Introduction:
Tibial shaft fractures are the most common fractures of long bones, with an incidence of 26-100,000 per year. The average age of patients is 37, with a male-female ratio of 3.5:11. Tibial shaft fractures commonly occur following high energy impact (HEI) - motor vehicle or extreme sport accidents and war zone casualties. The use of an external fixator device (EFD) is indicated in conditions such as infected fracture, interruption of bone coverage, when the medullary is too narrow for intramedullary nail, or as a temporary treatment, when definitive surgery is delayed for some reason1.
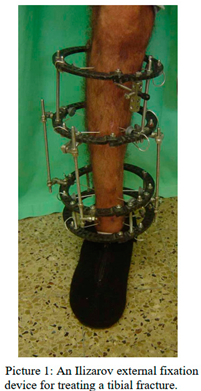
The EFD consist of wires and screws that are placed through the skin and into the bones, while the external pole is attached to a bar (unilateral), or wires that cross the bone and both external poles are attached to a ring (circular) (Figure 1). Surgeons determine the wire insertion sites according to fracture location, in consideration of the adjacent anatomic structures. The choice of the insertion site is critical, in order to avoid further damage to local tissue - nerves and vessels and to avoid fixating of tendons and muscular masses, which limit the adjacent joint’s range of movement. Referring to tibial fractures, in choosing the wires’ insertion site, the posterior compartments should better be spared as much as possible, in due to the muscular mass presents. The lateral aspect of the upper third of the shin contains the peroneal nerve and the posterior aspect contains the popliteal artery. The lower third, on its medial posterior aspect contains the tibial nerve and tibial artery. As a result, the anterior aspect on the shin is commonly used as a wire insertion site2. This site is anatomically similar to the location of acupuncture point St 36 also known as Zu San Li. The acupoint is located on the anterolateral aspect of the tibia, 6 centimeters below the knee joint and 2 centimeters lateral to the anterior tibial crest3. According to The World Health Organization (WHO) ST36 is located on the anterior aspect of the leg, on the line connecting ST35 with ST41, 3 B-cun inferior to the depression lateral to the patellar ligament4. St 36 is one of the most commonly used acupoint in an acupuncture treatment, with variable indications such as neuromuscular pain, stomachache, pain syndrome, hypertension, diabetes and gastrointestinal disorders (Stuart S. Anatomical Atlas of Chinese Acupuncture Points. The Cooperative Group of Shandong Medical College and Shandong College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1990). Moreover, it is one of the most researched acupoint, with numerous studies examining its effect on various medical conditions5–9.
Acupuncture has been used therapeutically in China for thousands of years and is growing in popularity throughout the developed world8. Acupuncture treatment is based on the insertion of fine needles in various anatomical points, called acupoint Acupuncture treatment is associated with significant changes in bioactive chemicals- including opioids, N/OFQ, serotonin, norepinephrine, glutamate receptors and transporters, cytokines, and signal molecules in peripheral injury sites, the spinal cord, and supraspinal structures10,11. Acupuncture is commonly used for pain management. various studies have shown that acupuncture is safe and cost-effective compared to routine care12–19. It has been indicated that certain modes of acupuncture improved postoperative pain on the first day after surgery and reduced opioid use14. This study examines the possible analgesic effect of locating an EFD wire in the similar anatomical location of acupoint St 36, and the possibility of the EFD wire creating an acupuncture like effect as a result of its anatomical location.
Upon searching literature, few authors suggest the complementary treatment of acupuncture for acute post orthopedic operation pain12,14,17. Only one study examined the possible effect of the EFD’s wires on acupoints (Verkhozina T., Solomin SL. Results Analysis of S-screws and K-wires Insertion through Acupuncture Points. unpublished data, 3rd Meet ASAMI Int - Istanbul 2004), although, no studies were conducted with the goal of examining the possible pain relieve due to the insertion on the EFD’s wires through acupoints.
Material and Methods:
The study was approved by the Ziv Helsinki ethics committee. Data was collected retrospectively using the Ziv medical center archive. Patients’ records were reviewed between the years 2015 to 2018. A total of 107 patients treated with an EFD (the majority with Ilizarov EFD device) after tibial fractures were found.13 patients’ files were excluded due to age limit (below 18 or above 80 years old),18 patients were excluded due to post-operation hospitalization that was shorter than 5 days, 36 patients were excluded for multi trauma injury, 8 cases were found to be recorded twice due to two separate admissions, thus, excluded and finally, 13 patients were excluded due to missing hospitalization data.
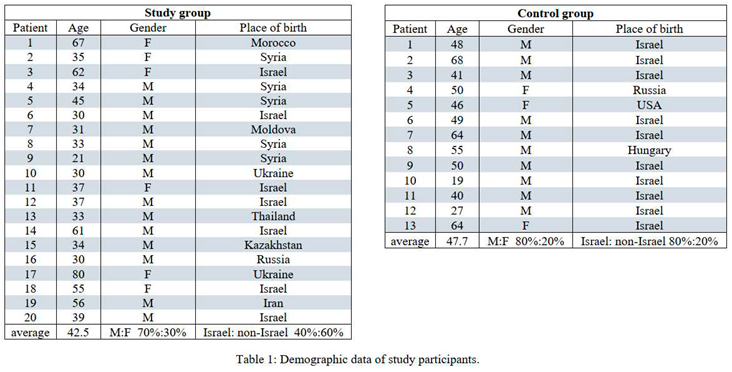
33 patient files were found to be eligible for the review. Males and females, aged 18-80, demographic data included Israeli citizens (Jews and Arabs) and 5 Syrians war casualties treated in the Ziv medical center, as well as one Thai immigrant.
All patients suffered from tibial fractures, open or closed, with no other major injuries. All patients were treated with an external fixator device, either as temporary or definitive treatment.
Following reviewing patients’ X-ray records (Figure 2), Patients were divided in two groups. The study group (SG) included 20 patients having one of the external fixation device’s wires inserted through the ST36 (Zusanli) acupoint location, the control group (CG) included 13 patients that had the external fixator device’s wire inserted elsewhere. The SG included 14 males and 6 females. The average age was 42.5. The CG included 10 males and 3 females. The average age was 47.7.
Patient's records were retrospectively reviewed for 5 days following surgery. Patients’ data collected for the study included Pain level and analgesic consumption. Pain level was measured by the use of a VAS (visual analog scale- 0 no pain, 10 Max pain). Pain level is taken three times a day as a standard practice in the orthopedic department. Patient's Analgesic consumption for 5 days following surgery was also reviewed, to be used as second parameter for patient's pain level.
The drugs that were registered include: Metamizole (OPTALGIN®), Oxycodone, Oxycodone with Acetaminophen (Percocet), Oxycodone with naloxone controlled-release (CR) tablets (Targin) and Tramadol Hydrochloride (Tramadex OD PO, Tramadex IV).
Statistical analysis: For categorical variables, summary tables provided giving sample size, absolute, and relative frequencies. For continuous variables, summary tables provided giving arithmetic mean (M) and standard deviation (SD). Pearson’s chi-squared was applied for testing the correlations between the study groups for the categorical parameters. Pearson correlations provided the power of the correlation between the continuous variables. The independent sample t-tests groups or Mann Whitney non parametric test was applied to measure the differences between the study (control vs. cases).
P-value of 5% or less is considered statistically significant. The data was analysed using the SPSS version 25 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results:
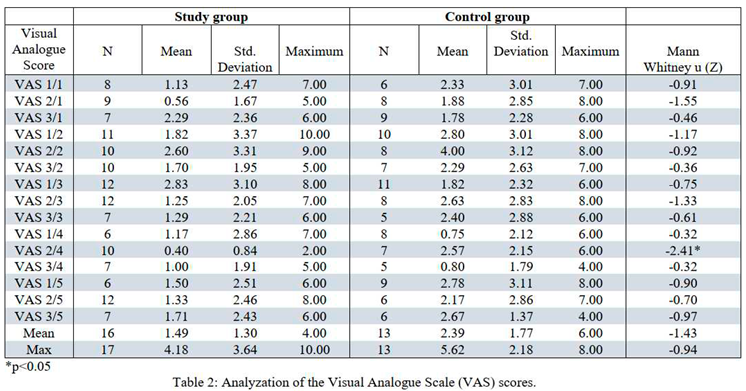
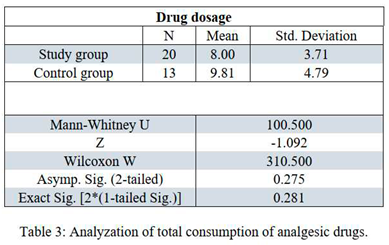
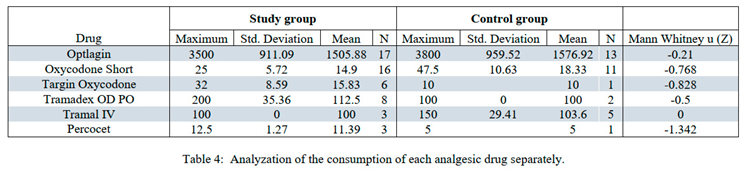
Demographic data is presented in Tables 1 and 2. Pain levels as measured by VAS are summarized in Table 3. no statistical difference was found between the control and study groups (2.3885 ± 1.77 for the CG and 1.4853 ± 1.30 for the SG, xxx P value) although a slight tendency towards the SG can be detected. Only on day 4 of hospitalization there was a statistical difference between the study groups (0.40 ± 0.843 among the SG and 2.57 ± 2.149 among the CG (Z= -2.413, P<0.05. calculated by the Mann-Whitney U). Regarding analgesic consumption, no statistical difference was found in the total consumption (the number or times an analgesic drug was taken, regardless type or dose), among the SG, the average consumption was 8 ± 3.71 and among the CG the average was 9.31 ± 4.9 (Table 4). Observing each drug separately, no statistical correlation was demonstrated (Table 5). Some drugs were consumed more among the CG, whereas other drugs were higher among the SG.
Discussion:
The location of an external fixation device following a tibial fracture involves many anatomical considerations. The possible positive effect of inserting a surgical wire\nail through an active acupuncture point has yet to be studied.
Postoperative pain results from surgical trauma and is a significant challenge for healthcare providers. About 75% of patients experience moderate or severe pain following surgery15. The mainstay of treating postoperative pain is the use of opioid analgesics such a morphine, hydro morphine, meperidine, or fentanyl. However, these drugs are associated with a number of undesirable side effects which can delay patient recovery including nausea, vomiting, dizziness, sedation, and decreased gut motility13. A delay in opioid consumption can be considered a proxy of lower pain levels; it has been suggested that acupuncture led to a modest delay in analgesic requests, leading to possible benefits in the critical immediate time window following surgery. Similarly, Tedesco et al. have found that acupuncture provides significant pain improvement in patients undergoing TKA and total hip arthroplasty in the first 2 days after surgery14.
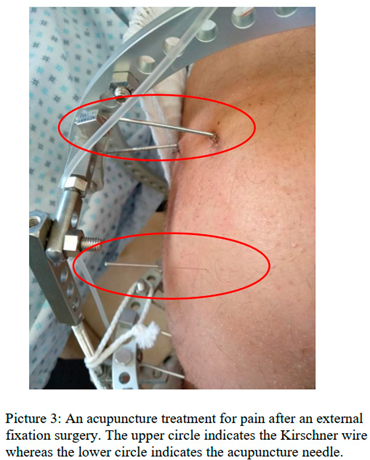
It is important to emphasis the differences between standard acupuncture treatment and the external fixation devices (Table 6, Figure 3). Both the acupuncture needles and the Kirschner wires are made of stainless steel. However, the needle’s diameter is significantly smaller, as well as its depth or penetration. Moreover, the duration of stimulation is also to be noted. The acupuncture needle remains inserted for up to thirty minutes, while the external fixation devices stay in place for days or months
Furthermore, the different effect of acupuncture and electroacupuncture (EA), should be taken in consideration13.
Another difference to take in consideration is the fact that standard acupuncture treatment is performed by inserting needles in multi various locations in accordance with traditional acupuncture diagnosis, while in this study only one acupoint was stimulated. A method of acupuncture which stimulates only one acupoint (Single Needle Therapy, SNT) has been published in the literature5–7,20–23, but it is clearly not the majority of clinical practices or studies. Having that said, Ceccherelli et al. 24 examined the differences between 3,5 and 11 needles treatment for painful cervical myofascial syndrome and found no clinically relevant differences among groups.
A further study, using a complementary full acupuncture in accordance with the ST36 stimulation by the wires may reveal new information.
This was a retrospective pilot study that examined a small sample of 33 patients. It is possible that performing an identical study with a larger patient sample could lead to clearer results, possibly with a higher P value. Furthermore, patients’ files were reviewed for only five days following surgery, with regard only to the acute postoperative phase. A longer follow up of the post operative rehabilitation process could produce a more precise data.
Conclusions:
In patients suffering from a tibial fracture treated with an EFD, locating an EFD wire in the anatomical similar site of acupoint St 36, did not lower patients pain levels or analgesic consumption.
According to the results of this study, stimulating the ST36 acupoint by inserting a wire does not have an analgesic effect.
Only on the 4th day, the difference of the VAS score between the two groups was of statistical relevance. Upon researching literature, we did not find any specific effect four days following the acupuncture treatment. Therefore, we see it as a coincidental finding.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Acknowledgment
Basem Hijazi, statistical analysis. Bar-Ilan University.
References
- Charles AR, David PG, Robert WB, James DH. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001.
- Leonid LS. The Basic Principles of External Skeletal Fixation Using the Ilizarov and Other Devices. 2nd ed. Springer, 2012.
- Stuart S. Anatomical Atlas of Chinese Acupuncture Points. The Cooperative Group of Shandong Medical College and Shandong College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1990.
-
WHO Standard Acupuncture Point Locations in the Western Pacific Region. World Health Organization; 2008.
- Yang Q, Xie YD, Zhang M xin, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture stimulation at Zusanli acupoint (ST36) on gastric motility: possible through PKC and MAPK signal transduction pathways. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2014;14(1):137. [CrossRef]
- Fitrullah null, Rousdy A. Effectiveness of Acupressure at the Zusanli (ST-36) Acupoint as a Comfortable Treatment for Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Study in Indonesia. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2017;10(2):96-103. [CrossRef]
- Kimura K, Ishida K, Takahashi N, Toge Y, Tajima F. Effects of acupuncture at the ST-36 point on muscle sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in normal adults. Auton Neurosci. 2017;208:131-136. [CrossRef]
- Cevik C, Işeri SO. The effect of acupuncture on high blood pressure of patients using antihypertensive drugs. Acupunct Electrother Res. 2013;38(1-2):1-15. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi B, Forouzanfar F, Azizi H, Khoshdel-Sarkarizi H, Sadeghnia H, Rajabzadeh A. Effect of Electroacupuncture and Glibenclamide on Blood Glucose Level and Oxidative Stress Parameters in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats and Possible Human Implications. Acupuncture & Electro-Therapeutics Research. 2020;44(3-4):213-228. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang Y, Xing J jing, Li J, Zeng BY, Liang F rong. History of acupuncture research. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2013;111:1-23. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Lao L, Ren K, Berman BM. Mechanisms of acupuncture-electroacupuncture on persistent pain. Anesthesiology. 2014;120(2):482-503. [CrossRef]
- Cho YH, Kim CK, Heo KH, et al. Acupuncture for acute postoperative pain after back surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Pract. 2015;15(3):279-291. [CrossRef]
- Wu MS, Chen KH, Chen IF, et al. The Efficacy of Acupuncture in Post-Operative Pain Management: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150367. [CrossRef]
- Tedesco D, Gori D, Desai KR, et al. Drug-Free Interventions to Reduce Pain or Opioid Consumption After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(10):e172872. [CrossRef]
- Gan TJ, Habib AS, Miller TE, White W, Apfelbaum JL. Incidence, patient satisfaction, and perceptions of post-surgical pain: results from a US national survey. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(1):149-160. [CrossRef]
- Zeng YJ, Tsai SY, Chen KB, Hsu SF, Chen JYR, Wen YR. Comparison of electroacupuncture and morphine-mediated analgesic patterns in a plantar incision-induced pain model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:659343. [CrossRef]
- Chen CC, Yang CC, Hu CC, Shih HN, Chang YH, Hsieh PH. Acupuncture for pain relief after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2015;40(1):31-36. [CrossRef]
- Lan F, Ma YH, Xue JX, Wang TL, Ma DQ. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on acupoints reduces fentanyl requirement for postoperative pain relief after total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012;78(8):887-895.
- Lin JG, Lo MW, Wen YR, Hsieh CL, Tsai SK, Sun WZ. The effect of high and low frequency electroacupuncture in pain after lower abdominal surgery. Pain. 2002;99(3):509-514. [CrossRef]
- Erthal V, Maria-Ferreira D, Werner MF de P, Baggio CH, Nohama P. Anti-inflammatory effect of laser acupuncture in ST36 (Zusanli) acupoint in mouse paw edema. Lasers Med Sci. 2016;31(2):315-322. [CrossRef]
- Chang SL, Lin KJ, Lin RT, Hung PH, Lin JG, Cheng JT. Enhanced insulin sensitivity using electroacupuncture on bilateral Zusanli acupoints (ST 36) in rats. Life Sci. 2006;79(10):967-971. [CrossRef]
- Wu SY, Chen WH, Hsieh CL, Lin YW. Abundant expression and functional participation of TRPV1 at Zusanli acupoint (ST36) in mice: mechanosensitive TRPV1 as an “acupuncture-responding channel.” BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:96. [CrossRef]
- Kim KS, Nam YM. The analgesic effects of capsicum plaster at the Zusanli point after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesth Analg. 2006;103(3):709-713. [CrossRef]
- Ceccherelli F, Marino E, Caliendo A, Dezzoni R, Roveri A, Gagliardi G. 3,5,11 needles: looking for the perfect number of needles--a randomized and controlled study. Acupunct Electrother Res. 2014;39(3-4):241-258. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).