Submitted:
02 May 2023
Posted:
03 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.1.1. Recruitment Procedure
2.1.2. Randomization and Group-Allocation Procedure
2.1.3. Investigational product
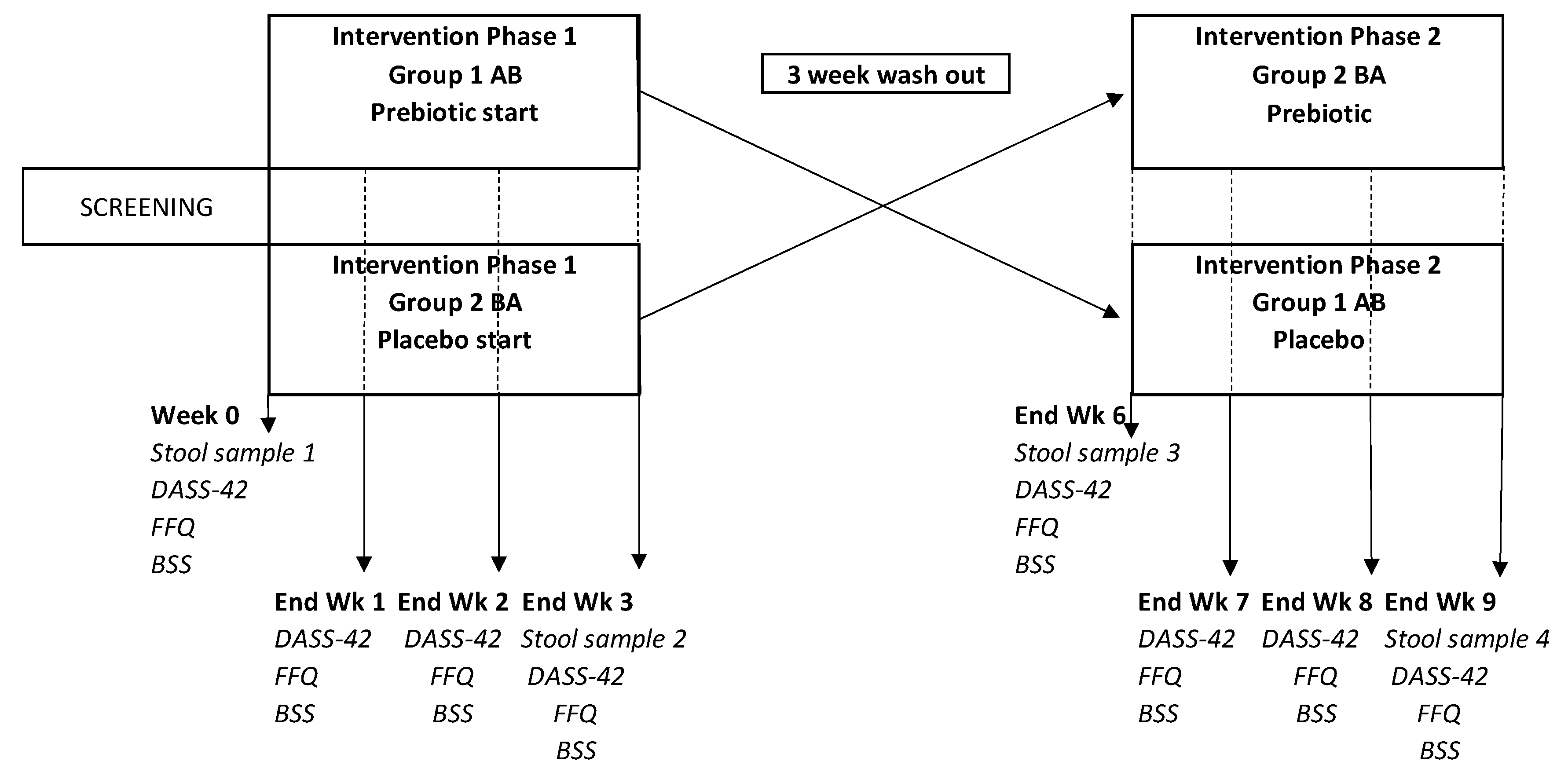
2.1.4. Study design and Procedure
2.2. Gut Microbiome Analysis
2.2.1. Sample collection and analysis
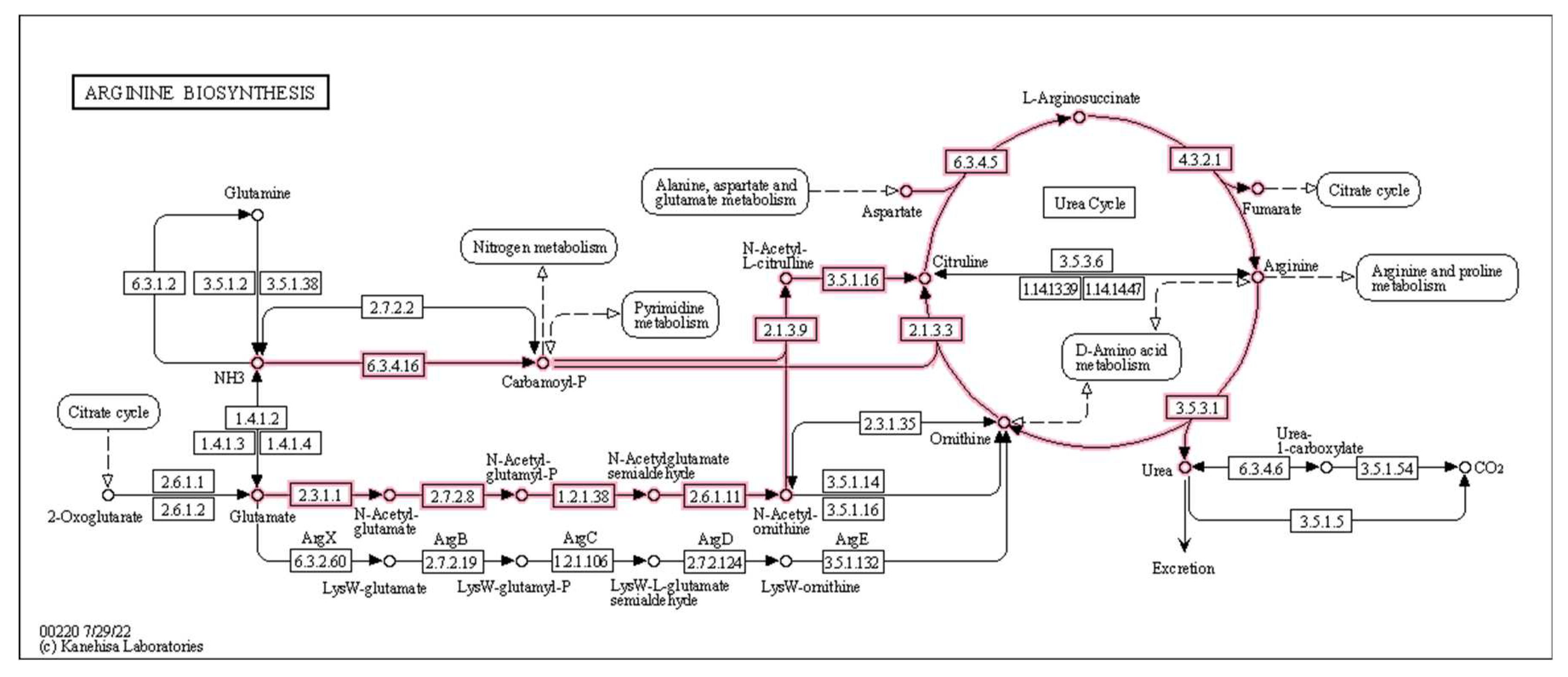
2.2.2. KEGG Pathways and Modules
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Habitual dietary intake of inulin and oligo fructose
3.2. Stool Consistency
3.3. Safety and side effects
3.4. Depression, Anxiety and Stress
3.5. Microbiome Composition Changes Due to the Intervention
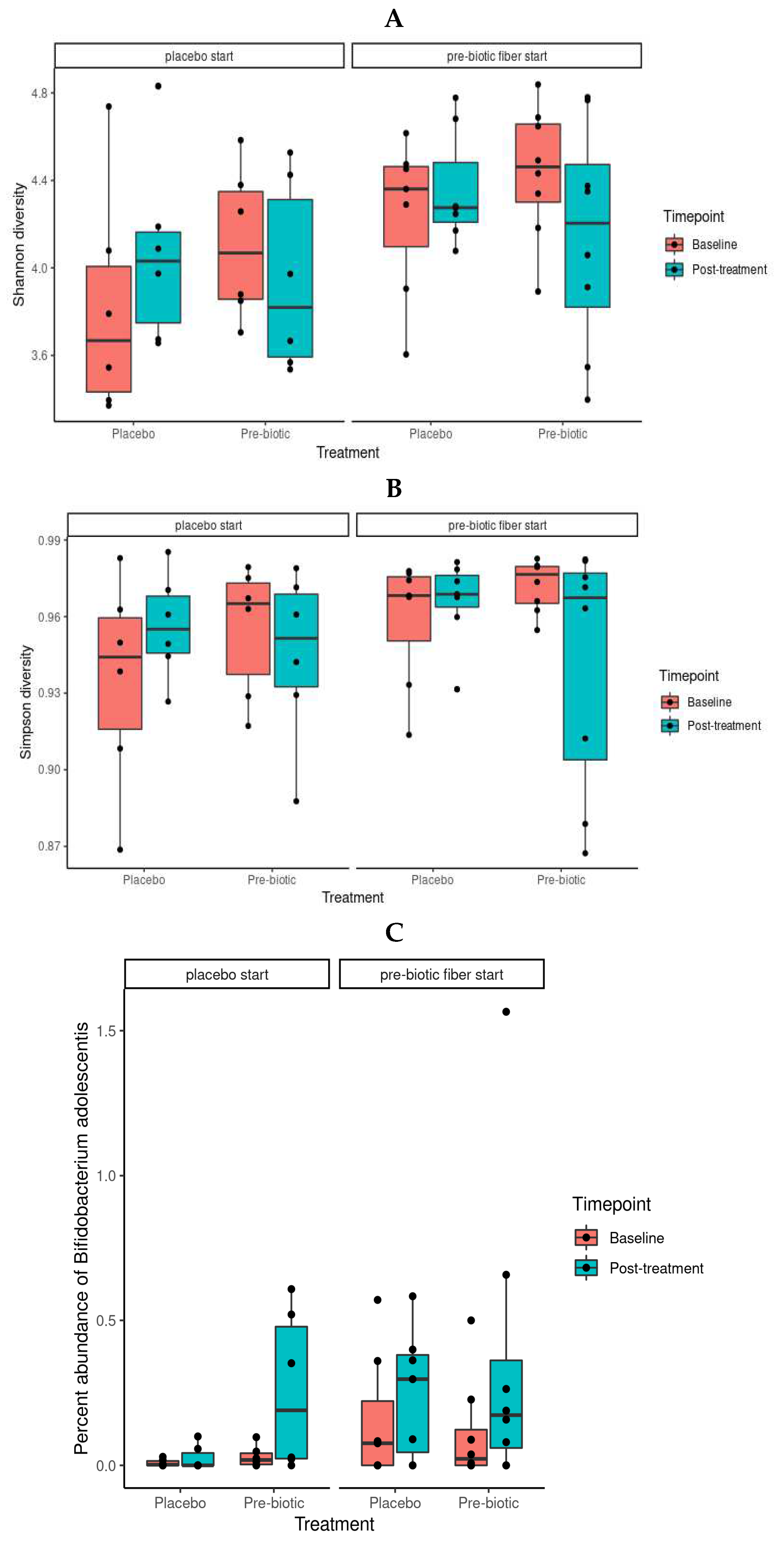
3.5.1. Alpha Diversity Analysis
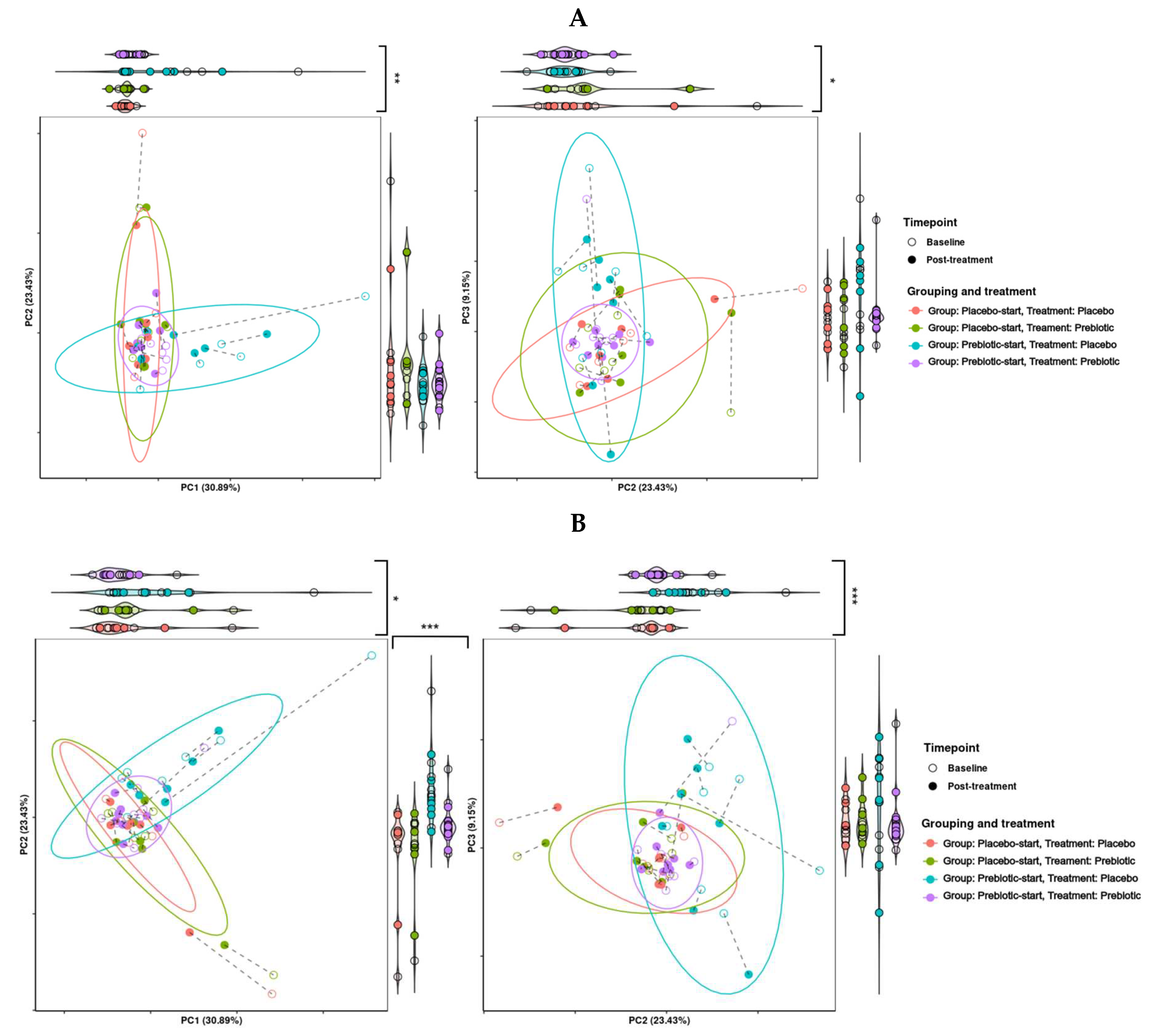
3.5.2. Beta Diversity Analysis
3.5.3. Between-Intervention Differential Abundance Analysis
3.5.4. Microbiome Functional Changes Due to the Intervention
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Adler, E. (1977) Adler 1977, Wood Sci. Technol, 11 , pp. 169.
- Agostoni, C., Bresson, J., Fairweather-Tait, S., Flynn, A., Golly, I., Korhonen, H., Lagiou, P., Løvik, M., Marchelli, R., Martin, A., Moseley, B., Neuhäuser-Berthold, M., Przyrembel, H., Salminen, S., Sanz, Y., , S., Strain, J. J. )., Strobel, S., Tetens, I., Tomé, D., Van Loveren, H., Verhagen, H., Asp, G., Becker, W., Van Den Berg, H., Hulshof, K., Flynn, A., Martin, A., Przyrembel, H., Tetens, I., , E., Valtueña, S. and , M. (2010) Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for carbohydrates and dietary fibre, EFSA Journal, 8 (3), pp. n/a. [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Junior, L. D., Curimbaba, T. F. S., Chagas, A. S., Quaglio, A. E. V. and Di Stasi, L. C. (2017) Dietary intervention with green dwarf banana flour (musa sp. AAA) modulates oxidative stress and colonic SCFAs production in the TNBS model of intestinal inflammation, Journal of Functional Foods, 38 , pp. 497-504. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R., Dharmaprakash, V., Nighot, P., Guo, S., Nighot, M., Do, T. and Ma, T. Y. (2021) Bifidobacterium bifidum enhances the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier and protects against intestinal inflammation by targeting the toll-like receptor-2 pathway in an NF-κB-independent manner, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22 (15), pp. 8070. [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Jasso, G. M., Camacho-Díaz, B. H., Arenas Ocampo, M. L., Jiménez-Ferrer, J. E., Mora-Escobedo, R. and Osorio-Díaz, P. (2020) Prebiotic effects of a mixture of agavins and green banana flour in a mouse model of obesity, Journal of Functional Foods, 64 , pp. 103685. [CrossRef]
- Alves-Santos, A. M., Sugizaki, C. S. A., Lima, G. C. and Naves, M. M. V. (2020) Prebiotic effect of dietary polyphenols: A systematic review, Journal of Functional Foods, 74 , pp. 104169. [CrossRef]
- Amaretti, A., Raimondi, S., Leonardi, A., Quartieri, A. and Rossi, M. (2015) Hydrolysis of the rutinose-conjugates flavonoids rutin and hesperidin by the gut microbiota and bifidobacteria, Nutrients, 7 (4), pp. 2788-2800. [CrossRef]
- Andrews S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data [Online]. 2010. Available: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Annunziata, G., Sureda, A., Orhan, I. E., Battino, M., Arnone, A., Jiménez-García, M., Capó, X., Cabot, J., Sanadgol, N., Giampieri, F., Tenore, G. C., Kashani, H. R. K., Silva, A. S., Habtemariam, S., Nabavi, S. F. and Nabavi, S. M. (2021) The neuroprotective effects of polyphenols, their role in innate immunity and the interplay with the microbiota, Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 128 , pp. 437-453. [CrossRef]
- Asogwa, I. S., Ibrahim, A. N. and Agbaka, J. I. (2021) African baobab: Its role in enhancing nutrition, health, and the environment, Trees, Forests and People (Online), 3, pp. 100043. [CrossRef]
- Assimakopoulos, S. F., Triantos, C., Maroulis, I. and Gogos, C. (2018) The role of the gut barrier function in health and disease, Gastroenterology Research, 11 (4), pp. 261-263. [CrossRef]
- AURA, A., MARTIN-LOPEZ, P., OLEARY, K. A., WILLIAMSON, G., OKSMAN-CALDENTEY, K., POUTANEN, K. and SANTOS-BUELGA, C. (2005) In vitro metabolism of anthocyanins by human gut microflora, European Journal of Nutrition, 44 (3), pp. 133-142. [CrossRef]
- Bang, S., Kim, G., Lim, M. Y., Song, E., Jung, D., Kum, J., Nam, Y., Park, C. and Seo, D. (2018) The influence of in vitro pectin fermentation on the human fecal microbiome, AMB Express, 8 (1), pp. 98. [CrossRef]
- Barber, T. M., Kabisch, S., Pfeiffer, A. F. H. and Weickert, M. O. (2020) The Health Benefits of Dietary Fibre, Nutrients, -10-21, 12 (10). [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R. S. D. and Vieira-Coelho, M. A. (2020) Probiotics and prebiotics: Focus on psychiatric disorders – a systematic review, Nutrition Reviews, 78 (6), pp. 437-450. [CrossRef]
- Baxter, N. T., Schmidt, A. W., Venkataraman, A., Kim, K. S., Waldron, C. and Schmidt, T. M. Dynamics of Human Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Response to Dietary Interventions with Three Fermentable Fibers, .
- Beghini, F., Mciver, L. J., Blanco-Míguez, A., Dubois, L., Asnicar, F., Maharjan, S., Mailyan, A., Manghi, P., Scholz, M., Thomas, A. M., Valles-Colomer, M., Weingart, G., Zhang, Y., Zolfo, M., Huttenhower, C., Franzosa, E. A. and Segata, N. (2021) Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3, eLife, -05-04, 10 . [CrossRef]
- Belenguer, A., Duncan, S. H., Calder, A. G., Holtrop, G., Louis, P., Lobley, G. E. and Flint, H. J. (2006) Two routes of metabolic cross-feeding between bifidobacterium adolescentis and butyrate-producing anaerobes from the human gut, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72 (5), pp. 3593-3599. [CrossRef]
- Berger, K., Burleigh, S., Lindahl, M., Bhattacharya, A., Patil, P., Stålbrand, H., Nordberg Karlsson, E., Hållenius, F., Nyman, M. and Adlercreutz, P. (2021) Xylooligosaccharides Increase Bifidobacteria and Lachnospiraceae in Mice on a High-Fat Diet, with a Concomitant Increase in Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Especially Butyric Acid, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69 (12), pp. 3617. [CrossRef]
- Blatchford, P., Stoklosinski, H., Eady, S., Wallace, A., Butts, C., Gearry, R., Gibson, G. and Ansell, J. (2017) Consumption of kiwifruit capsules increases faecalibacterium prausnitzii abundance in functionally constipated individuals: A randomised controlled human trial, Journal of Nutritional Science, 6 , pp. e52. [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M. and Usadel, B. (2014) Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data, Bioinformatics, 30 (15), pp. 2114-2120. [CrossRef]
- Boto-Ordóñez M, Urpi-Sarda M, Queipo-Ortuño MI, Tulipani S, Tinahones FJ, Andres-Lacueva C. High levels of Bifidobacteria are associated with increased levels of anthocyanin microbial metabolites: a randomized clinical trial. Food Funct. 2014 Aug;5(8):1932-8. PMID: 24958563. [CrossRef]
- Bouhnik, Y., Raskine, L., Champion, K., Andrieux, C., Penven, S., Jacobs, H. and Simoneau, G. (2007) Prolonged administration of low-dose inulin stimulates the growth of bifidobacteria in humans, Nutrition Research (New York, N.Y.), 27 (4), pp. 187-193. [CrossRef]
- Bravo, L., Abia, R. and Saura-Calixto, F. (1994) Polyphenols as dietary fiber associated compounds. comparative study on in vivo and in vitro properties, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 42 (7), pp. 1481-1487. [CrossRef]
- Butler, T. D. and Gibbs, J. E. (2020) Circadian host-microbiome interactions in immunity, Frontiers in Immunology, 11 , pp. 1783. [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J. L., Erickson, J. M., Lloyd, B. B. and Slavin, J. L. (2018) Health effects and sources of prebiotic dietary fiber, Current Developments in Nutrition, 2 (3), pp. nzy005. [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Cedillo, E. G., Rodríguez-Avila, J. A., Arredondo-Soto, K. C. and Cornejo-Bravo, J. M. (2019) Advantages, Disadvantages, and Future Trends on the Use of Design of Experiments in Cross-Over Trials in Nutritional Clinical Investigation, in: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Future Trends on the Use of Design of Experiments in Cross-Over Trials in Nutritional Clinical Investigation, in: Design of Experiments for Chemical, Pharmaceutical, Food, and Industrial Applications, IGI Global, pp. 158-173. [CrossRef]
- CEEREAL Statement on Dietary Fibre, (2022) -02nd, https://ceereal.eu/images/technical-docs/20220210_Statement_on_FIBRE-FINAL.pdf, Accessed 09/03/2023.
- Chan AO, Leung G, Tong T, Wong NY. Increasing dietary fiber intake in terms of kiwifruit improves constipation in Chinese patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Sep 21;13(35):4771-5. PMID: 17729399; PMCID: PMC4611199. [CrossRef]
- Chang, C., Lin, T., Tsai, Y., Wu, T., Lai, W., Lu, C. and Lai, H. (2019) Next generation probiotics in disease amelioration, Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 27 (3), pp. 615-622. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Xu, J. and Chen, Y. (2021) Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders, Nutrients, 13 (6), pp. 2099. [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M. N. (2004) Diet-derived phenols in plasma and tissues and their implications for health, Planta Medica, 70 (12), pp. 1103-1114. [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, A. G., Werner, S. L. and Brown, M. (2020) The effects of prebiotics and substances with prebiotic properties on metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review, Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 120 (4), pp. 587-607.e2. [CrossRef]
- Conway de Macario, E. and Macario, A. J. L. (2009) Methanogenic archaea in health and disease: A novel paradigm of microbial pathogenesis, International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 299 (2), pp. 99-108. [CrossRef]
- Cronin, P., Joyce, S. A., O’Toole, P. W. and O’Connor, E. M. (2021) Dietary fibre modulates the gut microbiota, Nutrients, 13 (5), pp. 1655. [CrossRef]
- 20 February; 73, 36. John H Cummings, George T Macfarlane, Hans N Englyst, Prebiotic digestion and fermentation, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, Volume 73, Issue 2, February 2001, Pages 415s–420s, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.2.415s. [CrossRef]
- Daglia, M. (2012) Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents, Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 23 (2), pp. 174-181. [CrossRef]
- David, L. A., Maurice, C. F., Carmody, R. N., Gootenberg, D. B., Button, J. E., Wolfe, B. E., Ling, A. V., Devlin, A. S., Varma, Y., Fischbach, M. A., Biddinger, S. B., Dutton, R. J. and Turnbaugh, P. J. (2014) Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome, Nature, 505 (7484), pp. 559-563. [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E. C., Duar, R. M., Armet, A. M., Perez-Muñoz, M. E., Jin, M. and Walter, J. (2019) Modulation of the Gastrointestinal Microbiome with Nondigestible Fermentable Carbohydrates To Improve Human Health, Microbiology Spectrum, -06-05, 5 (5). [CrossRef]
- Deleu, S., Machiels, K., Raes, J., Verbeke, K. and Vermeire, S. (2021) Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD? EBioMedicine, 66 , pp. 103293. [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G., van Eunen, K., Groen, A. K., Venema, K., Reijngoud, D. and Bakker, B. M. (2013) The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism, Journal of Lipid Research, 54 (9), pp. 2325-2340. [CrossRef]
- Desai, V., Kozyrskyj, A. L., Lau, S., Sanni, O., Dennett, L., Walter, J. and Ospina, M. B. (2021) Effectiveness of Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotic Supplementation to Improve Perinatal Mental Health in Mothers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Frontiers in Psychiatry, -04th, 12 . [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T. G. and Cryan, J. F. (2017) Microbes, Immunity, and Behavior: Psychoneuroimmunology Meets the Microbiome, Neuropsychopharmacology, 42 (1), pp. 178. [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S. H., Louis, P., Thomson, J. M. and Flint, H. J. (2009) Role of pH in determining the species composition of the human colonic microbiota, Environmental Microbiology, 11 (8), pp. 2112-2122. [CrossRef]
- DUNN, S., DATTA, A., KALLIS, S., LAW, E., MYERS, C. E. and WHELAN, K. (2011) Validation of a food frequency questionnaire to measure intakes of inulin and oligofructose, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 65 (3), pp. 402-408. [CrossRef]
- Durazzi, F., Sala, C., Castellani, G., Manfreda, G., Remondini, D. and De Cesare, A. (2021) Comparison between 16S rRNA and shotgun sequencing data for the taxonomic characterization of the gut microbiota, Scientific Reports, 11 (1), pp. 3030. [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, F., Crichton, M., Dahl, C., Nucera, R., Jenkins, J., Marx, W. and Marshall, S. (2019) Role of dietary fibre in older adults with asymptomatic (AS) or symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease (SUDD): Systematic review and meta-analysis, Maturitas, 130 , pp. 57-67. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C. A., Havlik, J., Cong, W., Mullen, W., Preston, T., Morrison, D. J. and Combet, E. (2017) Polyphenols and health: Interactions between fibre, plant polyphenols and the gut microbiota, Nutrition Bulletin, 42 (4), pp. 356-360. [CrossRef]
- El Mohsen, M. A., Marks, J., Kuhnle, G., Moore, K., Debnam, E., Srai, S. K., Rice-Evans, C. and Spencer, J. P. E. (2006) Absorption, tissue distribution and excretion of pelargonidin and its metabolites following oral administration to rats, British Journal of Nutrition, 95 (1), pp. 51-58. [CrossRef]
- El Oufir, L., Flourié, B., Bruley des Varannes, S., Barry, J. L., Cloarec, D., Bornet, F. and Galmiche, J. P. (1996) Relations between transit time, fermentation products, and hydrogen consuming flora in healthy humans, Gut, 38 (6), pp. 870-877. [CrossRef]
- Falcomer, A. L., Riquette, R. F. R., de Lima, B. R., Ginani, V. C. and Zandonadi, R. P. (2019) Health benefits of green banana consumption: A systematic review, Nutrients, 11 (6), pp. 1222. [CrossRef]
- Falony, G., Vlachou, A., Verbrugghe, K. and Vuyst, L. D. (2006) Cross-feeding between bifidobacterium longum BB536 and acetate-converting, butyrate-producing colon bacteria during growth on oligofructose, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72 (12), pp. 7835-7841. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Daglia, M., Zhang, J., Zhu, Y., Bai, J., Zhu, L. and Xiao, X. (2023) Recent advances in targeted manipulation of the gut microbiome by prebiotics: From taxonomic composition to metabolic function, Current Opinion in Food Science, 49 , pp. 100959. [CrossRef]
- Feduraev, P., Skrypnik, L., Riabova, A., Pungin, A., Tokupova, E., Maslennikov, P. and Chupakhina, G. (2020) Phenylalanine and tyrosine as exogenous precursors of wheat (triticum aestivum L.) secondary metabolism through PAL-associated pathways, Plants, 9 (4), pp. 476. [CrossRef]
- Flint, H. J., Duncan, S. H., Scott, K. P. and Louis, P. (2015) Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 74 (1), pp. 13-22. [CrossRef]
- Flint, H. J., Scott, K. P., Duncan, S. H., Louis, P. and Forano, E. (2012) Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut, Gut Microbes, 3 (4), pp. 289-306. [CrossRef]
- Flowers, S. A., Baxter, N. T., Ward, K. M., Kraal, A. Z., McInnis, M. G., Schmidt, T. M. and Ellingrod, V. L. (2019) Effects of atypical antipsychotic treatment and resistant starch supplementation on gut microbiome composition in a cohort of patients with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia, Pharmacotherapy, 39 (2), pp. 161-170. [CrossRef]
- Foltz, M., Zahradnik, A. C., Van den Abbeele, P., Ghyselinck, J. and Marzorati, M. (2021) A pectin-rich, baobab fruit pulp powder exerts prebiotic potential on the human gut microbiome in vitro, Microorganisms (Basel), 9 (9), pp. 1981. [CrossRef]
- Francisco Javier Álvarez-Martínez, Enrique Barrajón-Catalán, José Antonio Encinar, Juan Carlos Rodríguez-Díaz and Vicente Micol (2020) Antimicrobial capacity of plant polyphenols against gram-positive bacteria: A comprehensive review, Current Medicinal Chemistry, 27 (15), pp. 2576-2606. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mazcorro, J. F., Pedreschi, R., Chew, B., Dowd, S. E., Kawas, J. R. and Noratto, G. D. (2018) Dietary supplementation with raspberry extracts modifies the fecal microbiota in obese diabetic db/db mice, Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 28 (8), pp. 1247-1259. [CrossRef]
- Garthoff, J. A., Heemskerk, S., Hempenius, R. A., Lina, B. A. R., Krul, C. A. M., Koeman, J. H. and Speijers, G. J. A. (2010) Safety evaluation of pectin-derived acidic oligosaccharides (pAOS): Genotoxicity and sub-chronic studies, Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 57 (1), pp. 31-42. [CrossRef]
- Gasaly, N., de Vos, P. and Hermoso, M. A. (2021) Impact of bacterial metabolites on gut barrier function and host immunity: A focus on bacterial metabolism and its relevance for intestinal inflammation, Frontiers in Immunology, 12 , pp. 658354. [CrossRef]
- Ge, L., Qi, J., Shao, B., Ruan, Z., Ren, Y., Sui, S., Wu, X., Sun, X., Liu, S., Li, S., Xu, C. and Song, W. (2022) Microbial hydrogen economy alleviates colitis by reprogramming colonocyte metabolism and reinforcing intestinal barrier, Gut Microbes, -01-13, 14 (1). [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. S., Wang, J., Yannie, P. J. and Ghosh, S. (2020) Intestinal barrier dysfunction, LPS translocation, and disease development, Journal of the Endocrine Society, 4 (2), pp. bvz039. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G. R., Probert, H. M., Loo, J. V., Rastall, R. A. and Roberfroid, M. B. (2004) Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Updating the concept of prebiotics, Nutrition Research Reviews, 17 (2), pp. 259-275. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G. R., Hutkins, R., Sanders, M. E., Prescott, S. L., Reimer, R. A., Salminen, S. J., Scott, K., Stanton, C., Swanson, K. S., Cani, P. D., Verbeke, K. and Reid, G. (2017) Expert consensus document: The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics, Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 14 (8), pp. 491-502. [CrossRef]
- González-Aguilar, G. A., Blancas-Benítez, F. J. and Sáyago-Ayerdi, S. G. (2017) Polyphenols associated with dietary fibers in plant foods: Molecular interactions and bioaccessibility, Current Opinion in Food Science, 13 , pp. 84-88. [CrossRef]
- Gråsten, S., Liukkonen, K., Chrevatidis, A., El-Nezami, H., Poutanen, K. and Mykkänen, H. (2003) Effects of wheat pentosan and inulin on the metabolic activity of fecal microbiota and on bowel function in healthy humans, Nutrition Research, -11th, 23 (11), pp. 1503. [CrossRef]
- Guan, J., Liu, F., Zhao, S., Evivie, S. E., Shi, J., Li, N., Zhao, L., Yue, Y., Xie, Q., Huo, G. and Li, B. (2021) Effect of bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum on the proliferative and tight-junction activities of human fetal colon epithelial cells, Journal of Functional Foods, 86 , pp. 104715. [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M. P. L., Altomare, A., Emerenziani, S., Di Rosa, C., Ribolsi, M., Balestrieri, P., Iovino, P., Rocchi, G. and Cicala, M. (2020) Mechanisms of action of prebiotics and their effects on gastro-intestinal disorders in adults, Nutrients, 12 (4), pp. 1037. [CrossRef]
- Guo, C., Cui, Q., Cheng, J., Chen, J., Zhao, Z., Guo, R., Dai, X., Wei, Z. and Li, W. (2021) Probiotic-fermented chinese dwarf cherry [cerasus humilis (bge.) sok.] juice modulates the intestinal mucosal barrier and increases the abundance of akkermansia in the gut in association with polyphenols, Journal of Functional Foods, 80 , pp. 104424. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., Xie, J. Y., Deng, K., Li, X. K., Yuan, Y., Xuan, Q., Xie, J. Y., He, X. J., Wang, Q., Li, J. K. and Luo, H. (2019) Prophylactic Effects of Bifidobacterium adolescentis on Anxiety and Depression-Like Phenotypes After Chronic Stress: A Role of the Gut Microbiota-Inflammation Axis, Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, -06-18, 13 . [CrossRef]
- Gwiazdowska, D., Juś, K., Jasnowska-Małecka, J. and Kluczyńska, K. (2015) The impact of polyphenols on bifidobacterium growth, Acta Biochimica Polonica, 62 (4), pp. 895-901. [CrossRef]
- Han, K. S., Balan, P., Molist Gasa, F. and Boland, M. (2011) Green kiwifruit modulates the colonic microbiota in growing pigs, Letters in Applied Microbiology, 52 (4), pp. 379-385. [CrossRef]
- He, Q., Si, C., Sun, Z., Chen, Y. and Zhang, X. (2022) The intervention of prebiotics on depression via the Gut–Brain axis, Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 27 (12), pp. 3671. [CrossRef]
- Healey, G., Murphy, R., Butts, C., Brough, L., Whelan, K. and Coad, J. (2018) Habitual dietary fibre intake influences gut microbiota response to an inulin-type fructan prebiotic: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, human intervention study, British Journal of Nutrition, 119 (2), pp. 176-189. [CrossRef]
- Hiel, S., Bindels, L. B., Pachikian, B. D., Kalala, G., Broers, V., Zamariola, G., Chang, B. P., Kambashi, B., Rodriguez, J., Cani, P. D., Neyrinck, A. M., Thissen, J., Luminet, O., Bindelle, J. and Delzenne, N. M. (2019) Effects of a diet based on inulin-rich vegetables on gut health and nutritional behavior in healthy humans, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 109 (6), pp. 1683. [CrossRef]
- Hill, C. (2012) Virulence or niche factors: What's in a name? Journal of Bacteriology, 194 (21), pp. 5725-5727. [CrossRef]
- Ho, J., Nicolucci, A. C., Virtanen, H., Schick, A., Meddings, J., Reimer, R. A. and Huang, C. (2019) Effect of prebiotic on microbiota, intestinal permeability, and glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 104 (10), pp. 4427-4440. [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H. D., Bauer, L. L., Gourineni, V., Pelkman, C. L., Fahey, J., George C and Swanson, K. S. (2015) Agave inulin supplementation affects the fecal microbiota of healthy adults participating in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial, The Journal of Nutrition, 145 (9), pp. 2025-2032. [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, A. T., Olano-Martin, E., Grace, W. E., Gibson, G. R. and Rastall, R. A. (20032-04-204) Pectic Oligosaccharides as Prebiotics, ACS Symposium Series, 20032-04-204, , pp. 54. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R. L., Alvarado, D. A., Swanson, K. S. and Holscher, H. D. (2022) The prebiotic potential of inulin-type fructans: A systematic review, Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 13 (2), pp. 492-529. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R. L., Marco, M. L., Hughes, J. P., Keim, N. L. and Kable, M. E. (2019) The role of the gut microbiome in predicting response to diet and the development of precision nutrition Models—Part I: Overview of current methods, Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 10 (6), pp. 953-978. [CrossRef]
- Ioniță-Mîndrican, C., Ziani, K., Mititelu, M., Oprea, E., Neacșu, S. M., Moroșan, E., Dumitrescu, D., Roșca, A. C., Drăgănescu, D. and Negrei, C. (2022) Therapeutic benefits and dietary restrictions of fiber intake: A state of the art review, Nutrients, 14 (13), pp. 2641. [CrossRef]
- Islam, T., Albracht-Schulte, K., Ramalingam, L., Schlabritz-Lutsevich, N., Park, O., Zabet-Moghaddam, M., Kalupahana, N. S. and Moustaid-Moussa, N. (2023) Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of polyphenols in adipose tissue: Role of gut microbiota, intestinal barrier integrity and zinc homeostasis, The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 115 , pp. 109242. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P. P. J., Wijeyesekera, A. and Rastall, R. A. (2023) Inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides—their role within the food industry as fat and sugar replacers and texture modifiers—what needs to be considered, Food Science & Nutrition, 11 (1), pp. 17-38. [CrossRef]
- Jangid, A., Fukuda, S., Suzuki, Y., Taylor, T. D., Ohno, H. and Prakash, T. (123456789) Shotgun metagenomic sequencing revealed the prebiotic potential of a grain-based diet in mice, Scientific Reports, 123456789th, 12 (1). [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J., Yun, K., Mun, S., Chung, W., Choi, S., Nam, Y., Lim, M. Y., Hong, C. P., Park, C., Ahn, Y. J. and Han, K. (123456789) The effect of taxonomic classification by full-length 16S rRNA sequencing with a synthetic long-read technology, Scientific Reports, 123456789th, 11 (1). [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R., Zhao, S., Wang, R., Feng, H., Zhang, J., Li, X., Mao, Y., Yuan, X., Fei, Z., Zhao, Y., Yu, X., Poon, W. S., Zhu, X., Liu, N., Kang, D., Sun, T., Jiao, B., Liu, X., Yu, R., Zhang, J., Gao, G., Hao, J., Su, N., Yin, G., Zhu, X., Lu, Y., Wei, J., Hu, J., Hu, R., Li, J., Wang, D., Wei, H., Tian, Y., Lei, P., Dong, J. and Zhang, J. (2018) Safety and efficacy of atorvastatin for chronic subdural hematoma in chinese patients: A randomized ClinicalTrial, JAMA Neurology, 75 (11), pp. 1338-1346. [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, N., Milesi, C., Burn, O., Van Den Bogert, B., Nauta, A., Hart, K., Sowden, P., Burnet, P. W. J. and Cohen Kadosh, K. (123456789) Anxiolytic effects of a galacto-oligosaccharides prebiotic in healthy females (18–25 years) with corresponding changes in gut bacterial composition, Scientific Reports, 123456789th, 11 (1). [CrossRef]
- Joossens, M., Huys, G., Van Steen, K., Cnockaert, M., Vermeire, S., Rutgeerts, P., Verbeke, K., Vandamme, P. and De Preter, V. (2011) High-throughput method for comparative analysis of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles from human fecal samples reveals significant increases in two bifidobacterial species after inulin-type prebiotic intake, FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 75 (2), pp. 343-349. [CrossRef]
- Junghare, M., Spiteller, D. and Schink, B. (2019) Anaerobic degradation of xenobiotic isophthalate by the fermenting bacterium syntrophorhabdus aromaticivorans, The ISME Journal, 13 (5), pp. 1252-1268. [CrossRef]
- Kabbashi, N. A., Mirghani, M. E. S. and Bello, I. (2017) Characterization of the Baobab fruit shells as adsorption material, -12th, .
- Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M., Sato, Y. and Morishima, K. (2017) KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs, Nucleic Acids Research, 45 (D1), pp. D353-D361. [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. W., Tang, X., Walton, C. J., Brown, M. J., Brewer, R. A., Maddela, R. L., Zheng, J. J., Agus, J. K. and Zivkovic, A. M. (2022) Multi-Omic Analyses Reveal Bifidogenic Effect and Metabolomic Shifts in Healthy Human Cohort Supplemented With a Prebiotic Dietary Fiber Blend. Frontiers Media SA.
- Kawabata, K., Baba, N., Sakano, T., Hamano, Y., Taira, S., Tamura, A., Baba, S., Natsume, M., Ishii, T., Murakami, S. and Ohigashi, H. (2018) Functional properties of anti-inflammatory substances from quercetin-treated bifidobacterium adolescentis, Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 82 (4), pp. 689-697. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E. D., Bottacini, F.,Callaghan, J., Motherway, M. O.,Connell, K. J., Stanton, C. and van Sinderen, D. (2016) Glycoside hydrolase family 13 α-glucosidases encoded by bifidobacterium breve UCC2003; A comparative analysis of function, structure and phylogeny, International Journal of Food Microbiology, 224 , pp. 55-65. [CrossRef]
- Khorasaniha, R., Olof, H., Voisin, A., Armstrong, K., Wine, E., Vasanthan, T. and Armstrong, H. (2023) Diversity of fibers in common foods: Key to advancing dietary research, Food Hydrocolloids, 139 , pp. 108495. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y., Je, Y. and Giovannucci, E. L. (2021) Association between dietary fat intake and mortality from all-causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies, Clinical Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 40 (3), pp. 1060-1070. [CrossRef]
- Kleessen, B., Hartmann, L. and Blaut, M. (2001) Oligofructose and long-chain inulin: Influence on the gut microbial ecology of rats associated with a human faecal flora, British Journal of Nutrition, 86 (2), pp. 291-300. [CrossRef]
- Kleessen, B., Schwarz, S., Boehm, A., Fuhrmann, H., Richter, A., Henle, T. and Krueger, M. (2007) Jerusalem artichoke and chicory inulin in bakery products affect faecal microbiota of healthy volunteers, British Journal of Nutrition, 98 (3), pp. 540-549. [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, N. S., Odintsova, V. E., Revel-Muroz, A. and Tyakht, A. V. (2022) The hallmarks of dietary intervention-resilient gut microbiome, NPJ Biofilms and Microbiomes, 8 (1), pp. 77. [CrossRef]
- Kolida, S., Meyer, D. and Gibson, G. R. (2007) Double-blind placebo-controlled study to establish the bifidogenic dose of inulin in healthy humans, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 61 (10), pp. 1189-1195. [CrossRef]
- Kumarihami, H. M. P. C., Kim, J. G., Kim, Y. G., Lee, M., Lee, Y., Kwack, Y. and Kim, J. G. (2021) Preharvest Application of Chitosan Improves the Postharvest Life of ‘Garmrok’ Kiwifruit through the Modulation of Genes Related to Ethylene Biosynthesis, Cell Wall Modification and Lignin Metabolism, Foods, -02-09, 10 (2). [CrossRef]
- Le Bastard, Q., Chapelet, G., Javaudin, F., Lepelletier, D., Batard, E. and Montassier, E. (2020) The effects of inulin on gut microbial composition: A systematic review of evidence from human studies, European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 39 (3), pp. 403-413. [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, G., Guttula, K., Kellingray, L., Tett, A. J., Ten Hoopen, R., Kemsley, E. K., Savva, G. M., Ibrahim, A. and Narbad, A. (2018) Metabolite quantification of faecal extracts from colorectal cancer patients and healthy controls, Oncotarget, 9 (70), pp. 33278-33289. [CrossRef]
- Leeming, E. R., Johnson, A. J., Spector, T. D. and Le Roy, C. I. (2019) Effect of diet on the gut microbiota: Rethinking intervention duration, Nutrients, 11 (12), pp. 2862. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.J. and K.W., Heaton (1997) Stool From Scale as a Useful guide to Intestinal Transit Time, Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 32:9, 920-924. [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Li, M., Song, Y., Huang, X., Wu, T., Xu, Z. Z. and Lu, H. (2022) Green banana flour contributes to gut microbiota recovery and improves colonic barrier integrity in mice following antibiotic perturbation, Frontiers in Nutrition (Lausanne), 9 , pp. 832848. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H. and Peddada, S. D. (2020) Analysis of microbial compositions: A review of normalization and differential abundance analysis, NPJ Biofilms and Microbiomes, 6 (1), pp. 60. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F., Prabhakar, M., Ju, J., Long, H. and Zhou, H. (2017) Effect of inulin-type fructans on blood lipid profile and glucose level: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71 (1), pp. 9. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F., Li, P., Chen, M., Luo, Y., Prabhakar, M., Zheng, H., He, Y., Qi, Q., Long, H., Zhang, Y., Sheng, H. and Zhou, H. (2017) Fructooligosaccharide (FOS) and Galactooligosaccharide (GOS) Increase Bifidobacterium but Reduce Butyrate Producing Bacteria with Adverse Glycemic Metabolism in healthy young population, Scientific Reports, -09-18, 7 (1). [CrossRef]
- Liu, R. T., Walsh, R. F. L. and Sheehan, A. E. (2019) Prebiotics and probiotics for depression and anxiety: A systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials, Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 102 , pp. 13-23. [CrossRef]
- Livingston, K. A., Chung, M., Sawicki, C. M., Lyle, B. J., Wang, D. D., Roberts, S. B. and Mckeown, N. M. (2016) Development of a Publicly Available, Comprehensive Database of Fiber and Health Outcomes: Rationale and Methods, Plos One, -06-27, 11 (6). [CrossRef]
- LoCascio, R. G., Desai, P., Sela, D. A., Weimer, B. and Mills, D. A. (2010) Broad conservation of milk utilization genes in bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis as revealed by comparative genomic hybridization, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76 (22), pp. 7373-7381. [CrossRef]
- Louis, P. and Flint, H. J. (2017) Formation of propionate and butyrate by the human colonic microbiota, Environmental Microbiology, 19 (1), pp. 29-41. [CrossRef]
- Lovibond, P. F. and Lovibond, S. H. (1995) The structure of negative emotional states: Comparison of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and Anxiety Inventories, Behaviour Research and Therapy, 33 (3), pp. 335. [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C. A., Hamady, M., Cantarel, B. L., Coutinho, P. M., Henrissat, B., Gordon, J. I. and Knight, R. (2008) Convergence of carbohydrate active gene repertoires in human gut microbes, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences - PNAS, 105 (39), pp. 15076-15081. [CrossRef]
- Lund, P., Tramonti, A. and De Biase, D. (2014) Coping with low pH: Molecular strategies in neutralophilic bacteria, FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 38 (6), pp. 1091-1125. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X., Liu, S., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Gu, T., Li, Y., Xin, F. and Wen, B. (2023) In vitro fermentation of beechwood lignin-carbohydrate complexes provides evidence for utilization by gut bacteria, Nutrients, 15 (1), pp. 220. [CrossRef]
- Mailing, L. J., Allen, J. M., Pence, B. D., Rytych, J., Sun, Y., Bhattacharya, T. K., Park, P., Cross, T. L., McCusker, R. H., Swanson, K. S., Fahey, G. C., Rhodes, J. S., Kelley, K. W., Johnson, R. W. and Woods, J. A. (2019) Behavioral response to fiber feeding is cohort-dependent and associated with gut microbiota composition in mice, Behavioural Brain Research, 359 , pp. 731-736. [CrossRef]
- Maiuolo, J., Gliozzi, M., Musolino, V., Carresi, C., Scarano, F., Nucera, S., Scicchitano, M., Oppedisano, F., Bosco, F., Ruga, S., Zito, M. C., Macri, R., Palma, E., Muscoli, C. and Mollace, V. (2021) The Contribution of Gut Microbiota–Brain Axis in the Development of Brain Disorders, Frontiers in Neuroscience, -03-23, 15 . [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, M., Drożdż, I., Tarko, T. and Duda-Chodak, A. (2021) The interactions between polyphenols and microorganisms, especially gut microbiota, Antioxidants, 10 (2), pp. 188. [CrossRef]
- Makki, K., Deehan, E. C., Walter, J. and Bäckhed, F. (2018) The impact of dietary fiber on gut microbiota in host health and disease, Cell Host & Microbe, 23 (6), pp. 705-715. [CrossRef]
- Manderson, K., Pinart, M., Tuohy, K. M., Grace, W. E., Hotchkiss, A. T., Widmer, W., Yadhav, M. P., Gibson, G. R. and Rastall, R. A. (2005) In vitro determination of prebiotic properties of oligosaccharides derived from an orange juice manufacturing by-product stream, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71 (12), pp. 8383-8389. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M., Ohishi, H. and Benno, Y. (2004) H +-ATPase activity in bifidobacterium with special reference to acid tolerance, International Journal of Food Microbiology, 93 (1), pp. 109-113. [CrossRef]
- Mazur, S. P., Nes, A., Wold, A., Remberg, S. F. and Aaby, K. (2014) Quality and chemical composition of ten red raspberry (rubus idaeus L.) genotypes during three harvest seasons, Food Chemistry, 160 , pp. 233-240. [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P. J. and Holmes, S. (2013) Phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data, PLoS ONE, 8 (4), pp. e61217. [CrossRef]
- Metges, C. C. (2000) Contribution of microbial amino acids to amino acid homeostasis of the host, The Journal of Nutrition, 130 (7), pp. 1857S-1864S. [CrossRef]
- Míguez, B. (2016) Pectic Oligosaccharides and Other Emerging Prebiotics, in: Pectic Oligosaccharides and Other Emerging Prebiotics, in: IntechOpen. [CrossRef]
- Moens, F., Verce, M. and De Vuyst, L. (2017) Lactate- and acetate-based cross-feeding interactions between selected strains of lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and colon bacteria in the presence of inulin-type fructans, International Journal of Food Microbiology, 241 , pp. 225-236. [CrossRef]
- Mora, D. and Arioli, S. (2014) Microbial urease in health and disease, PLoS Pathogens, 10 (12), pp. e1004472. [CrossRef]
- Moshfegh, A. J., Friday, J. E., Goldman, J. P. and Chug Ahuja, J. K. (1999) Presence of inulin and oligofructose in the diets of americans, The Journal of Nutrition, 129 (7S), pp. 1407-1411. [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A., Kobiita, A., Ye, T. and Chambon, P. (2013) Homeostasis in intestinal epithelium is orchestrated by the circadian clock and microbiota cues transduced by TLRs, Cell, 153 (4), pp. 812-827. [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M., Tognini, P., Liu, Y., Eckel-Mahan, K. L., Baldi, P. and Sassone-Corsi, P. (2016) Gut microbiota directs PPARγ-driven reprogramming of the liver circadian clock by nutritional challenge, EMBO Reports, 17 (9), pp. 1292-1303. [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S. I. and Mancilha, I. M. (2007) Non-digestible oligosaccharides: A review, Carbohydrate Polymers, 68 (3), pp. 587-597. [CrossRef]
- Myhrstad, M. C. W., Tunsjø, H., Charnock, C. and Telle-Hansen, V. H. (2020) Dietary fiber, gut microbiota, and metabolic Regulation—Current status in human randomized trials, Nutrients, 12 (3), pp. 859. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A., Kurihara, S., Takahashi, D., Ohashi, W., Nakamura, Y., Kimura, S., Onuki, M., Kume, A., Sasazawa, Y., Furusawa, Y., Obata, Y., Fukuda, S., Saiki, S., Matsumoto, M. and Hase, K. (2021) Symbiotic polyamine metabolism regulates epithelial proliferation and macrophage differentiation in the colon, Nature Communications, -04-08, 12 (1). [CrossRef]
- NDNS (2016. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/943114/NDNS_UK_Y9-11_report.pdf, Accessed 9/03/2023.
- Neri-Numa, I. A. and Pastore, G. M. (2020) Novel insights into prebiotic properties on human health: A review, Food Research International, 131 , pp. 108973. [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A. M., Nazare, J., Rodriguez, J., Jottard, R., Dib, S., Sothier, M., Berghe, L. V. D., Alligier, M., Alexiou, H., Maquet, V., Vinoy, S., Bischoff, S. C., Walter, J., Laville, M. and Delzenne, N. M. (2020) Development of a Repertoire and a Food Frequency Questionnaire for Estimating Dietary Fiber Intake Considering Prebiotics: Input from the FiberTAG Project, Nutrients, 12 (9). [CrossRef]
- Niemi, Pritta, Anna-Marja Aura, Johanna Maukonen, Annika I. Smeds, Ismo Mattila, Klaus Niemelä, Tarja Tamminen, Craig B. Faulds, Johanna Buchert, and Kaisa Poutanen (2013) Interactions of a Lignin-Rich Fraction from Brewer’s Spent Grain with Gut Microbiota in Vitro, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61 (27), 6754-6762. [CrossRef]
- Nikolaieva, N., Sevcikova, A., Omelka, R., Martiniakova, M., Mego, M. and Ciernikova, S. (2022) Gut microbiota-MicroRNA interactions in intestinal homeostasis and cancer development, Microorganisms (Basel), 11 (1), pp. 107. [CrossRef]
- Novakovic, M., Rout, A., Kingsley, T., Kirchoff, R., Singh, A., Verma, V., Kant, R. and Chaudhary, R. (2020) Role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular diseases, World Journal of Cardiology, 12 (4), pp. 110-122. [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Gómez, V., Periago, M. J., Navarro-González, I., Campos-Cava, M. P., Baenas, N. and González-Barrio, R. (2021) Influence of raspberry and its dietary fractions on the in vitro activity of the colonic microbiota from normal and overweight subjects, Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (Dordrecht), 76 (4), pp. 494-500. [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S. J. D. (2018) The need to reassess dietary fiber requirements in healthy and critically ill patients, Gastroenterology Clinics of North America, 47 (1), pp. 219-229. [CrossRef]
- Oksanen J, Blanchet GF, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, B. O’Hara R, et al. Community Ecology Package: Ordination, Diversity and Dissimilarities. https://CRANR-project.org/package=vegan. 2022. Available: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.
- Ozdal, T., Sela, D. A., Xiao, J., Boyacioglu, D., Chen, F. and Capanoglu, E. (2016) The reciprocal interactions between polyphenols and gut microbiota and effects on bioaccessibility, Nutrients, 8 (2), pp. 78. [CrossRef]
- Parkar, S. G., Rosendale, D., Paturi, G., Herath, T. D., Stoklosinski, H., Phipps, J. E., Hedderley, D. and Ansell, J. (2012) In vitro utilization of gold and green kiwifruit oligosaccharides by human gut microbial populations, Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (Dordrecht), 67 (3), pp. 200-207. [CrossRef]
- Parks, D. H., Chuvochina, M., Rinke, C., Mussig, A. J., Chaumeil, P. and Hugenholtz, P. (2022) GTDB: An ongoing census of bacterial and archaeal diversity through a phylogenetically consistent, rank normalized and complete genome-based taxonomy, Nucleic Acids Research, 50 (D1), pp. D785-D794. [CrossRef]
- Pascale, N., Gu, F., Larsen, N., Jespersen, L. and Respondek, F. (2022) The potential of pectins to modulate the human gut microbiota evaluated by in vitro fermentation: A systematic review, Nutrients, 14 (17), pp. 3629. [CrossRef]
- Peron, G., Gargari, G., Meroño, T., Miñarro, A., Lozano, E. V., Escuder, P. C., González-Domínguez, R., Hidalgo-Liberona, N., Del Bo’, C., Bernardi, S., Kroon, P. A., Carrieri, B., Cherubini, A., Riso, P., Guglielmetti, S. and Andrés-Lacueva, C. (2021) Crosstalk among intestinal barrier, gut microbiota and serum metabolome after a polyphenol-rich diet in older subjects with “leaky gut”: The MaPLE trial, Clinical Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 40 (10), pp. 5288-5297. [CrossRef]
- Popoola-Akinola, O. O., Raji, T. J. and Olawoye, B. (2022) Lignocellulose, dietary fibre, inulin and their potential application in food, Heliyon, 8 (8), pp. e10459. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X., Yun, C., Pang, Y. and Qiao, J. (2021) The impact of the gut microbiota on the reproductive and metabolic endocrine system, Gut Microbes, -01-01, 13 (1). [CrossRef]
- Qian, X., Si, Q., Lin, G., Zhu, M., Lu, J., Zhang, H., Wang, G. and Chen, W. (2022) Bifidobacterium adolescentis is effective in relieving type 2 diabetes and may be related to its dominant core genome and gut microbiota modulation capacity, Nutrients, 14 (12), pp. 2479. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Farias, C., Slezak, K., Fuller, Z., Duncan, A., Holtrop, G. and Louis, P. (2009) Effect of inulin on the human gut microbiota: Stimulation of bifidobacterium adolescentis and faecalibacterium prausnitzii, British Journal of Nutrition, 101 (4), pp. 541-550. [CrossRef]
- Rao, S. S. C., Yu, S. and Fedewa, A. (2015) Systematic review: Dietary fibre and FODMAP-restricted diet in the management of constipation and irritable bowel syndrome, Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 41 (12), pp. 1256-1270. [CrossRef]
- Rao, J. N., Xiao, L. and Wang, J. (2020) Polyamines in Gut Epithelial Renewal and Barrier Function, Physiology, -09-01, 35 (5), pp. 328. [CrossRef]
- Regan, M., Chiang, E., Liu, Y., Tonelli, M., Verdoorn, K., Gugel, S., Suen, G., Carey, H. and Assadi-Porter, F. (2021) Urea nitrogen recycling via gut symbionts increases in hibernators over the winter fast. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
- Ren, W., Chen, S., Yin, J., Duan, J., Li, T., Liu, G., Feng, Z., Tan, B., Yin, Y. and Wu, G. (2014) Dietary arginine supplementation of mice alters the microbial population and activates intestinal innate immunity, The Journal of Nutrition, 144 (6), pp. 988-995. [CrossRef]
- Riva, A., Kolimár, D., Spittler, A., Wisgrill, L., Herbold, C. W., Abrankó, L. and Berry, D. (2020) Conversion of Rutin, a Prevalent Dietary Flavonol, by the Human Gut Microbiota, Frontiers in Microbiology, -12-21, 11 . [CrossRef]
- Rivière, A., Gagnon, M., Weckx, S., Roy, D. and De Vuyst, L. (2015) Mutual cross-feeding interactions between bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum NCC2705 and eubacterium rectale ATCC 33656 explain the bifidogenic and butyrogenic effects of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides, Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81 (22), pp. 7767-7781. [CrossRef]
- Rivière, A., Selak, M., Lantin, D., Leroy, F. and De Vuyst, L. (2016) Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: Importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut, Frontiers in Microbiology, 7 , pp. 979. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M. C., Pulido-Mateos, E. C., Lupien-Meilleur, J., Guyonnet, D., Desjardins, Y. and Roy, D. (2021) Polyphenol-mediated gut microbiota modulation: Toward prebiotics and further, Frontiers in Nutrition (Lausanne), 8 , pp. 689456. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M., Roquim, M., Dudonné, S., Pilon, G., Levy, E., Marette, A., Roy, D. and Desjardins, Y. (2020) Berry polyphenols and fibers modulate distinct microbial metabolic functions and gut microbiota enterotype-like clustering in obese mice, Frontiers in Microbiology, 11 , pp. 2032. [CrossRef]
- Rößle, C., Ktenioudaki, A. and Gallagher, E. (2011) Inulin and oligofructose as fat and sugar substitutes in quick breads (scones): A mixture design approach, European Food Research & Technology, 233 (1), pp. 167-181. [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I., Gibson, G., Heinken, A., Scott, K., Swann, J., Thiele, I. and Tuohy, K. (2018) Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components, European Journal of Nutrition, 57 (1), pp. 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Rush, E. C., Patel, M., Plank, L. D. and Ferguson, L. R. (2002) Kiwifruit promotes laxation in the elderly, Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 11 (2), pp. 164-168. [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, J. C. (2014) The emerging role of urease as a general microbial virulence factor, PLoS Pathogens, 10 (5), pp. e1004062. [CrossRef]
- Ryvchin, R., Dubinsky, V., Rabinowitz, K., Wasserberg, N., Dotan, I. and Gophna, U. (2021) Alteration in urease-producing bacteria in the gut microbiomes of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases, Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, 15 (12), pp. 2066-2077. [CrossRef]
- Salazar, N., Dewulf, E. M., Neyrinck, A. M., Bindels, L. B., Cani, P. D., Mahillon, J., de Vos, W. M., Thissen, J., Gueimonde, M., de los Reyes-Gavilán, C. G. and Delzenne, N. M. (2015) Inulin-type fructans modulate intestinal bifidobacterium species populations and decrease fecal short-chain fatty acids in obese women, Clinical Nutrition, 34 (3), pp. 501-507. [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A., Lahti, L. M., Salojärvi, J., Holtrop, G., Korpela, K., Duncan, S. H., Date, P., Farquharson, F., Johnstone, A. M., Lobley, G. E., Louis, P., Flint, H. J. and de Vos, W. M. (2014) Impact of diet and individual variation on intestinal microbiota composition and fermentation products in obese men, The ISME Journal, 8 (11), pp. 2218-2230. [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, C. M., Livingston, K. A., Obin, M., Roberts, S. B., Chung, M. and Mckeown, N. M. (2017) Dietary Fiber and the Human Gut Microbiota: Application of Evidence Mapping Methodology, Nutrients, -02-10, 9 (2). [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K., Cowen, P. J., Harmer, C. J., Tzortzis, G., Errington, S. and Burnet, P. W. J. (2015) Prebiotic intake reduces the waking cortisol response and alters emotional bias in healthy volunteers, Psychopharmacology, 232 (10), pp. 1793-1801. [CrossRef]
- Schwab, C., Ruscheweyh, H., Bunesova, V., Pham, V. T., Beerenwinkel, N. and Lacroix, C. (2017) Trophic interactions of infant bifidobacteria and eubacterium hallii during L-fucose and fucosyllactose degradation, Frontiers in Microbiology, 8 , pp. 95. [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. P., Martin, J. C., Chassard, C., Clerget, M., Potrykus, J., Campbell, G., Mayer, C., Young, P., Rucklidge, G., Ramsay, A. G. and Flint, H. J. (2011) Substrate-driven gene expression in roseburia inulinivorans: Importance of inducible enzymes in the utilization of inulin and starch, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences - PNAS, 108 (Supplement 1), pp. 4672-4679. [CrossRef]
- Sealed Envelope Ltd (2022) Simple randomisation service. [Online] Available from: https://www.sealedenvelope.com/simple-randomiser/v1. Accessed 27.02.2023.
- Sender, R., Fuchs, S. and Milo, R. (2016) Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body, PLoS Biology, 14 (8), pp. e1002533. [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, P., Louis, P., Tsompanidou, E., Shaw, S., Harmsen, H., Duncan, S., Flint, H. and Walker, A. (2021) Distribution, organization and expression of genes concerned with anaerobic lactate-utilization in human intestinal bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
- Shetty, S. A., Kuipers, B., Atashgahi, S., Aalvink, S., Smidt, H. and Vos, W. M. d. (2022) Inter-species metabolic interactions in an in-vitro minimal human gut microbiome of core bacteria, NPJ Biofilms and Microbiomes, 8 (1), pp. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Shinde, T., Perera, A. P., Vemuri, R., Gondalia, S. V., Beale, D. J., Karpe, A. V., Shastri, S., Basheer, W., Southam, B., Eri, R. and Stanley, R. (2020) Synbiotic supplementation with prebiotic green banana resistant starch and probiotic bacillus coagulans spores ameliorates gut inflammation in mouse model of inflammatory bowel diseases, European Journal of Nutrition, 59 (8), pp. 3669-3689. [CrossRef]
- Silva, M., Cueva, C., Alba, C., Rodriguez, J. M., de Pascual-Teresa, S., Jones, J., Caturla, N., Victoria Moreno-Arribas, M. and Bartolomé, B. (2022) Gut microbiome-modulating properties of a polyphenol-enriched dietary supplement comprised of hibiscus and lemon verbena extracts. monitoring of phenolic metabolites, Journal of Functional Foods, 91 , pp. 105016. [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y. P., Bernardi, A. and Frozza, R. L. (2020) The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in gut-brain communication, Frontiers in Endocrinology, 11 , pp. 25. [CrossRef]
- Simpson (1949) Measurements of diversity, Nature, Vol. 163.
- Singh, R. P. (2019) Glycan utilisation system in bacteroides and bifidobacteria and their roles in gut stability and health, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 103 (18), pp. 7287-7315. [CrossRef]
- Singhal, R., Donde, H., Ghare, S., Stocke, K., Zhang, J., Vadhanam, M., Reddy, S., Gobejishvili, L., Chilton, P., Joshi-Barve, S., Feng, W., Mcclain, C., Hoffman, K., Petrosino, J., Vital, M. and Barve, S. (2021) Decrease in acetyl-CoA pathway utilizing butyrate-producing bacteria is a key pathogenic feature of alcohol-induced functional gut microbial dysbiosis and development of liver disease in mice, Gut Microbes, -01-01, 13 (1). [CrossRef]
- So, D., Whelan, K., Rossi, M., Morrison, M., Holtmann, G., Kelly, J. T., Shanahan, E. R., Staudacher, H. M. and Campbell, K. L. Dietary fiber intervention on gut microbiota composition in healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, . [CrossRef]
- Srour, B., Fezeu, L. K., Kesse-Guyot, E., Allès, B., Méjean, C., Andrianasolo, R. M., Chazelas, E., Deschasaux, M., Hercberg, S., Galan, P., Monteiro, C. A., Julia, C. and Touvier, M. (2019) Ultra-processed food intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: prospective cohort study (NutriNet-Santé), Bmj, -05-29, . [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, H. M., Irving, P. M., Lomer, M. C. E. and Whelan, K. (2017) The challenges of control groups, placebos and blinding in clinical trials of dietary interventions, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 76 (3), pp. 203-212. [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A. M., Champ, M. M. -., Cloran, S. J., Fleith, M., van Lieshout, L., Mejborn, H. and Burley, V. J. (2017) Dietary fibre in europe: Current state of knowledge on definitions, sources, recommendations, intakes and relationships to health, Nutrition Research Reviews, 30 (2), pp. 149-190. [CrossRef]
- Suzek, B. E., Wang, Y., Huang, H., McGarvey, P. B. and Wu, C. H. (2015) UniRef clusters: A comprehensive and scalable alternative for improving sequence similarity searches, Bioinformatics, 31 (6), pp. 926-932. [CrossRef]
- Swann, J. R., Rajilic-Stojanovic, M., Salonen, A., Sakwinska, O., Gill, C., Meynier, A., Fança-Berthon, P., Schelkle, B., Segata, N., Shortt, C., Tuohy, K. and Hasselwander, O. (2020) Considerations for the design and conduct of human gut microbiota intervention studies relating to foods, European Journal of Nutrition, 59 (8), pp. 3347-3368. [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K. S., de Vos, W. M., Martens, E. C., Gilbert, J. A., Menon, R. S., Soto-Vaca, A., Hautvast, J., Meyer, P. D., Borewicz, K., Vaughan, E. E. and Slavin, J. L. (2020) Effect of fructans, prebiotics and fibres on the human gut microbiome assessed by 16S rRNA-based approaches : A review, Beneficial Microbes, 11 (2), pp. 101-129. [CrossRef]
- Talavera, M. M., Nuthakki, S., Cui, H., Jin, Y., Liu, Y. and Nelin, L. D. (2017) Immunostimulated arginase II expression in intestinal epithelial cells reduces nitric oxide production and apoptosis, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 5 , pp. 15. [CrossRef]
- Tandon, D., Haque, M. M., Gote, M., Jain, M., Bhaduri, A., Dubey, A. K. and Mande, S. S. (2019) A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response relationship study to investigate efficacy of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on human gut microflora, Scientific Reports, 9 (1), pp. 5473. [CrossRef]
- Tanes, C., Bittinger, K., Gao, Y., Friedman, E. S., Nessel, L., Paladhi, U. R., Chau, L., Panfen, E., Fischbach, M. A., Braun, J., Xavier, R. J., Clish, C. B., Li, H., Bushman, F. D., Lewis, J. D. and Wu, G. D. (2021) Role of dietary fiber in the recovery of the human gut microbiome and its metabolome, Cell Host & Microbe, 29 (3), pp. 394-407.e5. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H., Fang, Z. and Ng, K. (2020) Dietary fiber-based colon-targeted delivery systems for polyphenols, Trends in Food Science & Technology, 100 , pp. 333-348. [CrossRef]
- Teufel, R., Mascaraque, V., Ismail, W., Voss, M., Perera, J., Eisenreich, W., Haehnel, W., Fuchs, G. and Harwood, C. S. (2010) Bacterial phenylalanine and phenylacetate catabolic pathway revealed, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences - PNAS, 107 (32), pp. 14390-14395. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M. S., Hui Yan, T., Saari, N. and Sarbini, S. R. (2022) A review: Resistant starch, a promising prebiotic for obesity and weight management, Food Bioscience, 50 , pp. 101965. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R. S., Roller, R., Mika, A., Greenwood, B. N., Knight, R., Chichlowski, M., Berg, B. M. and Fleshner, M. (2017) Dietary prebiotics and bioactive milk fractions improve NREM sleep, enhance REM sleep rebound and attenuate the stress-induced decrease in diurnal temperature and gut microbial alpha diversity, Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 10 , pp. 240. [CrossRef]
- Threapleton, D. E., Greenwood, D. C., Evans, C. E. L., Cleghorn, C. L., Nykjaer, C., Woodhead, C., Cade, J. E., Gale, C. P. and Burley, V. J. (2013) Dietary fibre intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis, Bmj, -12-19, 347 (dec19 2), pp. f6879. [CrossRef]
- Tian, X., Li, R., Jiang, Y., Zhao, F., Yu, Z., Wang, Y., Dong, Z., Liu, P. and Li, X. (2020) Bifidobacterium breve ATCC15700 pretreatment prevents alcoholic liver disease through modulating gut microbiota in mice exposed to chronic alcohol intake, Journal of Functional Foods, 72 , pp. 104045. [CrossRef]
- Tomas, M. (2022) Effect of dietary fiber addition on the content and in vitro bioaccessibility of antioxidants in red raspberry puree, Food Chemistry, 375 , pp. 131897. [CrossRef]
- Toribio-Mateas, M. A., Bester, A. and Klimenko, N. (2021) Impact of plant-based meat alternatives on the gut microbiota of consumers: A real-world study, Foods, 10 (9), pp. 2040. [CrossRef]
- Tsitko, Wiik-Miettinen, Mattila, Rosa-Sibakov, Maukonen, Nordlund and Saarela (2019) A Small In Vitro Fermentation Model for Screening the Gut Microbiota Effects of Different Fiber Preparations, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, -04-18, 20 (8). [CrossRef]
- Unseenbio.com (2023) https://my.unseenbio.com/en/taxa/species/cag-81-sp900066785 Accessed 28.02.2023.
- USDA ARS (2021). https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400530/pdf/1720/Table_1_NIN_GEN_1720.pdf Accessed 9.03.2023.
- Uyanga, V. A., Amevor, F. K., Liu, M., Cui, Z., Zhao, X. and Lin, H. (2021) Potential Implications of Citrulline and Quercetin on Gut Functioning of Monogastric Animals and Humans: A Comprehensive Review, Nutrients, -10-25, 13 (11). [CrossRef]
- Van Den Abbeele, P., Ghyselinck, J., Marzorati, M., Koch, A., Lambert, W., Michiels, J. and Chalvon-Demersay, T. (2022) The Effect of Amino Acids on Production of SCFA and bCFA by Members of the Porcine Colonic Microbiota, Microorganisms, -03-31, 10 (4). [CrossRef]
- Van Rymenant, E., Abrankó, L., Tumova, S., Grootaert, C., Van Camp, J., Williamson, G. and Kerimi, A. (2017) Chronic exposure to short-chain fatty acids modulates transport and metabolism of microbiome-derived phenolics in human intestinal cells, The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 39 , pp. 156-168. [CrossRef]
- Vandeputte, D., Falony, G., Vieira-Silva, S., Wang, J., Sailer, M., Theis, S., Verbeke, K. and Raes, J. (2017) Prebiotic inulin-type fructans induce specific changes in the human gut microbiota, Gut, -02-17, 66 (11), pp. 1968. [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, A., Sieber, J. R., Schmidt, A. W., Waldron, C., Theis, K. R. and Schmidt, T. M. (2016) Variable responses of human microbiomes to dietary supplementation with resistant starch, Microbiome, -06-29, 4 (1). [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M., Turroni, F., Zomer, A., Foroni, E., Giubellini, V., Bottacini, F., Canchaya, C., Claesson, M. J., He, F., Mantzourani, M., Mulas, L., Ferrarini, A., Gao, B., Delledonne, M., Henrissat, B., Coutinho, P., Oggioni, M., Gupta, R. S., Zhang, Z., Beighton, D., Fitzgerald, G. F., O'Toole, P. W. and van Sinderen, D. (2009) The bifidobacterium dentium Bd1 genome sequence reflects its genetic adaptation to the human oral cavity, PLoS Genetics, 5 (12), pp. e1000785. [CrossRef]
- Vieira Bezerra, C., Da, A. M., Rodrigues3, C., Amante, E. R., Luiza, H., Meller, D. A. and Silva (2013) NUTRITIONAL POTENTIAL OF GREEN BANANA FLOUR OBTAINED BY DRYING IN SPOUTED BED 1 POTENCIAL NUTRICIONAL DA FARINHA DE BANANA VERDE OBTIDA POR SECAGEM EM LEITO DE JORRO, Rev. Bras. Frutic., Jaboticabal -SP, , pp. 1140.
- Vrancken, G., Rimaux, T., Wouters, D., Leroy, F. and De Vuyst, L. (2009) The arginine deiminase pathway of lactobacillus fermentum IMDO 130101 responds to growth under stress conditions of both temperature and salt, Food Microbiology, 26 (7), pp. 720-727. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B. D., Grunwald, G. K., Zerbe, G. O., Mikulich-Gilbertson, S. K., Robertson, C. E., Zemanick, E. T. and Harris, J. K. (2018) On the Use of Diversity Measures in Longitudinal Sequencing Studies of Microbial Communities, Frontiers in Microbiology, -05th, 9 . [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Huang, X., Tan, H., Chen, X., Chen, C. and Nie, S. (2022) Interaction between dietary fiber and bifidobacteria in promoting intestinal health, Food Chemistry, 393 , pp. 133407. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Wang, P., Li, D., Hu, X. and Chen, F. (2020) Beneficial effects of ginger on prevention of obesity through modulation of gut microbiota in mice, European Journal of Nutrition, 59 (2), pp. 699-718. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M., Wichienchot, S., He, X., Fu, X., Huang, Q. and Zhang, B. (2019) In vitro colonic fermentation of dietary fibers: Fermentation rate, short-chain fatty acid production and changes in microbiota, Trends in Food Science & Technology, 88 , pp. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Xiao, Y., Tian, F., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., Zhai, Q. and Chen, W. (2020) Rational use of prebiotics for gut microbiota alterations: Specific bacterial phylotypes and related mechanisms, Journal of Functional Foods, 66 , pp. 103838. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W., Xu, S., Ren, Z., Tao, L., Jiang, J. and Zheng, S. (2015) Application of metagenomics in the human gut microbiome, World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG, 21 (3), pp. 803-814. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Zhang, D., Jiang, H., Zhang, S., Pang, X., Gao, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Xiao, Q., Chen, L., Wang, S., Qi, D. and Li, Y. (2021) Gut Microbiota Variation With Short-Term Intake of Ginger Juice on Human Health, Frontiers in Microbiology, -02nd, 11 . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Ramos, M., Jefferson, M., Zhang, W., Beraza, N., Carding, S., Powell, P. P., Stewart, J. P., Mayer, U. and Wileman, T. (2022) Control of infection by LC3-associated phagocytosis, CASM, and detection of raised vacuolar pH by the V-ATPase-ATG16L1 axis, Science Advances, 8 (43), pp. eabn3298. [CrossRef]
- Watson, A. W., Houghton, D., Avery, P. J., Stewart, C., Vaughan, E. E., Meyer, P. D., de Bos Kuil, M. J. J., Weijs, P. J. M. and Brandt, K. (2019) Changes in stool frequency following chicory inulin consumption, and effects on stool consistency, quality of life and composition of gut microbiota, Food Hydrocolloids, 96 , pp. 688-698. [CrossRef]
- Weickert, M. O., Möhlig, M., Schöfl, C., Arafat, A. M., Otto, B., Viehoff, H., Koebnick, C., Kohl, A., Spranger, J. and Pfeiffer, A. F. H. (2006) Cereal fiber improves whole-body insulin sensitivity in overweight and obese women, Diabetes Care, 29 (4), pp. 775-780. [CrossRef]
- Weickert, M. O., Roden, M., Isken, F., Hoffmann, D., Nowotny, P., Osterhoff, M., Blaut, M., Alpert, C., Gögebakan, Ö, Bumke-Vogt, C., Mueller, F., Machann, J., Barber, T. M., Petzke, K. J., Hierholzer, J., Hornemann, S., Kruse, M., Illner, A., Kohl, A., Loeffelholz, C. V., Arafat, A. M., Möhlig, M. and Pfeiffer, A. F. (2011) Effects of supplemented isoenergetic diets differing in cereal fiber and protein content on insulin sensitivity in overweight humans, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 94 (2), pp. 459-471. [CrossRef]
- Willis, A. D. (2019) Rarefaction, alpha diversity, and statistics, Frontiers in Microbiology, 10 , pp. 2407. [CrossRef]
- Wongkaew, M., Tangjaidee, P., Leksawasdi, N., Jantanasakulwong, K., Rachtanapun, P., Seesuriyachan, P., Phimolsiripol, Y., Chaiyaso, T., Ruksiriwanich, W., Jantrawut, P. and Sommano, S. R. (2022) Mango Pectic Oligosaccharides: A Novel Prebiotic for Functional Food, Frontiers in Nutrition, -03rd, 9 . [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. and Morris, J., S M (1998) Arginine metabolism: Nitric oxide and beyond, Biochemical Journal, 336 ( Pt 1) (1), pp. 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Wu, M., Xiao, H., Shao, F., Tan, B. and Hu, S. (2020) Arginine accelerates intestinal health through cytokines and intestinal microbiota, International Immunopharmacology, 81 , pp. 106029. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M. B. and Roberfroid (1995) Dietary Modulation of the Human Colonie Microbiota: Introducing the Concept of Prebiotics, J. Nutr, 125 , pp. 1401.
- Yang, Y., Bin, P., Tao, S., Zhu, G., Wu, Z., Cheng, W., Ren, W. and Wei, H. (2021) Evaluation of the mechanisms underlying amino acid and microbiota interactions in intestinal infections using germ-free animals, Infectious Microbes & Diseases, 3 (2), pp. 79-86. [CrossRef]
- Yao, B., Fang, H., Xu, W., Yan, Y., Xu, H., Liu, Y., Mo, M., Zhang, H. and Zhao, Y. (2014) Dietary fiber intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: A dose-response analysis of prospective studies, European Journal of Epidemiology, 29 (2), pp. 79-88. [CrossRef]
- Zarei, I., Koistinen, V. M., Kokla, M., Klåvus, A., Babu, A. F., Lehtonen, M., Auriola, S. and Hanhineva, K. (2022) Tissue-wide metabolomics reveals wide impact of gut microbiota on mice metabolite composition, Scientific Reports, 12 (1), pp. 15018. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B., Li, G., Shahid, M. S., Gan, L., Fan, H., Lv, Z., Yan, S. and Guo, Y. (2020) Dietary l-arginine supplementation ameliorates inflammatory response and alters gut microbiota composition in broiler chickens infected with salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium, Poultry Science, 99 (4), pp. 1862-1874. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Ran, Lei Wang, Chengcheng Shi, Qipeng Shi, Fuying Ma, Xiaoyu Zhang, Wen Yu, and Hongbo Yu (2021) Structural Characterization of Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes (LCCs) and Their Biotransformation by Intestinal Microbiota In Vitro, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 69 (43), 12880-12890. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Chen, R., Zhang, D., Qi, S. and Liu, Y. (2023) Metabolite interactions between host and microbiota during health and disease: Which feeds the other? Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 160 , pp. 114295. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S., Peng, X., Zhou, Q., Huang, Y., Rao, X., Tu, J., Xiao, H. and Liu, D. (2021) Bacillus coagulans 13002 and fructo-oligosaccharides improve the immunity of mice with immunosuppression induced by cyclophosphamide through modulating intestinal-derived and fecal microbiota, Food Research International, 140 , pp. 109793. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. and Jiang, Q. (2021) Roles of the Polyphenol–Gut microbiota interaction in alleviating colitis and preventing colitis-associated colorectal cancer, Advances in Nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 12 (2), pp. 546-565. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y., Bek, M. K., Prince, N. Z., Peralta Marzal, L. N., Garssen, J., Perez Pardo, P., Kraneveld, A. D., Afd Pharmacology and Pharmacology (2021) The role of bacterial-derived aromatic amino acids metabolites relevant in autism spectrum disorders: A comprehensive review, Frontiers in Neuroscience, 15 , pp. 1-738220. [CrossRef]
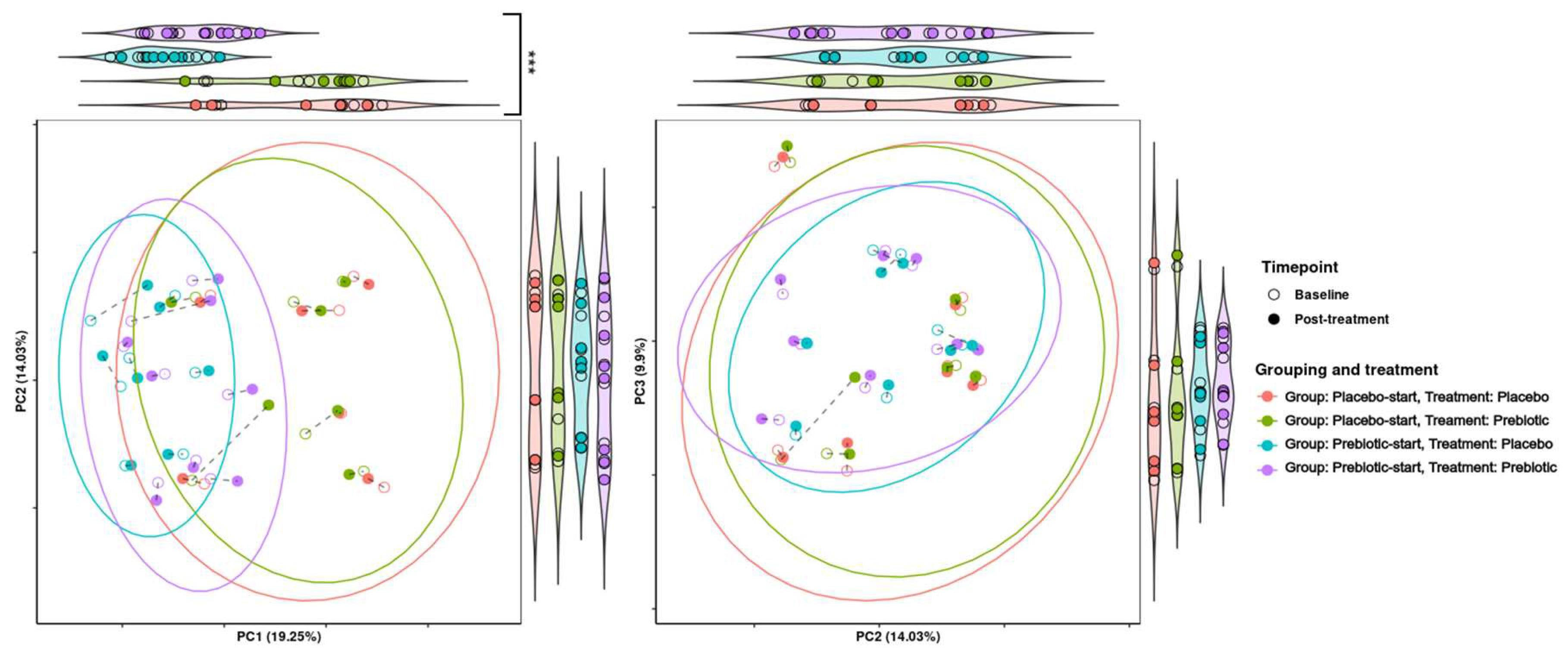
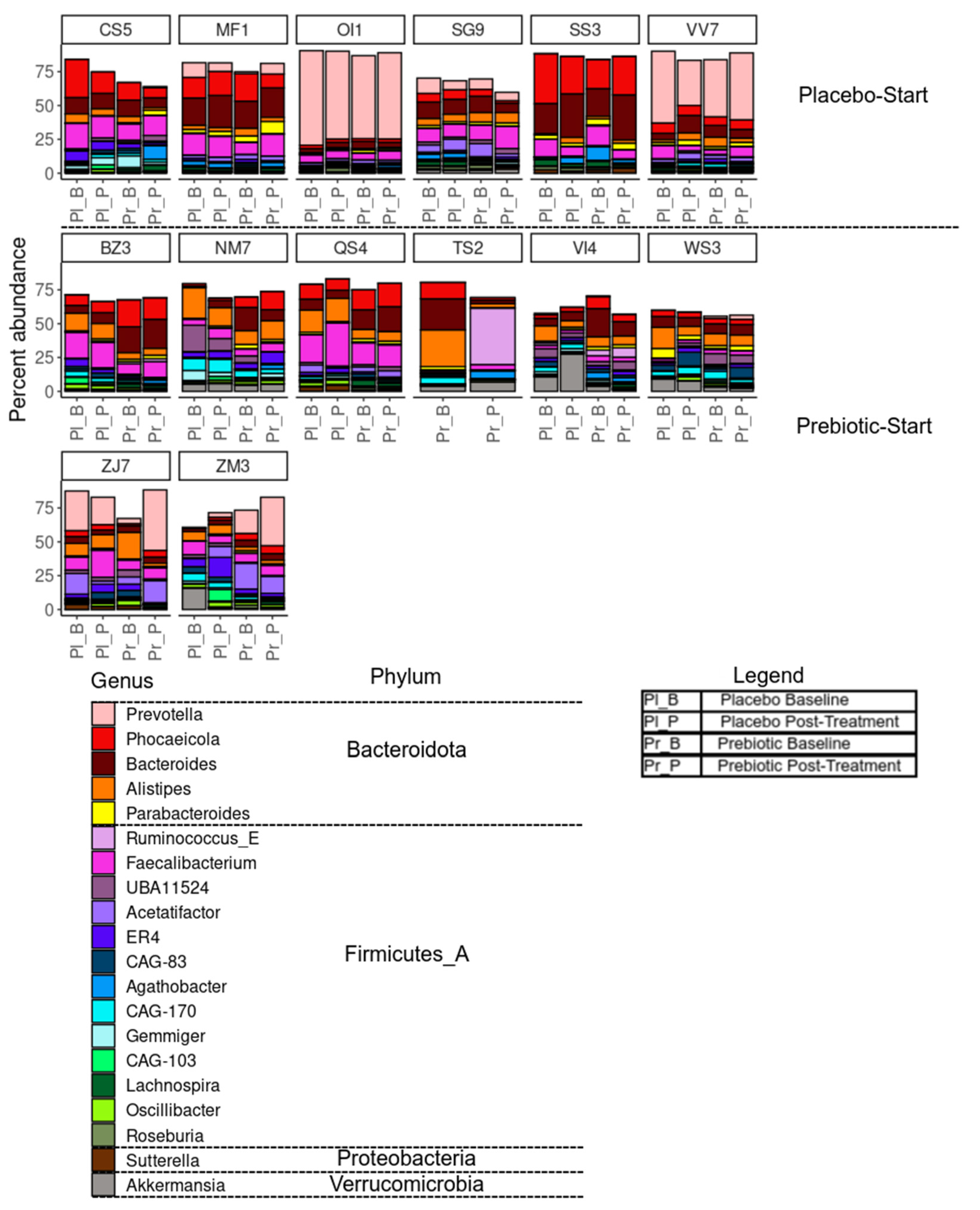
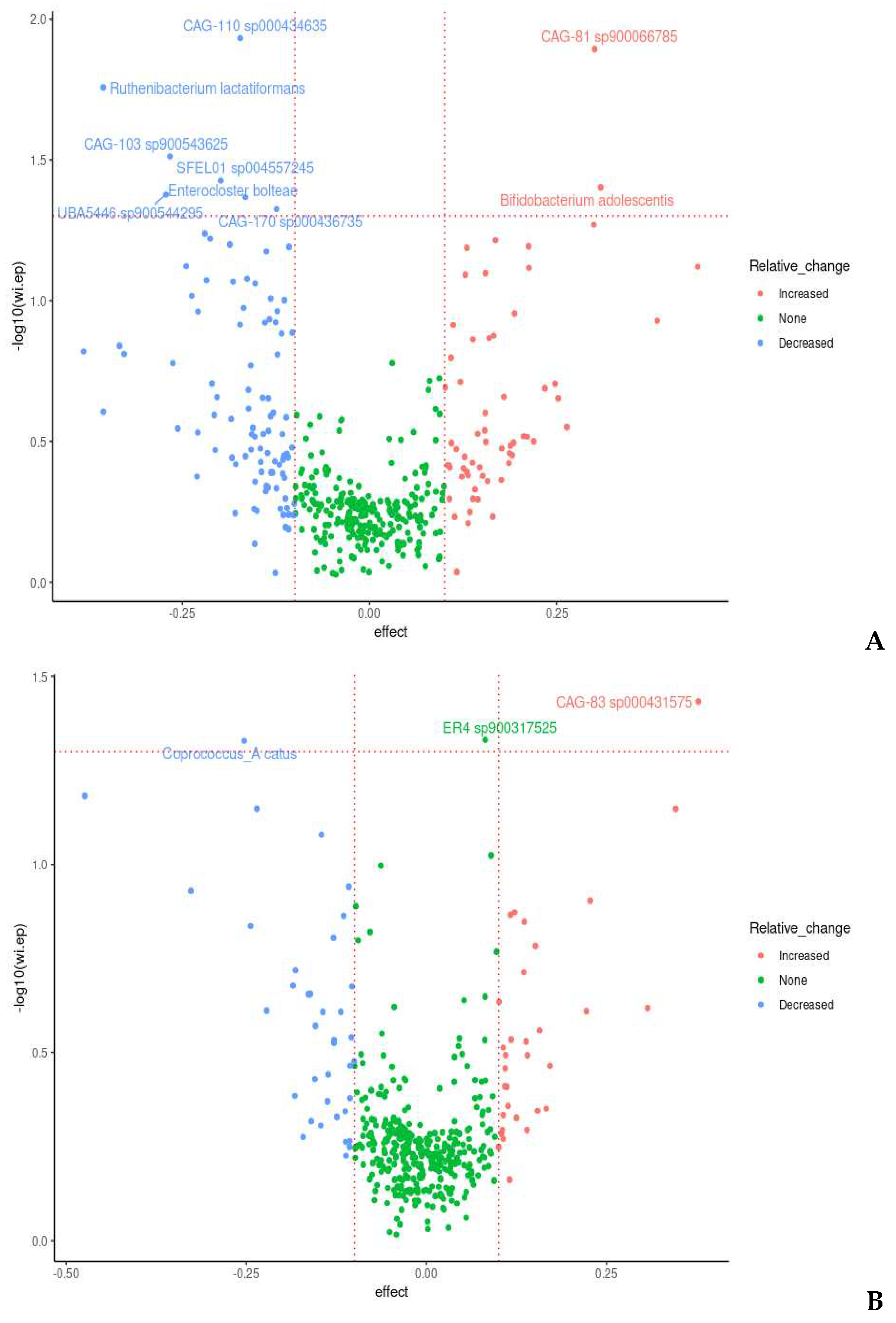
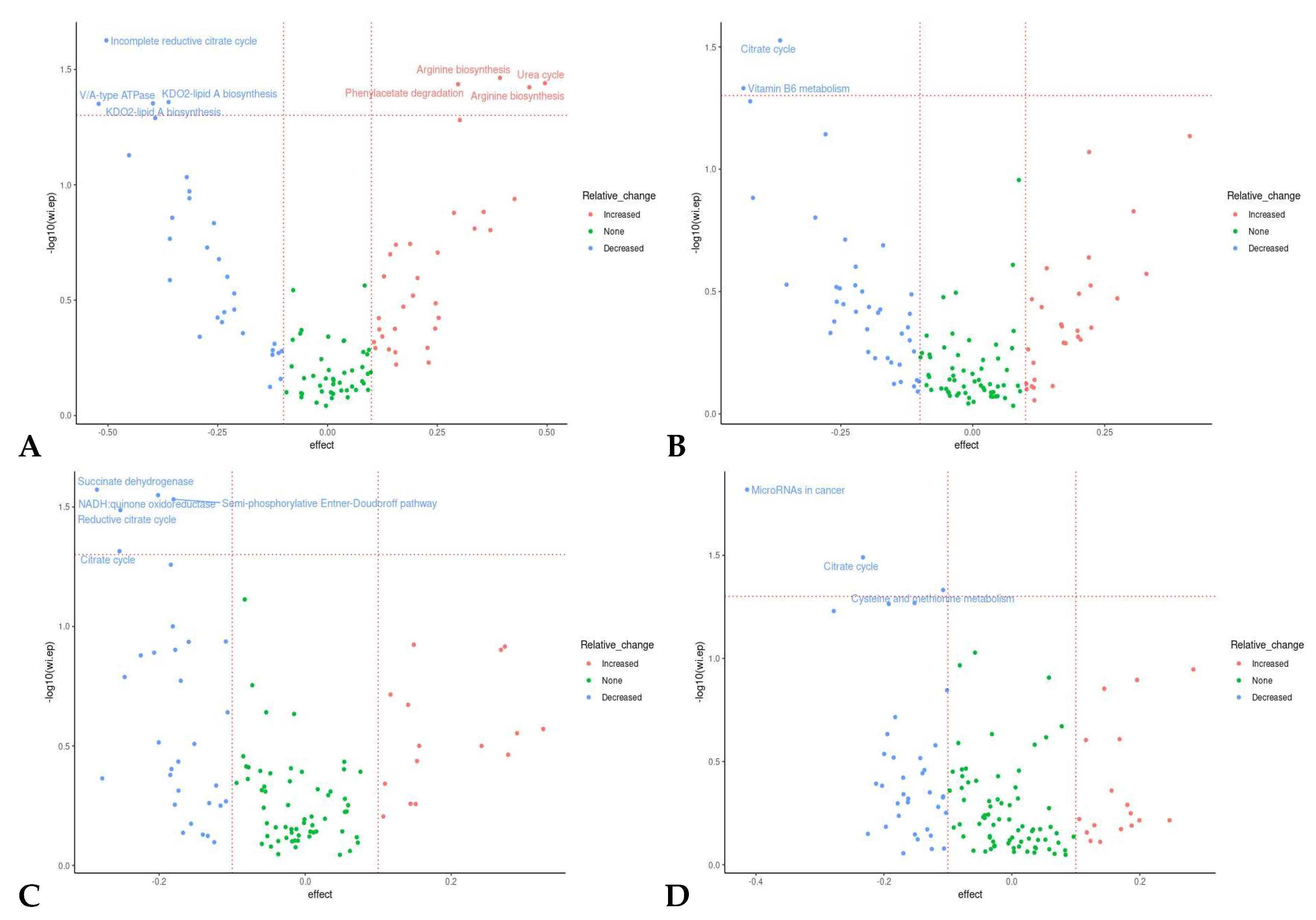
| Group/Treatment order | Phase | Inulin | Between group p value | Oligofructose | Between group p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 2 | 4.0 ± 1.65 | .04* | 3.47 ± 1.28 | .78 |
| BA | 1 | 6.44 ± 2.1 | 5.62 ± 2.52 |
| Treatment order | AB Prebiotic phase | AB Placebo phase | BA Placebo phase | BA Prebiotic phase | Baseline between-group differences (p values) | ||||
| Results | Pre-post p value | Individual responsesN=8 | Pre-post p value | Individual responsesN = 7 | Pre-post p value | Individual responsesN = 6 | Pre-post p value | Individual responsesN = 6 | |
| Verrucomicrobiota | .125.25 | 7 ↑, 1↓ | .4531.0 | 5 ↑, 2↓ | .062.372 | 5 ↑, 1↔ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 2↓, 1↔ | .181 |
| Proteobactera | .453.67 | 5 ↑, 3↓ | .4530.9 | 5 ↑, 2↓ | .6881.0 | 4 ↑, 2↓ | .6881.0 | 4 ↑, 2↓ | .534 |
| Firmicutes | 1.0 | 4 ↑, 4↓ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 4↓ | .6881.0 | 2 ↑, 4↓ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 3↓ | .534 |
| Desulfobacteria | .016*.09 | 8 ↑ | .453.67 | 5 ↑, 2↓ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 3↓ | .6881.0 | 4 ↑, 2↓ | .628 |
| Bacteroidetes | .453.54 | 2 ↑, 6↓ | .125.75 | 1 ↑, 6↓ | .219.65 | 1 ↑, 5↓ | .6881.0 | 4 ↑, 2↓ | .101 |
| Actinobacteria | .016*.048* | 8 ↑ | .453.54 | 5 ↑, 2↓ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 3↓ | 1.0 | 3 ↑, 3↓ | .366 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





