Submitted:
02 May 2023
Posted:
03 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleemann: A.; Engel, J.; Kutscher, B.; Reichert, D.; (eds.), Pharmaceutical Substances. In Syntheses, Patents and Applications of the most relevant APIs, 5th Edition, completely revised ed.; Georg Thieme Verlag KG: Stuttgart, 2009.
- Langhammer, J. P.; Führ, F.; Büning-Pfaue, H., Verbleib von Sulfonamid-Rückständen aus der Gülle in Boden und Nutzpflanze. Lebensmittelchemie 1990, 44, 93.
- Thiele, S., Adsorption of the antibiotic pharmaceutical compound sulfapyridine by a long-term differently fertilized loess Chernozem. J.Plant Nutr.Soil Sci. 2000, 163, (6), 589-594. [CrossRef]
- Tolls, J., Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ.Sci.Technol. 2001, 35, (17), 3397-3406. [CrossRef]
- Hamscher, G.; Sczesny, S.; Höper, H.; Nau, H., Determination of persistent tetracycline residues in soil fertilized with liquid manure by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry 2002, 74, 1509-1518. [CrossRef]
- Halling-Sørensen, B.; Nors Nielsen, S.; Lanzky, P. F.; Ingerslev, F.; Holten Lützhøft, H. C.; J›rgensen, S. E., Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment - a review. Chemosphere 1998, 36, (2), 357-393. [CrossRef]
- Sarmah, A. K.; Meyer, M. T.; Boxall, A. B. A., A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 2006, 65, (5), 725-759. [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Liu, W., Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 2012, 32, (2), 309-327. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, K.; Xu, P.; Ok, Y. S.; Jones, D. L.; Zou, J., Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soils: A systematic analysis. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2023, 53, (7), 847-864. [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Natasha; Bibi, I.; Sarwar, T.; Shah, A. H.; Niazi, N. K., A review of environmental contamination and health risk assessment of wastewater use for crop irrigation with a focus on low and high-income countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018, 15, (5).
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J. L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E., Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and their metabolites in sewage sludge and soil: A review on their distribution and environmental risk assessment. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry 2021, 30. [CrossRef]
- Frey, L.; Tanunchai, B.; Glaser, B., Antibiotics residues in pig slurry and manure and its environmental contamination potential. A meta-analysis. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 2022, 42, (2).
- Xiao, R.; Huang, D.; Du, L.; Song, B.; Yin, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Huang, H.; Zeng, G., Antibiotic resistance in soil-plant systems: A review of the source, dissemination, influence factors, and potential exposure risks. Science of the Total Environment 2023, 869. [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Barra Caracciolo, A., Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchemical Journal 2018, 136, 25-39. [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, K. J.; Reyes, A.; Wang, B.; Selleck, E. M.; Sommer, M. O. A.; Dantas, G., The shared antibiotic resistome of soil bacteria and human pathogens. Science 2012, 337, (6098), 1107-1111. [CrossRef]
- Tiedje, J. M.; Wang, F.; Manaia, C. M.; Virta, M.; Sheng, H.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Topp, E., Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Human-Impacted Environment: A One Health Perspective. Pedosphere 2019, 29, (3), 273-282. [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, X., What happens when pharmaceuticals meet colloids. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, (10), 2100-2114. [CrossRef]
- Ghirardini, A.; Grillini, V.; Verlicchi, P., A review of the occurrence of selected micropollutants and microorganisms in different raw and treated manure – Environmental risk due to antibiotics after application to soil. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 707. [CrossRef]
- Tasho, R. P.; Cho, J. Y., Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Science of the Total Environment 2016, 563-564, 366-376.
- Verlicchi, P.; Zambello, E., Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in untreated and treated sewage sludge: Occurrence and environmental risk in the case of application on soil - A critical review. Science of the Total Environment 2015, 538, 750-767. [CrossRef]
- Kuppusamy, S.; Kakarla, D.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M.; Yoon, Y.-E.; Lee, Y. B., Veterinary antibiotics (VAs) contamination as a global agro-ecological issue: A critical view. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2018, 257, 47-59.
- Riviere, J. E., Comparative Pharmacokinetics: Principles, Techniques and Applications. 2 ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, 2011.
- Thiele-Bruhn, S., Environmental risks from mixtures of antibiotic pharmaceuticals in soils – a literature review. In UBA Texte, UBA: Dessau, Germany, 2019; Vol. 32, p 120.
- Chadwick, D. R.; Chen, S., Agriculture, Hydrology and Water Quality-Manures. In Agriculture, Hydrology and Water Quality, Haygarth, P. M. a. J. S. C., Ed. Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp 57-82.
- Leenheer, J. A.; Rostad, C. E., Fractionation and characterization of organic matter in wastewater from a swine waste-retention basin. In Scientific Investigations Report 2004-5217, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, Virginia, 2004; p 21.
- He, Z.; Pagliari, P. H.; Waldrip, H. M., Applied and environmental chemistry of animal manure: A review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, (6), 779-816. [CrossRef]
- Aust, M. O.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Eckhardt, K. U.; Leinweber, P., Composition of organic matter in particle size fractionated pig slurry. Bioresource Technology 2009, 100, (23), 5736-5743. [CrossRef]
- Senesi, N.; Xing, B.; Huang, P. M., Biophysico-Chemical Processes Involving Natural Nonliving Organic Matter in Environmental Systems. John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, 2009; p 876.
- Peltre, C.; Gregorich, E. G.; Bruun, S.; Jensen, L. S.; Magid, J., Repeated application of organic waste affects soil organic matter composition: Evidence from thermal analysis, FTIR-PAS, amino sugars and lignin biomarkers. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2017, 104, 117-127. [CrossRef]
- Cambier, P.; Pot, V.; Mercier, V.; Michaud, A.; Benoit, P.; Revallier, A.; Houot, S., Impact of long-term organic residue recycling in agriculture on soil solution composition and trace metal leaching in soils. Science of the Total Environment 2014, 499, 560-573. [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, J.; Carter, L.; Sinclair, C. J.; Rooney, P.; Kay, P., Influence of manure application method on veterinary medicine losses to water. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 334. [CrossRef]
- Navon, R.; Hernandez-Ruiz, S.; Chorover, J.; Chefetz, B., Interactions of carbamazepine in soil: Effects of dissolved organic matter. Journal of Environmental Quality 2011, 40, (3), 942-948. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, X.; Xu, J.; Hao, L.; Kong, D.; Gao, S., Sorption and transport of five sulfonamide antibiotics in agricultural soil and soil–manure systems. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part B Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes 2015, 50, (1), 23-33.
- Chabauty, F.; Pot, V.; Bourdat-Deschamps, M.; Bernet, N.; Labat, C.; Benoit, P., Transport of organic contaminants in subsoil horizons and effects of dissolved organic matter related to organic waste recycling practices. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2016, 23, (7), 6907-6918. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Seo, Y.; Essington, M. E., Sorption and transport of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soil - A laboratory study. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2014, 78, (5), 1531-1543. [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, M.; Stamm, C.; Waul, C.; Singer, H.; Müller, S. R., Surface runoff and transport of sulfonamide antibiotics and tracers on manured grassland. Journal of Environmental Quality 2005, 34, 1363-1371. [CrossRef]
- Borgman, O.; Chefetz, B., Combined effects of biosolids application and irrigation with reclaimed wastewater on transport of pharmaceutical compounds in arable soils. Water Research 2013, 47, (10), 3431-3443. [CrossRef]
- Gbadegesin, L. A.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, J., Transport of Veterinary Antibiotics in Farmland Soil: Effects of Dissolved Organic Matter. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, (3).
- Albero, B.; Tadeo, J. L.; Escario, M.; Miguel, E.; Pérez, R. A., Persistence and availability of veterinary antibiotics in soil and soil-manure systems. Science of the Total Environment 2018, 643, 1562-1570. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, N.; Li, B.; Bi, E., Roles of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fractions of dissolved organic matter in sorption of ketoprofen to biochars. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018, 25, (31), 31486-31496. [CrossRef]
- Leek, A. B. G.; Hayes, E. T.; Curran, T. P.; Callan, J. J.; Beattie, V. E.; Dodd, V. A.; O’Doherty, J. V., The influence of manure composition on emissions of odour and ammonia from finishing pigs fed different concentrations of dietary crude protein. Bioresource Technology 2007, 98, (18), 3431-3439. [CrossRef]
- Turner, B. L.; Leytem, A. B., Phosphorus compounds in sequential extracts of animal manures: Chemical speciation and a novel fractionation procedure. Environmental Science and Technology 2004, 38, (22), 6101-6108. [CrossRef]
- Kerr, B. J.; Trabue, S. L.; Andersen, D. S.; Van Weelden, M. B.; Pepple, L. M., Dietary composition and particle size effects on swine manure characteristics and gas emissions. Journal of Environmental Quality 2020, 49, (5), 1384-1395. [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D. P.; Rahman, S.; Borhan, M. S.; Engel, C., The effect of feeding high fat diet to beef cattle on manure composition and gaseous emission from a feedlot pen surface. Journal of Animal Science and Technology 2016, 58. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Fadel, J. G.; Zhang, R.; El-Mashad, H. M.; Ying, Y.; Rumsey, T., Evaluation of sample preservation methods for poultry manure. Poultry Science 2009, 88, (8), 1528-1535. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, X.; Thiele-Bruhn, S., Interaction of pig manure-derived dissolved organic matter with soil affects sorption of sulfadiazine, caffeine and atenolol pharmaceuticals. Environmental Geochemistry and Health 2021, 43, (10), 4299-4313. [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U., Differenzierung der Eisenoxide des Bodens durch photochemische Extraktion mit saurer Ammoniumoxalat-Lösung. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Düng. Bodenk. 1964, 105, 194-202.
- Sukul, P.; Lamshöft, M.; Zühlke, S.; Spiteller, M., Sorption and desorption of sulfadiazine in soil and soil-manure systems. Chemosphere 2008, 73, (8), 1344-1350. [CrossRef]
- OECD, Test No. 106: Adsorption - Desorption Using a Batch Equilibrium Method. 2000.
- Ngigi, A. N.; Ok, Y. S.; Thiele-Bruhn, S., Biochar affects the dissipation of antibiotics and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in pig manure. Bioresource Technology 2020, 315. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, S.; Han, M.; Cho, J., Sorption characteristics of oxytetracycline, amoxicillin, and sulfathiazole in two different soil types. Geoderma 2012, 185-186, 97-101.
- Filep, T.; Szabó, L.; Kondor, A. C.; Jakab, G.; Szalai, Z., Evaluation of the effect of the intrinsic chemical properties of pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) on sorption behaviour in soils and goethite. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2021, 215. [CrossRef]
- Kiecak, A.; Sassine, L.; Boy-Roura, M.; Elsner, M.; Mas-Pla, J.; La Salle, C. L.; Stumpp, C., Sorption properties and behaviour at laboratory scale of selected pharmaceuticals using batch experiments. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 2019, 225, 11. [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.; Jorquera, M.; Demanet, R.; Elgueta, S.; Briceño, G.; Mora, M. L., Urea fertilizer and pH influence on sorption process of flumetsulam and MCPA acidic herbicides in a volcanic soil. Journal of Environmental Quality 2016, 45, (1), 323-330. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. B.; Yu, X. Q.; Xu, B. L.; Peng, D.; Guo, X. T., Sorption of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on soil and soil components: Influencing factors and mechanisms. Science of the Total Environment 2021, 753, 15. [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Diva, R. A.; Vasudevan, D.; Mackay, A. A., Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere 2010, 79, (8), 786-793. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Pedersen, J. A., Sorption of sulfonamide antimicrobial agents to humic acid-clay complexes. Journal of Environmental Quality 2010, 39, (1), 228-235. [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D. L., Soil Physical Chemistry. CRC Press: Boka Ratoon, 1999; Vol. 2, p 409.
- Ngigi, A. N.; Ok, Y. S.; Thiele-Bruhn, S., Biochar-mediated sorption of antibiotics in pig manure. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2019, 663-670. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. A.; Gypser, S.; Leinweber, P.; Freese, D.; Kühn, O., Infrared spectroscopic characterization of phosphate binding at the goethite-water interface. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2019, 21, (8), 4421-4434. [CrossRef]
- Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Seibicke, T.; Schulten, H. R.; Leinweber, P., Sorption of sulfonamide pharmaceutical antibiotics on whole soils and particle-size fractions. Journal of Environmental Quality 2004, 33, (4), 1331-1342. [CrossRef]
- Le Guet, T.; Hsini, I.; Labanowski, J.; Mondamert, L., Sorption of selected pharmaceuticals by a river sediment: role and mechanisms of sediment or Aldrich humic substances. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018, 25, (15), 14532-14543. [CrossRef]
- Fiore, S.; Zanetti, M. C., Sorption of phenols: Influence of groundwater pH and of soil organic carbon content. American Journal of Environmental Sciences 2009, 5, (4), 546-554.
- Li, F.; Pan, B.; Liang, N.; Chang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Xing, B., Reactive mineral removal relative to soil organic matter heterogeneity and implications for organic contaminant sorption. Environmental Pollution 2017, 227, 49-56. [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Conte, P.; Trivellone, E.; Van Lagen, B., Reduced heterogeneity of a lignite humic acid by preparative HPSEC following interaction with an organic acid. Characterization of size-separates by Pyr-GC-MS and H-1-NMR spectroscopy. Environmental Science & Technology 2002, 36, (1), 76-84.
- Haham, H.; Oren, A.; Chefetz, B., Insight into the role of dissolved organic matter in sorption of sulfapyridine by semiarid soils. Environmental Science and Technology 2012, 46, (21), 11870-11877. [CrossRef]
- Strauss, C.; Harter, T.; Radke, M., Effects of pH and manure on transport of sulfonamide antibiotics in soil. Journal of Environmental Quality 2011, 40, (5), 1652-1660. [CrossRef]
- Spielmeyer, A.; Höper, H.; Hamscher, G., Long-term monitoring of sulfonamide leaching from manure amended soil into groundwater. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 232-238. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. D.; Bi, E. P.; Chen, H. H., Effects of dissolved humic acid on fluoroquinolones sorption and retention to kaolinite. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019, 178, 43-50. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Thiele-Bruhn, S.; Arenz-Leufen, M. G.; Jacques, D.; Lichtner, P.; Engelhardt, I., Impact of manure-related DOM on sulfonamide transport in arable soils. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 2016, 192, 118-128. [CrossRef]
| Compound | Molecular | CAS number | Molar mass | pKa | KOW a | Water solubility | |
| formula | (g·mol−1) | 1 | 2 | (mg·L−1) | |||
| Pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) | |||||||
| Sulfadiazine | 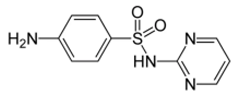 |
68-35-9 | 250.30 | 1.57 b | 6.50 b | 0.812 b | 2000 |
| Atenolol | 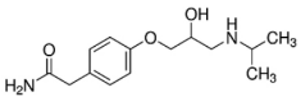 |
29122-68-7 | 266.34 | 9.60 c | 1.445 d | 429 | |
| Caffeine | 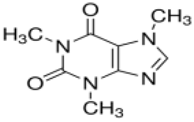 |
58-08-2 | 194.19 | 0.40 c | 10.4 c | 0.851 c | 21600 |
| Model compounds (manure constituents) e | |||||||
| Urea | CO(NH2)2 | 57-13-6 | 60.06 | 0.18 | 0.008 | 5.45e+5 | |
| Monopotassium phosphate | KH2PO4 | 7778-77-0 | 136.09 | 2.15 | 6.82 | – | 2.22e+5 |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | 64-19-7 | 60.05 | 4.76 | -0.17 | 4.76e+5 | |
| Phenol | C6H5OH | 108-95-2 | 94.11 | 9.99 | 28.84 | 8.28e+4 | |
| Nonadecanoic acid C:19 | C18H37COOH | 646-30-0 | 298.50 | 4.78 | 2.75e+8 | 0.002 | |
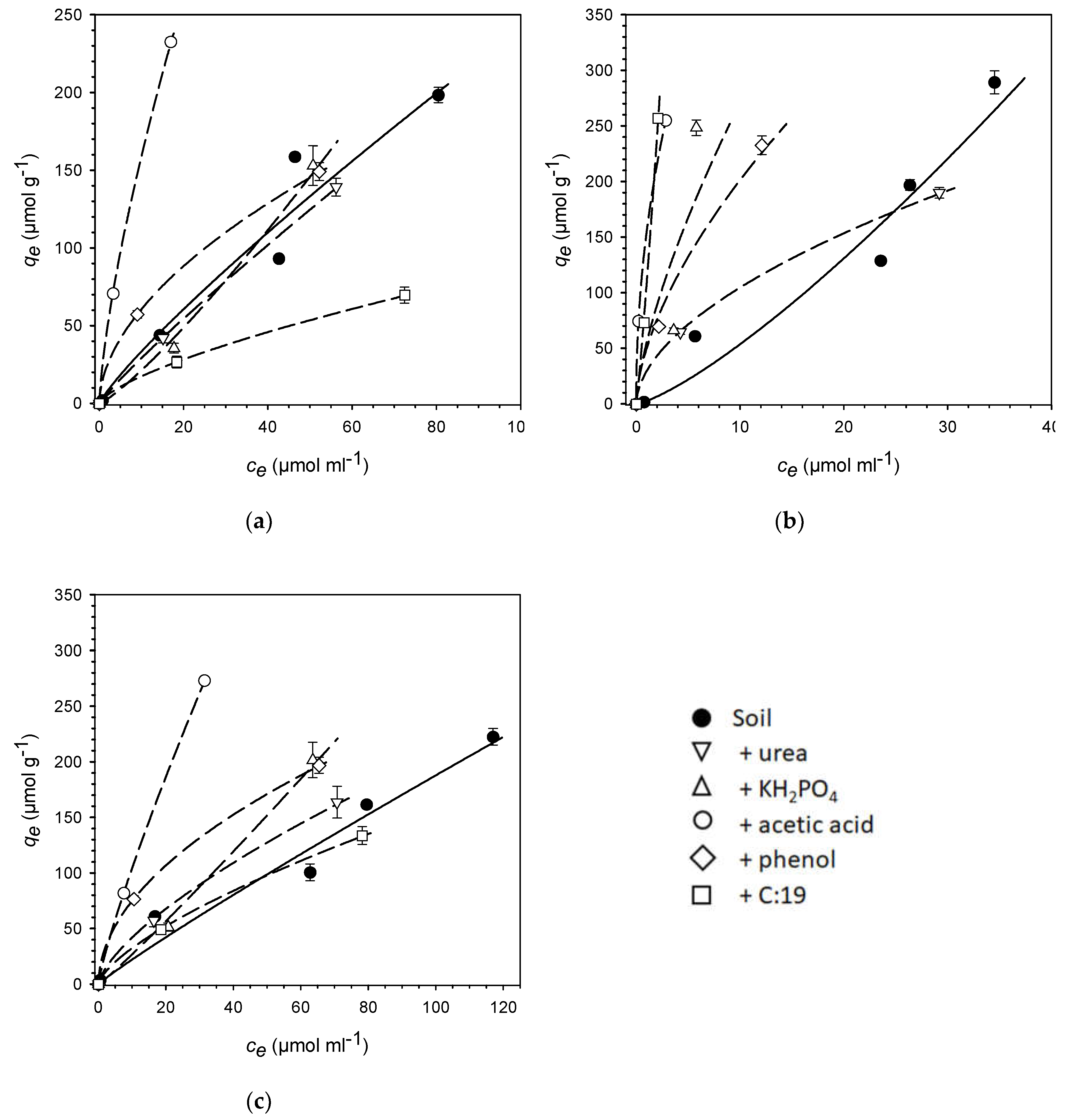
| Soil | +urea | +KH2PO4 | +acetic acid | +phenol | +C:19 | |
| OC (mg·g-1) | 11.57 | 11.63 | 11.57 | 11.78 | 11.93 | 12.71 |
| pH | 4.98 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 2.56 | 4.49 | 4.46 |
| PhAC | Isotherm parameter | Soil | +urea | +KH2PO4 | +acetic acid | +phenol | +C:19 |
| Sulfadia | Kf | 4.66 | 3.71 | 1.39 | 31.1 | 17.5 | 3.56 |
| zine | n | 0.86 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.69 |
| R² | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | |
| SE | 2.41 | 1.15 | 1.43 | 3.85 | 2.55 | 1.26 | |
| Kd | 3.36 | 2.94 | 2.15 | 15.9 | 6.08 | 1.76 | |
| KOC | 290 | 253 | 186 | 1,350 | 510 | 138 | |
| Atenolol | Kf | 2.79 | 29.6 | 55.1 | 155 | 50.0 | 107 |
| n | 1.28 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.61 | 1.16 | |
| R² | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.94 | 0.97 | |
| SE | 2.47 | 4.28 | 24.3 | 2.47 | 2.37 | 0.18 | |
| Kd | 5.38 | 10.5 | 27.1 | 46.6 | 20.1 | 154 | |
| KOC | 465 | 902 | 2,340 | 3,950 | 1,690 | 12,100 | |
| Caffeine | Kf | 2.65 | 8.63 | 2.29 | 15.3 | 23.0 | 6.71 |
| n | 0.93 | 0.69 | 1.07 | 0.84 | 0.51 | 0.69 | |
| R² | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SE | 1.37 | 3.98 | 2.05 | 1.99 | 3.17 | 1.76 | |
| Kd | 2.23 | 4.21 | 2.71 | 10.5 | 7.50 | 3.25 | |
| KOC | 193 | 362 | 234 | 888 | 629 | 256 |
| sulfadiazine | atenolol | caffeine | ||
| OC a | r | -0.164 | 0.942 | -0.049 |
| p | 0.756 | 0.005 | 0.927 | |
| OC b | r | 0.518 | 0.366 | 0.785 |
| p | 0.371 | 0.544 | 0.116 | |
| pH a | r | -0.918 | -0.181 | -0.827 |
| p | 0.010 | 0.732 | 0.042 | |
| pH c | r | 0.034 | -0.501 | -0.274 |
| p | 0.957 | 0.390 | 0.655 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





