Submitted:
07 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Patient selection
| Criteria | Lists |
|---|---|
| Inclusion | 1) Those requiring implant placement |
| 2) The anatomical conditions under which non-submerged implant placement was favorable at stage I surgery | |
| 3) Those who agreed to participate in the clinical study and signed the consent form for the clinical study. | |
| Exclusion | 1) The heavy smokers (> 10 cigarettes/day) |
| 2) The presence of bone defects requiring bone augmentation | |
| 3) Those requiring implant placement following implant failure | |
| 4) Those uncontrolling medical condition | |
| 5) Those confirming or suspecting psychological problems |
| Visit | Observation period | Observation and clinical examination items |
|---|---|---|
| 1V | Pre-operative | Obtaining written informed consent, evaluating the suitability of the research participant, allocating the participant identification code, and taking the dental CBCT |
| 2V | Implant surgery | Measurement of implant stability by all the devices |
| 3V | Stitch removal | Measurement of implant stability by Anycheck |
| 4V | 1- month follow-up | Measurement of implant stability by Anycheck |
| 5V | 2-months follow-up | Measurement of implant stability by all the devices |
| 6V | Before final restoration delivery (3- to 4-month follow-up) |
Measurement of implant stability by all the devices |
| 7V | After final restoration delivery (3- to 4-month follow-up) |
Measurement of implant stability by Anycheck |
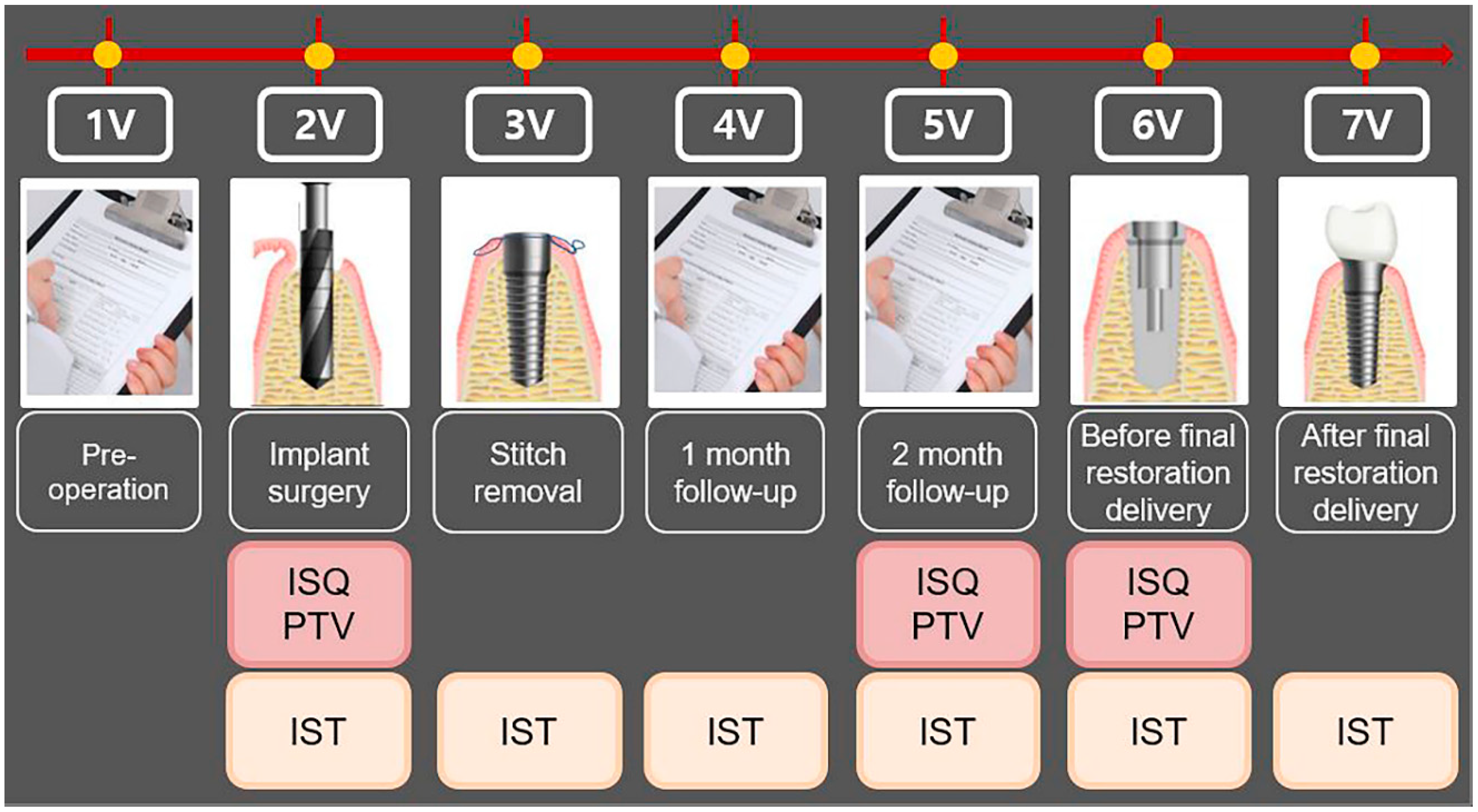
2.3. Surgical procedure
| Location of implant placement | Abbreviation | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Maxillary right posterior | A | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Maxillary anterior | B | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Maxillary left posterior | C | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Mandibular right posterior | D | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Mandibular anterior | E | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Mandibular left posterior | F | 10 (Male: 5, Female: 5) |
| Characteristics | Size (mm) | Number |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 8.5 | 21 |
| 10.0 | 35 | |
| 11.5 | 4 | |
| Diameter | 3.5 | 3 |
| 4.0 | 20 | |
| 4.5 | 17 | |
| 5.0 | 20 |
2.4. Measurement of implant stability
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
| Value | 2V | 5V | 6V | ||||||
| Correlation coefficient | Size of Correlation | P-value | Correlation coefficient | Size of Correlation | P-value | Correlation coefficient | Size of Correlation | P-value | |
| ISQ-PTV | -.208 | weak | .049* | -.298 | weak | .001* | -.252 | weak | .005* |
| ISQ-IST | .567 | moderate | <.001* | .367 | weak | .003* | .503 | moderate | <.001* |
| PTV-IST | -.490 | moderate | <.001* | -.701 | strong | <.001* | -.479 | moderate | <.001* |
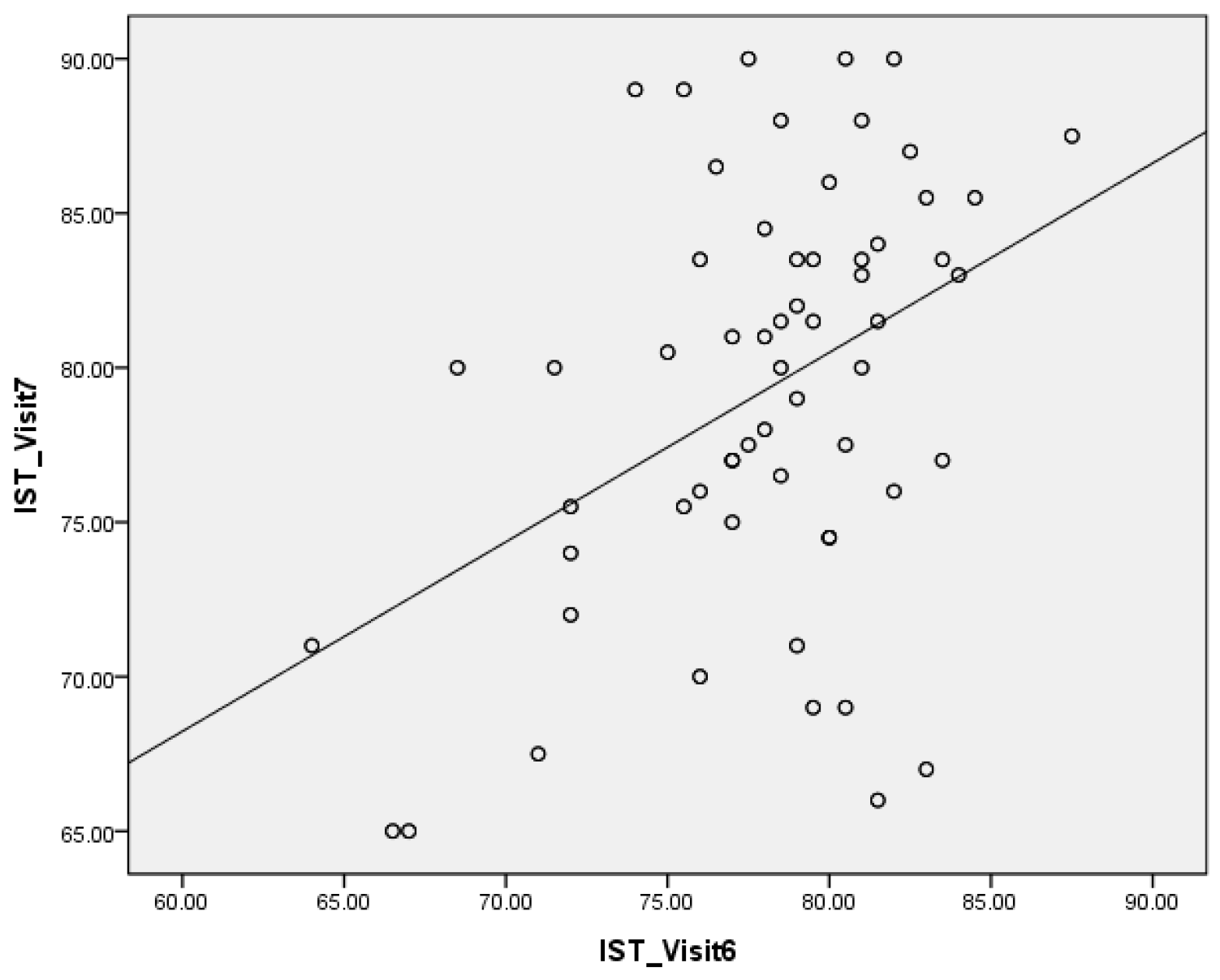
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
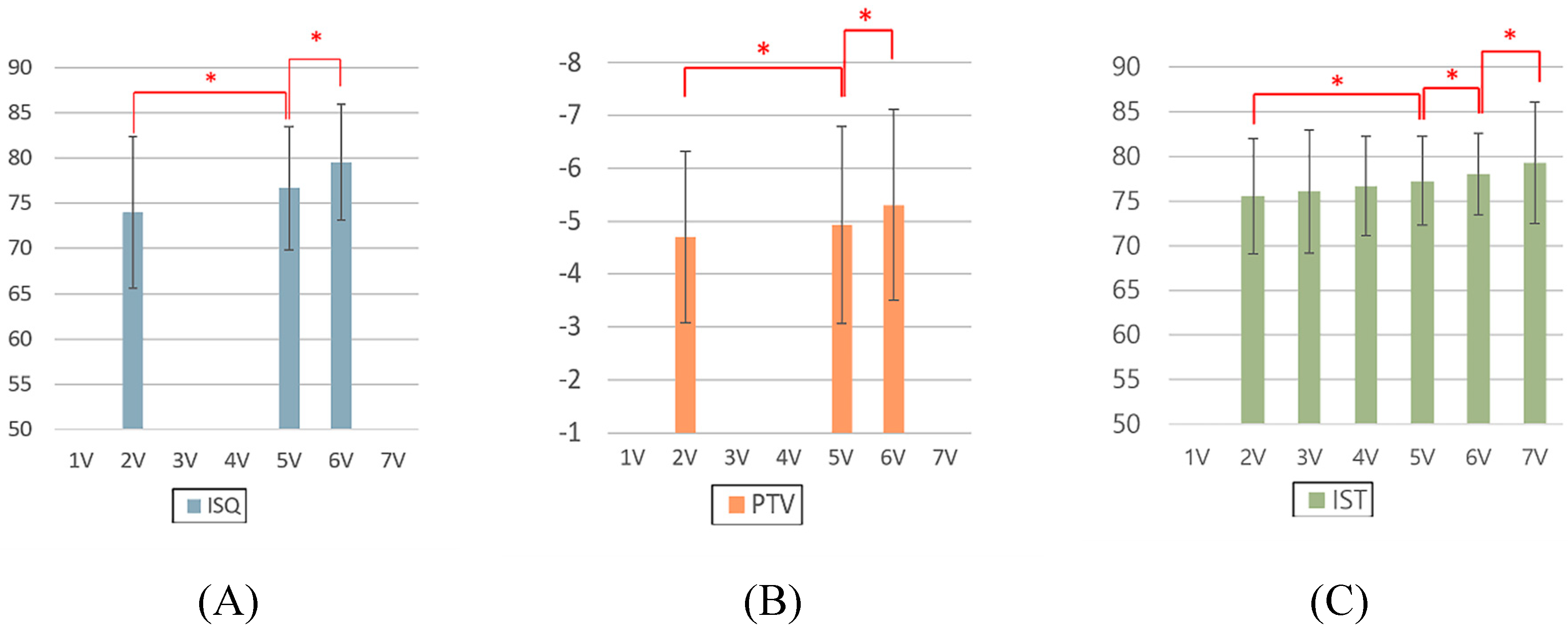
- For all the ISQ, PTV, and IST results, the implant stability results at the 2-month follow-up and before the final restoration delivery were significantly higher than those at the time of implant surgery.
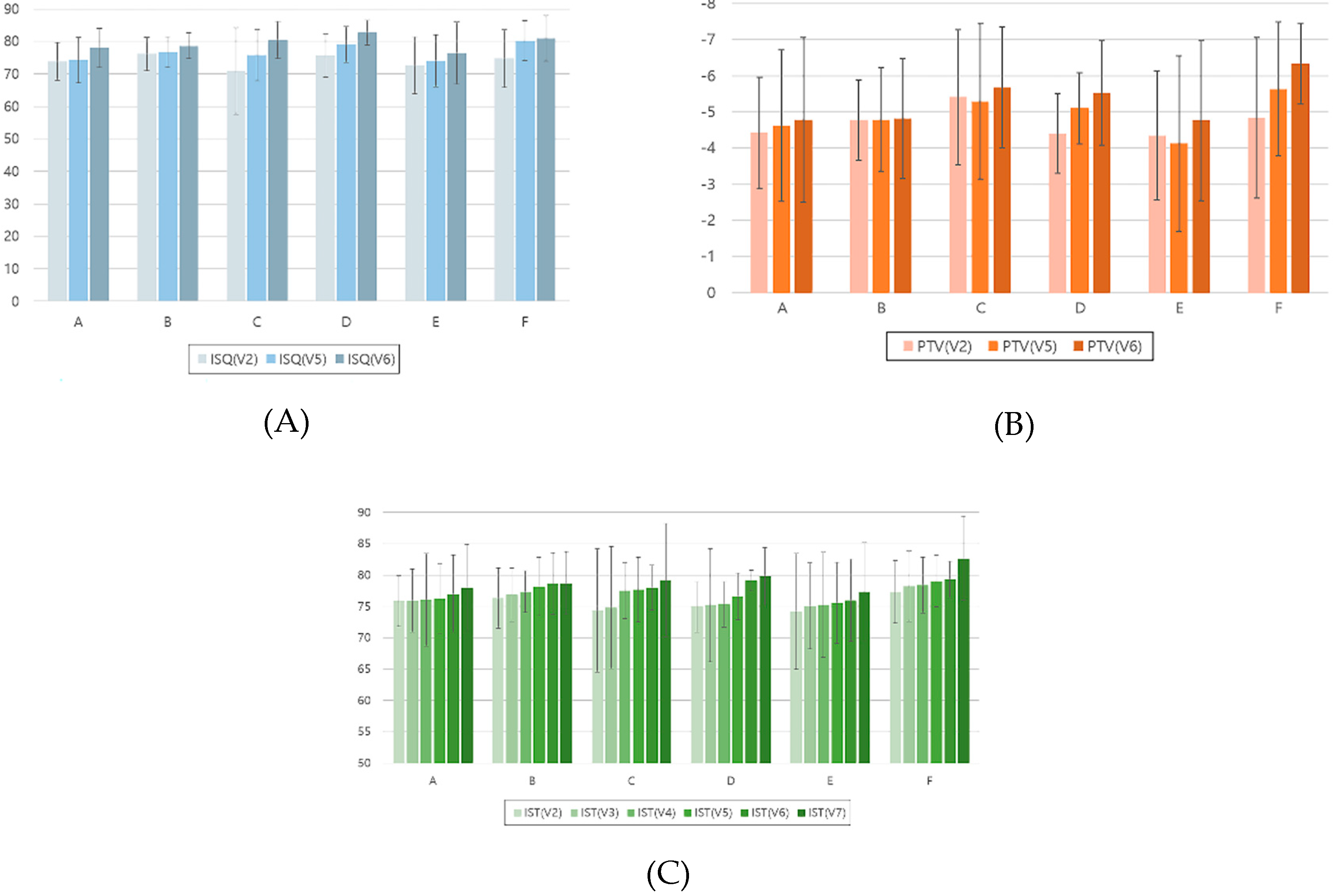
- The lowest ISQ results occurred in the mandibular anterior location at the 2-month follow-up and before the final restoration delivery.
- In all the mandibular locations, the IST results after final restoration delivery were significantly higher than those at implant surgery, stitch removal, 1-month follow-up, and 2-month follow-up.
- At implant surgery, 2-month follow-up, and before final restoration delivery, the ISQ results were negatively correlated with the PTV results and positively correlated with the IST results, and the PTV results were negatively correlated with the IST results.
- The IST results in the healing abutment states and those in the prosthesis delivered states were positively correlated.
Supplementary Materials
References
- Lages, F.S.; Douglas-de Oliveira, D.W.; Costa, F.O. Relationship between implant stability measurements obtained by insertion torque and resonance frequency analysis: a systematic review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, 11, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, D.; Aracil, L.; Martin, C.; Sanz, M. Diagnosis of implant stability and its impact on implant survival: a prospective case series study. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2010, 21, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsumi, M.; Park, S.H.; Wang, H.L. Methods used to assess implant stability: current status. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2007, 22, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, S.; Laval, J.Y.; Axmann, D.; Weber, H. Influence of implant geometry on primary insertion stability and simulated peri-implant bone loss: an in vitro study using resonance frequency analysis and damping capacity assessment. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2011, 26, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, S.; Laval, J.Y.; Jäger, B.; Axmann, D.; Gomez-Roman, G.; Groton, M.; Weber, H. Resonance frequency analysis and damping capacity assessment. Part 2: Peri-implant bone loss follow-up. An in vitro study with the Periotest and Osstell instruments. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2006, 17, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, N.; Alleyne, D.; Cawley, P. Quantitative determination of the stability of the implant-tissue interface using resonance frequency analysis. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 1996, 7, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, S.; Morris, H.F.; Spray, J.R. Stability of implants and natural teeth as determined by the Periotest over 60 months of function. J. Oral. Implantol. 2001, 27, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Shin, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Shim, J.S.; Shin, S.W.; Lee, J.Y. The reliability of Anycheck device related to healing abutment diameter. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2020, 12, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, A.M.; Goiato, M.C., Nobrega, A.S.; da Silva, E.V.F.; Filho, H.G.; Pellizzer, E.P.; dos Santos, D.M. Relationship between implant stability measurements obtained by two different devices: a systematic review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 281–288. [CrossRef]
- Krafft, T.; Winter, W.; Wichmann, M.; Karl, M. In vitro validation of a novel diagnostic device for intraoperative determination of alveolar bone quality. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2012, 27, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- AAl, M.A.; El Far, M.; Sheta, N.M.; Fayyad, A.; Desouky, E.E.; Nabi, N.A.; Ibrahim, M. Correlation of implant stability between two noninvasive methods using submerged and nonsubmerged healing protocols: a randomized clinical trial. J. Oral. Implantol. 2020, 46, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Implant stability measurements using resonance frequency analysis: biological and biomechanical aspects and clinical implications. Periodontol. 2000. 2008, 47, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.S.; Kim, S.G. Clinical study of the relationship between implant stability measurements using Periotest and Osstell mentor and bone quality assessment. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. 2012, 113, e35–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
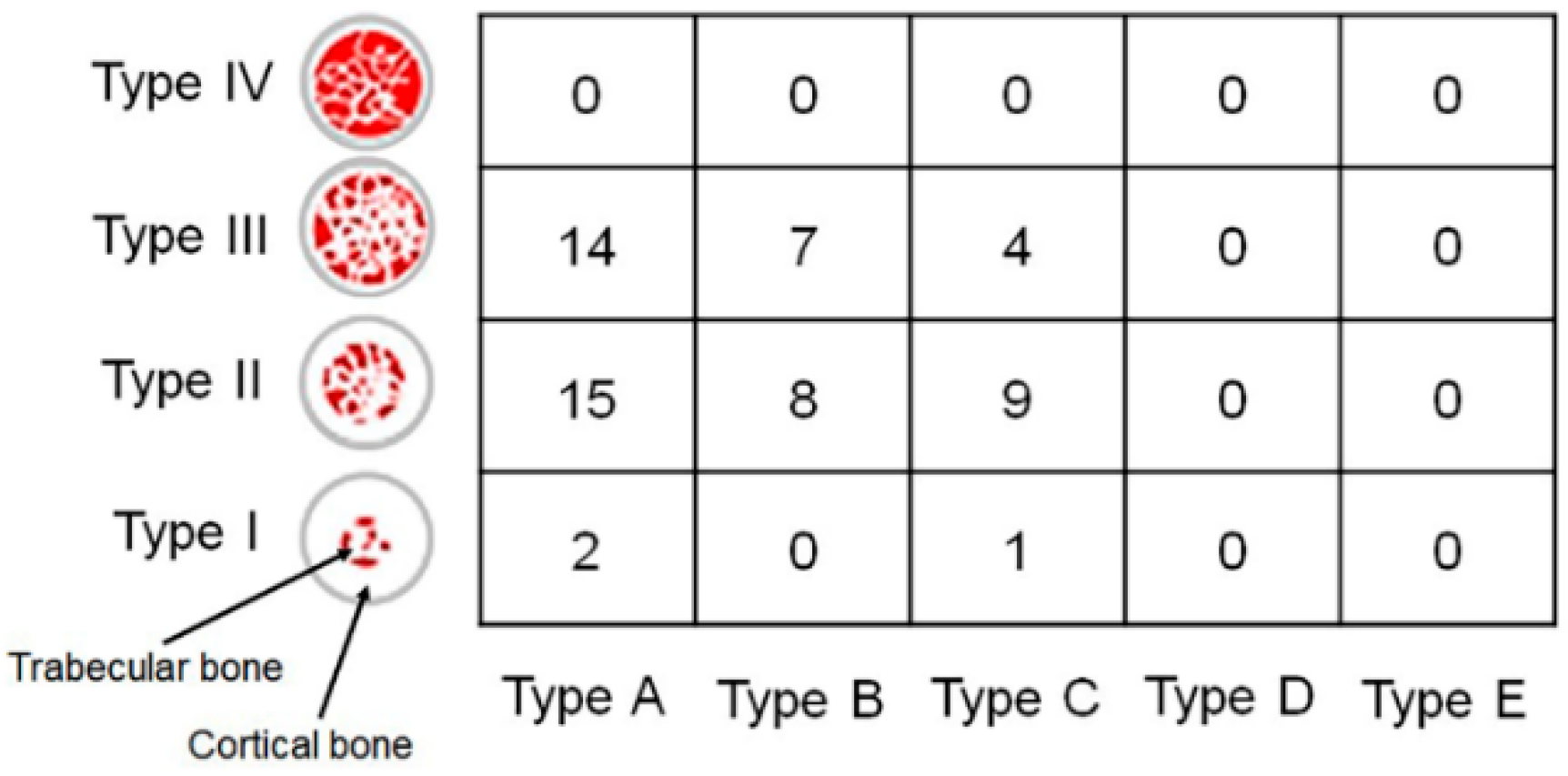
- Lekholm, U.; Zarb, G.A. Patient selection and preparation. Branemark, P.I., Zarb, G.A., Albrektsson, T., editors. Tissue integrated prostheses: osseointegration in clinical dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence.; 1985. pp.199–209.
- Banjanin, M.K.; Stojčić, M.; Danilović, D.; Ćurguz, Z.; Vasiljević, M.; Puzić, G. Classification and prediction of sustainable quality of experience of telecommunication service users using machine learning models. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghanathan, N. Assortativity analysis of real-world network graphs based on Centrality metrics. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2016, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, C.; Lang, N.P.; Rangert, B. Validity and clinical significance of biomechanical testing of implant/bone interface. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2006, 17, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.M.; Chiu, C.L.; Yeh, C.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Factors influencing the resonance frequency of dental implants. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.P.; Lang, N.P. Factors Influencing Resonance Frequency Analysis Assessed by Osstell mentor during implant tissue integration: I. Instrument positioning, bone structure, implant length. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2010, 21, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, M.G.; Giannitsios, D.; Lipsett, A.W.; Wolfaardt, J.F. The use and abuse of the Periotest for 2-piece implant/abutment systems. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2001, 16, 486–494. [Google Scholar]
- Derhami, K.; Wolfaardt, J.F.; Faulkner, G.; Grace, M. Assessment of the periotest device in baseline mobility measurements of craniofacial implants. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 1995, 10, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.H.; Leesungbok, R.; Lee, S.W.; Paek, J.; Lee, J.Y. Differences in percussion-type measurements of implant stability according to height of healing abutments and measurement angle. J. Korean. Acad. Prosthodont. 2018, 56, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truhlar, R.S.; Morris, H.F.; Ochi, S. Stability of the bone-implant complex. Results of longitudinal testing to 60 months with the Periotest device on endosseous dental implants. Ann. Periodontol. 2000, 5, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.M.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H. Clinical outcomes of magnesium-incorporated oxidised implants: a randomised double-blind clinical trial. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2014, 25, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cehreli, M.C.; Karasoy, D.; Akca, K.; Eckert, S.E. Meta-analysis of methods used to assess implant stability. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2009, 24, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.S.; Kim, S.G., Lim, S.C.; Ong, J.L. A comparative study of two noninvasive techniques to evaluate implant stability: periotest and Osstell Mentor. Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Rad. Endod. 2009, 107, 513–518. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, H.; Horner, K.; Ledgerton, D. A comparison of maxillary and mandibular bone mineral densities. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1998, 79, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; Santos-García, R.; Jaramillo-Santos, R.; Romero-Ruiz, M.M.; Fernández-Palacin, A.; Lázaro-Calvo, P.; Bullón, P.; Ríos-Santos, J.V. Assessment of Osstell ISQ’s reliability for implant stability measurement: a cross-sectional clinical study. Med. Oral. Patol. Oral. Cir. Bucal. 2013, 18, e877–e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, W.; Möhrle, S.; Holst, S.; Karl, M. Parameters of implant stability measurements based on resonance frequency and damping capacity: a comparative finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2010, 25, 532–539. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguhi, J. An attempt to measure viscoelasticity of human facial skin by impact hammer method. J. Kanagawa. Odontol. Soc. 1992, 26, 387–411. [Google Scholar]
- Friberg, B.; Sennerby, L.; Linden, B.; Gröndahl, K.; Lekholm, U. Stability measurements of one-stage Brånemark implants during healing in mandibles. A clinical resonance frequency analysis study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 1999, 28, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedir, R.; Bischof, M.; Szmukler-Moncler, S.; Bernard, J.P.; Samson, J. Predicting osseointegration by means of implant primary stability. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 2004, 15, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, H.F.; Winkler, S.; Ochi, S. The ankylos endosseous dental implant: assessment of stability up to 18 months with the Periotest. J. Oral. Implantol. 2000, 26, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.; Morris, H.F.; Ochi, S. Periotest values of dental implants in the first 2 years after second-stage surgery: DICRG interim Report No. 8. Dental implant clinical Research Group. Implant. Dent. 1997, 6, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, N.; Friberg, B.; Sennerby, L.; Aparicio, C. Relationship between contact time measurements and PTV values when using the Periotest to measure implant stability. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1998, 11, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- van Steenberghe, D.; Tricio, J.; Naert, I.; Nys, M. Damping characteristics of bone-to-implant interfaces. A clinical study with the Periotest device. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 1995, 6, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, H.F.; Ochi, S.; Crum, P.; Orenstein, I.; Plezia, R. Bone density: its influence on implant stability after uncovering. J. Oral. Implantol. 2003, 29, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerlinck, J.; Quirynen, M.; Darius, P.; van Steenberghe, D. Periotest: an objective clinical diagnosis of bone apposition toward implants. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 1991, 6, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hürzeler, M.B.; Quiñones, C.R.; Schüpbach, P.; Vlassis, J.M.; Strub, J.R.; Caffesse, R.G. Influence of the suprastructure on the peri-implant tissues in beagle dogs. Clin. Oral. Implants. Res. 1995, 6, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, G.E.; Lang, N.P. Diagnostic parameters for monitoring peri-implant conditions. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implants. 2004, 19, 116–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sennerby, L.; Meredith, N. Resonance frequency analysis: measuring implant stability and osseointegration. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 1998, 19, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





