Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Insights into cell biology using multi-omics
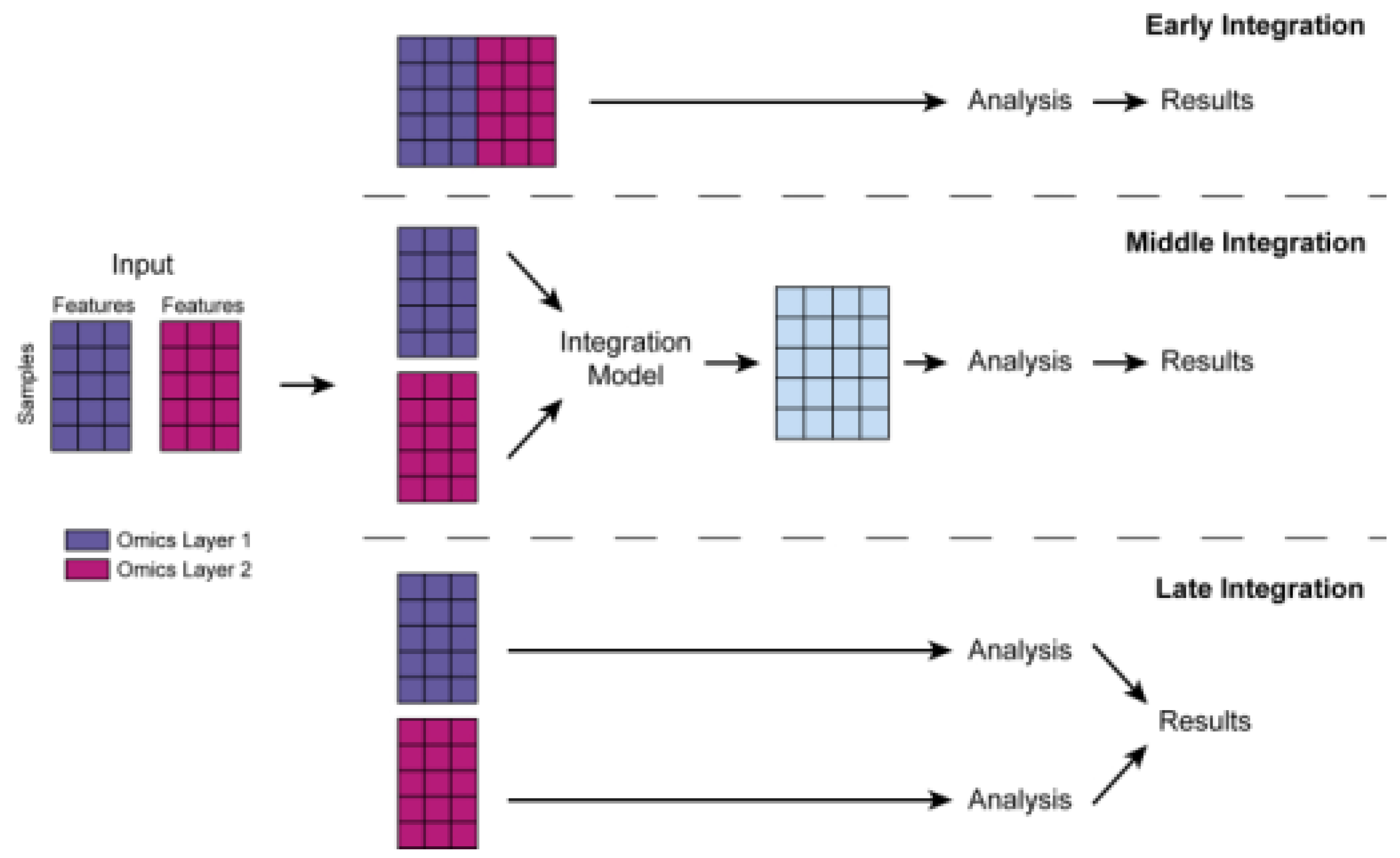
Integration of Multiomics Data
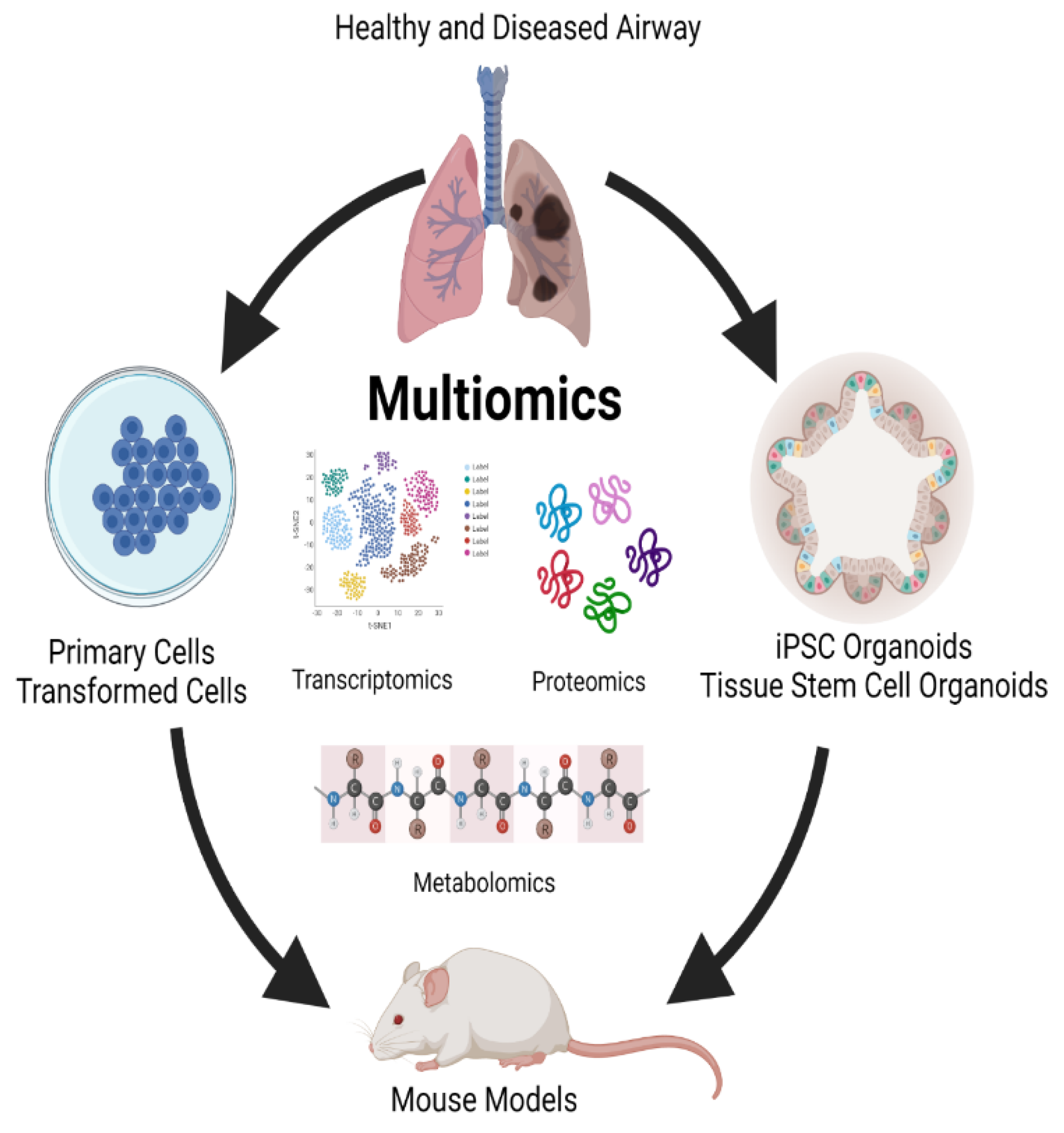
Lung multiomics Models
Multiomics Insight Into Clinical Disease
a. Cystic fibrosis
a. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
b. SARS-CoV-2 infection
c. Lung cancer
d. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
e. Pulmonary hypertension
| “Omic” technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Genome | The basic template of DNA. Technologies can identify genetic (DNA) variants associated with diseases. |
| Microbiome | Allows for accurate quantitative determination of microbial taxa, their abundance and diversity that can be associated with healthy and diseased states. |
| Transcriptome | Examines RNA levels transcribed from DNA template. A small amount of RNA is transcribed for protein synthesis, a much larger amount is encoded for other purposes, which may be implicated in disease. |
| Proteome | Quantifies peptides which may be used as disease biomarkers. |
| Metabolome | Detects and quantifies small molecules which include carbohydrates, amino and fatty acids, and other products of cellular metabolism. Abnormally high or low levels may predict disease. |
| Epigenome | Characterizes modifications of DNA or DNA associated proteins. |
Summary
References
- Humbert, M.V.; Spalluto, C.M.; Bell, J.; Blume, C.; Conforti, F.; Davies, E.R.; Dean, L.S.N.; Elkington, P.; Haitchi, H.M.; Jackson, C.; et al. Towards an artificial human lung: modelling organ-like complexity to aid mechanistic understanding. Eur Respir J 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.J.; Einarsson, G.G.; Gilpin, D.F.; Tunney, M.M. Multi-Omics Approaches: The Key to Improving Respiratory Health in People With Cystic Fibrosis? Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 569821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, J. NIH's 'precision nutrition' bet aims for individualized diets. Science 2021, 371, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Chiou, J.; Poirion, O.B.; Buchanan, J.; Valdez, M.J.; Verheyden, J.M.; Hou, X.; Kudtarkar, P.; Narendra, S.; Newsome, J.M.; et al. Single-cell multiomic profiling of human lungs reveals cell-type-specific and age-dynamic control of SARS-CoV2 host genes. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pliner, H.A.; Packer, J.S.; McFaline-Figueroa, J.L.; Cusanovich, D.A.; Daza, R.M.; Aghamirzaie, D.; Srivatsan, S.; Qiu, X.; Jackson, D.; Minkina, A.; et al. Cicero Predicts cis-Regulatory DNA Interactions from Single-Cell Chromatin Accessibility Data. Mol Cell 2018, 71, 858–871.e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Lim, K.; Sun, D.; Pett, J.P.; Jeng, Q.; Polanski, K.; Dong, Z.; Bolt, L.; Richardson, L.; Mamanova, L.; et al. A human fetal lung cell atlas uncovers proximal-distal gradients of differentiation and key regulators of epithelial fates. Cell 2022, 185, 4841–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, M.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Teichmann, S.A.; Vento-Tormo, R. CellPhoneDB: inferring cell-cell communication from combined expression of multi-subunit ligand-receptor complexes. Nat Protoc 2020, 15, 1484–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Poulos, R.C.; Liu, J.; Zhong, Q. Machine learning for multi-omics data integration in cancer. iScience 2022, 25, 103798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitnik, M.; Nguyen, F.; Wang, B.; Leskovec, J.; Goldenberg, A.; Hoffman, M.M. Machine Learning for Integrating Data in Biology and Medicine: Principles, Practice, and Opportunities. Inf Fusion 2019, 50, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R. Dynamic programming. Science 1966, 153, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.; Scott-Boyer, M.P.; Bodein, A.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Integration strategies of multi-omics data for machine learning analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2021, 19, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardini-Poleske, M.E.; Clark, R.F.; Ansong, C.; Carson, J.P.; Corley, R.A.; Deutsch, G.H.; Hagood, J.S.; Kaminski, N.; Mariani, T.J.; Potter, S.S.; et al. LungMAP: The Molecular Atlas of Lung Development Program. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2017, 313, L733–l740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Hitz, B.C.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Kagda, M.S.; Lam, B.; Myers, Z.; Sud, P.; Jou, J.; Lin, K.; et al. New developments on the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) data portal. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, D882–d889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundaje, A.; Meuleman, W.; Ernst, J.; Bilenky, M.; Yen, A.; Heravi-Moussavi, A.; Kheradpour, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ziller, M.J.; et al. Integrative analysis of 111 reference human epigenomes. Nature 2015, 518, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, N.J.; Oberti, M.; Thangudu, R.R.; Cai, S.; McGarvey, P.B.; Jacob, S.; Madhavan, S.; Ketchum, K.A. The CPTAC Data Portal: A Resource for Cancer Proteomics Research. J Proteome Res 2015, 14, 2707–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir Med 2020, 8, 585–596. [CrossRef]
- Atzrodt, C.L.; Maknojia, I.; McCarthy, R.D.P.; Oldfield, T.M.; Po, J.; Ta, K.T.L.; Stepp, H.E.; Clements, T.P. A Guide to COVID-19: a global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Febs j 2020, 287, 3633–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenert, D.C.; Willems, M.; Cassiman, J.J.; Frizzell, R.A. Established cell lines used in cystic fibrosis research. J Cyst Fibros 2004, 3 Suppl 2, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Birch, N.P.; Suresh, V. An Optimised Human Cell Culture Model for Alveolar Epithelial Transport. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0165225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanns, M.I.; Unger, R.E.; Kehe, K.; Peters, K.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Lung epithelial cell lines in coculture with human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells: development of an alveolo-capillary barrier in vitro. Lab Invest 2004, 84, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełbus, M.; Czapiński, J.; Kałafut, J.; Woś, J.; Stepulak, A.; Rivero-Müller, A. Genetically Engineered Lung Cancer Cells for Analyzing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallunki, T.; Barisic, M.; Jäättelä, M.; Liu, B. How to Choose the Right Inducible Gene Expression System for Mammalian Studies? Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.; Gruener, R.F.; Fessler, J.; Huang, R.S. More than fishing for a cure: The promises and pitfalls of high throughput cancer cell line screens. Pharmacol Ther 2018, 191, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitaeva, K.V.; Rutland, C.S.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Solovyeva, V.V. Cell Culture Based in vitro Test Systems for Anticancer Drug Screening. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.H.; Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.; Liu, Y.; Vong, C.M.; Wong, H.C.; Wong, P.K.; Wang, H.; et al. Drug screening of cancer cell lines and human primary tumors using droplet microfluidics. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The lungs at the frontlines of immunity. Nat Immunol 2015, 16, 17. [CrossRef]
- van der Vaart, J.; Clevers, H. Airway organoids as models of human disease. J Intern Med 2021, 289, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, K.B.; Hawkins, F.; Serra, M.; Thomas, D.C.; Jacob, A.; Kotton, D.N. Efficient Derivation of Functional Human Airway Epithelium from Pluripotent Stem Cells via Temporal Regulation of Wnt Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, K.B.; Hawkins, F.; Kotton, D.N. Derivation of Epithelial-Only Airway Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol 2018, 45, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.A.; Hu, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hoe, N.B.; Wei, T.S.; Mu, D.; Sun, Y.; Joo, L.S.; Dagher, R.; Zielonka, E.M.; et al. Distal airway stem cells yield alveoli in vitro and during lung regeneration following H1N1 influenza infection. Cell 2011, 147, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, S.; Shimizu, T.; Kishioka, C.; Fujita, K.; Sakakura, Y. Secretory cell differentiation and mucus secretion in cultures of human nasal epithelial cells: use of a monoclonal antibody to study human nasal mucin. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2000, 109, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, N.; Papaspyropoulos, A.; Zomer-van Ommen, D.D.; Heo, I.; Böttinger, L.; Klay, D.; Weeber, F.; Huelsz-Prince, G.; Iakobachvili, N.; Amatngalim, G.D.; et al. Long-term expanding human airway organoids for disease modeling. Embo j 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, M.C.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Chu, H.; Cai, J.P.; Zhou, B.; et al. A bipotential organoid model of respiratory epithelium recapitulates high infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Cell Discov 2022, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluhmki, T.; Traub, S.; Müller, A.K.; Bitzer, S.; Schruf, E.; Bammert, M.T.; Leist, M.; Gantner, F.; Garnett, J.P.; Heilker, R. Functional human iPSC-derived alveolar-like cells cultured in a miniaturized 96-Transwell air-liquid interface model. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 17028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Shi, F.; Liu, H. Human lung organoid: Models for respiratory biology and diseases. Dev Biol 2023, 494, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Liu, F.; Liang, X.; Duan, L.; Li, Q.; Pan, G.; Ma, C.; Liu, M.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; et al. iPSC-Derived Airway Epithelial Cells: Progress, Promise, and Challenges. Stem Cells 2023, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, P.; Shen, S.; Xi, Y. Organoid: a powerful tool to study lung regeneration and disease. Cell Regen 2021, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Na, F. Organoid technology and applications in lung diseases: Models, mechanism research and therapy opportunities. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 1066869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sanden, S.M.G.; Sachs, N.; Koekkoek, S.M.; Koen, G.; Pajkrt, D.; Clevers, H.; Wolthers, K.C. Enterovirus 71 infection of human airway organoids reveals VP1-145 as a viral infectivity determinant. Emerg Microbes Infect 2018, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Sachs, N.; Chiu, M.C.; Wong, B.H.; Chu, H.; Poon, V.K.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Wen, L.; et al. Differentiated human airway organoids to assess infectivity of emerging influenza virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, 6822–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, I.; Dutta, D.; Schaefer, D.A.; Iakobachvili, N.; Artegiani, B.; Sachs, N.; Boonekamp, K.E.; Bowden, G.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Willems, R.J.L.; et al. Modelling Cryptosporidium infection in human small intestinal and lung organoids. Nat Microbiol 2018, 3, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.P.Y.; Ching, R.H.H.; Chan, S.K.H.; Nicholls, J.M.; Sachs, N.; Clevers, H.; Peiris, J.S.M.; Chan, M.C.W. Tropism, replication competence, and innate immune responses of influenza virus: an analysis of human airway organoids and ex-vivo bronchus cultures. Lancet Respir Med 2018, 6, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.C.; Alva-Ornelas, J.A.; Sucre, J.M.; Vijayaraj, P.; Durra, A.; Richardson, W.; Jonas, S.J.; Paul, M.K.; Karumbayaram, S.; Dunn, B.; et al. Development of a Three-Dimensional Bioengineering Technology to Generate Lung Tissue for Personalized Disease Modeling. Stem Cells Transl Med 2017, 6, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Dye, B.R.; Ferrer-Torres, D.; Hill, D.R.; Overeem, A.W.; Shea, L.D.; Spence, J.R. Generation of lung organoids from human pluripotent stem cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 2019, 14, 518–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, M.; Buijs-Offerman, R.M.; Aarbiou, J.; Colledge, W.H.; Sheppard, D.N.; Touqui, L.; Bot, A.; Jorna, H.; de Jonge, H.R.; Scholte, B.J. Mouse models of cystic fibrosis: phenotypic analysis and research applications. J Cyst Fibros 2011, 10 Suppl 2, S152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, D.M.; Kleeberger, S.R. Mouse models of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 2008. Chapter 5, Unit 5.46,. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, J.; Rubio, G.A.; Limper, A.H.; Williams, K.; Elliot, S.J.; Ninou, I.; Aidinis, V.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Glassberg, M.K. Exploring Animal Models That Resemble Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2017, 4, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, J.; Naninck, T.; Delache, B.; Creppy, J.; Huber, P.; Holzapfel, M.; Bouillier, C.; Contreras, V.; Martinon, F.; Kahlaoui, N.; et al. Non-human primate models of human respiratory infections. Mol Immunol 2021, 135, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.C.; Berns, A. Mouse models for lung cancer. Mol Oncol 2013, 7, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Choi, A.J.; Owen, C.A.; Choi, A.M. Genetically manipulated mouse models of lung disease: potential and pitfalls. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2012, 302, L485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Deutsch, G.H.; Wert, S.E. Comprehensive anatomic ontologies for lung development: A comparison of alveolar formation and maturation within mouse and human lung. J Biomed Semantics 2019, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, R.L.; Burns, J.L.; Ramsey, B.W. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 168, 918–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, S.M.; Heltshe, S.L.; Gonska, T.; Donaldson, S.H.; Borowitz, D.; Gelfond, D.; Sagel, S.D.; Khan, U.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Van Dalfsen, J.M.; et al. Clinical mechanism of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator potentiator ivacaftor in G551D-mediated cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014, 190, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, D.; Chmiel, J.; Berger, M. Chronic inflammation in the cystic fibrosis lung: alterations in inter- and intracellular signaling. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2008, 34, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiser, N.W.; Birket, S.E.; Evans, I.A.; Tyler, S.R.; Crooke, A.K.; Sun, X.; Zhou, W.; Nellis, J.R.; Stroebele, E.K.; Chu, K.K.; et al. Defective innate immunity and hyperinflammation in newborn cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-knockout ferret lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2015, 52, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Connor, J.B.; Mottlowitz, M.M.; Wagner, B.D.; Boyne, K.L.; Stevens, M.J.; Robertson, C.E.; Harris, J.K.; Laguna, T.A. Divergence of bacterial communities in the lower airways of CF patients in early childhood. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0257838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twomey, K.B.; Alston, M.; An, S.Q.; O'Connell, O.J.; McCarthy, Y.; Swarbreck, D.; Febrer, M.; Dow, J.M.; Plant, B.J.; Ryan, R.P. Microbiota and metabolite profiling reveal specific alterations in bacterial community structure and environment in the cystic fibrosis airway during exacerbation. PLoS One 2013, 8, e82432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanick, E.T.; Wagner, B.D.; Robertson, C.E.; Stevens, M.J.; Szefler, S.J.; Accurso, F.J.; Sagel, S.D.; Harris, J.K. Assessment of airway microbiota and inflammation in cystic fibrosis using multiple sampling methods. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2015, 12, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.A.; Phelan, V.V.; Whiteson, K.L.; Garg, N.; Bailey, B.A.; Lim, Y.W.; Conrad, D.J.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rohwer, F.L. Microbial, host and xenobiotic diversity in the cystic fibrosis sputum metabolome. Isme j 2016, 10, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorth, P.; Ehsan, Z.; Rezayat, A.; Caldwell, E.; Pope, C.; Brewington, J.J.; Goss, C.H.; Benscoter, D.; Clancy, J.P.; Singh, P.K. Direct Lung Sampling Indicates That Established Pathogens Dominate Early Infections in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Cell Rep 2019, 27, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuvanshi, R.; Vasco, K.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Jiang, L.; Morton, J.T.; Li, D.; Gonzalez, A.; DeRight Goldasich, L.; Humphrey, G.; Ackermann, G.; et al. High-Resolution Longitudinal Dynamics of the Cystic Fibrosis Sputum Microbiome and Metabolome through Antibiotic Therapy. mSystems 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, A.; Whiteson, K.; Davis, T.J.; Phan, J.; Sami, I.; Koumbourlis, A.C.; Freishtat, R.J.; Crandall, K.A.; Bean, H.D. Longitudinal Associations of the Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiome and Volatile Metabolites: A Case Study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Connor, J.B.; Mottlowitz, M.; Kruk, M.E.; Mickelson, A.; Wagner, B.D.; Harris, J.K.; Wendt, C.H.; Laguna, T.A. Network Analysis to Identify Multi-Omic Correlations in the Lower Airways of Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 805170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoen, A.G.; Li, J.; Moulton, L.A.; O'Toole, G.A.; Housman, M.L.; Koestler, D.C.; Guill, M.F.; Moore, J.H.; Hibberd, P.L.; Morrison, H.G.; et al. Associations between Gut Microbial Colonization in Early Life and Respiratory Outcomes in Cystic Fibrosis. J Pediatr 2015, 167, 138–147.e131-133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LiPuma, J.J. Assessing Airway Microbiota in Cystic Fibrosis: What More Should Be Done? J Clin Microbiol 2015, 53, 2006–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, M.; Cogen, J.; Hoffman, L.R. The pediatric microbiome and the lung. Curr Opin Pediatr 2015, 27, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevaes, S.M.; de Winter-de Groot, K.M.; Janssens, H.M.; de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.; Tramper-Stranders, G.A.; Wyllie, A.L.; Hasrat, R.; Tiddens, H.A.; van Westreenen, M.; van der Ent, C.K.; et al. Development of the Nasopharyngeal Microbiota in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016, 193, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkova, N.J.; Standiford, T.J.; Stringer, K.A. The emerging field of quantitative blood metabolomics for biomarker discovery in critical illnesses. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011, 184, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuschi, P.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Lucidi, V.; Ciabattoni, G.; Raia, V.; Calabrese, C.; Bush, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Motta, A. NMR spectroscopy metabolomic profiling of exhaled breath condensate in patients with stable and unstable cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2012, 67, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, M.E.; Pérez, J.J.; Dwivedi, P.; Zhou, M.; McCarty, N.A.; Stecenko, A.A.; Fernández, F.M. Ion mobility and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry strategies for exhaled breath condensate glucose quantitation in cystic fibrosis studies. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2013, 27, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, J.E.; Esther, C.R., Jr.; O'Connell, T.M. Metabolomic analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from cystic fibrosis patients. Biomarkers 2009, 14, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esther, C.R., Jr.; Coakley, R.D.; Henderson, A.G.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wright, F.A.; Boucher, R.C. Metabolomic Evaluation of Neutrophilic Airway Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2015, 148, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esther, C.R., Jr.; Turkovic, L.; Rosenow, T.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Boucher, R.C.; Ranganathan, S.; Stick, S.M. Metabolomic biomarkers predictive of early structural lung disease in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 2016, 48, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Russell, P.H.; Hobbs, B.D.; Parker, M.M.; Castaldi, P.J.; Rudra, P.; Vestal, B.; Hersh, C.P.; Saba, L.M.; et al. Unsupervised discovery of phenotype-specific multi-omics networks. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4336–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.A.; Adem, S.; Mills, R.H.; Comstock, W.; DeRight Goldasich, L.; Humphrey, G.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; da Silva, R.; Ackermann, G.; et al. Neutrophilic proteolysis in the cystic fibrosis lung correlates with a pathogenic microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hafiz, M.; Najafi, M.; Helmi, S.; Pratte, K.A.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, W.; Kechris, K.J.; Bowler, R.P.; Lange, L.; Banaei-Kashani, F. Significant Subgraph Detection in Multi-omics Networks for Disease Pathway Identification. Front Big Data 2022, 5, 894632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Yi, X.; Wei, M.; Ecklu-Mensah, G.; Buschmann, M.M.; Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Liang, W.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of airway host-microbe interactions in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease identify potential therapeutic interventions. Nat Microbiol 2022, 7, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, C.J.; Sweatt, A.J.; Maron, B.A. Harnessing Big Data to Advance Treatment and Understanding of Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ Res 2022, 130, 1423–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Liang, Z.; Wang, F.; Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Yi, X.; et al. Multi-omic meta-analysis identifies functional signatures of airway microbiome in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Isme j 2020, 14, 2748–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, T.; Qi, F.; Fan, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Gao, X.; Zeng, H.; et al. Multiomics approach reveals the ubiquitination-specific processes hijacked by SARS-CoV-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterman, A.; Sumida, T.S.; Nouri, N.; Yan, X.; Zhao, A.Y.; Gasque, V.; Schupp, J.C.; Asashima, H.; Liu, Y.; Cosme, C., Jr.; et al. Single-cell multi-omics reveals dyssynchrony of the innate and adaptive immune system in progressive COVID-19. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Wheelock Å, M. Multiomics integration-based molecular characterizations of COVID-19. Brief Bioinform 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Wu, C. An integrative multiomics analysis identifies putative causal genes for COVID-19 severity. Genet Med 2021, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantwell, A.M.; Singh, H.; Platt, M.; Yu, Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.; Xiang, Y.; Gonzalez-Juarbe, N.; Dube, P.H. Kinetic Multi-omic Analysis of Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Model of Severe COVID-19. J Virol 2021, 95, e0101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, A.J.; Lee, M.J.; Wei, B.; Parks, B.; Pi, R.; Martínez-Colón, G.J.; Ranganath, T.; Zhao, N.Q.; Taylor, S.; Becker, W.; et al. Multi-omic profiling reveals widespread dysregulation of innate immunity and hematopoiesis in COVID-19. J Exp Med 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [CrossRef]
- CGARN. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, A.R.; Gandhi, T.; Heyckendorf, J.; Grimm, S.L.; Rajapakshe, K.; Nishiguchi, T.; Reimann, M.; Kirchner, H.L.; Kahari, J.; Dlamini, Q.; et al. Gene expression signatures identify biologically and clinically distinct tuberculosis endotypes. Eur Respir J 2022, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.J.; Nagaraja, A.K.; Hanash, S.M.; Matzuk, M.M.; Gunaratne, P.H. A bioinformatics tool for linking gene expression profiling results with public databases of microRNA target predictions. Rna 2008, 14, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, D127–d131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Karagkouni, D.; Georgakilas, G.; Vergoulis, T.; Kanellos, I.; Anastasopoulos, I.L.; Maniou, S.; Karathanou, K.; Kalfakakou, D.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v7.0: indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, D153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Q. Identification of a Potentially Functional microRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Lung Adenocarcinoma Using a Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 641840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, L.; Wang, W. Systematic assessment of microRNAs associated with lung cancer and physical exercise. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 917667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.D.; Yau, C.; Bowlby, R.; Liu, Y.; Brennan, K.; Fan, H.; Taylor, A.M.; Wang, C.; Walter, V.; Akbani, R.; et al. Genomic, Pathway Network, and Immunologic Features Distinguishing Squamous Carcinomas. Cell Rep 2018, 23, 194–212.e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaiparambil, J.; Dong, J.; Grimm, S.L.; Perera, D.; Ambati, C.S.R.; Putluri, V.; Robertson, M.J.; Patel, T.D.; Mistretta, B.; Gunaratne, P.H.; et al. Integrative metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals novel therapeutic vulnerabilities in lung cancer. Cancer Med 2023, 12, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, B.J.; Kaplan, A.; Hodgson, S.W.; Peterson, M.; Avdulov, S.; Higgins, L.; Markowski, T.; Yang, P.; Limper, A.H.; Griffin, T.J.; et al. Multi-omic molecular profiling of lung cancer in COPD. Eur Respir J 2018, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.J.; Erbe, R.; Danilova, L.; Phyo, Z.; Bigelow, E.; Stein-O'Brien, G.; Thomas, D.L., 2nd; Charmsaz, S.; Gross, N.; Woolman, S.; et al. Multi-omic profiling of lung and liver tumor microenvironments of metastatic pancreatic cancer reveals site-specific immune regulatory pathways. Genome Biol 2021, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Gaynor, S.; Zhou, H.; Li, Z.; Bossé, Y.; Lam, S.; Tsao, M.S.; Tardon, A.; et al. Integration of multiomic annotation data to prioritize and characterize inflammation and immune-related risk variants in squamous cell lung cancer. Genet Epidemiol 2021, 45, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.C.; Reuben, A.; Hu, X.; McGranahan, N.; Chen, R.; Jalali, A.; Negrao, M.V.; Hubert, S.M.; Tang, C.; Wu, C.C.; et al. Multiomics profiling of primary lung cancers and distant metastases reveals immunosuppression as a common characteristic of tumor cells with metastatic plasticity. Genome Biol 2020, 21, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.A.; Dysart, K.; Gantz, M.G.; McDonald, S.; Bamat, N.A.; Keszler, M.; Kirpalani, H.; Laughon, M.M.; Poindexter, B.B.; Duncan, A.F.; et al. The Diagnosis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Very Preterm Infants. An Evidence-based Approach. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019, 200, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Perl, A.K.; Li, R.; Bell, S.M.; Sajti, E.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Kalin, T.V.; Misra, R.S.; Deshmukh, H.; Clair, G.; et al. A census of the lung: CellCards from LungMAP. Dev Cell 2022, 57, 112–145.e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, C.V.; Kandasamy, J.; Dolma, K.; Ramani, M.; Kumar, R.; Wilson, L.; Aghai, Z.; Barnes, S.; Blalock, J.E.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Early airway microbial metagenomic and metabolomic signatures are associated with development of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2018, 315, L810–l815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, C.V.; Olave, N.; Travers, C.; Rezonzew, G.; Dolma, K.; Simpson, A.; Halloran, B.; Aghai, Z.; Das, P.; Sharma, N.; et al. Exosomal microRNA predicts and protects against severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in extremely premature infants. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, C.V.; Travers, C.; Aghai, Z.H.; Eipers, P.; Jilling, T.; Halloran, B.; Carlo, W.A.; Keeley, J.; Rezonzew, G.; Kumar, R.; et al. The Airway Microbiome at Birth. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 31023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pammi, M.; Lal, C.V.; Wagner, B.D.; Mourani, P.M.; Lohmann, P.; Luna, R.A.; Sisson, A.; Shivanna, B.; Hollister, E.B.; Abman, S.H.; et al. Airway Microbiome and Development of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review. J Pediatr 2019, 204, 126–133.e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Coarfa, C.; Dong, X.; Jiang, W.; Hayward-Piatkovskyi, B.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Lingappan, K. MicroRNA-30a as a candidate underlying sex-specific differences in neonatal hyperoxic lung injury: implications for BPD. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2019, 316, L144–l156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coarfa, C.; Zhang, Y.; Maity, S.; Perera, D.N.; Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Couroucli, X.; Moorthy, B.; Lingappan, K. Sexual dimorphism of the pulmonary transcriptome in neonatal hyperoxic lung injury: identification of angiogenesis as a key pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2017, 313, L991–l1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Saie, A.; Fu, C.; Grimm, S.L.; Robertson, M.J.; Hoffman, K.; Putluri, V.; Ambati, C.S.R.; Putluri, N.; Shivanna, B.; Coarfa, C.; et al. Metabolome and microbiome multi-omics integration from a murine lung inflammation model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldi, G.; Hummler, H.; Pillay, T. T Lymphocytes, Multi-Omic Interactions and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Front Pediatr 2021, 9, 694034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Miao, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Feng, H.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, C.; Lin, Z.; et al. Microbiome and metabolome dysbiosis of the gut-lung axis in pulmonary hypertension. Microbiol Res 2022, 265, 127205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konigsberg, I.R.; Borie, R.; Walts, A.D.; Cardwell, J.; Rojas, M.; Metzger, F.; Hauck, S.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Yang, I.V.; Schwartz, D.A. Molecular Signatures of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2021, 65, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titz, B.; Szostak, J.; Sewer, A.; Phillips, B.; Nury, C.; Schneider, T.; Dijon, S.; Lavrynenko, O.; Elamin, A.; Guedj, E.; et al. Multi-omics systems toxicology study of mouse lung assessing the effects of aerosols from two heat-not-burn tobacco products and cigarette smoke. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2020, 18, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Wong, B.; Rhodes, C.J.; Kurt, Z.; Schwantes-An, T.H.; Mickler, E.A.; Gräf, S.; Eyries, M.; Lutz, K.A.; Pauciulo, M.W.; et al. Integrative Multiomics to Dissect the Lung Transcriptional Landscape of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammi, M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Neu, J. Multiomics, artificial intelligence, and precision medicine in perinatology. Pediatr Res 2023, 93, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





