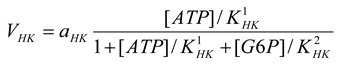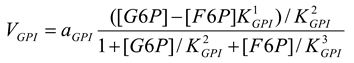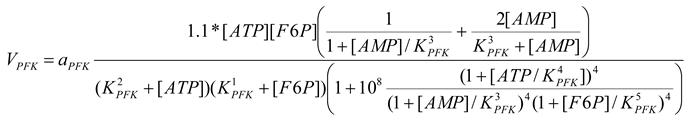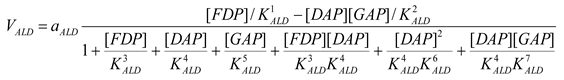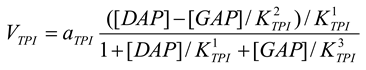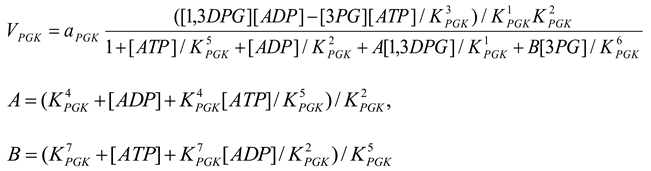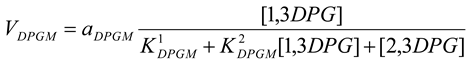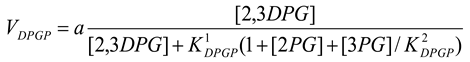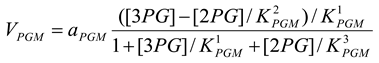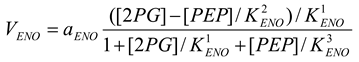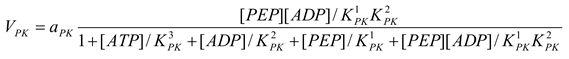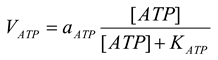1. Introduction
Erythrocytes with encapsulated enzymes which are not presented naturally in these cells, are named as erythrocyte-bioreactors (EBRs) and may be used for many biological and medical tasks [
1,
2]. Such EBRs can be used for consumption or production of different substances during circulation in the blood. The efficiency of the EBR may be affected by different factors, such as the permeability of the erythrocyte cell membrane to substrates and/or products of encapsulated enzymes, the stability of encapsulated enzymes inside erythrocytes etc. Also, an interaction of encapsulated enzymes with erythrocyte metabolic systems may affect the function of both encapsulated enzymes and metabolic systems. Many different applications of EBRs were described in the literature, including removal of asparagine from blood for antitumor therapy [
3,
4], removal of excess adenosine at adenosine deaminase deficiency [
5], transformation of thymidine to thymine at deficiency of thymidine phosphorylase [
6,
7], removal of ammonium [
8,
9,
10,
11] and alcohol (ethanol) [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17] from blood in case of intoxication, etc.
It was shown previously, that encapsulated into erythrocytes ammonium neutralizing enzymes may significantly affect energy metabolism in cells [
18]. Here, using mathematical modeling, we investigated the effects of the interaction of glycolysis with enzymes encapsulated in EBR prepared for removal of alcohol from the blood.
Excessive alcohol consumption is a rather important problem of modern society. Therefore, the fight against alcohol intoxication is not only an important social task, but also an urgent task of modern medicine [
19]. Several attempts have been described in the literature to produce EBRs that remove ethanol from the bloodstream [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. The most effective and promising version of such EBRs are those prepared with simultaneous encapsulation of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) [
15,
16,
17]. In such EBRs ethanol is first oxidized to acetaldehyde in ADH reaction:
where ETH denotes ethanol and ACALD denotes acetaldehyde. Next, acetaldehyde produced in the ADH reaction is further oxidized to acetate in ALDH reaction, which is irreversible under intracellular conditions [
20]:
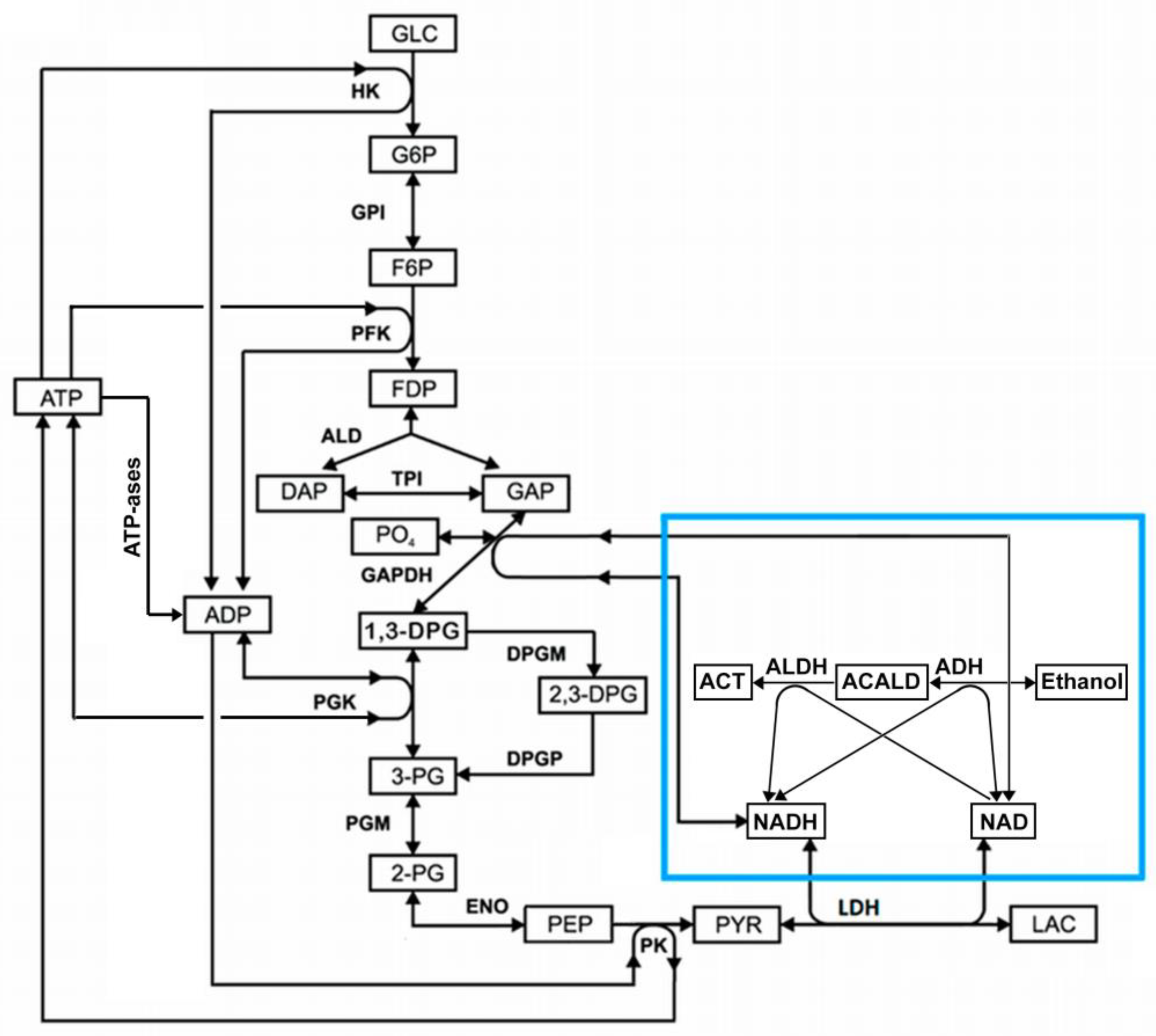
Since glycolysis and the EBR-encapsulated ADH and ALDH enzymes use NAD and NADH as substrates, they can affect each other via these metabolites. The general scheme demonstrating an interaction of glycolysis with the ADH and ALDH reactions via NAD and NADH (NAD/NADH loop) is shown in
Figure 1.
In this work, we constructed and analyzed a mathematical model of the EBR, which describes the metabolic system shown in
Figure 1. Analysis of the model revealed that the interaction of glycolysis with the encapsulated into EBR enzymes ADH and ALDH via NAD/NADH loop can cause metabolic oscillations and the disappearance of the steady state in glycolysis that, in turn, can decrease the efficacy of alcohol consumption and cause the EBR death.
2. Results and Discussion
In the absence of ethanol or at zero activity of ADH and ALDH the model has a single steady state with variables values close to those obtained in other models and in intact erythrocytes [
10,
21,
22] (
Table 1).
Simulation of experimental conditions in the presence of ethanol shows that EBR can provide a consumption of ethanol, added to the blood or to erythrocyte suspension, at a rate proportional to the activity of ADH and ALDH in the EBR and to the ethanol concentration (
Figure 2A, B).
Concentration of NAD decreases in proportion to ADH and ALDH activity and ethanol concentration (
Figure 2C). If EBRs contain only ADH, at the initial ethanol concentration of 10 mM, equilibrium in the ADH reaction is achieved after consumption of 40 µM ethanol and accumulation of 40 µM acetaldehyde and no further ethanol consumption can be achieved (
Figure 2D). If we set the acetaldehyde concentration in the model equal to zero, the initial rate of ethanol consumption is slightly higher compared with the model in which the acetaldehyde concentration is calculated as an intermediate between the ADH and ALDH reactions (
Figure 2D). But the overall kinetics of ethanol consumption is almost the same in these two versions of the model (
Figure 2D). Thus, our results reveal that EBRs loaded with ADH alone cannot provide efficient ethanol removal. For efficient consumption of ethanol, EBRs must contain ALDH in addition to ADH. The model predicts very low acetaldehyde concentrations, which even decrease during ethanol consumption in EBRs containing both ADH and ALDH (
Figure 2F). Those low acetaldehyde levels decrease the reverse ADH reaction rate and thus provide efficient ethanol consumption in the model. The model well describes the results obtained earlier in
in vitro experiments with EBRs containing ADH and ALDH [
15] (
Figure 2F).
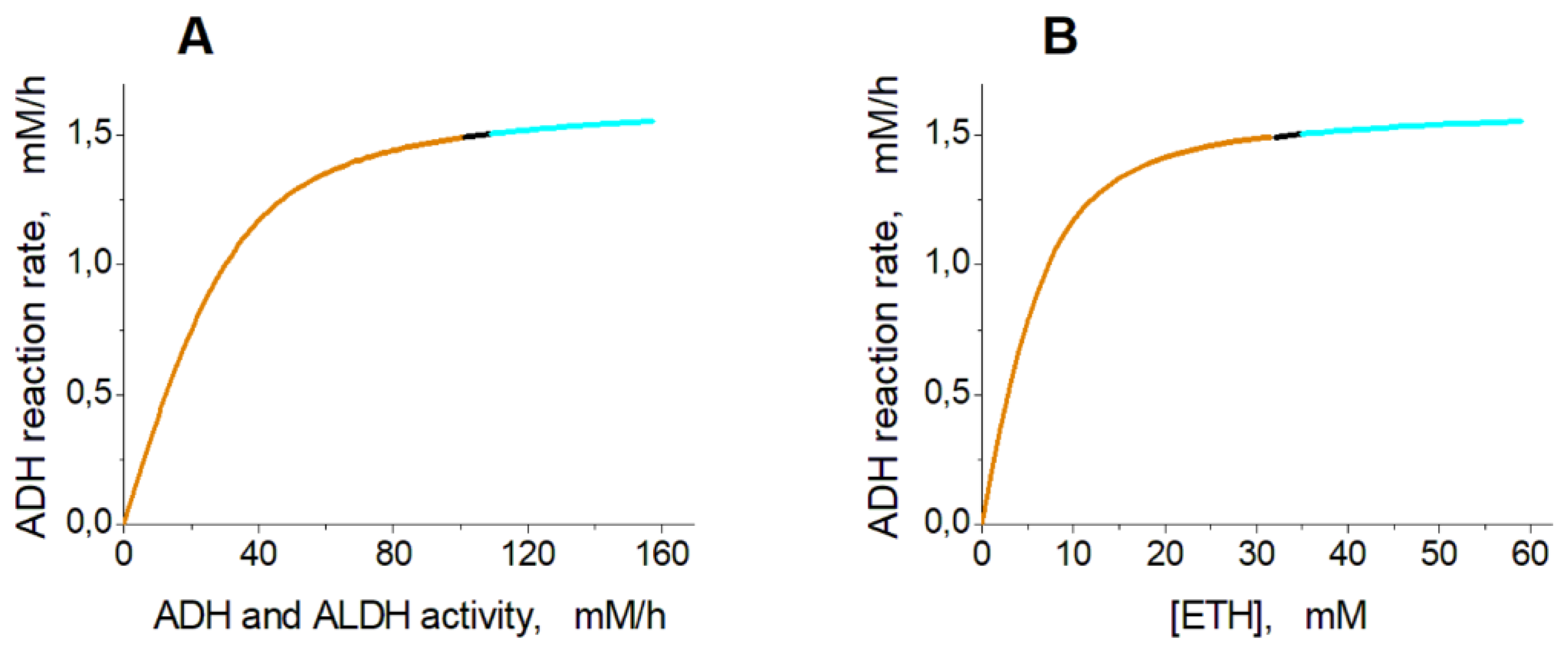
Figure 3 shows the dependence of the steady-state ethanol consumption rate in EBRs on activity of encapsulated ADH and ALDH (
Figure 3A) and on concentration of ethanol (
Figure 3B). The graphs were obtained under an assumption that the ethanol concentration is constant.
Analysis of the model shows that the steady-state rate of ethanol consumption increases with the increase in the activity of ADH and ALDH inside the EBR or with the increase in the ethanol concentration (
Figure 3). At the ethanol concentration of 10 mM the model has a single non-zero stable steady state in the range of ADH and ALDH activity from 0 to 101.5 mM/h (
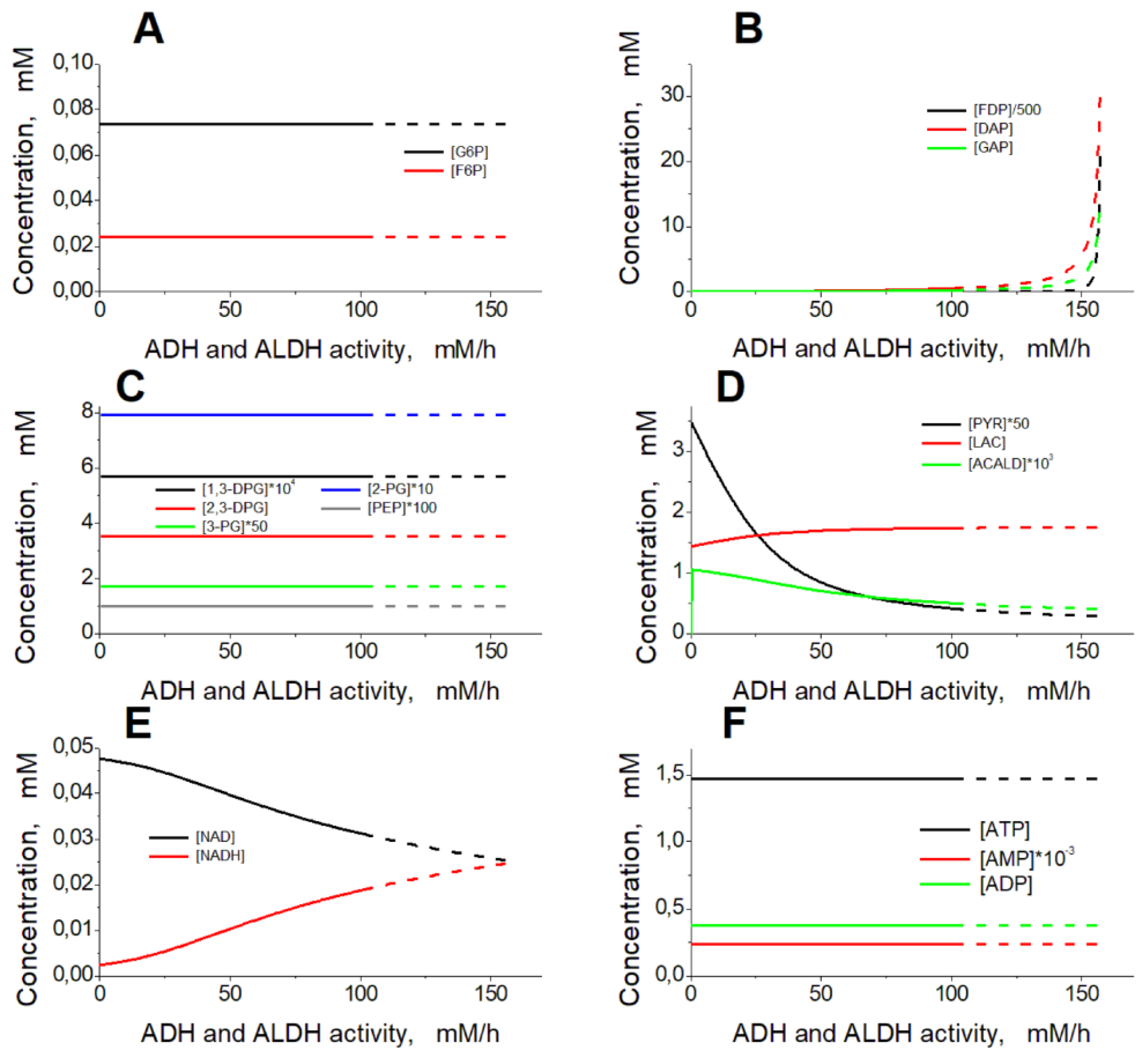
Figure 3A). The glycolysis rate remains constant, as well as the most of the model variables, except for the concentrations of FDP, DAP, G3P, PYR, LAC, NAD, NADH, and acetaldehyde (
Figure 4). The steady-state rates of HK and PFK are 1.12 mM/h, the steady-state rates of GAPGH and PK are 2.24 mM/h, and the steady-state rate of PGK reaction is 1.61 mM/h. The rate of the PGK reaction is lower compared with the rates of the GAPDH and PK reactions, since part of the glycolytic flux bypasses the PGK via the 2,3-DPG shunt (
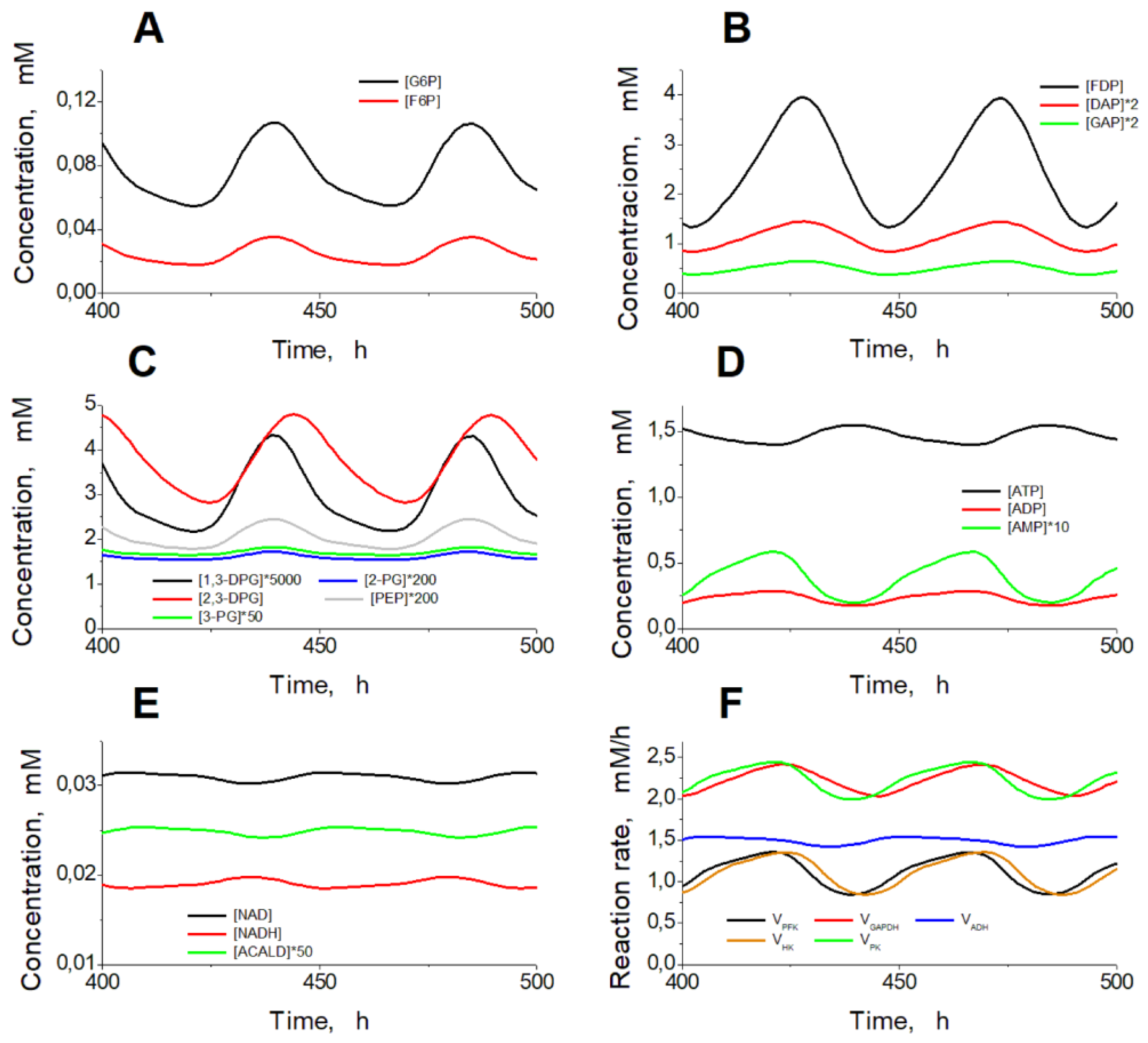
Figure 1). After the increase in the ADH and ALDH activity above 101.5 mM/h, the non-zero steady state in the model becomes unstable and the system switches to an oscillation mode (Figures 4, 5). In
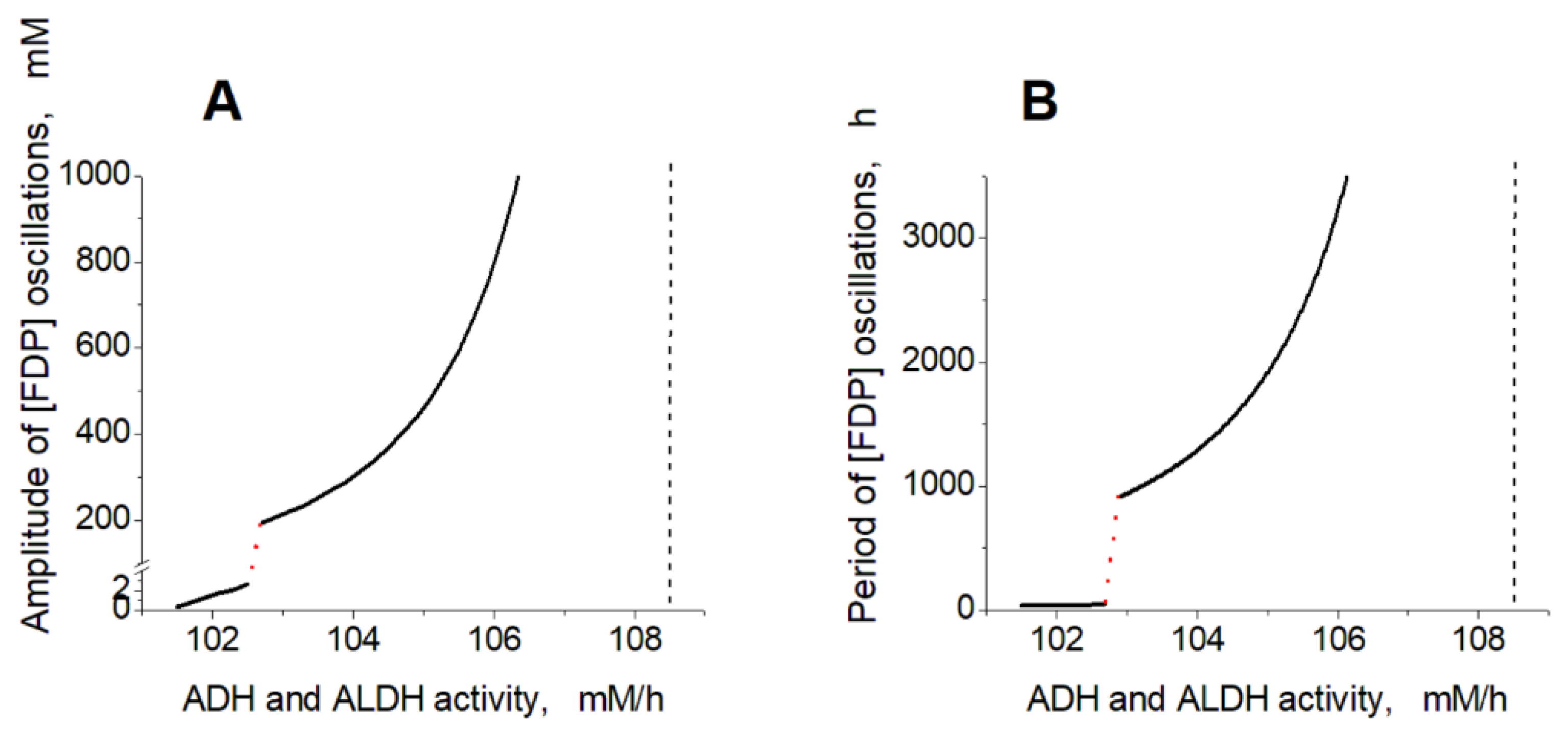
Figure 5A-C one can see synchronous oscillations in groups of metabolites interconnected via rapid, near-equilibrium enzymatic reactions. The amplitude and period of oscillations increase with the increase in the ADH and ALDH activity from 101.5 to 108.5 mM/h (
Figure 6). Interestingly, the oscillations in the ethanol consumption rate (V
ADH) are quite small compared with the steady-state rate of ethanol consumption (
Figure 5F). Thus, the steady-state rate can be used to characterize the rate of ethanol consumption in the oscillation mode.The increase in the ADH and ALDH activity above 108.5 mM/h causes a switch from the oscillation mode to an infinite accumulation of glycolysis intermediates such as FDP, DAP, and GAP (
Figure 7A). Finally, the steady state in the model disappears at the activity of the encapsulated enzymes equal to 157 mM/h, that is also associated with the accumulation of glycolysis intermediates (
Figure 7A).
Figure 2.
Kinetics of ethanol consumption in the model. (A) – Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in а 50% EBR suspension at ADH and ALDH activities equal to 30 (black line), 60 (red line), and 90 (green line) mM/h after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 10 mM. (B) – Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in the 50% EBR suspension at ADH and ALDH activities equal to 60 mM/h after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 5 mM (black line), 10 mM (red line), and 20 mM (green line). (C) – Kinetics of NAD concentration in the model at activity of the encapsulated enzymes equal to 30 mM/h at 10 mM ethanol (black line), 60 mM/h at 10 mM ethanol (red line), and 60 mM/h at 20 mM ethanol (green line). (D) - Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in the EBR suspension (hematocrit 50%) at ADH activity equal to 60 mM/h. Activity of ALDH was equal to 60 mM/h (black and red lines) or to zero (green line). Acetaldehyde concentration was calculated from the model (black and green lines) or set to zero (red line). (E) – Kinetics of acetaldehyde concentration in the model under conditions described for panel C. (F) – Experimental dependence of ethanol concentration on time obtained in [
15] for the 25% suspension of human EBRs loaded with ADH (78 mM/h) and ALDH (18 mM/h), after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 30 mM (symbols) and simulation results obtained for the same parameter values (line).
Figure 2.
Kinetics of ethanol consumption in the model. (A) – Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in а 50% EBR suspension at ADH and ALDH activities equal to 30 (black line), 60 (red line), and 90 (green line) mM/h after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 10 mM. (B) – Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in the 50% EBR suspension at ADH and ALDH activities equal to 60 mM/h after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 5 mM (black line), 10 mM (red line), and 20 mM (green line). (C) – Kinetics of NAD concentration in the model at activity of the encapsulated enzymes equal to 30 mM/h at 10 mM ethanol (black line), 60 mM/h at 10 mM ethanol (red line), and 60 mM/h at 20 mM ethanol (green line). (D) - Simulated dependence of ethanol concentration on time in the EBR suspension (hematocrit 50%) at ADH activity equal to 60 mM/h. Activity of ALDH was equal to 60 mM/h (black and red lines) or to zero (green line). Acetaldehyde concentration was calculated from the model (black and green lines) or set to zero (red line). (E) – Kinetics of acetaldehyde concentration in the model under conditions described for panel C. (F) – Experimental dependence of ethanol concentration on time obtained in [
15] for the 25% suspension of human EBRs loaded with ADH (78 mM/h) and ALDH (18 mM/h), after addition of ethanol to a final concentration of 30 mM (symbols) and simulation results obtained for the same parameter values (line).
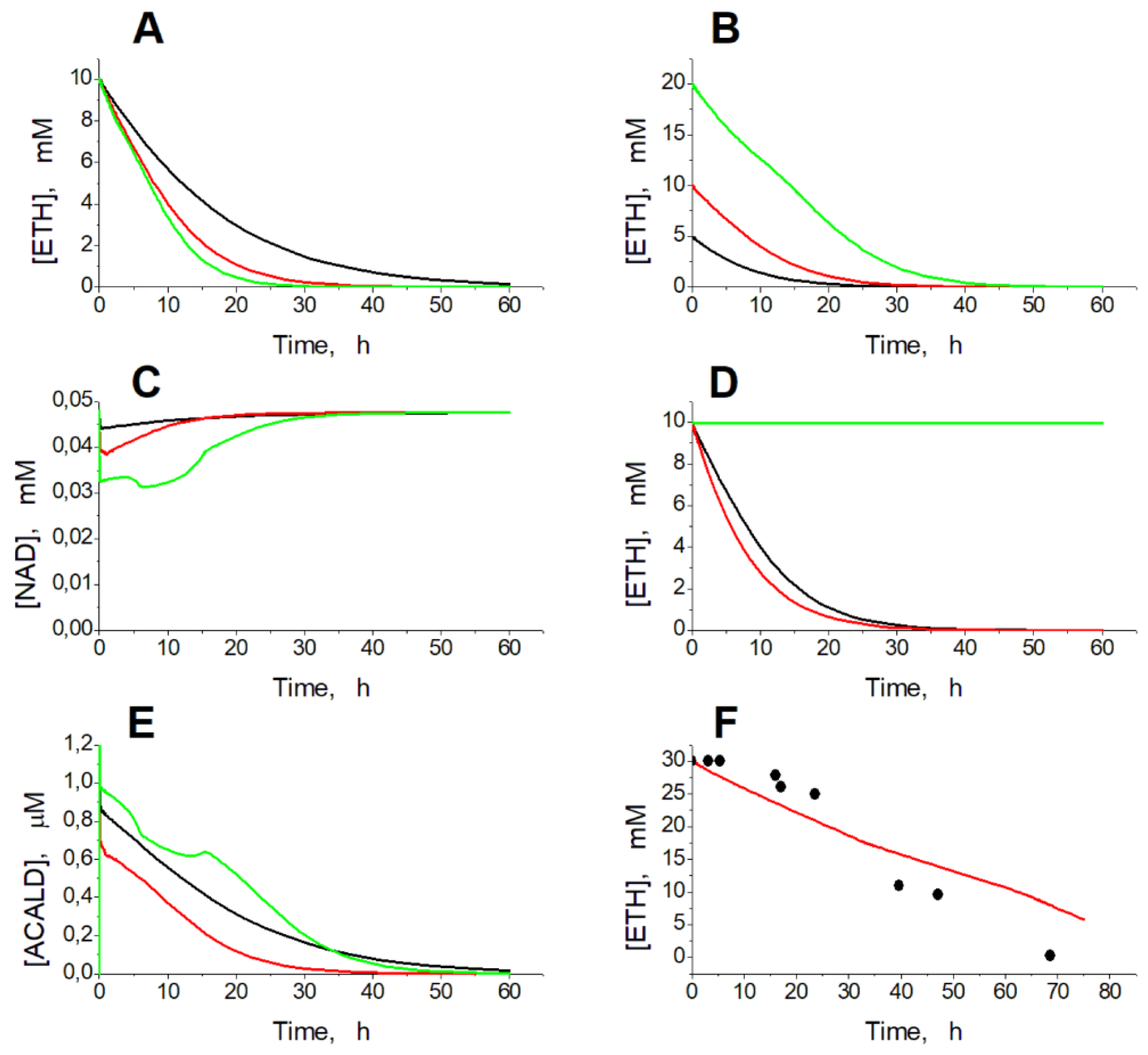
A similar behavior of the model was observed with increasing ethanol concentration. At ADH and ALDH activity of 40 mM/h the model has one stable steady state in the ethanol concentration range from 0 to 31 mM. The increase in the ethanol concentration above 31 mM causes instability of the steady state, that switches the model into the oscillation mode. At the further increase in the ethanol concentration (above 34 mM) the oscillation mode is replaced by the infinite accumulation of glycolysis intermediates (FDP, DAP, and GAP). Eventually, the model loses its stationary state at the ethanol concentration of 59 mM.
Figure 3.
Dependence of the steady-state ethanol consumption rate in the model on the activity of ADH and ALDH and on the ethanol concentration. (A) – The ethanol consumption rate was calculated at the ethanol concentration of 10 mM assuming that the ADH activity is equal to the ALDH activity. (B) – The ethanol consumption rate was calculated assuming that the ethanol concentration was constant and the activities of ADH and ALDH were equal to 40 mM/h. The orange, black, and cyan lines indicate stable steady states, unstable steady states with oscillation mode, and unstable steady states with metabolite accumulation respectively.
Figure 3.
Dependence of the steady-state ethanol consumption rate in the model on the activity of ADH and ALDH and on the ethanol concentration. (A) – The ethanol consumption rate was calculated at the ethanol concentration of 10 mM assuming that the ADH activity is equal to the ALDH activity. (B) – The ethanol consumption rate was calculated assuming that the ethanol concentration was constant and the activities of ADH and ALDH were equal to 40 mM/h. The orange, black, and cyan lines indicate stable steady states, unstable steady states with oscillation mode, and unstable steady states with metabolite accumulation respectively.
Interestingly, within the oscillation mode, the model predicts the existence of a sharp transition between relatively fast low-amplitude oscillations and relatively slow high-amplitude oscillations (
Figure 6).
The interaction of ethanol consuming enzymes with glycolysis in the EBRs is provided via NAD, a common substrate for GAPDH, ADH, and ALDH. The increase in ethanol consumption rate due to the increase in the ADH and ALDH activity or due to the increase in ethanol concentration causes a decrease in the NAD concentration (
Figure 4E) and thus a temporal decrease in the GAPDH reaction rate. This causes the accumulation of GAP, the second substrate of GAPDH (
Figure 4B). The increased GAP concentration allows the rate of the GAPDH reaction (and the rate of ATP production) to be maintained at a normal physiological steady-state level despite the decrease in [NAD]. Thus, increasing ethanol consumption rate in EBR is associated with a decrease in [NAD] and an increase in [GAP] (Figures 3, 4).
The concentrations of GAP, DAP and FDP are in equilibrium. These concentrations increase significantly (up to 0.26, 0.55, and 2.3 mM, respectively) with the increase in the ethanol consumption rate to 1.49 mM/h ([NAD] decreases to 0.031 mM), and small changes in the concentration of NAD cause significant changes in the concentrations of GAP, DAP and FDP (
Figure 4B, E). Under these conditions, glycolysis cannot respond fast enough to changes in the system, that causes a loss of the steady state stability and turns the system to an oscillation mode.
Figure 4.
Dependence of the model steady state on the activity of ADH and ALDH. The ethanol concentration was constant and equal to 10 mM. The activity of ADH was equal to the ALDH activity. Dashed lines correspond to unstable steady states.
Figure 4.
Dependence of the model steady state on the activity of ADH and ALDH. The ethanol concentration was constant and equal to 10 mM. The activity of ADH was equal to the ALDH activity. Dashed lines correspond to unstable steady states.
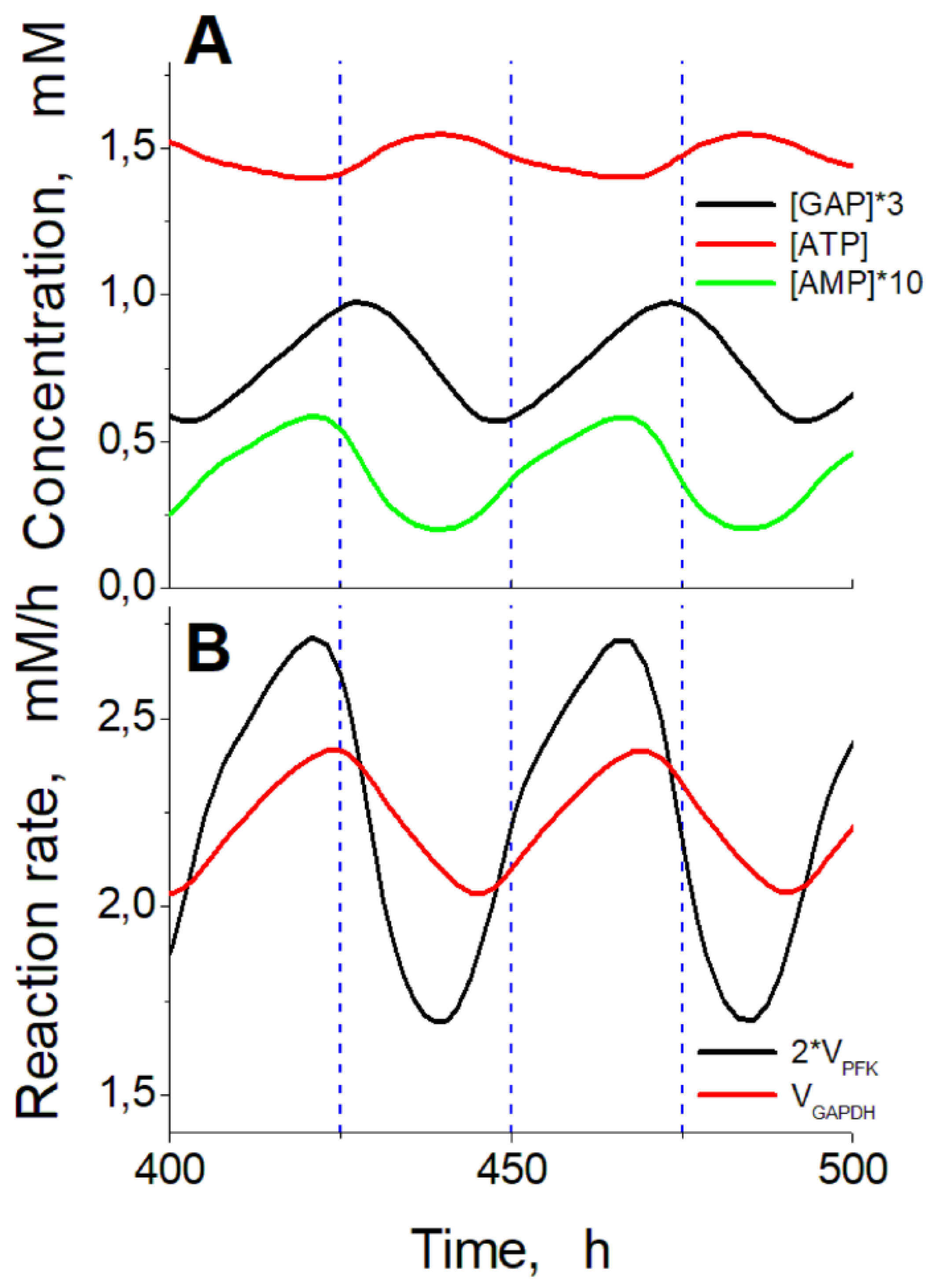
An analysis of the phase shifts between oscillations in the concentrations of different metabolites (
Figure 8) allows us to suggest the following explanation for the oscillations. At high ATP concentrations, corresponding to low AMP concentrations in cells (
Figure 8A) the PFK reaction is suppressed, since ATP is a strong inhibitor while AMP is a strong activator of this enzyme [
23]. Under these conditions, the doubled rate of PFK reaction is lower than the rate of GAPDH reaction (
Figure 8B) that causes a decrease in [GAP], a decrease in GAPDH reaction rate and a decrease in ATP production in the following glycolytic reactions. As a result, the ATP level decreases while the AMP level increases, that activates the PFK reaction and, finally, the doubled PFK reaction rate begins to exceed the GAPDH reaction rate. At this moment, the GAP level begins to increase, followed by an increase in the GAPDH reaction rate. This causes the increase in the ATP production rate, the increase in ATP concentration, the decrease in AMP concentration and the decrease in the inhibition of the PFK reaction. Then the next cycle begins. Thus, oscillations appear due to the interaction between the upper and the lower parts of glycolysis under conditions when the decreased NAD level limits the GAPDH reaction rate and the ATP production rate in the lower part of glycolysis. Ethanol-consuming enzymes ADH and ALDH decrease NAD levels. This decreases the GAPDH reaction rate providing conditions for the oscillations in glycolysis.
Figure 5.
Steady oscillations of the metabolite concentrations and enzymatic reaction rates in the model. Oscillations of the metabolite concentrations in the upper part of glycolysis (A), the lower part of glycolysis (B, C), adenine nucleotides (D), NAD, NADH, and acetaldehyde (E), and enzymatic reaction rates (F). Calculations were made at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and at the ADH and ALDH activities equal to 102.5 mM/h.
Figure 5.
Steady oscillations of the metabolite concentrations and enzymatic reaction rates in the model. Oscillations of the metabolite concentrations in the upper part of glycolysis (A), the lower part of glycolysis (B, C), adenine nucleotides (D), NAD, NADH, and acetaldehyde (E), and enzymatic reaction rates (F). Calculations were made at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and at the ADH and ALDH activities equal to 102.5 mM/h.
Figure 6.
Dependence of oscillation parameters in the model on the ADH and ALDH activity. The dependence of [FDP] oscillation amplitude (A) and period (B) on the ADH and ALDH activity. The red dotted lines show a switch of the model between fast low-amplitude and slow high-amplitude oscillations. Vertical black dashed lines indicate a border of the oscillation mode at high activity of the encapsulated enzymes. The ethanol concentration was constant and equal to 10 mM. The activity of ADH was equal to the ALDH activity.
Figure 6.
Dependence of oscillation parameters in the model on the ADH and ALDH activity. The dependence of [FDP] oscillation amplitude (A) and period (B) on the ADH and ALDH activity. The red dotted lines show a switch of the model between fast low-amplitude and slow high-amplitude oscillations. Vertical black dashed lines indicate a border of the oscillation mode at high activity of the encapsulated enzymes. The ethanol concentration was constant and equal to 10 mM. The activity of ADH was equal to the ALDH activity.
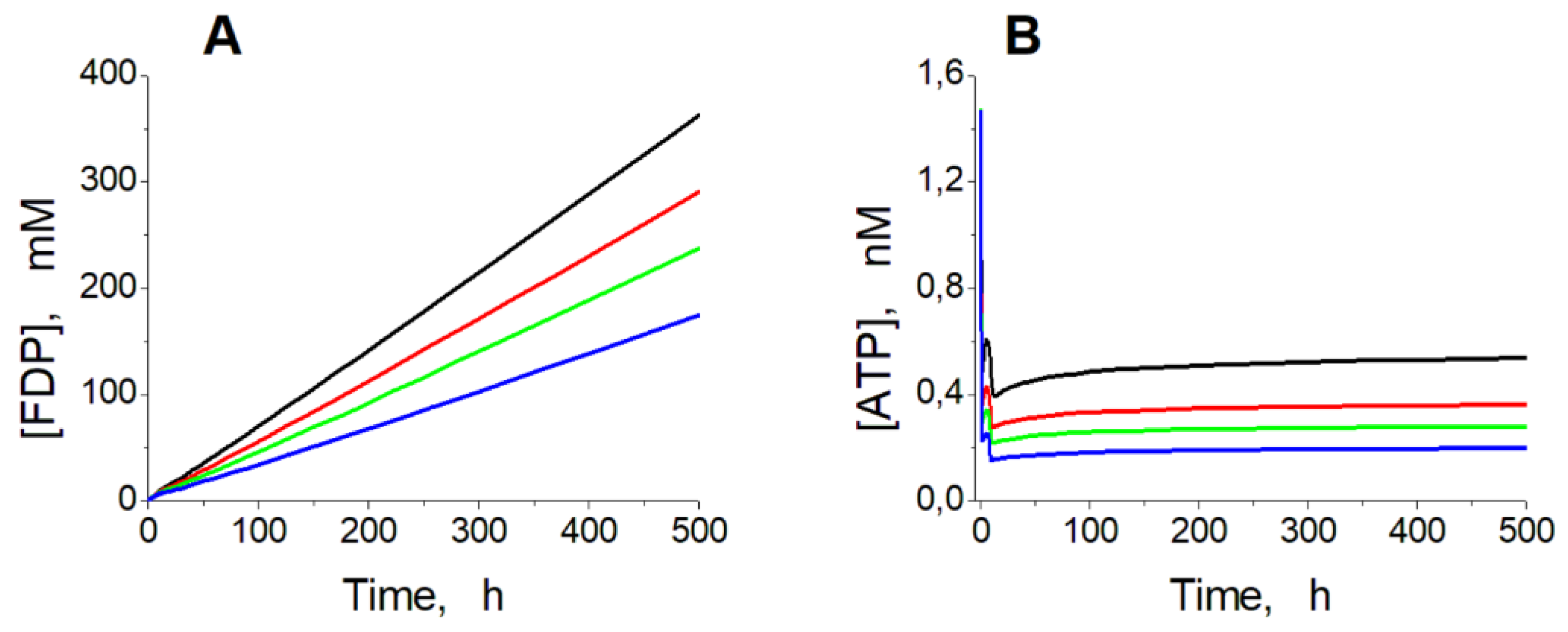
Figure 7.
Kinetics of [FDP] (A) and [ATP] (B) in the model at high ADH and ALDH activity. Calculations were performed at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and ADH and ALDH activity equal to 120 (black line), 150 (red line), 180 (green line), and 240 (blue line) mM/h.
Figure 7.
Kinetics of [FDP] (A) and [ATP] (B) in the model at high ADH and ALDH activity. Calculations were performed at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and ADH and ALDH activity equal to 120 (black line), 150 (red line), 180 (green line), and 240 (blue line) mM/h.
Above the ethanol consumption rate of 1.50 mM/h (with [NAD] decreased to 0.030 mM), the oscillation mode is replaced by an infinite accumulation of glycolysis intermediates. Finally, when the ethanol consumption rate increases to 1.55 mM/h (with [NAD] decreased to 0.025 mM), the increase in the GAP concentration cannot compensate for the decrease in the GAPDH reaction rate caused by the decrease in the NAD level. The steady state in the model disappears.
Interestingly, the rate of glycolytic intermediates accumulation decreases with increasing activity of ADH and ALDH (
Figure 7A). It happens because the accumulation of glycolytic intermediates is associated with a significant decrease in ATP concentration (
Figure 7B). Under these conditions, the PFK reaction rate decreases because [ATP] drops so significantly that PFK gets limited by ATP as a substrate.
Figure 8.
Time shifts between principal metabolite concentrations and reaction rates during steady oscillations in the model. (A) – Comparison of ATP concentration with GAP concentration multiplied by 3 and AMP concentration multiplied by 10. (B) – Comparison of doubled PFK reaction rate and GAPDH reaction rate. Calculations were carried out at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and ADH and ALDH activities of 102.5 mM/h.
Figure 8.
Time shifts between principal metabolite concentrations and reaction rates during steady oscillations in the model. (A) – Comparison of ATP concentration with GAP concentration multiplied by 3 and AMP concentration multiplied by 10. (B) – Comparison of doubled PFK reaction rate and GAPDH reaction rate. Calculations were carried out at the constant ethanol concentration of 10 mM and ADH and ALDH activities of 102.5 mM/h.
Thus, our data shows that the maximal rate of ethanol consumption by EBRs loaded with ADH and ALDH is about 1.5 mM/h (
Figure 3).
In conclusion, we would like to note that, along with ADH, ALDH is an essential component of EBR, which is necessary to provide an efficient removal of ethanol from the blood. Our results reveal that attempts to encapsulate the maximum activity of ADH and ALDH into EBR make no sense. Indeed, at very high ALD and ALDH activities, EBR glycolysis can go into the oscillation mode or into endless accumulation of glycolytic intermediates. In the oscillation mode, the concentrations of metabolites can increase by more than 30 mM above their normal physiological levels (Figures 5, 6), that can cause osmotic damage of EBR [
24]. Of course, the endless accumulation of glycolysis intermediates (FDP, DAP, and GAP) (
Figure 7) should also cause such osmotic damage. We mast note that the oscillation mode as well as the permanent accumulation of glycolysis intermediates, were obtained in the model under the assumption about the constant ethanol concentration, that is not the case in most real situations. However, these modes may be actual in other EBR applications, when the function of encapsulated enzymes is associated with the consumption of intracellular NAD.
3. Mathematical model
The mathematical model is a system of 16 ordinary differential equations and 3 algebraic equations describing the kinetics of concentrations of glycolysis intermediates, ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD, NADH, ethanol, and acetaldehyde (
Table 2). Equations for the reaction rates in glycolysis and for the rates of ATP consumption, as well as the parameter values were taken from [
21] with a few modifications (
Table 3). The model was supplemented with equations describing the pyruvate and lactate transport across the erythrocyte cell membrane (
Table 2) in accordance with the information presented in [
25]. Equations for the ADH and ALDH reaction rates and the parameter values were taken from [
17,
26,
27]. All model equations describing the enzymatic reaction rates and the pyruvate and lactate transport across the cell membrane are presented in
Table 3.
The following modifications in the glycolysis reaction rate equations were made:
TPI (α
TPI), PGK (α
PGK), and ENO (α
ENO) activities were changed from 3000, 7330, and 83 mM/h [
21] to more correct values of 19522, 2115, and 120 mM/h, respectively [
28].
The following assumptions were made regarding the model:
The rate of hexokinase reaction does not depend on glucose concentration because the normal physiological glucose concentration in the blood is significantly bigger than the value of hexokinase Michaelis constant for glucose [
29].
The concentration of orthophosphate is constant and equal to 1.0 mM [
21].
The sums of concentrations [NAD]+[NADH] and [ATP]+[ADP]+[AMP] are constant and equal to 0.05 and 1.744 mM respectively [
21,
30].
Adenylate kinase reaction is in equilibrium because of the high activity of adenylate kinase in erythrocytes [
21,
30].
The erythrocyte cell membrane is impermeable to glycolysis metabolites, except for glucose, pyruvate, and lactate [
25,
31].
The extracellular concentrations of pyruvate ( [PYR]ext) and lactate ( [LAC]ext) are constant and equal to 0.07 and 1.2 mM respectively [
21].
The permeability of erythrocyte cell membrane for ethanol and acetate is high, and intracellular concentrations of these metabolites are equal to the extracellular concentrations [
32,
33].
The extracellular concentration of acetate is zero.
Acetaldehyde produced in the EBR from ethanol does not leave the cells.
The possible effect of the transmembrane potential on the transport of metabolites was not taken into account.
The erythrocyte cell volume is constant.
All metabolite concentrations, enzyme activities, and enzymatic reaction rates were normalized per liter of cells (erythrocytes) and expressed in mM or mM/h respectively.
All numeric solutions of the model system of equations were obtained in MATLAB using a variable-step variable-order solver based on numerical differentia-tion formulas of order 1 to 5 (the ode15s function) [
34]. Steady-state values of concentrations and reaction rates were obtained as solutions of algebraic equations systems with trust-region algorithm (fsolve function).
Kinetics of ethanol consumption by EBR was simulated using metabolite concentrations shown in
Table 1 as initial values. The initial ACALD concentration was set equal to zero. Volume fractions occupied by erythrocytes and by external medium were taken into account in such simulations.
Table 2.
Differential and algebraic equations describing the kinetics of metabolite concentrations in the model of erythrocyte-bioreactors prepared for ethanol consumption.
Table 2.
Differential and algebraic equations describing the kinetics of metabolite concentrations in the model of erythrocyte-bioreactors prepared for ethanol consumption.
| № |
Variablea)
|
Equationb)
|
| 1 |
[G6P] |
|
| 2 |
[F6P] |
|
| 3 |
[FDP] |
|
| 4 |
[DAP] |
|
| 5 |
[GAP] |
|
| 6 |
[1,3-DPG] |
|
| 7 |
[2,3-DPG] |
|
| 8 |
[3-PG] |
|
| 9 |
[2-PG] |
|
| 10 |
[PEP] |
|
| 11 |
[PYR] |
|
| 12 |
[LAC] |
|
| 13 |
[NAD] |
|
| 14 |
Energy charge (Φ)c)
|
|
| 15 |
[ETH] |
|
| 16 |
[ACALD] |
|
| 17 |
Adenylate pool |
[ATP]+[ADP]+[AMP] = P
|
| 18 |
Adenylate kinase equilibrium |
|
| 19 |
NAD/NADH pool |
[NAD]+[NADH] = N
|
Table 3.
Model equations for the rates of enzymatic reactions.
Table 3.
Model equations for the rates of enzymatic reactions.
Hexokinase [21]
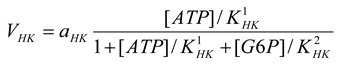
mM/h, |
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase [21]
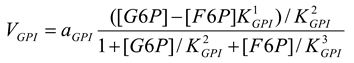
mM/h, , |
Phosphofructokinase [21]
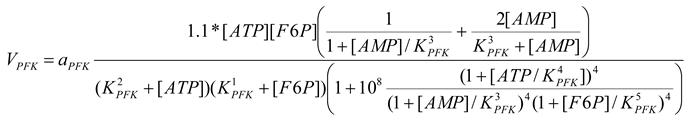
mM/h |
Aldolase [21]
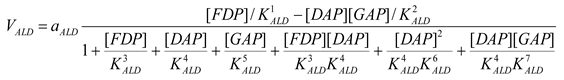
mM/h |
Triosephosphate isomerase [21,28]
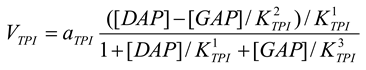
mM/h, , , |
Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase [21]
mM/h, , , , , , mM |
Phosphoglycerate kinase [21,28]
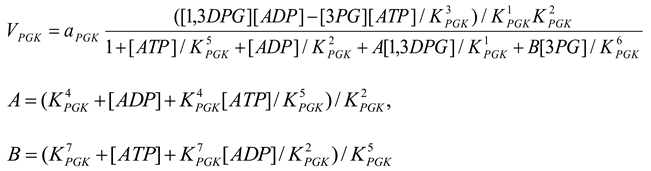
mM/h, , , , , , , |
Diphosphoglycerate mutase [21]
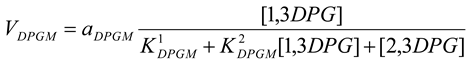
mM/h, , |
Diphosphoglycerate phosphatase [21]
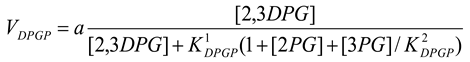
mM/h, , mM
|
Phosphoglycerate mutase [21]
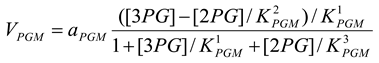
mM/h |
Enolase [21,28]
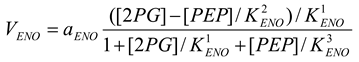
mM/h, , , |
Pyruvate kinase [21]
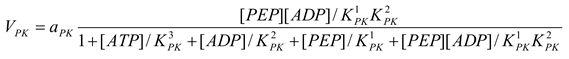
mM/h, , , |
Lactate dehydrogenase [21]
mM/h, , , , , , , |
Na+-K+-АТPase [21]

mM/h, [30] |
All other ATPases are presented by the following equation [21]
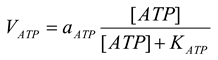
mM/h, |
Alсohol dehydrogenase [26,27]
- ADH activity – this is a varied parameter in the model. |
Acetaldehyde dehydrogenase [20]
– ALDH activity - this is a varied parameter in the model |
Pyruvate transport [25]
; ; |
Lactate transport [25]
; ; |