Submitted:
05 May 2023
Posted:
08 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
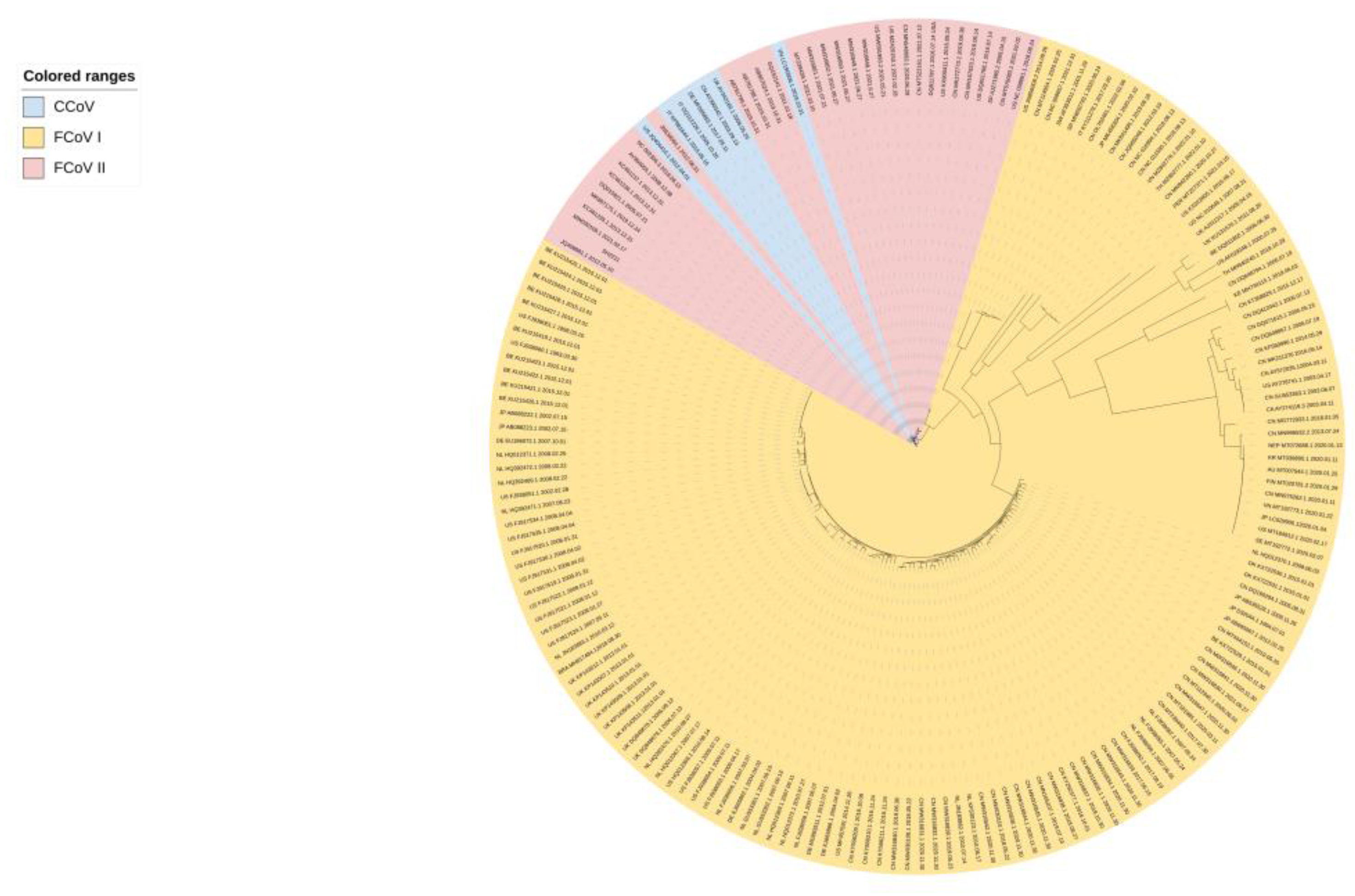
2. Serotype study of the etiologic agent of FIP
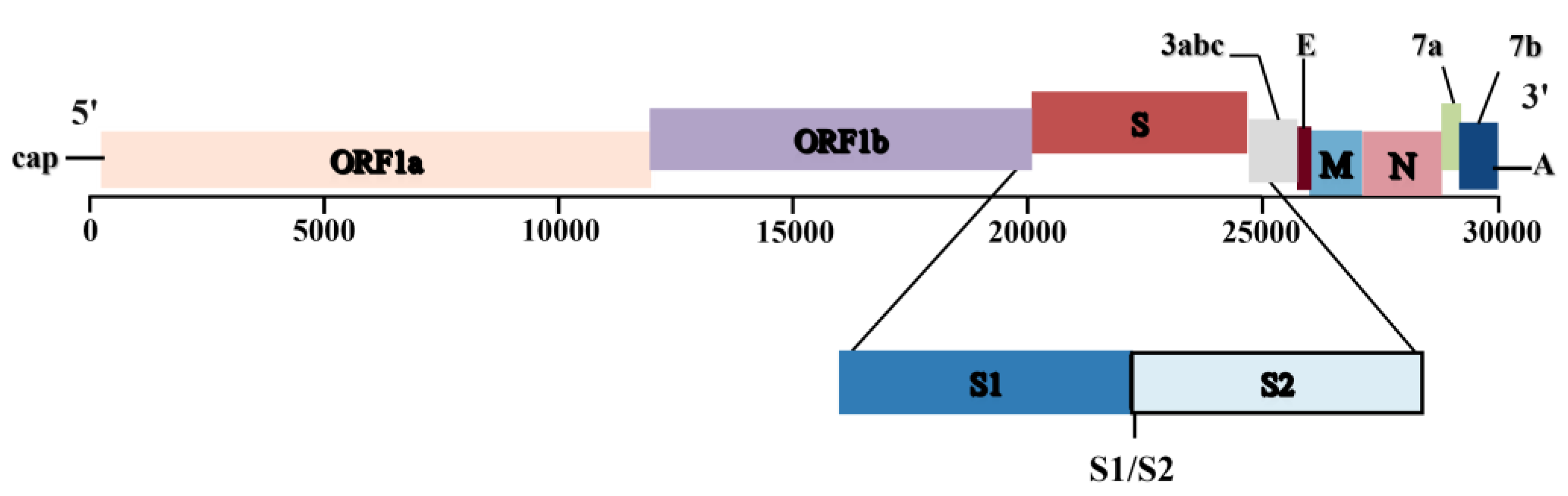
3. Pathogenesis
4. Innate Immune Response and Immune Escape Mechanisms
5. Diagnostic Methods
5.1. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Assays
5.2. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
5.3. Serology
5.4. Tests on Effusion Fluid
5.5. Other Diagnosis Method
6. Therapy and Prevention
6.1. Antivirals
6.2. Vaccine
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Dodd, K.A.; Pesavento, P.A. Significance of Coronavirus Mutants in Feces and Diseased Tissues of Cats Suffering from Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2009, 1, 166–184, . [CrossRef]
- Ratti, G.; Stranieri, A.; Giordano, A.; Oltolina, M.; Bonacina, E.; Magnone, W.; Morici, M.; Ravasio, G.; Paltrinieri, S.; Lauzi, S. Molecular Detection of Feline Coronavirus in Captive Non-Domestic Felids from Zoological Facilities. Animals 2022, 12, 1864, . [CrossRef]
- Stout, A.E.; André, N.M.; Whittaker, G.R. Feline coronavirus and feline infectious peritonitis in nondomestic felid species. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2021, 52, 14–27, . [CrossRef]
- Drechsler, Y.; Alcaraz, A.; Bossong, F.J.; Collisson, E.W.; Diniz, P.P.V. Feline Coronavirus in Multicat Environments. Veter- Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pr. 2011, 41, 1133–1169, . [CrossRef]
- A Fiscus, S.; A Teramoto, Y. Antigenic comparison of feline coronavirus isolates: evidence for markedly different peplomer glycoproteins. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 2607–2613, . [CrossRef]
- Herrewegh AA, Smeenk I, Horzinek MC, Rottier PJ, de Groot RJ. Feline coronavirus type II strains 79-1683 and 79-1146 orig inate from a double recombination between feline coronavirus type I and canine coronavirus. J. Virol. 1998, 72(5), 4508-4514.
- Herrewegh AA, Vennema H, Horzinek MC, Rottier PJ, de Groot RJ. The molecular genetics of feline coronaviruses: compar- ative sequence analysis of the ORF7a/7b transcription unit of different biotypes. Virology 1995, 212(2), 6226-6231.
- Holmes, E.C.; Rambaut, A. Viral evolution and the emergence of SARS coronavirus. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B: Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1059–1065, . [CrossRef]
- Smith EC, Denison MR. Denison. Implications of altered replication fidelity on the evolution and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Opin Virol, 2012, 2(5), 519-524.
- Gao YY, Liang XY, Wang Q, Zhang S, Zhao H, Wang K, Hu GX, Liu WJ, Gao FS. Mind the feline coronavirus: comparison with SARS-CoV-2. Gene, 2022, 825, 146443.
- Addie, D.D.; Schaap, I.A.T.; Nicolson, L.; Jarrett, O. Persistence and transmission of natural type I feline coronavirus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2735–2744, . [CrossRef]
- Kummrow, M.; Meli, M.L.; Haessig, M.; Goenczi, E.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lutz, H. Feline Coronavirus Serotypes 1 and 2: Seroprevalence and Association with Disease in Switzerland. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2005, 12, 1209–1215, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Boyle, J.F.; Floyd, K.; Fudge, A.; Barker, J. An enteric coronavirus infection of cats and its relationship to feline infectious peritonitis. Am J Vet Res. 1981, 42, 368–377.
- Pedersen, N.C.; Boyle, J.F.; Floyd, K. Infection studies in kittens, using feline infectious peritonitis virus propagated in cell culture. Am J Vet Res. 1981, 42, 363–7.
- Black, J.W. Recovery and in vitro cultivation of a coronavirus from laboratory-induced cases of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1980, 75, 811–4.
- Ritz S, Egberink H, Hartmann K. Effect of feline interferon-omega on the survival time and quality of life of cats with feline infectious peritonitis. J Vet Intern Med, 2007, 21(6), 1193-1197.
- McKeirnan, A.J.; Evermann, J.F.; Davis, E.V.; Ott, R.L. Comparative properties of feline coronaviruses in vitro. Can J Vet Res,. 1987, 51, 212–216.
- Jähne, S.; Felten, S.; Bergmann, M.; Erber, K.; Matiasek, K.; Meli, M.L.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Hartmann, K. Detection of Feline Coronavirus Variants in Cats without Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1671, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Liu, H.; Scarlett, J.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Golovko, L.; Kennedy, H.; Kamal, F.M. Feline infectious peritonitis: Role of the feline coronavirus 3c gene in intestinal tropism and pathogenicity based upon isolates from resident and adopted shelter cats. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 17–28, . [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A. Genetic determinants of pathogenesis by feline infectious peritonitis virus. Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 265–268, . [CrossRef]
- Healey EA, Andre NM, Miller AD, Whittaker GR, Berliner EA. Outbreak of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) in shelter-housed cats: molecular analysis of the feline coronavirus S1/S2 cleavage site consistent with a ’circulating virulent-avirulent theory’ of FIP pathogenesis. JFMS Open Rep, 2022, 8(1), 20551169221074226.
- Vennema, H.; Polanda, A.; Foleya, J.; Pedersen, N.C. Feline Infectious Peritonitis Viruses Arise by Mutation from Endemic Feline Enteric Coronaviruses. Virology 1998, 243, 150–157, . [CrossRef]
- Poland, A.M.; Vennema, H.; E Foley, J.; Pedersen, N.C. Two related strains of feline infectious peritonitis virus isolated from immunocompromised cats infected with a feline enteric coronavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 3180–3184, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258, . [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Troyer, J.L.; Pecon-Slattery, J.; Roelke, M.E.; O’brien, S.J. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1445–1452, . [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-W.; Egberink, H.F.; Halpin, R.; Spiro, D.J.; Rottier, P.J. Spike Protein Fusion Peptide and Feline Coronavirus Virulence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1089–1095, . [CrossRef]
- Bank-Wolf, B.R.; Stallkamp, I.; Wiese, S.; Moritz, A.; Tekes, G.; Thiel, H.-J. Mutations of 3c and spike protein genes correlate with the occurrence of feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Microbiol. 2014, 173, 177–188, . [CrossRef]
- Borschensky, C.; Reinacher, M. Mutations in the 3c and 7b genes of feline coronavirus in spontaneously affected FIP cats. Res. Veter- Sci. 2014, 97, 333–340, . [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Arshad, S.S.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Omar, A.R.; Zeenathul, N.A.; Alazawy, A. Diagnostic Methods for Feline Coronavirus: A Review. Veter- Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 809480, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C. An update on feline infectious peritonitis: Virology and immunopathogenesis. Veter- J. 2014, 201, 123–132, . [CrossRef]
- Benetka, V.; Kübber-Heiss, A.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Hofmann-Parisot, M.; Möstl, K. Prevalence of feline coronavirus types I and II in cats with histopathologically verified feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Microbiol. 2004, 99, 31–42, . [CrossRef]
- Patel JR, Heldens JG. Review of companion animal viral diseases and immunoprophylaxis. Vaccine, 2009, 27(4), 491-504.
- Goodson T, Randell S, Moore L. Feline infectious peritonitis. Compend Contin Educ Vet. 2009, 31(10), E1-8.
- Pedersen, N.C. An update on feline infectious peritonitis: Diagnostics and therapeutics. Veter- J. 2014, 201, 133–141, . [CrossRef]
- Hartmann K. Feline infectious peritonitis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2005, 35(1), 39-79.
- Jaimes, J.A.; Millet, J.K.; Stout, A.E.; André, N.M.; Whittaker, G.R. A Tale of Two Viruses: The Distinct Spike Glycoproteins of Feline Coronaviruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 83, . [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Okada, S.; Ishizuka, Y.; Yamada, H.; Koyama, H. The Prevalence of Types I and II Feline Coronavirus Infections in Cats.. J. Veter- Med Sci. 1992, 54, 557–562, . [CrossRef]
- Fehr, D.; Bolla, S.; A Herrewegh, A.; Horzinek, M.C.; Lutz, H. [Detection of feline coronavirus using RT-PCR: basis for the study of the pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)]. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1996, 138, 74–9.
- Decaro N, Lorusso A. Novel human coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): A lesson from animal coronaviruses. Vet Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108693.
- Gatherer, D.; Depledge, D.P.; Hartley, C.A.; Szpara, M.L.; Vaz, P.K.; Benkő, M.; Brandt, C.R.; Bryant, N.A.; Dastjerdi, A.; Doszpoly, A.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Herpesviridae 2021. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001673, . [CrossRef]
- Tekes G, Thiel HJ. Feline coronaviruses: pathogenesis of feline infectious peritonitis. Adv Virus Res. 2016, 96, 193-218.
- Kennedy MA. Feline infectious peritonitis: update on pathogenesis, diagnostics, and treatment. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract, 2020, 50(5), 1001-1011.
- Dye C, Siddell SG. Genomic RNA sequence of Feline coronavirus strain FIPV WSU-79/1146. J Gen Virol. 2005, 86(Pt 8), 2249-2253.
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L.; Baptiste, K.E.; Bowker, L.J.; Lutz, H. Sites of feline coronavirus persistence in healthy cats. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1698–1707, . [CrossRef]
- Desmarets, L.M.B.; Vermeulen, B.L.; Theuns, S.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Zeller, M.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Acar, D.D.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; et al. Experimental feline enteric coronavirus infection reveals an aberrant infection pattern and shedding of mutants with impaired infectivity in enterocyte cultures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20022–20022, . [CrossRef]
- Meli, M.; Kipar, A.; Müller, C.; Jenal, K.; Gönczi, E.; Borel, N.; Gunn-Moore, D.; Chalmers, S.; Lin, F.; Reinacher, M.; et al. High viral loads despite absence of clinical and pathological findings in cats experimentally infected with feline coronavirus (FCoV) type I and in naturally FCoV-infected cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2004, 6, 69–81, . [CrossRef]
- Kipar, A.; Meli, M.L.; Failing, K.; Euler, T.; Gomes-Keller, M.A.; Schwartz, D.; Lutz, H.; Reinacher, M. Natural feline coronavirus infection: Differences in cytokine patterns in association with the outcome of infection. Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 112, 141–155, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Allen, C.E.; Lyons, L.A. Pathogenesis of feline enteric coronavirus infection. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 529–541, . [CrossRef]
- Vogel, L.; Van der Lubben, M.; Lintelo, E.G.T.; Bekker, C.P.; Geerts, T.; Schuijff, L.S.; Grinwis, G.C.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J. Pathogenic characteristics of persistent feline enteric coronavirus infection in cats. Veter- Res. 2010, 41, 71–71, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.; Sato, R.; Foley, J.; Poland, A. Common virus infections in cats, before and after being placed in shelters, with emphasis on feline enteric coronavirus. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2004, 6, 83–88, . [CrossRef]
- Legendre, A.M.; Bartges, J.W. Effect of Polyprenyl Immunostimulant on the survival times of three cats with the dry form of feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 624–626, . [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Wakayama, Y.; Doki, T. Endocytic Pathway of Feline Coronavirus for Cell Entry: Differences in Serotype-Dependent Viral Entry Pathway. Pathogens 2019, 8, 300.40300. [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Izumiya, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Kida, K.; Koyama, H. Differences in virus receptor for type I and type II feline infectious peritonitis virus. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 839–850, . [CrossRef]
- Tekes, G.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Bank-Wolf, B.; Maier, R.; Thiel, H.-J.; Thiel, V. Chimeric Feline Coronaviruses That Encode Type II Spike Protein on Type I Genetic Background Display Accelerated Viral Growth and Altered Receptor Usage. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1326–1333, . [CrossRef]
- Van Hamme, E.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Cornelissen, E.; Verhasselt, B.; Nauwynck, H.J. Clathrin- and caveolae-independent entry of feline infectious peritonitis virus in monocytes depends on dynamin. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2147–2156, . [CrossRef]
- Van Hamme, E.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Cornelissen, E.; Nauwynck, H.J. Attachment and internalization of feline infectious peritonitis virus in feline blood monocytes and Crandell feline kidney cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2527–2532, . [CrossRef]
- Burkard C, Verheije MH, Wicht O, van Kasteren SI, van Kuppeveld FJ, Haagmans BL, Pelkmans L, Rottier PJ, Bosch BJ, de Haan CA. Coronavirus cell entry occurs through the endo-/lysosomal pathway in a proteolysis-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10(11), e1004502.
- Regan, A.D.; Shraybman, R.; Cohen, R.D.; Whittaker, G.R. Differential role for low pH and cathepsin-mediated cleavage of the viral spike protein during entry of serotype II feline coronaviruses. Veter- Microbiol. 2008, 132, 235–248, . [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.S.; Porter, E.; Matthews, D.; Kipar, A.; Tasker, S.; Helps, C.R.; Siddell, S.G. Genotyping coronaviruses associated with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1358–1368, . [CrossRef]
- Licitra, B.N.; Millet, J.K.; Regan, A.D.; Hamilton, B.S.; Rinaldi, V.D.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R. Mutation in Spike Protein Cleavage Site and Pathogenesis of Feline Coronavirus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1066–1073, . [CrossRef]
- Shirato, K.; Chang, H.-W.; Rottier, P.J. Differential susceptibility of macrophages to serotype II feline coronaviruses correlates with differences in the viral spike protein. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 14–23, . [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.; Tasker, S.; Day, M.J.; Harley, R.; Kipar, A.; Siddell, S.G.; Helps, C.R. Amino acid changes in the spike protein of feline coronavirus correlate with systemic spread of virus from the intestine and not with feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Res. 2014, 45, 49–49, . [CrossRef]
- Rottier, P.J.M.; Nakamura, K.; Schellen, P.; Volders, H.; Haijema, B.J. Acquisition of Macrophage Tropism during the Pathogenesis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Is Determined by Mutations in the Feline Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14122–14130, . [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.V.; Poma, R. Diagnosis and clinical signs of feline infectious peritonitis in the central nervous system.. 2009, 50, 1091–1093.
- Foley, J.E.; Lapointe, J.; Koblik, P.; Poland, A.; Pedersen, N.C. Diagnostic Features of Clinical Neurologic Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Veter- Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 415–423, . [CrossRef]
- Stiles, J. Ocular manifestations of feline viral diseases. Veter- J. 2014, 201, 166–173, . [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.; Belák, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Egberink, H.; Frymus, T.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Hartmann, K.; Hosie, M.J.; Lloret, A.; Lutz, H.; et al. Feline infectious peritonitis. ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 594–604, . [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.; Rand, C.; Leutenegger, C. Inflammation and changes in cytokine levels in neurological feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2003, 5, 313–322, . [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.D.; Jarrett, O. Use of a reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for monitoring the shedding of feline coronavirus by healthy cats. Veter- Rec. 2001, 148, 649–653, . [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.D.; Jarrett, O. Control of feline coronavirus infection in kittens. Vet Rec. 1990, 126, 164.
- Pedersen NC. Virologic and immunologic aspects of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987, 218, 529-550.
- Rissi, D.R. A retrospective study of the neuropathology and diagnosis of naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. J. Veter- Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 392–399, . [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yao, D.; Wu, L.; Fan, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z. Molecular epidemiology of type I and II feline coronavirus from cats with suspected feline infectious peritonitis in China between 2019 and 2021. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 189–194, . [CrossRef]
- Riemer, F.; A Kuehner, K.; Ritz, S.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Clinical and laboratory features of cats with feline infectious peritonitis – a retrospective study of 231 confirmed cases (2000–2010). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 348–356, . [CrossRef]
- Soma, T.; Wada, M.; Taharaguchi, S.; Tajima, T. Detection of Ascitic Feline Coronavirus RNA from Cats with Clinically Suspected Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Veter- Med Sci. 2013, 75, 1389–1392, . [CrossRef]
- A Worthing, K.; I Wigney, D.; Dhand, N.K.; Fawcett, A.; McDonagh, P.; Malik, R.; Norris, J.M. Risk factors for feline infectious peritonitis in Australian cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 405–412, . [CrossRef]
- Pesteanu-Somogyi, L.D.; Radzai, C.; Pressler, B.M. Prevalence of feline infectious peritonitis in specific cat breeds. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2006, 8, 1–5, . [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, B.W.; Legendre, A.M.; Baldwin, C.A.; Lein, D.H.; Reed, W.M.; Wilson, R.B. Epidemiology of feline infectious peritonitis among cats examined at veterinary medical teaching hospitals. J. Am. Veter- Med Assoc. 2001, 218, 1111–1115, . [CrossRef]
- Foley JE, Pedersen NC. The inheritance of susceptibility to feline infectious peritonitis in purebred catteries. Feline Practice. 1996, 24(1), 14-22.
- Dewerchin, H.L.; Cornelissen, E.; Nauwynck, H.J. Replication of feline coronaviruses in peripheral blood monocytes. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 2483–2500, . [CrossRef]
- de Groot-Mijnes JD, van Dun JM, van der Most RG, de Groot RJ. Natural history of a recurrent feline coronavirus infection and the role of cellular immunity in survival and disease. J Virol. 2005, 79(2),1036-1044.
- Acar, D.D.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Dedeurwaerder, A.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Baetens, W.; Van Bockstael, S.; De Gryse, G.M.A.; Desmarets, L.M.B.; Nauwynck, H.J. Upregulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules characterizes veins close to granulomatous infiltrates in the renal cortex of cats with feline infectious peritonitis and is indirectly triggered by feline infectious peritonitis virus-infected monocytes in vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2633–2642, . [CrossRef]
- Berg AL, Ekman K, Belák S, Berg M. Cellular composition and interferon-gamma expression of the local inflammatory response in feline infectious peritonitis (FIP). Vet Microbiol. 2005, 111(1-2), 15-23.
- Turin, L.; Riva, F. Toll-Like Receptor Family in Domestic Animal Species. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 28, 513–538, . [CrossRef]
- Mazaleuskaya, L.; Veltrop, R.; Ikpeze, N.; Martin-Garcia, J.; Navas-Martin, S. Protective Role of Toll-like Receptor 3-Induced Type I Interferon in Murine Coronavirus Infection of Macrophages. Viruses 2012, 4, 901–923, . [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Coban, C.; Akira, S. Innate immune response to viral infection. Cytokine 2008, 43, 336–341, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.009.
- Xu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Huang, G. Innate immune responses in RNA viral infection. Front. Med. 2020, 15, 333–346, . [CrossRef]
- Dedeurwaerder, A.; Olyslaegers, D.A.J.; Desmarets, L.M.B.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Theuns, S.; Nauwynck, H.J. ORF7-encoded accessory protein 7a of feline infectious peritonitis virus as a counteragent against IFN-α-induced antiviral response. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 393–402, . [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Hashemi, V.; Shomali, N.; Asghari, F.; Gharibi, T.; Akbari, M.; Gholizadeh, S.; Jafari, A. Innate and adaptive immune responses against coronavirus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110859–110859, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tian, J.; Li, Z.; Kang, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Yin, H.; Hu, X.; Qu, L. Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Nsp5 Inhibits Type I Interferon Production by Cleaving NEMO at Multiple Sites. Viruses 2019, 12, 43, . [CrossRef]
- Dedeurwaerder, A.; Desmarets, L.M.; Olyslaegers, D.A.; Vermeulen, B.L.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. The role of accessory proteins in the replication of feline infectious peritonitis virus in peripheral blood monocytes. Veter- Microbiol. 2013, 162, 447–455, . [CrossRef]
- Capozza, P.; Pratelli, A.; Camero, M.; Lanave, G.; Greco, G.; Pellegrini, F.; Tempesta, M. Feline Coronavirus and Alpha-Herpesvirus Infections: Innate Immune Response and Immune Escape Mechanisms. Animals 2021, 11, 3548, . [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhao, X. Natural killer cells play an important role in virus infection control: Antiviral mechanism, subset expansion and clinical application. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 227, 108727–108727, . [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, B.L.; Devriendt, B.; Olyslaegers, D.A.; Dedeurwaerder, A.; Desmarets, L.M.; Favoreel, H.W.; Dewerchin, H.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. Suppression of NK cells and regulatory T lymphocytes in cats naturally infected with feline infectious peritonitis virus. Veter- Microbiol. 2013, 164, 46–59, . [CrossRef]
- Giori, L.; Giordano, A.; Giudice, C.; Grieco, V.; Paltrinieri, S. Performances of different diagnostic tests for feline infectious peritonitis in challenging clinical cases. J. Small Anim. Pr. 2011, 52, 152–157, . [CrossRef]
- Kipar A, Meli ML. Feline infectious peritonitis: still an enigma? Vet Pathol. 2014, 51(2), 505-526.
- Singh, M.; Foster, D.; Child, G.; Lamb, W. Inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid analysis in cats: clinical diagnosis and outcome. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2005, 7, 77–93, . [CrossRef]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Comazzi, S.; Spagnolo, V.; Giordano, A. Laboratory Changes Consistent with Feline Infectious Peritonitis in Cats from Multicat Environments. J. Veter- Med. Ser. A 2002, 49, 503–510, . [CrossRef]
- Hartmann K, Binder C, Hirschberger J, Cole D, Reinacher M, Schroo S, Frost J, Egberink H, Lutz H, Hermanns W. Comparison of different tests to diagnose feline infectious peritonitis. J Vet Intern Med. 2003, 17(6), 781-790.
- Kipar, A.; Bellmann, S.; Kremendahl, J.; Köhler, K.; Reinacher, M. Cellular composition, coronavirus antigen expression and production of specific antibodies in lesions in feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 65, 243–257, . [CrossRef]
- Felten, S.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Balzer, H.-J.; Pantchev, N.; Matiasek, K.; Wess, G.; Egberink, H.; Hartmann, K. Sensitivity and specificity of a real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction detecting feline coronavirus mutations in effusion and serum/plasma of cats to diagnose feline infectious peritonitis. BMC Veter- Res. 2017, 13, 228, . [CrossRef]
- Sangl, L.; Matiasek, K.; Felten, S.; Gründl, S.; Bergmann, M.; Balzer, H.-J.; Pantchev, N.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Hartmann, K. Detection of feline coronavirus mutations in paraffin-embedded tissues in cats with feline infectious peritonitis and controls. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 21, 133–142, . [CrossRef]
- Emmler, L.; Felten, S.; Matiasek, K.; Balzer, H.-J.; Pantchev, N.; Leutenegger, C.; Hartmann, K. Feline coronavirus with and without spike gene mutations detected by real-time RT-PCRs in cats with feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 791–799, . [CrossRef]
- Felten, S.; Matiasek, K.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Sangl, L.; Herre, S.; Dörfelt, S.; Fischer, A.; Hartmann, K. Diagnostic Value of Detecting Feline Coronavirus RNA and Spike Gene Mutations in Cerebrospinal Fluid to Confirm Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Viruses 2021, 13, 186, . [CrossRef]
- Felten, S.; Hartmann, K. Diagnosis of Feline Infectious Peritonitis: A Review of the Current Literature. Viruses 2019, 11, 1068, . [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.A.; Abd-Eldaim, M.; Zika, S.E.; Mankin, J.M.; Kania, S.A. Evaluation of antibodies against feline coronavirus 7b protein for diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis in cats. Am. J. Veter- Res. 2008, 69, 1179–1182, . [CrossRef]
- Gut, M.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Huder, J.B.; Pedersen, N.C.; Lutz, H. One-tube fluorogenic reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction for the quantitation of feline coronaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 77, 37–46, . [CrossRef]
- Kiss I, Kecskeméti S, Tanyi J, Klingeborn B, Belák S. Preliminary studies on feline coronavirus distribution in naturally and experimentally infected cats. Res Vet Sci. 2000, 68(3), 237-242.
- A Herrewegh, A.; de Groot, R.J.; Cepica, A.; Egberink, H.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Rottier, P.J. Detection of feline coronavirus RNA in feces, tissues, and body fluids of naturally infected cats by reverse transcriptase PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 684–689, . [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.; Veiga, I.; Tavares, L. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic analysis of Feline Coronavirus sequences from Portugal. Veter- Microbiol. 2009, 138, 163–168, . [CrossRef]
- A Gunn-Moore, D.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.J.; A Harbour, D. Detection of feline coronaviruses by culture and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction of blood samples from healthy cats and cats with clinical feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Microbiol. 1998, 62, 193–205, . [CrossRef]
- Fish, E.J.; Diniz, P.P.V.; Juan, Y.-C.; Bossong, F.; Collisson, E.W.; Drechsler, Y.; Kaltenboeck, B. Cross-sectional quantitative RT-PCR study of feline coronavirus viremia and replication in peripheral blood of healthy shelter cats in Southern California. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 295–301, . [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Scott, F.W. Detection of feline coronaviruses in cell cultures and in fresh and fixed feline tissues using polymerase chain reaction. Veter- Microbiol. 1994, 42, 65–77, . [CrossRef]
- Herrewegh, A.; Mähler, M.; Hedrich, H.; Haagmans, B.; Egberink, H.; Horzinek, M.; Rottier, P.; de Groot, R. Persistence and Evolution of Feline Coronavirus in a Closed Cat-Breeding Colony. Virology 1997, 234, 349–363, . [CrossRef]
- Bosch BJ, van der Zee R, de Haan CA, Rottier PJ. The coronavirus spike protein is a class I virus fusion protein: structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J Virol. 2003, 77(16), 8801-8811.
- Barker, E.N.; Stranieri, A.; Helps, C.R.; Porter, E.L.; Davidson, A.D.; Day, M.J.; Knowles, T.; Kipar, A.; Tasker, S. Limitations of using feline coronavirus spike protein gene mutations to diagnose feline infectious peritonitis. Veter- Res. 2017, 48, 1–14, . [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, D.; Kwok, W.; Graham, E.; Armitage, A.; Irvine, R.; Johnston, P.; McDonald, M.; Montgomery, D.; Nicolson, L.; Robertson, E.; et al. Diagnosis of non-effusive feline infectious peritonitis by reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR from mesenteric lymph node fine-needle aspirates. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018, 21, 910–921, . [CrossRef]
- Longstaff, L.; Porter, E.; Crossley, V.J.; E Hayhow, S.; Helps, C.R.; Tasker, S. Feline coronavirus quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction on effusion samples in cats with and without feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 19, 240–245, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, NC. An overview of feline enteric coronavirus and infectious peritonitis virus infections. Feline Practice. 1995, 23, 7-20.
- Hazuchova, K.; Held, S.; Neiger, R. Usefulness of acute phase proteins in differentiating between feline infectious peritonitis and other diseases in cats with body cavity effusions. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 19, 809–816, . [CrossRef]
- Addie, D.D.; McLachlan, S.A.; Golder, M.; Ramsey, I.; Jarrett, O. Evaluation of an in-practice test for feline coronavirus antibodies. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2004, 6, 63–67, . [CrossRef]
- Hirschberger, J.; Hartmann, K.; Wilhelm, N.; Frost, J.; Lutz, H.; Kraft, W. [Clinical symptoms and diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis].. 1995, 23, 92–9.
- Lewis, K.M.; O’brien, R.T. Abdominal Ultrasonographic Findings Associated With Feline Infectious Peritonitis: A Retrospective Review of 16 Cases. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2010, 46, 152–160, . [CrossRef]
- Lamb CR. Small animal radiology and ultrasonography. A diagnostic atlas and text. J Feline Med Surg. 2004, 6(1), VI–VII . [CrossRef]
- Delaplace, M.; Huet, H.; Gambino, A.; Le Poder, S. Feline Coronavirus Antivirals: A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1150, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Kim, Y.; Liu, H.; Kankanamalage, A.C.G.; Eckstrand, C.; Groutas, W.C.; Bannasch, M.; Meadows, J.M.; Chang, K.-O. Efficacy of a 3C-like protease inhibitor in treating various forms of acquired feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 378–392, . [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and safety of the nucleoside analog GS-441524 for treatment of cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281, . [CrossRef]
- Murphy, B.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N. The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies. Veter- Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233, . [CrossRef]
- Cho A, Saunders OL, Butler T, Zhang L, Xu J, Vela JE, Feng JY, Ray AS, Kim CU. Synthesis and antiviral activity of a series of 1’-substituted 4-aza-7,9-dideazaadenosine C-nucleosides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012, 22(8), 2705-2507.
- Chang, H.-W.; de Groot, R.J.; Egberink, H.F.; Rottier, P.J.M. Feline infectious peritonitis: insights into feline coronavirus pathobiogenesis and epidemiology based on genetic analysis of the viral 3c gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 415–420, . [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Case, J.B.; Leist, S.R.; Pyrc, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Trantcheva, I.; et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, . [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, P.J.; Bannasch, M.; Thomasy, S.M.; Murthy, V.D.; Vernau, K.M.; Liepnieks, M.; Montgomery, E.; Knickelbein, K.E.; Murphy, B.; Pedersen, N.C. Antiviral treatment using the adenosine nucleoside analogue GS-441524 in cats with clinically diagnosed neurological feline infectious peritonitis. J. Veter- Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1587–1593, . [CrossRef]
- Yan VC, Pham CD, Yan MJ, Yan AJ, Khadka S, Arthur K, Ackroyd JJ, Georgiou DK, Roon LE, Bushman LR, et al. Pharmacokinetics of orally administered GS-441524 in dogs. bioRxiv, 2021, 02.04, 429674.
- Xie, J.; Wang, Z. Can remdesivir and its parent nucleoside GS-441524 be potential oral drugs? An in vitro and in vivo DMPK assessment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1607–1616, . [CrossRef]
- Kim Y, Lovell S, Tiew KC, Mandadapu SR, Alliston KR, Battaile KP, Groutas WC, Chang KO. Broad-spectrum antivirals against 3C or 3C-like proteases of picornaviruses, noroviruses, and coronaviruses. J Virol. 2012, 86(21), 11754-11762.
- Perera, K.D.; Kankanamalage, A.C.G.; Rathnayake, A.D.; Honeyfield, A.; Groutas, W.; Chang, K.-O.; Kim, Y. Protease inhibitors broadly effective against feline, ferret and mink coronaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 79–86, . [CrossRef]
- Vennema, H.; de Groot, R.J.; A Harbour, D.; Dalderup, M.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Horzinek, M.C.; Spaan, W.J. Early death after feline infectious peritonitis virus challenge due to recombinant vaccinia virus immunization. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1407–1409, . [CrossRef]
- Kim Y, Liu H, Galasiti Kankanamalage AC, Weerasekara S, Hua DH, Groutas WC, Chang KO, Pedersen NC. Reversal of the progression of fatal coronavirus infection in cats by a broad-spectrum coronavirus protease inhibitor. PLoS Pathog, 2016. 12(3), e1005531.
- Lv, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Jin, Y.; Dong, J. Effect of GS-441524 in combination with the 3C-like protease inhibitor GC376 on the treatment of naturally transmitted feline infectious peritonitis. Front. Veter- Sci. 2022, 9, 1002488, . [CrossRef]
- E Cook, S.; Vogel, H.; Castillo, D.; Olsen, M.; Pedersen, N.; Murphy, B.G. Investigation of monotherapy and combined anticoronaviral therapies against feline coronavirus serotype II in vitro. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2022, 24, 943–953, . [CrossRef]
- Doki, T.; Toda, M.; Hasegawa, N.; Hohdatsu, T.; Takano, T. Therapeutic effect of an anti-human-TNF-alpha antibody and itraconazole on feline infectious peritonitis. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1197–1206, . [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Akiyama, M.; Doki, T.; Hohdatsu, T. Antiviral activity of itraconazole against type I feline coronavirus infection. Veter- Res. 2019, 50, 5, . [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tanabe, E.; Nonaka, Y.; Uemura, M.; Tajima, T.; Ochiai, K. Ionophore Antibiotics Inhibit Type II Feline Coronavirus Proliferation In Vitro. Viruses 2022, 14, 1734, . [CrossRef]
- Ii, D.A.K.; Meujo, D.A.; Hamann, M.T. Polyether ionophores: broad-spectrum and promising biologically active molecules for the control of drug-resistant bacteria and parasites. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 109–146, . [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sato, Y.; Sasaki, T. Feline coronavirus replication is affected by both cyclophilin A and cyclophilin B. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 190–200, . [CrossRef]
- Ballin, A.C.; Schulz, B.; Helps, C.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Mueller, R.S.; Hartmann, K. Limited efficacy of topical recombinant feline interferon-omega for treatment of cats with acute upper respiratory viral disease. Veter- J. 2014, 202, 466–470, . [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Kawakami, C.; Yamada, S.; Satoh, R.; Hohdatsu, T. Antibody-Dependent Enhancement Occurs Upon Re-Infection with the Identical Serotype Virus in Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection. J. Veter- Med Sci. 2008, 70, 1315–1321, . [CrossRef]
- Hohdatsu, T.; Yamada, M.; Tominaga, R.; Makino, K.; Kida, K.; Koyama, H. Antibody-Dependent Enhancement of Feline Infectious Peritonitis Virus Infection in Feline Alveolar Macrophages and Human Monocyte Cell Line U937 by Serum of Cats Experimentally or Naturally Infected with Feline Coronavirus.. J. Veter- Med Sci. 1998, 60, 49–55, . [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Yamada, S.; Doki, T.; Hohdatsu, T. Pathogenesis of oral type I feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV) infection: Antibody-dependent enhancement infection of cats with type I FIPV via the oral route. J. Veter- Med Sci. 2019, 81, 911–915, . [CrossRef]
- Gerber, J.; Ingersoll, J.; Gast, A.; Christianson, K.; Selzer, N.; Landon, R.; Pfeiffer, N.; Sharpee, R.; Beckenhauer, W. Protection against feline infectious peritonitis by intranasal inoculation of a temperature-sensitive FIPV vaccine. Vaccine 1990, 8, 536–542, . [CrossRef]
- Fehr, D.; Holznagel, E.; Bolla, S.; Hauser, B.; Herrewegh, A.A.; Horzinek, M.C.; Lutz, H. Placebo-controlled evaluation of a modified life virus vaccine against feline infectious peritonitis: safety and efficacy under field conditions. Vaccine 1997, 15, 1101–1109, . [CrossRef]
- A Scherk, M.; Ford, R.B.; Gaskell, R.M.; Hartmann, K.; Hurley, K.F.; Lappin, M.R.; Levy, J.K.; E Little, S.; Nordone, S.K.; Sparkes, A.H. 2013 AAFP Feline Vaccination Advisory Panel Report. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2013, 15, 785–808, . [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, C.; Barlough, J.; Baldwin, C.; Scott, F. Attempted immunisation of cats against feline infectious peritonitis using canine coronavirus. Res. Veter- Sci. 1988, 45, 383–388, . [CrossRef]
- Haijema, B.J.; Volders, H.; Rottier, P.J.M. Live, Attenuated Coronavirus Vaccines through the Directed Deletion of Group-Specific Genes Provide Protection against Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3863–3871, . [CrossRef]
- Bálint, .; Farsang, A.; Szeredi, L.; Zádori, Z.; Belák, S. Recombinant feline coronaviruses as vaccine candidates confer protection in SPF but not in conventional cats. Veter- Microbiol. 2014, 169, 154–162, . [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




