Submitted:
05 June 2023
Posted:
06 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- In terms of data preprocessing, compared with predecessors, we use a text classification model to filter related information and remove similar blog posts within the same day. This is beneficial for cleansing the noise in social media data and standardizing the dataset as much as possible.
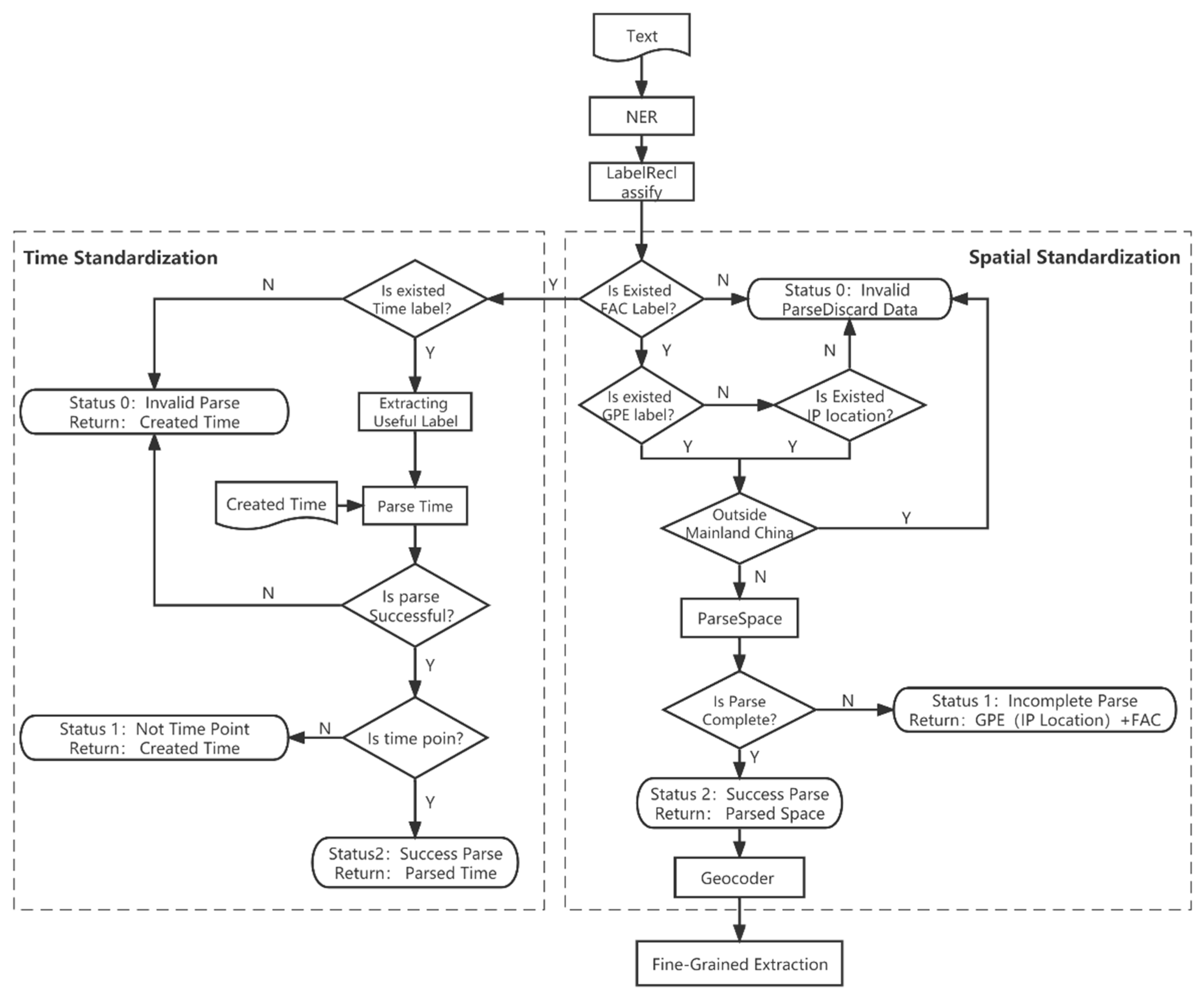
- For the extraction of coarse-grained spatiotemporal information, we propose a set of strict standardization rules for spatiotemporal information, allowing the maximum structuring of potential spatiotemporal information.
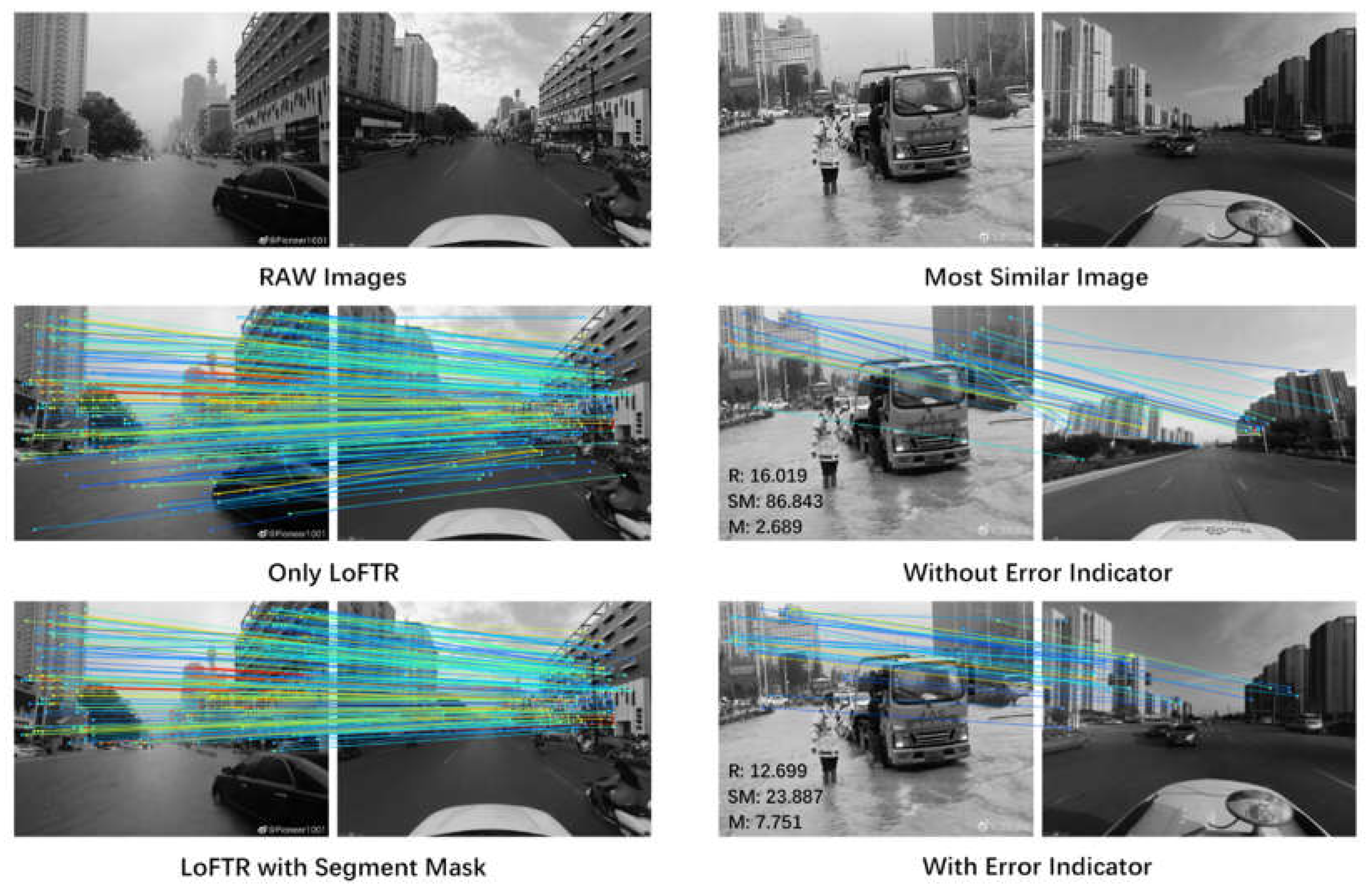
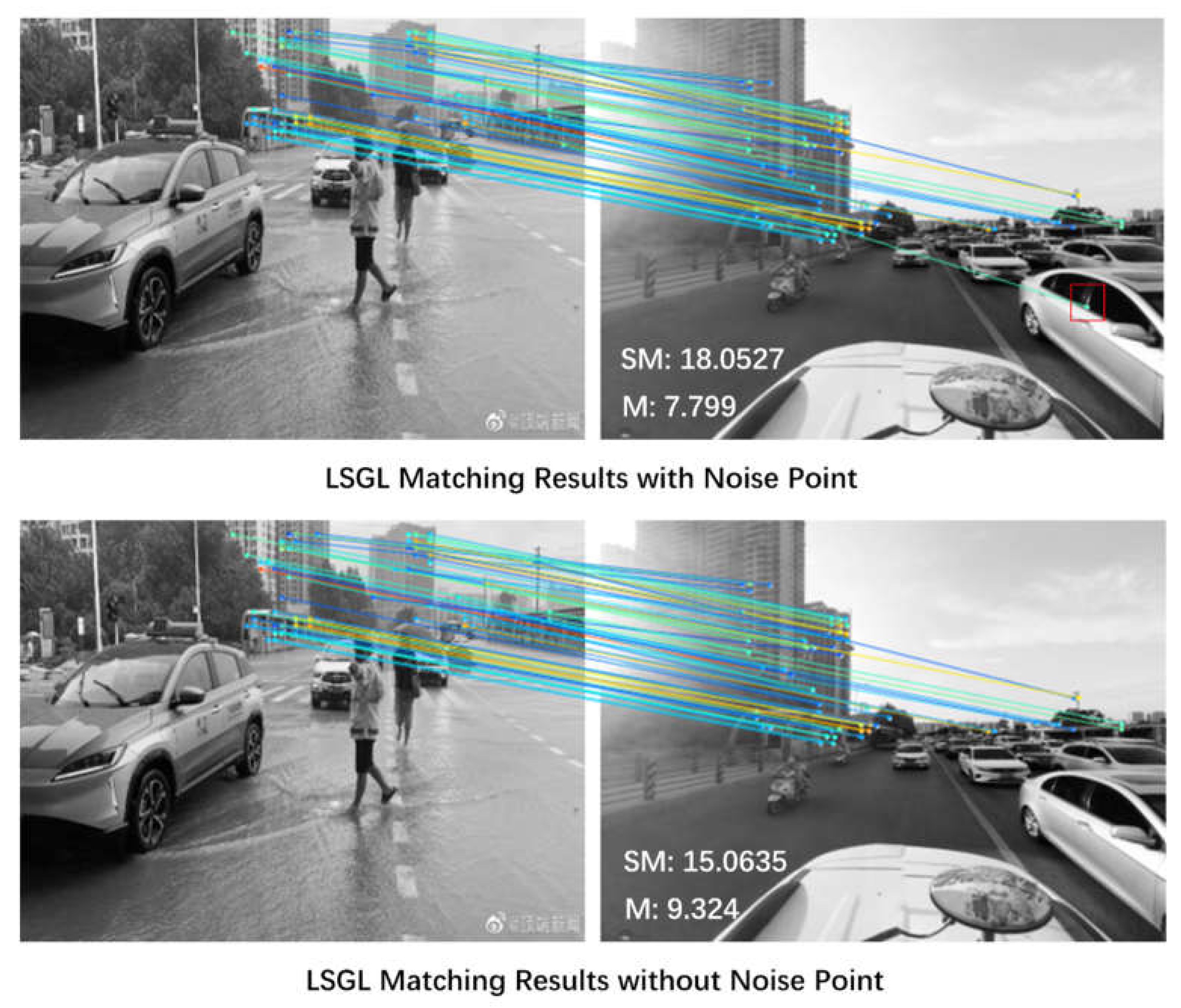
- For the extraction of fine-grained spatial information, we propose an LSGL method. This leverages cascading computer vision models to further improve the accuracy of spatial information extracted from coarse-grained data, thus enhancing the utilization of image and video modal data from social media.
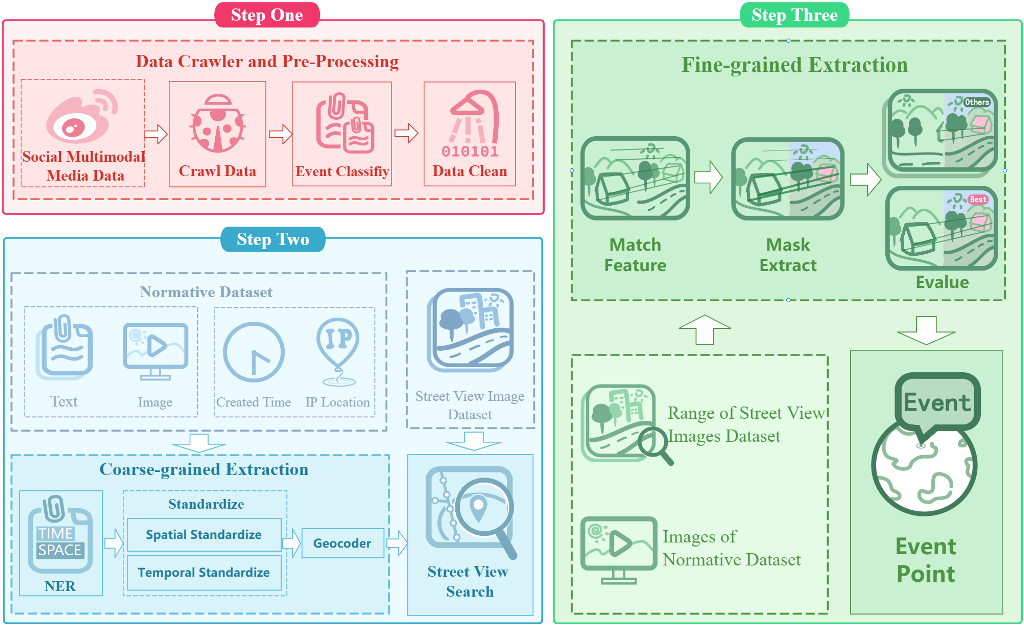
2. Methods
2.1. Technical process
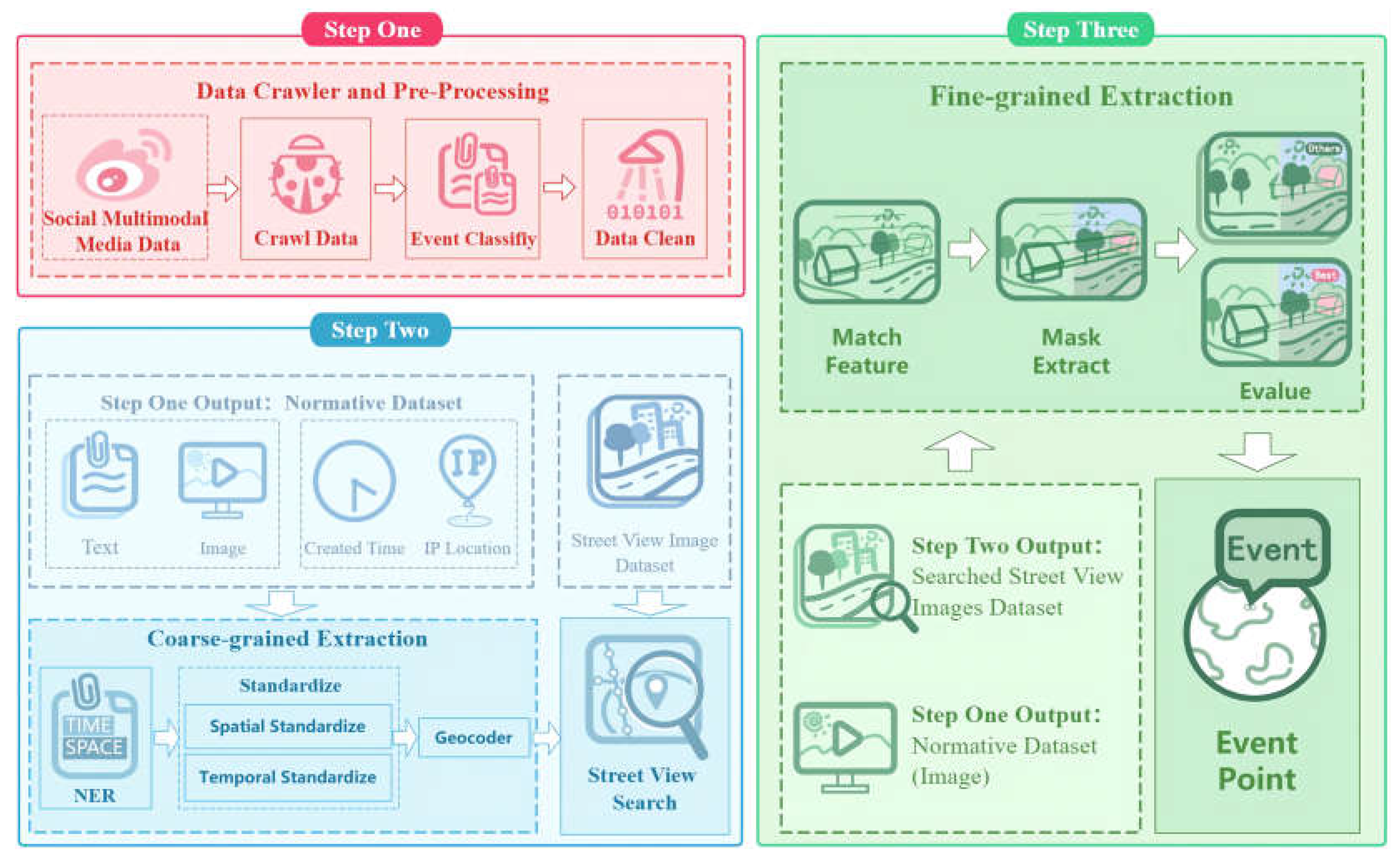
2.2. Data craw and Pre-Process
2.3. Coarse-grained spatio-temporal information extraction
2.4. Fine-grained extraction of spatial information
3. Experiments Setup
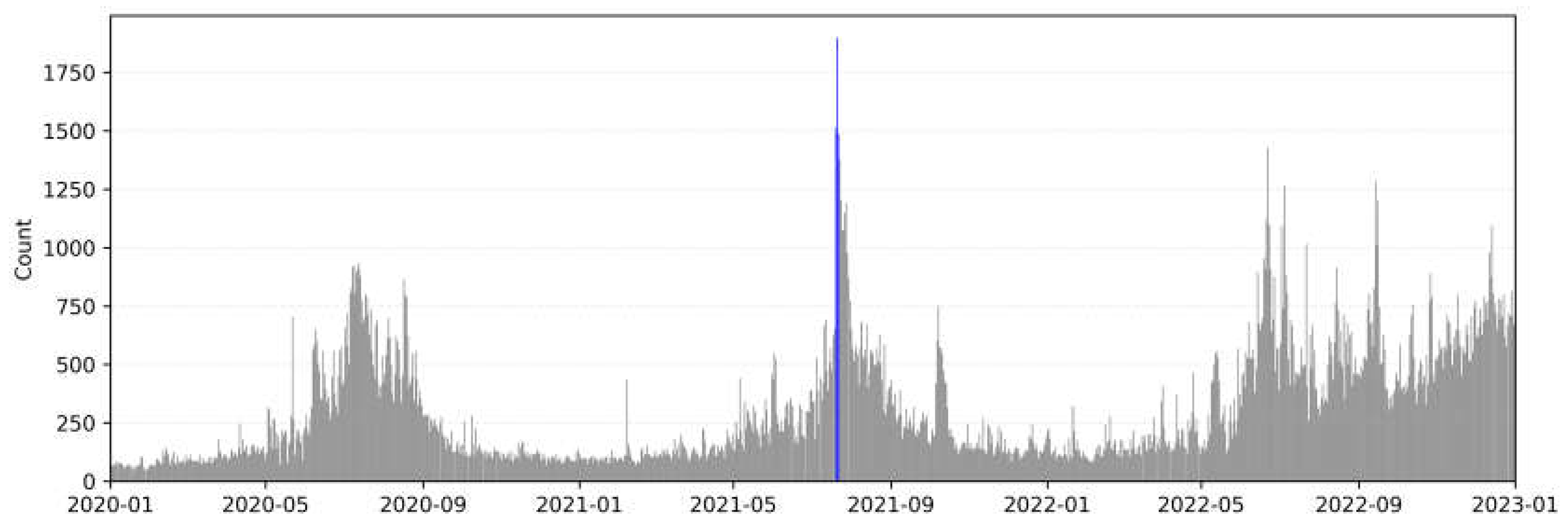
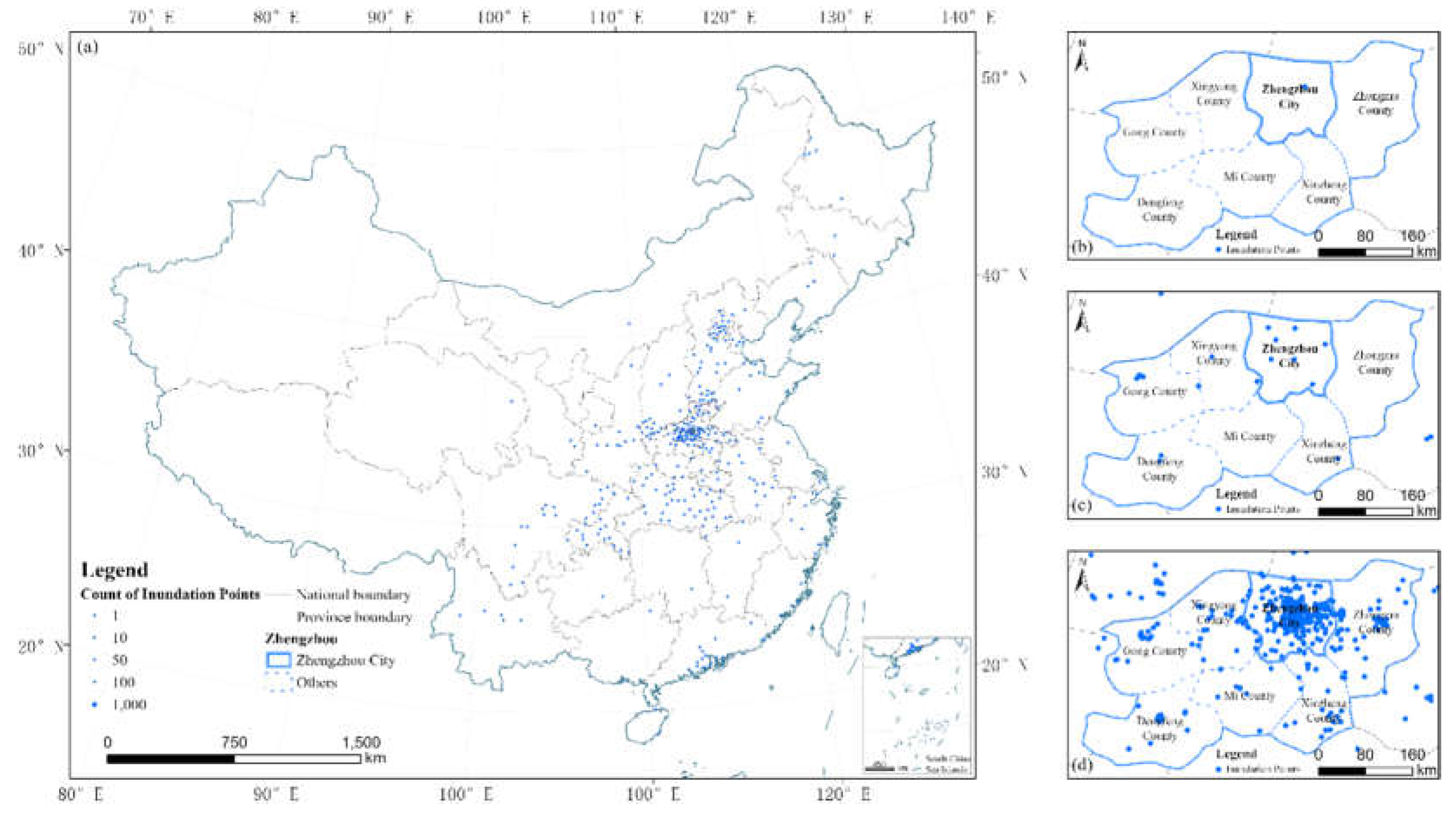
3.1. Research Event
3.2. Experiments environment
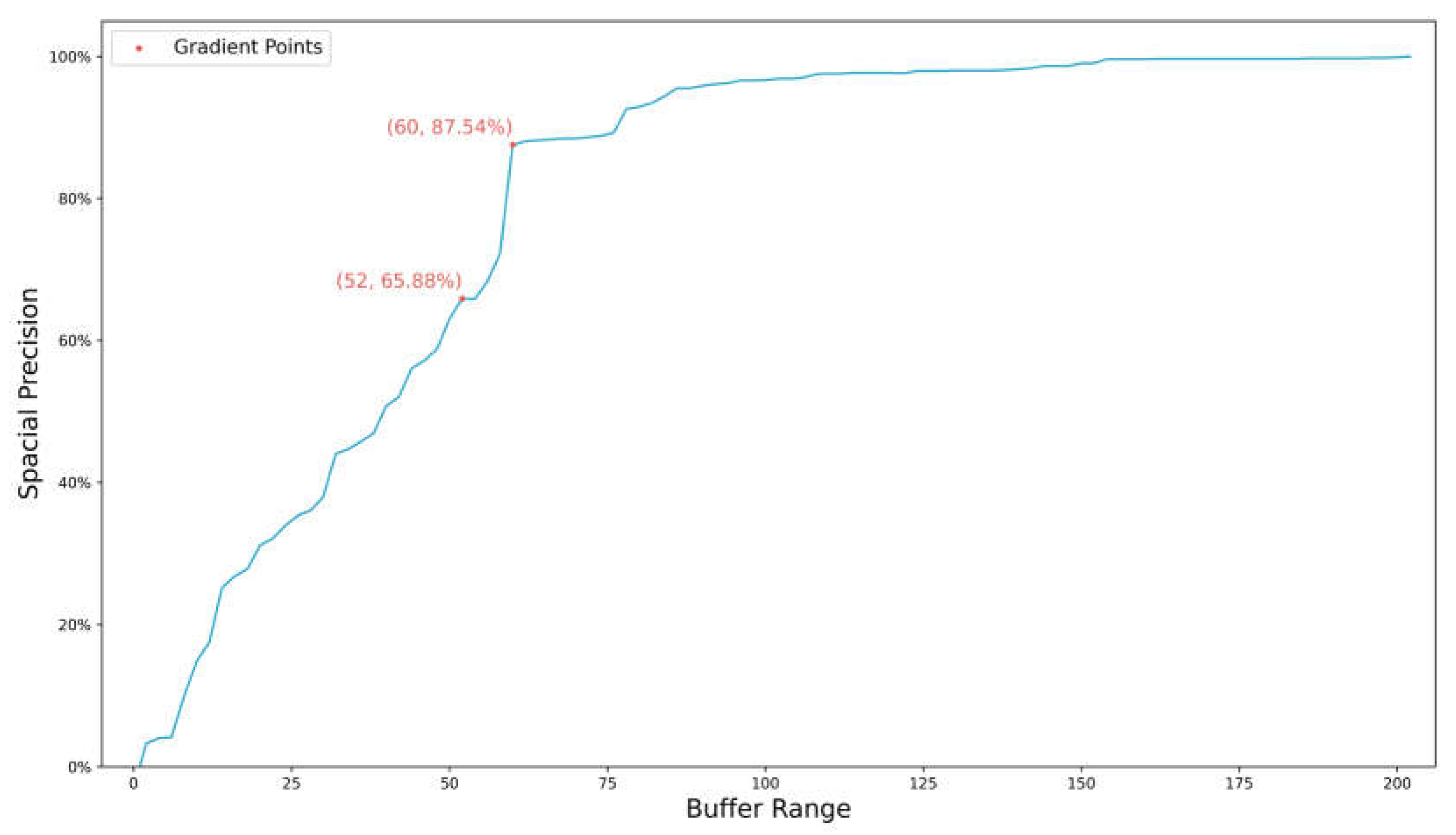
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
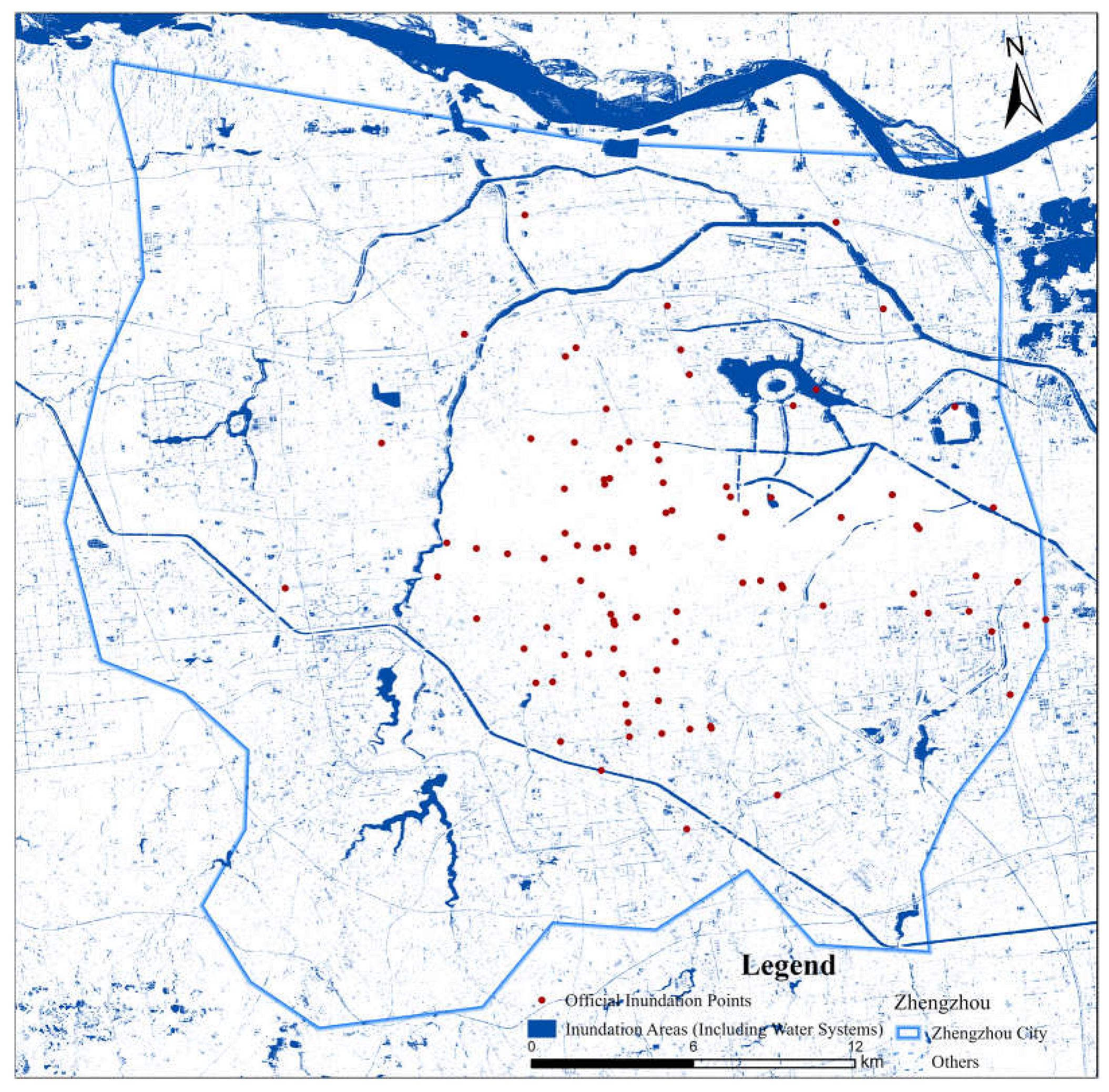
4.1. Effectiveness Analysis
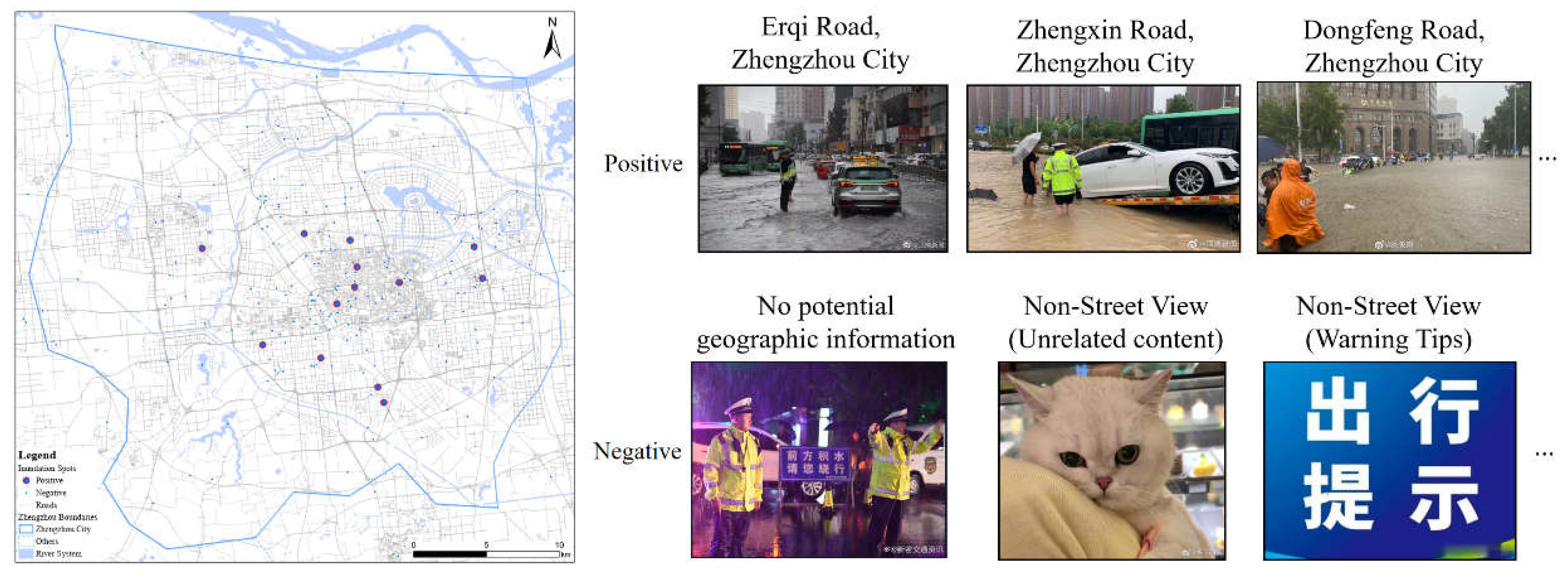
4.2. Analysis of Fine-grained extraction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryan, T.; Allen, K.A.; Gray, D.L.; McInerney, D.M. How Social Are Social Media? A Review of Online Social Behaviour and Connectedness. J. Relationships Res. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibo Reports Fourth Quarter and Fiscal Year 2022 Unaudited Financial Results. Available online: http://ir.weibo.com/node/8856/pdf (accessed on 15 May 15, 2023).
- Zhang, Z. Spatial analysis of Internet sensation based on social meadia—Taking the Jiuzhaigou earthquake as an example.NanJing University, 2019.
- Li, S. ,Zhao F.,Zhou Y.Analysis of public opinion and disaster loss estimates from typhoonsbased on Microblog data. Ch’ing-hua Ta Hsueh Hsueh Pao, Tzu Jan K’o Hsueh Pan J. Tsinghua Univ., Sci. Technol, 2022, 62(01),pp:43-51.
- Wu, Q. ,Qiu Y. Effectiveness Analysis of Typhoon Disaster Reflected by Microblog Data Location Information. J. Geomat.Sci. Technol. 2019,36(04),pp:406-411.
- Liang, C. ,Lin G.,Zhang M.,Assessing the Effectiveness of Social Media Data in Mapping the Distribution of Typhoon Disasters. J Geogr Inf Sci,2018,20(06),pp:807-816.
- Yu, M.; Bambacus, M.; Cervone, G.; Clarke, K.; Duffy, D.; Huang, Q.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q. spatio-temporal event detection: A review. International Journal of Digital Earth 2020, 13, 1339–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzioni, O.; Cafarella, M.; Downey, D.; Kok, S.; Popescu, A.-M.; Shaked, T.; Soderland, S.; Weld, D.S.; Yates, A. Web-scale information extraction in knowitall: (preliminary results). In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 13th international conference on World Wide Web, 2004; pp. 100–110.
- Ritter, A.; Etzioni, O.; Clark, S. Open domain event extraction from twitter. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, 2012; pp. 1104–1112.
- Huang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yu, K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging. arXiv arXiv:1508.01991 2015.
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.
- Ma, K.; Tan, Y.; Tian, M.; Xie, X.; Qiu, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Extraction of temporal information from social media messages using the BERT model. Earth Sci. Informatics 2022, 15, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, Z. Extracting Spatio-Temporal Information from Chinese Archaeological Site Text. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 2022, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEachren, A. M. , Jaiswal, A., Robinson, A. C., Pezanowski, S., Savelyev, A., Mitra, P., Zhang, X., & Blanford, J. (2011). SensePlace2: GeoTwitter analytics support for situational awareness. In VAST 2011 - IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology 2011, Proceedings,pp:181-190.
- Zou, Z.; Gan, H.; Huang, Q.; Cai, T.; Cao, K. Disaster Image Classification by Fusing Multimodal Social Media Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Information 2021, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofli, F.; Alam, F.; Imran, M. Analysis of social media data using multimodal deep learning for disaster response. arXiv arXiv:2004.11838 2020.
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L.-P. Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2018, 41, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X. ,Hu S.,Liu Ql. Internet media-based acquisition and processing model of earthquake disaster situation.J. Nat. Disasters,2013,22(3),pp:178-184.
- Zhang, S. ,Yang Z.,Wang Y. Simulation on Flood Disaster in Urban Building Complex System Based on LBM. J Simul,2022,34(12),pp:2584-2594.11. Yuan, F.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Mostafavi, A. Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks for road network inundation status prediction during urban flooding. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 2022, 97, 101870. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Mostafavi, A. Spatio-temporal graph convolutional networks for road network inundation status prediction during urban flooding. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ma, A. Coarse-to-fine waterlogging probability assessment based on remote sensing image and social media data. Geo-spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, 24, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteras, G.; Cervone, G. Enhancing the temporal resolution of satellite-based flood extent generation using crowdsourced data for disaster monitoring. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2017, 39, 1459–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. ,Wang Z.,Fang D.Optimal Design of Urban Waterlogging Monitoring and WarningSystem in Wuhan Based on Internet of Things and GPRS Technology. Saf Environ Eng,2018,25(02),pp:37-43.
- Zeng, Z. Xv J.,Wang Y.Advances in flood risk identification and dynamic modelling based on remote sensing spatial information. Adv Water Sci, 2020,31(03),pp:463-472.[27]Wang, R.-Q.; Mao, H.; Wang, Y.; Rae, C.; Shaw, W. Hyper-resolution monitoring of urban flooding with social media and crowdsourcing data. Computers & Geosciences 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Songchon, C.; Wright, G.; Beevers, L. Quality assessment of crowdsourced social media data for urban flood management. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 90, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BLE, SOCIAL MEDIA & FLOOD RISK AWARENESS. Available online: https://www.fema.gov/sites/default/files/documents/fema_ble-social-media-flood-risk-awareness.pdf (accessed on 15 May 15, 2023).
- Songchon Chanin,Wright Grant,Beevers Lindsay. Quality assessment of crowdsourced social media data for urban flood management. Comput Environ Urban Syst,2021,Volume 90, pp: 101690.
- Wang, X.; Kondratyuk, D.; Christiansen, E.; Kitani, K.M.; Alon, Y.; Eban, E. Wisdom of committees: An overlooked approach to faster and more accurate models. arXiv arXiv:2012.01988 2020.
- JioNLP. Available online: https://github.com/dongrixinyu/JioNLP (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhou, X. LoFTR: Detector-free local feature matching with transformers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2021; 8922–8931. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 2020, Proceedings, Part I 16, 2020, August 23–28; pp. 213–229.
- Schmitt, X.; Kubler, S.; Robert, J.; Papadakis, M.; LeTraon, Y. A replicable comparison study of NER software: StanfordNLP, NLTK, OpenNLP, SpaCy, Gate. In Proceedings of the 2019 Sixth International Conference on Social Networks Analysis, 2019, Management and Security (SNAMS); pp. 338–343.


| Blog post | Blog Information | Blog Information Values |
|---|---|---|
 |
Created time | 2021/7/19 14:28:17 |
| IP Location | Nodata | |
| 7月19日,记者在郑州金岱路距离南四环一公里处发现,金岱路的车道上积水严重,南北双向六车道有近1公里的积水带,最深处能淹没半个车轮,道路双向的外侧车道水更深,机动车速度稍快行驶,就会激起高于车身两倍的水花。目前这一积水情况还在持续,现场记者没有看到抽水作业,这一路段的积水为何如此严重?为何没有排水作业?河南交通广播的记者也会持续关注。(5G现场记者:靖一、雷静) | Is relevant | True |
| Mid | 4660679711922369 |
| Label type | Named entity labels | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TIME | DATE | Absolute or relative dates or periods |
| TIME | Times smaller than a day | |
| GPE | GPE | Geopolitical entity, i.e. countries, cities, states. |
| FAC | LOC | Non-GPE locations, mountain ranges, bodies of water |
| FAC | Buildings, airports, highways, bridges, etc. |
| Type | Only text | With Text + Images(Video) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | 12338 | 14222 | 26560 |
| Text classify | 6750 | 7886 | 14636 |
| Data clean | 1096 | 1951 | 3047 |
| Space Filter | 623 | 942 | 1565 |
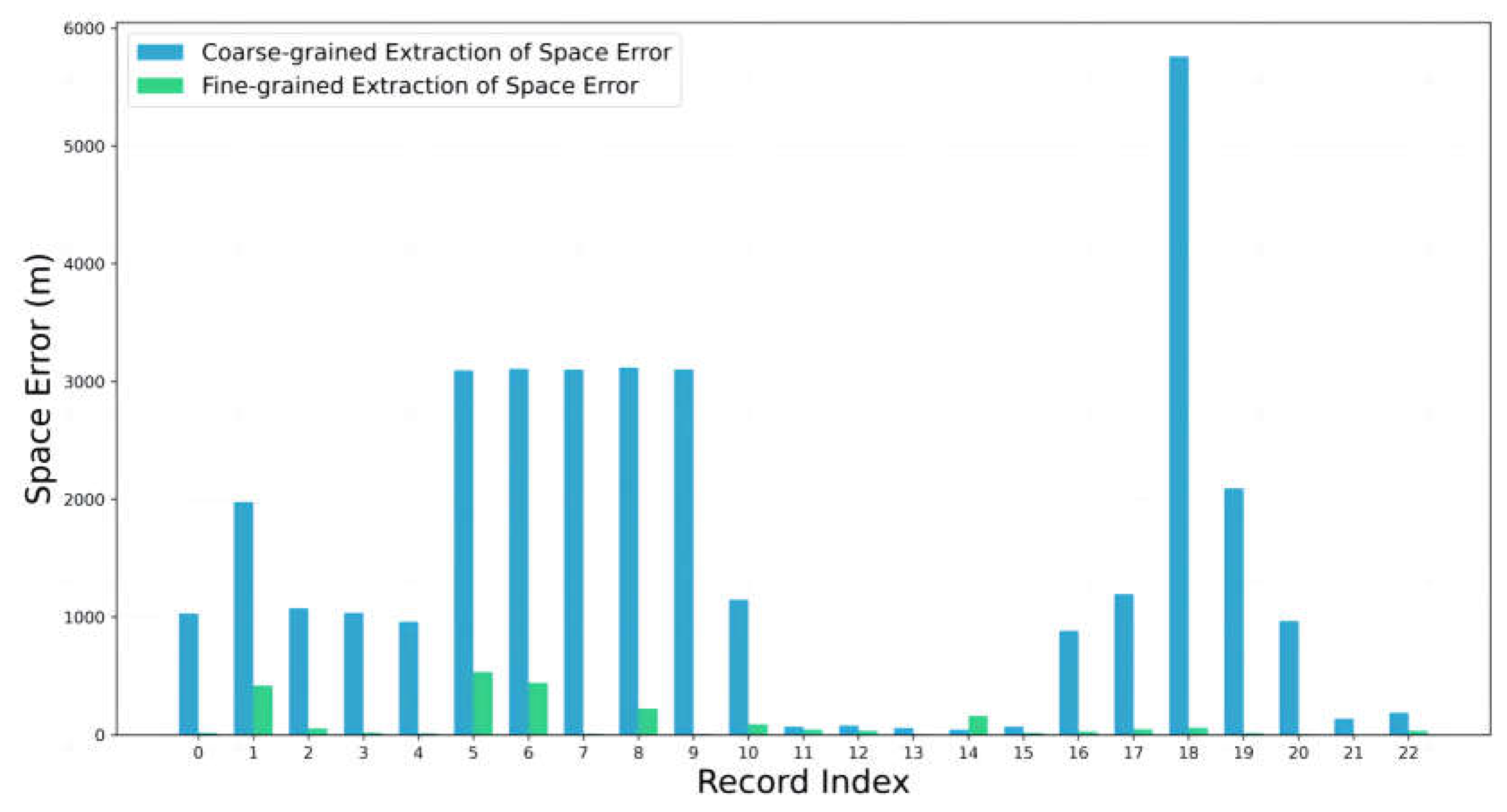
| Space Error | Only Text | Text + Images | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAESE | 1491.13 | 66.63 | 95.53% |
| RMSESE | 2068.43 | 131.88 | 93.62% |
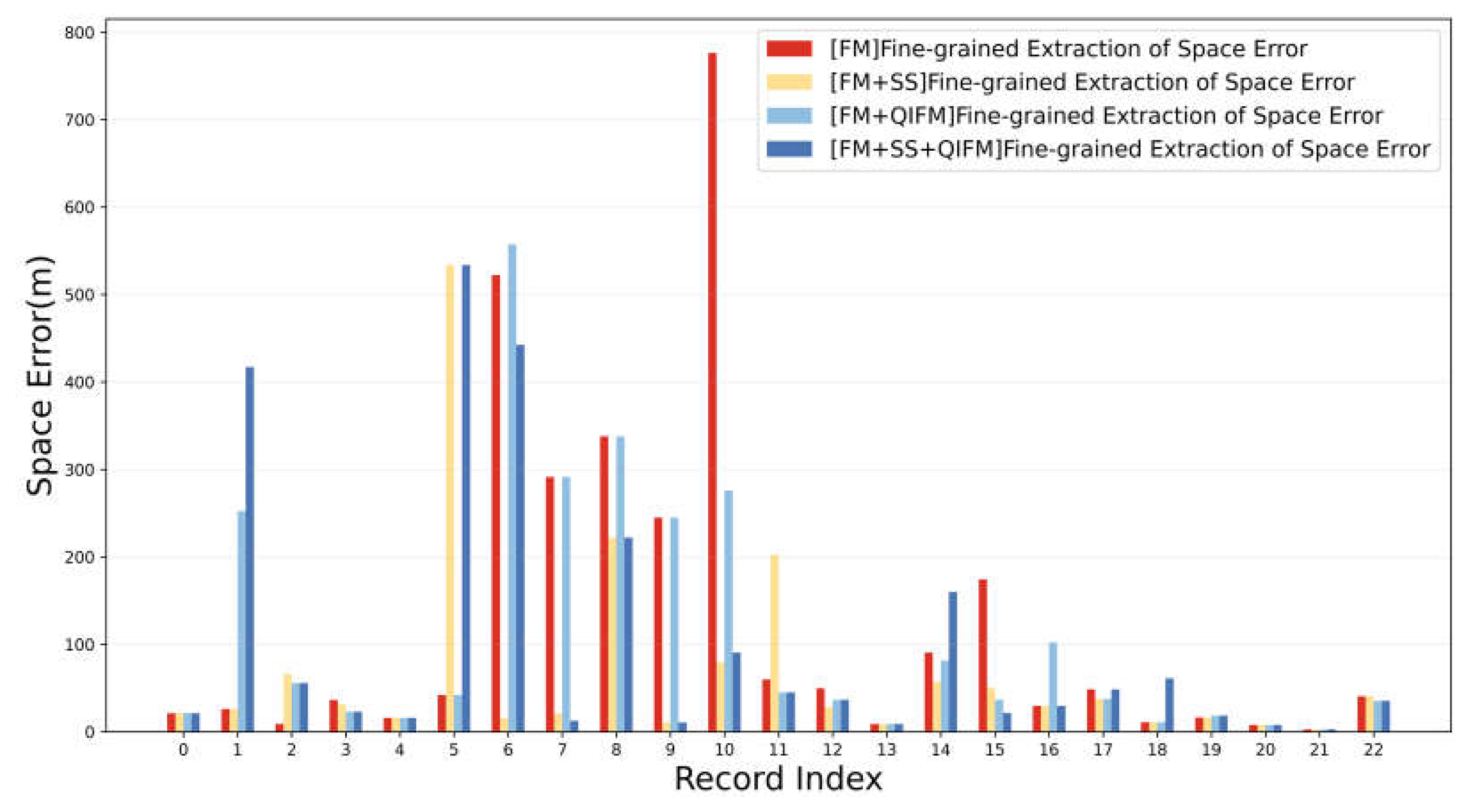
| Space Error | FM | FM+SS | FM+QIFM | FM+SS+QIFM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAESE | 124.30 | 66.63 | 110.33 | 100.74 | |
| RMSESE | 227.35 | 131.88 | 179.42 | 181.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




