Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and reagents
2.2. Synthesis of CNPs
2.3. X-ray photoelectronic spectroscopy (XPS)measurements
2.4. Antibacterial test
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Anand, A.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Wei, S.-C.; Chou, C. P.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Huang, C.-C. Graphene oxide and carbon dots as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents – a minireview. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, N.; Qazi, U. Y.; Mansha, A.; Bhatti, I. A.; Javaid, R.; Abbas, Q.; Nadeem, N.; Rehan, Z. A.; Noreen, S.; Zahid, M. , Recent developments for antimicrobial applications of graphene-based polymeric composites: A review. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2021, 100, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A.; Wang, Y.-J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, T.; Gao, G. , Chemical Insights into Antibacterial N-Halamines. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4806–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, D.; Luan, X.; He, P.; Wei, G. , Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A. M. , Antibacterial Activity of Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 2018, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Pascual, A. M. , Antibacterial Action of Nanoparticle Loaded Nanocomposites Based on Graphene and Its Derivatives: A Mini-Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, R. J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in the 21st Century. Perspect Medicin Chem 2014, 6, PMC.S14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K. T.; Calderon, L. E.; Saman, D. M.; Abusalem, S. K. , The use of surveillance and preventative measures for methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infections in surgical patients. Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control 2014, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Sun, H.; Qu, X. , Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: Recent achievements and challenges. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 105, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M. I.; Leong, D. T.; Xie, J. , Antimicrobial Gold Nanoclusters. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6904–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S. I. , Antibiotic Resistance and Regulation of the Gram-Negative Bacterial Outer Membrane Barrier by Host Innate Immune Molecules. mBio 2016, 7, e01541–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseinnejad, M.; Jafari, S. M.; Katouzian, I. , Inorganic and metal nanoparticles and their antimicrobial activity in food packaging applications. null 2018, 44, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Setyawati, M. I.; Leong, D. T.; Xie, J. , Surface Ligand Chemistry of Gold Nanoclusters Determines Their Antimicrobial Ability. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Perumal, E. , Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2017, 49, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N. H. M.; Ann, L. C.; Bakhori, S. K. M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. , Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nano-Micro Letters 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, A. , A review on bidirectional analogies between the photocatalysis and antibacterial properties of ZnO. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019, 783, 898–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankhanittha, T.; Nanan, S. , Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of ofloxacin (OFL) antibiotic and Rhodamine B (RhB) dye by solvothermally grown ZnO/Bi2MoO6 heterojunction. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 582, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, X. , Review on formation of biofouling in the marine environment and functionalization of new marine antifouling coatings. Journal of Materials Science 2022, 57, 18221–18242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Lin, Z.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z.; Qin, M.; Zheng, S.; Lu, W. , Where does the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles come from: The nanoparticles, the ions, or a combination of both? Journal of Hazardous Materials 2016, 308, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S. J.; Parak, W. J.; Rejman, J.; Manshian, B. , (Intra)Cellular Stability of Inorganic Nanoparticles: Effects on Cytotoxicity, Particle Functionality, and Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2109–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Lv, M.; Xiu, P.; Huynh, T.; Zhang, M.; Castelli, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C.; Fang, H.; Zhou, R. , Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets. Nature Nanotechnology 2013, 8, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitounis, D.; Ali-Boucetta, H.; Hong, B. H.; Min, D.-H.; Kostarelos, K. , Prospects and Challenges of Graphene in Biomedical Applications. Advanced Materials 2013, 25, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, J.; Teng, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, G.; Liu, S.; Luo, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L. , The Antibacterial Applications of Graphene and Its Derivatives. Small 2016, 12, 4165–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. , Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.-J.; Wu, R.-S.; Lin, T.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Lin, H.-J.; Harroun, S. G.; Lai, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-C. , Super-Cationic Carbon Quantum Dots Synthesized from Spermidine as an Eye Drop Formulation for Topical Treatment of Bacterial Keratitis. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6703–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Q.; Shah, H.; Nawaz, A.; Xie, W.; Akram, M. Z.; Batool, A.; Tian, L.; Jan, S. U.; Boddula, R.; Guo, B.; Liu, Q.; Gong, J. R. , Antibacterial Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. Advanced Materials 2019, 31, 1804838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. , Graphene-Based Antibacterial Paper. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.; Kim, S. J. , The chemical and structural analysis of graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation. Carbon 2013, 53, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N. O.; Zhou, H.; Liao, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. , Graphene: An Emerging Electronic Material (Adv. Mater. 43/2012). Advanced Materials 2012, 24, 5776–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuilla, T.; Bhadra, S.; Yao, D.; Kim, N. H.; Bose, S.; Lee, J. H. , Recent advances in graphene based polymer composites. Progress in Polymer Science 2010, 35, 1350–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Kim, J.-K. , Structure, and Properties of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. In Graphene for Transparent Conductors: Synthesis, Properties and Applications, Zheng, Q.; Kim, J.-K., Eds. Springer New York: New York, NY, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Garcia, B.; Velazquez, M. M.; Rossella, F.; Bellani, V.; Diez, E.; Garcia Fierro, J. L.; Perez-Hernandez, J. A.; Hernandez-Toro, J.; Claramunt, S.; Cirera, A. , Functionalization of reduced graphite oxide sheets with a zwitterionic surfactant. Chemphyschem 2012, 13, 3682–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Diaz, D.; Velazquez, M. M.; Blanco de La Torre, S.; Perez-Pisonero, A.; Trujillano, R.; Garcia Fierro, J. L.; Claramunt, S.; Cirera, A. , The role of oxidative debris on graphene oxide films. Chemphyschem 2013, 14, 4002–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, R. S.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M. M. , Graphene Oxide Thin Films: Influence of Chemical Structure and Deposition Methodology. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2697–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, S.; Varea, A.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M. M.; Cornet, A.; Cirera, A. , The Importance of Interbands on the Interpretation of the Raman Spectrum of Graphene Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10123–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Díaz, D.; López Holgado, M.; García-Fierro, J. L.; Velázquez, M. M. , Evolution of the Raman Spectrum with the Chemical Composition of Graphene Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 20489–20497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Diaz, D.; Merchán, M. D.; Velázquez, M. M. , The behavior of graphene oxide trapped at the air water interface. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science 2020, 286, 102312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyer, D. R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C. W.; Ruoff, R. S. , The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem Soc Rev 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.-S.; Shao, Y.-T.; Huang, K.-S.; Chou, T.-M.; Yang, C.-H. , Antimicrobial Amino-Functionalized Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Eliminating Multidrug-Resistant Species in Dual-Modality Photodynamic Therapy and Bioimaging under Two-Photon Excitation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2018, 10, 14438–14446. [Google Scholar]
- Yaragalla, S.; Bhavitha, K. B.; Athanassiou, A. A Review on Graphene Based Materials and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Coatings 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T. H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. , Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Esfandiar, A. , Wrapping Bacteria by Graphene Nanosheets for Isolation from Environment, Reactivation by Sonication, and Inactivation by Near-Infrared Irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6279–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Akhavan, A. , Size-dependent genotoxicity of graphene nanoplatelets in human stem cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8017–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Andrade, M. D.; Chata, G.; Rouholiman, D.; Liu, J.; Saltikov, C.; Chen, S. , Antibacterial mechanisms of graphene-based composite nanomaterials. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Harroun, S. G.; Su, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-F.; Unnikrishnan, B.; Lin, H.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Huang, C.-C. , Synthesis of Self-Assembled Spermidine-Carbon Quantum Dots Effective against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2016, 5, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. , Antibacterial Property of Graphene Quantum Dots (Both Source Material and Bacterial Shape Matter). ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2016, 8, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- López-Díaz, D.; Solana, A.; García-Fierro, J. L.; Merchán, M. D.; Velázquez, M. M. , The role of the chemical composition on the photoluminescence properties of N-doped carbon nanoparticles. Journal of Luminescence 2020, 219, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Agullo, J.; Varela-Rizo, H.; Conesa, J. A.; Almansa, C.; Merino, C.; Martin-Gullon, I. , Evidence for growth mechanism and helix-spiral cone structure of stacked-cup carbon nanofibers. Carbon 2007, 45, 2751–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B. K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L. B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; Vithayathil, S. A.; Kaipparettu, B. A.; Marti, A. A.; Hayashi, T.; Zhu, J.-J.; Ajayan, P. M. , Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Letters 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. , Escherichia coli bacteria reduce graphene oxide to bactericidal graphene in a self-limiting manner. Carbon 2012, 50, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, P. , Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2011, 360, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J. C.; Asenjo, J. A. , The Monod equation and mass transfer. Biotechnol Bioeng 1995, 45, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.-X.; Schneider, R.; Marshall, K. C. , Modelling microbial growth: A statistical thermodynamic approach. Journal of Biotechnology 1994, 32, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwitya, S. S.; Hsueh, Y.-H.; Wang, S. S. S.; Lin, K.-S. , Ultrafine nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot structure and antibacterial activities against Bacillus subtilis 3610. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2023, 295, 127135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
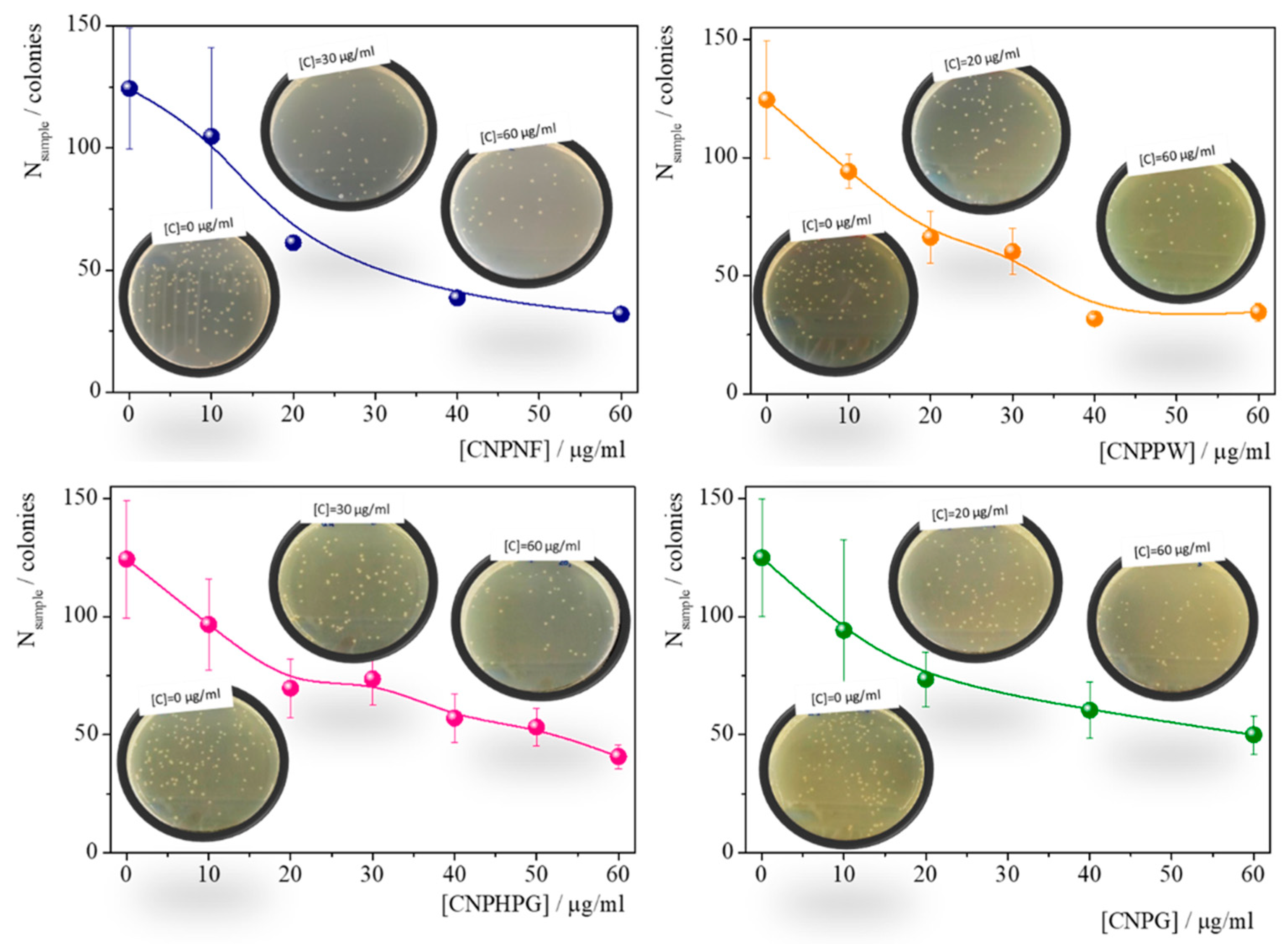
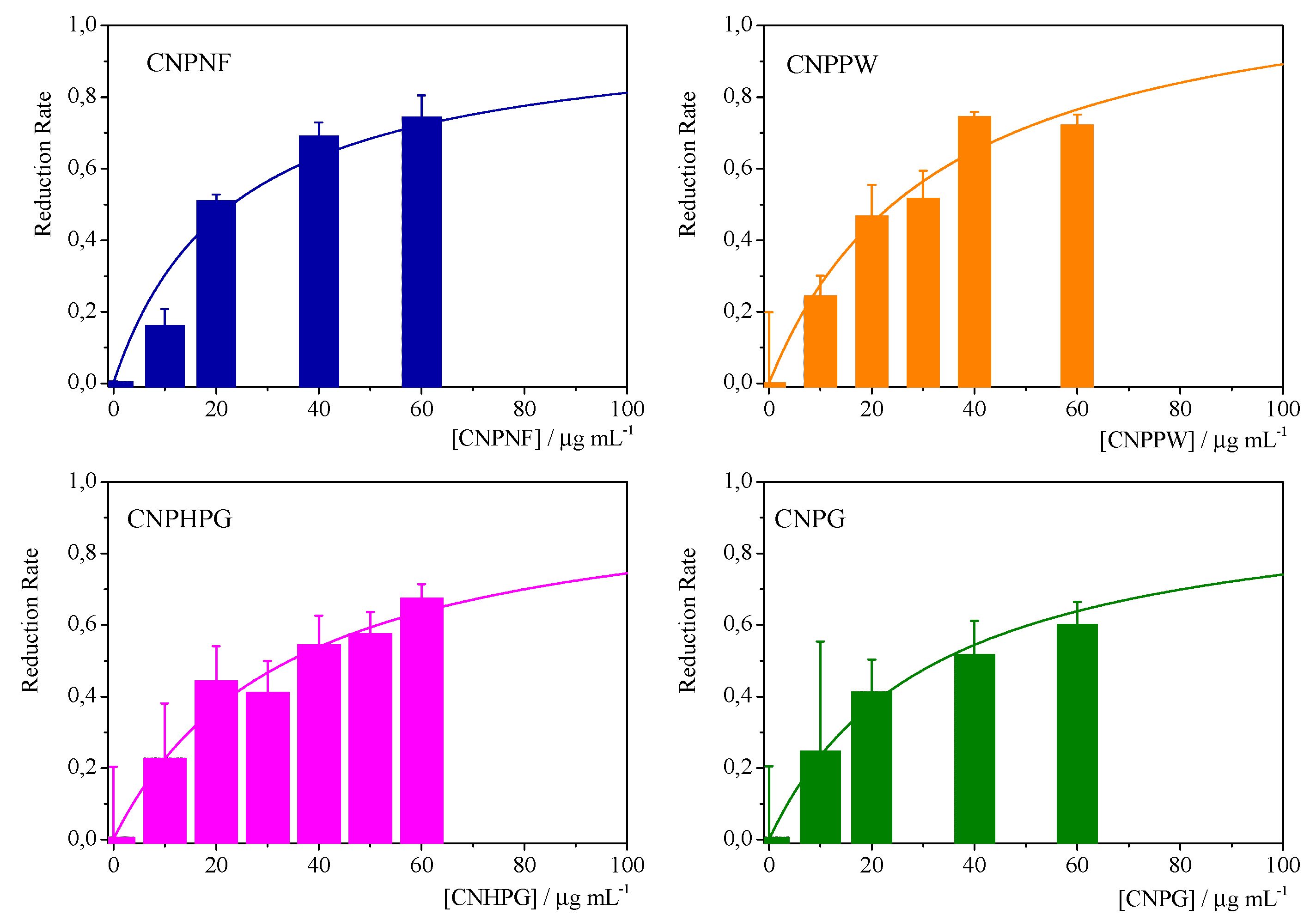
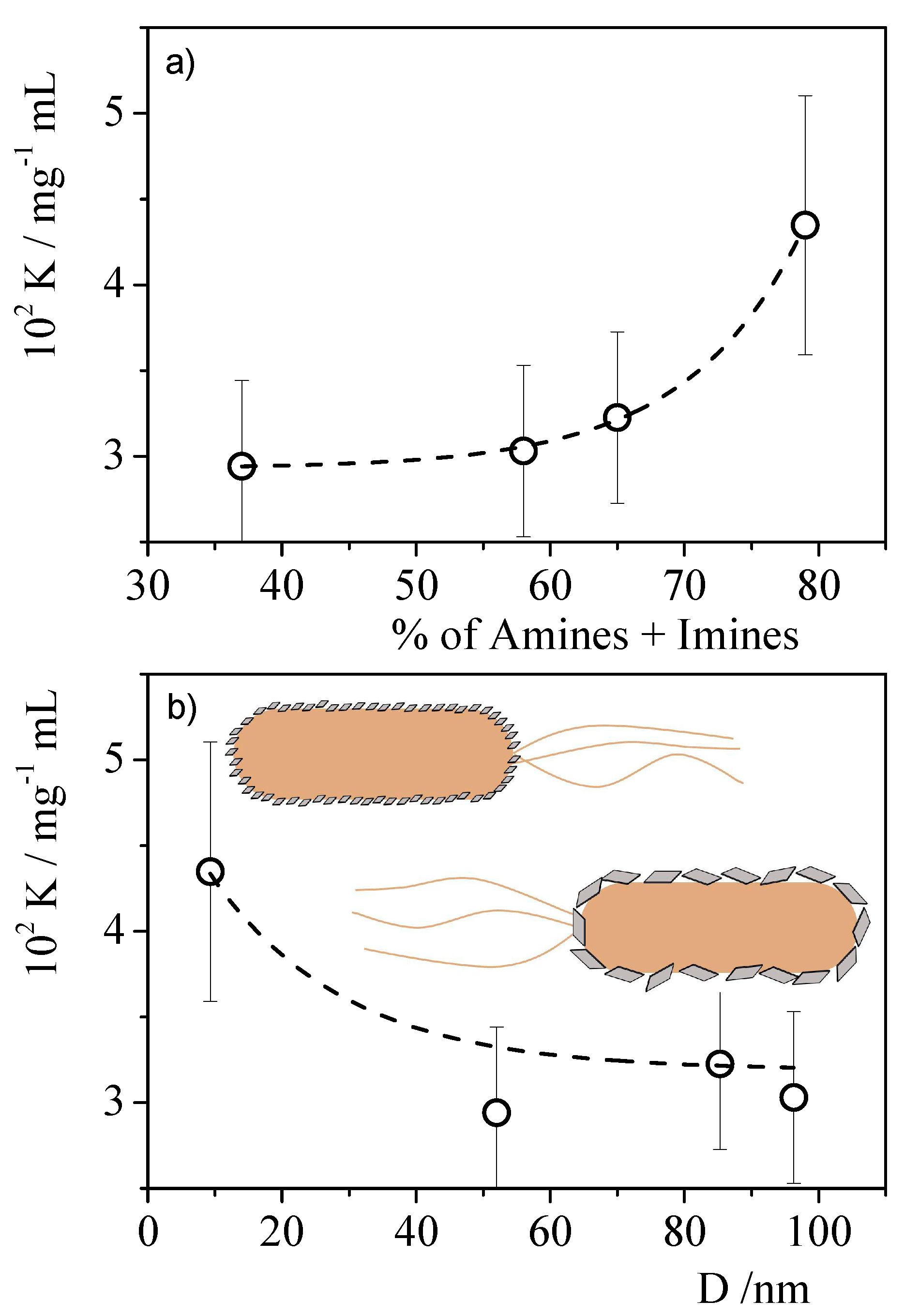
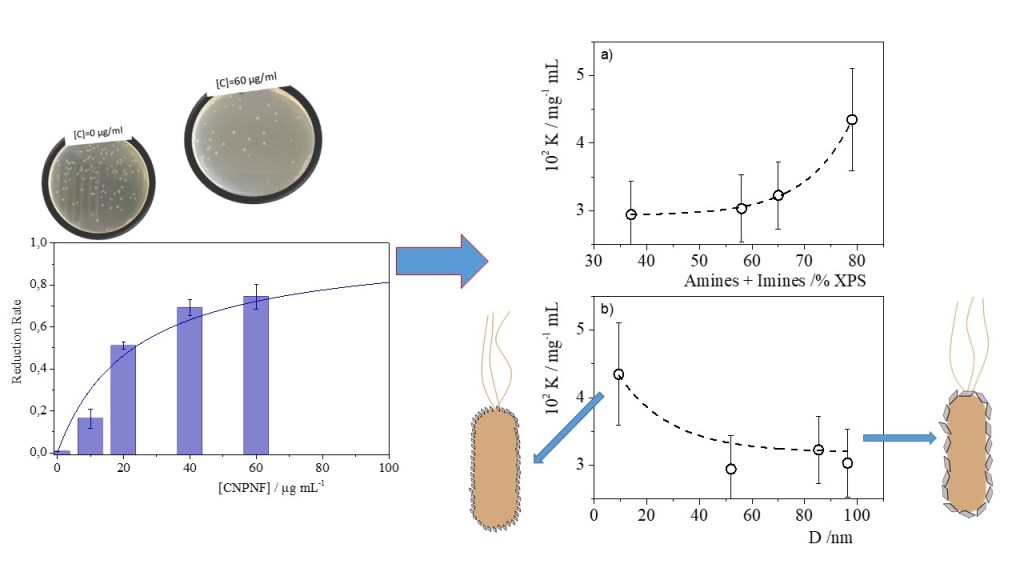
| Materials | Precursor | Diameter1 / nm | Amine groups1 % (XPS) |
Imine groups1 % (XPS) |
K /mg-1 l | Chi-Sqr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNPNF | Carbon nanofibers | 9.3 ± 0.9 | 47 ± 3 | 32 ± 3 | 0.043±0.007 | 0.942 |
| CNPPW | Graphite powder | 93.6 ± 3.8 | 36 ± 3 | 22 ± 2 | 0.030±0.005 | 0.955 |
| CNPHPG | Pyrolytic graphite | 52.0 ± 1 | 21 ± 2 | 16 ± 1 | 0.29±0.005 | 0.967 |
| CNPG | Graphite flakes | 85.3 ± 1.1 | 35 ± 3 | 30 ± 3 | 0.032±0.005 | 0.981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





