Introduction
Community-based social engagement programs that aid recovery from mental illness have grown in popularity (Davies et al., 2020), but the value for clinical mental health providers remains unclear (Jacobson & Greenley, 2001; Stanley et al., 2019). Social programs have been shown to reduce isolation, build resilience, end stigma, and help end-users find purpose (e.g., Baumeister & Leary, 1995; Pyne & Baumeister, 2017) in ways that should complement and reduce the need for clinical visits (Davidson et al., 2005; Jacobson & Greenley, 2001). As the global mental health crisis grows, social programs may offer cost relief (Pinals, 2020). Depression and anxiety alone were estimated to cost the global economy of US $1 trillion annually (Brunier & Mayhew, 2016). In the US, clinical utilization is largely overwhelmed (Hellebuyck et al., 2019) even though more than 50% of people with a known mental disorder never seek help (National Alliance of Mental Illness, 2020). For those who receive long-term treatment, improvement is just as common as progressive deterioration (Davidson 2009). Unmet social needs and stigma are thought to be major obstacles to improvement (Link & Cullen, 1983; Perlick et al., 2001).
The social drivers and consequences of mental health challenges, including isolation and stigma are well known, yet remain difficult to address (Stanley et al., 2019). For many, recovery from mental illness, including successfully living with mental illness, requires a social process that involves restoring relationships, sharing experiences and becoming part of a community (Jacobson & Greenley, 2001). In-person social support networks, including, peer support services (Fortuna et al., 2022; Shalaby & Agyapong, 2020), drop-in clubhouse (McKay et al., 2018), Living Room model (Heyland et al., 2013), and Men’s Sheds (Kelly et al., 2021), have been demonstrated to fill part of this gap; however, each model fulfills different goals, and has its own strengths and limitations. For example, the drop-in clubhouse model provides group activities, but typically requires a mental illness diagnosis and program rules can limit autonomy of choice (McKay et al., 2018). Overall, social support networks remain relatively infrequently utilized in the US, likely due to questions of cost effectiveness (Park et al., 2013). They also typically do not directly confront community-scale stigma that is experienced by those with mental illness. To address social stigma, an alternative approach to support mental health recovery was created. In this paper, a novel grassroots community-based mental health model was developed by bringing people together for social and recreational experiences, to grow interests, and to pursue the shared goal of reducing stigma in the broader region where members live.
The Momentum Center for Social Engagement (MC) was opened on April 20, 2017, in a mid-sized community in Western Michigan (Ottawa County, est. population: 286,383), USA where 17% of adults reported depressive disorder and 15% reported an anxiety disorder (Hill, 2017). While clinical treatment options exist, local stakeholders identified lack of programs, services, funding and continued stigma as the realities that prevent some people from seeking and receiving needed treatment.
Philosophy of the Momentum Center for Social Engagement
The MC acts as a complement to clinical and therapeutic services to improve the quality of life of people who struggle with mental illness, addictions and other disabilities. The MC creates a safe place for these marginalized populations by creating human connection for people at risk of isolation, through social integration as a means of reducing stigma, and by acting as a platform for anti-stigma outreach and understanding. The MC integrates individuals with their communities to create positive social networks, improve personal resilience, and reduce feelings of stigma. To define and establish needed programs, the MC used a three-step process: 1) identify community-specific gaps in mental health services using a modified social labs-type approach (Hassan, 2014); 2) create grassroots, entrepreneurial support for solutions; and 3) implement social programming and evaluate effectiveness in terms of personal wellbeing metrics and innovative program characteristics. Importantly, steps have been taken to define and replicate this framework in other communities. Unlike other predefined social programs, the MC relies on grassroots support to be flexible and responsive to the needs of each community. Anyone can join the MC as a member or participate in MC events (e.g. a monthly Town Hall discussion on racism in schools). Most members have mental illness and/or a disability; however, no clinical diagnosis or referral is required to join. Membership costs $1 annually. Additional details regarding the MC model can be found on their website (MomentumCenterGH.org).
Study Design and Purpose of Study
A retrospective cohort study was conducted using longitudinal Patient Health Information (PHI) from a community mental health services agency (CMHS) for the period 2016 – 2021. The purpose of this study was to explore if the social engagement program offered by the MC improves wellbeing for members and adds value to CMHS. We compared two small cohorts of members with mental illness before and after joining the MC. The “engaged” cohort represented those who were highly engaged after joining the MC while the “non-engaged” cohort joined the MC but were less engaged, similar to an experimental control group. To understand if engaging with the MC helped improve wellbeing, we validated the assumption that healthier clients go to the doctor less (Lin et al., 2010) by comparing CMHS’s overall wellbeing metric, the Adult Needs and Strengths Assessment (ANSA; with lower scores being better; ANSA Manual, 1999) to CMHS visit frequency. Then we used CMHS visit data before and after joining the MC to infer changes in wellbeing associated with the MC intervention.
For CMHS, visits represent their commitment and ability to help clients. Thus, reduced frequency of clinical visits of regular clients could indicate improved wellbeing, greater availability of resources for others and a direct step toward CMHS achieving their mission of improving lives. The total value of CMHS’s mission was considered to be its annual budget. In contrast, participants with difficult or worsening mental conditions that were stabilized by frequent CMHS treatments would be expected to maintain or increase their frequency of visits over time. The financial value of reduced visits was considered to be greater than total cost of visits because the change indicates lives were improved, and instead was valued as a percent of CMHS’s annual budget.
Methods
Institutional Review Approval
This study was undertaken for program quality improvement purposes utilizing existing data and as such, participant consent and ethical approval were not required, however, both were requested and received. Study participants signed a consent form allowing this collaborative CMHS and MC partnership to securely share and analyze PHI in compliance with HIPAA Privacy Rule and State of Michigan statutes regulating the disclosure, use, or reporting of confidential health care information. An application was submitted to the third author’s institutional review board (IRB) exemption determination, Study ID: STUDY00006689. It was determined that the program data comparison was not considered to be research. In addition, all MC members have provided consent to their inclusion in member population-related reporting and summaries.
Procedure
No new data were collected through human participants as all data were archival and all analyses were based on this existing data.
Study Participants
At the time of this study, approximately a third of MC members were clients of CMHS where they visited healthcare professionals and specialty facilities for treatment and monitoring. CMHS treats a wide range of patients, including those with mental illness and substance use disorders. Between March and April 2021 staff at the MC provided information about this study to adult members that visited the MC. Twelve adults (>18 years old) who were long-term CMHS clients (i.e. with more than five months of regular CMHS visits before and after joining the MC) participated in this study. Participants represent a semi-random sample of all MC members. The participants were predominantly described as non-Hispanic white (
Table 1). Seven participants identified as male and five as female.
Cohorts
Participants were split into two cohorts, engaged (n = 9) and non-engaged (n = 3) based on guidance provided by the MC Chief Operations Officer (COO). The COO has monitored member engagement on-site since the MC opened. Prior to the start of this study the COO ranked all members on a scale from 1 (less-engaged) to 3 (more-engaged) and provided notes on why some members were challenged to engage (e.g. lack of transportation, other health difficulties). Participants with a score of 3 without any noted challenges to engagement were grouped into the engaged cohort. All other participants were grouped into the non-engaged cohort.
Measures
Wellbeing
The wellbeing of long-term consistent CMHS clients was represented by their frequency of visits to CMHS. This relationship was validated by comparing visit frequency to a longitudinal measure of wellbeing, ANSA. ANSA was assessed by CMHS staff for 6 study participants, infrequently, starting in 2018. Most study participants had already joined the MC prior to their initial ANSA. However, trends in ANSA scores should well represent the overall trend of each client’s wellbeing and thus should be comparable to changes in visit frequency pre/post MC intervention, which also represent an overall long term change.
CMHS’s digital records were available from October 2016 - May 2021. Most participants were already CMHS clients prior to the start of the digital records. CMHS visit data included participant name, date, and visit type: appointment, clubhouse, crisis contact or initial. Appointments were most common. Clients were expected to receive the best care available tailored to their needs, and thus each visit type was considered equally important for mental health.
Visit frequency was calculated as the mean number of days between CMHS visits for the full available period before joining the MC (Pre-MC) and the period after joining the MC (Post-MC) until the start of the pandemic or the end of the record (as explained further below), totalling over 1800 visits. For two participants, a total of three record gaps (i.e. when several regular [e.g. weekly] visits were missed for unknown reasons), were removed from visit frequency averages. The date of joining the MC varied by participant (ranging from March 2017 - November 2020).
Pre-pandemic data were used for 9 of the 12 study participants. The start of the COVID pandemic disrupted in-person visits to the MC (e.g., MC temporarily ended in-person visitation on 3/15/2020) and the switch to virtual was highly successful for some and difficult for many others. The differential response to going virtual was beyond the scope of this study. Three members (one non-engaged and 2 engaged) who joined the MC after the start of the pandemic were included in the study because they continued to have regular CMHS visits and they did not experience the disruptive, temporary suspension of in-person MC visits. There were no other exclusion criteria. Members had no further responsibilities or interaction with the study procedure.
Data Analysis
Analyses were performed using R statistical software version 4.0.2. Percent change in ANSA per year was based on the first and last ANSA record divided by the number of years between. A Pearson correlation was used to understand the relationship between percent change in ANSA and percent change in visit frequency. For analyses, visit frequency was converted to visits/year and percent change for ease of interpretation. Percent change in visit frequency was expected to show a more consistent effect across the wide range of annual visit frequencies and thus it was used to bootstrap a 95% confidence interval (10,000 iterations). The mean percent change in visit frequency of the engaged cohort and the associated confidence interval were used to calculate the total reduction in visits expected for all engaged MC members who were CMHS clients.
The total change in number of visits annually by engaged MC members with confidence intervals was compared to the total annual CMHS visits. The percent difference in visits associated with the MC was multiplied by the CMHS budget to estimate value. Due to overwhelming demand for CMHS, the MC effect was not expected to reduce the total annual visits at CMHS. Instead, value calculations assume CMHS was able to successfully treat more people and achieve a step toward their mission with the same budget and same number of annual visits.
Results
Relationship between Wellbeing and Visit Frequency
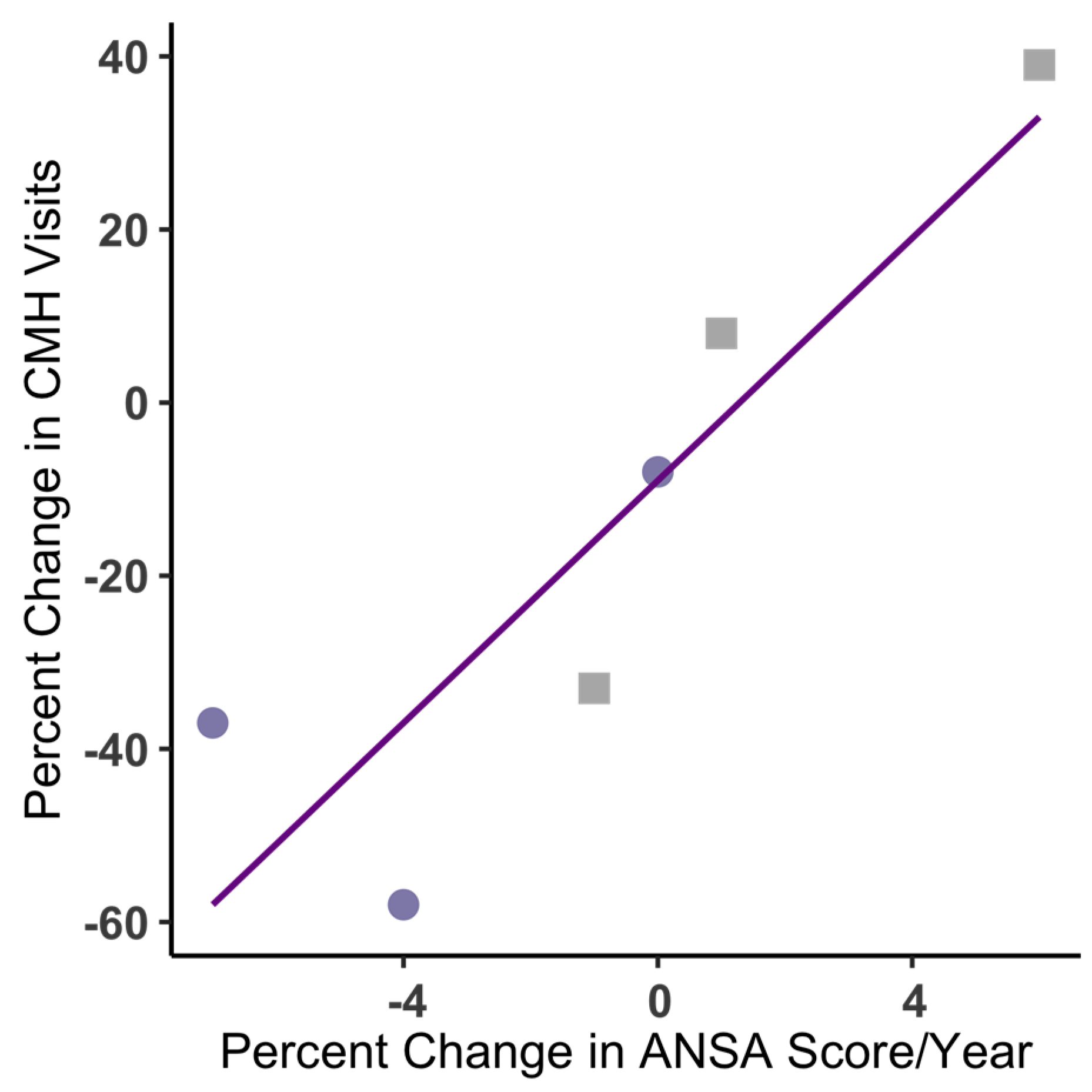
Changes in CMHS visit frequencies before and after joining the MC were strongly and positively correlated with change in ANSA scores, r(4) = 0.88, p = 0.018, for both engaged and non-engaged participants (n = 6;
Figure 1). Those with worsening wellbeing (higher ANSA) had more frequent CMHS visits, while those with improved wellbeing (lower ANSA) had less frequent CMHS visits. Note, ANSA data were not available for half of the study participants and scores were too infrequent for comparison with MC intervention timing. Further, the timing of ANSA change and visit change did not fully overlap for all participants, thus the trends of each were correlated but the exact relationship between variables was not determined.
Changes in CMHS Visit Frequency
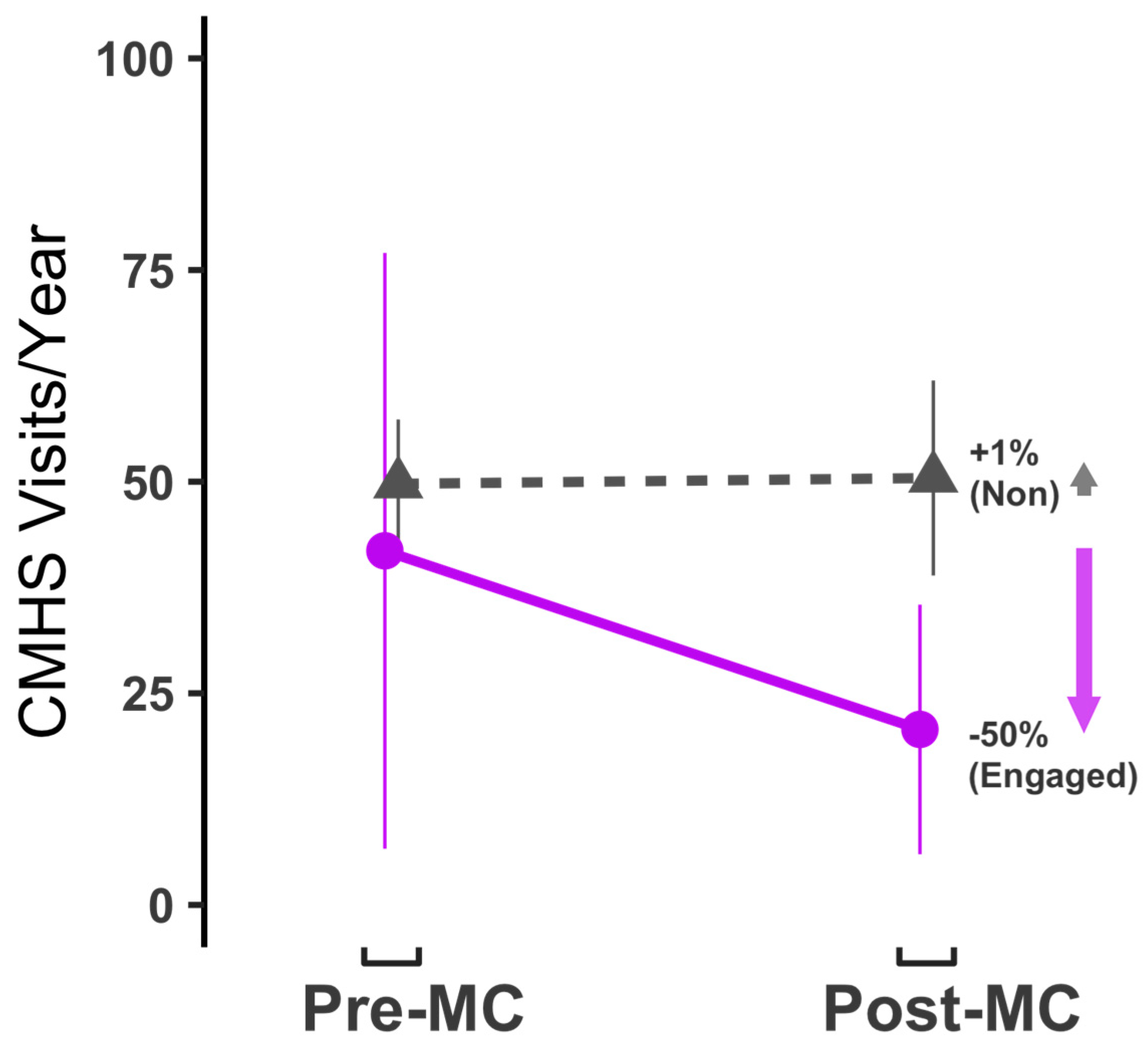
Prior to joining the MC, both cohorts on average, had 40 to 50 CMHS visits per year (
Figure 2; Engaged = 41.8 visits,
n = 9; Non-engaged = 49.7 visits,
n = 3). After joining the MC, engaged member’s visit frequency to CMHS declined 50% to 20.7 visits per year. All engaged members had reduced visit frequency (range: 10% to 84% reduction). Non-engaged members maintained a similar frequency of visits, on average after joining the MC (mean: 50.4 visits/year) a +1% increase. Two of the three non-engaged participants increased visit frequency and one decreased. Participants generally used the same types of visits at CMHS before and after joining the MC, with the exception of the CMHS Clubhouse, which had relatively less use by two participants.
To estimate the full effect of the MC on CMHS services we considered the total number of MC members who met the selection criteria of the Engaged cohort (i.e. both engaged and a CMHS client). Of the 200+ active MC members, at the time of this study, 80 had a high level of engagement. Of these highly-engaged MC members, 30 were long-term CMHS clients (including the 9 from this study) who could reasonably be expected to have also experienced similar wellbeing improvements and have an associated reduction in CMHS visits over time. Thus extrapolating 50% fewer visits by 30 MC members would account for 633 fewer visits annually, 95% CI: [360 - 864], or 2.3% of all CMHS visits, 95% CI: [1.3% - 3.2%].
Economic Value
In this study, visits represent CMHS’s primary tool to achieve their mission and improve the quality of life of patients with mental illness. The 2019 CMHS budget (~$44 million) allowed for more than 25,000 client visits. The number of reduced visits by engaged MC members were equivalent to 2.3% of all CMHS visits. Because this reduction in visits was attributed to wellbeing improvement, we can say the MC moved CMHS 2.3% closer to achieving their mission of improving lives. With a budget of ~$44 million annually, 2.3% equates to the MC contributing a value of $1.0 million annually, 95% CI: [$0.6 - $1.4 million]. This value represents the combined efforts of CMHS with the MC and does not take into account the MC budget received from CMHS (~$240,000), nor the value of CMHS appointments now available to others.
Discussion
Mental health has a growing importance as clinical resources remain overwhelmed in the US and major obstacles to improvement include unmet social needs and stigma. Many types of social support networks and recreational programs for adults with mental illness, addictions, and disabilities may supplement the care provided by existing health systems; however, it remains important to understand their anticipated effects, associated value and limitations. Since 2017, the MC has developed the only known model of community-scale engagement that utilizes a unique combination of programming, integration and outreach to reduce stigma, increase social connection and improve clinical outcomes to raise the quality of life for its members.
The MC serves members with a wide range of mental health needs. This pilot study focused on MC members who were long-term, regular clients of a public mental healthcare provider. Being a regular clinical client prior to joining the MC indicated that ongoing treatments were able to stabilize but not allow full recovery from a condition. CMHS uses visits to connect with their clients, apply treatments and achieve their mission of improved client wellbeing. Clients with improving mental health, as measured by percent change in ANSA scores (
Figure 1) required less frequent clinical visits, while worsening conditions required more frequent visits. ANSA was collected infrequently by CMHS staff for only some of the study participants. Visits were the most common type of clinical data, thus change in clinical visit frequency was used to infer change in client wellbeing.
Members of the MC are free to participate as they please and for this study they were categorized as either highly engaged or non-engaged. For social connection, we assumed greater engagement at the MC would have the largest effect. The engaged cohort had a significant decrease in clinical visit frequency, on average, while the non-engaged cohort had minimal change. Every participant in the engaged cohort had reduced clinical visits. In contrast, the non-engaged cohort had varied responses and the role of the MC for less engaged members could be highly nuanced. For example, infrequent visits can still have a profound value to members who report the importance of “knowing there is a resource.” The non-engaged cohort was exceptionally small (n = 3) but they well represented hypothetical individuals who maintain mental health through regular clinical visits but would benefit from a social component of recovery. They joined the MC for social connection but due to extenuating circumstances, were unable to fully engage.
The engaged cohort (n = 9) was expected to represent approximately 15% of all MC members (n = 30) who also are highly engaged and CMHS clients. To understand the full effect of the MC on CMHS, the cohort results were extrapolated to the larger group. The estimated reduction in clinical visits and associated improved wellbeing was considered a step towards achieving CMHS’s mission. Importantly however, due to over overwhelming demand and a limited budget, reduced visits should not be considered a cost-savings for CMHS. Instead, the results indicate that CMHS + MC added $1.0 million of value in community wellbeing more than CMHS would have achieved alone. The value of the MC to CMHS was four times the MC budget received from CMHS. All extrapolated values were estimated for reference only and should be interpreted with caution.
Not represented in this study are MC members who utilize other mental healthcare providers, who are inconsistent clients, or who avoid mental healthcare. By providing support and knowledge, internal reporting suggested that the MC may help some members become more comfortable and consistent with clinical visits. For these members, the MC could be responsible for creating mental healthcare clients and/or increasing visit frequency. Assuming a healthier connection to clinical care results in improved wellbeing, then, once again the MC helps CMHS achieve their mission of improving the quality of life. This value to the community was not assessed in this study but it underscores how the MC can be cost-effective without being a cost-savings.
Limitations and Future Directions
This pilot study solely intended to identify the existence of a potential benefit of the MC for quality improvement purposes. Due to the small number of participants, the use of complex analysis was minimized and the influence of demographics could not be assessed. Mean visit frequencies, before and after joining the MC, likely underestimated both the wellbeing improvement that was attributable to CMHS (pre-MC) and the long-term MC effects (post-MC). The study assumed both effects were underestimated equally.
The benefits of the MC could be limited for those who were not capable of engaging socially. In this study the non-engaged cohort had higher CMHS visit frequencies overall, which may indicate more severe mental illness that could have hindered deeper engagement. While the MC was designed to connect with isolated individuals, there are inevitably many who are difficult to reach. It is likely that a larger cohort of non-engaged members would have also included individuals who were non-engaged because they found other engaging activities (e.g. employment) that could improve their mental health. This limitation did not reduce the effect of those who successfully engaged with the MC, thus, future work should focus on characteristics of those who do and do not engage with the MC in order to understand how to best serve the largest population.
All engaged MC members had reduced visit frequency, however, two of the three largest changes were from individuals who reduced use of the CMHS Clubhouse after joining the MC. While the CMHS Clubhouse may have lower operating costs than other visit types, we have included clubhouse visits the following reasons: 1) CMHS includes clubhouse visits in their overall metric of client visits; 2) Values derived in this study were based on improved wellbeing rather than cost savings; 3) We assumed each CMHS visit type could be equally valuable to a client’s mental health; 4) Members who chose the MC over the Clubhouse represent direct evidence that the MC was more effective than the Clubhouse for those members.
We assumed the CMHS visit frequency of engaged members would stay constant if they had not engaged with the MC (similar to the non-engaged cohort). Changes to CMHS treatments and a multitude of other factors likely impacted member’s mental health (for better or worse) over the course of the study period. However, by applying the effort to engage with the MC, the engaged members showed they felt the MC intervention was helpful. Other than engagement with the MC and CMHS, there were no other anticipated similarities among the engaged members that could have accounted for their consistent improvements in wellbeing.
Finally, the MC has several other valuable roles that could not be quantified within the scope of this study that include but are not limited to: 1) Social engagement for members who use other local mental healthcare providers or are infrequent clients of CMHS; 2) Prevention for those without a mental illness; 3) Connection to those with mental illness who are unwilling to seek clinical treatment; 4). Community outreach and integration; and 5) Guidance to those seeking help but unsure where to go.
Conclusions
MC cost-effectiveness may derive from how it operates differently than other social groups. No mental illness diagnosis is required to join, allowing the MC to bring together those avoiding medical help with those receiving care. The common desire for socialization means members do not need to “out themselves” by participating. The MC provides a safe space for socialization, activities and community integration that allows often-disenfranchised individuals to engage in positive activities, moving out of isolation and into productive interactions in their community. Members are given autonomy of choice (i.e., activities are optional and the cafe area is always available during operating hours). While there are no requirements to become a member, the MC is oriented toward and seems to most benefit, individuals with mental illness and/or disability who would like to have greater purpose in their lives through socialization, shared experiences, and being part of something bigger than themselves by using the MC as a platform to end stigma in the broader community.
Investigator Disclosures: BLV is employed by Extended Grace, which owns and operates the MC. BLV conceived of the study, described the intervention, helped to interpret the results, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. BLV had no role in the collection of PHI by CMHS, data analyses or production of results. TA is Chief Scientist of a business consultancy that specializes in helping small companies and nonprofit organizations understand their existing data. The MC contracted TA who designed the study, conducted all statistical analyses, drafted the initial manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted. TA has no ownership stake or equity interest in the MC. GL is a faculty member at Michigan State University who is leading externally funded research at the MC. GL provided scientific guidance for the study, was reimbursed for resources contributed, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Funding
This project is funded by the MC through a grant from the Grand Haven Area Community Foundation and through an in-kind donation by Community Mental Health of Ottawa County.
References
- Baumeister, R. & Leary, M. (1995). The need to belong: Desire for interpersonal attachments as a fundamental human motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 117(3), 497-529. [CrossRef]
- runier, A. & Mayhew, M. (2016). Investing in treatment for depression and anxiety leads to fourfold return. World Health Organization.
- Davidson L., Tondora J, Staeheli M, et al. (2005). Recovery guides: An emerging model of community-based care for adults with psychiatric disabilities. In Lightburn A, Sessions P, (Eds.) Community Based Clinical Practice (pp.476-501). Oxford University Press.
- Davies, J., McKenna, M., Bayley, J., Denner, K., & Young, H. (2020). Using engagement in sustainable construction to improve mental health and social connection in disadvantaged and hard to reach groups: a new green care. Journal of Mental Health, 29(3), 350-357. [CrossRef]
- Fortuna K., Solomon P, Rivera J. (2022). An Update of Peer Support/Peer Provided Services Underlying Processes, Benefits, and Critical Ingredients. Psychiatric Quarterly, 93(2):571-86. [CrossRef]
- Hassan Z. (2014). The social labs revolution: A new approach to solving our most complex challenges. Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
- Hellebuyck, M., Halpern, M., Nguyen, T. & Fritze, D. (2018). The state of mental health in America 2019. Mental Health America.
- Heyland M., Emery C., Shattell M. (2013). The living room, a community crisis respite program: Offering people in crisis an alternative to emergency departments. Global Journal of Community Psychology Practice, 4(3):1-8. [CrossRef]
- Hill, D., (2017). 2017 Behavioral Risk Factor Survey, Ottawa County, MI. VIP Research and Evaluation. https://www.miottawa.org/health/ochd/pdf/BRFS/2017_BRFS.pdf.
- Hughes M., Waite L., Hawkley L. et al. (2004). A short scale for measuring loneliness in large surveys: Results from two population –based studies. Research on Aging, 26(6), 655-672. [CrossRef]
- Jacobson N. & Greenley D. (2001). What is recovery? A conceptual model and explication. Psychiatric Services, 52(4):482-5. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D., Steiner, A., Mason, H. et al. (2021). Men’s sheds as an alternative healthcare route? A qualitative study of the impact of Men’s sheds on user’s health improvement behaviors. BMC Public Health 21, 553. [CrossRef]
- Kroenke K., Spitzer R., Williams J. (2001). The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 16(9):606-13. [CrossRef]
- Lin, E., Katon, W., Rutter, C., Simon, G., Ludman, E., Oliver, M., Unützer, J. (2010). Chronic medical conditions and utilization of health services. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 25(3), 221–227.
- Link, B. G., & Cullen, F. T. (1983). Reconsidering the social rejection of ex-mental patients: Levels of attitudinal response. American Journal of Community Psychology, 11(3), 261- 273. [CrossRef]
- Manual, A. N. S. A. (1999). Adult Needs and Strengths Assessment. San Francisco.
- McKay C., Nugent K., Johnsen M., Eaton W., Lidz C. (2018). A systematic review of evidence for the clubhouse model of psychosocial rehabilitation. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 45(1):28-47. [CrossRef]
- National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI). (2020). https://www.nami.org/Learn-More/Mental-Health-By-the-Numbers.
- Shalaby R. & Agyapong V. (2020). Peer support in mental health: literature review. JMIR Mental Health, 7(6):e15572. [CrossRef]
- Skapinakis, P. (2007). The 2-item generalized anxiety disorder scale had high sensitivity and specificity for detecting GAD in primary care. Evidence-Based Medicine, 12, 149. [CrossRef]
- Stanley S., Ferguson L., Harrison L., et al. (2019). The Wellness Clinic: a model of integrated care to address the physical health of people with severe mental illness.
- Park, A., McDaid, D., Weiser, P. et al. (2013). Examining the cost effectiveness of interventions to promote the physical health of people with mental health problems: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 13, 787. [CrossRef]
- Perlick, D., Rosenheck, R., Clarkin, J., Sirey, J., Salahi, J., Struening, E., et al.
- (2001). Stigma as a barrier to recovery: Adverse effects of perceived stigma on social adaptation of persons diagnosed with bipolar affective disorder. Psychiatric Services, 52(12), 1627-1632. [CrossRef]
- Pinals D. (2020). Crisis Services: Meeting Needs, Saving Lives. Alexandria, VA: National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors.
- Pyne, J. & Baumeister, R. (2017). Social belonging and its relation to social identity, self-esteem, and well-being. In Handbook of Self and Identity (pp. 242-257). Guilford Publications.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).