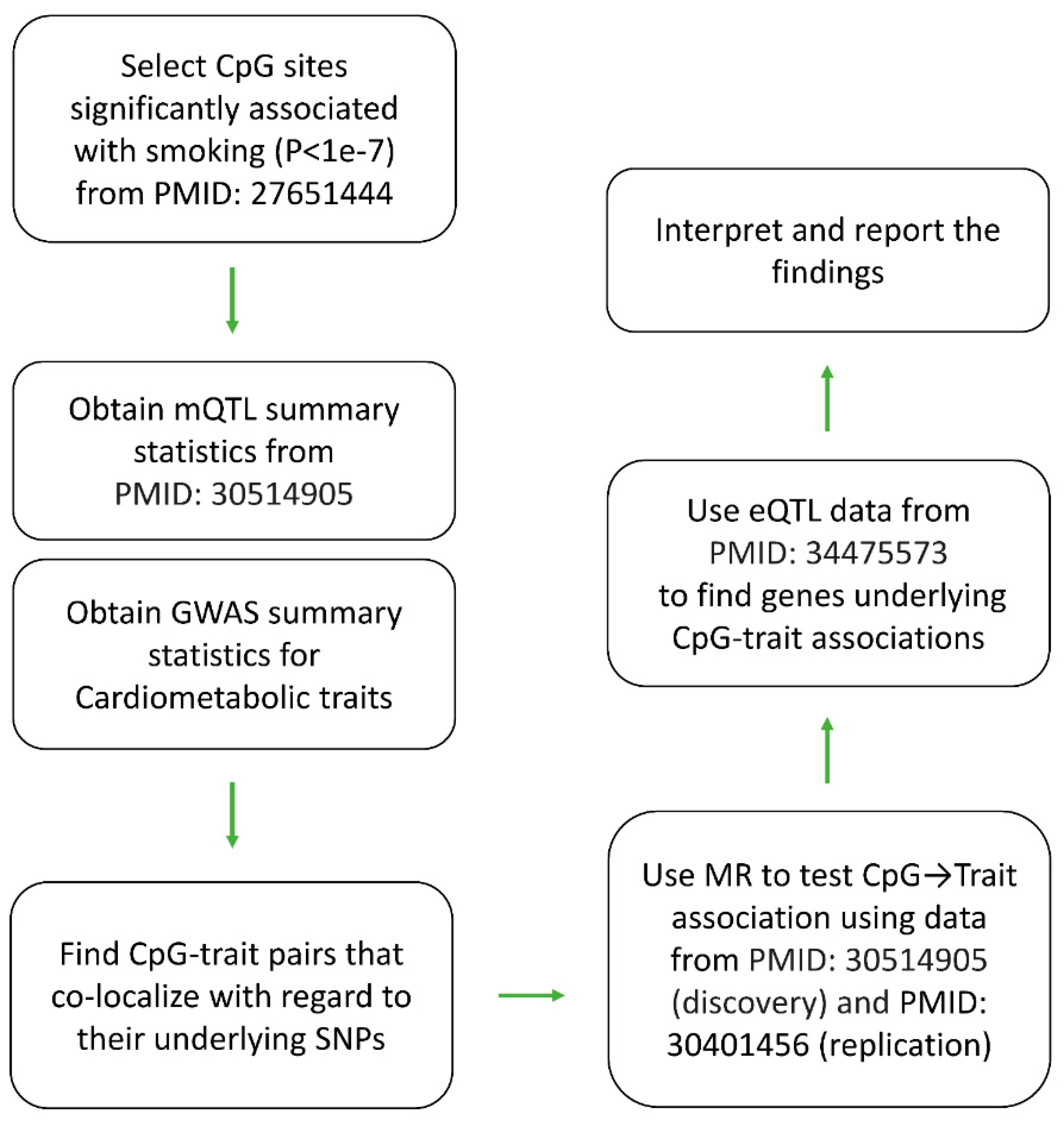
Introduction
Lifestyle choices could modify the risk of diseases partly through their impacts on the epigenome which are genomic sites that the interaction of genetics and environmental factors happen. Regular tobacco smoking is known to impact a number of phenotype conditions including cardiometabolic traits. The aim of this study was to investigate CpG methylation sites through which tobacco smoking impacts cardiometabolic traits. With the advancement of high-throughput screening methods, previous studies have already identified CpG sites that show differential levels of methylation in smokers as compared to non-smokers. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) also provided a comprehensive catalogue of biological entities (traits, biomarkers, … ) and their underlying SNPs; meanwhile, analytical tools have been developed that can infer the relation between two entities using the knowledge available at SNP level.[
1,
2] Motivated by these developments, in this study, I devised an analytical pipeline (
Figure 1) to integrate the previous findings in order to investigate epigenome paths through which smoking contributes to cardiometabolic traits.
Findings from such studies could have different applications. First, many complex phenotypes including cardiometabolic traits progress gradually over the time until they pass the liability threshold point and become diseases. As such, epigenomic biomarkers can greatly benefit preventive medicine, because they allow the health practitioners to detect the early presence of a disorder and monitor its condition over time. This is notable because epigenomic changes are reversible by changing the lifestyle. Second, at the molecular level, designing medications for every macromolecule (protein, metabolite, …) is not straightforward; however, with the development of CRISPER-based epigenome editing system, targeting the epigenome sites underlying a trait could be a universal therapeutic solution applicable to various diseases. Finally, understanding the molecular path through which a lifestyle habit causes a disease is important for biological insight and downstream research.
The nature of association between smoking, epigenome and cardiometabolic traits has been the subject of a number of studies.[
3,
4,
5] However, such studies normally measure DNA methylation and traits in the same group of subjects. Such a design does not differentiate between causation, and reverse causation. Furthermore, limited sample sizes hinder the power of such studies. Here, an analytical pipeline was used that relies on the concept of Mendelian randomization and allows integrating data from large GWAS consortia. In the Methods section, I detailed the approach.
Methods
Data sources:
Previously Joehanes et al.[
6] conducted a meta-analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation using DNA samples derived from the blood of 9,389 participants (2,433 current smokers and 6,956 never smokers). The authors identified 2,623 CpG sites that showed differential levels of methylation between smokers and never-smokers at Bonferroni threshold of P<1e
-7. In this study, I chose these sites and examined their contribution to cardiometabolic traits through the analytical pipeline described in
Figure 1.
Results
By choosing CpG sites that showed differential levels of methylation between smokers and never-smokers in Joehanes et al. study[
6], I examined their contribution to cardiometabolic traits through the SNP-based analytical pipeline described in
Figure 1. After applying rigorous statistical criteria, 11 CpG sites were identified that co-localized with cardiometabolic traits (
Table S1) and showed significant evidence of causal contribution (P<5e
-8) at both discovery and replication stages (
Table 1). The description of CpG sites and their nature of association with smoking is provided in
Table S2. By inspecting data from the EWAS atlas[
12] which is a repository of trait-epigenome modifications, I found confirmatory evidence from other studies with regard to the association of the identified CpG sites with smoking (
Table S3). Next, eQTL data from the eQTLGen consortium[
11] were integrated to investigate genes that may mediate the impact of CpG sites on the traits. In the following sections, I review the notable findings:
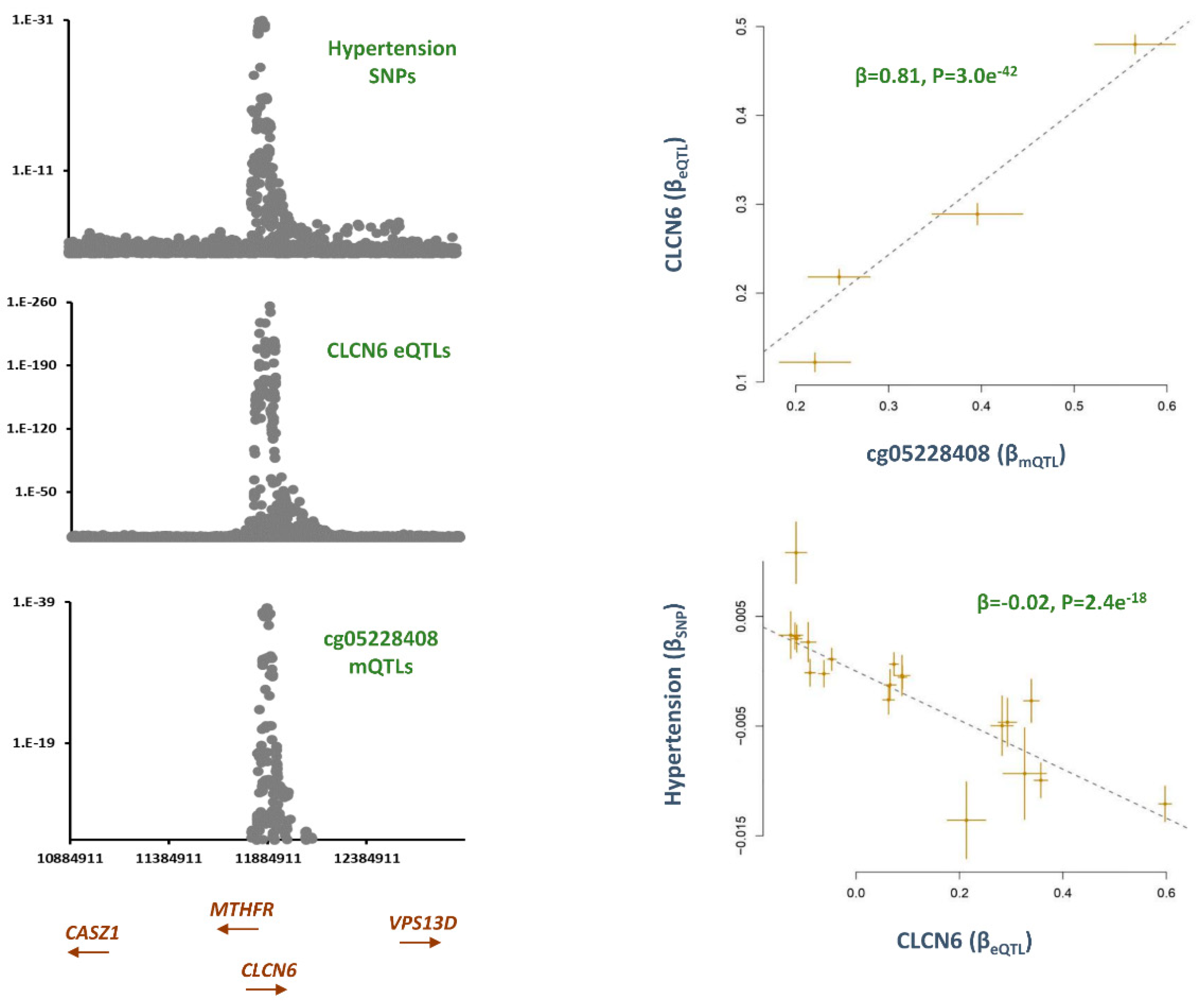
cg05228408, CLCN6
AGTRAP-PLOD1 is a well-established locus for hypertension.[
13,
14] Within this locus, I found cg05228408 undergoes hypomethylation as a result of smoking (B=-0.01, P=6.4e
-10,
Table S1) and consequently increases the risk of hypertension (
Table 1). Several genes are located within
AGTRAP-PLOD1 locus that are to varying degrees implicated in hypertension. By integrating the eQTL data, I noted GWAS signals for hypertension and cg05228408 overlap with eQTLs for
CLCN6 (
Figure 2). The outcome of MR analysis was also consistent. Namely, higher methylation at cg05228408 site was associated with higher levels of
CLCN6 (B=0.81, P=3.0e
-42,
Figure 2) and consequently this lowered the risk of hypertension (B=-0.02, P=2.4e
-18,
Figure 2).
CLCN6 encodes a protein that acts as a voltage-dependent chloride channel. This protein is primarily localized to late endosomes and functions as a chloride/proton antiporter.
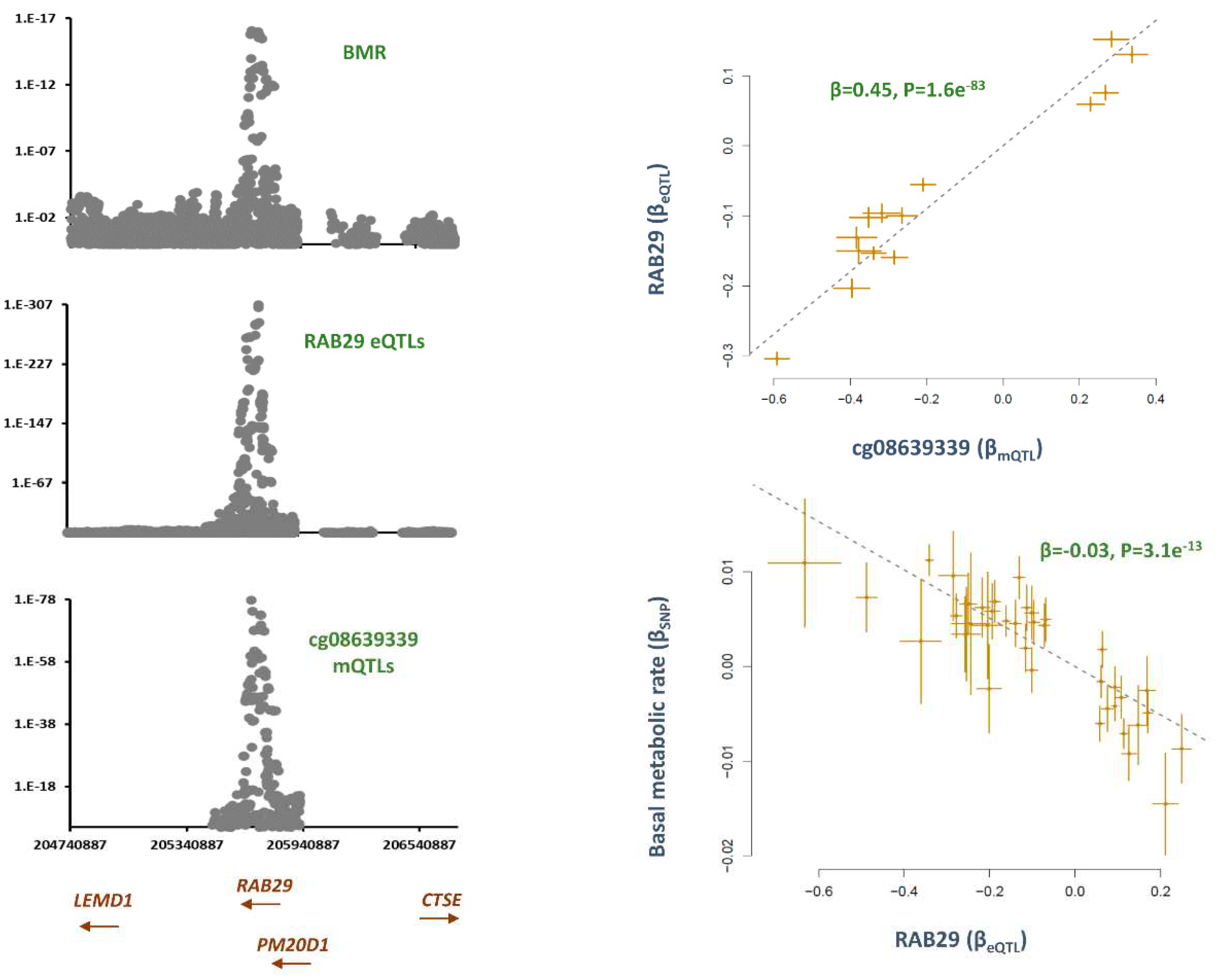
cg08639339, RAB29
Co-localizaion analysis revealed mQTLs for cg08639339 overlap with SNPs contributing to basal metabolic rate (P
SMR=1.1e
-11, P
HEIDI=0.07,
Table S1). The top SNP in this region, rs6673687-T was associated with higher basal metabolic rate (B=0.01, P=3.2e
−13) but lower methylation at cg08639339 (B =−0.60, P=1.5e
−78,
Table S1). Consistently, the MR analysis revealed that higher methylation at this site contributes to lower basal metabolic rate (B=−0.2, P=3.6e
−10,
Table 1). By investigating the eQTL data, I noted eQTLs for
RAB29 show overlap with mQTLs for cg08639339 and GWAS signals for basal metabolic rate (BMR) (
Figure 2). Higher methylation at cg08639339 site contributed to higher expression of
RAB29 (B=0.4, P=1.6e-83) and this lowered BMR (B=-0.03, P=3.1e-13,
Figure 3).
RAB29, formerly known as
RAB29 encodes a protein which is involved in lysosomal trafficking and maintenance.
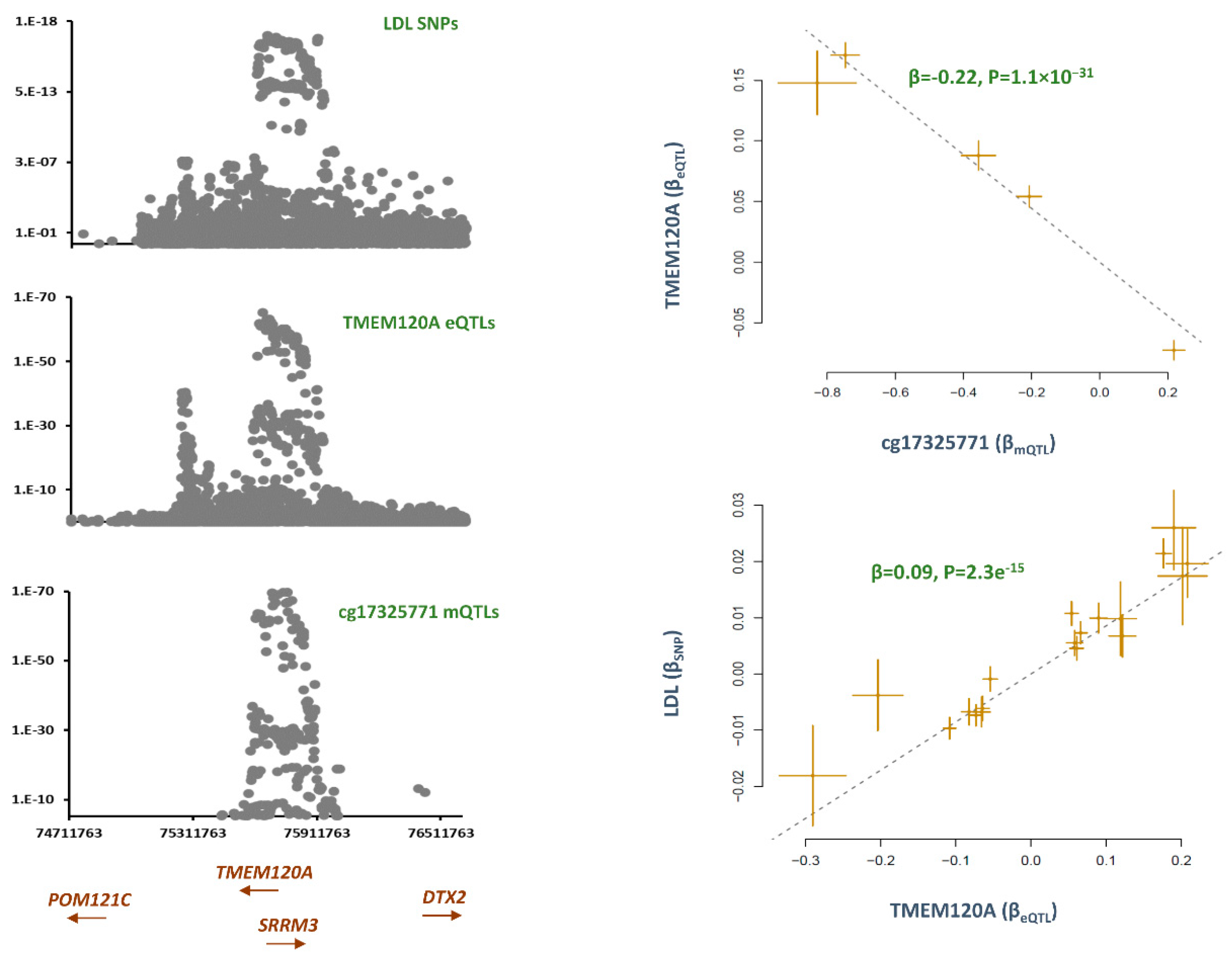
cg17325771, TMEM120A
The methylation site, cg17325771 was hypomethylated (B=-0.01, P=6.5e
-11) in smokers as compared to non-smokers. Co-localization analysis revealed mQTLs for cg17325771 overlap with SNPs contributing to LDL (P
SMR=3.4e
-14, P
HEIDI=0.013,
Table S1). Subsequently, Mendelian randomization revealed lower methylation at this site contributes to higher LDL levels (B=-0.03, P=6.9e
-14,
Table 1). By plotting the distribution of eQTLs, I found
TMEM120A to be the likely gene that mediate the impact of cg1732577 on LDL (
Figure 4). The outcome of MR analysis also revealed lower methylation at cg17325771 site is associated with higher expression of
TMEM120A (B=-0.22, P=1.1e
-31) and this consequently contributes to higher LDL level (B=0.09, P=2.3e
-15;
Figure 4). The protein encoded by
TMEM120A is a transmembrane protein induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α).
cg07029024, LTBP3
Among the identified CpG sites, cg07029024 showed the strongest association with smoking (B=0.01, P=5.5e
-21,
Table S2). I noted mQTLs for this site, colocalize with SNPs contributing to higher LDL (P
SMR=1.3e
-8, P
HEIDI=0.07,
Table S1). Mendelian randomization indicated higher methylation at this site is associated with higher heart rate (B=0.03, P=1.5e
-9,
Figure S1). The site is located on chromosome band 11q13.1. Among genes in this region, I detected an association between cg07029024 and the expression of
LTBP3. The outcome of analyses indicated as this site becomes methylated, the expression of
LTBP3 decreases (B=-0.7, P=6.7e
-21) and this contributes to higher heart rate (B=-0.04, P=3.4e-14;
Figure S1).
LTBP3 encoded protein forms a complex with transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) proteins and may be involved in their subcellular localization.
Discussion
Over the past two-decades high throughput studies have provided research community with vast amounts of findings which are continually being added to the databases. In the current time, there are efforts toward joining these data for new insights. This study is another attempt in this direction. Lifestyle habits can predispose or protect us against diseases. At the molecular level, investigating the paths through which such changes happen is important for downstream applications such as early diagnosis and intervention. In the current work, data from several studies were combined in order to investigate epigenome paths through which smoking contributes to cardiometabolic traits.
Using a discovery and replication study design and by setting stringent statistical criteria, I identified 11 CpG sites that mediated the impact of smoking on cardiometabolic traits (
Table 1). I found mQTLs for cg05228408, and eQTLs for
CLCN6 show overlap with GWAS signal for hypertension. MR analysis further underlined this finding. I noted as this site becomes hypomethylated (as observed in smokers) the expression of
CLCN6 decreases and this elevates the blood pressure. The role of
CLCN6 in blood pressure regulation is known as previous, GWAS and sequencing studies have linked mutations and variants within this gene to hypertension.[
13,
14] Recently, Klemens et al. provided functional evidence that
ClCN6 affects blood pressure by regulating golgi calcium reserves which in turn contribute to vascular smooth muscle function.[
13] Of note,
CLCN6 is within
AGTRAP-PLOD1 locus which contains several genes implicated in blood pressure regulation such as
MTHFR,
NPPA, and
NPPB; therefore, as underlined earlier[
14] further research is required to elucidate the role of this region in blood pressure regulation; however, finding from this study indicates hypermethylating the cg05228408 site could represent a novel therapeutic intervention for lowering the blood pressure. Furthermore, measuring methylation level at this site could represent a biomarker for early diagnosis of hypertension.
The analysis revealed cg08639339 mediates the impact of smoking on basal metabolic rate through
RAB29. A recent exome-sequencing study found this gene to be associated with cardiometabolic risk in ARIC cohort[
15]. The expression of
RAB29 is reported to be upregulated in presence of cholesterol biosynthesis.[
16]
RAB29 encoded protein is involved in lysosomal trafficking and maintenance and
RAB29 knock-out mice show lysosomal defects characterized by accumulation of lipids in kidney proximal tubule cells.[
17]
TMEM120A is a trans-membrane protein that is known to be expressed in fat tissue and impacts adipogenesis/fat metabolism differentiation.[
18,
19]
TMEM120A deficiency is reported to broadly impact lipid metabolism and causes lipodystrophy by altering genome topology.[
20] Here, I found the methylation site cg17325771 to mediate the impact of smoking on LDL through this gene.
cg07029024 site showed the strongest association with smoking. By integrating the eQTL data, I found
LTBP3 as the gene that mediates the impact of this site on heart rate.
LTBP3 encodes latent TGF-β binding protein-3 (LTBP-3), which belongs to a family of proteins that regulate TGF-β activity by enabling its secretion, directing it to specific sites in the extracellular matrix, and participating in its activation. It is impact on heart rate could be attributed to its cardiac function. The role of LTBP3-TGF-β signalling in differentiation of cardiac progenitor cells and formation of heart has been researched [
21]; besides,
LTBP3 pathogenic variants are reported to predispose individuals to thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections [
22].
The analytical pipeline that was used in this study relies on publicly available data and can be applied to other lifestyle traits. This underlines the value of data sharing by researchers and encourages future studies that aim to catalogue SNPs for less explored functional elements. In the long term, data from such studies will greatly facilitate functional annotations.
In this study, I took a conservative approach to lower the likelihood of false positives. Furthermore, mQTL data came from studies with relatively small sample sizes. Future studies that integrate data from larger consortiums and more dense methylation arrays are expected to provide a more comprehensive picture of epigenomic sites that mediate the impact of lifestyle traits on disease risks. In this regard, reporting trans-regulatory effects are very important, because they appear to be common[
23] but often remain unreported by the original QTL studies. In this study, we could not reveal any functional insight for a number of the identified sites. Therefore, future studies require integrating a more diverse and comprehensive set of data, in order to investigate the mechanism whereby a functional element impacts a phenotype.
In summary, here we combined findings from several studies to identify CpG sites that mediate the impact of smoking on cardiometabolic traits and investigate the underlying genes. This study provides a framework to investigate the molecular paths through which lifestyle habits modify disease risks.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Acknowledgments
This research work was enabled in part by computational resources and support provided by the Compute Ontario and the Compute Canada.
Conflicts of Interest
None
References
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Trzaskowski, M.; Maier, R.; Robinson, M.R.; McGrath, J.J.; Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; et al. Causal associations between risk factors and common diseases inferred from GWAS summary data. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligthart, S.; Steenaard, R.V.; Peters, M.J.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Sijbrands, E.J.G.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Bonder, M.J.; Hofman, A.; Franco, O.H.; et al.; BIOS consortium Tobacco smoking is associated with DNA methylation of diabetes susceptibility genes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.C.E.; Mens, M.M.J.; Kühnel, B.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Peters, A.; Prokisch, H.; Herder, C.; Grallert, H.; Kunze, S.; et al. Smoking-related changes in DNA methylation and gene expression are associated with cardio-metabolic traits. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fragou, D.; Pakkidi, E.; Aschner, M.; Samanidou, V.; Kovatsi, L. Smoking and DNA methylation: Correlation of methylation with smoking behavior and association with diseases and fetus development following prenatal exposure. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joehanes, R.; Just, A.C.; Marioni, R.E.; Pilling, L.C.; Reynolds, L.M.; Mandaviya, P.R.; Guan, W.; Xu, T.; Elks, C.E.; Aslibekyan, S.; et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Cigarette Smoking. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, A.F.; Marioni, R.E.; Shah, S.; Yang, J.; Powell, J.E.; Harris, S.E.; Gibson, J.; Henders, A.K.; Bowdler, L.; Painter, J.N.; et al. Identification of 55,000 Replicated DNA Methylation QTL. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsworth, B. , et al., The MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure. bioRxiv, 2020: p. 2020.08.10.244293. bioRxiv 2020, arXiv:2020.08.10.244293. [Google Scholar]
- Hannon, E.; Dempster, E.; Viana, J.; Burrage, J.; Smith, A.R.; Macdonald, R.; Clair, D.S.; Mustard, C.; Breen, G.; Therman, S.; et al. An integrated genetic-epigenetic analysis of schizophrenia: evidence for co-localization of genetic associations and differential DNA methylation. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, E.; Gorrie-Stone, T.J.; Smart, M.C.; Burrage, J.; Hughes, A.; Bao, Y.; Kumari, M.; Schalkwyk, L.C.; Mill, J. Leveraging DNA-Methylation Quantitative-Trait Loci to Characterize the Relationship between Methylomic Variation, Gene Expression, and Complex Traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Võsa, U. , et al., Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nature genetics 2021, 53, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zou, D.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Sang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Niu, G.; et al. EWAS Atlas: a curated knowledgebase of epigenome-wide association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D983–D988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemens, C.A.; Chulkov, E.G.; Wu, J.; Khan, A.H.; Levchenko, V.; Flister, M.J.; Imig, J.D.; Kriegel, A.J.; Palygin, O.; Staruschenko, A. Loss of Chloride Channel 6 (CLC-6) Affects Vascular Smooth Muscle Contractility and Arterial Stiffness via Alterations to Golgi Calcium Stores. Hypertension 2021, 77, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flister, M.J.; Tsaih, S.-W.; O’Meara, C.C.; Endres, B.; Hoffman, M.J.; Geurts, A.M.; Dwinell, M.R.; Lazar, J.; Jacob, H.J.; Moreno, C. Identifying multiple causative genes at a single GWAS locus. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feofanova, E.V.; Lim, E.; Chen, H.; Lee, M.; Liu, C.; Cupples, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E. Exome sequence association study of levels and longitudinal change of cardiovascular risk factor phenotypes in European Americans and African Americans from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Genet. Epidemiology 2021, 45, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helip-Wooley, A.; Thoene, J.G. Sucrose-induced vacuolation results in increased expression of cholesterol biosynthesis and lysosomal genes. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 292, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Inoue, K.; D’agati, V.D.; Fujimoto, T.; Eguchi, T.; Saha, S.; Wolozin, B.; Iwatsubo, T.; Abeliovich, A. LRRK2 and RAB7L1 coordinately regulate axonal morphology and lysosome integrity in diverse cellular contexts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J. , et al., TMEM120A is a coenzyme A-binding membrane protein with structural similarities to ELOVL fatty acid elongase. eLife 2021, 10, e71220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakou, D.G.; Heras, J.I.d.L.; Czapiewski, R.; Mouras, R.; Schirmer, E.C. TMEM120A and B: Nuclear Envelope Transmembrane Proteins Important for Adipocyte Differentiation. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0127712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapiewski, R.; Batrakou, D.G.; Heras, J.I.d.L.; Carter, R.N.; Sivakumar, A.; Sliwinska, M.; Dixon, C.R.; Webb, S.; Lattanzi, G.; Morton, N.M.; et al. Genomic loci mispositioning in Tmem120a knockout mice yields latent lipodystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cashman, T.J.; Nevis, K.R.; Obregon, P.; Carney, S.A.; Liu, Y.; Gu, A.; Mosimann, C.; Sondalle, S.; Peterson, R.E.; et al. Latent TGF-β binding protein 3 identifies a second heart field in zebrafish. Nature 2011, 474, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.-c. , et al., LTBP3 Pathogenic Variants Predispose Individuals to Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2018, 102, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikpay, M.; Ravati, S.; McPherson, R. Genome-wide screening identifies DNA methylation sites that regulate the blood proteome. Epigenomics 2022, 14, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).