Submitted:
04 May 2023
Posted:
05 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Fertilizers
2.3. Weather Conditions
2.4. Data Handling and Statistics
3. Results
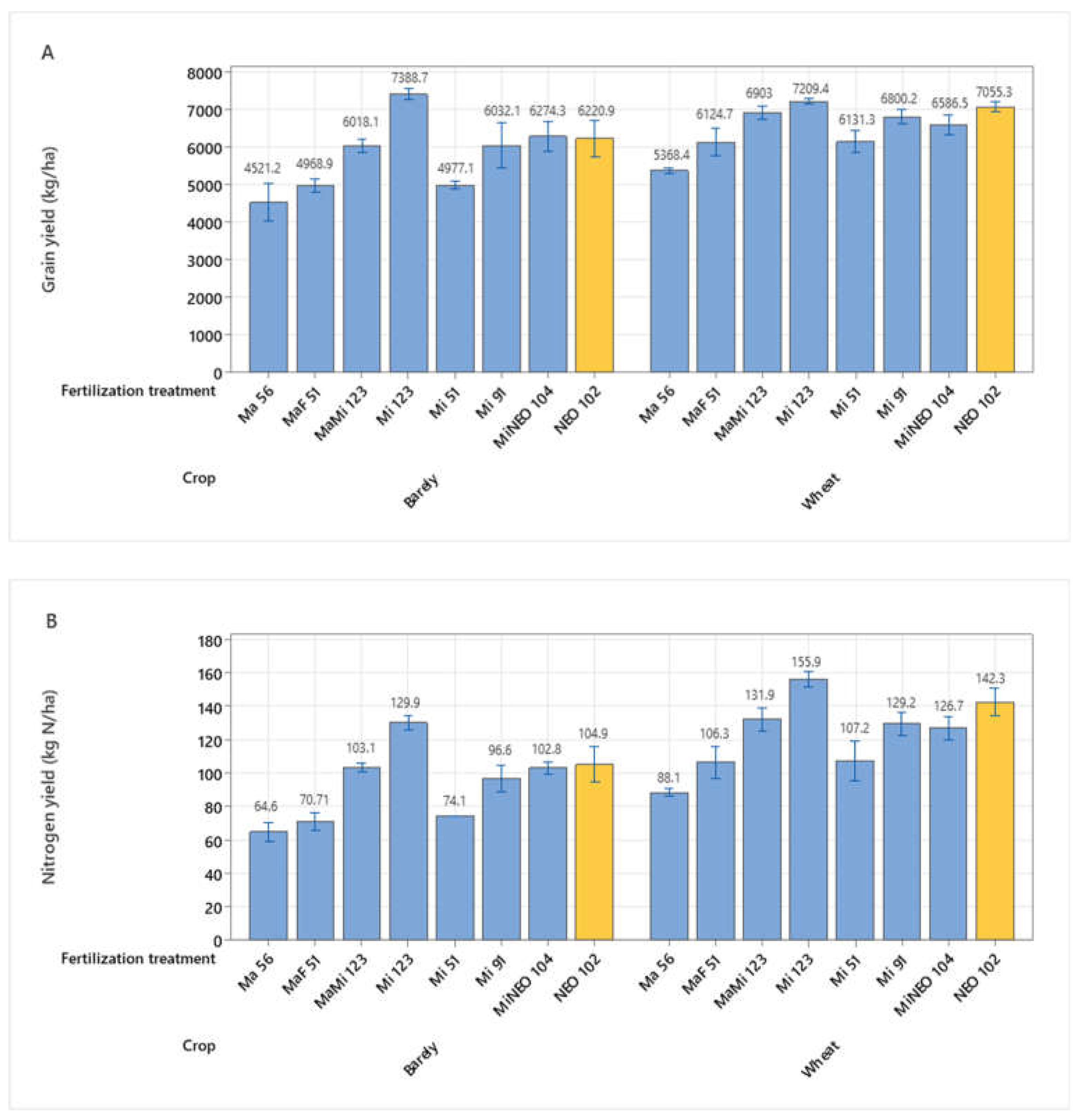
3.1. Grain Yield and Nitrogen Yield in Barley and Wheat – Series 1 2020
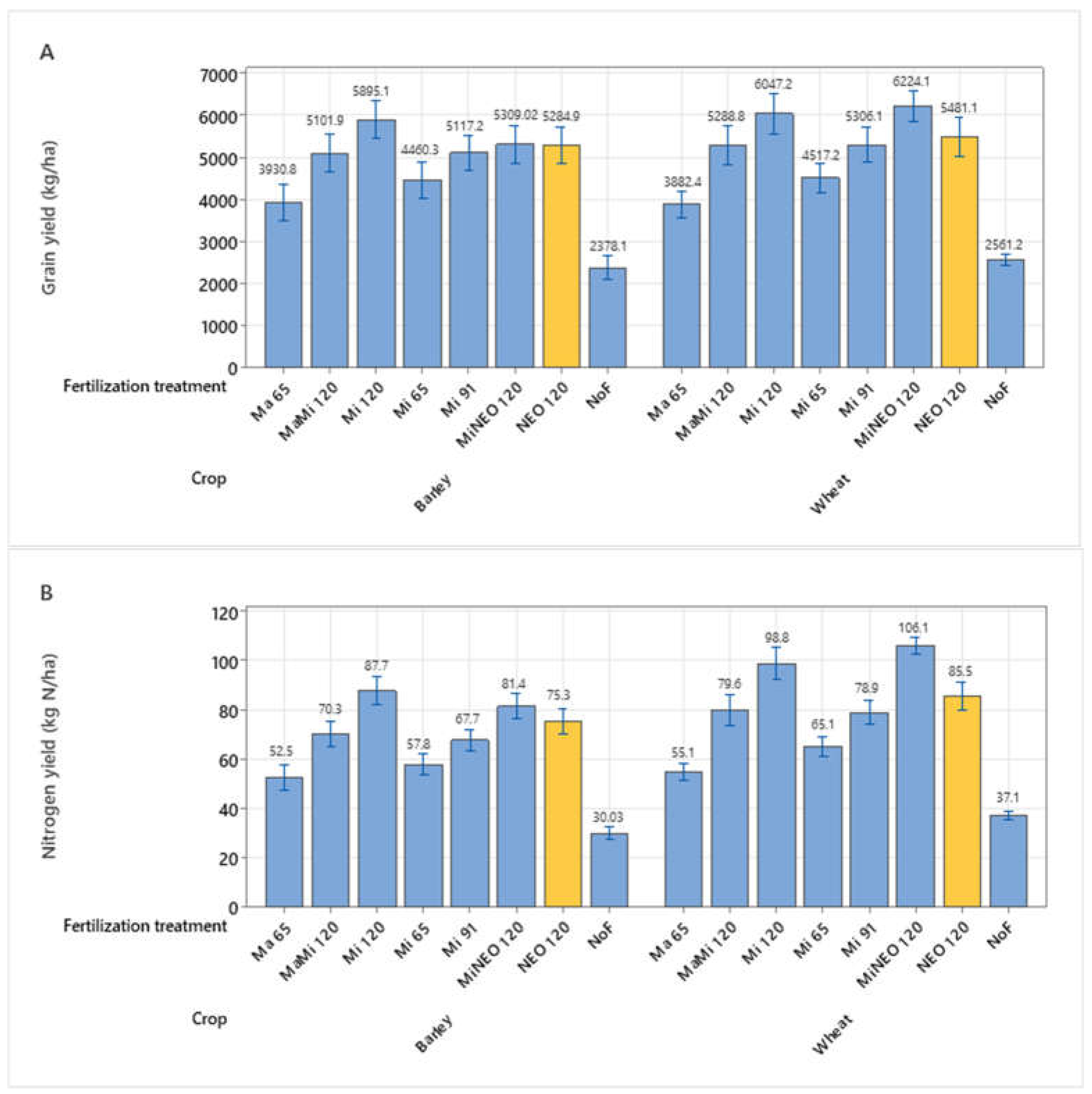
3.2 Grain Yield and Nitrogen Yield in Barley and Wheat – Series 1 2021 and 2022
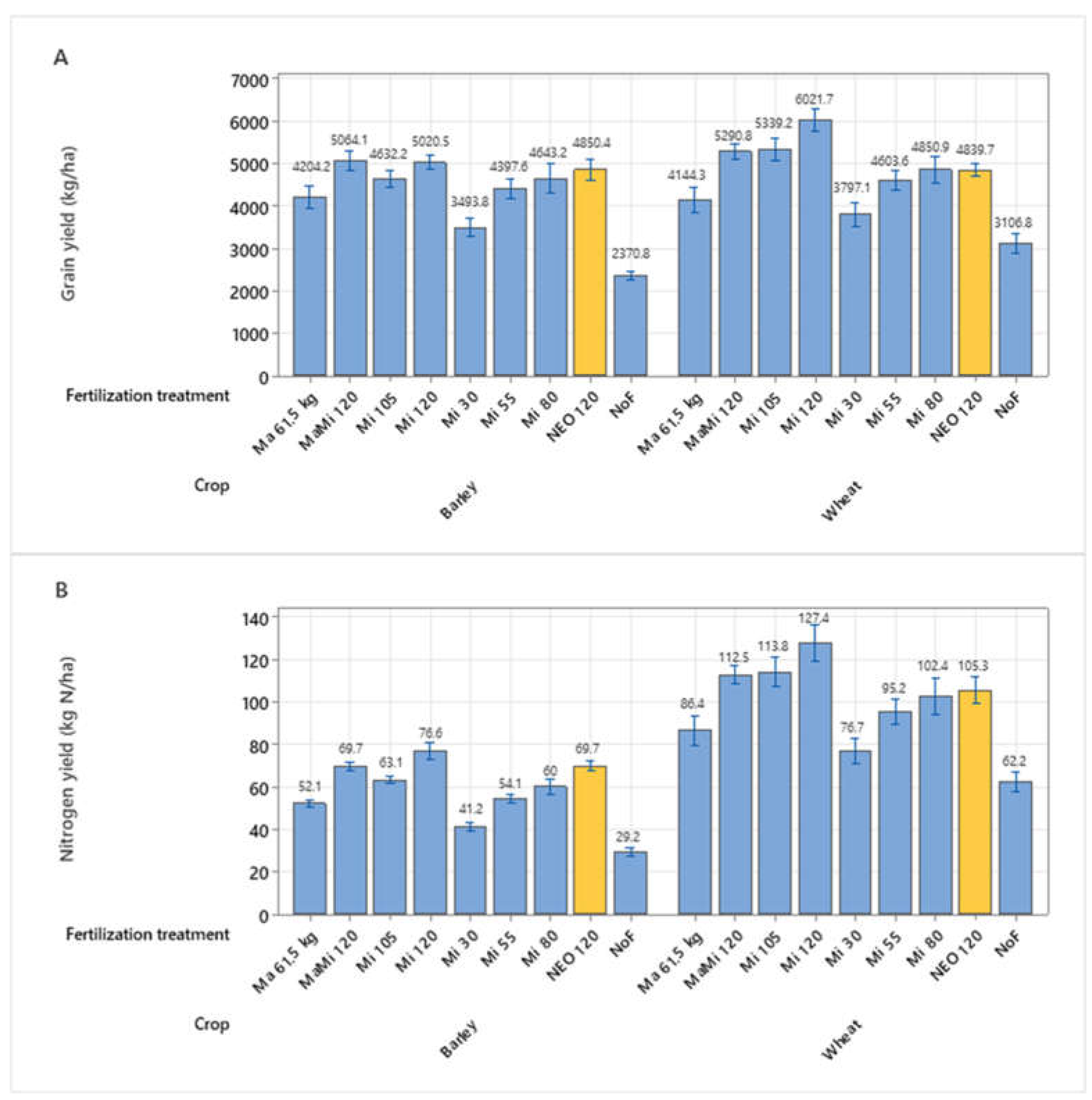
3.3. Grain Yield and Nitrogen Yield in Barley and Wheat – Series 2 2021-2022
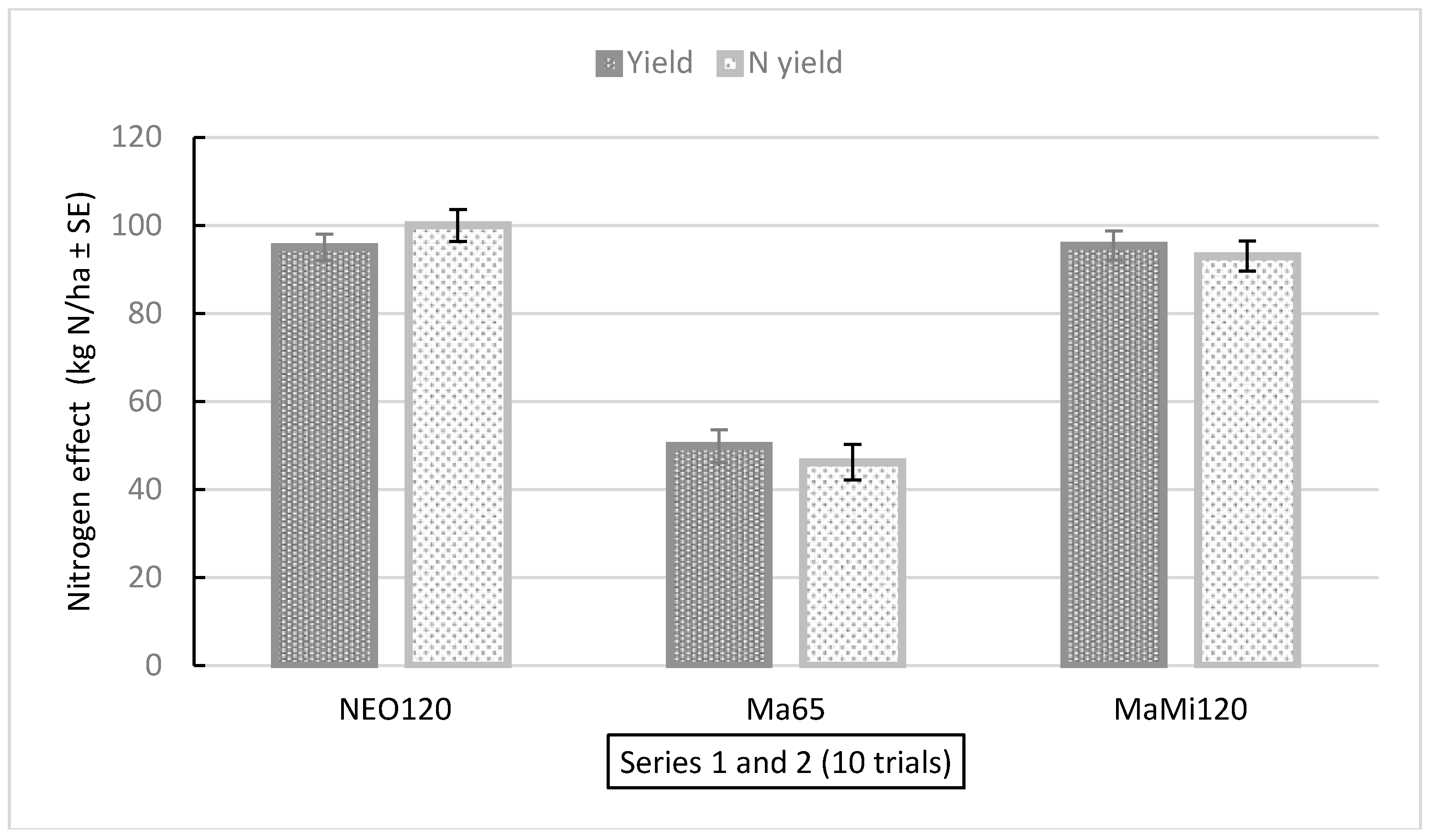
3.4. Nitrogen Effects: Results from all 10 Trials in Series 1 and 2 in 2021 and 2022
3.5. Sum Up all Average Yields
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Nitrogen-enriched fertilizer (NEO) from cattle slurry can be spread onto barley and wheat at three leaf stage without harming the plants.
- 120 kg N ha-1 in NEO yielded the same as 95 kg N ha-1 in mineral fertilizer as average to barley and spring wheat.
- On average, 39 tons ha-1 of untreated slurry supplemented with mineral fertilizers Opti-NS up to 120 kg N ha-1 yielded 5083 kg ha-1 of barley and 5290 kg ha-1 of spring wheat.
- Filtrating 39 tons of untreated slurry and running it through the N2 Applied unit gave 35 tons of NEO with 120 kg N. 35 tons ha-1 of NEO yielded 5068 kg ha-1 of barley and 5155 kg ha-1 of spring wheat.
- Filtrating the slurry increased grain yields by 756 and 447 kg ha-1 in spring wheat and barley, respectively, compared to the untreated slurry.
- 120 kg N ha-1 in mineral fertilizer yielded 5443 kg ha-1 of barley and 6123 kg ha-1 of spring wheat.
- Combining 12 kg N ha-1 in mineral fertilizer at sowing day and 108 kg N ha-1 in NEO at three leaf stage led to a higher yield in wheat than 120 kg ha-1 NEO spread at sowing day in two out of three experiment years.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The future of food and agriculture: Trends and challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy: ISBN 978-92-5-109551-5, 2017.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change and Land: IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2022.
- Vermeir, I.; Verbeke, W. Sustainable Food Consumption: Exploring the Consumer “Attitude – Behavioral Intention” Gap. Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics 2006, 19, 169–194. [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.A.; Riley, M.; Stockmann, R.; Bennett, L.; Kahl, A.; Lockett, T.; Osmond, M.; Sanguansri, P.; Stonehouse, W.; Zajac, I.; et al. Role of food processing in food and nutrition security. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2016, 56, 115–125. [CrossRef]
- Janker, J.; Mann, S.; Rist, S. Social sustainability in agriculture – A system-based framework. Journal of Rural Studies 2019, 65, 32–42. [CrossRef]
- Rajic, S.; Đorđević, V.; Tomasevic, I.; Djekic, I. The role of food systems in achieving the sustainable development goals: Environmental perspective. Business Strategy and the Environment 2022, 31, 988–1001. [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B.; Bakken, L.B.; Jensen, M.B.; Ingels, R. Plasma Activated Organic Fertilizer. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing 2019, 39, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Ingels, R.; Graves, D.B. Improving the Efficiency of Organic Fertilizer and Nitrogen Use via Air Plasma and Distributed Renewable Energy. Plasma Medicine 2015, 5, 257–270. [CrossRef]
- N2 Applied. Nitrogen Enriched Organic fertiliser. Available online: https://n2applied.com/ (accessed on July 19th, 2022).
- Mousavi, H.; Cottis, T.; Hoff, G.; Solberg, S.Ø. Nitrogen Enriched Organic Fertilizer (NEO) and Its Effect on Ryegrass Yield and Soil Fauna Feeding Activity under Controlled Conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2005.
- Mousavi, H.; Cottis, T.; Pommeresche, R.; Dörsch, P.; Solberg, S.Ø. Plasma-Treated Nitrogen-Enriched Manure Does Not Impose Adverse Effects on Soil Fauna Feeding Activity or Springtails and Earthworms Abundance. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2314.
- Mousavi, H.; Solberg, S.Ø.; Cottis, T.; Dörsch, P. Nitrogen-Enriched Organic fertilizer (NEO) elevates nitrification rates shortly after application but has no lasting effect on nitrification in agricultural soils. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hoel, B. Delt gjødsling til bygg og havre (Divided fertilization of wheat and barley); Bioforsk: https://nibio.brage.unit.no/, 2007.
- Yara. YaraMila™. Available online: https://www.yara.com/crop-nutrition/products-and-solutions/global-fertilizer-brands/yaramila/ (accessed on July 20th 2022).
- Yara International. Yara Opti NS. Available online: https://www.yara.no/gjoedsel/produkter/yarabela/yarabela-opti-ns-27-0-0-4s/ (accessed on 03.05.2023).
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research 1974, 14, 415–421. [CrossRef]
- yr.no. Weather data history. 2023.
- Strand, E. Jord-og plantekultur 2021 Forsøk i korn, olje-og belgvekster, engfrøavl og potet 2020; NIBIO: https://nibio.brage.unit.no/nibio-xmlui/handle/11250/2740694, 2021.
- Watson, C.A.; Atkinson, D.; Gosling, P.; Jackson, L.R.; Rayns, F.W. Managing soil fertility in organic farming systems. Soil Use and Management 2002, 18, 239–247. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Micallef, S.A. Safety and Practice for Organic Food; Academic Press: 2019.
- Sutton, M.; Howard, C.; Mason, K.; Brownlie, W.; Cordovil, C. Nitrogen opportunities for agriculture, food & environment. UNECE guidance document on integrated sustainable nitrogen management. 2022.
- Alcoz, M.M.; Hons, F.M.; Haby, V.A. Nitrogen Fertilization Timing Effect on Wheat Production, Nitrogen Uptake Efficiency, and Residual Soil Nitrogen. Agronomy Journal 1993, 85, 1198–1203. [CrossRef]
- Cox, W.J.; Reisenauer, H.M. Growth and ion uptake by wheat supplied nitrogen as nitrate, or ammonium, or both. Plant and Soil 1973, 38, 363–380. [CrossRef]
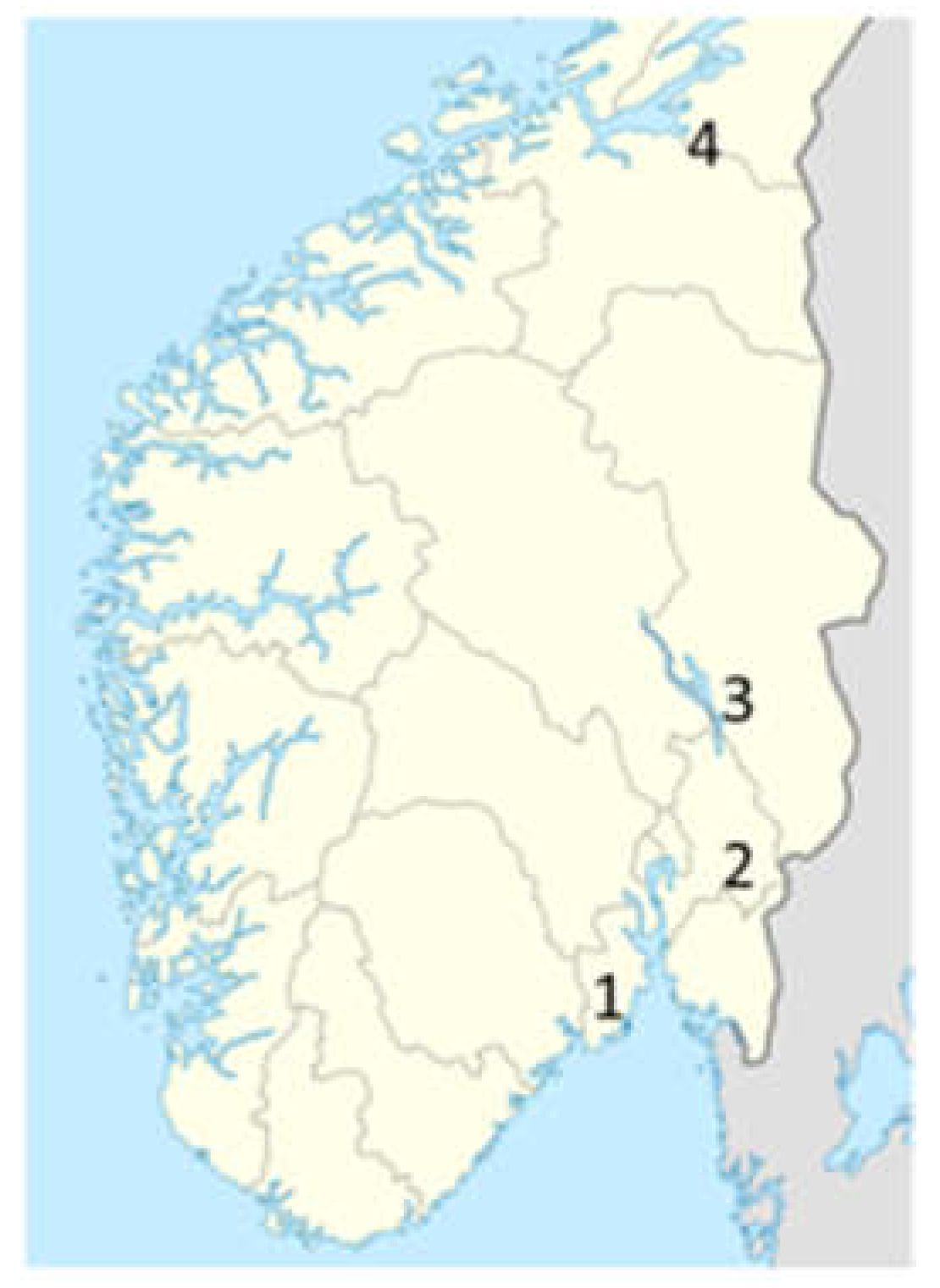
| Series | Trial | Location | Crops, Varieties, and Years | Detailed Location and Coordinates | Soil Type and Key Soil Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 3 | Barley' Salome' 2020, Wheat 'Betong' 2021, Barley' Bente' 2022 | 3 km east of Hamar (60,81830°N, 011,17968°E) | Loam, 4,5 % organic, pH 7,4 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Wheat 'Mirakel' 2020, Barley' Anita’ 2021, Wheat ‘Betong’ 2022 | 3 km east of Hamar (60,81830°N, 011,17968°E) | Loam, 4,5 % organic, pH 7,4 |
| 1 | 3 | 2 | Wheat ‘Helmi’ 2021 | 3 km west of Årnes (60,12604°N, 11,39471°E) | Silt loam, 4,0 % organic, pH 6,0 |
| 1 | 4 | 2 | Barley ‘Brage’ 2021 | 3 km west of Årnes (60,12604°N, 11,39471°E) | Silt loam, 4,0 % organic, pH 6,0 |
| 2 | 5 | 1 | Wheat ‘Betong’ 2021 | 5 km west of Tønsberg (59.294937°N, 10.318813°E) | Silt loam, 6,5 % organic, pH 6,2 |
| 2 | 5 | 1 | Wheat ‘Betong’ 2022 | 15 km north of Tønsberg (59.384537°N, 10.232651°E) | Silt loam, 4,8 % organic, pH 6,9 |
| 2 | 6 | 4 | Barley ‘Thermus’ 2021 | 4 km north of Stjørdal (7041109°N, 593647°E) | Loam, 2,7 % organic, pH 6,1 |
| 2 | 6 | 4 | Barley ‘Thermus’ 2022 | 4 km north of Stjørdal (7037496°N 597733°E) | Loam, 2,7 % organic, pH 6,1 |
| Fertilizer and Year | N-min (Kg ton-1) |
NH4+ (Kg ton-1) |
NO3- (Kg ton-1) |
NO2- (Kg ton-1) |
Total N (Kg ton-1) |
pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEO 2020 | 3.4 | 1.68 | 1.24 | 0.52 | 4.7 | 5.3 |
| Untreated 2020 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 | 7.1 |
| NEO 2021 | 3.2 | 1.5 | 0.92 | 0.8 | 4.38 | 5.59 |
| Untreated 2021 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 2.68 | 7.17 |
| NEO 2022 | 3.55 | 1.66 | 1.19 | 0.69 | Not analyzed | 5.15 |
| Untreated 2022 | 1.75 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | Not analyzed | 7.35 |
| Year | Location | Average Temperature (oC) |
Normal Temperature (oC) |
Average Precipitation (mm) |
Normal Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Hamar | 8,5 | 9,9 | 23 | 55 |
| 2021 | Tønsberg | 9,9 | 10,8 | 95,1 | 71 |
| 2021 | Årnes | 9,3 | 10,2 | 88,4 | 59 |
| 2021 | Hamar | 9,5 | 9,9 | 77,9 | 55 |
| 2021 | Stjørdal | 9,6 | 9,0 | 33,1 | 63 |
| 2022 | Tønsberg | 11,4 | 10,8 | 36,5 | 71 |
| 2022 | Hamar | 9.8 | 9,9 | 31,8 | 55 |
| 2022 | Stjørdal | 9,6 | 9,0 | 72,6 | 63 |
| Fertilization Treatment | Average Yield (kg ha-1) all Trials 2021 and 2022 Barley (5 Trials) | Average Yield (kg ha-1) all Trials 2021 and 2022 Wheat (5 Trials) | Average Yield (kg ha-1) Series 1 2021 and 2022 Barley (3 Trials) |
Average Yield (kg ha-1) Series 1 2021 and 2022 Wheat (3 Trials) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ma65 | 4068 | 4013 | 3931 | 3882 |
| MaMi120 | 5083 | 5290 | 5102 | 5289 |
| NEO120 | 5068 | 5155 | 5285 | 5481 |
| MiNEO120 | - | - | 5309 | 6224 |
| Mi120 | 5443 | 6123 | 5895 | 6047 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





