Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
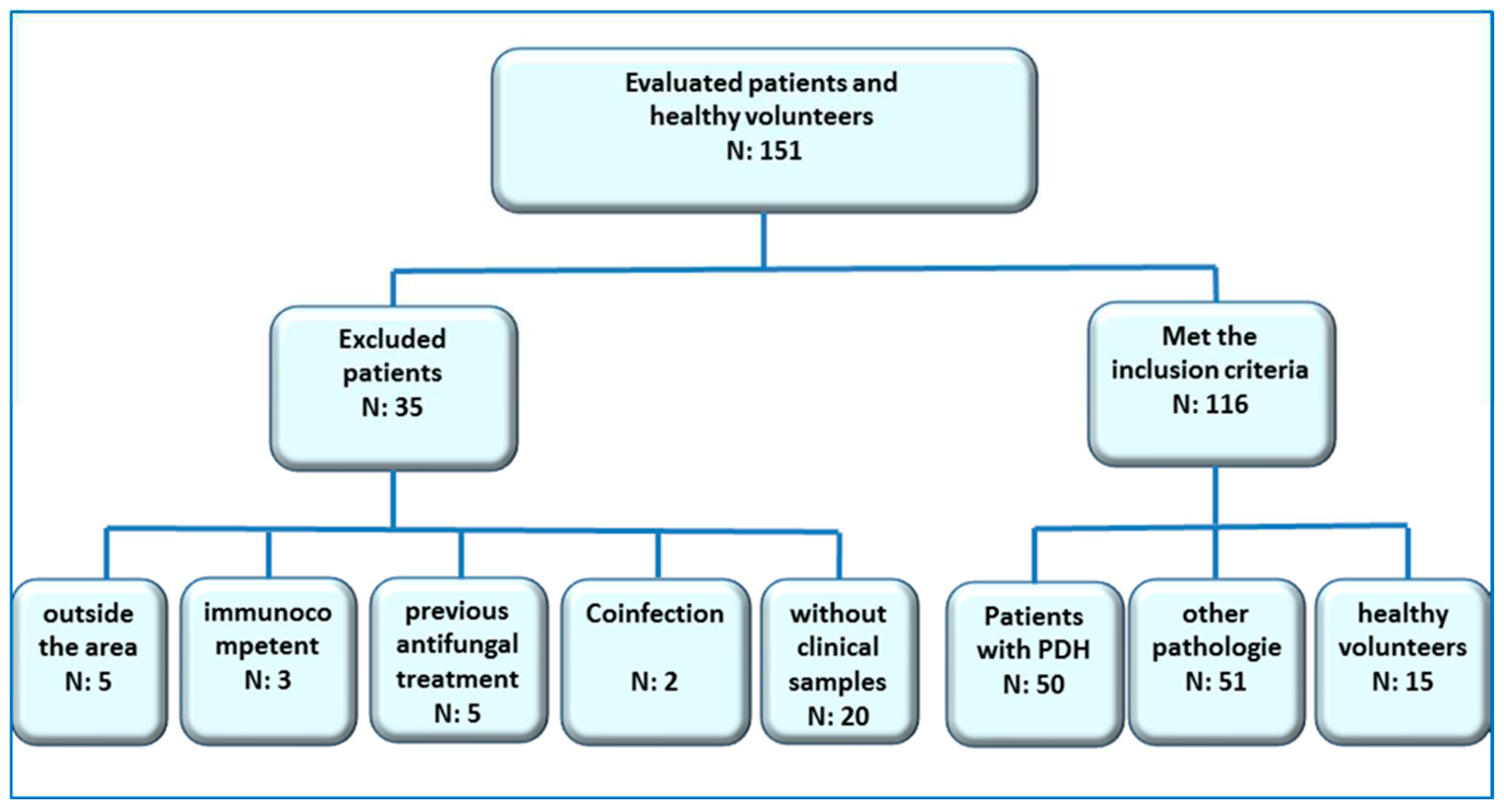
Type of study
- HIV + patients over 18 years old with PPDH
- HIV + patients over 18 with other infectious pathologies contemplated in the differential diagnosis, which were treated at the Mycology Unit of F.J. Muñiz Hospital in the mentioned period.
- Healthy volunteers (no apparent disease).
- Patients under 18 years old
- Patients who were not residents of the endemic area
- Patients without characteristic symptoms or clear clinical follow-up
- Patients that had proven coinfections with other etiological agents considered in this study, or treatment confirmed with amphotericin B, itraconazole or fluconazole pre-clinical sampling.
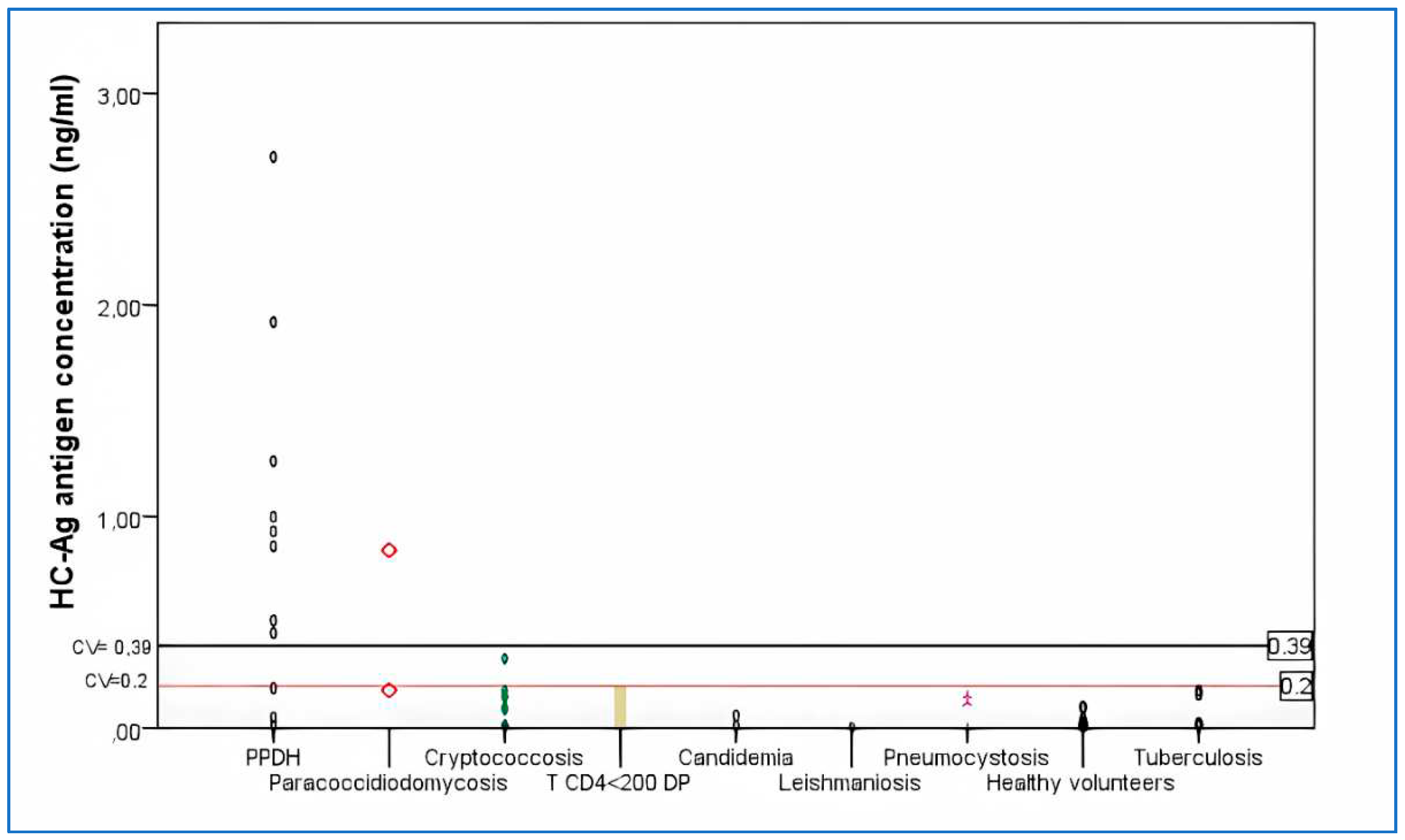
- Patients with PPDH. Fifty HIV+ patients were included in this group. A positive case of PPDH was defined as an individual with positive culture and/or histopathological findings of intracellular yeasts and granuloma consistent with this fungal infection and by Gomori-Grocott stains [parameter according to recommendations of the EORCT/MSG Consensus Group] [36].
- HIV + patients with other infectious pathologies. Fifty one patients were included: 3 pneumocystosis, 12 cryptococcosis, 1 leishmaniosis, 2 candidemias, 6 tuberculosis, 3 paracoccidioidomycosis, 24 patients with T CD4+ lymphocyte counts <200 cells/µl and different pathologies; with no characteristics signs or clinical symptoms, nor epidemiological history or other diagnostic elements of mycosis or tuberculosis (18 with impregnation syndrome and fever, 2 pemphigus vulgaris and 4 febrile neutropenia).
- Healthy volunteers. 15 individuals older than 18 years old without apparent diseases.
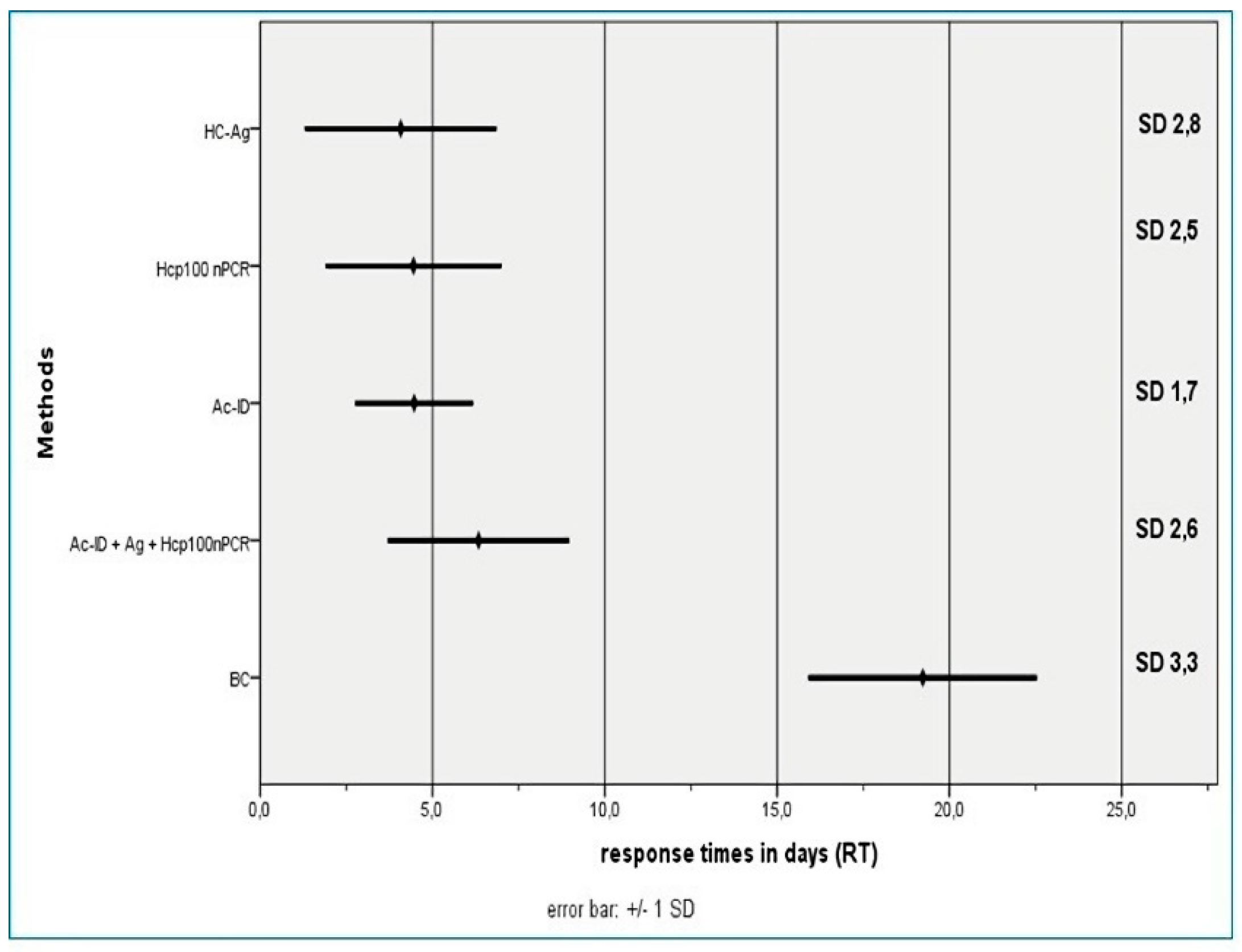
- Blood culture by lysis-centrifugation (BC). Peripheral blood samples pretreated with 5% saponin and sodium polyanethol sulfonate were cultured on Sabouraud agar and Brain-Heart Infusion agar at 28 °C and 37 °C, according to the technique described by Bianchi et al. [37].
- Serological tests. Detection of circulating anti H. capsulatum antibodies was performed by agar gel immunodiffusion techniques and counter-immunoelectrophoresis with secondary immunodiffusion in agarose gel (Ac-ID) [40], in serum samples from the 3 groups of patients. The antigen used was an aqueous extract of the yeast phase of H. capsulatum [41].
- Antigen detection (HC-Ag). The presence of H. capsulatum galactomannan antigen was determined in urine samples of all patients and healthy volunteers with commercial EIA using monoclonal antibodies HGM 201 (IMMY®, Norman, OK, USA). The used cutoff value was 0.2 ng/ml.
3. Results
| HC-Ag | Hcp100 nPCR | BC | Ac-ID | HC-Ag + Hcp100 nPCR + Ac-ID | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 94.0% (86.4% a 100.0%) | 82.0% (70.3% to 93) | 70.0% (56.3 to 83.7%) | 26.0% (12.8% to 39.2%) | 100% (99% a 100%) |
| E | 95.5% (89,7% a 100.0%) | 97.0% (92.8% to 100%) | 100% (99.2% to 100%) | 100% (99.2% to 100%) | 92.4% (85.3% a 99.6%) |
| PPV | 94.0% (86,4% a 100.0%) | 95.4% (87.9% to 100%) | 100% (98.6% to 100%) | 100% (96.2% to 100%) | 90.9% (82.4% a 99.4%) |
| NPV | 95.5% (89.7% a 100.0%) | 87.7% (79.4% to 95.9%) | 81.5% (72.4% to 90.6%) | 64.1% (54.3% to 73.8%) | 100% (99.2% a 100%) |
| Validity index | 94.8% (90.4% a 99.3%) | 90.5% (84.8% to 96.3%) | 87.1% (80.5% to 93.6%) | 68.1% (59.2% to 77.0%) | 95,7% (91,6% a 99,8%) |
| Hcp100 nPCR | HC-Ag | BC | Ac-ID | PPDH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hcp100 nPCR | 1 | 0.851 | 0.715 | 0.432 | 0.851 |
| HC-Ag | 0.851 | 1 | 0.711 | 0.399 | 0.920 |
| BC | 0.715 | 0.711 | 1 | 0.513 | 0.794 |
| Ac-ID | 0.432 | 0.399 | 0.513 | 1 | 0.483 |
| PPDH | 0.851 | 0.920 | 0.794 | 0.483 | 1 |
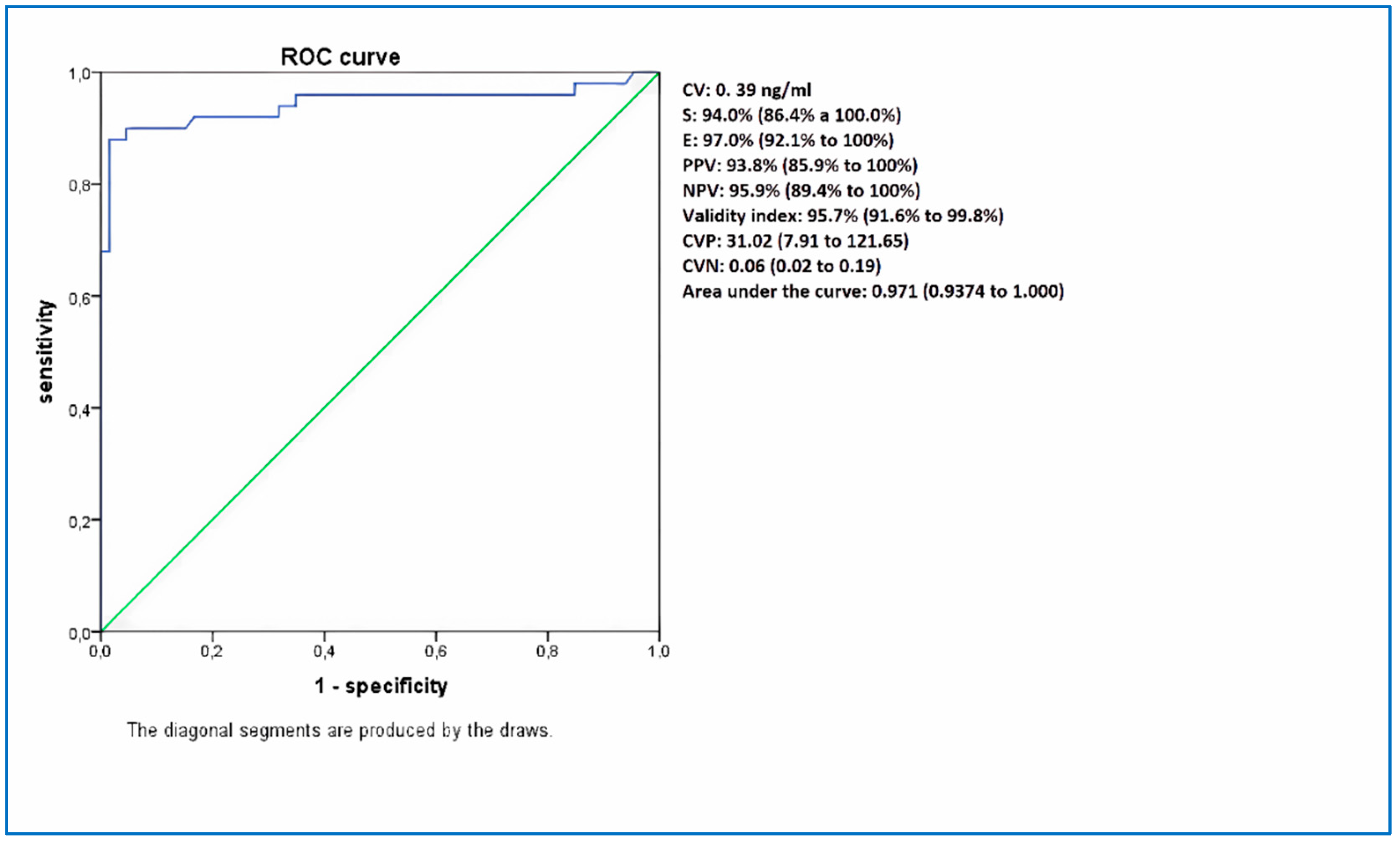
| HC-Ag 0.2 ng/ml | HC-Ag 0.39 ng/ml | |
|---|---|---|
| S | 94.0% (86.4% a 100.0%) | 94,0% (86.4% to 100%) |
| E | 95.5% (89.7% a 100.0%) | 97.0% (92.1% to 100%) |
| PPV | 94.0% (86.4% a 100.0%) | 93.8% (85.9% to 100%) |
| VPN | 95.5% (89.7% a 100.0%) | 95.9% (89.4% to 100%) |
| Validity index | 94.8% (90.4% a 99.3%) | 95.7% (91.6% to 99.8%) |
| CVP | 20.68 (6.83 to 62.61) | 31.02 (7.91 to 121.65) |
| CVN | 0.06 (0.02 to 0.19) | 0.06 (0.02 to 0.19) |
| Kappa | 0.920 | 0.933 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colombo AL, Tobón A, Restrepo A, Queiroz-Telles F, Nucci M. Epidemiology of endemic systemic fungal infections in Latin America. Med Mycol. 4 de mayo de 2011;1-14.
- Samayoa B, Roy M, Medina N, Cleveland AA, Lau-Bonilla D, Scheel CM, et al. High Mortality and Coinfection in a Prospective Cohort of Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Patients with Histoplasmosis in Guatemala. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 12 de julio de 2017;97(1):42-8.
- Nacher M, Adenis A, Mc Donald S, Do Socorro Mendonca Gomes M, Singh S, Lopes Lima I, et al. Disseminated Histoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients in South America: A Neglected Killer Continues on Its Rampage. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 21 de noviembre de 2013;7(11):e2319.
- Negroni R. Histoplasmosis in Latin-America. Biomédica. 2011;31(3):301-4.
- Rubinstein P, Negroni R. Histoplasmosis: en Micosis broncopulmonares del adulto y del niño 2da.Rubinstein P, Negroni R. Rubinstein P, Negroni R editors. Buenos Aires: Editorial Beta SRL; 1981. Pp. 249-290. Editorial Beta SRL. 1981;249-90.
- Negroni R, Arechavala AI, Maiolo EI. Histoplasmosis clásica en pacientes inmunocomprometidos. Med Cutan Iber Lat Am. 2010;38(2):59-69.
- Corti ME, Negroni R, Esquivel P, Villafañe MF. Histoplasmosis diseminada en pacientes con SIDA: análisis epidemiológico, clínico, microbiológico e inmunológico de 26 pacientes. :8.
- Daneri AGL, Arechavala A, Iovannitti CA, Mujica MT. Histoplasmosis diseminada en pacientes HIV/SIDA. Buenos Aires, 2009-2014. 2016;6.
- Durkin MM, Connolly PA, Karimi K, Wheat E, Schnizlein-Bick C, Allen SD, et al. Pathogenic Differences between North American and Latin American Strains of Histoplasma capsulatum var. capsulatum in Experimentally Infected Mice. J Clin Microbiol. 1 de septiembre de 2004;42(9):4370-3.
- Karimi K, Wheat LJ, Connolly P, Cloud G, Hajjeh R, Wheat E, et al. Differences in histoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States and Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1 de diciembre de 2002;186(11):1655-60.
- Kauffman CA. Histoplasmosis: a Clinical and Laboratory Update. Clin Microbiol Rev. enero de 2007;20(1):115-32.
- Cano-Torres JO, Olmedo-Reneaum A, Esquivel-Sánchez JM, Camiro-Zuñiga A, Pérez-Carrisoza A, Madrigal-Iberri C, et al. Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis in Latin America and the Caribbean in people receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection: A systematic review. Med Mycol. 1 de octubre de 2019;57(7):791-9.
- Adenis AA, Aznar C, Couppié P. Histoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients: A Review of New Developments and Remaining Gaps. Curr Trop Med Rep [Internet]. 28 de marzo de 2014 [citado 4 de junio de 2020]; Disponible en: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40475-014-0017-8.
- Dantas KC, Freitas RS de, da Silva MV, Criado PR, Luiz O do C, Vicentini AP. Comparison of diagnostic methods to detect Histoplasma capsulatum in serum and blood samples from AIDS patients. Ito E, editor. PLOS ONE. 17 de enero de 2018;13(1):e0190408.
- Garbee DD, Pierce SS, Manning J. Opportunistic Fungal Infections in Critical Care Units. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. marzo de 2017;29(1):67-79.
- Frola C, Bermejo V, Spadaccini L, Guelfand L, Pérez H. Impacto de la histoplasmosis diseminada en pacientes HIV positivos. 2013;5.
- Wheat J. Endemic Mycoses in AIDS: a Clinical Review. CLIN MICROBIOL REV. 1995;8:14.
- Pietrobon D, Negro-Marquínez L, Kilstein J, Galíndez J, Greca A, Battagliotti C. [Disseminated histoplasmosis and AIDS in an Argentine hospital: clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. marzo de 2004;22(3):156-9.
- The neglected histoplasmosis in Latin America Group. Disseminated histoplasmosis in Central and South America, the invisible elephant: the lethal blind spot of international health organizations. AIDS. enero de 2016;30(2):167-70.
- Adenis AA, Valdes A, Cropet C, McCotter OZ, Derado G, Couppie P, et al. Burden of HIV-associated histoplasmosis compared with tuberculosis in Latin America: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(10):1150-9.
- Toranzo AI, Tiraboschi IN, Fernández N, Ibarra-Camou B, Rivas MC, Lee W, et al. Diagnóstico molecular de histoplasmosis humana en muestras de sangre entera. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2009;7.
- Fandiño-Devia E, Rodríguez-Echeverri C, Cardona-Arias J, Gonzalez A. Antigen Detection in the Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis: A Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Performance. Mycopathologia. abril de 2016;181(3-4):197-205.
- Messina FA, Corti M, Negroni R, Arechavala A, Bianchi M, Santiso G. [Histoplasmosis in AIDS patients without tegumentary manifestations]. Rev Chil Infectologia Organo Of Soc Chil Infectologia. 2018;35(5):560-5.
- Zatti M da S, Arantes TD, Fernandes JAL, Bay MB, Milan EP, Naliato GFS, et al. Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification and nested PCR of the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) for Histoplasma capsulatum detection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis [Internet]. 26 de agosto de 2019 [citado 21 de mayo de 2021];13(8). Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6730939/.
- Bialek R, Feucht A, Aepinus C, Just-Nübling G, Robertson VJ, Knobloch J, et al. Evaluation of two nested PCR assays for detection of Histoplasma capsulatum DNA in human tissue. J Clin Microbiol. mayo de 2002;40(5):1644-7.
- Buitrago MJ, Martín-Gómez MT. Timely Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis in Non-endemic Countries: A Laboratory Challenge. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:467.
- Caceres DH, Adenis A, de Souza JVB, Gomez BL, Cruz KS, Pasqualotto AC, et al. The Manaus Declaration: Current Situation of Histoplasmosis in the Americas, Report of the II Regional Meeting of the International Histoplasmosis Advocacy Group. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 1 de diciembre de 2019;13(4):244-9.
- Caceres DH, Scheel CM, Tobón AM, Ahlquist Cleveland A, Restrepo A, Brandt ME, et al. Validation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay that detects Histoplasma capsulatum antigenuria in Colombian patients with AIDS for diagnosis and follow-up during therapy. Clin Vaccine Immunol CVI. septiembre de 2014;21(9):1364-8.
- Wheat LJ, Azar MM, Bahr NC, Spec A, Relich RF, Hage C. Histoplasmosis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. marzo de 2016;30(1):207-27.
- Wheat LJ, Kohler RB, Tewari RP. Diagnosis of disseminated histoplasmosis by detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigen in serum and urine specimens. N Engl J Med. 9 de enero de 1986;314(2):83-8.
- Williams B, Fojtasek M, Connolly-Stringfield P, Wheat J. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis by antigen detection during an outbreak in Indianapolis, Ind. Arch Pathol Lab Med. diciembre de 1994;118(12):1205-8.
- Scheel CM, Samayoa B, Herrera A, Lindsley MD, Benjamin L, Reed Y, et al. Development and Evaluation of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay To Detect Histoplasma capsulatum Antigenuria in Immunocompromised Patients. Clin Vaccine Immunol. junio de 2009;16(6):852-8.
- Theel ES, Harring JA, Dababneh AS, Rollins LO, Bestrom JE, Jespersen DJ. Reevaluation of commercial reagents for detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigen in urine. J Clin Microbiol. abril de 2015;53(4):1198-203.
- Zhang X, Gibson B, Daly TM. Evaluation of Commercially Available Reagents for Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis Infection in Immunocompromised Patients. J Clin Microbiol. 1 de diciembre de 2013;51(12):4095-101.
- Cáceres DH, Samayoa BE, Medina NG, Tobón AM, Guzmán BJ, Mercado D, et al. Multicenter Validation of Commercial Antigenuria Reagents To Diagnose Progressive Disseminated Histoplasmosis in People Living with HIV/AIDS in Two Latin American Countries. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56(6).
- De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, Pappas PG, Maertens J, Lortholary O, Kauffman CA, Denning DW, Patterson TF, Maschmeyer G, Bille J, Dismukes WE, Herbrecht R, Hope WW, Kibbler CC, Kullberg BJ, Marr KA, Muñoz P, Odds FC, Perfect JR, Restrepo A, Ruhnke M, Segal BH, Sobel JD, Sorrell TC, Viscoli C, Wingard JR, Zaoutis T, Bennett JE; European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG) Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46:1813-21.
- Bianchi M, Robles AM, Vitale R, Helou S, Arechavala A, Negroni R. The usefulness of blood culture in diagnosing HIV-related systemic mycoses: evaluation of a manual lysis centrifugation method. Med Mycol. 2000;4.
- Bianchi MH, Santiso GM, Lehmann EA, Walker LG, Arechavala AI, Maiolo EI, et al. Utilidad del citodiagnóstico de Tzank en un hospital de enfermedades infecciosas de la ciudad de Buenos Aires. Dermatol Argent. 30 de mayo de 2012;18(2):42-6.
- A. Tzanck. Le cytodiagnostic immediate en dermatologie. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syph. 1947;7:68-70.
- Arechavala A, Robles AM, Negroni R, Bianchi M, Taborda A. Valor de los métodos directos e indirectos de diagnóstico de las micosis sistémicas asociadas al SIDA. Rev Inst Med Trop São Paulo. 35:163-9.
- Negroni R, Iovannitti CA, Arechavala A, Carnovale S, kumiko E. Preparación y estudio de un exo antígeno de la fase levaduriforme de Histoplasma capsulatum para reacciones serológicas. 1998;15:282-5.
- Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini MG, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo CW. InfoStat versión 2018. Centro de Transferencia InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Argentina. Disponible en: http://www.infostat.com.ar.
- Gómez BL. Histoplasmosis: Epidemiology in Latin America. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 19 de octubre de 2011;5(4):199.
- Nacher M, Couppié P, Epelboin L, Djossou F, Demar M, Adenis A. Disseminated Histoplasmosis: Fighting a neglected killer of patients with advanced HIV disease in Latin America. PLOS Pathog. 14 de mayo de 2020;16(5):e1008449.
- Caceres DH, Tobón AM, Restrepo A, Brandt ME, Chiller T, Berbesi DY, et al. Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Persons Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome and Histoplasmosis from a Colombian Hospital. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 5 de octubre de 2016;95(4):918-24.
- Damasceno LS, Ramos AN, Alencar CH, Gonçalves MVF, de Mesquita JRL, Soares ATD, et al. Disseminated histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: determinants of relapse and mortality in a north-eastern area of Brazil. Mycoses. julio de 2014;57(7):406-13.
- Negroni R, Messina F, Arechavala A, Santiso G, Bianchi M. [Efficacy of the treatment and secondary antifungal prophylaxis in AIDS-related histoplasmosis. Experience at the Francisco J. Muñiz Infectious Diseases Hospital in Buenos Aires]. Rev Iberoam Micol. junio de 2017;34(2):94-8.
- Wheat LJ, Slama TG, Zeckel ML. Histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. febrero de 1985;78(2):203-10.
- Banco de Recursos de Comunicación del Ministerio de Salud de la Nación | Boletín sobre el VIH, sida e ITS en la Argentina N° 37 [Internet]. [citado 21 de julio de 2021]. Disponible en: https://bancos.salud.gob.ar/recurso/boletin-sobre-el-vih-sida-e-its-en-la-argentina-ndeg-37.
- Bava AJ. Histoplasmosis in the Muñiz Hospital of Buenos Aires. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. Diciembre de 1995; 37(6):531-5.
- Pasqualotto AC, Quieroz-Telles F. Histoplasmosis dethrones tuberculosis in Latin America. Lancet Infect Dis. 1 de octubre de 2018;18(10):1058-60.
- Falci DR, Monteiro AA, Braz Caurio CF, Magalhães TCO, Xavier MO, Basso RP, et al. Histoplasmosis, An Underdiagnosed Disease Affecting People Living With HIV/AIDS in Brazil: Results of a Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study Using Both Classical Mycology Tests and Histoplasma Urine Antigen Detection. Open Forum Infect Dis [Internet]. 1 de abril de 2019 [citado 4 de junio de 2020];6(4). Disponible en: https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofz073/5319214.
- Banco de Recursos de Comunicación del Ministerio de Salud de la Nación | Boletín sobre Tuberculosis en Argentina No 4 [Internet]. [citado 21 de julio de 2021]. Disponible en: https://bancos.salud.gob.ar/recurso/boletin-sobre-tuberculosis-en-argentina-no-4.
- Lindsley MD, Holland HL, Bragg SL, Hurst SF, Wannemuehler KA, Morrison CJ. Production and evaluation of reagents for detection of Histoplasma capsulatum antigenuria by enzyme immunoassay. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Jun;14(6):700-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Messina FA. Histoplasmosis en pacientes con sida sin manifestaciones tegumentarias. 2014 [citado 15 de octubre de 2020]; Disponible en: http://repositorio.unne.edu.ar/xmlui/handle/123456789/464.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





