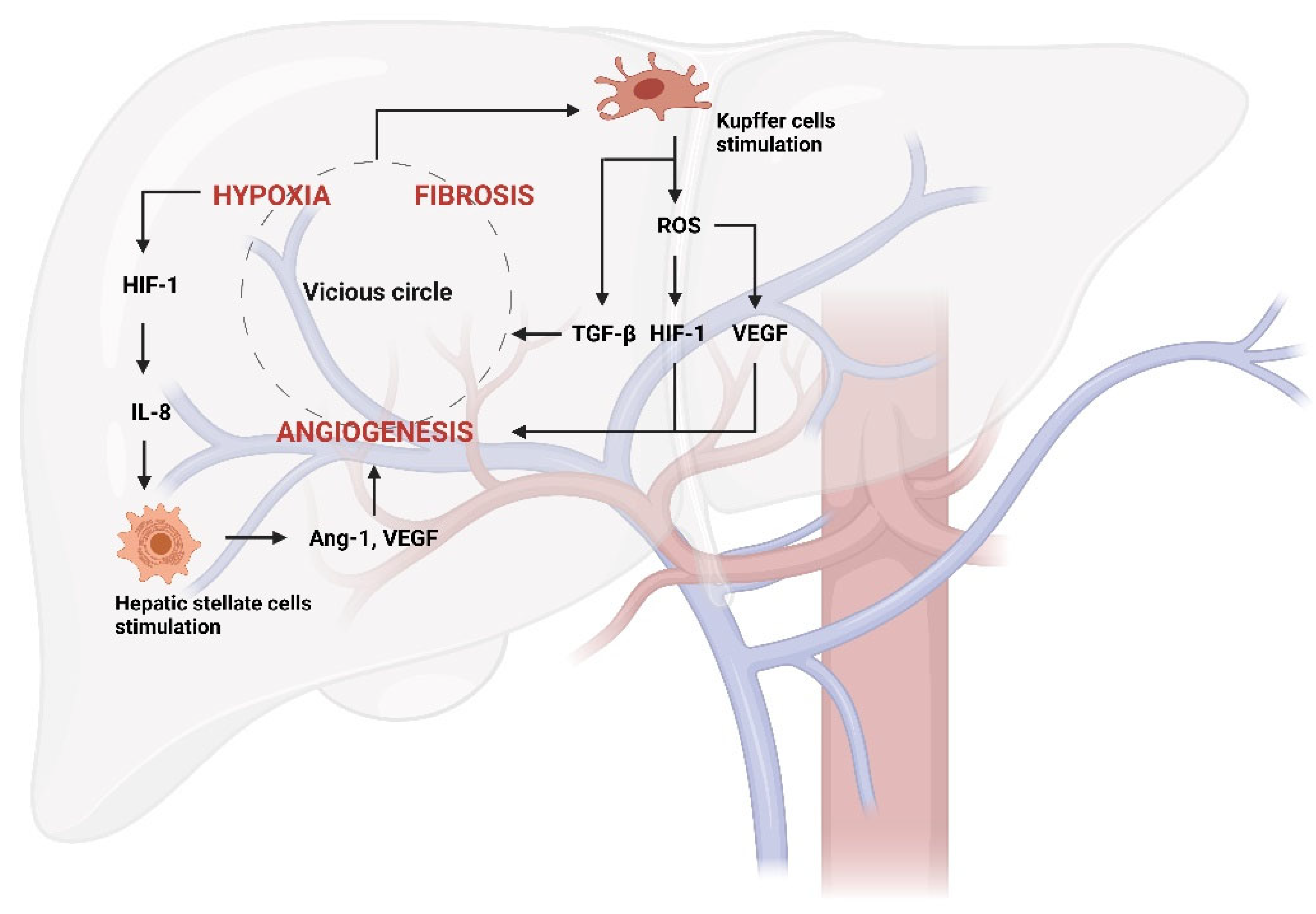
2.1. Angiogenesis and Hepatic Inflammation
3.1. Phytochemicals to Counteract the Stages of Liver Disease via Angiogenesis Inhibition
3.1.1. Quercetin
3.1.2. Silybin
3.1.3. Breviscapine
3.1.4. ALS-L1023
3.1.5. Curcumin
3.1.6. Sulforaphane
3.1.7. Cordycepin
3.1.7. Methoxyeugenol
3.1.8. Naringenin
3.1.9. Ferulic Acid
3.1.10. Betaine
3.1.11. Catechins
3.1.12. Puerarin
3.1.13. Resveratrol
3.1.14. Fucoidan
3.1.15. Carnosol and Carnosic Acid
| PHYTOCHEMICALS | MAIN DIETARY SOURCES | DESIGNED STUDY | ANTIANGIOGENIC EFFECTS |
REF. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | apples, red grapes, citrus fruits, tomatoes, onions and green leafy vegetables | Mice | HMGB1/TLR2/4-NF-κB signaling pathway downregulation; TGF-β1/Smads and PI3K/Akt crosstalk regulation |
92; 93 |
| Silybin | Silybum marianum | Rats | NF-κB, PGE 2 and LTB 4 inhibition | 102; 106 |
| Breviscapine | Erigeron breviscapus | Mice | TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)/ NF-κB signaling pathway Inhibition | 114 |
| ALS-L1023 | Melissa officinalis | Mice | mRNA modulation of VEGF-A, FGF-2, MMP-2, MMP-9 TIMP-1, TIMP-2, TSP-1 | 122; 123 |
| Curcumin | Curcuma longa | Mice | NF-κB inhibition; TGF-β downregulation | 133; 136 |
| Sulforaphane | Broccoli, cauliflowers | Hep G2 and HUVEC cells | NF-κB/VEGF, STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway inhibition; HO-1, NQO1, MRP2 genes upregulation |
140; 142-144 |
| Cordycepin | Cordyceps militaris | HCC cells | CXCR4 downregulation; NLRP3 suppression; NF-κB inhibition |
148-150 |
| Methoxyeugenol | Brazilian red propolis | Mice | mRNA up-regulation of PPARγ; TNF-α, IL-6 e IL-8 genes downregulation |
156 |
| Naringenin | citrus fruits | Mice | mRNA downregulation of NF-κB, IL-1β, IL-18 NLRP3 | 162 |
| Ferulic acid | cereals, vegetables, and plants such as Angelica sinensis | Mice | AMPKα up-regulation; lipogenic genes downregulation; Nrf2/HO-1 and PPARγ pathways activation; nuclear translocation block of NF-κB; PTP1B inhibition |
166-169 |
| Betaine | Beta vulgaris | HUVEC cells | NF-κB and Akt inhibition; FGF-2 MMP-2 MMP-downregulation |
174; 177; 178 |
| Catechins | grapes, apple and cocoa | Haec cells; Mice |
IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α inhibition; ErbB2 gene downregulation |
186; 188 |
| Puerarin | Pueraria lobata | Rats | (JAK2)/STAT3 signaling pathway regulation; JNK activity regulation, | 190; 193 |
| Resveratrol | grape skins, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts | Primary hepatocyte; Mice |
Nrf2 ubiquitination inhibition; TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 mRNA inhibition |
197; 200; 201 |
| Fucoidan | edible brown seaweeds | HCC; Huh-7 cells | VEGF-A gene downregulation | 204; 205 |
|
Carnosol and Carnosic Acid |
Rosmarinus officinalis |
BAECs and HUVEC cells | NF-κB inhibition | 208 |
4.1. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D. H. The liver. Current biology. 2017, CB, 27, R1147–R1151. [CrossRef]
- Racanelli, V.; Rehermann, B. The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2006, 43, S54–S62. [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.; Russell, J. O.; Molina, L. M.; Monga, S. P. Liver Progenitors and Adult Cell Plasticity in Hepatic Injury and Repair: Knowns and Unknowns. Annual review of pathology. 2020, 15, 23–50. [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S. L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2017, 14, 397–411. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S. L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B. A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A. J.Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nature medicine. 2018, 24, 908–922. [CrossRef]
- Gilgenkrantz, H.; Collin de l'Hortet, A. Understanding Liver Regeneration: From Mechanisms to Regenerative Medicine. The American journal of pathology. 2018, 188, 1316–1327. [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F.; Rector, R. S.; Hammoud, G. M.; Ibdah, J. A. Pathogenesis and Prevention of Hepatic Steatosis. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2015, 11, 167–175.
- Forbes, S. J., Newsome, P. N. Liver regeneration - mechanisms and models to clinical application. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2016, 13, 473–485. [CrossRef]
- Seth, D.; Haber, P. S.; Syn, W. K.; Diehl, A. M.; Day, C. P. Pathogenesis of alcohol-induced liver disease: classical concepts and recent advances. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2011, 26, 1089–1105. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H. Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z. J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C. W.; & Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [CrossRef]
- Ceni, E.; Mello, T.; & Galli, A. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: role of oxidative metabolism. World journal of gastroenterology. 2014, 20, 17756–17772. [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Basilicata, M. G.; Pepe, G.; De Anseris, R.; Di Mauro, A.; Scognamiglio, G.; Palma, G.; Vestuto, V.; Buccolo, S.; Luciano, A.; Barbieri, M.; Bruzzese, F.; Maurea, C.; Pumpo, R.; Ostacolo, C.; Campiglia, P.; Berretta, M.; Maurea, N. Combination of Spirulina platensis, Ganoderma lucidum and Moringa oleifera Improves Cardiac Functions and Reduces Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers in Preclinical Models of Short-Term Doxorubicin-Mediated Cardiotoxicity: New Frontiers in Cardioncology?. Journal of cardiovascular development and disease. 2022, 9, 423. [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Sun, J.; Sullivan, M. A.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wang, K. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and cell death by suppressing oxidative stress and hepatic apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. International journal of biological macromolecules. 2018, 111, 1133–1139. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. Acetaldehyde stimulates the activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta1 and induces expression of the type II receptor of the cytokine in rat cultured hepatic stellate cells. The Biochemical journal. 2002, 368, 683–693. [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; & Robino, G. Oxidative stress-related molecules and liver fibrosis. Journal of hepatology. 2001, 35, 297–306. [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, B. S.; Cai, P.; Khan, M. F.; Okorodudu, A. O.; Ansari, G. A. Fatty acid ethyl esters: markers of alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Alcohol. 2004, 34, 151–158. [CrossRef]
- Cederbaum, A. I. Nrf2 and antioxidant defense against CYP2E1 toxicity. Sub-cellular biochemistry. 2013, 67, 105–130. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Kang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Jia, J.; Jin, Z.; Xue, Y. NF-κB-mediated regulation of rat CYP2E1 by two independent signaling pathways. PloS one. 2019, 14, e0225531. [CrossRef]
- Magne, L.; Blanc, E.; Legrand, B.; Lucas, D.; Barouki, R.; Rouach, H.; Garlatti, M. ATF4 and the integrated stress response are induced by ethanol and cytochrome P450 2E1 in human hepatocytes. Journal of hepatology. 2011, 54, 729–737. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Yun, H.; Moon, S.; Cho, Y. E.; Gao, B. Role of Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2021, 12, 751802. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Kang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; Jia, J.; Jin, Z.; Xue, Y. NF-κB-mediated regulation of rat CYP2E1 by two independent signaling pathways. PloS one. 2019, 14, e0225531. [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Assiri, M. A.; Shearn, C. T.; Fritz, K. S. Lipid peroxidation derived reactive aldehydes in alcoholic liver disease. Current opinion in toxicology. 2019, 13, 110–117. [CrossRef]
- Abu-Freha, N.; Cohen, B.; Gordon, M.; Weissmann, S.; Fich, A.; Munteanu, D.; Yardeni, D.; Etzion, O. Comorbidities and Malignancy among NAFLD Patients Compared to the General Population, A Nation-Based Study. Biomedicines. 2023, 11, 1110. [CrossRef]
- Kosmalski, M.; Śliwińska, A.; Drzewoski, J. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—The Chicken or the Egg Dilemma. Biomedicines. 2023, 11, 1097. [CrossRef]
- Cusi K. Role of insulin resistance and lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinics in liver disease. 2009, 13, 545–563. [CrossRef]
- Grønbaek, H.; Thomsen, K. L.; Rungby, J.; Schmitz, O.; Vilstrup, H. Role of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes. Expert review of gastroenterology & hepatology. 2008, 2, 705–711. [CrossRef]
- Day, C. P.; James, O. F. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two "hits"?. Gastroenterology. 1998, 114, 842–845. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Thiemermann, C. Role of Metabolic Endotoxemia in Systemic Inflammation and Potential Interventions. Frontiers in immunology. 2021, 11, 594150. [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P. K.; Zhou, Y.; Sädevirta, S.; Leivonen, M.; Arola, J.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Hepatic ceramides dissociate steatosis and insulin resistance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of hepatology. 2016, 64, 1167–1175. [CrossRef]
- Adolph, T. E.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Adipokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Multiple Interactions. International journal of molecular sciences. 2017, 18, 1649. [CrossRef]
- Vestuto, V.; Di Sarno, V.; Musella, S.; Di Dona, G.; Moltedo, O.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.M.; Bertamino, A.; Ostacolo, C.; Campiglia, P.; Ciaglia, T. New Frontiers on ER Stress Modulation: Are TRP Channels the Leading Actors?.International journal of molecular sciences. 2023, 24, 185. [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, E.; Magkos, F.; Mohammed, B. S.; Pietka, T.; Abumrad, N. A.; Patterson, B. W.; Okunade, A.; Klein, S. Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009, 106, 15430–15435. [CrossRef]
- Baffy, G. Kupffer cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: the emerging view. Journal of hepatology. 51, 212–223. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, M.; Palisi, A.; Marino, C.; Montoro, P.; Capasso, A.; Novi, S.; Tecce, M. F.; D'Ursi, A. M. NMR-based metabolomic profile of hypercholesterolemic human sera: Relationship with in vitro gene expression?. PloS one. 2020, 15(4), e0231506. [CrossRef]
- Asif, S.; Kim, R. Y.; Fatica, T.; Sim, J.; Zhao, X.; Oh, Y.; Denoncourt, A., Cheung, A. C., Downey, M., Mulvihill, E. E., & Kim, K. H. (). Hmgcs2-mediated ketogenesis modulates high-fat diet-induced hepatosteatosis. Molecular metabolism. 2022, 61, 101494. [CrossRef]
- Czaja M. J. JNK regulation of hepatic manifestations of the metabolic syndrome. Trends in endocrinology and metabolism: TEM. 2010, 21, 707–713. [CrossRef]
- Najjar, S.M.; Abdolahipour, R.; Ghadieh, H.E.; Jahromi, M.S.; Najjar, J.A.; Abuamreh, B.A.M.; Zaidi, S.; Kumarasamy, S.; Muturi, H.T. Regulation of Insulin Clearance by Non-Esterified Fatty Acids. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 1899. [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S. A.; Kountouras, J.; Zavos, C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the pathogenetic roles of insulin resistance and adipocytokines. Current molecular medicine. 2009, 9, 299–314. [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D. E. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annual review of medicine. 2002, 53, 409–435. [CrossRef]
- Montagner, A.; Polizzi, A.; Fouché, E.; Ducheix, S.; Lippi, Y.; Lasserre, F.; Barquissau, V.; Régnier, M.; Lukowicz, C.; Benhamed, F.; Iroz, A.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Al Saati, T.; Cano, P.; Mselli-Lakhal, L.; Mithieux, G.; Rajas, F.; Lagarrigue, S.; Pineau, T.; Loiseau, N.; Guillou, H. Liver PPARα is crucial for whole-body fatty acid homeostasis and is protective against NAFLD. Gut. 2016, 65, 1202–1214. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Pan, X.; Luo, J.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Bestman, P. L.; Luo, M. Association of Inflammatory Cytokines With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Frontiers in immunology. 2022, 13, 880298. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R. S.; Bril, F.; Cusi, K.; Newsome, P. N. Modulation of Insulin Resistance in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2019, 70, 711–724. [CrossRef]
- Syn, W. K.; Choi, S. S.; Diehl, A. M. Apoptosis and cytokines in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinics in liver disease. 2009, 13, 565–580. [CrossRef]
- Auguet, T.; Bertran, L.; Binetti, J.; Aguilar, C.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Lopez-Dupla, J. M.; Porras, J. A.; Riesco, D.; Del Castillo, D.; Richart, C. Relationship between IL-8 Circulating Levels and TLR2 Hepatic Expression in Women with Morbid Obesity and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. International journal of molecular sciences. 2020, 21, 4189. [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W. Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C. A.; Kau, A. L.; Eisenbarth, S. C.; Jurczak, M. J.; Camporez, J. P.; Shulman, G. I.; Gordon, J. I.; Hoffman, H. M.; Flavell, R. A. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature. 2012, 482, 179–185. [CrossRef]
- Baker, R. G.; Hayden, M. S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell metabolism. 2011, 13, 11–22. [CrossRef]
- Oates, J. R.; McKell, M. C.; Moreno-Fernandez, M. E.; Damen, M. S. M. A.; Deepe, G. S.; Jr, Qualls, J. E.; Divanovic, S. Macrophage Function in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Mac Attack. Frontiers in immunology. 2019, 10, 2893. [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E. A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism: clinical and experimental. 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Schwabe, R. F. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: functional links and key pathways. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2015. 61, 1066–1079. [CrossRef]
- Torres, S.; Segalés, P.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J. C. Mitochondria and the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Alcoholic and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cells. 2022, 11, 1475. [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H. K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic liver disease. Nature reviews. Disease primers. 2018, 4, 16. [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J. M.; Kelley, R. K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A. G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature reviews. Disease primers. 2021, 7, 6. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. M., Cho, Y. E., & Hwang, S. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Liver Injury in the Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Liver Disease. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022, 23, 774. [CrossRef]
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.). 2020, 245, 96–108. [CrossRef]
- Pappachan, J. M.; Babu, S.; Krishnan, B.; Ravindran, N. C. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Clinical Update. Journal of clinical and translational hepatology. 2017, 5, 384–393. [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V., Bellentani, S., Cortez-Pinto, H., Day, C., & Marchesini, G. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. Journal of hepatology. 2010, 53, 372–384. [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Ju, C. Hepatic Macrophages in Liver Injury. Frontiers in immunology. 2020, 11, 322. [CrossRef]
- Wree, A.; McGeough, M. D.; Peña, C. A.; Schlattjan, M.; Li, H.; Inzaugarat, M. E.; Messer, K.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H. M.; Feldstein, A. E. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is required for fibrosis development in NAFLD. Journal of molecular medicine (Berlin, Germany). 2014, 92, 1069–1082. [CrossRef]
- Papa, S.; Bubici, C.; Zazzeroni, F.; Franzoso, G. Mechanisms of liver disease: cross-talk between the NF-kappaB and JNK pathways. Biological chemistry, 2009, 390(10), 965–976. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. S.; Zheng, Z.; Mendez, R.; Ha, S. W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K. Pharmacologic ER stress induces non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in an animal model. Toxicology letters. 2012, 211, 29–38. [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E. M.; Tiniakos, D. G. Pathology of steatohepatitis. Best practice & research. Clinical gastroenterology. 2002, 16, 691–707. [CrossRef]
- Tiniakos, D. G.; Vos, M. B.; Brunt, E. M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathology and pathogenesis. Annual review of pathology. 2010, 5, 145–171. [CrossRef]
- Wong, V. W.; Wong, G. L.; Choi, P. C.; Chan, A. W.; Li, M. K.; Chan, H. Y.; Chim, A. M.; Yu, J.; Sung, J. J.; Chan, H. L. Disease progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a prospective study with paired liver biopsies at 3 years. Gut. 2010, 59, 969–974. [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Lawitz, E.; Mantry, P. S.; Jayakumar, S.; Caldwell, S. H.; Arnold, H.; Diehl, A. M.; Djedjos, C. S.; Han, L.; Myers, R. P.; Subramanian, G. M.; McHutchison, J. G.; Goodman, Z. D.; Afdhal, N. H.; Charlton, M. R.; GS-US-384-1497 Investigators. The ASK1 inhibitor selonsertib in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, phase 2 trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2018, 67, 549–559. [CrossRef]
- Bianco, C.; Casirati, E.; Malvestiti, F.; Valenti, L. Genetic predisposition similarities between NASH and ASH: Identification of new therapeutic targets. JHEP reports: innovation in hepatology. 2021, 3, 100284. [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri B. A. Therapeutic Landscape for NAFLD in 2020. Gastroenterology. 2020, 158, 1984–1998.e3. [CrossRef]
- Philip Esteban, J.; Dinani, A. Lifestyle Interventions Beyond Diet and Exercise for Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2020, 16, 119–130.
- Norata, G. D.; Pellegatta, F.; Catapano, A. L. "Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors" e patologie cardiovascolari [Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and cardiovascular disorders]. Italian heart journal. Supplement: official journal of the Italian Federation of Cardiology. 2003, 4, 8–18.
- Loria, P.; Adinolfi, L. E.; Bellentani, S.; Bugianesi, E.; Grieco, A.; Fargion, S.; Gasbarrini, A.; Loguercio, C.; Lonardo, A.; Marchesini, G.; Marra, F.; Persico, M.; Prati, D.; Baroni, G. S.; NAFLD Expert Committee of the Associazione Italiana per lo studio del Fegato Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. A decalogue from the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver (AISF) Expert Committee. Digestive and liver disease: official journal of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver. 2010, 42, 272–282. [CrossRef]
- Seaman, S.; Stevens, J.; Yang, M. Y.; Logsdon, D.; Graff-Cherry, C.; St Croix, B. Genes that distinguish physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Cancer cell. 2007, 11, 539–554. [CrossRef]
- Bocca, C.; Novo, E.; Miglietta, A.; Parola, M. Angiogenesis and Fibrogenesis in Chronic Liver Diseases. Cellular and molecular gastroenterology and hepatology. 2015, 1, 477–488. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Semela, D.; Bruix, J.; Colle, I.; Pinzani, M.; Bosch, J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. Journal of hepatology. 2009, 50, 604–620. [CrossRef]
- Camenisch, G.; Pisabarro, M. T.; Sherman, D.; Kowalski, J.; Nagel, M.; Hass, P.; Xie, M. H.; Gurney, A.; Bodary, S.; Liang, X. H.; Clark, K.; Beresini, M.; Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H. P. ANGPTL3 stimulates endothelial cell adhesion and migration via integrin alpha vbeta 3 and induces blood vessel formation in vivo. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2002, 277, 17281–17290. [CrossRef]
- Valfrè di Bonzo, L.; Novo, E.; Cannito, S.; Busletta, C.; Paternostro, C.; Povero, D.; Parola, M. Angiogenesis and liver fibrogenesis. Histology and histopathology. 2009, 24, 1323–1341. [CrossRef]
- Baumeister, S. E.; Völzke, H.; Marschall, P.; John, U.; Schmidt, C. O.; Flessa, S.; Alte, D. Impact of fatty liver disease on health care utilization and costs in a general population: a 5-year observation. Gastroenterology. 2008, 134, 85–94. [CrossRef]
- Nath, B.; Szabo, G. Hypoxia and hypoxia inducible factors: diverse roles in liver diseases. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2012, 55, 622–633. [CrossRef]
- Kukla M. Angiogenesis: a phenomenon which aggravates chronic liver disease progression. Hepatology international. 2013, 7, 4–12. [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Marra, F.; Pinzani, M. Myofibroblast - like cells and liver fibrogenesis: Emerging concepts in a rapidly moving scenario. Molecular aspects of medicine. 2008, 29:58–66 . [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Ei Mourabit, H.; Housset, C.; Cadoret, A.; Lemoinne, S. Role of Angiogenesis in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Journal of clinical medicine. 2021, 10, 1338. [CrossRef]
- Coulon, S.; Heindryckx, F.; Geerts, A.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Colle, I.; Van Vlierberghe, H. Angiogenesis in chronic liver disease and its complications. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2011, 31, 146–162. [CrossRef]
- Dooley, S.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-β in progression of liver disease. Cell and tissue research. 2012, 347, 245–256. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Lin, N.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.; Ling, Y.; Pan, W.; Xu, R. Activated hepatic stellate cells promote angiogenesis via interleukin-8 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of translational medicine. 2015, 13, 365. [CrossRef]
- Copple, B. L.; Bai, S.; Burgoon, L. D.; Moon, J. O. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α regulates the expression of genes in hypoxic hepatic stellate cells important for collagen deposition and angiogenesis. Liver international: official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2011, 31, 230–244. [CrossRef]
- Weiskirchen, R.; Meurer, S. K.; Liedtke, C.; Huber, M. Mast Cells in Liver Fibrogenesis. Cells. 2019, 8, 1429. [CrossRef]
- Raevens, S.; Coulon, S.; Van Steenkiste, C.; Colman, R.; Verhelst, X.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Geerts, A.; Perkmann, T.; Horvatits, T.; Fuhrmann, V.; Colle, I. Role of angiogenic factors/cell adhesion markers in serum of cirrhotic patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver. 2015, 35, 1499–1507. [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Miglioli, L.; Masutti, F.; Castiglione, A.; Crocè, L. S.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S. Incidence and natural course of fatty liver in the general population: the Dionysos study. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2007, 46, 1387–1391. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Lee, M.E.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, K.H.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Ahn, J.B.; Chung, H.C.; Rha, S.Y. Dovitinib (TKI258), a Multi-Target Angiokinase Inhibitor, Is Effective Regardless of KRAS or BRAF Mutation Status in Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 72–86.
- Lopes-Coelho, F.; Martins, F.; Pereira, S.A.; Serpa, J. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3765. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. D.; Tang, Z. Y.; Sun, H. C. Targeting angiogenesis for liver cancer: Past, present, and future. Genes & diseases. 2020, 7, 328–335. [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Spagnuolo, C.; Tedesco, I.; Bilotto, S.; Russo, G. L. The flavonoid quercetin in disease prevention and therapy: facts and fancies. Biochemical pharmacology. 2012, 83, 6–15. [CrossRef]
- Hisaka, T.; Sakai, H.; Sato, T.; Goto, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Fukutomi, S.; Fujita, F.; Mizobe, T.; Nakashima, O.; Tanigawa, M.; Naito, Y.; Akiba, J.; Ogasawara, S.; Nakashima, K.; Akagi, Y.; Okuda, K.; Yano, H. Quercetin Suppresses Proliferation of Liver Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro. Anticancer research. 2020, 40, 4695–4700. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu H. C.; Yao, Q. Y.; Xu, B. L.; Zhang, S. C.; Tu, C. T. Quercetin Protects Mice from ConA-Induced Hepatitis by Inhibiting HMGB1-TLR Expression and Down-Regulating the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway. Inflammation. 2016, 96–106. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Mo, W.; Feng, J.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Xu, S.; Wang, W.; Lu, X.; Yu, Q.; Chen, K.; Xia, Y.; Lu, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, X.; Guo, C. Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagy via the TGF-β1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways. Scientific reports. 2017, 7(1), 9289. [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in liver homeostasis and pathology. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2014, 59, 2034–2042. [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F.; Zimmermann, H. W. Macrophage heterogeneity in liver injury and fibrosis. Journal of hepatology. 2014, 60, 1090–1096. [CrossRef]
- Pradere, J. P.; Kluwe, J.; De Minicis, S.; Jiao, J. J.; Gwak, G. Y.; Dapito, D. H.; Jang, M. K.; Guenther, N. D.; Mederacke, I.; Friedman, R.; Dragomir, A. C.; Aloman, C.; Schwabe, R. F. Hepatic macrophages but not dendritic cells contribute to liver fibrosis by promoting the survival of activated hepatic stellate cells in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2013, 58, 1461–1473. [CrossRef]
- Kren, V.; Walterová, D. Silybin and silymarin--new effects and applications. Biomedical papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia. 2005, 149, 29–41. [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Kohli, K.; Ali, M. Reassessing bioavailability of silymarin. Alternative medicine review : a journal of clinical therapeutic. 2011, 16, 239–249.
- Surai P. F. Silymarin as a Natural Antioxidant: An Overview of the Current Evidence and Perspectives. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2015, 4, 204–247. [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z. M.; Koenig, A. B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2016, 64, 73–84. [CrossRef]
- Hahn, G.; Lehmann, H. D.; Kürten, M.; Uebel, H.; Vogel, G. Zur Pharmakologie und Toxikologie von Silymarin, des antihepatotoxischen Wirkprinzipes aus Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn [On the pharmacology and toxicology of silymarin, an antihepatotoxic active principle from Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn]. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 1968, 18, 698–704.
- Kondylis, V.; Kumari, S.; Vlantis, K.; Pasparakis, M. The interplay of IKK, NF-κB and RIPK1 signaling in the regulation of cell death, tissue homeostasis and inflammation. Immunological reviews. 2017, 277, 113–127. [CrossRef]
- Gobejishvili L, Barve S, Joshi-Barve S, Uriarte S, Gobejishvili, L.; Barve, S.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Uriarte, S.; Song, Z.; McClain, C. Chronic ethanol-mediated decrease in cAMP primes macrophages to enhanced LPS-inducible NF-kappaB activity and TNF expression: relevance to alcoholic liver disease. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2006, 291, G681–G688. [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y. S.; He, Q.; Wang, M. Q.; Li, P. Nuclear factor kappa B and hepatitis viruses. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2008, 12, 265–280. [CrossRef]
- Muriel P. NF-kappaB in liver diseases: a target for drug therapy. Journal of applied toxicology: JAT. 2009, 29, 91–100. [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C. S.; Leo, M. A.; Cao, Q.; Ren, C.; DeCarli; L. M. Silymarin retards the progression of alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis in baboons. Journal of clinical gastroenterology. 2003, 37, 336–339. [CrossRef]
- Wenfeng, Z.; Yakun, W.; Di, M.; Jianping, G.; Chuanxin, W.; Chun, H. Kupffer cells: increasingly significant role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annals of hepatology. 2014, 13, 489–495. [CrossRef]
- Trubitsyna, I.E.; Chikunova, B.Z.; Tkachenko, E.V.; Tsaregorodtseva, T.M.; Vinokurova, L.V.; Varvanina, G.G. [Pathophysiology of hormonal, immune, metabolic changes in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Experimental and clinical studies]. Eksp Klin Gastroenterol. 2008, 7, 40-4.
- Pengyue, Z.; Tao, G.; Hongyun, H.; Liqiang, Y.; Yihao, D. Breviscapine confers a neuroprotective efficacy against transient focal cerebral ischemia by attenuating neuronal and astrocytic autophagy in the penumbra. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017,90, 69-76 . [CrossRef]
- Lin, L. L.; Liu, A. J.; Liu, J. G.; Yu, X. H; Qin, L. P.; Su, D. F. Protective effects of scutellarin and breviscapine on brain and heart ischemia in rats. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology. 2007, 50, 327–332. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Q. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: A comprehensive review. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2018, 190, 105–127. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, P. H.; Zhang, X. X.; Dai, Y.; He, Q. Breviscapine ameliorates CCl4-induced liver injury in mice through inhibiting inflammatory apoptotic response and ROS generation. International journal of molecular medicine. 2018, 42, 755–768. [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Ma, X.; Lin, P.; Kang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Cheng, J.; Li, Y. Scutellarin Prevents Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Hyperlipidemia via PI3K/AKT-Dependent Activation of Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-Derived 2)-Like 2 (Nrf2) in Rats. Medical science monitor: international medical journal of experimental and clinical research. 2017, 23, 5599–5612. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Song, K.; Gusdon, A. M.; Li, L.; Bu, L.; Qu, S. Melatonin improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via MAPK-JNK/P38 signaling in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. Lipids in health and disease. 2016, 15, 202. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. K.; Hu, L. F.; Lou, D. S.; Wang, B. C.; Tan, J. Targeting DUSP16/TAK1 signaling alleviates hepatic dyslipidemia and inflammation in high fat diet (HFD)-challenged mice through suppressing JNK MAPK. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2020, 524, 142–149. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Nie, H.; Zhang, X. J.; Zhang, P.; She, Z. G.; Li, H.; Ji, Y. X.; Cai, J. Hepatic Regulator of G Protein Signaling 5 Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Activated Kinase 1-c-Jun-N-Terminal Kinase/p38 Signaling. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2021, 73, 104–125. [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J. Inhibition of lncRNA HULC improves hepatic fibrosis and hepatocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the MAPK signaling pathway in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of cellular physiology. 2019, 234, 18169–18179. [CrossRef]
- Park, B. Y.; Lee, H.; Woo, S.; Yoon, M.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.; Lee, H. S.; Park, E. K.; Hahm, J. C.; Kim, J. W.; Shin, S. S.; Kim, M. Y.; Yoon, M. Reduction of Adipose Tissue Mass by the Angiogenesis Inhibitor ALS-L1023 from Melissa officinalis. PloS one. 2015, 10, e0141612. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lim, J.; Oh, J.; Shin, S. S.; Yoon, M. The Angiogenesis Inhibitor ALS-L1023 from Lemon-Balm Leaves Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Regulating the Visceral Adipose-Tissue Function. International journal of molecular sciences. 2017, 18, 846. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. K.; Kim, Y. J.; Kim, J. Y.; Song, H. B.; Yu, H. G. Melissa officinalis extract inhibits laser-induced choroidal neovascularization in a rat model. PloS one. 2014, 9, e110109. [CrossRef]
- Sipos, S.; Moacă, E.-A.; Pavel, I.Z.; Avram, Ş.; Crețu, O.M.; Coricovac, D.; Racoviceanu, R.-M.; Ghiulai, R.; Pană, R.D.; Şoica, C.M.; Borcan, F.; Dehelean, C.A.; Crăiniceanu, Z. Melissa officinalis L. Aqueous Extract Exerts Antioxidant and Antiangiogenic Effects and Improves Physiological Skin Parameters. Molecules. 2021, 26, 2369. [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Yoon, M.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.; Kim, M. Y.; Shin, S. S.; Yoon, M. The anti-angiogenic herbal extract from Melissa officinalis inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and suppresses adipocyte hypertrophy in high fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2016, 178, 238–250. [CrossRef]
- Park, B. Y.; Lee, H.; Woo, S.; Yoon, M.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y.; Lee, H. S.; Park, E. K.; Hahm, J. C.; Kim, J. W.; Shin, S. S.; Kim, M. Y.; Yoon, M. Reduction of Adipose Tissue Mass by the Angiogenesis Inhibitor ALS-L1023 from Melissa officinalis. PloS one. 2015, 10, e0141612. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lim, J.; Oh, J.; Shin, S. S.; Yoon, M. The Angiogenesis Inhibitor ALS-L1023 from Lemon-Balm Leaves Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Regulating the Visceral Adipose-Tissue Function. International journal of molecular sciences. 2017, 18, 846. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lim, J.; Lee, H.; Yoon, S.; Shin, S. S.; Yoon, M. The lemon balm extract ALS-L1023 inhibits obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in female ovariectomized mice. Food and chemical toxicology: an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association. 2017, 106, 292–305. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.E.; Yoon, E.L.; Lee, S.R.; Jun, D.W. ALS-L1023 from Melissa officinalis Alleviates Liver Fibrosis in a Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model. Life. 2023, 13, 100. [CrossRef]
- Howells, L. M.; Iwuji, C. O. O.; Irving, G. R. B.; Barber, S.; Walter, H.; Sidat, Z.; Griffin-Teall, N.; Singh, R.; Foreman, N.; Patel, S. R.; Morgan, B.; Steward, W. P.; Gescher, A.; Thomas, A. L.; Brown, K. Curcumin Combined with FOLFOX Chemotherapy Is Safe and Tolerable in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in a Randomized Phase IIa Trial. The Journal of nutrition. 2019, 149, 1133–1139. [CrossRef]
- Marino, P.; Pepe, G.; Basilicata, M.G.; Vestuto, V.; Marzocco, S.; Autore, G.; Procino, A.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.M.; Manfra, M.; Campiglia, P. Potential Role of Natural Antioxidant Products in Oncological Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 704. [CrossRef]
- Longobardi, C.; Damiano, S.; Andretta, E.; Prisco, F.; Russo, V.; Pagnini, F.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Curcumin Modulates Nitrosative Stress, Inflammation, and DNA Damage and Protects against Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2021, 10, 1239. [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Longobardi, C.; Andretta, E.; Prisco, F.; Piegari, G.; Squillacioti, C.; Montagnaro, S.; Pagnini, F.; Badino, P.; Florio, S.; Ciarcia, R. Antioxidative Effects of Curcumin on the Hepatotoxicity Induced by Ochratoxin A in Rats. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2021, 10, 125. [CrossRef]
- Randino, R.; Grimaldi, M.; Persico, M.; De Santis, A.; Cini, E.; Cabri, W.; Riva, A.; D'Errico, G.; Fattorusso, C.; D'Ursi, A. M.; & Rodriquez, M. Investigating the Neuroprotective Effects of Turmeric Extract: Structural Interactions of β-Amyloid Peptide with Single Curcuminoids. Scientific reports. 2016, 6, 38846. [CrossRef]
- Vera-Ramirez, L.; Pérez-Lopez, P.; Varela-Lopez, A.; Ramirez-Tortosa, M.; Battino, M.; Quiles, J.L. Curcumin and liver disease. BioFactors. 2013, 39, 88-100. [CrossRef]
- Bhandarkar, S. S.; Arbiser, J. L. Curcumin as an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2007, 595, 185–195. [CrossRef]
- Damiano, S.; Jarriyawattanachaikul, W.; Girolami, F.; Longobardi, C.; Nebbia, C.; Andretta, E.; Lauritano, C.; Dabbou, S.; Avantaggiato, G.; Schiavone, A.; Badino, P.; Ciarcia, R. Curcumin Supplementation Protects Broiler Chickens Against the Renal Oxidative Stress Induced by the Dietary Exposure to Low Levels of Aflatoxin B1. Frontiers in veterinary science. 2022, 8, 822227. [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M. H.; Zobeiri, M.; Parvizi, F.; El-Senduny, F. F.; Marmouzi, I.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Naseri, R.; Nabavi, S. M.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective. Nutrients. 2018, 10, 855. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, X., Wang, J.; He, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Li, R.; Gong, M.; Luo, S.; Xiao, X. Curcumin protects against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by inhibiting HIF-1α through an ERK-dependent pathway. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2014, 19, 18767–18780. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. E.; Lee, S. J.; Kim, S. J.; Lee, H. S.; Kwon, O. S. Curcumin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Inhibition of O-GlcNAcylation. Nutrients. 2019, 11(11), 2702. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Umeda, T.; Higuchi, O.; Tsuzuki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Miyazawa, T. Evaporative light-scattering analysis of sulforaphane in broccoli samples: Quality of broccoli products regarding sulforaphane contents. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2006, 54, 2479–2483. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A. E.; Baniasadi, M.; Giansiracusa, D.; Giansiracusa, M.; Garcia, M.; Fryda, Z.; Wong, T. L.; Bishayee, A. Sulforaphane: A Broccoli Bioactive Phytocompound with Cancer Preventive Potential. Cancers. 2021, 13, 4796. [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shen, G.; Chen, C.; Gélinas, C.; Kong, A. N. Suppression of NF-kappaB and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression by sulforaphane and PEITC through IkappaBalpha, IKK pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Oncogene. 2005, 24, 4486–4495. [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Singh, K. P.; Kurzrock, R.; Shankar, S. Sulforaphane inhibits angiogenesis through activation of FOXO transcription factors. Oncology reports. 2009, 22, 1473–1478. [CrossRef]
- Hahm, E. R.; Singh, S. V. Sulforaphane inhibits constitutive and interleukin-6-induced activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer prevention research (Philadelphia, Pa.). 2010, 3, 484–494. [CrossRef]
- Noh, J. R.; Kim, Y. H.; Hwang, J. H.; Choi, D. H.; Kim, K. S.; Oh, W. K.; Lee, C. H. Sulforaphane protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Food and chemical toxicology: an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association. 2015, 80, 193–200. [CrossRef]
- S, Sato; K, Moriya; M, Furukawa; S, Saikawa; T, Namisaki; M, Kitade; H, Kawaratani; K, Kaji; H, Takaya; N, Shimozato; Y, Sawada; K, Seki; K, Kitagawa; T, Akahane; A, Mitoro; Y, Okura; H, Yoshiji; J, Yamao Sulforaphane Inhibits Liver Cancer Cell Growth and Angiogenesis. Annals of Behavioural Science. 2018, 4, – . [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H. S.; Sharma, A. K.; Sandhu, S. S.; Kashyap, D. Cordycepin: a bioactive metabolite with therapeutic potential. Life sciences. 2013, 93, 863–869. [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Xu, R.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, D.; Wan, Q. The protective effect of Cordycepin on diabetic nephropathy through autophagy induction in vivo and in vitro. International urology and nephrology. 2019, 51, 1883–1892. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S. Y.; Park, S. J.; Park, Y. J. The Anticancer Properties of Cordycepin and Their Underlying Mechanisms. International journal of molecular sciences. 2018, 19, 3027. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Dai, G.; Huang, Y. Cordycepin suppresses the migration and invasion of human liver cancer cells by downregulating the expression of CXCR4. International journal of molecular medicine. 2020, 45, 141–150. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y. Z.; Hylemon, P. B.; Zhang, L. Y.; Zhou, H. P. Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses by modulating NOD-Like Receptor Protein 3 inflammasome activation. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie. 2017, 95, 1777–1788. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. H.; Kim, D.; Jung, J.; Kang, H.; Cho, H. NLRP3 Deficiency in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Enhances Surveillance of NK-92 through a Modulation of MICA/B. International journal of molecular sciences. 2021, 22, 9285. [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Weng, Q.; Jiang, S.; Tian, S.; Xu, T.; Hu, S.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Rong, X.; Guo, J. Cordycepin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Activation of the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2021, 74, 686–703. [CrossRef]
- Costa, B. P.; Nassr, M. T., Diz; F. M., Fernandes; K. H. A., Antunes; G. L., Grun, L. K.; Barbé-Tuana, F. M.; Nunes, F. B.; Branchini, G.; de Oliveira, J. R. Methoxyeugenol regulates the p53/p21 pathway and suppresses human endometrial cancer cell proliferation. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2021, 267, 113645. [CrossRef]
- Antunes, G. L.: Matzenbacher, L. S.; Costa, B. P.; de Sousa Basso, B.; Levorse, V. G. S.; Antunes, K. H.; Costa-Ferro, Z. S. M.; de Oliveira, J. R. Methoxyeugenol Protects Against Lung Inflammation and Suppresses Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in an LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury Model. Inflammation. 2022, 45, 1534–1547. [CrossRef]
- Hoda, S.; Vermani, M.; Joshi, R. K.; Shankar, J.; Vijayaraghavan, P. Anti-melanogenic activity of Myristica fragrans extract against Aspergillus fumigatus using phenotypic based screening. BMC complementary medicine and therapies. 2020, 20, 67. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Song, F.; Hu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhai, Q.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wang, G. The Protective Effect of Myristica fragrans Houtt. Extracts Against Obesity and Inflammation by Regulating Free Fatty Acids Metabolism in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 2507. [CrossRef]
- de Souza Basso, B.; Haute, G. V.; Ortega-Ribera, M.; Luft, C.; Antunes, G. L.; Bastos, M. S.; Carlessi, L. P.; Levorse, V. G.; Cassel, E.; Donadio, M. V. F.; Santarém, E. R.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Rodrigues de Oliveira, J. Methoxyeugenol deactivates hepatic stellate cells and attenuates liver fibrosis and inflammation through a PPAR-ɣ and NF-kB mechanism. Journal of ethnopharmacology. 2021, 280, 114433. [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A. Z.; Althagafi, I. I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications. European journal of medicinal chemistry. 2019, 166, 502–513. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J. H.; Song, J.; Park, K. W. The multifaceted factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in metabolism, immunity, and cancer. Archives of pharmacal research. 2015, 38, 302–312. [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I. E.; Nabavi, S. F.; Daglia, M.; Tenore, G. C.; Mansouri, K.; Nabavi, S. M. Naringenin and atherosclerosis: a review of literature. Current pharmaceutical biotechnology. 2015, 16, 245–251. [CrossRef]
- Wali, A. F., Rashid, S., Rashid, S. M., Ansari, M. A., Khan, M. R., Haq, N., Alhareth, D. Y., Ahmad, A., & Rehman, M. U. Naringenin Regulates Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Dysfunction: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Plants (Basel, Switzerland). 2020, 9(4), 550. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, C.; Shen, F.; Wang, M.; Jia, N.; Wang, C. Naringenin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury through its anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activity and by inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2017, 14, 2228–2234. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Hu, G.; Wen, C.; Yue, S., Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, H.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, R. Naringenin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulating the NLRP3/NF-κB pathway in mice. British journal of pharmacology. 2020, 177, 1806–1821. [CrossRef]
- Kohno, M.; Musashi, K.; Ikeda, H. O.; Horibe, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Kawakami, K. Oral administration of ferulic acid or ethyl ferulate attenuates retinal damage in sodium iodate-induced retinal degeneration mice. Scientific reports. 2020, 10, 8688. [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, A.; Chinnaiyan, M.; Karundevi, B. Ferulic acid exerts its antidiabetic effect by modulating insulin-signalling molecules in the liver of high-fat diet and fructose-induced type-2 diabetic adult male rat. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolism. 2015, 40, 769–781. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Sheng, Y.C.; Ji, L.L.; Wang, Z.T. Ferulic acid prevents liver injury and increases the anti-tumor effect of diosbulbin B in vivo. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2014, 15, 540-7. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, A. K.; Li, Y.; Tao, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, W.; Li, Z.; Liang, X. Screening and tissue distribution of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors in mice following oral administration of Garcinia mangostana L. ethanolic extract. Food chemistry. 2021, 357, 129759. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A. M.; Hussein, O. E.; Hozayen, W. G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abd El-Twab, S. M. Ferulic acid prevents oxidative stress, inflammation, and liver injury via upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in methotrexate-induced rats. Environmental science and pollution research international. 2020, 27, 7910–7921. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, X.; Fan, G.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, Q., Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Li, S.; Huang, G.; Ma, L.; Li, X. Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrotic Liver Injury by Inhibiting PTP1B Activity and Subsequent Promoting AMPK Phosphorylation. Frontiers in pharmacology. 2021, 12, 754976. [CrossRef]
- Hawley, S. A.; Ford, R. J.; Smith, B. K.; Gowans, G. J.; Mancini, S. J.; Pitt, R. D.; Day, E. A.; Salt, I. P.; Steinberg, G. R.; Hardie, D. G. The Na+/Glucose Cotransporter Inhibitor Canagliflozin Activates AMPK by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Function and Increasing Cellular AMP Levels. Diabetes. 2016, 65, 2784–2794. [CrossRef]
- Craig S. A. Betaine in human nutrition. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 2004, 80, 539–549. [CrossRef]
- Holm, P. I.; Ueland, P. M.; Vollset, S. E.; Midttun, Ø.; Blom, H. J.; Keijzer, M. B.; den Heijer, M. Betaine and folate status as cooperative determinants of plasma homocysteine in humans. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2005, 25, 379–385. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. K.; Choi, K. H.; Kim, Y. C. Effect of acute betaine administration on hepatic metabolism of S-amino acids in rats and mice. Biochemical pharmacology. 2003, 65, 1565–1574. [CrossRef]
- Go, E. K.; Jung, K. J.; Kim, J. Y.; Yu, B. P.; Chung, H. Y. Betaine suppresses proinflammatory signaling during aging: the involvement of nuclear factor-kappaB via nuclear factor-inducing kinase/IkappaB kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinases. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences. 2005, 60, 1252–1264. [CrossRef]
- Yi, E. Y.; Kim, Y. J. Betaine inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through suppression of the NF-κB and Akt signaling pathways. International journal of oncology. 2012, 41, 1879–1885. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R. S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature. 2005, 438, 967–974. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Chápuli, R., Quesada, A. R., & Angel Medina, M. Angiogenesis and signal transduction in endothelial cells. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 2004, 61, 2224–2243. [CrossRef]
- Blavier, L.; Lazaryev, A.; Dorey, F.; Shackleford, G. M.; DeClerck, Y. A. Matrix metalloproteinases play an active role in Wnt1-induced mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer research. 2006, 66, 2691–2699. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R. M.; Anwar, M. M.; Farghaly, H. S.; Kandeil, M. A. Gallic acid and ferulic acid protect the liver from thioacetamide-induced fibrosis in rats via differential expression of miR-21, miR-30 and miR-200 and impact on TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. Chemico-biological interactions. 2020, 324, 109098. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A. N.; de L Nascimento, T. R.; Gondim, B. L. C.; Velo, M. M. A. C.; de A Rêgo, R. I.; do C Neto, J. R.; Machado, J. R.; da Silva, M. V.; de Araújo, H. W. C.; Fonseca, M. G.; Castellano, L. R. C. Catechins as Model Bioactive Compounds for Biomedical Applications. Current pharmaceutical design. 2020, 26, 4032–4047. [CrossRef]
- Badolati, N.; Masselli, R.; Sommella, E.; Sagliocchi, S.; Di Minno, A.; Salviati, E.; Campiglia, P.; Dentice, M.; Tenore, G. C.; Stornaiuolo, M.; Novellino, E. The Hepatoprotective Effect of Taurisolo, a Nutraceutical Enriched in Resveratrol and Polyphenols, Involves Activation of Mitochondrial Metabolism in Mice Liver. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland). 2020, 9, 410. [CrossRef]
- Vestuto, V.; Amodio, G.; Pepe, G.; Basilicata, M.G.; Belvedere, R.; Napolitano, E.; Guarnieri, D.; Pagliara, V.; Paladino, S.; Rodriquez, M.; Bertamino, A.; Campiglia, P.; Remondelli, P.; Moltedo, O. Cocoa Extract Provides Protection against 6-OHDA Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Dopaminergic Neurons by Targeting PERK. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, H.; Akazome, Y.; Shoji, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Yasue, M.; Kanda, T.; Ohtake, Y. Oligomeric procyanidins in apple polyphenol are main active components for inhibition of pancreatic lipase and triglyceride absorption. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2007, 55, 4604–4609. [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Saito, K.; Miyoshi, N., Ohishi, T.; Oishi, Y.; Miyoshi, M.; Nakamura, Y. Anti-Cancer Effects of Green Tea by Either Anti- or Pro- Oxidative Mechanisms. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention: APJCP. 2016, 17, 1649–1654. [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Ijiri, M.; Suzuki, T.; Taguchi, K.;Koyama, Y.; Isemura, M. Green tea with a high catechin content suppresses inflammatory cytokine expression in the galactosamine-injured rat liver. Biomedical research (Tokyo, Japan). 2005,26, 187–192. [CrossRef]
- Tipoe, G. L.; Leung, T. M.; Liong, E. C.; Lau, T. Y.; Fung, M. L.; Nanji, A. A. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces liver inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicology. 2010, 273, 45–52. [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Qian, K. Epigallocatechin gallate attenuated non-alcoholic steatohepatitis induced by methionine- and choline-deficient diet. European journal of pharmacology. 2015, 761, 405–412. [CrossRef]
- Tang, F. Y.; Nguyen, N.; Meydani, M. Green tea catechins inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vitro through suppression of VE-cadherin phosphorylation and inactivation of Akt molecule. International journal of cancer. 2003, 106, 871–878. [CrossRef]
- Kenny, T. P.; Keen, C. L.; Jones, P.; Kung, H. J.; Schmitz, H. H.; Gershwin, M. E. Cocoa procyanidins inhibit proliferation and angiogenic signals in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells following stimulation by low-level H2O2. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.). 2004, 229, 765–771. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, F.; Sun, C.; Zhou, T.; Yang, J.; Zhan, X. Puerarin inhibits TRPM3/miR-204 to promote MC3T3-E1 cells proliferation, differentiation and mineralization. Phytotherapy research: PTR. 2018, 32, 996–1003. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Ji, G.; Ma, Z.; Liu, T.; Xin, L.; Wu, H.; Liang, X.; Liu, J. Therapeutic effect of puerarin on non-alcoholic rat fatty liver by improving leptin signal transduction through JAK2/STAT3 pathways. The American journal of Chinese medicine. 2009, 37, 69–83. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, N.; Aldhahrani, A.; Soliman, M. M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, F. Puerarin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats by regulating hepatic lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Frontiers in immunology. 2022, 13, 956688. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Min, J. S.; Kim, B.; Chae, U. B.; Yun, J. W.; Choi, M. S.; Kong, I. K.; Chang, K. T.; Lee, D. S. Mitochondrial ROS govern the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory response in microglia cells by regulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Neuroscience letters. 2015, 584, 191–196. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. Q.; Ding, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, C. M. Puerarin attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver oxidative stress and hyperlipidaemia in mouse by JNK/c-Jun/CYP7A1 pathway. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology. 2014, 115, 389–395. [CrossRef]
- BedÊ, T. P.; Jesuz, V. A.; Souza, V. R.; Elias, M. B.; Oliveira, F. L.; Dias, J. F.; Teodoro, A. J.; Azeredo, V. B. Effects of grape juice, red wine and resveratrol on liver parameters of rat submitted high-fat diet. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias. 2020, 92, e20191230. [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Park, S.; Kim, M. J.; Yang, W. K.; Im, D. U.; Yang, K. R.; Hong, J.; Choe, W.; Kang, I.; Kim, S. S.; Ha, J. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates the antioxidant effects of resveratrol through regulation of the transcription factor FoxO1. The FEBS journal. 2014, 281, 4421–4438. [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Park, S.; Kim, M. J.; Yang, W. K.; Im, D. U.; Yang, K. R.; Hong, J.; Choe, W.; Kang, I.; Kim, S. S.; Ha, J. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates the antioxidant effects of resveratrol through regulation of the transcription factor FoxO1. The FEBS journal. 2014, 281, 4421–4438. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S. M.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X. J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular basis of disease. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular cell research. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [CrossRef]
- Di Pascoli, M.; Diví, M.; Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A.; Rosado, E.; Gracia-Sancho, J.; Vilaseca, M.; Bosch, J.; García-Pagán, J. C. Resveratrol improves intrahepatic endothelial dysfunction and reduces hepatic fibrosis and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Journal of hepatology. 2013, 58, 904–910. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C. M.; Martins, L. A. M.; de Sousa, A. C.; Moraes, K. D. S.; Costa, B. P.; Vieira, M. Q.; Coelho, B. P.; Borojevic, R.; de Oliveira, J. R.; Guma, F. C. R. Resveratrol increases the activation markers and changes the release of inflammatory cytokines of hepatic stellate cells. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. 2021, 476, 649–661. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. S.; Shin, M. O.; Yoon, S.; Moon, J. O. Resveratrol inhibits dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Archives of pharmacal research. 2010, 33, 925–932. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: structure and bioactivity. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Chang, A. K.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Zou, X. Fucoidan extract derived from Undaria pinnatifida inhibits angiogenesis by human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Phytomedicine: international journal of phytotherapy and phytopharmacology. 2012, 19, 797–803. [CrossRef]
- Abdollah, M. R. A.; Ali, A. A.; Elgohary, H. H.; Elmazar, M. M. Antiangiogenic drugs in combination with seaweed fucoidan: A mechanistic in vitro and in vivo study exploring the VEGF receptor and its downstream signaling molecules in hepatic cancer. Frontiers in pharmacology. 2023, 14, 1108992. [CrossRef]
- Lin, K. I.; Lin, C. C.; Kuo, S. M.; Lai, J. C.; Wang, Y. Q.; You, H. L.; Hsu, M. L.; Chen, C. H.; Shiu, L. Y. Carnosic acid impedes cell growth and enhances anticancer effects of carmustine and lomustine in melanoma. Bioscience reports. 2018, 38, BSR20180005. [CrossRef]
- Johnson J. J. Carnosol: a promising anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory agent. Cancer letters. 2011, 305, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, A.; García-Caballero, M.; Medina, M. Á.; Quesada, A. R. Anti-angiogenic properties of carnosol and carnosic acid, two major dietary compounds from rosemary. European journal of nutrition. 2013, 52, 85–95. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





