1. Introduction
The ultrasound examination of the chest has shown to be an important auxiliary diagnostic tool in the evaluation of a wide range of peripheral, parenchymal, pleural and chest wall diseases [
1,
2]. Although computed tomography (CT) is still the gold standard for the diagnosis of these conditions, transthoracic ultrasound (TUS) can be used to detect pleural effusions, as well as to assess—although not to characterize—pleuro-pulmonary lesions involving the surfaces of the lungs through the intercostal spaces and adhering to 70% of the sonographically visible parietal pleura [
1]. The technique is particularly useful in the intensive care unit, where suboptimal radiography may mask or mimic clinically significant abnormalities and where differentiation of pleural from parenchymal opacities can be challenging [
3]. Furthermore, TUS is increasingly used to guide interventional procedures of the chest, such as explorative and/or evacuative thoracenteses for pleural effusion and transthoracic biopsies for pleural lesions and peripheral lung consolidations [
4,
5].
The availability of portable scanners, that can be immediately used at the bedside, allowed the development of several protocols in the emergency settings with the aim to fast “answer” to clinical doubts when present [
6]. Advantages of bedside TUS examination in respiratory diseases are the widely availability, the low-cost, the absence of exposure to ionizing radiation and the real-time imaging. However, decisive factors for an optimal ultrasound examination and interpretation of the results are the equipment and probe technology together with the experience of examiner.
To date, technological advances have led to the introduction of ultra-portable handheld ultrasound (HHU) devices. They consist in single or multiple probe devices that have the ability to display generated images on personal smart devices or proprietary displays sold with the product. In the current literature, several studies have explored the use of HHU devices in the lung examination. To this regard, a recent review showed high concordance between HHU and high-end ultrasound evaluations [
7].
Connectivity between the probe and the display may occur through a traditional cable system or employing a wireless communication. The addition of the wireless application to sonographic probes have been predicted as the next revolution in bedside medical imaging. Once the probe is connected to the monitor via Wi-Fi and the specific application has been started, it will be possible to carry out normal work operations. Because of their portability and ease of use, wireless probes are proving to permit a quicker ultrasound scan of the patients directly in their rooms, without the hindering of connection cables [
8]. Anyhow, while on the one hand this technology may promote the use of portable ultrasound assessment as an extension to traditional physical medical examinations, on the other hand it may result in a compromised image quality, thus reducing the diagnostic accuracy and complicating the interpretation of the results. No full-bodied evidence is currently available in the scientific literature regarding of the clinical effectiveness such new generation devices [
9]. Examples of wirelessly connected probes include those manufactured by SonoQue (Yorba Linda, CA), Clarius (Vancouver, BC) and OTE Medical (Cormano, MI).
The aim of the current study was to estimate the efficacy of a wireless US system with respect to a high-end US unit in a cohort of consecutive respiratory patients. The study focused on the OTE-L/C501CD probe, which is available at the authors’ institution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Enrolment
This prospective observational study enrolled a total of 132 consecutive respiratory patients who were admitted between February and April 2021 in the department of Internal Medicine of the Research Hospital “Fondazione Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza” of San Giovanni Rotondo, Foggia, Italy. The inclusion criteria were: 1) age > 18 year and 2) agreeing to participate in the study by giving written informed consent. The exclusion criteria were 1) refusal or 2) inability to give informed consent. The study followed the amended Declaration of Helsinki and the local institutional Ethical Review Board approved the protocol (TACE-CSS, n 106/2018).
2.2. Ultrasound Equipments
The ultrasound machines used were:
- -
a high-end Esaote MyLab-Twice scanner (Esaote-Biomedica, Genoa, Italy) equipped with a low-mid frequency convex probe (3.5–5 MHz) and a high-definition linear transducer (8–12.5 MHz);
- -
a wireless double-head linear (7.5-10 MHz) and convex (3,5-5 MHz) probe OTE-L/C501CD (OTE Medical, Cormano, MI) connected with a tablet-type display monitor on which the relative APP was installed.
2.3. Examination Technique
All ultrasound examinations were conducted by two highly experienced and comparably qualified medical doctor using the correct setting for the adult thoracic study (gain: max 50%, focus pointed at the hyperechoic pleural line, activation of the tissue harmonic imaging). The two examiners were blinded to each other’s findings and to the findings of the chest CT scan performed at admission.
The examination with the portable OTE-L/C501CD wireless probe was performed first, either at bedside or in the ultrasound laboratory. The examination with the high-end Esaote MyLab-Twice scanner was performed thereafter by the second examiner in the same day or within the next 5 days in the ultrasound laboratory. In suitable patients the latter examination was followed by interventional procedures (i.e., explorative and/or evacuative thoracentesis and transthoracic biopsies).
Patients’ chests were examined with intercostal longitudinal and transversal scans from the lung base to the apex, posteriorly (along the para-vertebral, hemi-scapular and posterior-axillary lines), laterally (along the middle-axillary line) and anteriorly (along anterior-axillary, hemi-clavicular and para-sternal lines) in a sitting or semi-sitting position [
1]. Convex probes were used for the study of the whole thorax in the first instance. Linear probes were used to complete the ultrasound examination, better detailing and study the pleural line.
2.4. Ultrasound findings definition
Ultrasound scans were focused on the following assessments: presence and characteristic of pleural effusion, presence of peripheral lung consolidations, presence of focal pleural lesions, thickness and qualitative appearance (i.e., regular or irregular) of the hyperechoic pleural line, presence of posterior pericardial effusion.
Pleural effusion was defined as a fluid collection in the pleural space showing a dependent location. According to its ultrasound appearance, the pleural effusion was described as anechoic (black), complex non septated (black with white strands), complex septated (black with white septa), or homogeneously echogenic (white) [
1,
4].
- -
Peripheral lung consolidations were defined as subpleural large hypoechoic or mixed hypo-hyperechoic areas interrupting the overlying pleural line echogenicity and characteristically showing blurred deep margins [
1].
- -
Pleural lesions were defined as focal hypoechoic or moderately echogenic pleural thickenings [
1].
- -
A conventional cut-off of 3.0 mm was used to define the pleural line as normal (≤ 3.0 mm) or thickened (> 3.0 mm) using a low-mid frequency convex probe (3.5–5 MHz) [
10]. Pleural line was judged as irregular if it appeared irregularly thickened or showed focal interruptions over its course [
1,
11].
- -
Posterior pericardial effusion was defined as a build up of fluid in the space around the heart in a left anterior longitudinal scan [
1].
2.5. Rating of the Image Quality
The image quality of the wireless US device was evaluated according to a five points scale: 0: assessment not possible (e.g., due to technical problems); 1: non-diagnostic; 2: major diagnostic limitations; 3: minor diagnostic limitations; 4: good [
8].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables and as absolute numbers (n) and frequencies (%) for categorical variables. The comparisons between the results of the two ultrasound devices were made with the χ2-square test for categorical variables. A p-value <0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. Sensitivity and specificity of the wireless US unit with respect to the high-end US machine (used as reference standard) was calculated with a 95% confidence interval (CI). In addition, the empiric Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to study the diagnostic performance of the wireless US unit versus the high-end US machine for all the pleuro-pulmonary findings.
3. Results
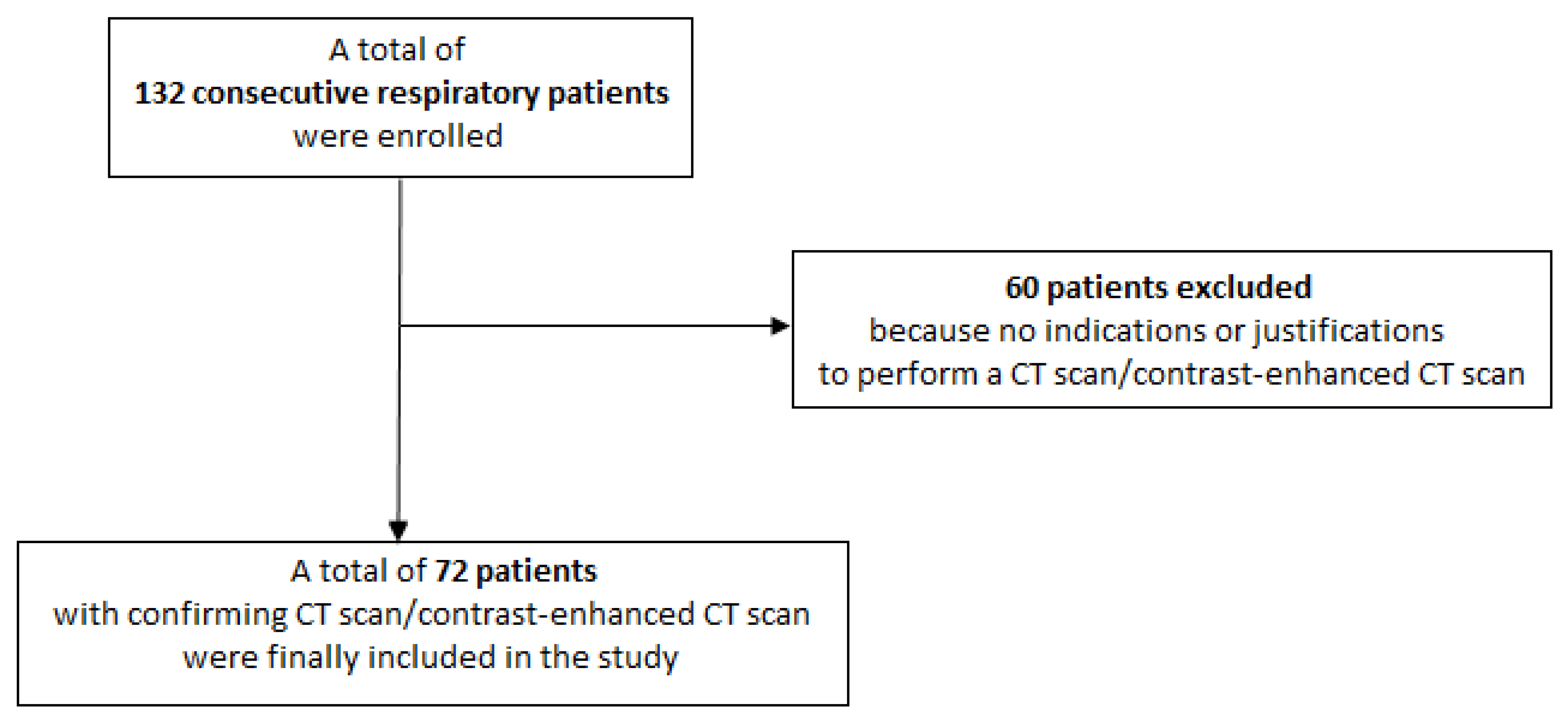
As there were no indications or justifications to perform a CT scan/contrast-enhanced CT scan in all the 132 enrolled patients, the comparison of the two ultrasound devices in the assessment of pleuro-pulmonary findings was conducted exclusively for those patients in whom these alterations have been confirmed by a Chest CT scan with and without contrast medium [
12]. A total of 72 patients were finally included in the study. The study flow chart is illustrated in
Figure 1.
Enrolled patients mean age was of 67 ± 13 years (range: 26-101). 42% (30/72) were males, and 58% (42/72) were females. Patients’ signs and symptoms (multiple signs and symptoms possible) justifying the ultrasound examinations were (in descending frequency): dyspnoea (89%, 64/72), cough (56%, 40/72), fever (28%, 20/72), chest tightness (8%, 6/72), weight loss (7%, 5/72).
Results of the two TUS examinations performed with the two US devices (multiple finding per patient possible) are shown and compared in
Table 1.
Diagnostic accuracy of the portable wireless ultrasound with respect to pleuro-pulmonary findings
A total of 8 patients (11%) showed intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules on the gold standard Chest CT scan, that was not possible to assess both by the high-end US unit and the wireless portable probe.
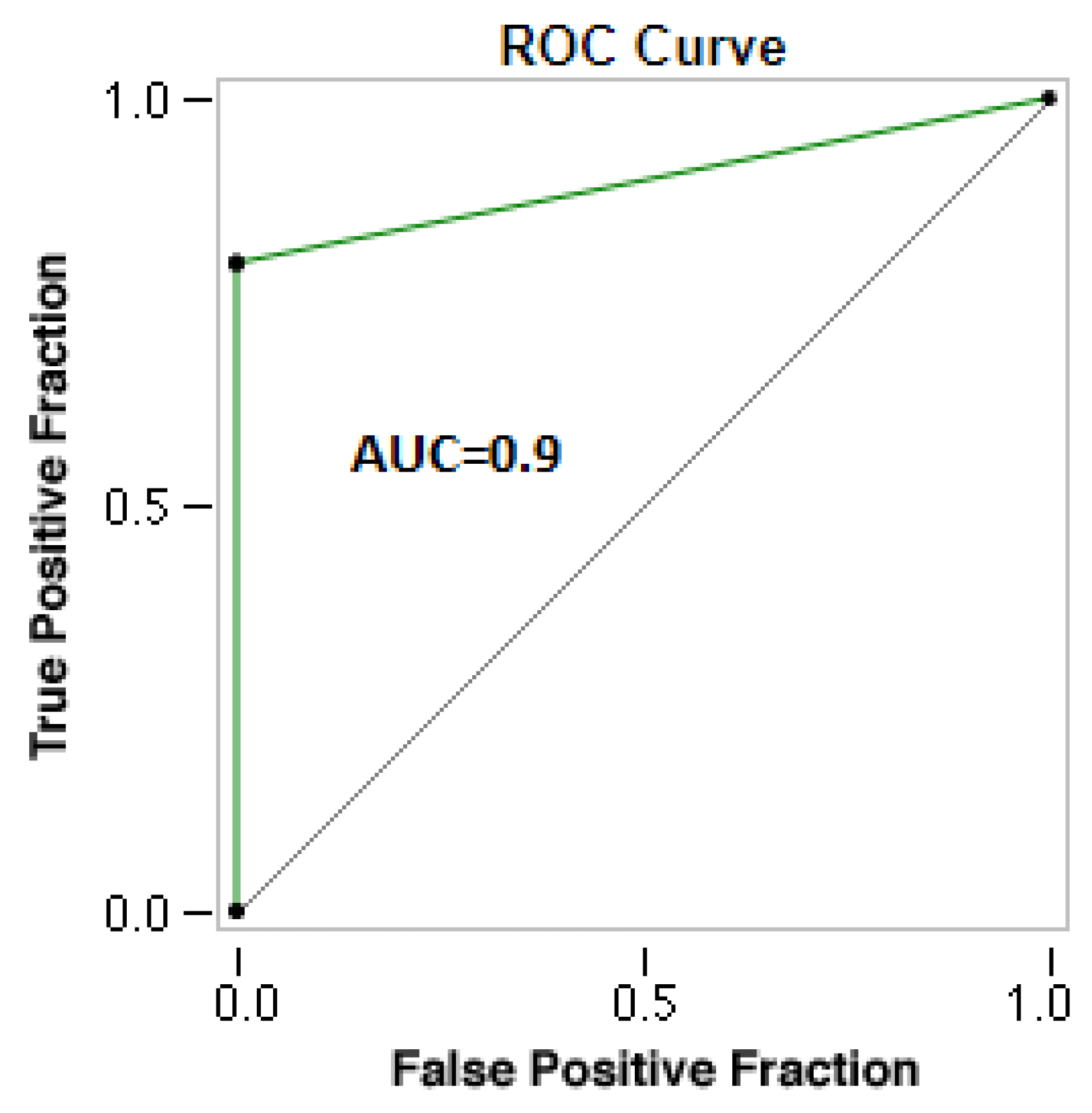
Considering all together the positive cases of pleuro-pulmonary alterations (n = 64) assessed by the high-end US machine, the wireless US unit resulted in 13 false negative results showing an overall sensitivity of 79.69% (67.77-88.72%). The respective overall specificity was 100%
(63.06-100.00%) (
Figure 2).
The overall resolution of the portable wireless US unit was judged as good in 22 (31%) cases, affected by minor diagnostic limitations in 26 (36%) cases and affected by major diagnostic limitations in 24 (33%).
The diagnostic accuracy of the wireless US device for all the specific ultrasound findings that was possible to assess with the stationary US unit are detailed in
Table 2.
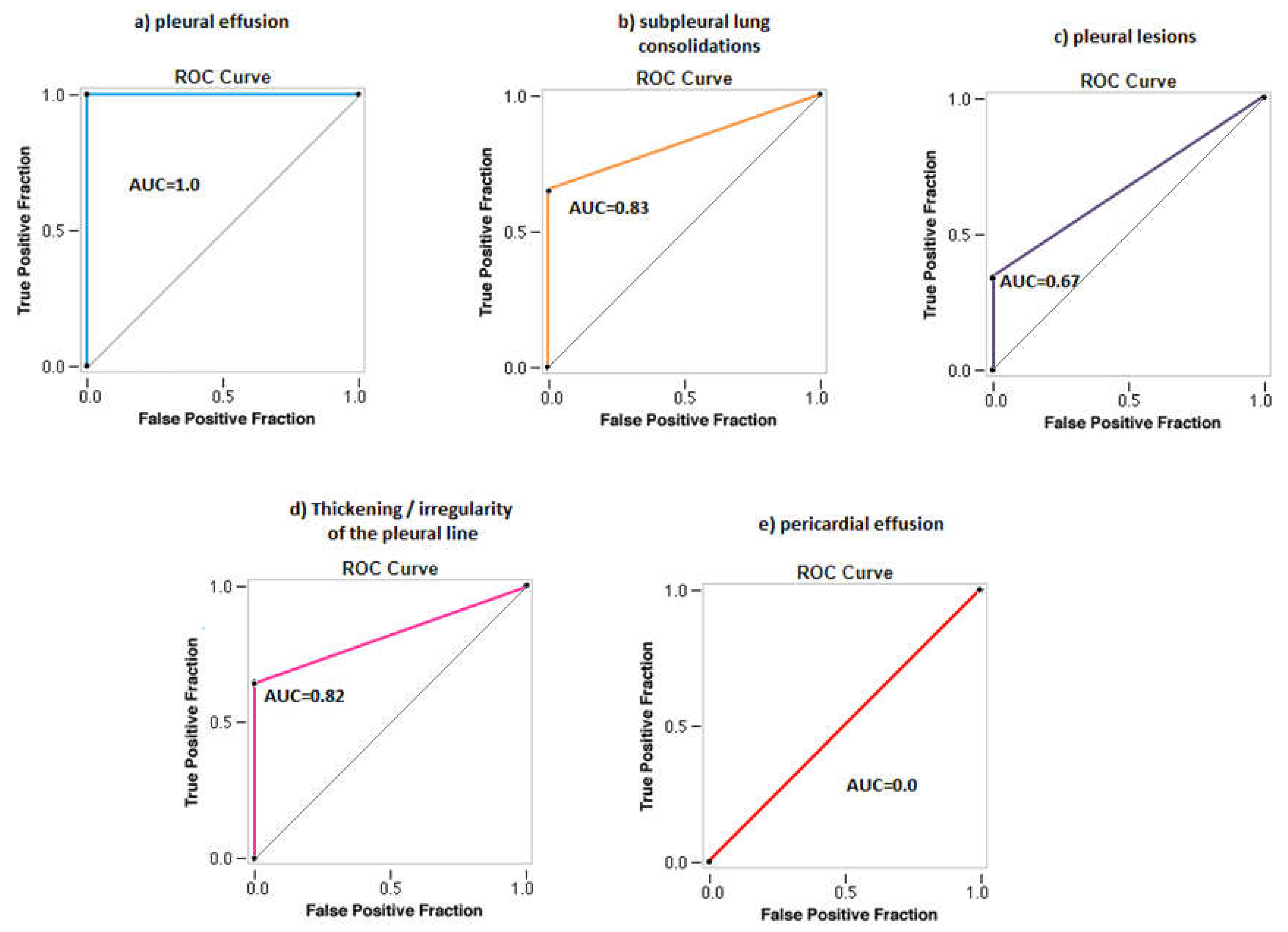
ROC curves showing the diagnostic accuracy of the wireless US unit in the assessment of all the specific ultrasound findings are illustrated in
Figure 3.
A pleural effusion was viewable in 28 (39%) of the patients both with the high-end US machine and with the portable wireless unit. Therefore, the cases of pleural effusion did not differ between the two devices, resulting in a sensitivity of 100% (87.66% to 100.00%) and specificity of 100% (91.96% to 100.00%) for the portable wireless ultrasound.
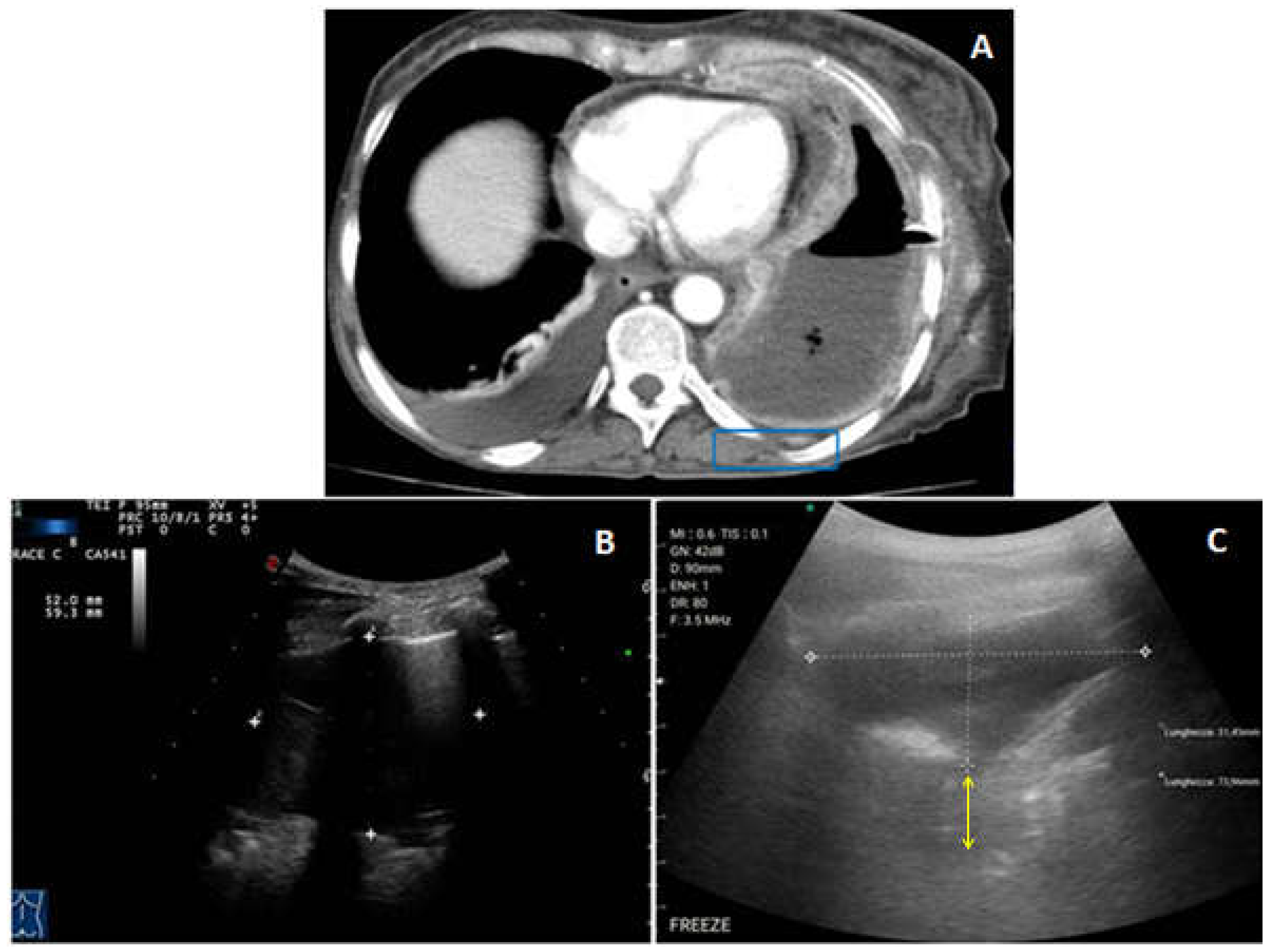
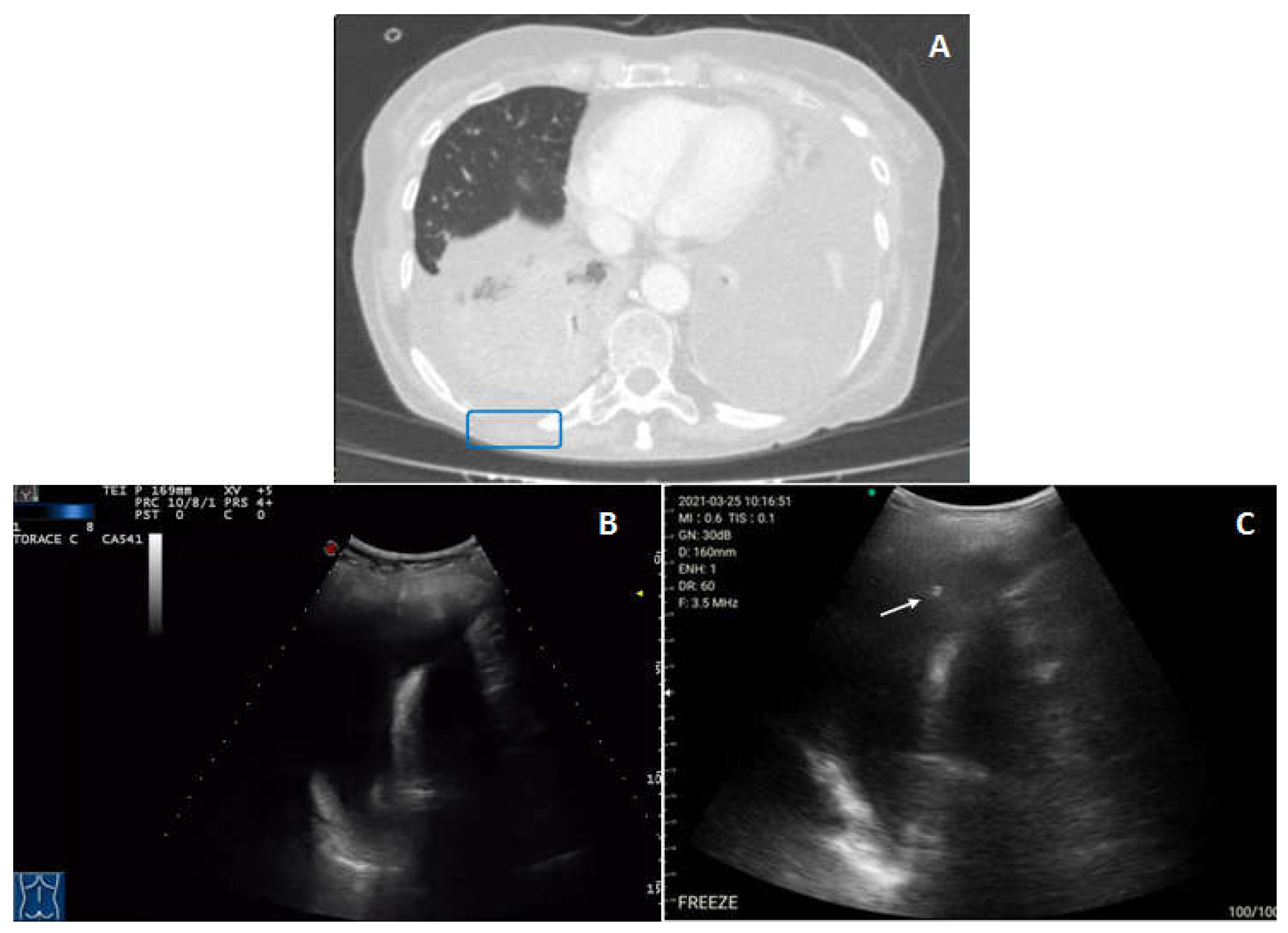
The resolution of the exam for the portable wireless US was judged as good in 13 cases, affected by minor diagnostic limitations in 10 cases and affected by major diagnostic limitations in 5 cases. According to the high-end US examination, in 18 patients pleural effusion had an anechoic appearance, in 6 subjects it was complex non-septated, in 2 patients it was complex septated and 2 patients showed a hyperechoic pleural effusion. On the wireless US examination pleural effusion generally appeared less defined and more echogenic. An excessive hyperechogenicity on US images obtained with the US wireless probe sometimes resulted in a discrepancy in the measurement of the pleural effusion size, especially in depth, between the two US devices (
Figure 4).
A total of 17 real-time ultrasound-guided thoracentesis were performed, of which 6 with only a diagnostic purpose (explorative thoracentesis) and 11 with a therapeutic purpose (evacuative thoracentesis). In 6 cases for which the examination resolution was good, the thoracentesis procedure was performed under the guidance of the wireless US probe (
Figure 5). A mean of about 650 cc (min: 20 cc–max: 1600 cc) of fluid was removed. Macroscopically, in 8 patients the pleural effusion showed a citrine yellow appearance, in 6 patients a slightly xanthromic colour and in 3 patients a serum-blood tint.
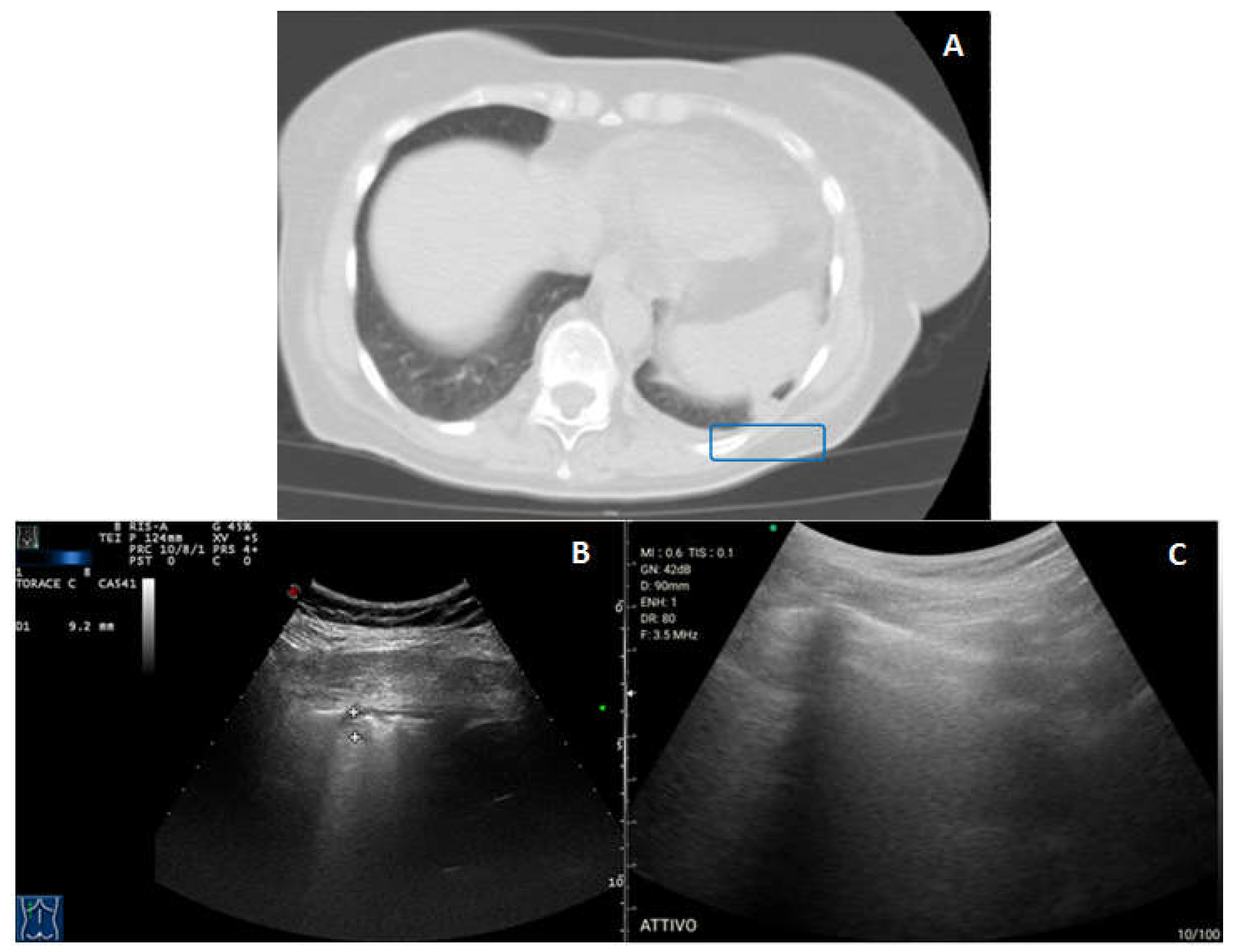
Subpleural pulmonary consolidations were viewable in 20 (28%) patients with the stationary high-end US machine. Presence of subpleural pulmonary consolidations was confirmed by a Chest CT performed at the admission in all the patients. The portable wireless US unit identified subpleural lung consolidations in 13 (18%) patients, resulting in a sensitivity of 65% (40.78% to 84.61%) and specificity of 100% (93.15% to 100.00%). The resolution of the wireless US examination was judged as good in 6 cases, affected by minor diagnostic limitations in 6 cases and affected by major diagnostic limitations in 8 cases (
Figure 6). In 5 subjects the subpleural consolidations showed malignant features on the contrast-enhanced CT scan or a PET-CT scan and were subsequently subjected to a TUS-guided percutaneous needle biopsy for diagnostic assessment.
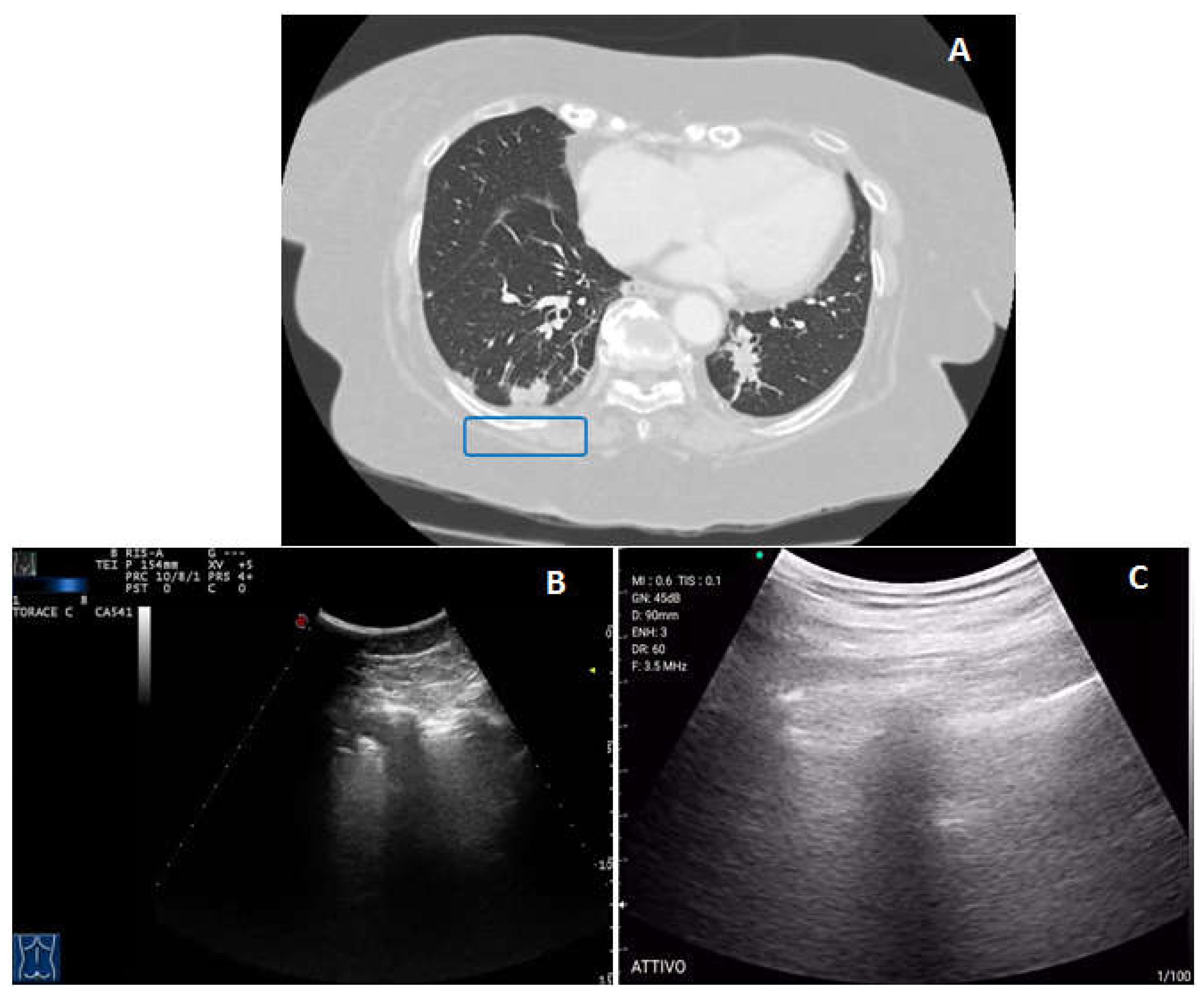
Pleural lesions were assessed in 3 (4%) patients with the stationary ultrasound unit and in 1 (1%) patient with the portable wireless ultrasound, resulting in a sensitivity of 33% (0.84% to 90.57%) and specificity of 100% (94.79% to 100.00%) for the second device. The resolution on the portable wireless ultrasound examination was affected by minor diagnostic limitations in 2 cases and major diagnostic limitations in 1 case (
Figure 7). 1 patient, for which the presence of a suspected pleural lesion was confirmed by a contrast-enhanced CT scan and a PET-CT scan, was subjected to a TUS-guided percutaneous needle biopsy for diagnostic assessment.
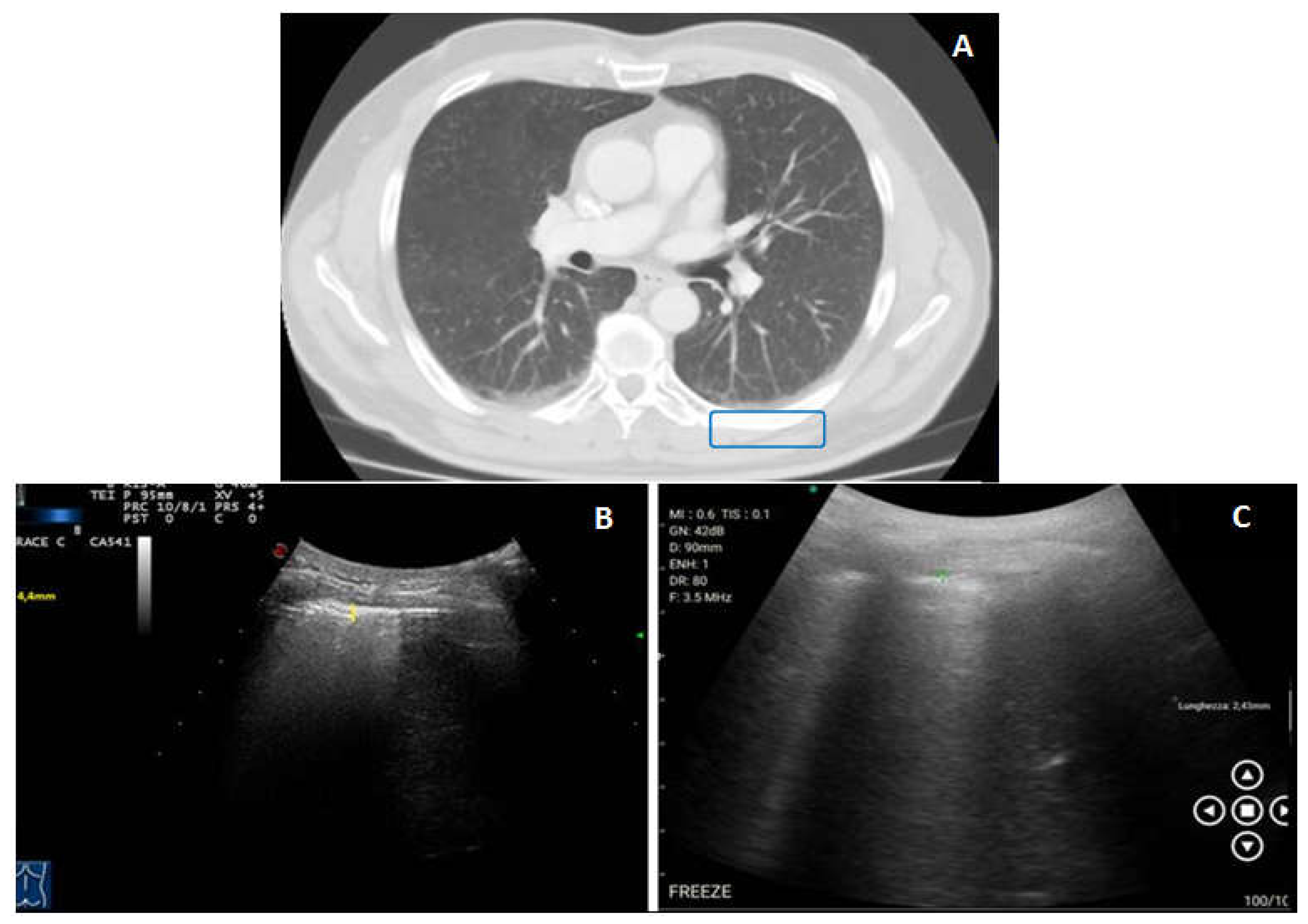
The presence of thickenings and/or irregularities of the hyperechoic pleural line was assessed in 31 (43%) cases with the stationary ultrasound machine and in 20 (28%) cases with the portable wireless unit, resulting in a sensitivity of 67% (47.19% to 82.71%) and specificity of 100% (91.40% to 100.00%) for the second device. The portable wireless ultrasound examination was good in 4 cases, affected by minor diagnostic limitations in 15 cases and affected by major diagnostic limitations in 12 cases (
Figure 8).
A pericardial effusion was assessed in 3 (4%) patients with the stationary ultrasound unit but in no case with the portable wireless ultrasound, resulting in a sensitivity of 0% (0.00% to 70.76%) and specificity of 100% (94.79% to 100.00%) for the second device. The portable wireless ultrasound examination was judged as affected by major diagnostic limitations in all the 3 cases.
4. Discussion
Results of our study show a good, even if not excellent, sensitivity (i.e., 79.69%) for the wireless US examination compared to a traditional high-end US examination. An AUC value of 0.90 seems to suggest an excellent concordance between the two US devices. Other authors have suggested that the main advantage in the use of a portable wireless US probe relies in the possibility to achieve shorter examination times compared to a bedside US examination with a conventional high-end instrument [
8,
13]. This is probably due to both the saved time for the transfer of the portable US unit and the rapid set-up and disassembly of the device [
8]. Thus, an increasing utilization of the wireless technology seems reasonable in the intensive care units for bedside emergency imaging.
The wireless US examination was judged to be affected by minor and major limitations in most cases (i.e., in the 36% and in the 33% of cases, respectively). The patient’s constitution and compliance are of course decisive in influencing the image quality. However, also the depth of assessment and detail of the portable wireless US unit seems to be inferior compared to high-end devices [
14].
In our experience, the only finding in the detection of which the wireless US unit showed a diagnostic accuracy comparable to that of a high-end US machine was pleural effusion. During the thoracentesis procedure, the portable wireless US probe also allowed fairly well to check the position of the needle and to evaluate the lung re-expansion during the drainage of pleural fluid. This suggests that a portable wireless US could be used, not only for a rapid bedside diagnosis of pleural effusion, but also in performing US-guided thoracenteses avoiding the occurrence of eventual complication after puncture. On the other hand, regarding the appearance, pleural effusion was generally less defined and more echogenic when using the wireless US probe. This sometimes resulted in a discrepancy in the measurement of the pleural effusion size, especially in depth, between the two US devices.
Although there was not a statistically significant difference in the number of diagnosed cases for peripheral lung consolidations, pleural lesions and pleural lines’ alterations compared to the standard high-end US examination, the sensitivity of the wireless US examination in the assessment of such findings resulted considerably low. As a result, the portable wireless US device does not seem to allow a detailed US evaluation of the pleuro-pulmonary lesions and of the pleural line.
To this regard we should remember that US examination itself is burdened by technical limitation when oriented to the exploration of the pulmonary parenchyma. Theoretically, the normal lung cannot be detected by US. Due to a dramatic change in acoustic impedance between the soft tissues of the chest wall and the aired parenchyma, more than 96% of the ultrasound beam undergoes to a specular reflection at this interface and only the parietal pulmonary surface is indirectly imaged on US by an artefact also known as “hyperechoic pleural line”. Furthermore, only the 70% of such parietal pulmonary surface can be indirectly explored by US because of the acoustic barrier represented by the bony structures of the thoracic cage. When the acoustic impedance at the chest wall/aired lung interface is removed by the filling of the peripheral aired parenchyma with fluid, inflammatory exudates, cellular infiltrates and/or growing tissue, US becomes able to visualize the pathologic parenchyma. Anyhow, the interposition of only few mm of air are able to block US signal, thus hiding even very big space-occupying lesions [
1]. A volumetric study through a chest CT scan is needed to detect parenchymal alterations when they are located in parts of the lung that are not accessible to US, such as the central and perihilar pulmonary zones, the retroscapular and costo-vertebral pleuro-pulmonary areas and the pleuro-pulmonary zone facing to the mediastinal pleura. As a confirm, in our study 8 patients showed intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules on the gold standard Chest CT scan, that was not possible to assess both by the high-end US unit and the wireless portable probe.
In addition, US could not exclude the malignant nature of a pulmonary consolidation based on his sonographic appearance [
5]. Similarly, other US findings are highly unspecific. For example, an irregular thickening of the hyperechoic pleural line may be described in case of fibrotic interstitial lung disease, conditions of peripheral inflammation, subpleural bronchiectasis, cysts, blebs and emphysema [
11,
15,
16]. “B-lines” or “ring-downs” are another US artefact presenting as continuous and parallel hyperechoic stripes, arising from the pleural line and extending indefinitely along the direction of the US beam on the screen. They generate when the US beam, after crossing soft tissues of the chest wall, encounters micro-bubbles of air surrounded by an increased proportion of liquid film or interstitial tissue in peripheral alveoli. An increased number of B-lines has been described in several pathological conditions, including conditions of fluid accumulation in the lungs (i.e., heart failure [
17] or end-stage renal disease accompanied by pulmonary congestion [
18]), pulmonary fibrosis [
11,
15], pulmonary contusion [
19], pneumonia [
20], acute respiratory distress syndrome [
21], acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma [
22,
23] and neoplastic lymphangitis [
24]. No statistical significance has been attributed to B-line number in discriminate one condition from another [
25]. An unspecific increase in B-lines may also be found in healthy individuals, generally at the bases, where the hydrostatic pressure gives a more fluid-rich interstitium [
26]. Furthermore, a thickened pleural line and an increase in B-lines are also frequent findings in a senile lung [
27,
28].
An increase of such artefacts may also be influenced by the type of US probe used, by the position of the US probe with respect to the curvature of the patient’s chest and by the patient’s respiratory rate [
29]. As the proposal of B-line counting is contrary to efforts to improve the reliability and objectivity of an US assessment [
30], they were not valued in this study. Of course, a chest CT scan enables a better characterization and discrimination of different pleuro-pulmonary alterations. That said, even after a positive standard high-end US examination, a chest CT scan is always required as a second-line imaging method for reaching a correct diagnosis.
In our study, the wireless US device showed the worst diagnostic accuracy in the detection of pericardial effusion. A possible explanation may perhaps be that the anterior thoracic zones are those more penalized by technical limitations during the bedside wireless US assess.
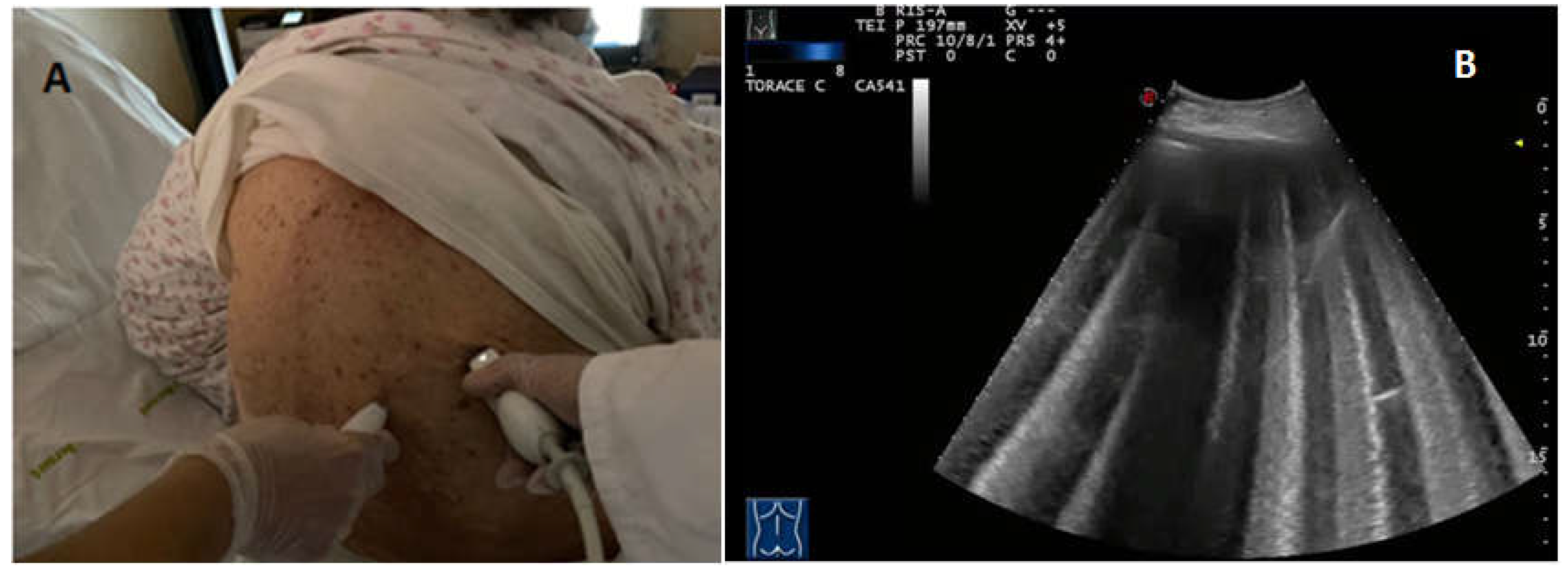
As a curiosity note, while placing the reference US probe on one side of the patient’s chest, when the wireless US probe was still located nearby, a reverberating vertical lines artefact was generated. We have called this artefact originating from the simultaneous use of two US probes as “plissè artefact” because it resembles a pleated skirt (
Figure 9). It might be due to the accumulation of multiple echoes being formed and received by the transducer. Indeed, wireless US equipment uses wireless signal transfer with an ultra-broadband mode, which would be virtually free from the risk of environmental interference, such as that deriving from the possible presence of electromagnetic fields or Wi-Fi fields, on data transmission. However, there are no studies dedicated to wireless probes in this regard.
The main limitations of our study consist in the small number of subjects enrolled and in the use of a single type of wireless probe. Anyhow, this was a preliminary report of our experience with the use of a type of wireless HHU device which is available at ours institution.
Another study limitation relies in the missing calculation of the inter-operators agreement coefficients for results obtained on each US devices. The diagnostic reliability of US examination is strongly dependent upon the experience of the examiner, highlighting the need of an accurate and prolonged training of the operators. This seems to be even more important during the use such new-generation mobile devices. However, the operators who performed chest examinations in our experience were expert sonographers that periodically undergo training programs and constantly control their performances.
Although a larger cohort of patients and the assessment of inter-operators agreement are required to confirm our results, we believe that the presentation of our experience will give the opportunity to enhance the attention on the effectiveness of clinical use of new generation wireless US devices in pleuro-pulmonary examination.
5. Conclusions
Results of our study suggest that portable wireless US devices may allow a rapid emergency diagnosis of pleural effusion. Moreover, in our experience the portable wireless US probe allowed fairly well to evaluate the lung re-expansion during the drainage of pleural fluid, thus avoiding the occurrence of pneumothorax after puncture. However, other systematic studies are needed to evaluate if this new device could be useful and safe in performing US-guided thoracenteses at the bedside. On the other hand, the wireless device seemed to be burdened by technical limitations in assessing subpleural pulmonary consolidations and pleural alterations. To this regard, a wireless US probe would appear to be not paragonable with a high-end US equipment. The hope is that the future technological innovation of the devices will overcome these problems. Anyway, given the limitations inherent the thoracic exploration by US, second-line imaging techniques (i.e., Chest CT scan and PET-CT assessment) are always required to clarify complex clinical issues.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Validation, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Formal analysis, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Lucia Angela Fiore, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Investigation, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Lucia Angela Fiore, Michela Salvemini, Federica D’Agostino and Giulia Tuccari; Data curation, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Lucia Angela Fiore, Michela Salvemini, Federica D’Agostino, Giulia Tuccari, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Writing—original draft, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Lucia Angela Fiore, Antonio Mirijello, Salvatore De Cosmo, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Writing—review & editing, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Donato Lacedonia, Giulia Scioscia, Michela Salvemini, Rosanna Villani, Federica D’Agostino, Giulia Tuccari, Stefano Notarangelo, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Visualization, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Supervision, Carla Maria Irene Quarato, Donato Lacedonia, Giulia Scioscia, Rosanna Villani, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo; Project administration, Donato Lacedonia, Rosanna Villani, Salvatore De Cosmo, Evaristo Maiello and Marco Sperandeo.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study followed the amended Declaration of Helsinki and the local institutional Ethical Review Board approved the protocol (TACE-CSS, n 106/2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical and privacy reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sperandeo M, Rotondo A, Guglielmi G, Catalano D, Feragalli B, Trovato GM. Transthoracic ultrasound in the assessment of pleural and pulmonary diseases: use and limitations. Radiol Med. 2014;119(10):729-740. [CrossRef]
- Buda N, Kosiak W, Wełnicki M, et al. Recommendations for Lung Ultrasound in Internal Medicine. Diagnostics. 2020;10(8):597. [CrossRef]
- Yousefifard M, Baikpour M, Ghelichkhani P, et al. Screening Performance Characteristic of Ultrasonography and Radiography in Detection of Pleural Effusion; a Meta-Analysis. Emergency. 2016;4(1):1./pmc/articles/PMC4744606/. Accessed October 16, 2022.
- Sperandeo M, Maria C, Quarato I, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Real-Time Transthoracic Ultrasound-Guided Thoracentesis. Diagnostics 2022, Vol 12, Page 725. 2022;12(3):725. [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo M, Maiello E, Graziano P, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Guiding Percutaneous Needle Biopsy in the Lung and Comparison vs. CT Scan in Assessing Morphology of Subpleural Consolidations. Diagnostics 2021, Vol 11, Page 1641. 2021;11(9):1641. [CrossRef]
- Whitson MR, Mayo PH. Ultrasonography in the emergency department. Crit Care. 2016;20(1):1-8. [CrossRef]
- Haji-Hassan M, Lenghel LM, Bolboacă SD. Hand-Held Ultrasound of the Lung: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2021, Vol 11, Page 1381. 2021;11(8):1381. [CrossRef]
- Stock KF, Klein B, Steubl D, et al. Comparison of a pocket-size ultrasound device with a premium ultrasound machine: diagnostic value and time required in bedside ultrasound examination. Abdom Imaging 2015 407. 2015;40(7):2861-2866. [CrossRef]
- Clark M, Ford C. Smartphone-, Tablet-, or App-Based Portable Ultrasound: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness. Smartphone-, Tablet-, or App-Based Portable Ultrasound A Rev Clin Eff. September 2019:1-6. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549528/. Accessed October 11, 2022.
- Sperandeo M, De Cata A, Molinaro F, et al. Ultrasound signs of pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis as timely indicators for chest computed tomography. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(5):389-398. [CrossRef]
- Lacedonia D, Scioscia G, Giardinelli A, et al. The Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in the Study of Interstitial Lung Diseases: High-Resolution Computed Tomography Versus Ultrasound Patterns: Our Preliminary Experience. Diagnostics. 2021;11(3):439. [CrossRef]
- Fryback DG, Thornbury JR. The Efficacy of Diagnostic Imaging. Med Decis Mak. 1991;11(2):88-94. [CrossRef]
- Clevert DA, Schwarze V, Nyhsen C, D’Onofrio M, Sidhu P, Brady AP. ESR statement on portable ultrasound devices. Insights Imaging. 2019;10(1). [CrossRef]
- Jung EM, Dinkel J, Verloh N, et al. Wireless point-of-care ultrasound: First experiences with a new generation handheld device. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2021;79(3):463. [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo M, Rea G. Interstitial Lung Diseases. In: Thoracic Ultrasound and Integrated Imaging. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020:61-82. [CrossRef]
- Scioscia G, Lacedonia D, Quarato CMI, et al. Could transthoracic ultrasound be useful to suggest a small airways disease in severe uncontrolled asthma? Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2022;129(4):461-466. [CrossRef]
- Muniz RT, Mesquita ET, Souza Junior CV, Martins W de A. Pulmonary ultrasound in patients with heart failure—Systematic review. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018;110(6):577-584. [CrossRef]
- Ross DW, Abbasi MM, Jhaveri KD, et al. Lung ultrasonography in end-stage renal disease: Moving from evidence to practice-a narrative review. Clin Kidney J. 2018;11(2):172-178. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi S, Shaker H, Zareiee F, et al. Screening performance of Ultrasonographic B-lines in Detection of Lung Contusion following Blunt Trauma; a Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Emerg (Tehran, Iran). 2018;6(1):e55. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30584571. Accessed January 17, 2021.
- Cortellaro F, Colombo S, Coen D, Duca PG. Lung ultrasound is an accurate diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2012;29(1):19-23. [CrossRef]
- Chaari A, Bousselmi K, Assar W, et al. Usefulness of ultrasound in the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2019;9(1):11-15. [CrossRef]
- Sriram KB, Singh M. Lung ultrasound B-lines in exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Intern Med J. 2017;47(3):324-327. [CrossRef]
- Attanasi M, Porreca A, Piloni F, et al. New application of point-of-care lung ultrasound in pediatric asthma exacerbations. In: European Respiratory Journal. Vol 56. European Respiratory Society (ERS); 2020:4179. [CrossRef]
- Carlino MV, Mancusi C, De Simone G, et al. Interstitial syndrome-lung ultrasound B lines: a potential marker for pulmonary metastases? A case series. Ital J Med. 2018;12(3):223-226. [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo M, Varriale A, Sperandeo G, et al. Assessment of ultrasound acoustic artifacts in patients with acute dyspnea: a multicenter study. Acta radiol. 2012;53(8):885-892. [CrossRef]
- Sperandeo M, Varriale A, Sperandeo G, et al. Characterization of the normal pulmonary surface and pneumonectomy space by reflected ultrasound. J Ultrasound. 2011;14(1):22-27. [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese F, Chiesa AM, Feletti F, et al. The Senile Lung as a Possible Source of Pitfalls on Chest Ultrasonography and Computed Tomography. Respiration. 2015;90(1):56-62. [CrossRef]
- Winter DH, Manzini M, Salge JM, et al. Aging of the Lungs in Asymptomatic Lifelong Nonsmokers: Findings on HRCT. Lung. 2015;193(2):283-290. [CrossRef]
- Quarato CMI, Venuti M, Sperandeo M. The artificial count of artifacts for thoracic ultrasound: what is the clinical usefulness? J Clin Monit Comput. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rea G, Trovato GM. A Farewell to B-Lines: Ageing and Disappearance of Ultrasound Artifacts as a Diagnostic Tool. Respiration. 2015;90(6):522-522. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).