Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Study design and Procedure Steps (PS)
2.3. Physiotherapy Treatment
2.4. Fluids charactersitics, pH and glucose concentration
2.5. Drop Deposition of Synovial Fluid and Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.6. Rheological measurements of synovial fluids
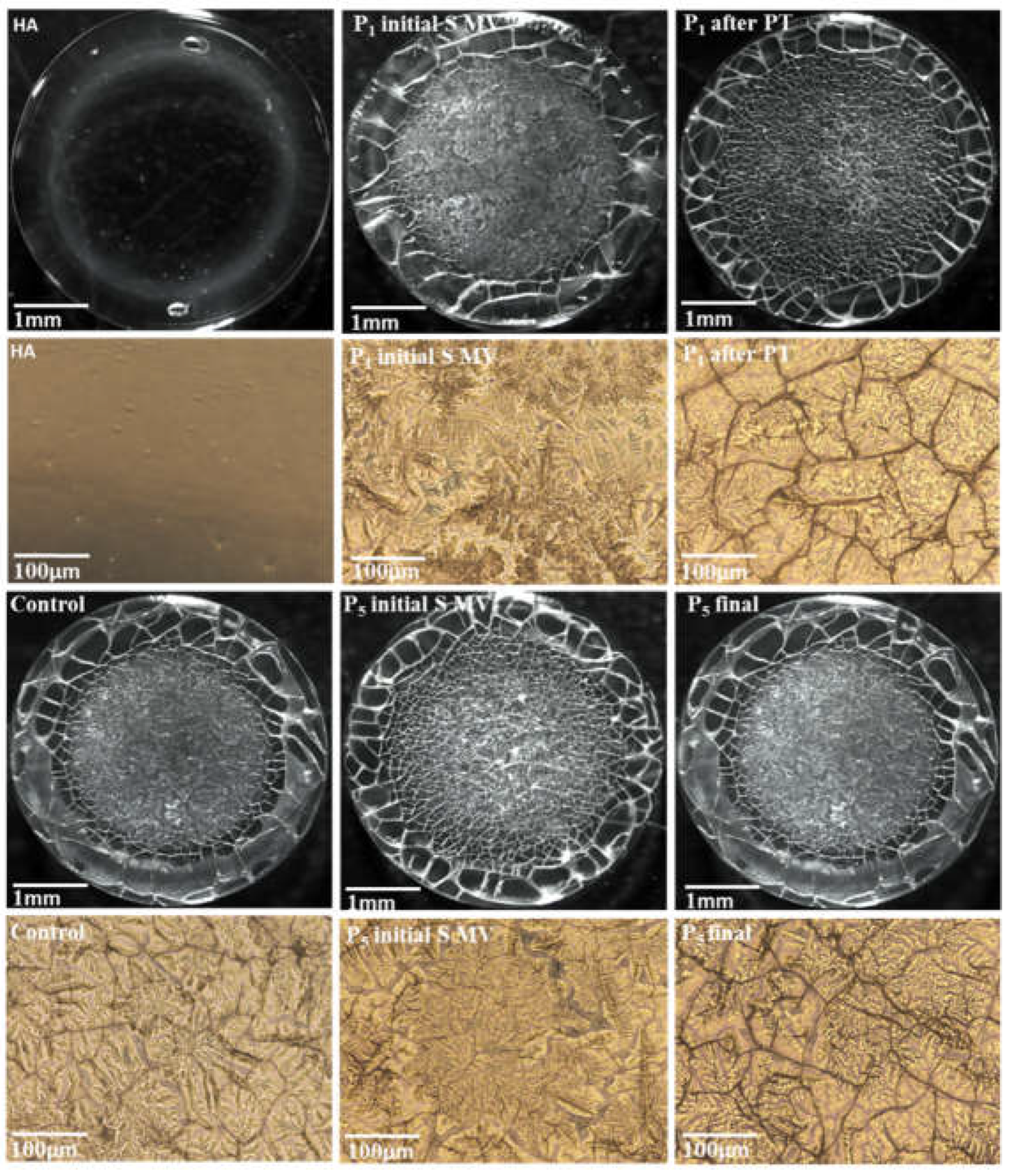
2.7. Bioadhesive characteristics
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Hyaluronic acid effect on synovial fluid characteristics
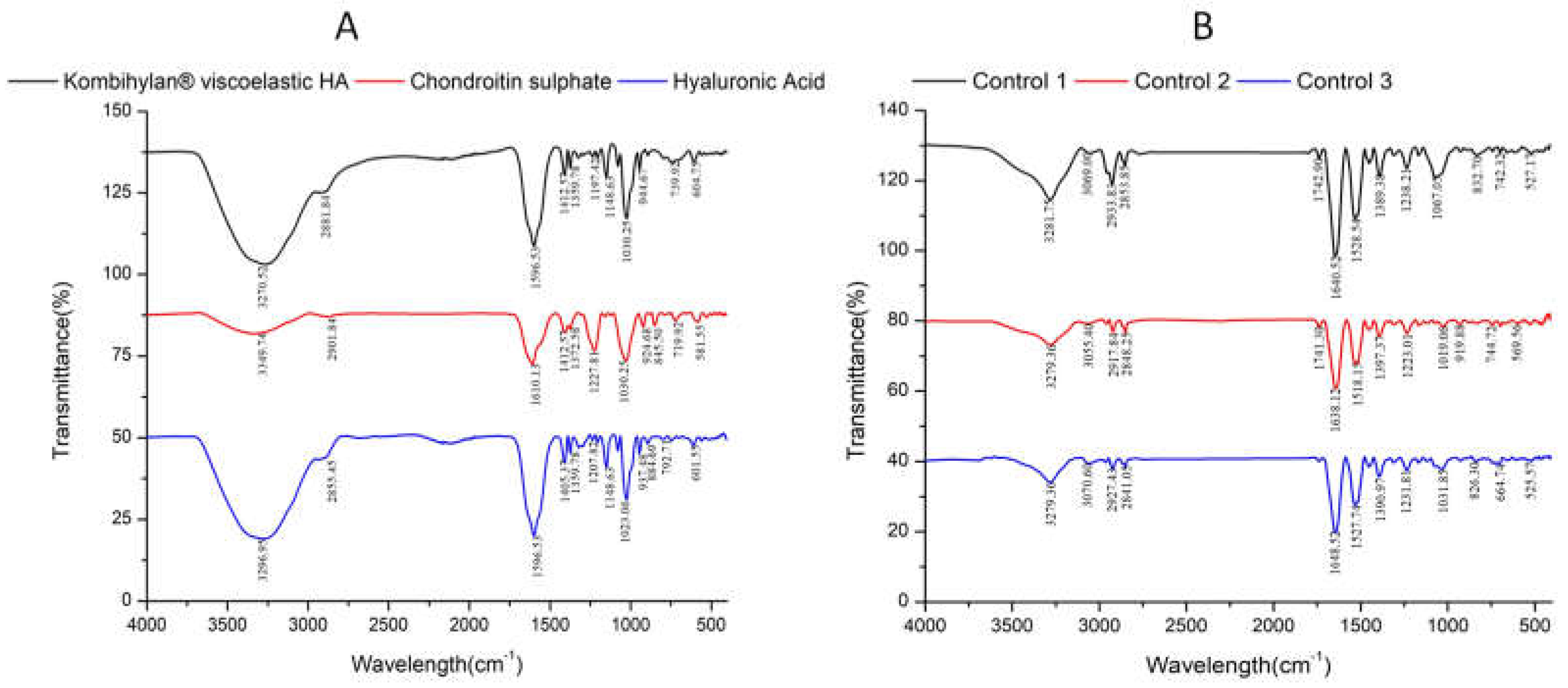
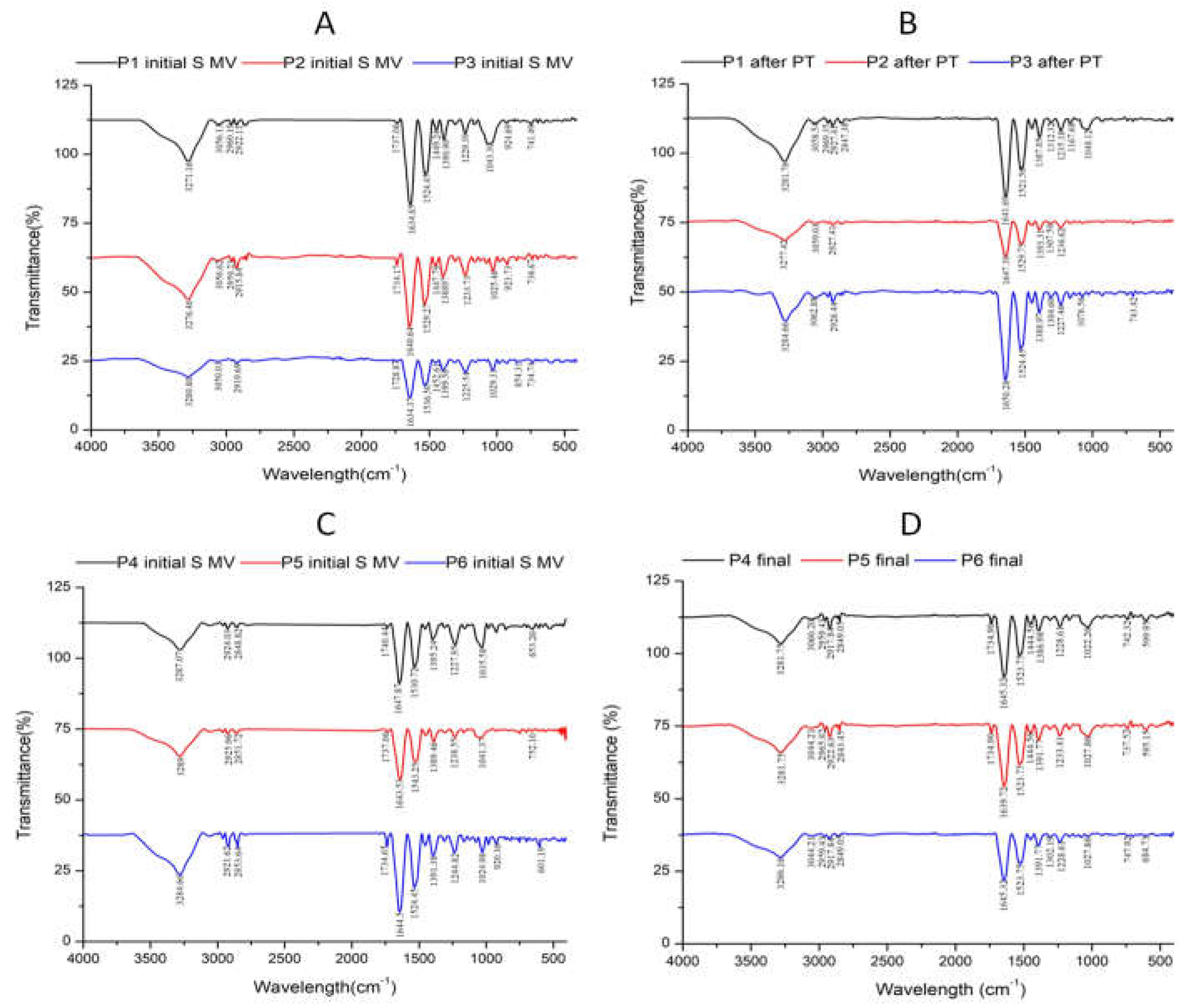
3.2. Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) data
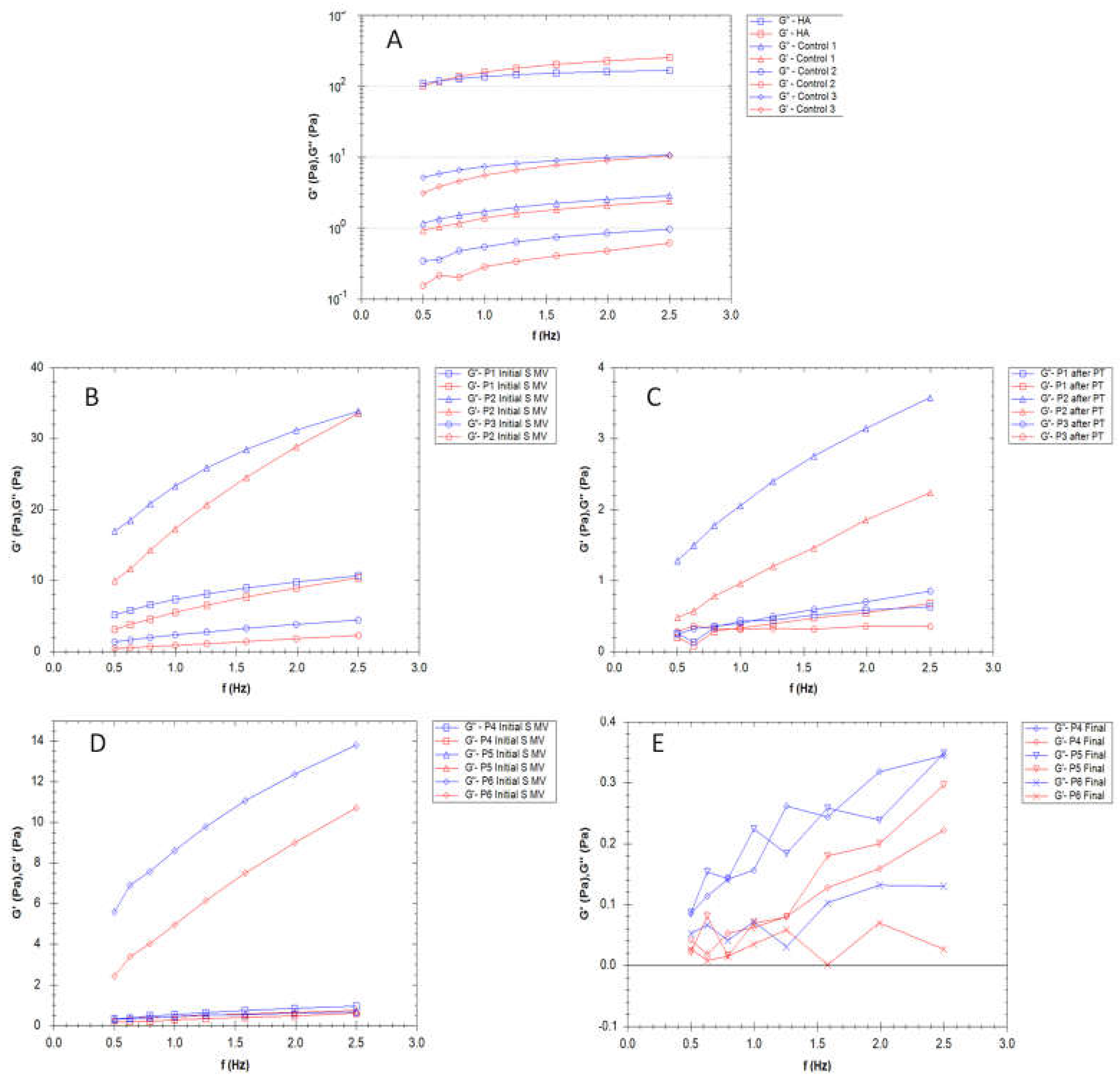
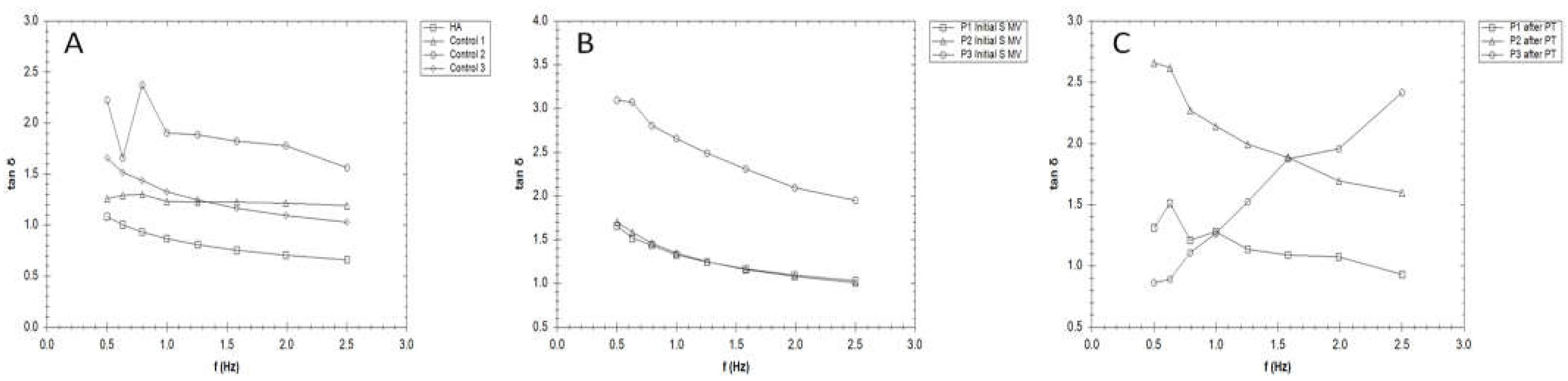
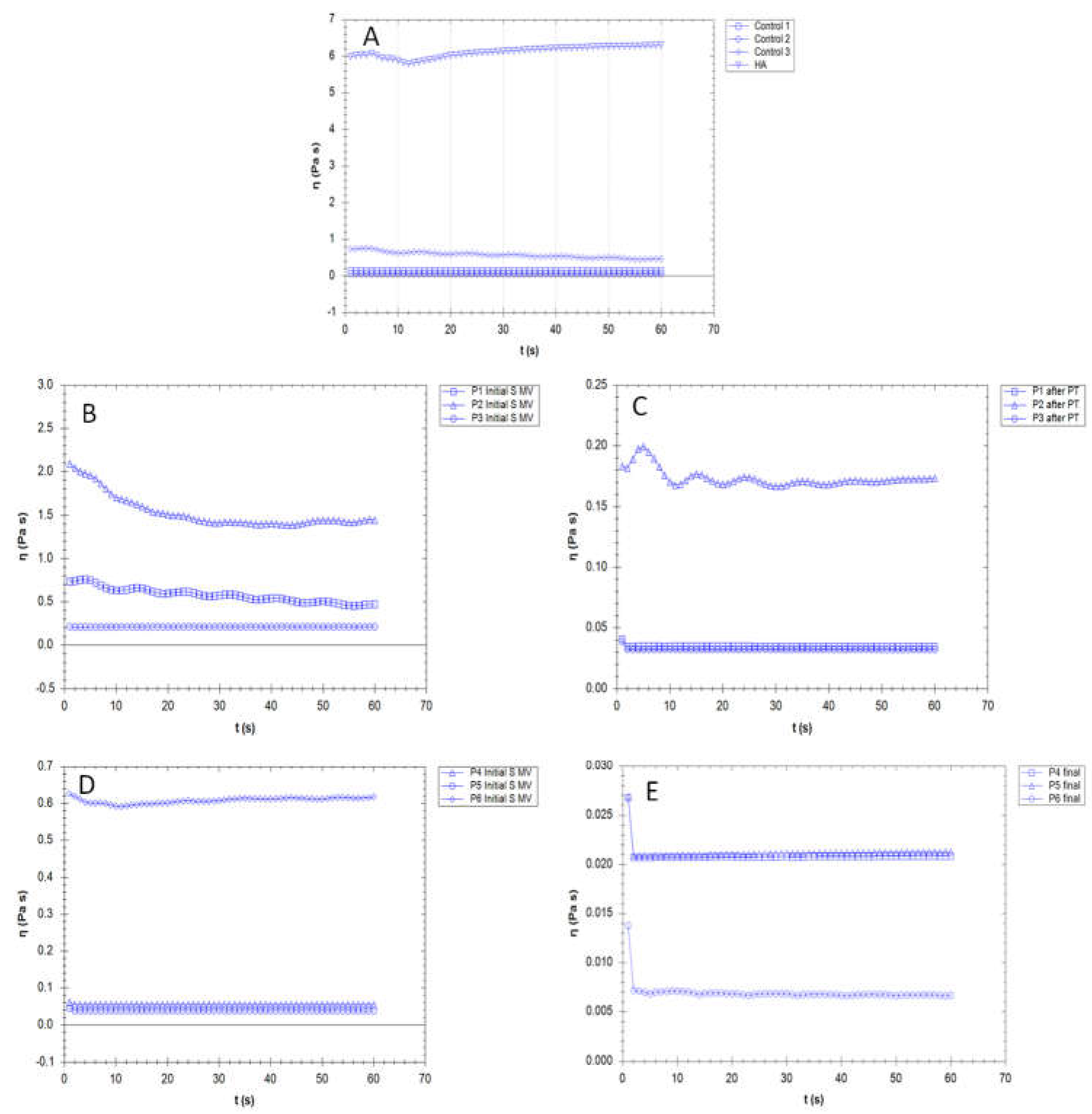
3.3. Rheological properties
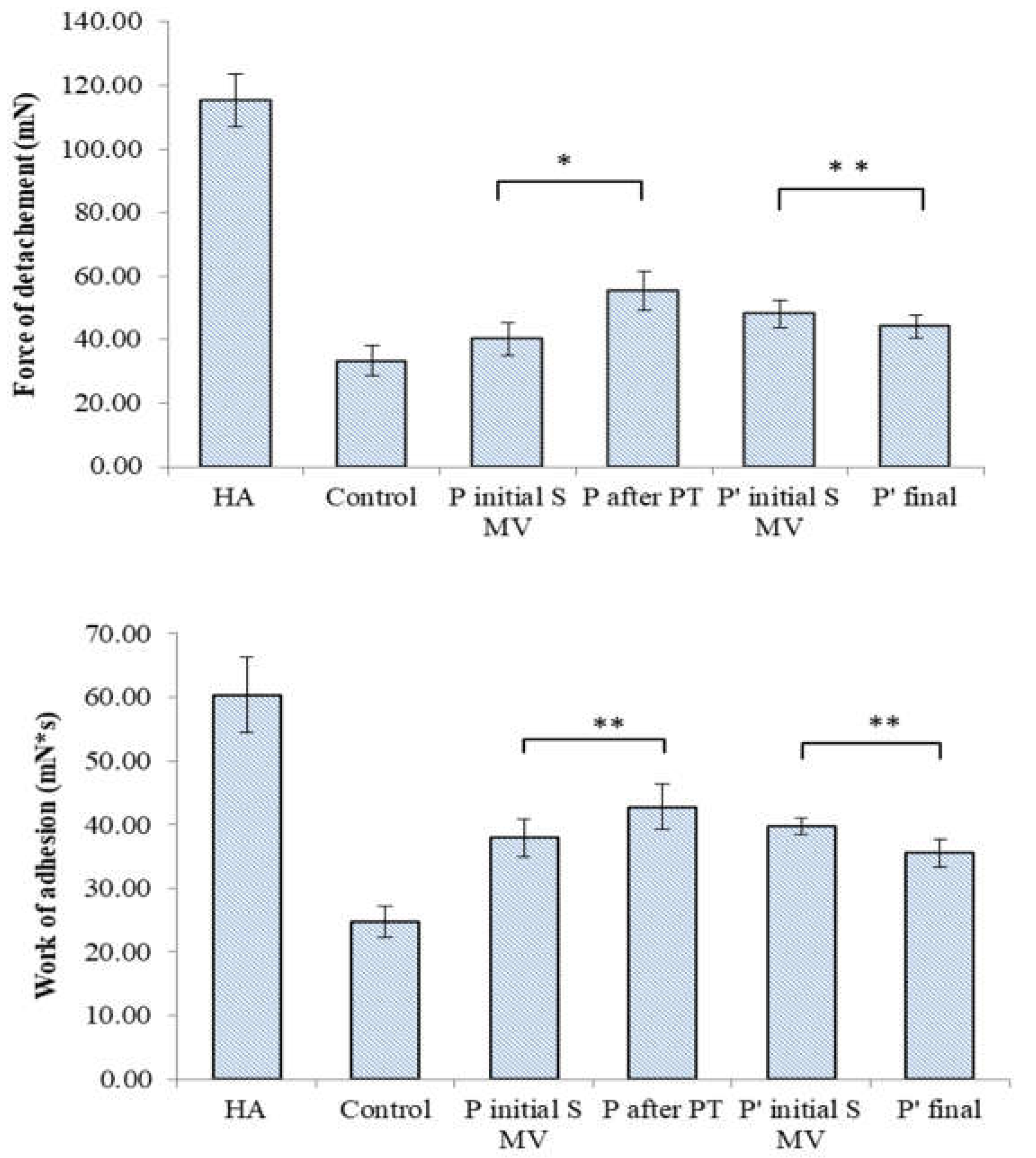
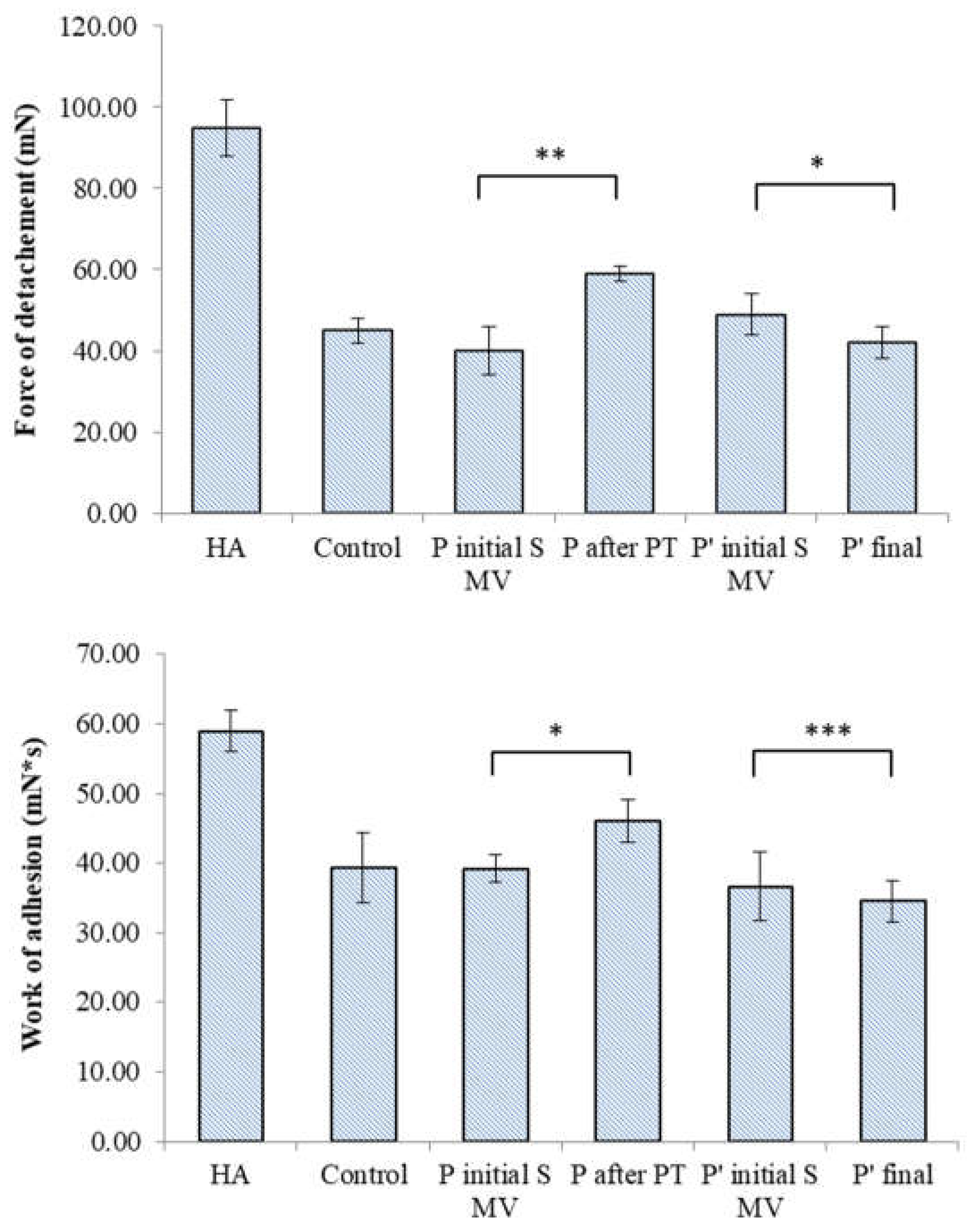
3.4. Filmogen characteristics and bioadhesive properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Eakin, G.S., Amodeo, K.L., Kahlon, R.S. Arthritis and its Public Health Burden. Dela J Public Health, 2017, 22(3), 36-44. https://doi.org/10.32481/djph.2017.03.006. [CrossRef]
- Song, P., Cui, Z., Hu, L. Applications and prospects of intra-articular drug delivery system in arthritis therapeutics. Journal of Controlled Release, 2022, 352, 946-960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.11.018. [CrossRef]
- Andreev, D., Kachler, K., Schett, G., Bozec, A. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoimmunology: The adverse impact of a deregulated immune system on bone metabolism. Bone, 2022, 162, 116468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2022.116468. [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, Kumar, L., Karthik, R., Gayathri, N., Sivasudha, T. Advancement in contemporary diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2016, 79, 52-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.02.001. [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F., Goldring, S.R., Scanzello, C.R., Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum, 2012 64(6), 1697-707. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34453. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y., Wang, X., Liao, J., Shen, J., Li, Y., Cai, Z., et al. Shear-responsive boundary-lubricated hydrogels attenuate osteoarthritis. Bioact, 2022, 16, 472–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.02.016. [CrossRef]
- Rothammer, B., Marian, M., Rummel, F., Schroeder, S., Uhler, M., Kretzer, J.P., Tremmel, S., Wartzack, S., Rheological behavior of an artificial synovial fluid – influence of temperature, shear rate and pressure. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2021, 115, 104278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104278. [CrossRef]
- Kujath, P., Michelsen, A. Wounds - from physiology to wound dressing. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2008, 105(13), 239-48. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2008.0239. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Chanmee, T.; Itano, N. Hyaluronan: Metabolism and Function. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111525. [CrossRef]
- McNary, S.M., Athanasiou, K.A., Reddi, A.H. Engineering lubrication in articular cartilage. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012, 18(2), 88-100. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2011.0394. [CrossRef]
- Bhuanantanondh, P. Rheological study of viscosupplements and synovial fluid in patients with osteoarthritis, J. Med. Biol. Eng, 2012, 32(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.5405/jmbe.834. [CrossRef]
- Bannuru, R.R.; Osani, M.C.; Vaysbrot, E.E.; Arden, N.K.; Bennell, K.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Kraus, V.B.; Lohmander, L.S.; Abbott, J.H.; Bhandari, M.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1578–1589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2019.06.011. [CrossRef]
- Chae, K.J.; Choi, M.J.; Kim, K.Y.; Ajayi, F.F.; Chang, I.S.; Kim, I.S. Osteoarthritis: Careand Management: Clinical Guideline; National Institute for Health and Care, 2014, Available online: https://www.nice.org (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Onu, I.; Matei, D.; Sardaru, D.-P.; Cascaval, D.; Onu, A.; Gherghel, R.; Serban, I.L.; Mocanu, G.D.; Iordan, D.A.; Murariu, G.; et al. Rehabilitation of Patients with Moderate Knee Osteoarthritis Using Hyaluronic Acid Viscosupplementation and Physiotherapy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ app12063165. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation: Mechanisms, Clinical Application and Evidence. Rev Pain. 2007, 1(1),7-11. https://doi.org/10.1177/204946370700100103. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Henry, JL. Changes in Abeta non-nociceptive primary sensory neurons in a rat model of osteoarthritis pain. Mol Pain. 2010, 6:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-6-37. [CrossRef]
- Iijima, H.; Eguchi, R.; Shimoura, K.; Yamada, K.; Aoyama, T.; Takahashi, M. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Improves Stair Climbing Capacity in People with Knee Osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7294. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64176-0. [CrossRef]
- Cherian, J.J.; Harrison, P.E.; Benjamin, S.A.; Bhave, A.; Harwin, S.F.; Mont, M.A. Do the Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Knee Osteoarthritis Pain and Function Last? J. Knee Surg. 2016, 29, 497–501. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1566735. [CrossRef]
- Do Carmo Almeida, T.C.; Dos Santos Figueiredo, F.W.; Barbosa Filho, V.C.; de Abreu, L.C.; Fonseca, F.L.A.; Adami, F. Effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on Proinflammatory Cytokines: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 1094352. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1094352. [CrossRef]
- Tábata Cristina do Carmo Almeida, et. al "Reduction on Proinflammatory Cytokines after Application of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) in Patients with a Breast Cancer: A Nonrandomized, Open, and Single-Arm Study Protocol with Paired Analysis", Mediators of Inflammation, 2022, 8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1350813. [CrossRef]
- Johns LD. Nonthermal effects of therapeutic ultrasound: the frequency resonance hypothesis. J Athl Train. 2002, 37(3), 293-299.
- Paliwal, S.; Mitragotri, S. Therapeutic Opportunities in Biological Responses of Ultrasound. Ultrasonics, 2008, 48, 271–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2008.02.002. [CrossRef]
- Schumann, D.; Kujat, R.; Zellner, J.; Angele, M.K.; Nerlich, M.; Mayr, E.; Angele, P. Treatment of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cellswith Pulsed Low Intensity Ultrasound Enhances the Chondrogenic Phenotype In Vitro. Biorheology, 2006, 43, 431–443.
- Rothenberg, J.B.; Jayaram, P.; Naqvi, U.; Gober, J.; Malanga, G.A. The Role of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound on Cartilage Healing in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. PM&R, 2017, 9, 1268–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.05.008. [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Perrucini, P.D.; Poli-Frederico, R.C.; de Almeida Pires-Oliveira, D.A.; Dragonetti Bertin, L.; Beltrão Pires, F.; Shimoya- Bittencourt, W.; Martins Santos, V.; Medeiros Coelho, J.; Franco de Oliveira, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Healing Effects of Pulsed Ultrasound Therapy on Fibroblasts. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabilit. 2019, 99, 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000001265. [CrossRef]
- Smoot, B.; Chiavola-Larson, L.; Lee, J.; Manibusan, H.; Allen, D.D. Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy on Pain and Swelling in Women with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer Surviv. 2015, 9, 287–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-014-0411-1. [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, B.; Viharos, L.; Gervain, M.; Gálfi, M. The Effect of Low-Level Laser in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2009, 27, 577–584. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2008.2297. [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, J.B.; Jayaram, P.; Naqvi, U.; Gober, J.; Malanga, G.A. The Role of Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound on Cartilage Healing in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. PM&R 2017, 9, 1268–1277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.05.008. [CrossRef]
- Stausholm, MB.; Naterstad, IF.; Joensen, J. et al. Efficacy of low-level laser therapy on pain and disability in knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2019, 9,10,031142. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-031142. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, G.M.; Cunha, J.E.; Cunha, T.M.; Martinho, L.B.; Castro, P.A.T.S.; Oliveira, F.F.B.; Cunha, F.Q.; Ramalho, F.S.; Salvini, T.F. Clinical-like Cryotherapy Improves Footprint Patterns and Reduces Synovial Inflammation in a Rat Model of Post-Traumatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14518. doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50958-8.
- Garcia, C.; Karri, J.; Zacharias, NA.; Abd-Elsayed, A. Use of Cryotherapy for Managing Chronic Pain: An Evidence-Based Narrative. Pain Ther. 2021 10(1),81-100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-020-00225-w. [CrossRef]
- Dantas, L.O.; Jorge, A.E.; Regina Mendes da Silva Serrão, P.; Aburquerque-Sendín, F.; de Fatima Salvini, T. Cryotherapy Associated with Tailored Land-Based Exercises for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Protocol for a Double-Blind Sham-Controlled Randomised Trial. BMJ. 2020, 10, e035610. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035610. [CrossRef]
- Ziemann, E.; Olek, RA.; Kujach, S., et al. Five-day whole-body cryostimulation, blood inflammatory markers, and performance in high-ranking professional tennis players. J Athl Train. 2012, 47, 664–672. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-47.6.13. [CrossRef]
- Jastrząbek, R.; Straburzyńska-Lupa, A.; Rutkowski, R.; Romanowski, W. Effects of different local cryotherapies on systemic levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and clinical parameters in active rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2013, 33, 2053–2060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2692-5. [CrossRef]
- Lubkowska, A.; Szyguła, Z.; Chlubek, D.; Banfi, G. The effect of prolonged whole-body cryostimulation treatment with different amounts of sessions on chosen pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines levels in healthy men. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011, 71, 419–425. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365513.2011.580859. [CrossRef]
- Brophy, Robert H. MD; Fillingham, Yale A. MD. AAOS Clinical Practice Guideline Summary: Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee (Nonarthroplasty), Third Edition. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2022, 30(9), e721-e729. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-21-01233. [CrossRef]
- American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Osteoarthritis Guidelines. Recommendations for the medical management of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: 2000 update. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43(9), 1905–15.
- Pendleton, A.; Arden, N.; Dougados, M.; Doherty, M.; Bannwarth, B.; Bijlsma, JW., et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of knee osteoarthritis: report of a task force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT) Ann Rheum Dis. 2000, 59(12), 936–44. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.59.12.936. [CrossRef]
- Bosomworth, NJ. Exercise and knee osteoarthritis: benefit or hazard? Can Fam Physician. 2009, 55(9),871-8.
- Li, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; et al. The effects of resistance exercise in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 947–959. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269215515610039. [CrossRef]
- DeVita, P.; Aaboe, J.; Bartholdy, C.; Leonardis, J. M.; Bliddal, H.; and Henriksen, M. Quadriceps-strengthening exercise and quadriceps and knee biomechanics during walking in knee osteoarthritis: A two-Centre randomized controlled trial. Clin. Biomech. 2018, 59, 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2018.09.016. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Wan, Q.; and Shang, S. The effects of a home-based exercise intervention on elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis: a quasi-experimental study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20,160. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2521-4. [CrossRef]
- Samut, G.; Dincer, F.; and Ozdemir, O. The effect of isokinetic and aerobic exercises on serum interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels, pain, and functional activity in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 919–924. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2015.1038425. [CrossRef]
- Miyaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, A.; Kadoya, Y.; Ohashi, H.; Yamano, Y. and Takaoka, K. Biochemical change in joint fluid after isometric quadriceps exercise for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1063-4584(02)00372-2. [CrossRef]
- Garg, T., Goyal, A.K. Biomaterial-based scaffolds– current status and future directions. Expert. Opin. Drug. Deliv, 2014, 11, 767-789. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2014.891014. [CrossRef]
- Brako, F., Thorogate, R., Mahalingam, S., Abraham, B.R., Craig, DQM., Edirisinghe, M. Mucoadhesion of Progesterone-Loaded Drug Delivery Nanofiber Constructs. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10, 13381-13389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b03329. [CrossRef]
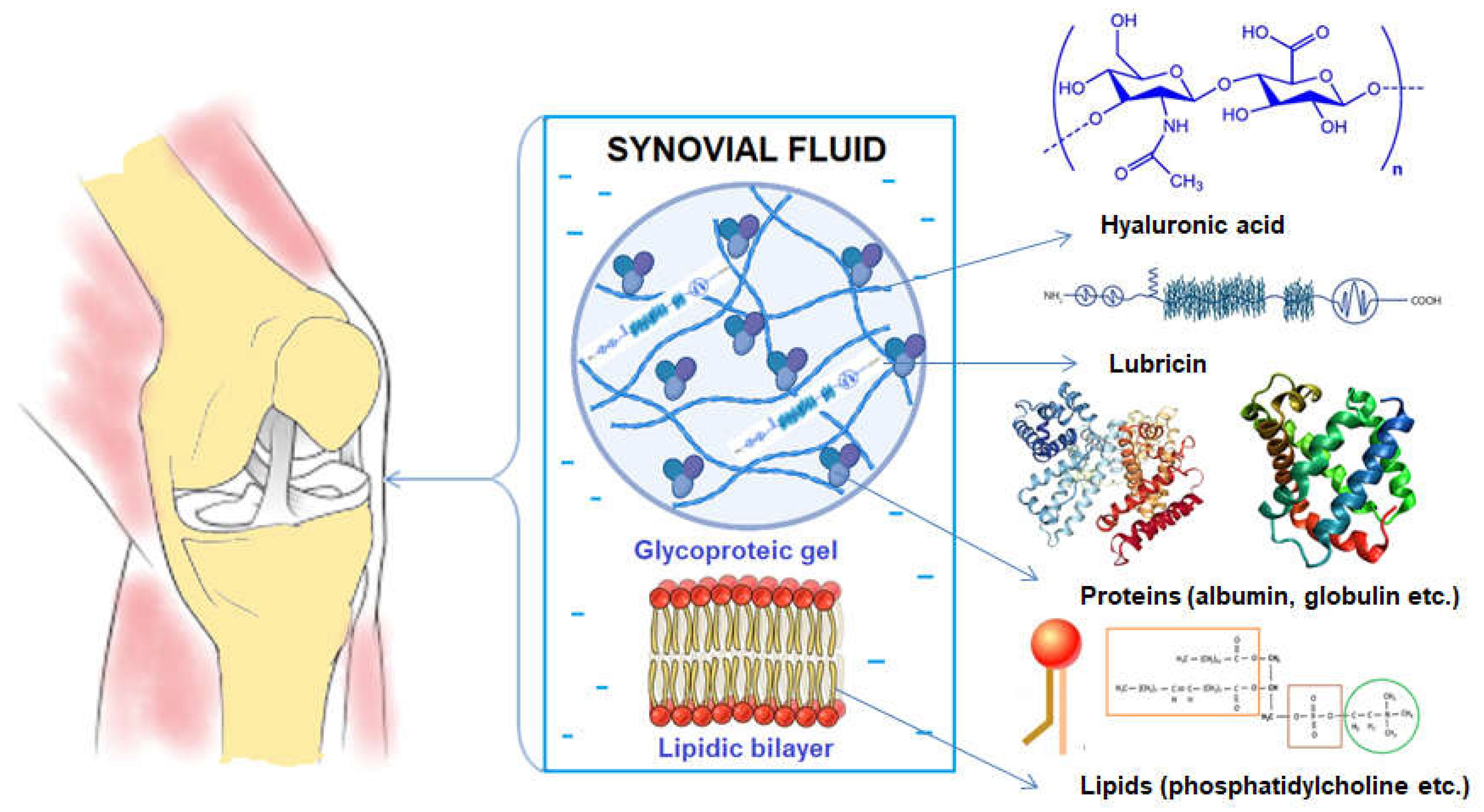
- Tamer, T.M., Hyaluronan and synovial joint: function, distribution and healing. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2013, 6(3), 111-25. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2013-0019. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhong, H.; Peng, W.; Xie, R. Recent Advances in Understanding the Role of Cartilage Lubrication in Osteoarthritis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26206122. [CrossRef]
- Ucm. R., Aem. M., Lhb. Z., Kumar, V., Taherzadeh, M.J., Garlapati, V.K., Chandel A.K. Comprehensive review on biotechnological production of hyaluronic acid: status, innovation, market and applications. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(4), 9645-9661. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2057760. [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. Hyaluronic Acid and Controlled Release: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 2649. Doi: 3390/molecules25112649. [CrossRef]
- Prekasan, D., Saju, K.K., Review of the tribological characteristics of synovial fluid. Procedia Technology, 2016, 25, 1170 – 1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.08.235. [CrossRef]
- Bennike, T., Ayturk, U., Haslauer, C.M., Froehlich, J.W., Proffen, B.L., Barnaby, O., Birkelund, S., Murray, M.M., Warman, M.L., Stensballe, A. and Steen, H. A normative study of the synovial fluid proteome from healthy porcine knee joints. J Proteome Res, 2014, 13(10), 4377-87. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr500587x. [CrossRef]
- Jay, G.D., Waller, K.A. The biology of lubricin: near frictionless joint motion. Matrix Biol, 2014, 39, 17-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2014.08.008. [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. Advances in Tribology of Lubricin and Lubricin-Like Synthetic Polymer Nanostructures. Lubricants 2018, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants6020030. [CrossRef]
- Stamm, J., Weißelberg, S., Both, A., Failla, A.V., Nordholt, G., Büttner, H., Linder, S., Aepfelbacher, M., Rohde, H.. Development of an artificial synovial fluid useful for studying Staphylococcus epidermidis joint infections. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022, 29;12:948151. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.948151. [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, Y.T., Mandelin, J., Li, T.F., Salo, J., Lassus, J., Liljestrom, M., Hukkanen, M., Takagi, M., Virtanen, I., Santavirta, S. Acidic cysteine endoproteinase cathepsin K in the degeneration of the superficial articular hyaline cartilage in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46:953–960. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10185. [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.F., Ma, Y., Jang, H., Jerban, S., Tang, Q., Searleman, A.C., Meyer, R.S., Du, J., Chang, E.Y. AcidoCEST-UTE MRI Reveals an Acidic Microenvironment in Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci., 2022, 18;23(8):4466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084466. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G. Alteration of Metabolic Pathways in Osteoarthritis. Metabolites. 2019, 9, 9(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9010011. [CrossRef]
- Malek, S., Marini, F., McClure, J.T. Evaluation of longterm storage on infrared spectral patterns of serum and synovial fluid of dogs with knee, Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2022, 30, S81-S438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2022.02.135. [CrossRef]
- Das Gupta, S., Shrestha, P., Ali, N., Turkiewicz, A., Hughes, V., Jonsson, E., Tjornstand, J., Neuman, P., €Onnerfjord, P., Rieppo, L., Englund, M., Saarakkala, S. Infrared spectroscopy can detect end-stage steoarthritis from human synovial fluid: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2022, 30, S81-S438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2022.02.135. [CrossRef]
- Leone, G., Consumi, M., Lamponi, S., Magnani, A. New hyaluronan derivative with prolonged half-life for ophthalmic formulation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2012, 88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.047. [CrossRef]
- Carole, E. Schante., Zuber, G., Herlin, C., Vandamme, T.F. Chemical modifications of hyaluronic acid for the synthesis of derivatives for a broad range of biomedical application, Carbohydrate Polymers, 2011, 85(3), 469-489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.03.019. [CrossRef]
- Alberto-Silva, C., Malheiros, F.B.M. & Querobino, S.M. Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy, physicochemical and biochemical properties of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine as supporting information on quality control of raw materials. Futur J Pharm Sci, 2020, 6, 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00120-3. [CrossRef]
- Esmonde-White, K.A., Mandair, G.S., Raaii, F., Jacobson, J.A., Miller, B.S., Urquhart, A.G., Roessler, B.J., Morris, M.D. Raman spectroscopy of synovial fluid as a tool for diagnosing osteoarthritis. J Biomed Opt, 2009, 14(3), 034013. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3130338. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Hunter, D.J., Jin, X., Ding, C. The importance of synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis: current evidence from imaging assessments and clinical trials. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 2018, 26(2), 65-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2017.11.015. [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K., Percival, S.S., Conrad, B.P., Seay, A.N., Montero, C., Vincent, K.R. Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Viscosupplementation on Synovial Fluid Inflammation in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study. Open Orthop J, 2013, 20, 7, 378-84. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874325001307010378. [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, H.R., Paul, C., Hitchon, C.A., El-Gabalawy, H., Zonay, L., Clayburne, G., Sieck, M., Schwab, E. Hyaluronate effects on synovium and synovial fluid. A prospective blinded study in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2006, 14(5), 501-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2005.11.013. [CrossRef]
- Neville, A., Morina, A., Liskiewicz, T. and Yan, Y. Synovial joint lubrication – does nature teach more effective engineering lubrication strategies? Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2007, 221(10), 1223-1230. ISSN 0954-4062, doi: 0.1243/09544062JMES72. [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, M., Manjoo, A., Shaw, P., Niazi, F., Rosen, J. A Comparison Between Rheological Properties of Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Preparations and Reported Human Synovial Fluid. Adv Ther, 2018, 35(4), 523-530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-018-0688-y. [CrossRef]
- Hlavácek, M. The thixotropic effect of the synovial fluid in squeeze-film lubrication of the human hip joint. Biorheology, 2001, 38(4), 319-34.
- Logerstedt, D.S., Ebert, J.R., MacLeod, T.D., Heiderscheit, B.C., Gabbett, T.J., Eckenrode, B.J. Effects of and Response to Mechanical Loading on the Knee. Sports Med, 2022, 52(2), 201-235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-021-01579-7. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, L., Bhattacharjee, M., Ahmad, S. et al. Differential proteomic analysis of synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients. Clin Proteom, 2014, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1559-0275-11-1. [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M., Davydova, V.N., Volod’ko, A.V. Mucoadhesive Marine Polysaccharides, Mar. Drugs, 2022, 20(522). https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080522. [CrossRef]
- Suchaoin, W., Bonengel, S., Griessinger, J.A., Pereira de Sousa, I., Hussain, S., Huck, C.W., Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Novel bioadhesive polymers as intra-articular agents: Chondroitin sulfate-cysteine conjugates. Eur J Pharm Biopharm, 2016, 101, 25-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.01.006. [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A., Greimel, A. Thiomers. American J. Drug Deliv, 2005, 3, 141-154. doi.org/10.2165/ 00137696-200503030-00001.
- Smart, J.D. The basics and underlying mechanisms of mucoadhesion. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev, 2005, 57, 1556–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2005.07.001. [CrossRef]
| No | Encoded | Characteristics | Solid (mg/ml) |
pH | Colour | Clarity | Glucose* (mg/dL) |
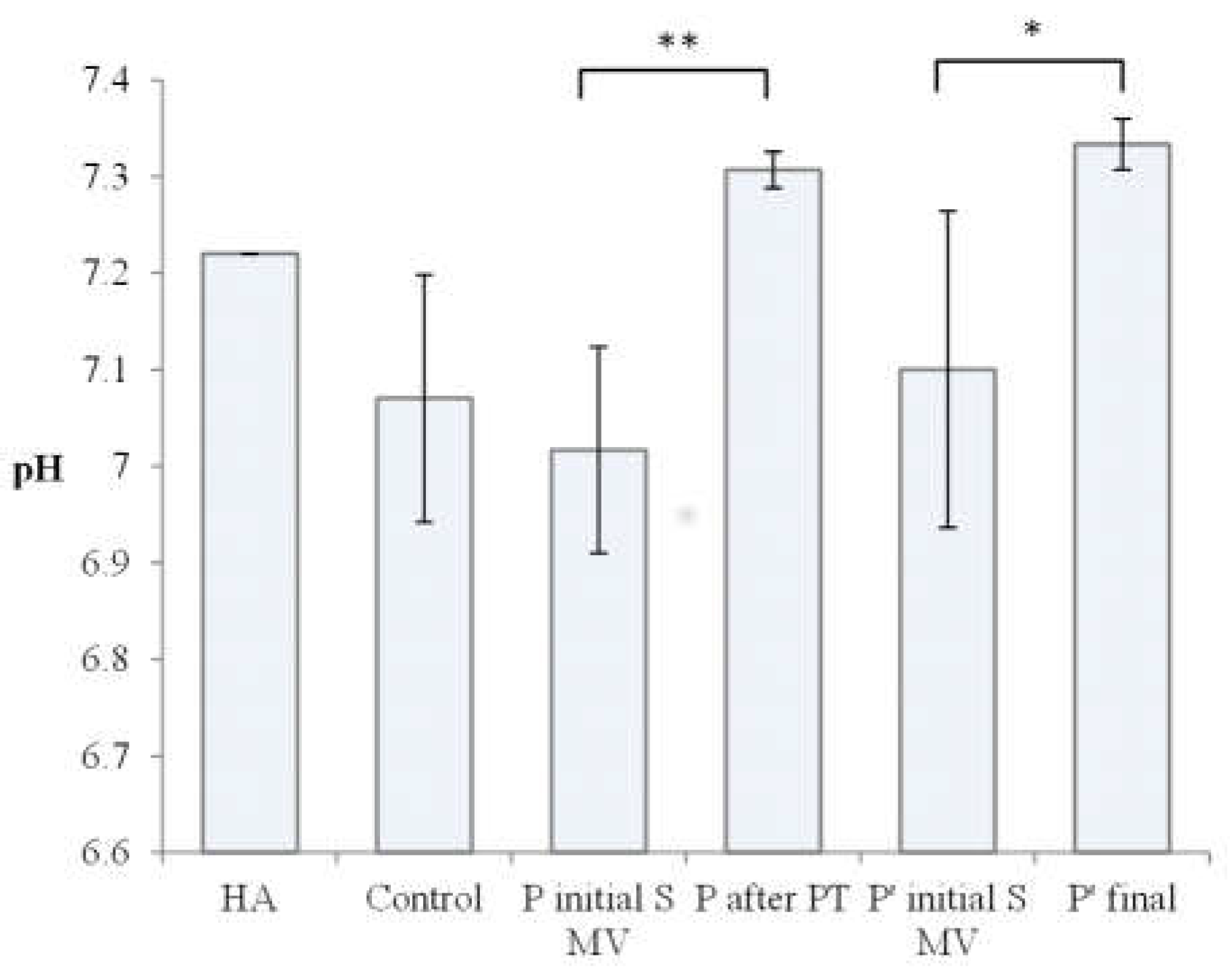
| 1. | HA | Raw Kombihylan® viscoelastic HA | 76 | 7.22 | Clear | Transparent | 0 |
| 2. | Control 1 | Patient with no procedure | 0.88 | 7.14 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 144 ± 4 |
| 3. | Control 2 | Patient with no procedure | 0.86 | 7.18 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 143 ± 1 |
| 4. | Control 3 | Patient with no procedure | 0.83 | 6.89 | Yellow | Transparent | 101 ± 2 |
| 5. | P1 Initial S MV | Patient 1 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.40 | 7.03 | Yellow | Transparent | 110 ± 3 |
| 6. | P2 Initial S MV | Patient 2 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.68 | 6.88 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 61 ± 2 |
| 7. | P3 Initial S MV | Patient 3 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.88 | 7.14 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 53 ± 1 |
| 8. | P1 Final | Patient 1 after PT (2 weeks PT + 4 weeks rest) | 0.66 | 7.32 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 99 ± 5 |
| 9. | P2 Final | Patient 2 after PT (2 weeks PT + 4 weeks rest) | 0.68 | 7.28 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 67 ± 1 |
| 10. | P3 Final | Patient 3 after PT (2 weeks PT + 4 weeks rest) | 0.64 | 7.42 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 69 ± 2 |
| 11. | P4 Initial S MV | Patient 4 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.72 | 7.19 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 104 ± 2 |
| 12. | P5 Initial S MV | Patient 5 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.76 | 6.87 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 120 ± 4 |
| 13. | P6 Initial S MV | Patient 6 initial(supplemented) 5-10 min movement | 0.76 | 7.24 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 59 ± 2 |
| 14, | P 4 final | Patient 4 final (6week rest) | 0.74 | 7.32 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 113 ± 3 |
| 15. | P 5 final | Patient 5 final (6week rest) | 0.62 | 7.51 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 128 ± 3 |
| 16. | P 6 final | Patient 6 final (6week rest) | 0.70 | 7.37 | Amber-Yellow | Transparent | 70 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





