1. Introduction
Aging is seen as a disruption of homeostasis and affects all organs [
1]. One key factor is oxidative stress (OS) induced by an imbalance of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a weakened antioxidant cellular defense, though, in normal aging, the excess of ROS can be still tackled [
2]. Nevertheless, this imbalance together with mitochondrial dysfunction, damaged protein accumulation, epigenetic alterations, telomere shortening, and abnormal intracellular signaling result in the frailty syndrome, which is defined by a lowered physiological reserve and reduced resistance to stressors [
3]. In accelerated aging, ROS production cannot anymore be controlled and age-related diseases like cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, cancer, and neurodegeneration are the consequence [
1,
2,
3]. Particularly in industrialized countries, health care improved and consequently life expectancy increased [
4,
5]. Thus, the prevalence of age-related diseases is increasing significantly and becomes a severe burden for the quality of life of patients, health care and socio-economic systems (as analyzed, e.g., by Bae et al. for Korea [
6]).
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic retinopathy (DR) belong to this group of OS-triggered, age-related disorders [
7,
8,
9]. AMD is the major cause of blindness in elderly patients in industrialized countries and DR is the main reason of severe vision loss in the working age population [
10]. In contrast to an imbalance of angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors as seen in neovascular AMD (nAMD), the avascular form of AMD (aAMD) is mainly triggered by inflammatory processes and increased OS [
11]. Bruch’s membrane and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells become dysfunctional, and metabolic waste products (“drusen”) accumulate [
11]. This breakdown of the retinal homeostasis leads to RPE cell death, followed by photoreceptor and finally, retinal neuron cell death cumulating in geographic atrophy (GA), the late stage of aAMD [
11]. In DR, badly controlled hyperglycemia leads to microangiopathy, vessel occlusion, and leakage of the blood-retina barrier causing hemorrhages, edema, and diminished retinal neuronal function; finally, it results in retinal neurodegeneration and cell death [
12]. It has to be noted that the brain and the eyes are particularly prone for OS and the development of associated diseases due to their particularly high oxygen consumption but, on the other hand, restraint antioxidant defense capacities [
2,
13]. A better understanding of underlying pathomechanisms and treatment approaches for these diseases is highly demanded.
Novel treatments have to be tested in vivo in animals to get approved by regulatory authorities; however, ethical issues and limits in transferability to patients make the development of alternative models necessary [
14]. Cell culture is limited to preliminary testing due to missing complexity and transferability of the systems [
14,
15]. Organ cultures can be performed using human tissue and perfectly combine the methodological simplicity of in vitro studies with higher biological complexity as of in vivo models [
16]. Additionally, they save animals and are ethically preferable to in vivo projects (4R principles: refine, reduce, replace, responsible). For example, retina organ culture allows for analysis of pathomechanisms including OS, and for testing different treatments or doses of molecules on multiple samples from the same individual animal/human donor eye. It was first described in 1926 by Strangeways and Fells who cultured 64-72 h young chick embryonic eyes up to 32 d in an extract from 64-72 h young chick embryos mixed in a balanced salt solution [
17]. However, compared to the culture of fetal or newborn tissue that contains potent immature, retinal progenitor cells, the culture of adult, mature retinae remains challenging independent from the quality of the starting material and due to special demands in culture conditions. Murali et al. reported cell culture of isolated neural retinal cells (from 31-89 years old human donors) for up to 8 weeks as suspension culture [
18]. However, culture of the complex retinal tissue structure (from adult donors) can be maintained only for 7 to 14 d; missing vascular perfusion, RPE, connectivity to the brain via the optic nerve, and the continuous high demand of nutrients and oxygen are fostering degeneration by inflammation and OS [
19]. Moreover, except one report [
20], retinal function, i.e., electric activity can be recorded only up to 8 h post-mortem [
19,
21,
22]. Finally, the culture of aged and diseased human retinae - the tissue of interest in research of OS and ageing and useful to analyze pathomechanisms and to test novel treatment approaches in disease models, is even more challenging; OS-induced damage and other imbalances of normal retinal homeostasis are rendering maintenance of the tissue in culture additionally difficult. Despite these challenges, important insights into retinal physiology [
23,
24] and pathology [
25,
26] have been gained, and novel treatment options [
27,
28] been evaluated in retina organ culture.
We are working on the enhancement of adult/aged retina organ culture. It is used as a preclinical test system for novel treatments against retinal neurodegeneration like the cell-based non-viral ex vivo gene therapy approach to treat AMD. To recover a cell-protective, antioxidant retinal environment, RPE or iris pigment epithelial (IPE) cells are transfected using the non-viral Sleeping Beauty (SB100X) transposon system with the genes coding for PEDF and GM-CSF [
29,
30]. PEDF is a cell protective protein with multiple beneficial functions as evaluated, e.g., in models of osteosarcoma [
31] and photoreceptor and amacrine cell survival [
32]. PEDF, ubiquitously expressed by RPE cells, is a molecule that acts anti-angiogenic, anti-tumorigenic, and neurotrophic. It promotes survival and function of neurons, protects from oxidative damage, and inhibits apoptosis by activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway [
33]. GM-CSF is a multi-faceted factor expressed in RPE cells [
34] responsible for proliferation, differentiation, and maturation of myeloid cells and adaptive immune responses to inflammation and infection [
35] especially in the central nervous system [
36]. It counteracts oxidative damage by inhibiting apoptosis via the SRC-dependent STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) pathway, decreased BAD (Bcl-2 agonist of cell death) and increased BCL-2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) expression, and GM-CSF upregulates the production of neurotrophic factors [
37]. Alongside, the phytochemical Scutellarin, found in Scutellaria Barbata, S. lateriflora and S. baicalensis, is tested as antioxidant nutrient in DR [
38]. The flavonoid is used in Chinese medicine with confirmed efficiency in, e.g., cardiovascular diseases and diabetic complications [
39] due to its function as a potent radical scavenger, inhibitor of induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression, lipid peroxidation, and cell death [
39].
In the present work, different retina organ culture models were evaluated, and their advantages and drawbacks as preclinical test system discussed. Techniques were continuously improved and OS-triggered degeneration provoked by high-glucose or H2O2 treatment. The antioxidant and cell protective effects of Scutellarin, PEDF, and GM-CSF were analyzed in retina culture confirming the suitability of the model as pre-clinical test system in general and for OS-triggered retinal neurodegeneration particularly.
4. Discussion
ROS, continuously produced especially by mitochondria [
44,
45], are important signaling molecules in exerting beneficial effects to calorie, glucose limitation, and physical exercise (mitohormesis concept) [
46]. However, excess of ROS induced by mitochondrial dysfunction and a downregulation of antioxidant enzymes leads to OS and cell damage and plays a key role in normal aging and age-related diseases [
46,
47]. ROS like, e.g., the superoxide anion (O
2•−), H
2O
2, or the hydroxyl ion (OH
-) damage proteins, nucleic acids and lipids leading to cancerogenesis, cellular dysfunction and death [
47]. The body developed a three-level antioxidative defense system against cell damage: First, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and related enzymes remove H
2O
2 and lipid hydroperoxides. Secondly, thioredoxin, glutamate-cysteine ligase and the glutathione synthetase generate GSH, glutathione and thioredoxin reductases to reduce glutathione and thioredoxin disulfide. Finally, the NF-κB pathway and others are activated to eliminate oxidized macromolecules, repair damage, and inhibit apoptosis, e.g., by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 proteins [
46,
47]. In age, increased ROS level and decreased antioxidant defense results in the frailty syndrome characterized by a reduced physiological reserve and increased susceptibility to stressors; when this weakened balance is disrupted, age-related diseases evolve [
3].
AMD is a typical age-related disease and as long-term complication of diabetes, DR can also be numbered among this group; untreated, both lead to retinal neurodegeneration and blindness [
5]. As an organ with a particular high oxygen consumption and processing light to generate vision, the retina is constantly producing ROS and is thus particularly prone to OS [
48]. A key process in the pathogenesis of aAMD is the interplay of inflammation and OS that leads to dysfunction of the RPE. Mitochondrial damage, ATP depletion, inflammation, and RIPK-3-mediated membrane damage lead to apoptotic and necrotic cell death [
48]. Oxidatively-modified lipids, 89 proteins including the peroxiredoxin 1 enzyme from the antioxidant defense system, and trace elements accumulate at the interface of Bruch’s membrane and the RPE and form drusen [
49,
50]. As a consequence, the RPE cannot anymore support function and survival of photoreceptors which also undergo cell death [
11,
48]. The diabetic retina is harmed by lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and DNA damage, endogenous levels of antioxidant defense enzymes are diminished, while pro-apoptotic proteins are increased, and levels of neurotrophic factors are decreased [
51]. Prevalence of AMD and DR are increasing due to aging populations and increasing rates of diabetes [
52] and will become a severe burden for patients and health care systems [
6]. In industrialized countries, they are already the first cause of blindness in elderly patients (AMD) and the working-age population (DR) [
10]. Thus, there is an urgent need for innovative, reliable models for a better understanding of the pathogenesis of OS-triggered diseases and the development of novel therapies. Such models are ideally i) simple to generate and thus easily reproducible, ii) available at low-cost, iii) enable up-scaling, iv) ethically favorable, v) biologically complex, and vi) transferable to patients.
Cell culture systems fulfill many of the criteria; however, they cannot evaluate complex biological interactions and are limitedly transferable to patients. The Ala Octa
® affair demonstrated issues with in vitro studies: Perfluorooctane (Ala Octa
®) was a perfluorocarbon liquid used in retinal surgery as transient tamponade and cytotoxicity has been tested – accordingly to regulatory standards - on mouse fibroblasts. Pastor et al. could demonstrate that as a result of insufficient testing, cytotoxicity has been underestimated and led to severe ocular complications up to blindness in many patients [
15]. In vivo studies are more suitable to detect potential local and systemic adverse effects. However, research institutions, pharmacological industry, regulatory and governmental bodies are motivated to reduce animal experiments in biomedical research to a minimum following the 4R principles [
14]. Moreover, many animal models are only limitedly transferable to patients. Pennesi et al. reviewed AMD animal models [
52], of which most are working with mice while theses have no macula and are night-active with very different retinal anatomy and cellular composition compared to human. Often, the animals are of young age [
53] being useful to investigate distinct disease features, but insufficient to prove efficiency and safety of novel treatments against age-related maculopathies. Studies with larger animals and species that have a macula are possible; however, the larger the animal the higher the costs and the more ethical questions arise. Organ cultures offer an alternative. They are relatively easy to generate, available at low costs compared to in vivo studies, allow study of intercellular interactions of complex tissues, and are ethically favorable. Moreover, the use of human donor tissue promises transferability to patients and offers the evaluation of diseased or aged organs. Retina culture was reported first by Strangeways and Fells [
17] who analyzed ocular development for 32 d in cultured chick embryonic eyes. The culture of adult retinae is more challenging: recent research reported a suspension culture of retinal cells for 8 weeks [
18] but except single reports, organotypic culture with preserved tissue structure can be maintained for 7-14 d [
19,
54]. Thus, the retina culture is an excellent system to analyze organ development, disease pathogenesis, intoxications, novel drug candidates and treatment approaches, and particularly OS, but needs enhancement [
19,
54].
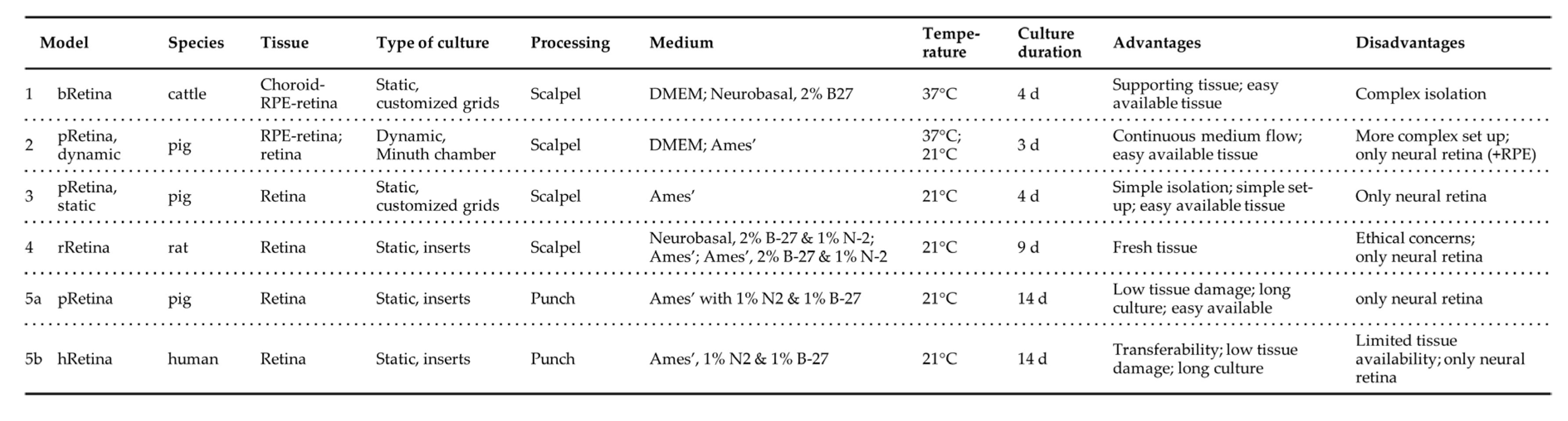
In the present study, five retina culture models comparing different isolation and tissue processing methods, media, temperature, mammalian species, and post-mortem times were presented (summarized in
Table 5). Briefly, the use of porcine or bovine eyes provided by food industry is ethically preferable compared to laboratory rat tissue. By applying enhanced isolation and tissue processing techniques, culture of retinae with prolonged post-mortem time is not inferior to fresh rat tissue regarding tissue morphology, degeneration, cell viability, and death. Ames’ culture medium, optimized by supplementation with growth factors N-2 and B-27 and retina incubation at 21°C revealed superior culture conditions. The implementation of an enhanced isolation and tissue processing technique (“minimal-touch technique”) allowed transfer of the culture system from animal to human donor retinae, which are most fragile due to a post-mortem time of several days. Culture of the neural retina together with the choroid and/or RPE cell layers seemed to be cell protective; however, the complex isolation techniques offset the benefit.
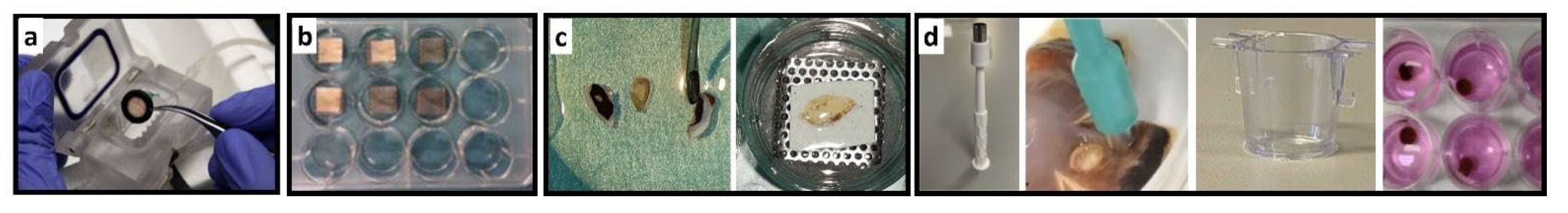
Table 5.
Comparison of presented retina culture models. The table summarizes the set-up of the presented Models 1 to 5. Photographs illustrate the different culture systems. a) Minuth chamber with a retina clamped into the culture ring. b) In the multi-well plate are pRetinas cultured on nitrocellulose membranes on customized stainless-steel grids. c) The smaller rat retina is cut into halfs before cultured on nitrocellulose membranes and customized grids. d) The panel shows the punch, how it is cutting tissue, and the culture insert before use and in culture.
Table 5.
Comparison of presented retina culture models. The table summarizes the set-up of the presented Models 1 to 5. Photographs illustrate the different culture systems. a) Minuth chamber with a retina clamped into the culture ring. b) In the multi-well plate are pRetinas cultured on nitrocellulose membranes on customized stainless-steel grids. c) The smaller rat retina is cut into halfs before cultured on nitrocellulose membranes and customized grids. d) The panel shows the punch, how it is cutting tissue, and the culture insert before use and in culture.
Various species are used for retina culture of which pig and cattle are frequently used since they are easily available. Kuehn et al. evaluated hypoxia-induced retinal degeneration following cobalt-chloride treatment in porcine retinae (8 d culture; Neurobasal medium supplemented with glutamine, B-27 and N-2; photoreceptors facing the multi-well inserts, 4-6 samples/retina; isolation using a 6 mm punch) [
25]. General tissue quality was very good enabling analysis of dose-dependent effects of the cobalt-chloride treatment. Similarly, Models 2, 3, and 5a used porcine tissue and confirmed excellent tissue quality that enabled retina culture up to 14 d (Model 5a). Model 1 used cattle as starting material, as did Peynshaert et al. (2 d culture; isolation and culture of neural retina and vitreous, Neurobasal medium supplemented with glutamine and B-27; 3 explants/eye,) [
23]. Results demonstrated excellent tissue quality in terms of tissue architecture, cell composition, nerve fiber layer and functionality comparable to data from Model 1. Schnichels et al. isolated young rat retinae immediately after sacrifice (7 d culture; R16-complete medium; retina of one eye cultured as one sample) [
55]. Retinal architecture was maintained for 7 d and tissue thickness decreased only moderately. In line with this data, Model 4 demonstrated a retarded degeneration and prolonged culture duration of up to 9-13 d when using freshly isolated rat retinae (2 samples/eye). It is assumed that the short post-mortem time and not the species was responsible for the positive influence on cell viability in both studies. Yet, since Model 4 requested the sacrifice of one animal for 4 samples it is ethically questionable and not scalable.
The perfusion culture presented in Model 2 reported first by Kobuch et al. [
56] guaranteed constant nutrient and oxygen delivery. The culture of the choroid-RPE-retina complex in a perfusion chamber allowed tissue preservation up to 10 d with POS showing first signs of degeneration after 1 d, apoptotic and necrotic cell death was seen after 4 d, while in control samples (static culture) tissue structure was disrupted after 4 d (10 d culture; DMEM, 15% porcine serum, 2.5% HEPES-buffer; 1 sample/retina) [
56]. Similarly, Model 2 reported a decelerated degeneration compared to Model 1; however, compared to Model 3 and 5 no significant advantage could be observed; it is assumed that daily medium change (in static culture) delivers sufficient nutrients and oxygen for optimal tissue preservation. Thus, considering the simpler set up and easier up-scaling of static cultures, this system seems preferable.
Model 1 and 2 cultured the neural retina with supportive choroid and/or RPE tissue since Kobuch et al. reported a benefit of this technique on retina conservation [
56]; also Peynshaert et al. reported low levels of inflammation, no significant changes in tissue thickness, and stable populations of bipolar cells after culture of the neural retina with supportive tissue (vitreous) [
23]. Indeed, especially POS were better preserved when cultured together with RPE cells (and the choroid); however, enlarged analyses performed with Model 2 did not confirm the prominent differences between the culture of the neural retina alone or with (choroid-)RPE tissue. The higher complexity of the isolation technique seemed to abolish the positive effect of the supportive tissue layers, i.e., not all samples could be put in culture or showed damages due to isolation.
It is known that hypothermia causes immunosuppression and slows down metabolism and, thus, protects organs from damage due to hypoxia, ischemia, or trauma as shown by Narayanamurthy et al. who presented a cooling device that protected the rat brain from hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy [
57]. An hypothermia-induced metabolism deceleration, significantly inhibited the development of OS and its consequences as shown by Choi et al. in a model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury [
58]. Also various ocular conditions like allergic conjunctivitis or retinal hypoxia and ischemia are treated by hypothermia [
59,
60]. Due to the high metabolic demand and metabolic turnover of the retina, the idea to rescue cultured retinal tissue by hypothermia was already evaluated by Ames and Gurian in 1963: They showed that rabbit retinae recovered more rapidly at 30°C than at 37°C after glucose and oxygen deprivation [
61]. Recently, Mueller-Buehl et al. reported a OS damage-reducing effect of hypothermia on H
2O
2-induced damage on porcine RGCs [
28]. Accordingly, Model 2 cultured retinae in hypothermic conditions (21°C) compared to 37°C-cultured samples and revealed significant tissue preservation by higher cell counts and a lowered rate of apoptosis. It has to be noted that pharmacokinetics analyses have to be analyzed carefully due to the slowed metabolism.
While in Model 1 retina samples were cultured in DMEM, in Model 2, Ames’ medium was introduced and used in all following systems. Results of Model 2 demonstrated a significant benefit of Ames’ medium that has been especially developed for the culture of retinal tissue [
62]. Many other groups are using Neurobasal medium for its protective function for neurons and report positive results [
23,
25]. However, particularly Model 5 confirmed that a medium that imitates the fluid that “bathes the retina in vivo” [
62] is ideal to support this complex tissue that is composed of multiple neural and non-neural cell types. It has to be noted, that in Model 4 the medium has been optimized by addition of growth factors B-27 and N2 enabling the two-week long culture among other factors.
The experimental series in high glucose conditions and after H
2O
2 treatment demonstrated the benefit of the retina culture models in preclinical testing. Model 3 cultured porcine retinae in static culture using Ames’ medium at 21°C. Tissue degeneration could be kept at a low level for 4 d during which the detrimental effect of OS induced by “high glucose” and the benefit of antioxidant Scutellarin treatment could be determined. It has to be noted that high doses of Scutellarin might negate the positive effect, but more detailed analyses have to be done to confirm this tendency. Model 4 has been implemented to prolong the culture and its avail was evaluated by analyzing the effect of PEDF and/or GM-CSF on cell viability and OS after H
2O
2-treatment. Rat retinae cultured immediately after sacrifice, allowed cultures up to 13 d and confirmed cell viability rates in freshly fixed retinae of around 31%, what has been also measured in IPE cells immediately after isolation [
63]. After H
2O
2-treatment, reduced GSH levels were expected as reported by Wang et al. in ARPE-19 cells [
64] and by Zheng et al. in retinae from 18-months old hydroquinone fed mice [
65]. In contrast, results showed lowest GSH concentrations in controls, while GSH levels in H
2O
2-treated samples were increased. It is assumed that while already improved compared to Models 1-3, tissue quality in Model 4 was not good enough to reliably measure GSH levels. This is supported by the low percentage of samples that delivered methodological valid results.
Thus, Model 5 has been developed to i) generally increase tissue quality and prolong culture duration, ii) implement a procedure that allows up-scaling of testing series, and iii) allow the transfer to human donor tissue with longer post-mortem time. Porcine retinae were cultured in static conditions at 21°C, in Ames’ medium supplemented with growth factors. Moreover, isolation and tissue processing techniques were improved; the novel “minimal-touch technique” includes sample preparation by 6 mm punches up to 32 samples/retina, special tissue handling and processing as detailed in section 2. It enabled significantly improved retina preservation shown by low degeneration scores at 14 d, high levels of viability, low apoptosis and inflammation. The results allowed transfer to human retinae with similar results and comparable to data reported by other groups like Jüttner et al. [
66] and Schnichels et al. [67]. Ongoing experiments repeat the analyses of Model 4 evaluating the protective effect of PEDF and GM-CSF in OS to confirm superiority of Model 5. Future enhancements will implement a co-culture of the neural retina with iPS-derived RPE cells to keep simplicity of the model while adding supportive RPE tissue. Electroretinogram examinations will be added to the panel of analyses and OS-related damage will be evaluated in more detail by analyzing SODs, lipid peroxidation products, and DNA-oxidation products. This will be of particular interest by using human donor eyes from AMD or DR patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.T., M.K.; methodology, G.T, M.K.; validation, G.T.; formal analysis, S.J., M.M., C.L., L.S., M.K.; resources, G.T.; data curation, M.K., S.J., M.M., C.L., L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.; writing—review and editing, M.M., C.L., L.S., N.H., T.B., EC, A.K., B.P., S.J., G.T.; visualization, M.K.; supervision, G.T., S.J., M.K; project administration, G.T., M.K.; funding acquisition, G.T. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
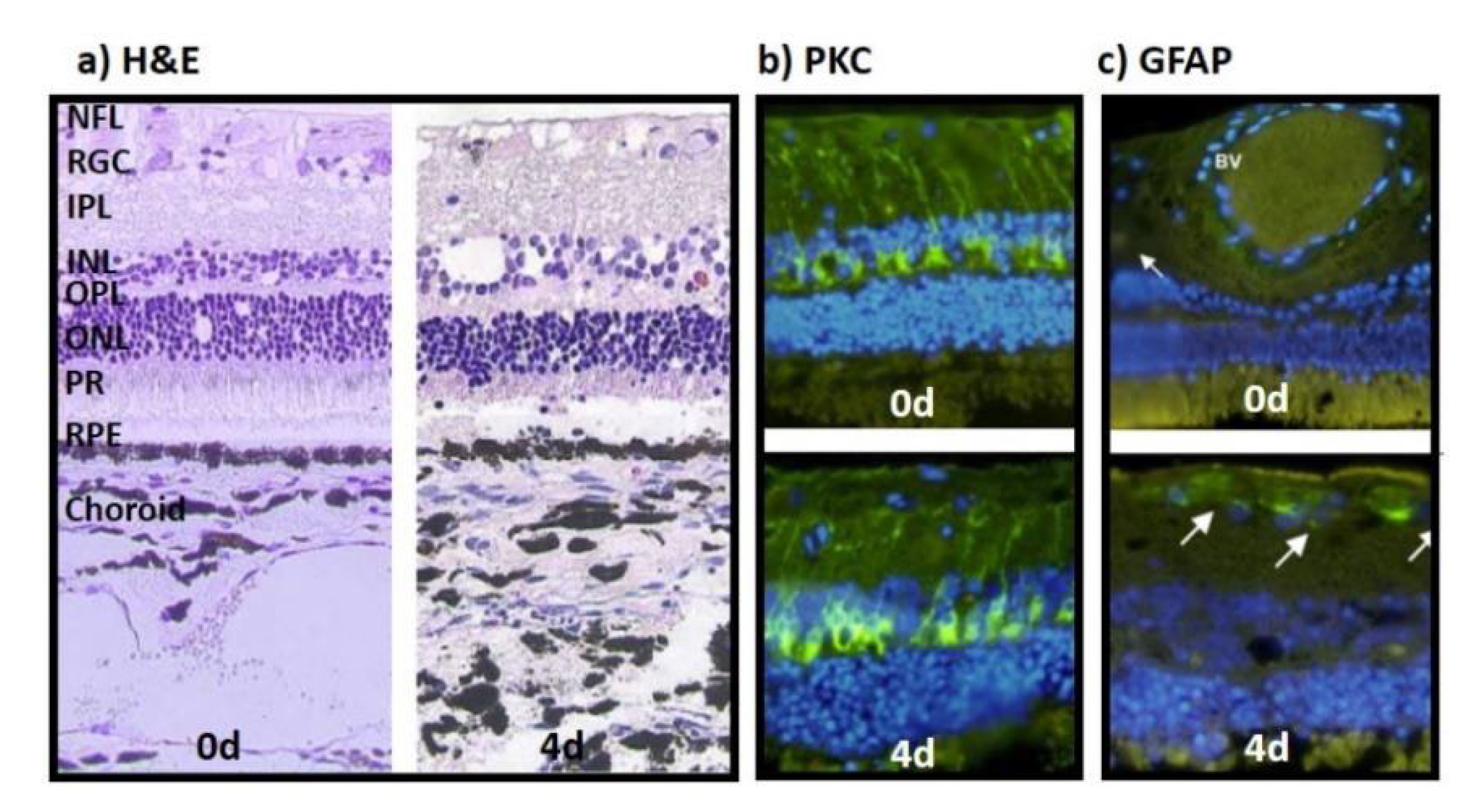
Figure 1.
Morphology, functional & inflammatory status of bovine retinae cultured with choroid and RPE. a) H&E-stained sections of the choroid-RPE-retina complex processed directly after isolation (0 d, left) and at 4 d in culture (right), both showed good tissue preservation. INL and RGC layer showed reduced cell numbers and holes at 4 d in culture. b) PKC expression in bipolar cells (green) was stable during ex vivo culture (bottom, 4 d) compared to sections stained directly after isolation (top, 0 d). c) GFAP expression was low in retinae at 4 d in culture (bottom, 4 d) compared to samples stained directly after isolation (top, 0 d). White arrows indicate areas of weak GFAP expression. Nuclei are counterstained using DAPI. NFL: nerve fiber layer; IPL: inter plexiform layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer; PR: photoreceptors; BV: blood vessel.
Figure 1.
Morphology, functional & inflammatory status of bovine retinae cultured with choroid and RPE. a) H&E-stained sections of the choroid-RPE-retina complex processed directly after isolation (0 d, left) and at 4 d in culture (right), both showed good tissue preservation. INL and RGC layer showed reduced cell numbers and holes at 4 d in culture. b) PKC expression in bipolar cells (green) was stable during ex vivo culture (bottom, 4 d) compared to sections stained directly after isolation (top, 0 d). c) GFAP expression was low in retinae at 4 d in culture (bottom, 4 d) compared to samples stained directly after isolation (top, 0 d). White arrows indicate areas of weak GFAP expression. Nuclei are counterstained using DAPI. NFL: nerve fiber layer; IPL: inter plexiform layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer; PR: photoreceptors; BV: blood vessel.
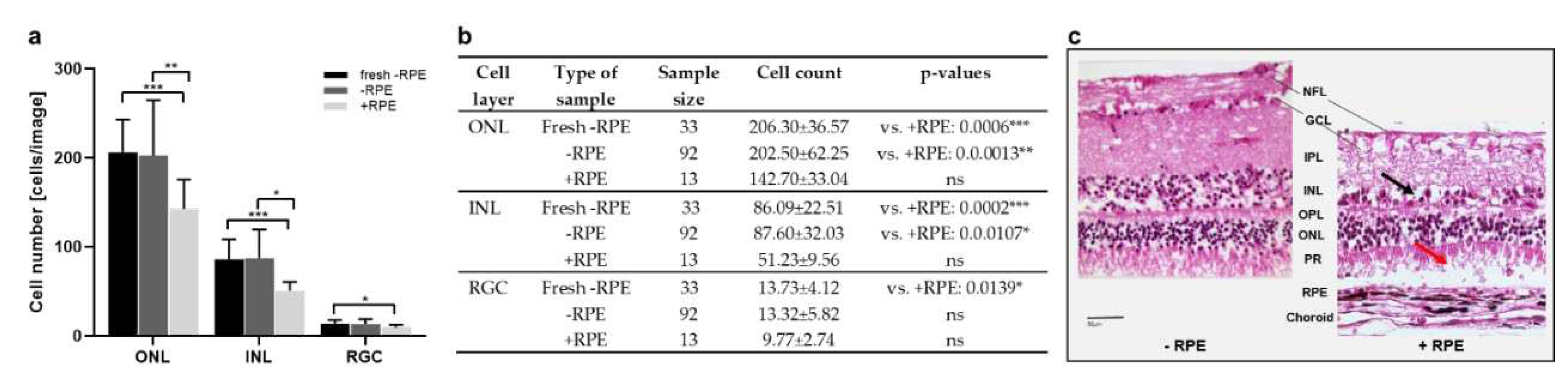
Figure 2.
Cell counts and morphology of porcine retinae cultured with & without RPE. a) Illustrated are cell counts in the ONL, INL, and RGC layers, determined in H&E-stained sections determined at 1 d from tissue samples isolated with (+RPE) and without (-RPE) RPE compared to sections directly stained after isolation without RPE (fresh -RPE). While cell counts of cultured neural retinae were similar to freshly processed tissue, cell numbers were significantly reduced in ONL, INL and RGC layers of cultures RPE-retina complexes. b) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count in ONL, INL, and RGC layers. c) Representative H&E-stained sections illustrate tissue degeneration in retinae cultured with/without RPE. Overall, the “+RPE” culture decreased in thickness and revealed holes and cell loss. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
Figure 2.
Cell counts and morphology of porcine retinae cultured with & without RPE. a) Illustrated are cell counts in the ONL, INL, and RGC layers, determined in H&E-stained sections determined at 1 d from tissue samples isolated with (+RPE) and without (-RPE) RPE compared to sections directly stained after isolation without RPE (fresh -RPE). While cell counts of cultured neural retinae were similar to freshly processed tissue, cell numbers were significantly reduced in ONL, INL and RGC layers of cultures RPE-retina complexes. b) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count in ONL, INL, and RGC layers. c) Representative H&E-stained sections illustrate tissue degeneration in retinae cultured with/without RPE. Overall, the “+RPE” culture decreased in thickness and revealed holes and cell loss. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
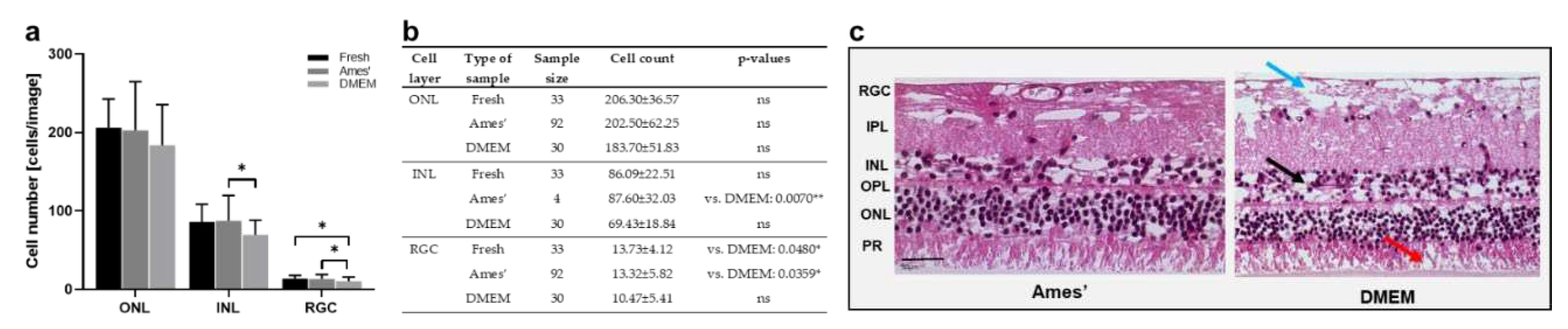
Figure 3.
Cell counts & morphology of porcine retinae cultured in Ames’ medium or DMEM. a) Illustrated are cell counts in the ONL, INL and RGC layers, counted in H&E-stained sections at 1d. The cell counts showed slightly reduced cell numbers in the ONL of tissue cultured in DMEM; in the INL and RGC layers this reduction was significant. b) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count in ONL, INL, and RGC layers after culture in Ames’ medium vs. DMEM. c) H&E-stained sections illustrate representative retinae cultured 1 d in Ames’ or DMEM medium. Cross sections demonstrated signs of degeneration in DMEM-cultured retinae with large holes in the RGC (blue arrow), holes and cell loss in the INL (black arrow) and less structured, degenerated POS (red arrow). Fresh = stained directly after isolation. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
Figure 3.
Cell counts & morphology of porcine retinae cultured in Ames’ medium or DMEM. a) Illustrated are cell counts in the ONL, INL and RGC layers, counted in H&E-stained sections at 1d. The cell counts showed slightly reduced cell numbers in the ONL of tissue cultured in DMEM; in the INL and RGC layers this reduction was significant. b) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count in ONL, INL, and RGC layers after culture in Ames’ medium vs. DMEM. c) H&E-stained sections illustrate representative retinae cultured 1 d in Ames’ or DMEM medium. Cross sections demonstrated signs of degeneration in DMEM-cultured retinae with large holes in the RGC (blue arrow), holes and cell loss in the INL (black arrow) and less structured, degenerated POS (red arrow). Fresh = stained directly after isolation. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
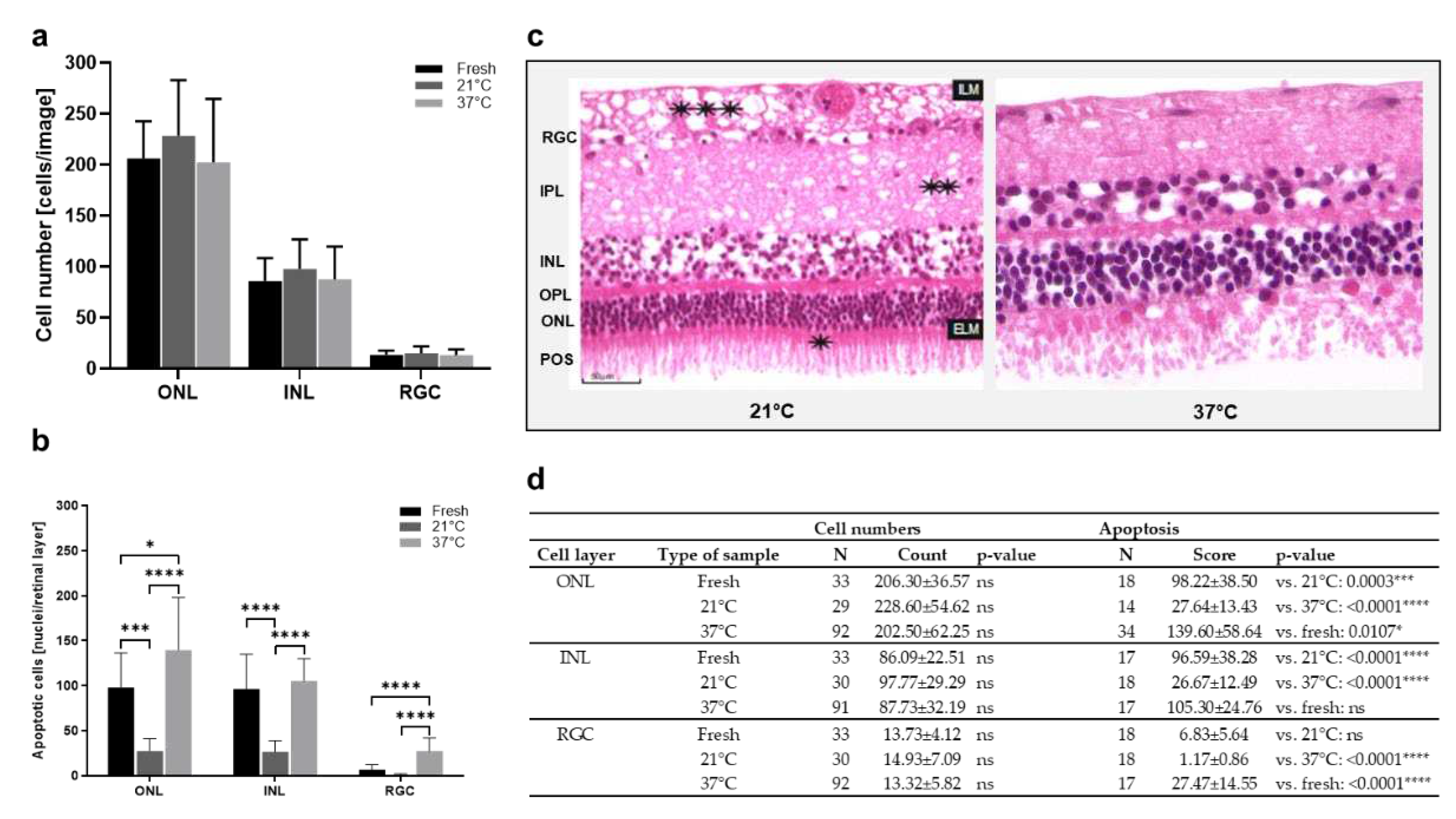
Figure 4.
Cell count and apoptosis in porcine retinae cultured at 37°C vs. 21°C. a) Increased cell counts were detected in the ONL of retinae cultured at 21°C for 1 d. Also in the INL, highest cell counts were found in 21°C-cultures. There was no important difference in cell counts in the RGC. b) The rate of apoptosis declined significantly in ONL, INL, and RGC layers of cultures incubated at 21°C. c) H&E-stained sections show representative examples of retinae cultured at 37°C or 21°C. Significant degeneration was seen after culture at 37°C with holes mainly in the INL and a significant loss of tissue integrity and POS. Also at 21°C, holes were found in the NFL and IPL (asterisks) layers. d) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count and apoptosis analysis in ONL, INL, and RGC layers. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
Figure 4.
Cell count and apoptosis in porcine retinae cultured at 37°C vs. 21°C. a) Increased cell counts were detected in the ONL of retinae cultured at 21°C for 1 d. Also in the INL, highest cell counts were found in 21°C-cultures. There was no important difference in cell counts in the RGC. b) The rate of apoptosis declined significantly in ONL, INL, and RGC layers of cultures incubated at 21°C. c) H&E-stained sections show representative examples of retinae cultured at 37°C or 21°C. Significant degeneration was seen after culture at 37°C with holes mainly in the INL and a significant loss of tissue integrity and POS. Also at 21°C, holes were found in the NFL and IPL (asterisks) layers. d) Individual values, n-numbers, and p-values of cell count and apoptosis analysis in ONL, INL, and RGC layers. Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm.
Figure 5.
Degeneration score in static porcine retina culture for 4 d. a) After isolation, retinae showed an integer structure without holes or clefts.
b) At 1 d of culture, the tissue was still of good quality, but first brighter areas let assume cell loss (white arrow). Tissue borders were particularly exposed to degeneration (black arrow).
c) At 2 days, degeneration became significant by bright spots, demonstrating lower cell density, i.e., cell loss (white arrows).
d) Degeneration further increased at 3 d and bright areas progressed to holes (red arrows).
e) After 4 d of culture, multiple holes and clefts demonstrated progressed tissue degeneration (red arrows); nevertheless, it must be noted that tissue assembly was still intact.
f) Degeneration was quantified by the degeneration score. Though degeneration progressed over time, it never reached the highest score of ‘3’, i.e., a destruction of the tissue assembly. Significant differences were found between 1 vs. 3 and vs. 4 d of culture (p=0.0496 and p=0.0234, respectively). N= 5-8. Magnification: 200x; scale bar: 200 µm [
41].
Figure 5.
Degeneration score in static porcine retina culture for 4 d. a) After isolation, retinae showed an integer structure without holes or clefts.
b) At 1 d of culture, the tissue was still of good quality, but first brighter areas let assume cell loss (white arrow). Tissue borders were particularly exposed to degeneration (black arrow).
c) At 2 days, degeneration became significant by bright spots, demonstrating lower cell density, i.e., cell loss (white arrows).
d) Degeneration further increased at 3 d and bright areas progressed to holes (red arrows).
e) After 4 d of culture, multiple holes and clefts demonstrated progressed tissue degeneration (red arrows); nevertheless, it must be noted that tissue assembly was still intact.
f) Degeneration was quantified by the degeneration score. Though degeneration progressed over time, it never reached the highest score of ‘3’, i.e., a destruction of the tissue assembly. Significant differences were found between 1 vs. 3 and vs. 4 d of culture (p=0.0496 and p=0.0234, respectively). N= 5-8. Magnification: 200x; scale bar: 200 µm [
41].
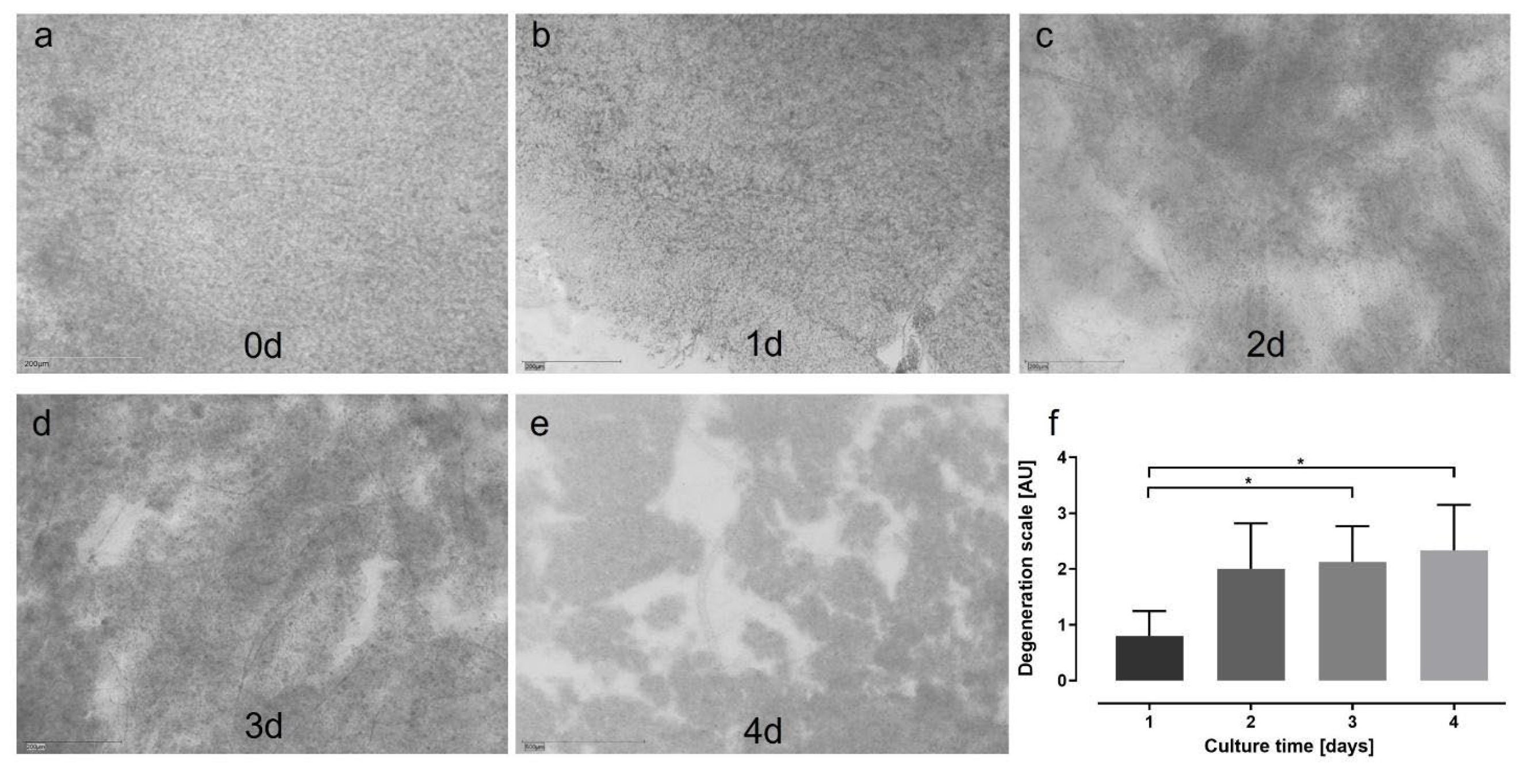
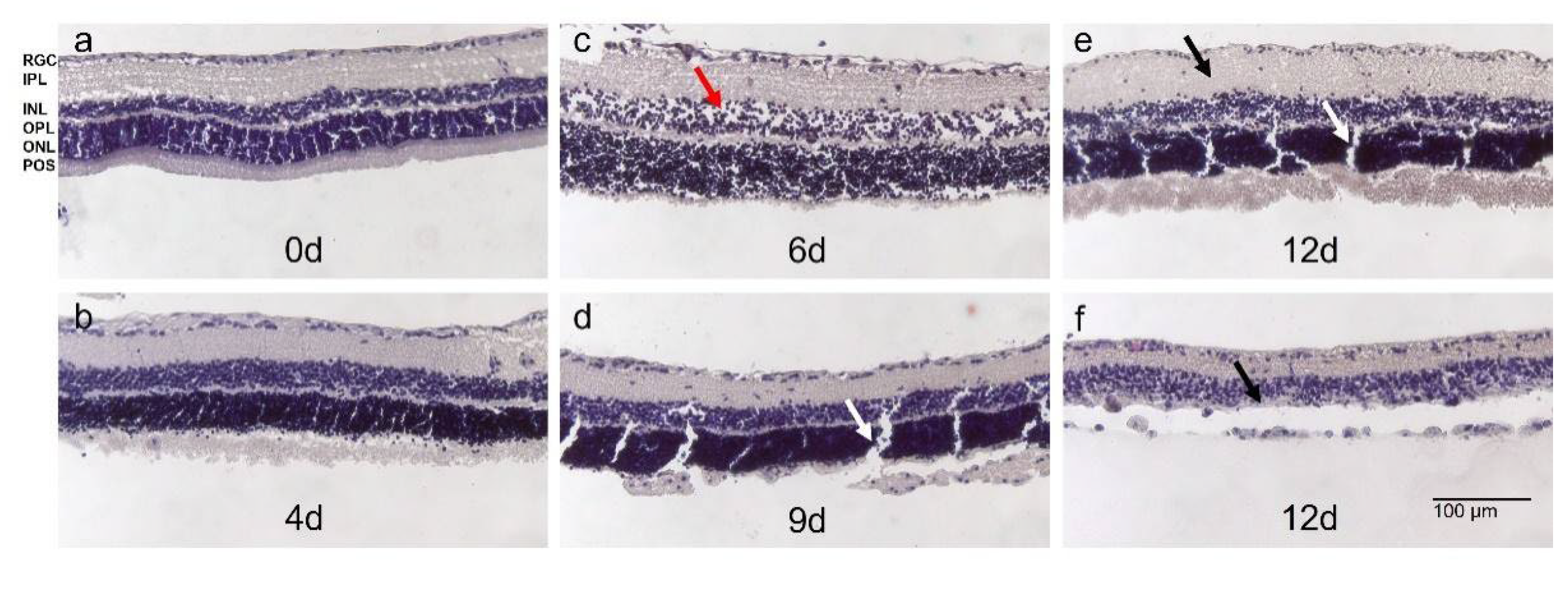
Figure 6.
Morphology of H&E-stained rat retina in static 12 d-long culture. a) Retinae stained directly after isolation showed the typical laminar structure without signs of degeneration; POS were present.
b) At 4 d, tissue quality was comparable to directly stained retinae without significant signs of degeneration and preserved laminar structure.
c) POS showed signs of degeneration after 6 d of culture. However, other retinal layers were preserved despite some holes indicating cell loss (red arrow).
d) Until 9 d of culture, tissue integrity was maintained without significant signs of degeneration except the loss of POS.
e+f) At 12 d of culture, degeneration became significant. Either retinae thickened indicating inflammatory processes (black arrow in (e)) or cell loss was significant and retinal layers, particularly INL and ONL, were no longer distinguishable (f). Clefts in (d) and (e) (white arrows) were due to tissue processing. N= 3. Magnification: 100x; scale bar: 100 µm [
44].
Figure 6.
Morphology of H&E-stained rat retina in static 12 d-long culture. a) Retinae stained directly after isolation showed the typical laminar structure without signs of degeneration; POS were present.
b) At 4 d, tissue quality was comparable to directly stained retinae without significant signs of degeneration and preserved laminar structure.
c) POS showed signs of degeneration after 6 d of culture. However, other retinal layers were preserved despite some holes indicating cell loss (red arrow).
d) Until 9 d of culture, tissue integrity was maintained without significant signs of degeneration except the loss of POS.
e+f) At 12 d of culture, degeneration became significant. Either retinae thickened indicating inflammatory processes (black arrow in (e)) or cell loss was significant and retinal layers, particularly INL and ONL, were no longer distinguishable (f). Clefts in (d) and (e) (white arrows) were due to tissue processing. N= 3. Magnification: 100x; scale bar: 100 µm [
44].
Figure 7.
Morphology and thickness of H&E-stained porcine and human retinae after static culture for 14 d. Sample isolation and tissue processing was improved (section 2.2.5) allowing for a 14 d-long culture. Shown are H&E-stained retinal sections from day 1 to day 14.
a) The presented sections illustrate the quality of retinae at the time point of isolation, at 6 and 14 d. On day 1, layers were distinguishable, no signs of degeneration were seen (i). Also at 6 d, retinae look normal, though little cell loss might have occurred in the INL and ONL (ii). POS were present. After 14 d of culture, POS are no longer visible in H&E-stained sections, but laminar retinal structure is still intact (iii). N=16.
b) The presented sections illustrate the quality of retinae at the time point of isolation, at 6 and 14 d. On day one, all layers were distinguishable, no signs of degeneration were seen (iv). On day 6, retinae look normal without significant signs of degeneration, though little cell loss might have occurred in the INL and ONL (black arrow) (v). POS were not visible. After 14 d of culture, laminar retinal structure is still intact (vi). N= 8.
c) Retinal thickness was determined in porcine and human retinae cultured for 14 d using micrographs of H&E-stained samples. It did not differ significantly over 14 d; an ANOVA excluded significant changes between time points for both porcine (pRetina) (p=0.4882) and human (hRetina) tissue (p=0.6126). Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm [
45].
Figure 7.
Morphology and thickness of H&E-stained porcine and human retinae after static culture for 14 d. Sample isolation and tissue processing was improved (section 2.2.5) allowing for a 14 d-long culture. Shown are H&E-stained retinal sections from day 1 to day 14.
a) The presented sections illustrate the quality of retinae at the time point of isolation, at 6 and 14 d. On day 1, layers were distinguishable, no signs of degeneration were seen (i). Also at 6 d, retinae look normal, though little cell loss might have occurred in the INL and ONL (ii). POS were present. After 14 d of culture, POS are no longer visible in H&E-stained sections, but laminar retinal structure is still intact (iii). N=16.
b) The presented sections illustrate the quality of retinae at the time point of isolation, at 6 and 14 d. On day one, all layers were distinguishable, no signs of degeneration were seen (iv). On day 6, retinae look normal without significant signs of degeneration, though little cell loss might have occurred in the INL and ONL (black arrow) (v). POS were not visible. After 14 d of culture, laminar retinal structure is still intact (vi). N= 8.
c) Retinal thickness was determined in porcine and human retinae cultured for 14 d using micrographs of H&E-stained samples. It did not differ significantly over 14 d; an ANOVA excluded significant changes between time points for both porcine (pRetina) (p=0.4882) and human (hRetina) tissue (p=0.6126). Magnification: 400x; scale bar: 50 µm [
45].
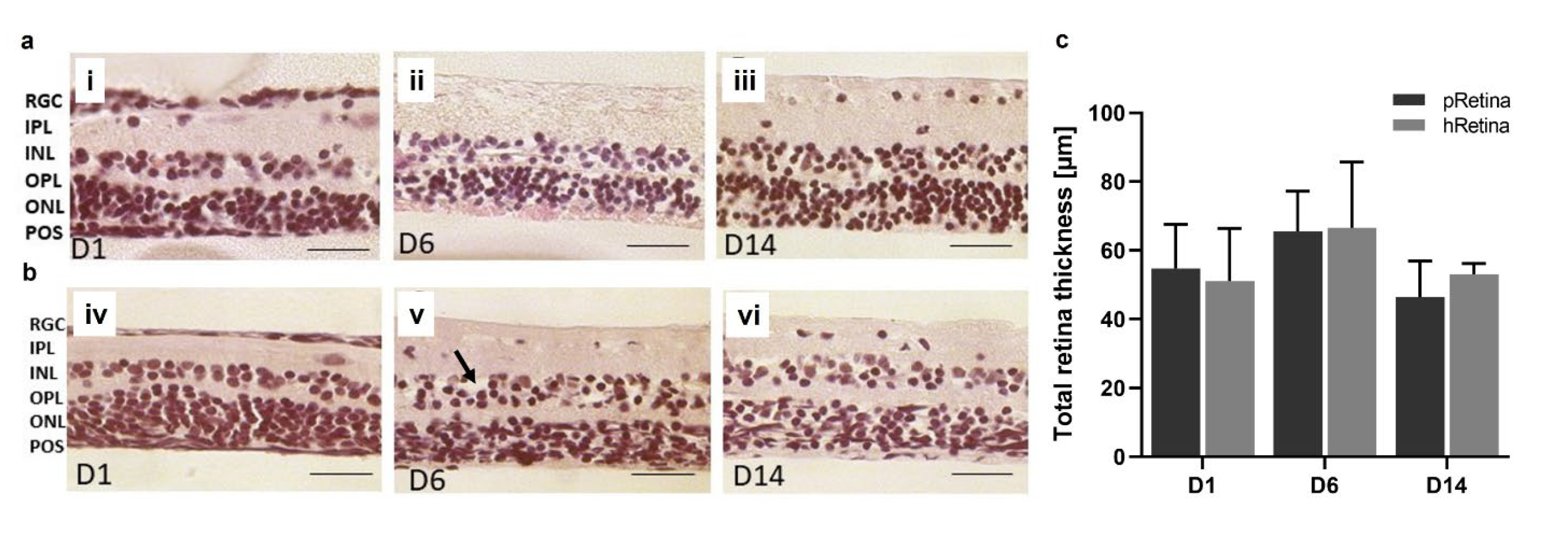
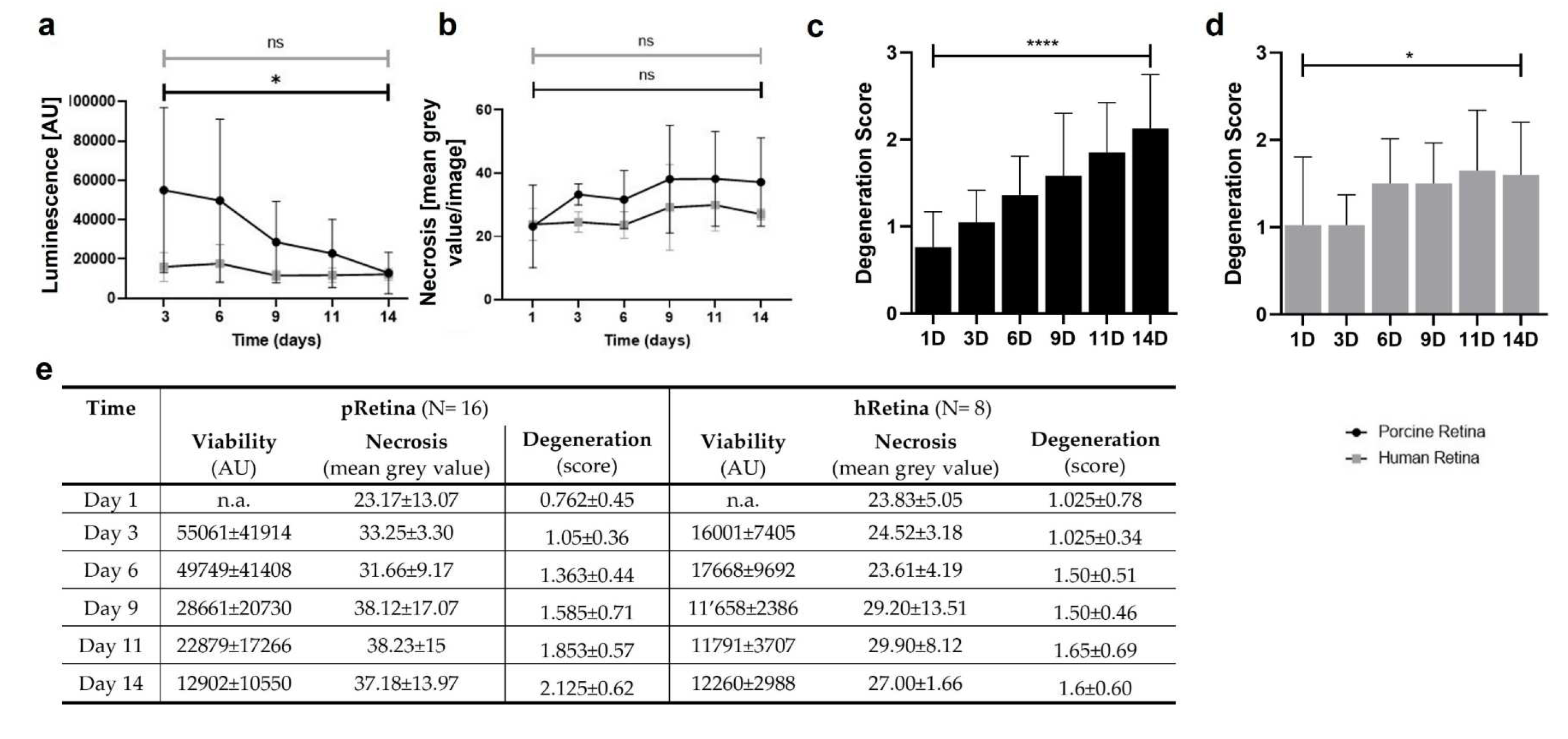
Figure 8.
Cell viability, death, & degeneration in static culture of p- and hRetina for 14 d. a) The curves show luminescence measured in culture media of p- and hRetina over 14 d. While luminescence remained low in hRetinae, it was high at the beginning in pRetinae followed by a decrease. Luminescence inversely correlates to viability indicating a high cell viability (or low cell death rate) for both species except within the first week in pRetinae.
b) Necrosis was determined by PI-staining revealing low and stable rates of necrosis for both species from day 1-14.
c) Degeneration in cultured pRetinae increased over time but remained moderate with a maximal increase to 2.13 (p<0.0001).
d) In hRetina, degeneration remained stably low with scores from 1.03 to 1.60 (p=0.0290).
e) Individual values of viability, death and degeneration analyses [
45].
Figure 8.
Cell viability, death, & degeneration in static culture of p- and hRetina for 14 d. a) The curves show luminescence measured in culture media of p- and hRetina over 14 d. While luminescence remained low in hRetinae, it was high at the beginning in pRetinae followed by a decrease. Luminescence inversely correlates to viability indicating a high cell viability (or low cell death rate) for both species except within the first week in pRetinae.
b) Necrosis was determined by PI-staining revealing low and stable rates of necrosis for both species from day 1-14.
c) Degeneration in cultured pRetinae increased over time but remained moderate with a maximal increase to 2.13 (p<0.0001).
d) In hRetina, degeneration remained stably low with scores from 1.03 to 1.60 (p=0.0290).
e) Individual values of viability, death and degeneration analyses [
45].
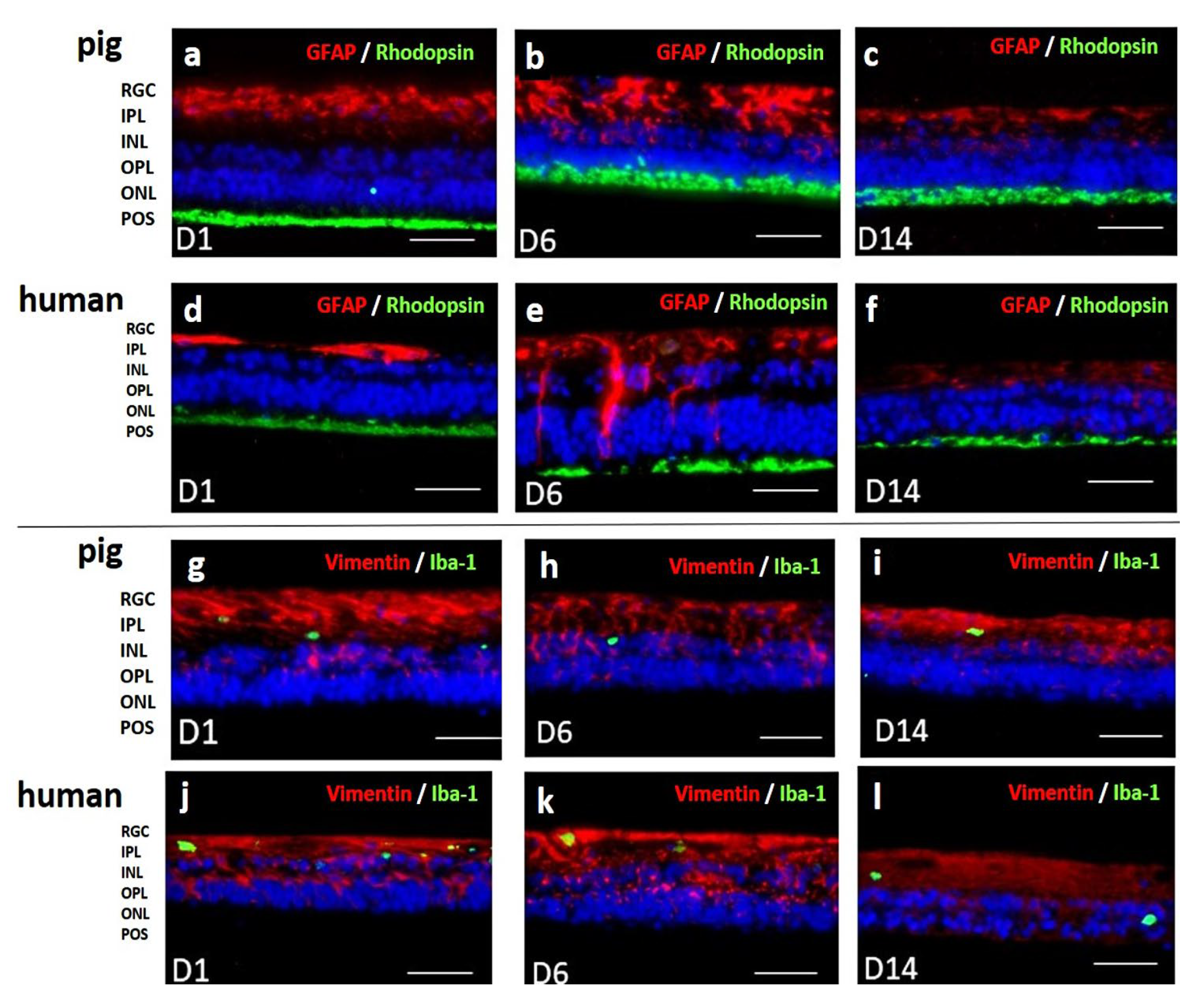
Figure 9.
Immunohistochemical staining of porcine and human retinae from 1-14 d of culture. a-f) Anti-GFAP-anti-rhodopsin double staining confirmed POS preservation up to day 14 (green). GFAP staining revealed inflammatory reactions in Müller cells at 6 d of culture that decreased in the second week of culture below base staining (red). The pattern was similar for pRetinae and hRetinae.
g-l) Vimentin staining proved stable Müller cell presence and morphology for 14 d (red). Microglia activation, shown by Iba-1
+ cell staining (green) remained low in both species at every time point. N= 16 (pRetinae); N=8 (hRetinae). Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 100 µm [
45].
Figure 9.
Immunohistochemical staining of porcine and human retinae from 1-14 d of culture. a-f) Anti-GFAP-anti-rhodopsin double staining confirmed POS preservation up to day 14 (green). GFAP staining revealed inflammatory reactions in Müller cells at 6 d of culture that decreased in the second week of culture below base staining (red). The pattern was similar for pRetinae and hRetinae.
g-l) Vimentin staining proved stable Müller cell presence and morphology for 14 d (red). Microglia activation, shown by Iba-1
+ cell staining (green) remained low in both species at every time point. N= 16 (pRetinae); N=8 (hRetinae). Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 100 µm [
45].
Figure 10.
Anti-oxidative cell protection by Scutellarin in HG. pRetinae were cultured for 4 d in static conditions (Model 3) in NG (6 mM) or HG conditions (30 mM) and treated with Scutellarin (1, 10 or 100 µM).
a) Viability determined at 1 d (D1) revealed comparable ATP level in both glucose conditions, but significantly increased viability after treatment with low (1 µM) or medium (10 µM) doses of Scutellarin, while high doses (100 µM) had a detrimental effect.
b) At 4 d (D4), viability decreased in HG, but increased after addition of low and medium doses of Scutellarin to levels of NG.
c) H&E staining of retinal sections fixed at 4 d of culture (plus one control fixed immediately after isolation: “fresh”), revealed a lowered degeneration in POS of Scutellarin-treated samples if administered in low to medium doses. NG = normal glucose; HG = high glucose; HG1 = high glucose + 1 µM Scutellarin; HG10 = high glucose + 10 µM Scutellarin; HG100 = high glucose + 100 µM Scutellarin. N=4. Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 200 µm [
38].
Figure 10.
Anti-oxidative cell protection by Scutellarin in HG. pRetinae were cultured for 4 d in static conditions (Model 3) in NG (6 mM) or HG conditions (30 mM) and treated with Scutellarin (1, 10 or 100 µM).
a) Viability determined at 1 d (D1) revealed comparable ATP level in both glucose conditions, but significantly increased viability after treatment with low (1 µM) or medium (10 µM) doses of Scutellarin, while high doses (100 µM) had a detrimental effect.
b) At 4 d (D4), viability decreased in HG, but increased after addition of low and medium doses of Scutellarin to levels of NG.
c) H&E staining of retinal sections fixed at 4 d of culture (plus one control fixed immediately after isolation: “fresh”), revealed a lowered degeneration in POS of Scutellarin-treated samples if administered in low to medium doses. NG = normal glucose; HG = high glucose; HG1 = high glucose + 1 µM Scutellarin; HG10 = high glucose + 10 µM Scutellarin; HG100 = high glucose + 100 µM Scutellarin. N=4. Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 200 µm [
38].
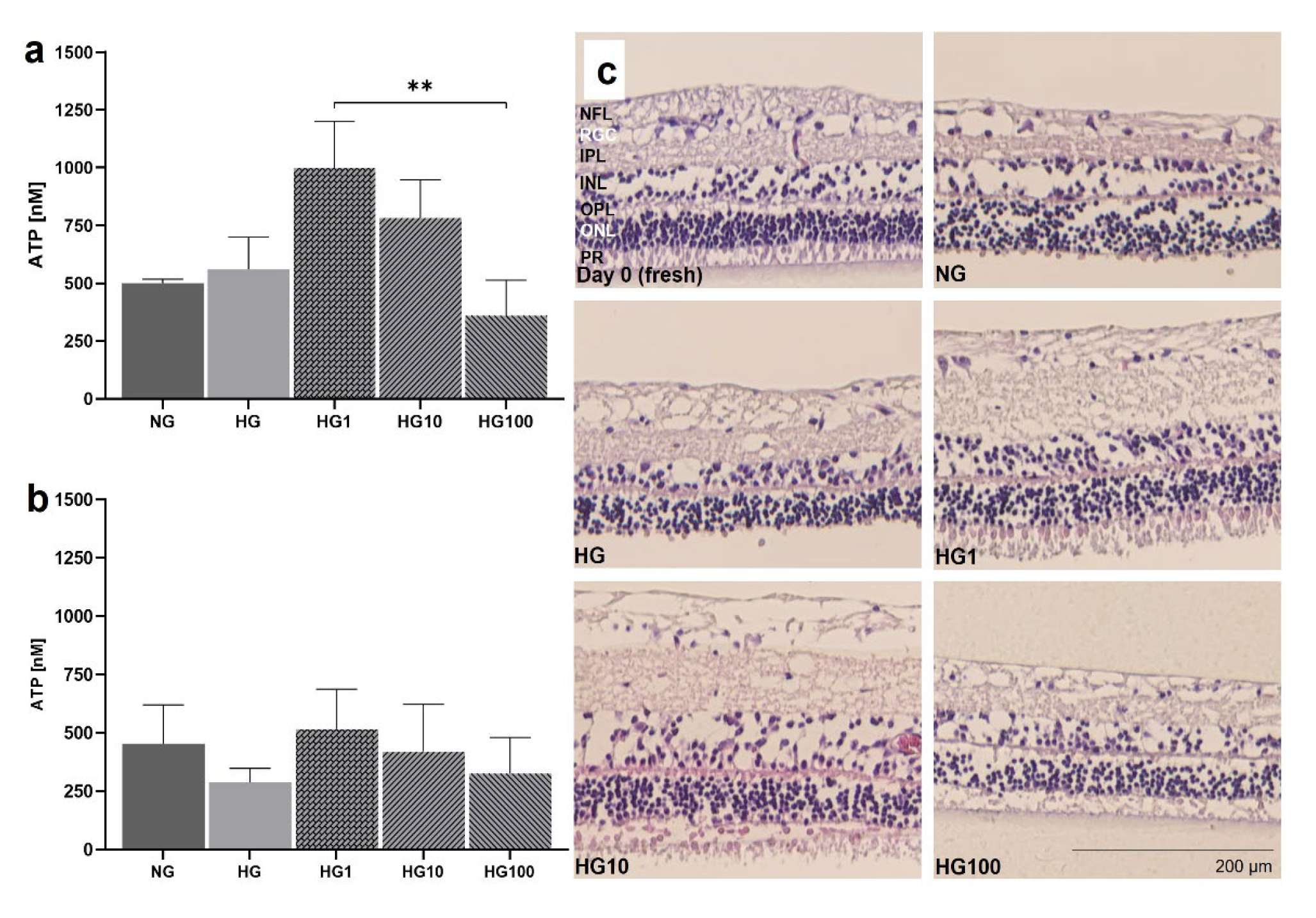
Figure 11.
Apoptosis at 1d and 4 d in HG and after treatment with the antioxidant Scutellarin. Apoptosis was measured by a TUNEL assay in retinal cross sections cultured in NG (6 mM) or HG (30 mM) treated with 1, 10, or 100 µM Scutellarin.
a) The number of apoptotic cells at 1 d increased in HG cultures compared to NG samples but decreased after Scutellarin treatment, independently from the dose.
b) At 4 d, the rate of apoptosis was generally increased compared to 1 d with similar differences between groups. The highest number of apoptotic cells was counted in HG, followed by NG. In all Scutellarin groups (HG1, HG10, HG100), apoptosis declined below NG values.
c) Micrographs show representative results at 4 d with increased numbers of apoptotic cells in HG, which could be decreased by Scutellarin (HG1, HG10, HG100). N=4-6. Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 100 µm. NG = normal glucose; HG = high glucose; HG1 = high glucose + 1 µM Scutellarin; HG10 = high glucose + 10 µM Scutellarin; HG100 = 100 µM Scutellarin. Data are shown as mean±SD [
38].
Figure 11.
Apoptosis at 1d and 4 d in HG and after treatment with the antioxidant Scutellarin. Apoptosis was measured by a TUNEL assay in retinal cross sections cultured in NG (6 mM) or HG (30 mM) treated with 1, 10, or 100 µM Scutellarin.
a) The number of apoptotic cells at 1 d increased in HG cultures compared to NG samples but decreased after Scutellarin treatment, independently from the dose.
b) At 4 d, the rate of apoptosis was generally increased compared to 1 d with similar differences between groups. The highest number of apoptotic cells was counted in HG, followed by NG. In all Scutellarin groups (HG1, HG10, HG100), apoptosis declined below NG values.
c) Micrographs show representative results at 4 d with increased numbers of apoptotic cells in HG, which could be decreased by Scutellarin (HG1, HG10, HG100). N=4-6. Magnification: 200x. scale bar: 100 µm. NG = normal glucose; HG = high glucose; HG1 = high glucose + 1 µM Scutellarin; HG10 = high glucose + 10 µM Scutellarin; HG100 = 100 µM Scutellarin. Data are shown as mean±SD [
38].
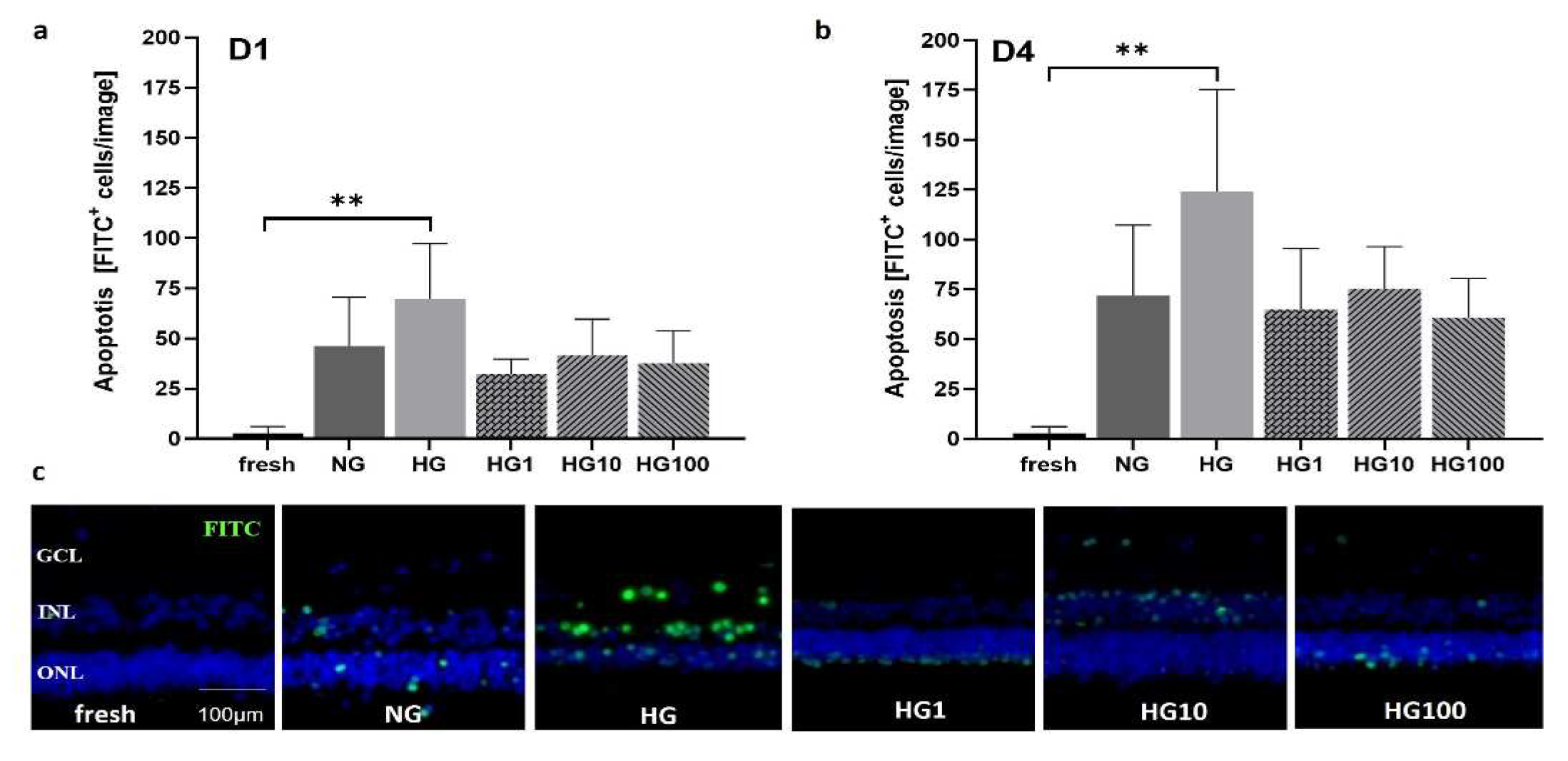
Figure 12.
OS in rat retinae incubated with H2O2 and treated with PEDF and/or GM-CSF. Retinae were treated for 3 d with PEDF and/or GM-CSF before incubation with H2O2 on day 3. At 4 d, viability and GSH levels were analyzed. Many samples were significantly degenerated and did not deliver technically valid results; thus, the number of valid results was analyzed as an additional parameter. a) Highest viabilities were detected in tissue treated with both proteins (after H2O2-incubation), followed by the PH group, GM-CSF and PEDF. Untreated, “normal” tissue without H2O2-incubation, had second lowest level. In groups H2O2 and GH, no valid results were measured. b) The number of valid viability measurements of data shown in (a) was increased in samples not H2O2-incubated and PEDF/GM-CSF-treated. The number of valid results decreased in PH and PGH groups, and no valid results were received in groups H2O2 and GH. c) Lowest GSH levels were measured in the groups fresh, PEDF, and GM-CSF. Medium levels were detected in groups H2O2 and PH, while highest GSH levels were determined in groups GH and PGH. d) The percentages of valid GSH assay results of data shown in (c) were highest in groups PH, GH, and PGH, followed by the H2O2. The lowest percentages were seen in groups fresh, PEDF, and GM-CSF. N=3-8. PH = PEDF+H2O2; GH = GM-CSF+H2O2; PGH = PEDF+GM-CSF. A chi-square test for trend was performed showing significant differences for the viability analysis (p<0.0001) and for the GSH assay (p=0.0069).
Figure 12.
OS in rat retinae incubated with H2O2 and treated with PEDF and/or GM-CSF. Retinae were treated for 3 d with PEDF and/or GM-CSF before incubation with H2O2 on day 3. At 4 d, viability and GSH levels were analyzed. Many samples were significantly degenerated and did not deliver technically valid results; thus, the number of valid results was analyzed as an additional parameter. a) Highest viabilities were detected in tissue treated with both proteins (after H2O2-incubation), followed by the PH group, GM-CSF and PEDF. Untreated, “normal” tissue without H2O2-incubation, had second lowest level. In groups H2O2 and GH, no valid results were measured. b) The number of valid viability measurements of data shown in (a) was increased in samples not H2O2-incubated and PEDF/GM-CSF-treated. The number of valid results decreased in PH and PGH groups, and no valid results were received in groups H2O2 and GH. c) Lowest GSH levels were measured in the groups fresh, PEDF, and GM-CSF. Medium levels were detected in groups H2O2 and PH, while highest GSH levels were determined in groups GH and PGH. d) The percentages of valid GSH assay results of data shown in (c) were highest in groups PH, GH, and PGH, followed by the H2O2. The lowest percentages were seen in groups fresh, PEDF, and GM-CSF. N=3-8. PH = PEDF+H2O2; GH = GM-CSF+H2O2; PGH = PEDF+GM-CSF. A chi-square test for trend was performed showing significant differences for the viability analysis (p<0.0001) and for the GSH assay (p=0.0069).
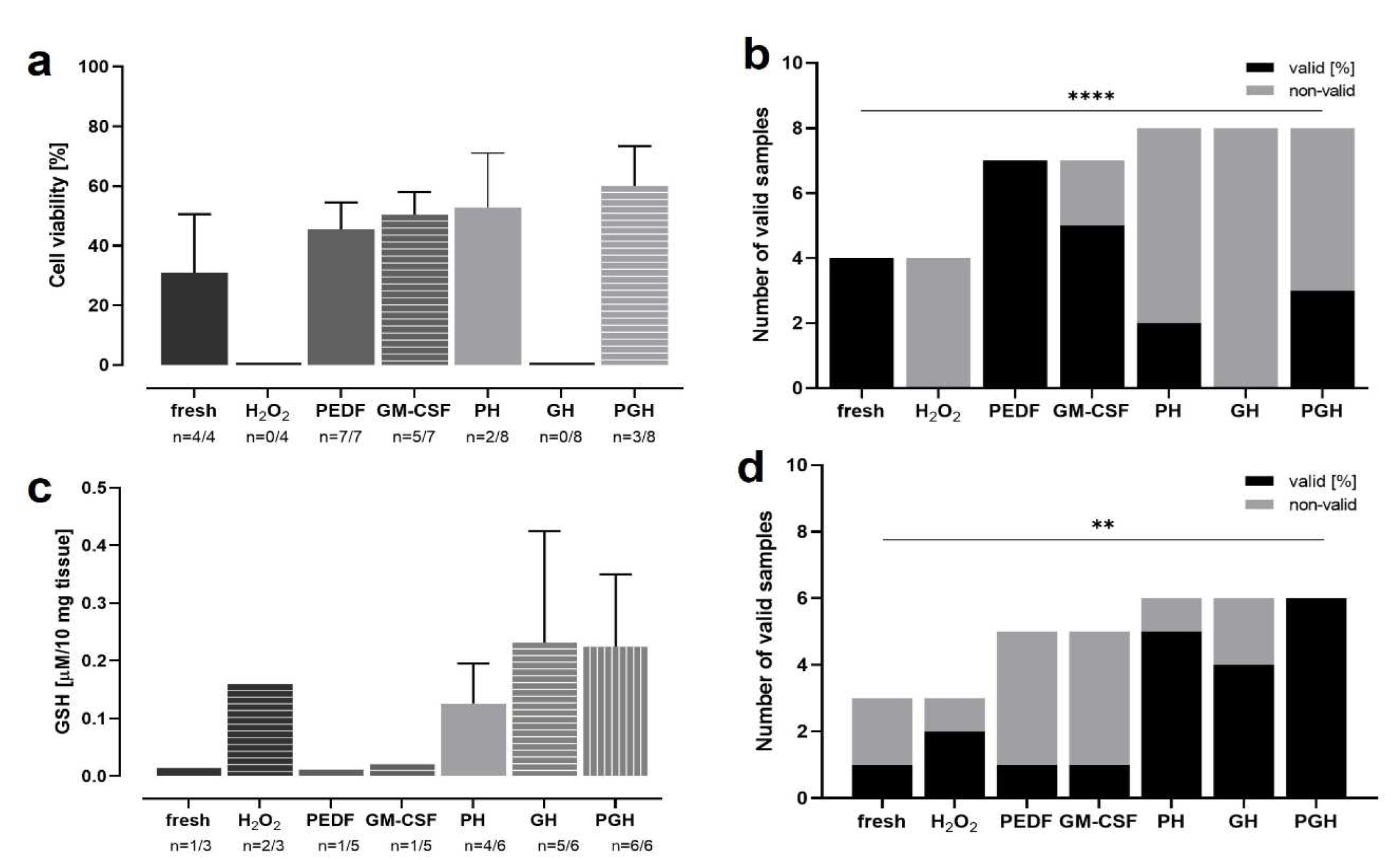
Table 1.
Hemalum and Eosin (H&E) staining protocol. The Table lists the staining protocol including the generally performed decreasing EtOH rehydration and increasing EtOH dehydration series.
Table 1.
Hemalum and Eosin (H&E) staining protocol. The Table lists the staining protocol including the generally performed decreasing EtOH rehydration and increasing EtOH dehydration series.
| Process |
Reagents |
Time |
Temperature |
| Deparaffinization |
Xylol |
3x3 min |
RT |
| Rehydration |
EtOH 2x 100%, 96%, 90%, 80%, 70%, 50%, dd H2O |
30 sec each
3 min |
RT |
| Staining |
Hemalum
Tap H2O
Acid alcohol
dd H2O
Eosin
dd H2O |
4 min
3x2 min
10 Sec
2x1 min
3 min
1 min |
RT |
| Dehydration |
50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 96% 2x100% EtOH |
30 sec each
2x2 min |
RT |
| Mounting |
Mounting medium |
1 min |
RT |
Table 2.
Degeneration score. The score has been created to quantify degeneration in BF micrographs from flat mount preparations of retinal samples.
Table 2.
Degeneration score. The score has been created to quantify degeneration in BF micrographs from flat mount preparations of retinal samples.
| Grade |
Tissue quality |
| 0 |
Healthy tissue, integral. No damage |
| 1 |
Irregular borders, small holes |
| 2 |
Big holes, patches of cell loss |
| 3 |
Big holes, major cell loss |
Table 3.
Immunofluorescence staining protocol.
Table 3.
Immunofluorescence staining protocol.
| Process |
Reagents |
Time |
Temperature |
| Deparaffinization |
Xylol |
3x3 min |
RT |
| Rehydration |
EtOH 100%, 96%, 90%, 80%, 70%, 50%, dd H2O |
3 min each
3x5 min |
RT |
| Demasking |
Citrate buffer, 0.1 M pH 6 (Boiling)
cooling |
15 min
30 min |
95oC-100oC
|
| Washing |
PBS |
3x10 min |
RT |
| Blocking |
PBS-BSA 3% |
2 h |
370C |
| Staining |
Primary antibody (PBS-BSA 1%) |
overnight |
40C |
| Washing |
PBS |
3x10 min |
RT |
| Staining |
Secondary antibody (PBS) |
30 min |
370C |
| Washing |
PBS |
3x10 min |
RT |
| Mounting |
Mounting medium with DAPI |
1 min |
RT |
Table 4.
Primary and secondary antibody used for immunofluorescence staining. GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein, IBA-1: Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1.
Table 4.
Primary and secondary antibody used for immunofluorescence staining. GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein, IBA-1: Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1.
| Specificity |
Cells labelled |
Host |
Conjugate |
Clonality |
Company |
ID |
Dilution |
| Primary antibodies |
| Protein kinase C |
Bipolar cells |
Chicken |
Unconjugated |
Polyclonal |
Abcam* ab14078 |
n.a. |
1:50 |
| Rhodopsin |
Rods |
Rabbit |
Unconjugated |
Polyclonal |
Novus Biological$ NLS1052 |
AB_2178795 |
1:700 |
| GFAP |
Astrocytes |
Mouse |
Unconjugated |
Monoclonal |
Millipore† MAB360 |
AB_11212597 |
1:300 |
| Iba-1 |
Microglia |
Rabbit |
Unconjugated |
Polyclonal |
Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation§ 01-1874 |
AB_2314666 |
1:750 |
| Vimentin |
Müller cells |
Mouse |
Unconjugated |
Monoclonal |
Merck† MAB3400 |
AB_94843 |
1:120 |
| Secondary antibodies |
| Mouse |
NA |
Donkey |
AlexaFlour 647 |
NA |
Abcam ab150107 |
AB_2890037 |
1:250 |
| Rabbit |
NA |
Donkey |
AlexaFlour 488 |
NA |
Jackson# 711546152 |
AB_2340619 |
1:100 |