Submitted:
27 April 2023
Posted:
03 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and discussion
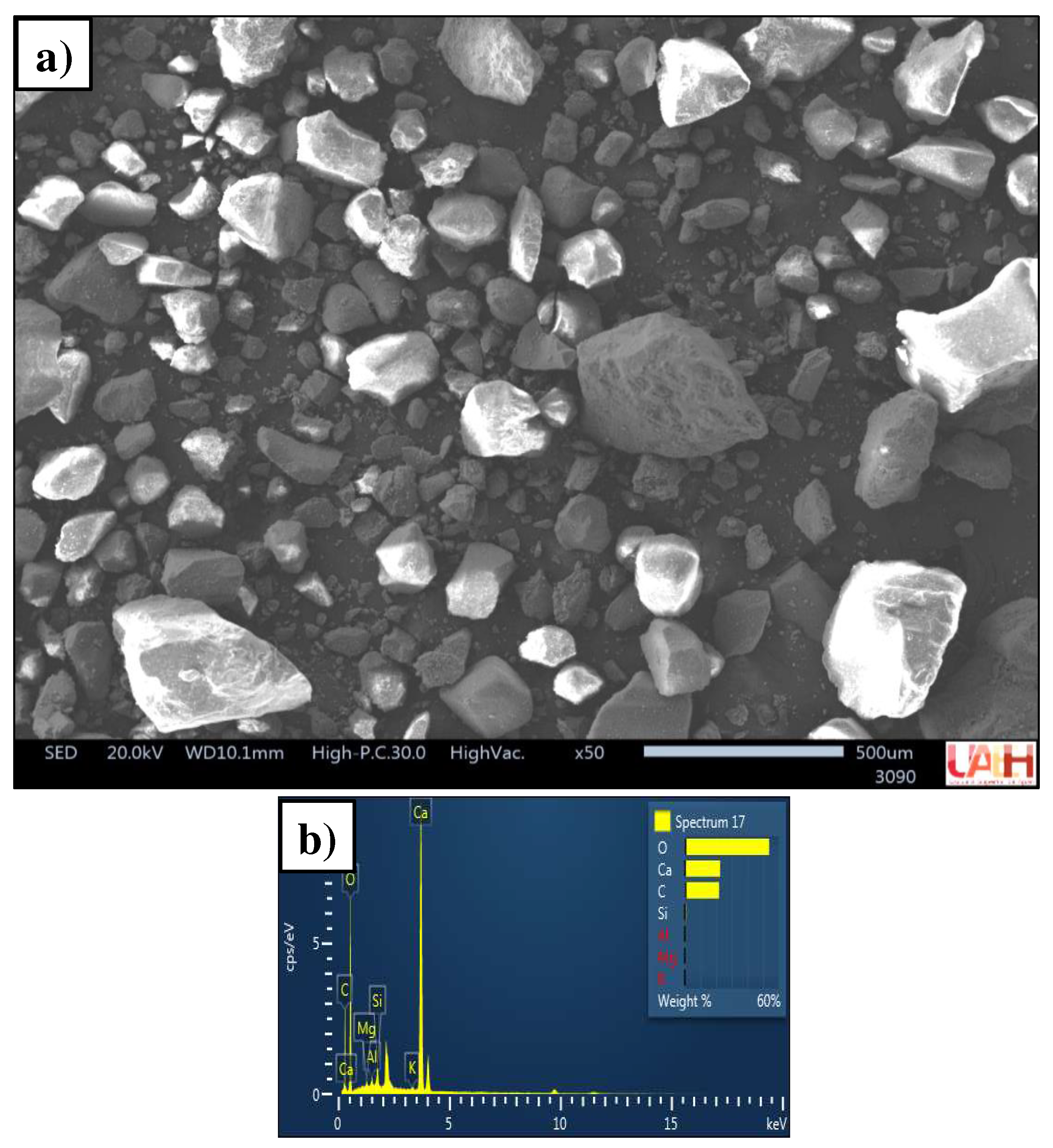
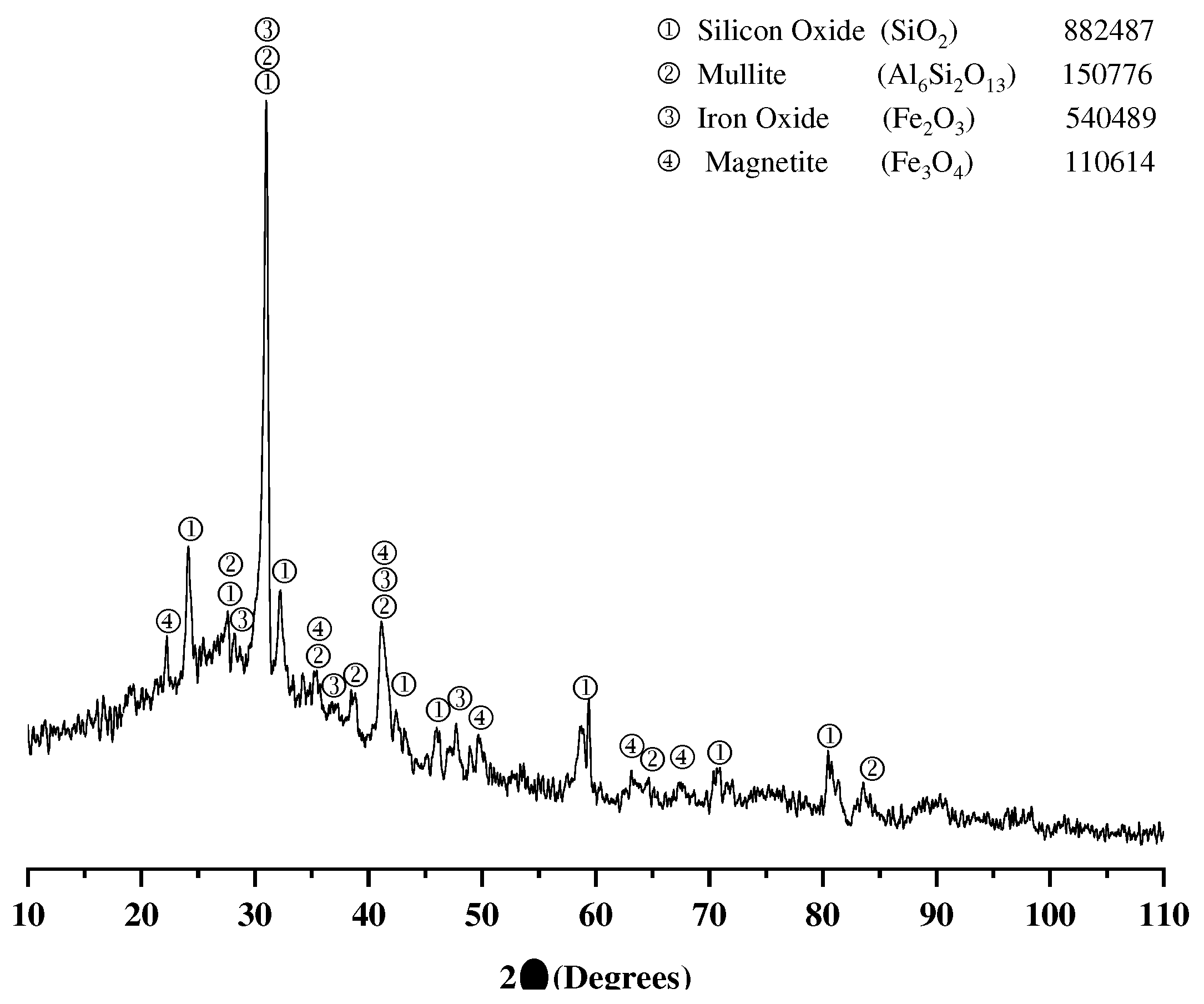
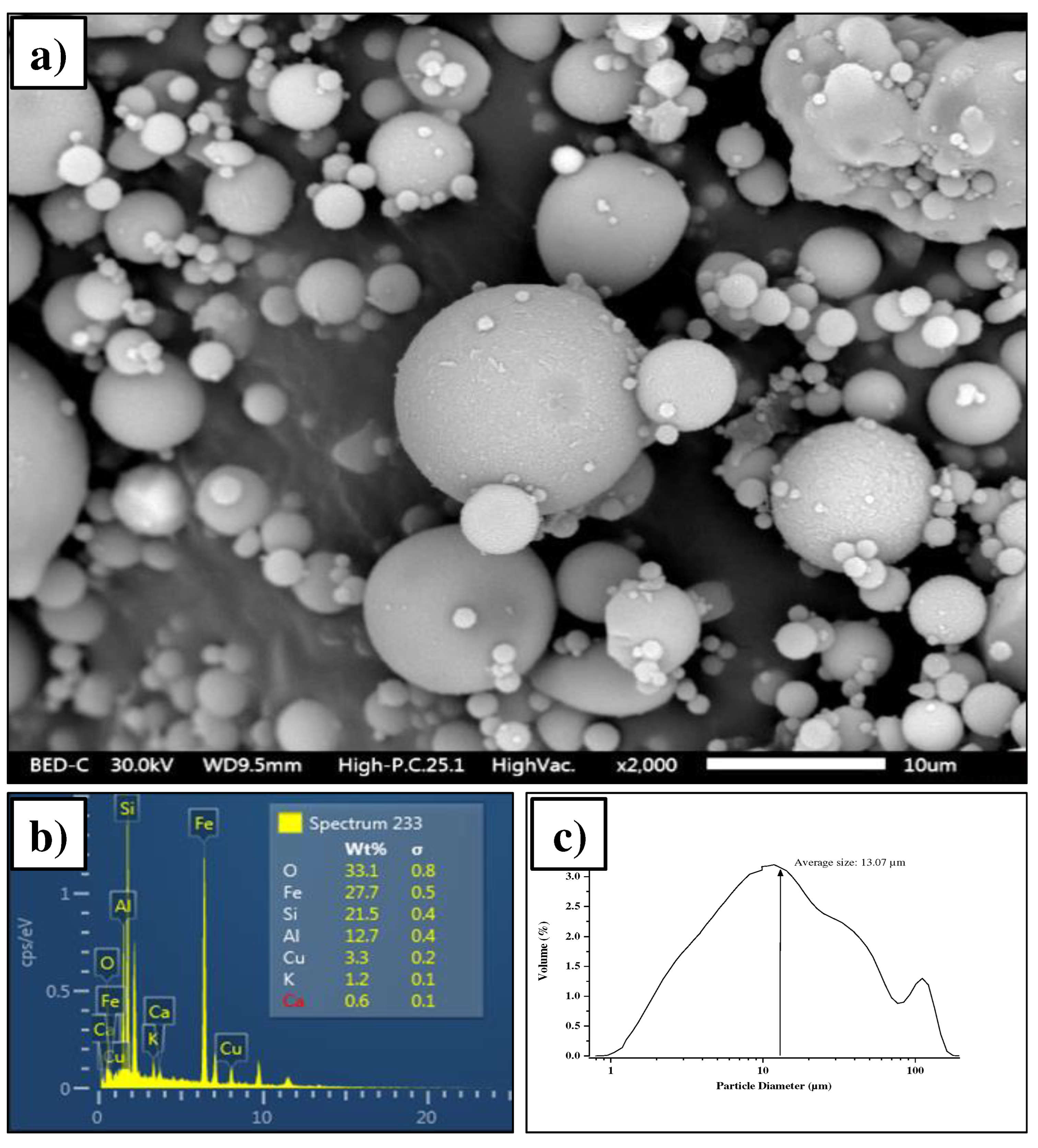
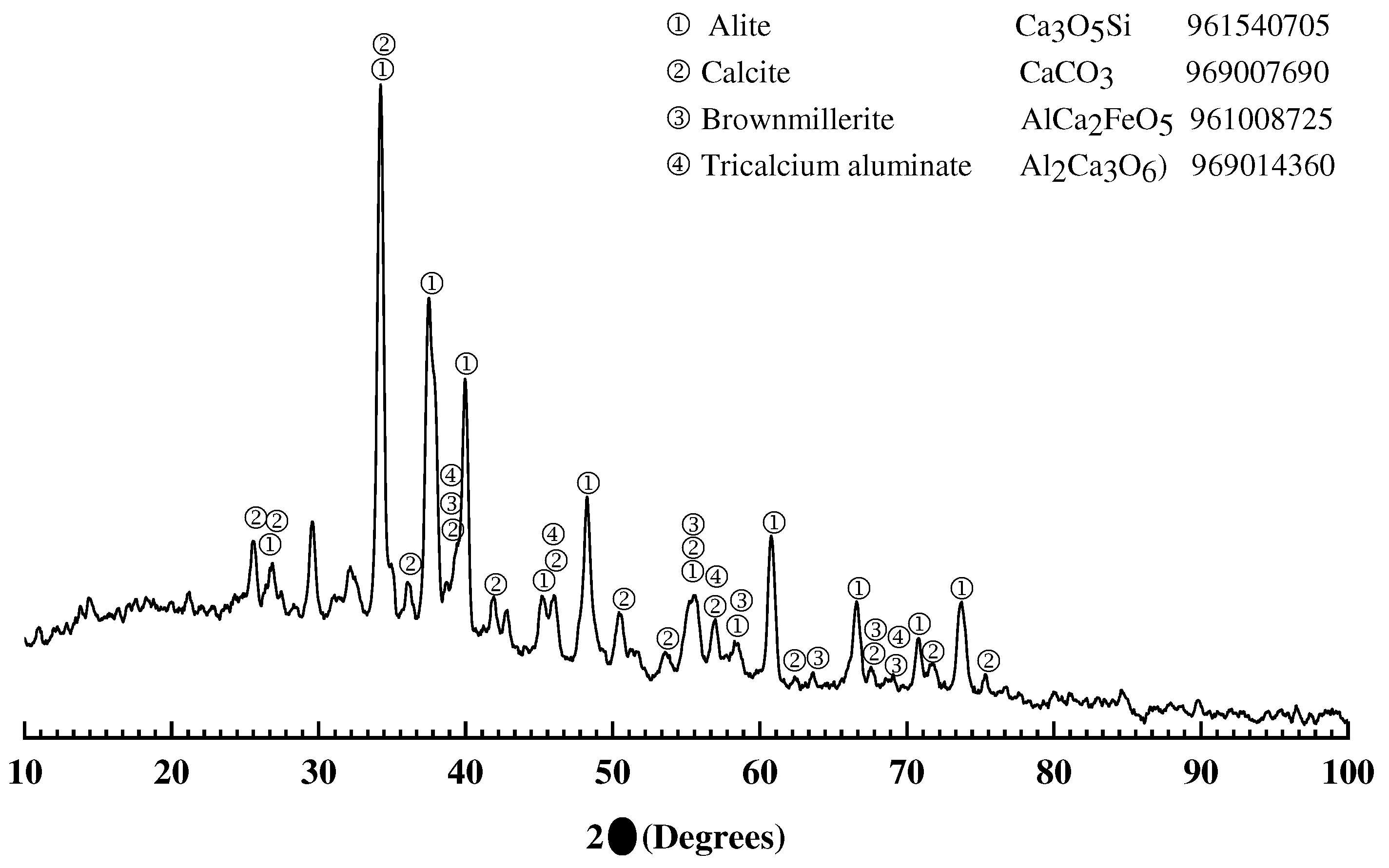
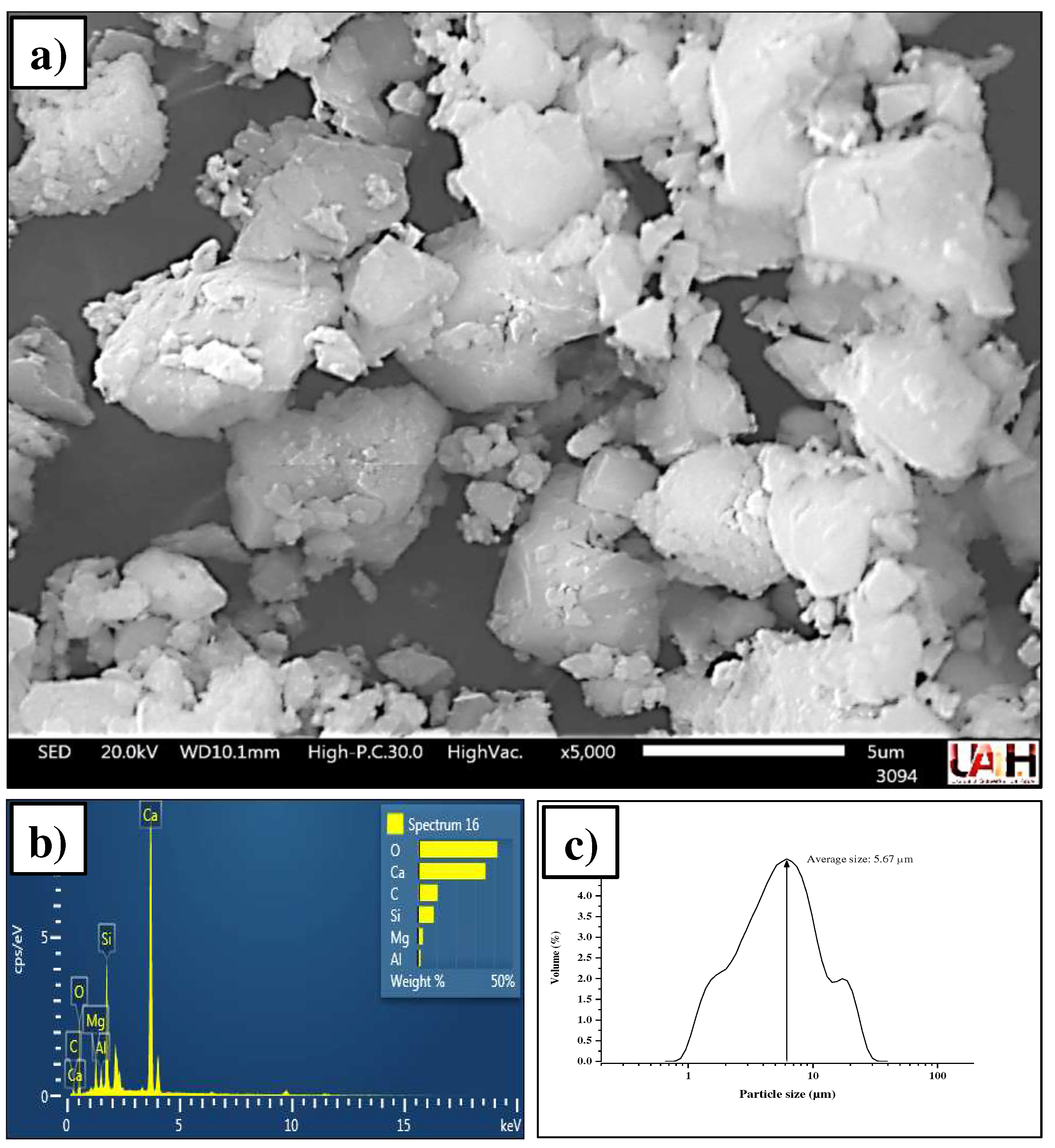
3.1. Characterization of source materials
3.1.1. Fly ash
3.1.2. Portland cement CPC-30R
3.1.3. Sand
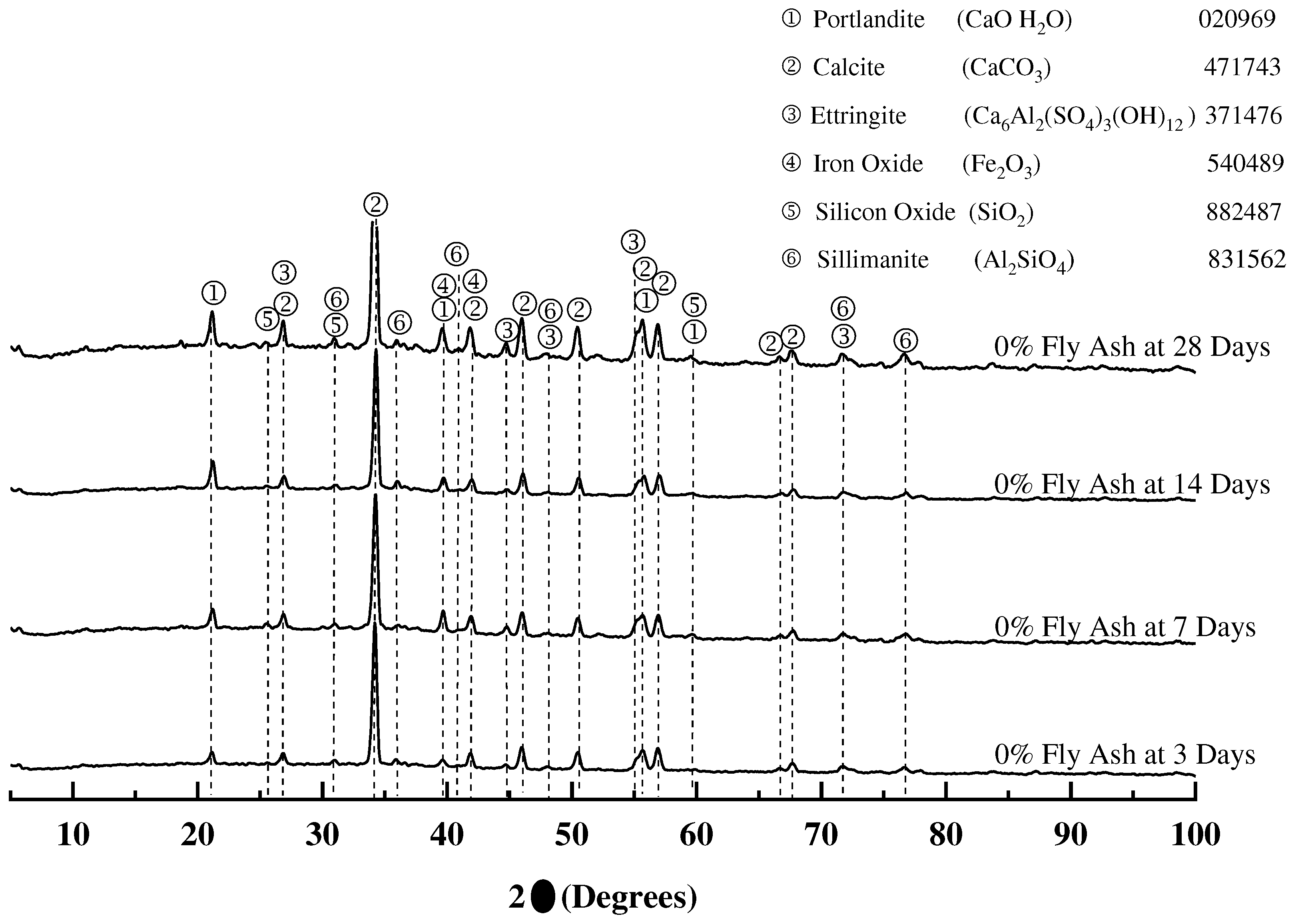
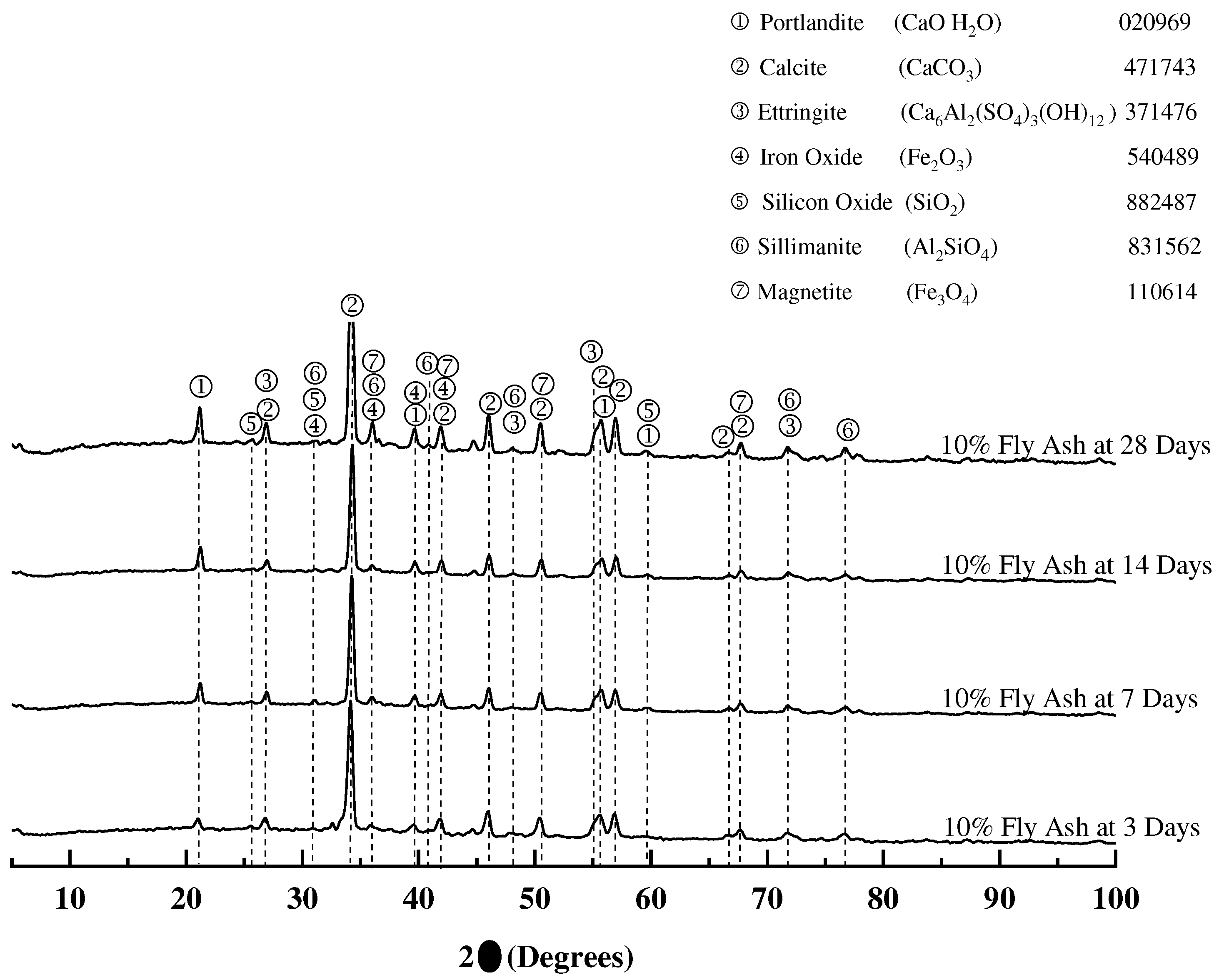
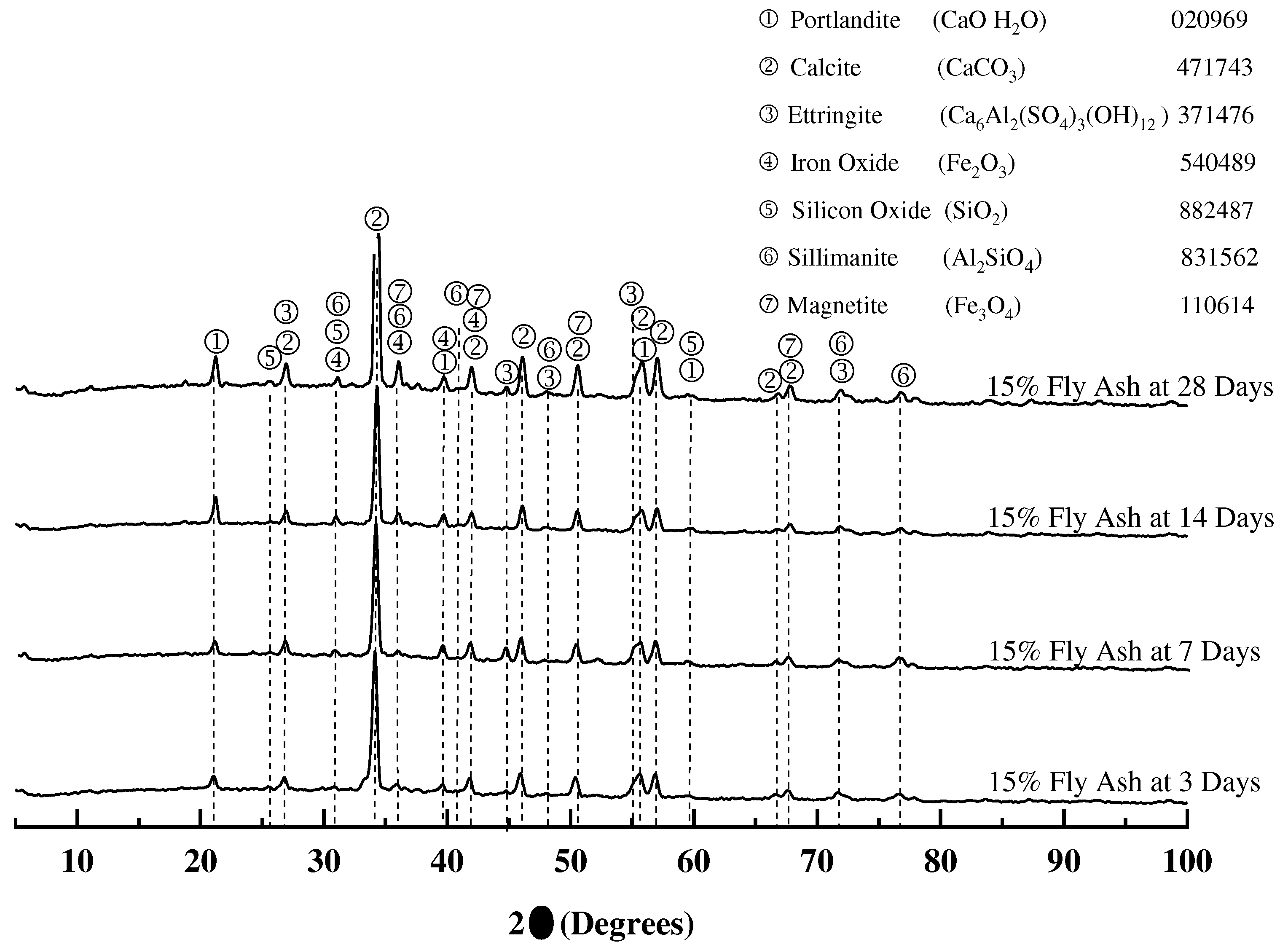
3.1.4. X-ray diffraction of mortar samples
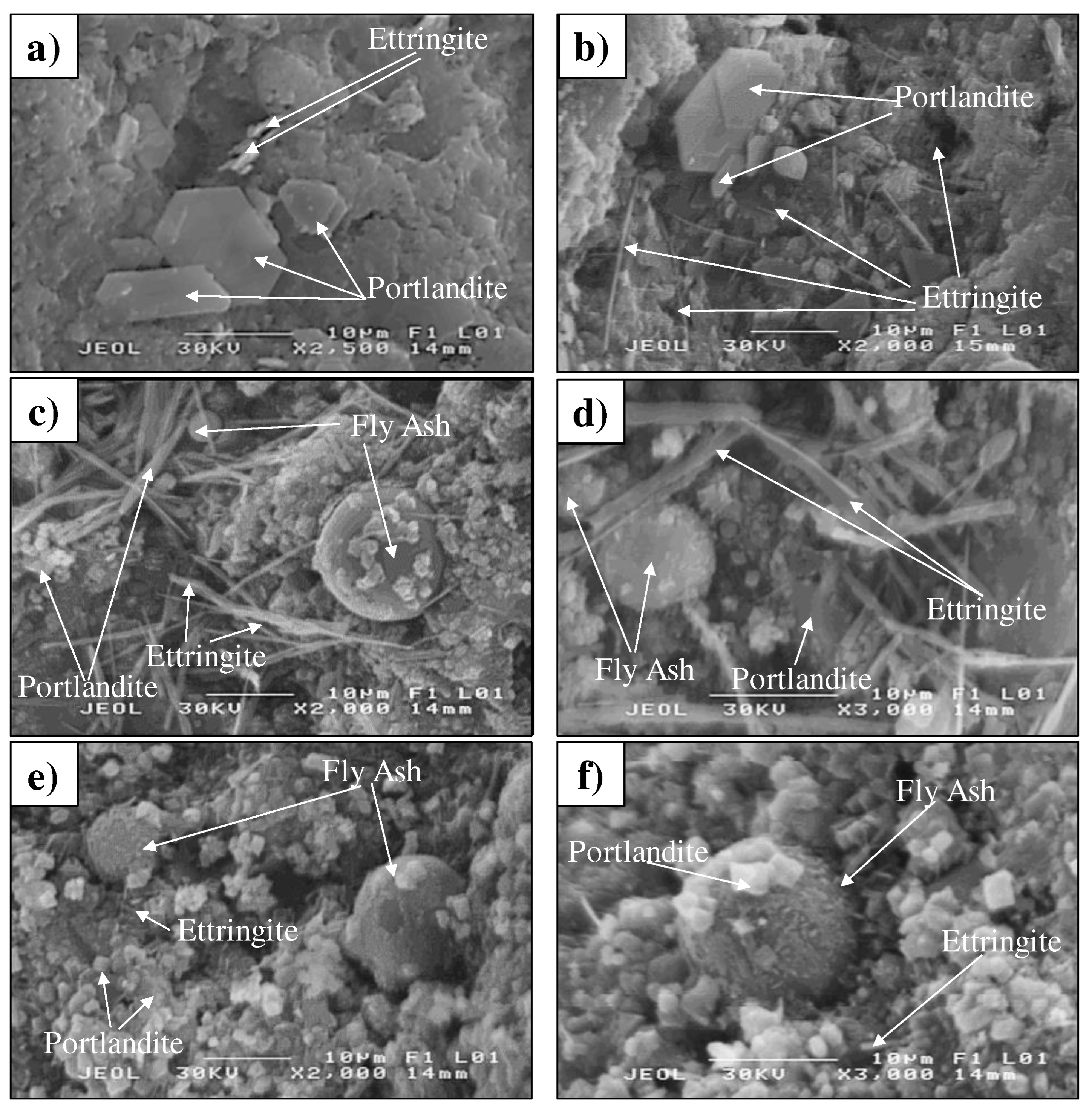
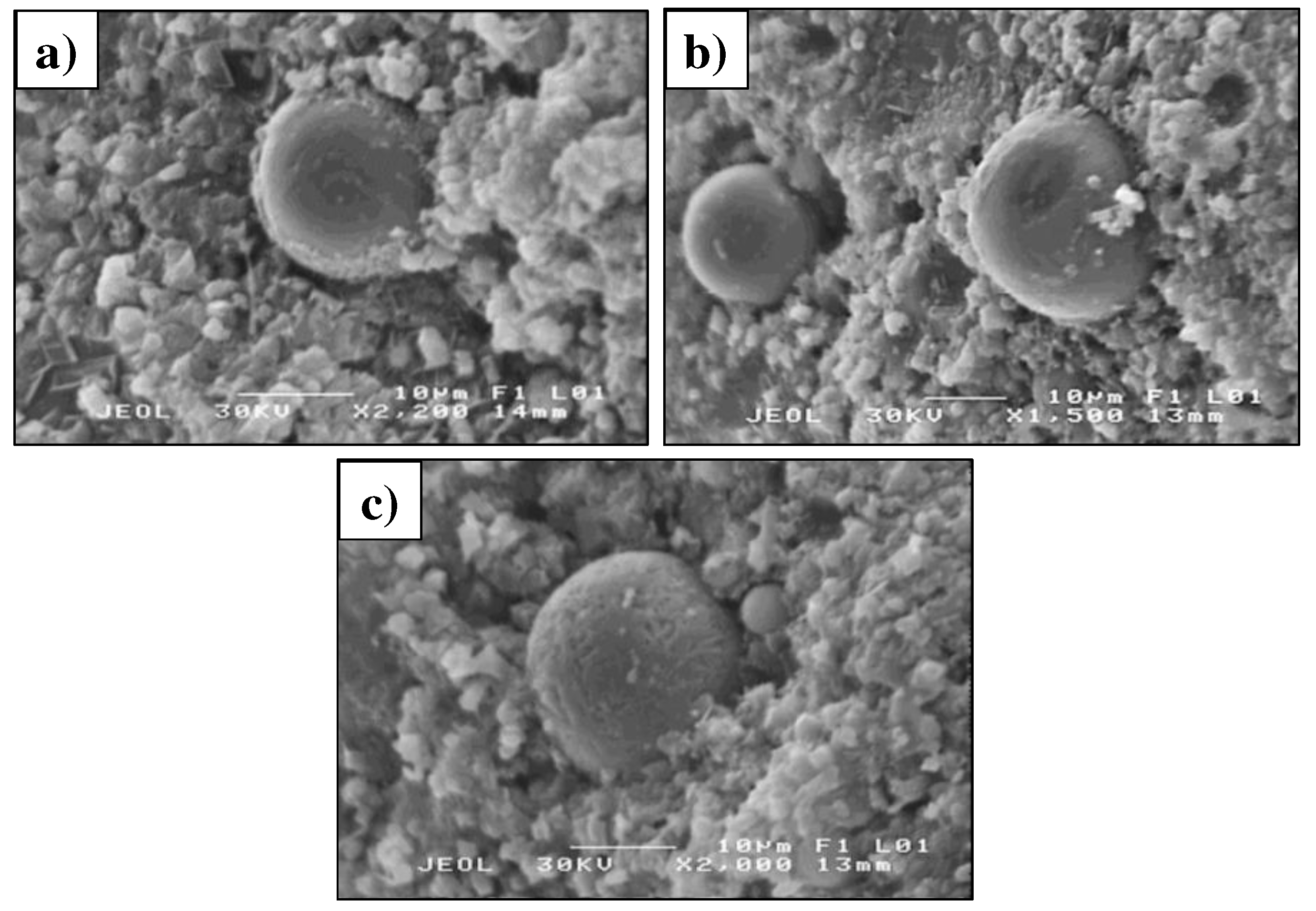
3.1.5. Morphology of mortars
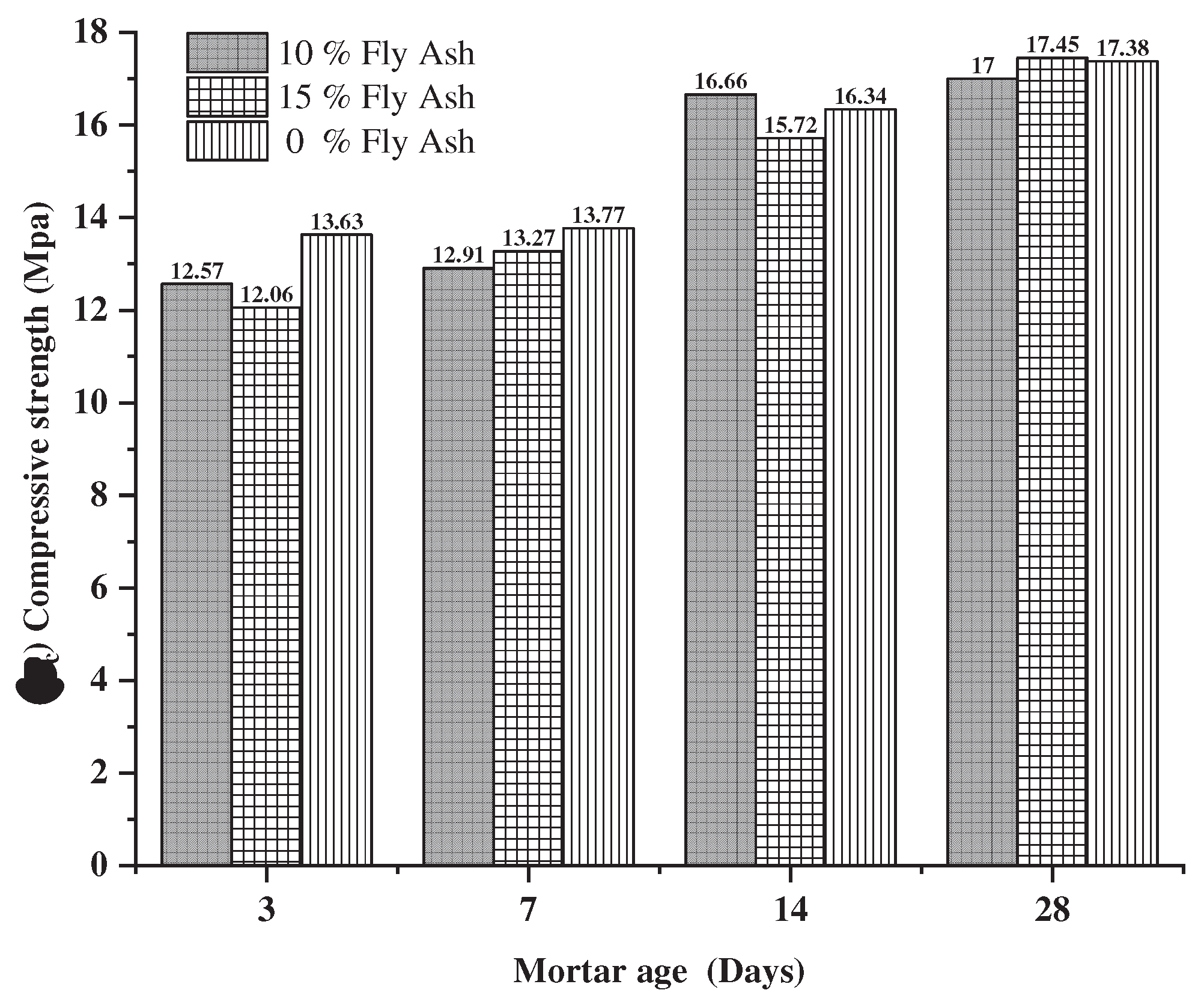
3.1.6. Compressive strength of mortars.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M.S. Imbabi, C. Carrigan, S. McKenna, Trends and developments in green cement and concrete technology, Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ., 1 (2012) 194–216. [CrossRef]
- M. Albitar, M.M. Ali, P. Visintin, M. Drechsler, Effect of granulated lead smelter slag on strength of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete, Constr Build Mater., 83 (2015) 128–135. [CrossRef]
- M.A. Rahman, P.K. Sarker, F.U.A. Shaikh, A.K. Saha, Soundness and compressive strength of Portland cement blended with ground granulated ferronickel slag, Constr Build Mater., 140 (2017) 194–202. [CrossRef]
- ASTM C618 - 03, Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete, (2003).
- Bendapudi SCK. Contribution of fly ash to the properties of mortar and concrete. Int J Earth Sci Eng 2011;04(06 SPL):1017–23.
- Malvar LJ, Lenke LR. Efficiency of fly ash in mitigating alkali silica reaction based on chemical composition. ACI Mater J 2006;103(5):319–26.
- Tahir M.A., Sabir M. (2005). A study on durability of fly ash-cement mortars, 30th conference on ‘‘Our world in concrete and structure’’: 23–24 August 2005, Singapore, article online Id: 100030019.
- Neville, A. M. (1995). Properties of concrete, Harlow. Essex: Addison Wesley Longman Limited.
- Chindaprasirt, P., & Rukzon, S. (2008). Strength, porosity and corrosion resistance of ternary blend Portland cement, rice husk ash and fly ash mortar. Constr Build Mater., 22(8), 1601-1606. [CrossRef]
- Supit, S. W., Shaikh, F. U., & Sarker, P. K. (2014). Effect of ultrafine fly ash on mechanical properties of high volume fly ash mortar. Constr Build Mater., 51, 278-286. [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P., Homwuttiwong, S., & Sirivivatnanon, V. (2004). Influence of fly ash fineness on strength, drying shrinkage and sulfate resistance of blended cement mortar. Cem Concr Res., 34(7), 1087-1092. [CrossRef]
- Cheerarot, R., & Jaturapitakkul, C. (2004). A study of disposed fly ash from landfill to replace Portland cement. J. Waste Manag., 24(7), 701-709. [CrossRef]
- Rukzon, S., & Chindaprasirt, P. (2009). Strength and chloride resistance of blended Portland cement mortar containing palm oil fuel ash and fly ash. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 16(4), 475-481. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X., Wang, Z., Tao, W., Yang, C., Hou, W., Dong, Y., & Wu, X. (2002). Studies on blended cement with a large amount of fly ash. Cem Concr Res., 32(7), 1153-1159. [CrossRef]
- Oner, A. D. N. A. N., Akyuz, S., & Yildiz, R. (2005). An experimental study on strength development of concrete containing fly ash and optimum usage of fly ash in concrete. Cem Concr Res., 35(6), 1165-1171. [CrossRef]
- Norma Mexicana. (2017). NMX-C-414-ONNCCE-2017. Industria de la Construcción-Cementantes Hidráulicos-Especificaciones y Métodos de Ensayo.
- Norma Mexicana. (2014). NMX-C-486-ONNCCE-2014, Industria de la construcción - Mampostería - Mortero para uso estructural - Especificaciones y métodos de ensayo.
- P. Echlin, Handbook of sample preparation for scanning electron microscopy and X-ray microanalysis, Springer Science & Business Media, 2011.
- P.C. Miguel, J.G. Jiménez, L.E. Giménez, Hormigón autocompactante expansivo. Diseño y eficacia en sistemas de refuerzo por confinamiento de pilares cilíndricos, (2012).
- Gomes, S., & François, M. (2000). Characterization of mullite in silicoaluminous fly ash by XRD, TEM, and 29Si MAS NMR. Cem Concr Res., 30(2), 175-181. [CrossRef]
- Kutchko, B. G., & Kim, A. G. (2006). Fly ash characterization by SEM–EDS. Fuel, 85(17-18), 2537-2544.
- Cui, Y., Wang, L., Liu, J., Liu, R., & Pang, B. (2022). Impact of particle size of fly ash on the early compressive strength of concrete: Experimental investigation and modelling. Constr Build Mater., 323, 126444. [CrossRef]
- Kiattikomol, K., Jaturapitakkul, C., Songpiriyakij, S., & Chutubtim, S. (2001). A study of ground coarse fly ashes with different finenesses from various sources as pozzolanic materials. Cem Concr Compos., 23(4-5), 335-343. [CrossRef]
- Young, G., & Yang, M. (2019). Preparation and characterization of Portland cement clinker from iron ore tailings. Constr Build Mater., 197, 152-156. [CrossRef]
- Giraldo, M. A., & Tobón, J. I. (2006). Evolución mineralógica del cemento portland durante el proceso de hidratación. Dyna, 73(148), 69-81.
- Carrete, J. C. (2001). La" portlandita"-hidróxido de calcio-y la" tobermorita"-silicatos de calcio hidratados-de la pasta de cemento: tratamiento estequiométrico de sus compartimentos. Cemento Hormigón, (824), 526-542.
- ABO-EL-ENEIN, S. A., SALEM, T., & HEKAL, E. E. (1988). Thermal and Physicochemical studies on ettringite. il Cemento—Roma, 85(1), 47-85.
- Chindaprasirt, P., Jaturapitakkul, C., & Sinsiri, T. (2007). Effect of fly ash fineness on microstructure of blended cement paste. Constr Build Mater., 21(7), 1534-1541. [CrossRef]
- Bijen, J., & Selst, I. (1992). CUR Report 144, Fly ash as addition to concrete, Research carried out by INTRON. Institute for Material and Environmental Research BV, AA Balkema, Rotterdam.
- Berry, E. E., Hemmings, R. T., & Cornelius, B. J. (1990). Mechanisms of hydration reactions in high volume fly ash pastes and mortars. Cem Concr Compos., 12(4), 253-261. [CrossRef]
- Berry, E. E., Hemmings, R. T., Zhang, M. H., Cornelius, B. J., & Golden, D. M. (1994). Hydration in high-volume fly ash concrete binders. Materials Journal, 91(4), 382-389.
- Xu, A., & Sarkar, S. L. (1994). Microstructural development in high-volume fly-ash cement system. Journal of materials in Civil Engineering, 6(1), 117-136.




| Sample |
Substitution (%) |
Portland cement CPC-30R. (g) |
Fly ash (g) |
Sand (g) |
Water (ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 786 | 0 | 2160) | 500 |
| 1 | 10 | 707 | 78.6 | 2160 | 500 |
| 2 | 15 | 668 | 117.9 | 2160 | 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





