1. Introduction
Conventional blood tests are observed with optical microscopes. These tests are time-consuming and can reduce the integrity of blood samples. Among the emerging laser-based methods for blood testing, Raman spectroscopy is one of the methods that involves nonlinear scattering. This method is adopted in a wide range of blood tests because of its various advantages, such as the requirement of only a minimal quantity of blood for testing, rapid analysis, and high-precision result interpretation, which simplify the collection and assessment of blood-related data. The effectiveness of Raman spectroscopy in clinical applications has been verified [
1,
2].
In Raman spectroscopy, the wavelength difference between incident and scattered light is compared to determine the changes in their energy levels and the sample’s lattice vibration characteristics, both of which can be used to analyze the composition and structure of the sample. Therefore, the values of Raman peaks can indicate the molecular structure of a sample [
3,
4].
Raman
scattering spectroscopy can be applied with blood testing to determine if an individual has contracted a certain disease. The Raman
characteristic peak positions and amplitudes of an infected individual differ markedly from those of an uninfected individual. Thus, Raman spectroscopy can enable rapid screening for certain pathogens. The prevalence of emerging viruses, such as COVID-19, will eventually be overlapped to that of influenza virus infection, and this trend has necessitated reliable and rapid and differential disease screening [
5]. Moreover, the acquisition of blood information through Raman spectroscopy enables the rapid and precise diagnosis of clinical diseases, such as liver disease, diabetes, cancer, allergies, genetic disorders, anemia, and leukemia [
6,
7,
8].
In the present study, Raman spectroscopy was employed to analyze samples of normal bloodand abnormal blood, in 3 types of preparation, including whole blood, plasma, and serum. The primary Raman
peaks of normal blood was observed to correspond to hemoglobin, and the other Raman peaks of normal blood corresponded to amino acid and other components [
9]. By contrast, the primary Raman peaks of plasma and serum corresponded to β-carotene [
10]. We also conducted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to examine the small molecules present in the aforementioned samples. Moreover, a prothrombin time experiment was performed to compare the Raman spectroscopy results of blood samples with and without calcium-containing coagulants. Clinically, coagulation or clotting, in which blood turns from liquid to nonflowing gel, is a critical process in hemostasis [
11,
12].
The goal was to determine whether patients’ intrinsic and common coagulation pathways were functioning normally.
2. Sample Preparation
All blood samples used in this study were obtained from the waste blood provided by National Cheng Kung University Hospital with the approval of its institutional review board. Three-types of sample preparation were collected for each blood specimen. None of the normal samples used in this study were subjected to any chemical or biological treatment. Blood samples were drawn using a syringe, dropped on a glass slide (100 μL), and then covered with a cover glass. An experiment was conducted on the blood samples at room temperature. Normal blood, which was obtained from healthy individuals, typically had a prothrombin time of 10.0–12.5 s. By comparison, abnormal blood, which was obtained from patients receiving anticoagulant drugs, had a clotting time of longer than 12.5 s. For experimental protocol, a calcium-containing coagulant had to be mixed with blood in a ratio of 2.8:1, and silver nanoparticles were mixed with the blood samples in a ratio of 1:3. To meet the requirements of clinical practice, the prepared whole blood and plasma samples were also examined.
Figure 1.
Preparation of blood samples.
Figure 1.
Preparation of blood samples.
3. Raman spectroscopy
Raman scattering spectroscopy and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) were performed at room temperature (RT) using a custom-made micro-Raman spectroscopy system consisting of a spectrometer (Princeton Instruments Acton Spectra Pro 2500i), a liquid nitrogen cooled CCD detector (Princeton Instruments Acton 7508-0002), four objective lenses from 20x to 100x, and a solid-state green laser (wavelength of 532 nm) as its excitation light source. To avoid laser heating damage of blood samples, each Raman scattering spectrum was recorded with the integration of 3 s for 5 times for the laser output power of 3 mW and the 20x objective lens. The spectral range was set between 400 and 2000 cm−1. The blood samples were contained on a glass slide sealed with a cover glass, and for SERS, the blood samples were mixed with Ag nanoparticles. All spectra were recorded a few minutes after each sample was made. The Raman characteristic peak position was calibrated with measurements of a Si(100) substrate under the same conditions, and the background intensity was subtracted. In addition, the Raman spectra is normalized to the characteristic peak of normal blood at 1562 cm-1, and the SERS spectra is normalized to the characteristic peak of normal blood at 521 cm-1.
4. Results and discussion
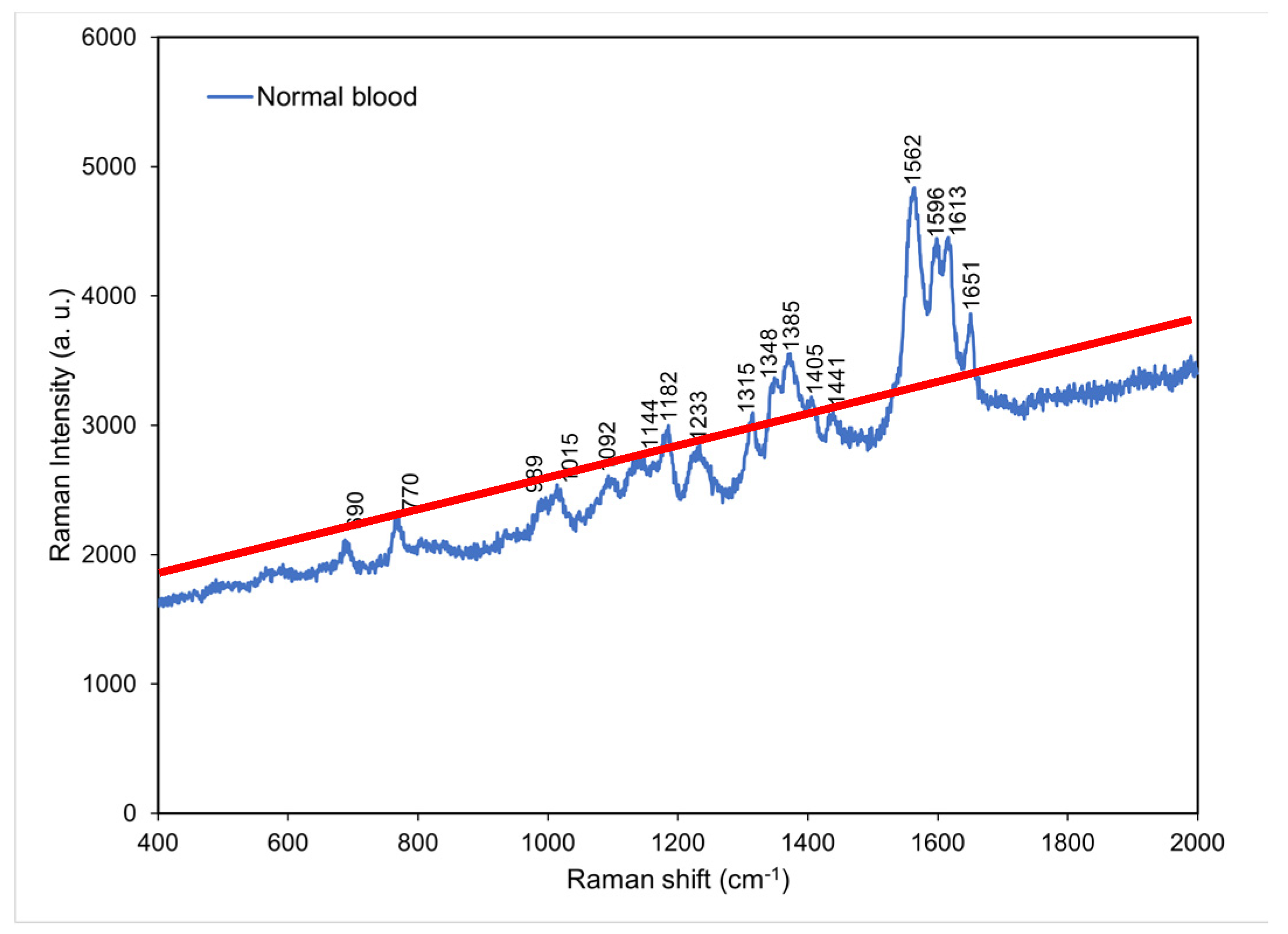
4.1. Raman spectrum for normal blood
On the basis of a literature review and matching inquiries in the Spectral Database for Organic Compounds [
13] we found that the most abundant component in normal whole blood is hemoglobin [
14], followed by amino acid, lactic acid, lactate, and acetate. Hemoglobin, which is a major component of whole blood, were observed to exhibit characteristic peaks at 690, 989, 1015, 1182, 1233, 1315, and 1562–1649 cm
−1. Hemoglobin accounts for 95% of the weight of a red blood cell and affects a red blood cell’s oxygen carrying capacity [
15]. In clinical practice, hemoglobin level can serve as a standard for anemia detection [
16], and the severity of COVID-19 disease can be predicted using blood oxygen level [
5]. Amino acid is small molecule [
17] which exhibited characteristic peaks at 770 and 1348 cm
−1. Moreover, lactic acid and lactate exhibited characteristic peaks at 1092 and 1144 cm
−1, respectively. Lactic acid is a metabolic product of carbohydrate, and blood lactic acid level can serve as a standard for the diagnosis of lactic acidosis in clinical practice [
18]. Lactate is a salt formed through the release of a hydron from lactic acid after lactic acid reacts with a charge-carrying sodium or potassium ion. An excessive lactate level is recognized as a potential cause for acidemia (acidosis) [
19]. The main characteristic peak of acetate was located at 1441 cm
−1. Acetate exists in animal tissues, excreta, and blood in the form of free acid (
Figure 2).
Table 1 presents the Raman peaks and vibrational modes of the components of normal blood [
20].
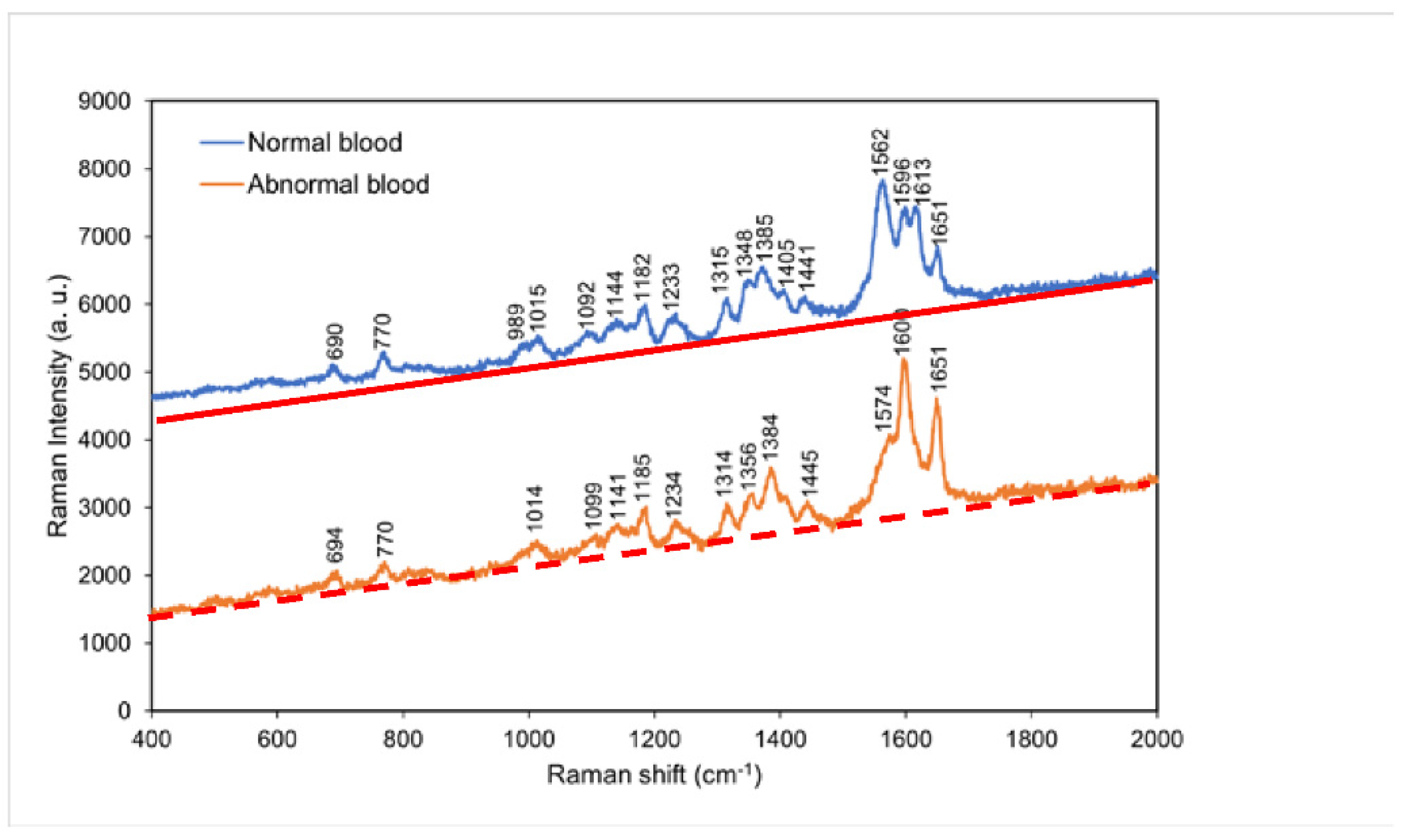
4.2. Comparison of the Raman spectra of normal blood and abnormal blood
According to
Figure 3, the greatest difference in the Raman spectra of normal blood and abnormal blood occurred between 1562 and 1651 cm
−1. The normal sample exhibited characteristic peaks at 1562 and 1613 cm
−1, whereas the abnormal sample exhibited a characteristic peak at 1574 cm
−1. This result suggests that the coagulation of hemoglobin was easier in normal blood than in abnormal blood because of the shorter tine period for clotting of normal blood. Accordingly, the characteristic peaks of aromatic ring breathing,
C==N antisymmetric stretching, and pyrrole ring stretching were
either absent or shifted in peak position in the abnormal blood Raman spectrum.
Table 2 presents the major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal whole blood and abnormal whole blood [
21].
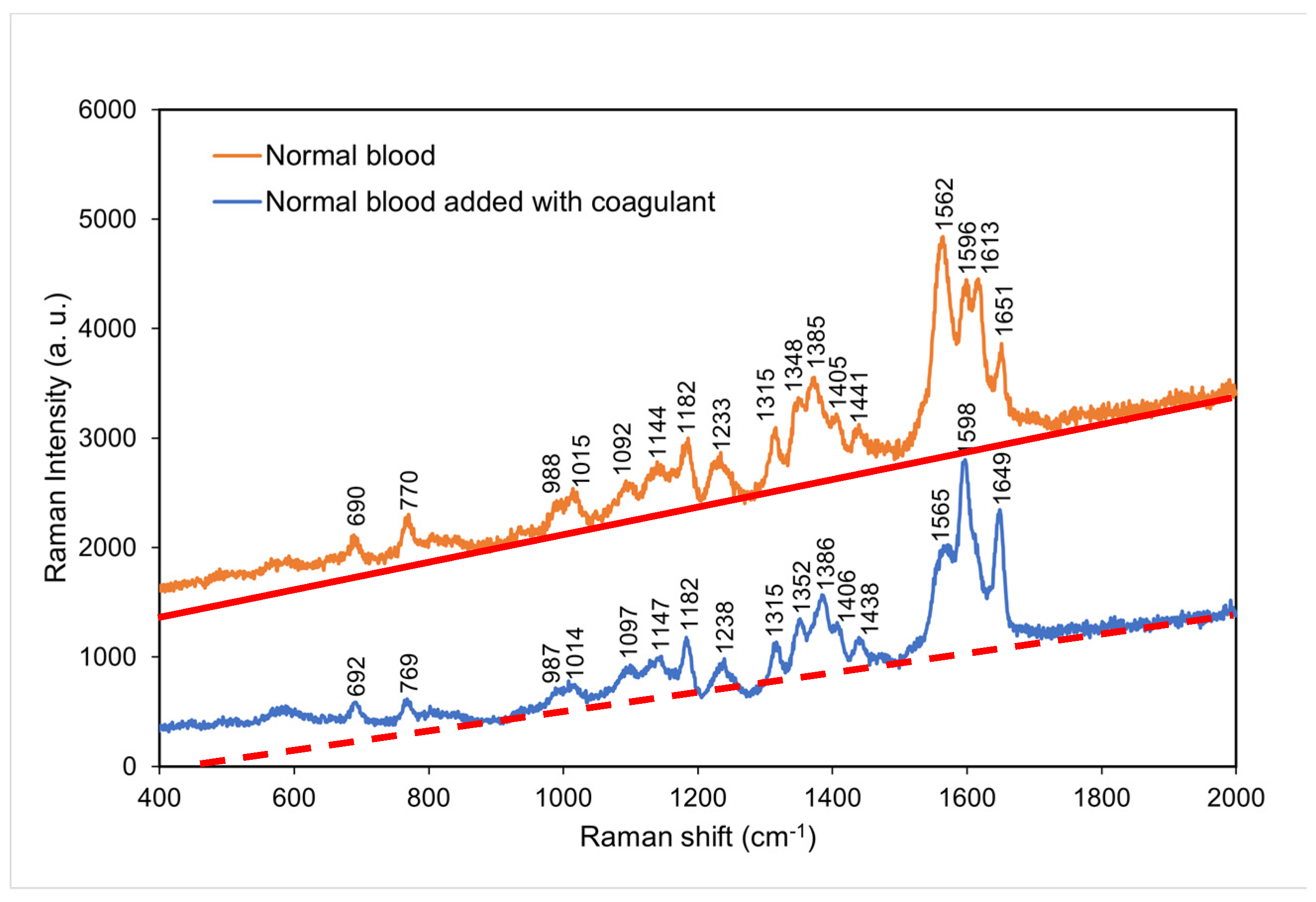
4.3. Comparison of the Raman spectra of normal blood with and without coagulant
Figure 4 compares the Raman spectra of normal blood with and without coagulant. Normal blood with coagulant has lower intensities at the characteristic peaks of 769, 987, 1014, 1315, 1352, and 1565 cm
−1 and higher intensities at the characteristic peaks of 1598 and 1649 cm
−1. This result suggests that hemoglobin was considerably affected by clotting process [
22,
23] and that an excessively short time period of clotting resulted in incomplete coagulation
. This led to incomplete molecular reactions in the blood and thus a decrease in the intensities of some characteristic peaks.
Table 3 presents the major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood with and without coagulant.
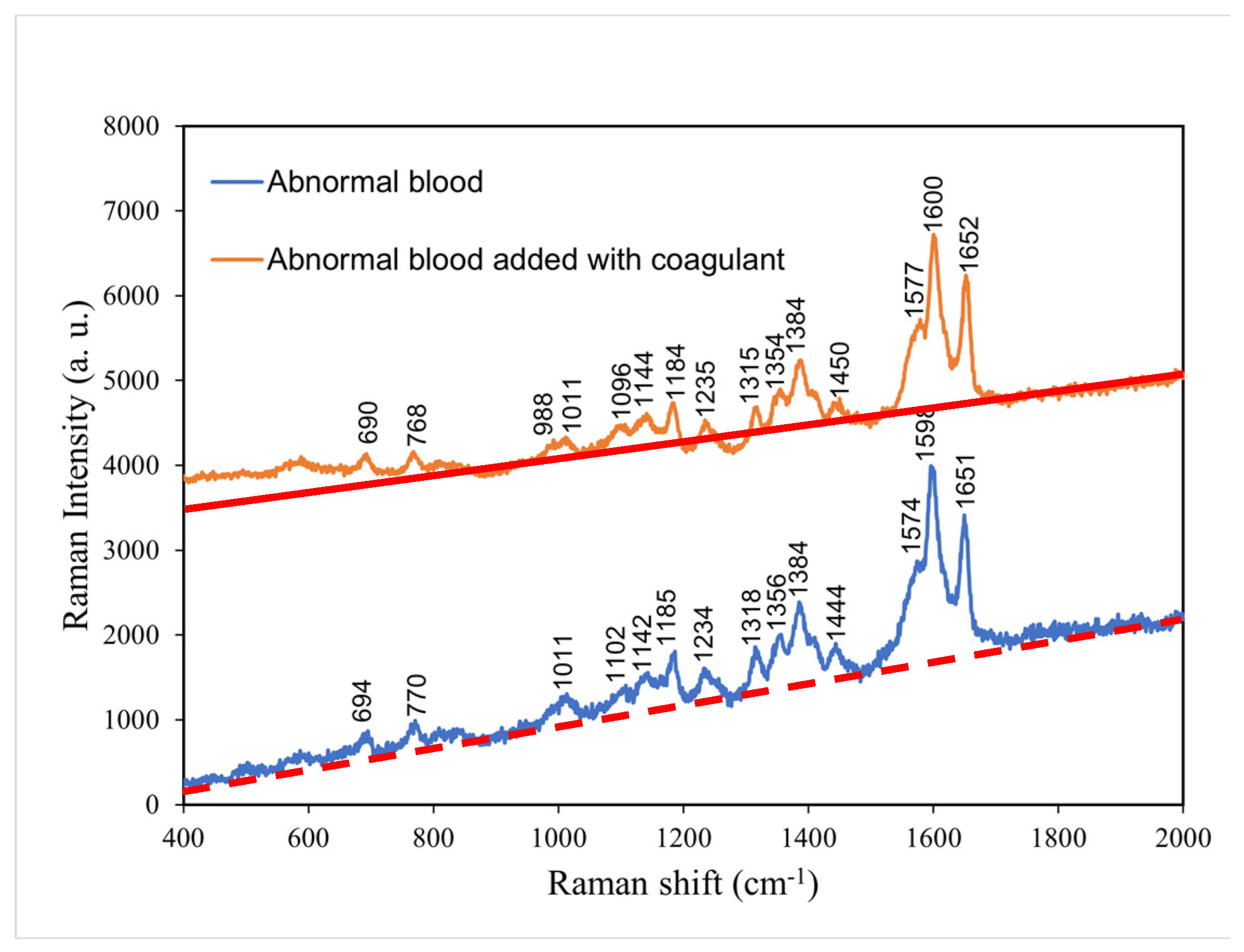
4.4. Comparison of the Raman spectra of abnormal blood with and without coagulant
According to
Figure 5,
the comparison between abnormal blood with and without coagulant, the abnormal blood with coagulant
had lower intensities at the characteristic peaks of 770, 1011, 1185, 1318, 1356, 1384, and 1712 cm
−1 and higher intensities at the characteristic peaks of 988 and 1577 cm
−1.
Such change in intensity without shift in peak position is attributed to (significant) change in clotting time of hemoglobin. The addition of coagulant shortens the clotting time, and therefore, the abnormal blood, originally having a long time period of clotting, became fully coagulated after the addition of coagulant.
Table 4 presents the major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood without coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant.
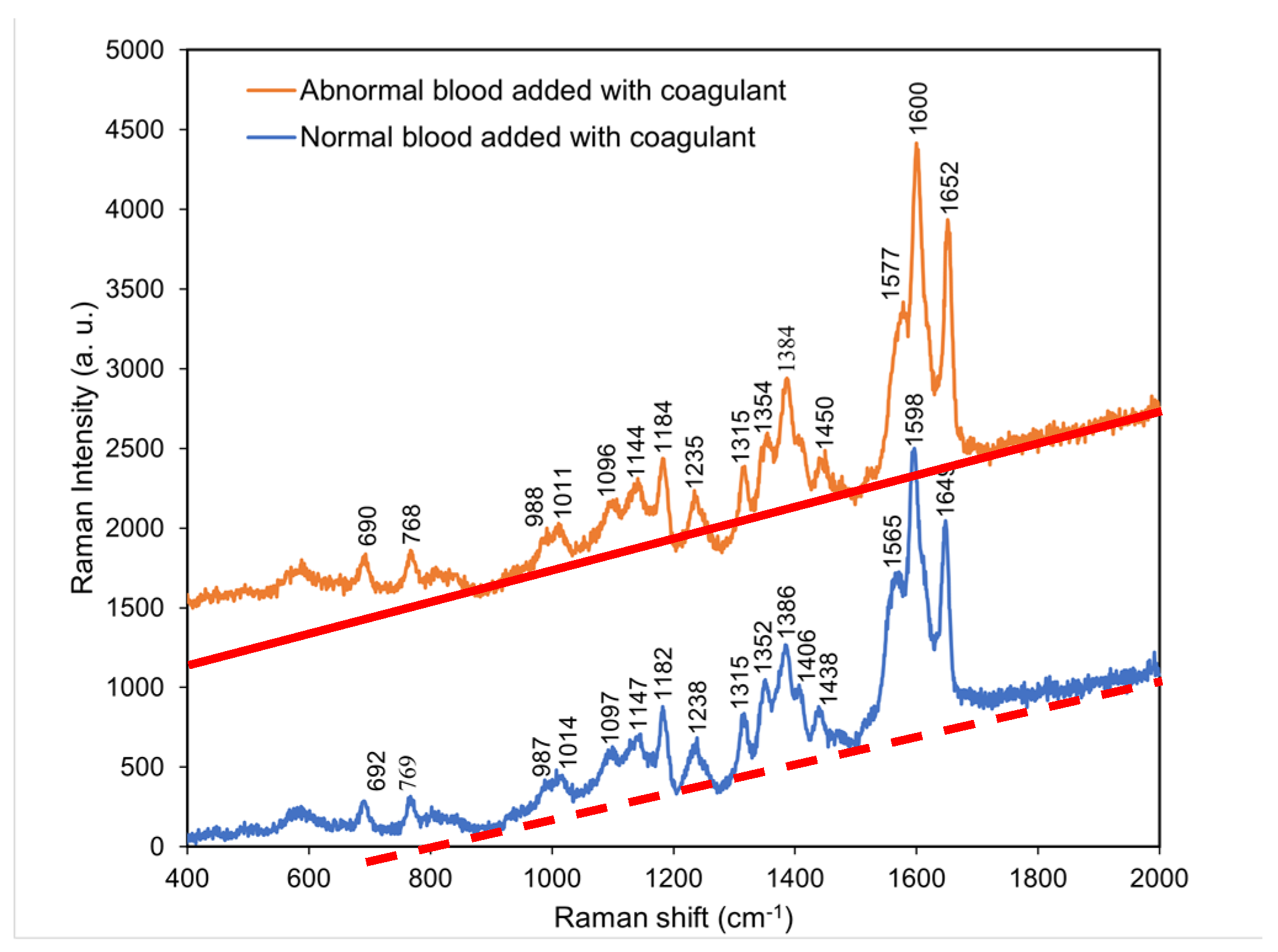
4.5. Comparison of the Raman spectra of normal blood with coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant
According to
Figure 6, the characteristic peaks of abnormal blood with coagulant were similar to those of normal blood with coagulant. Thus, the addition of coagulant to abnormal blood resulted in the locations and intensities of its characteristic peaks
gradually approaching those of the characteristic peaks of normal blood with coagulant.
This indicated that the coagulation cascades were commonly shared in individuals with either normal or abnormal blood samples, but the required time periods for full coagulation differed. In addition, the presence of coagulant effectively shortened the time period of clotting of abnormal blood and caused full coagulation.
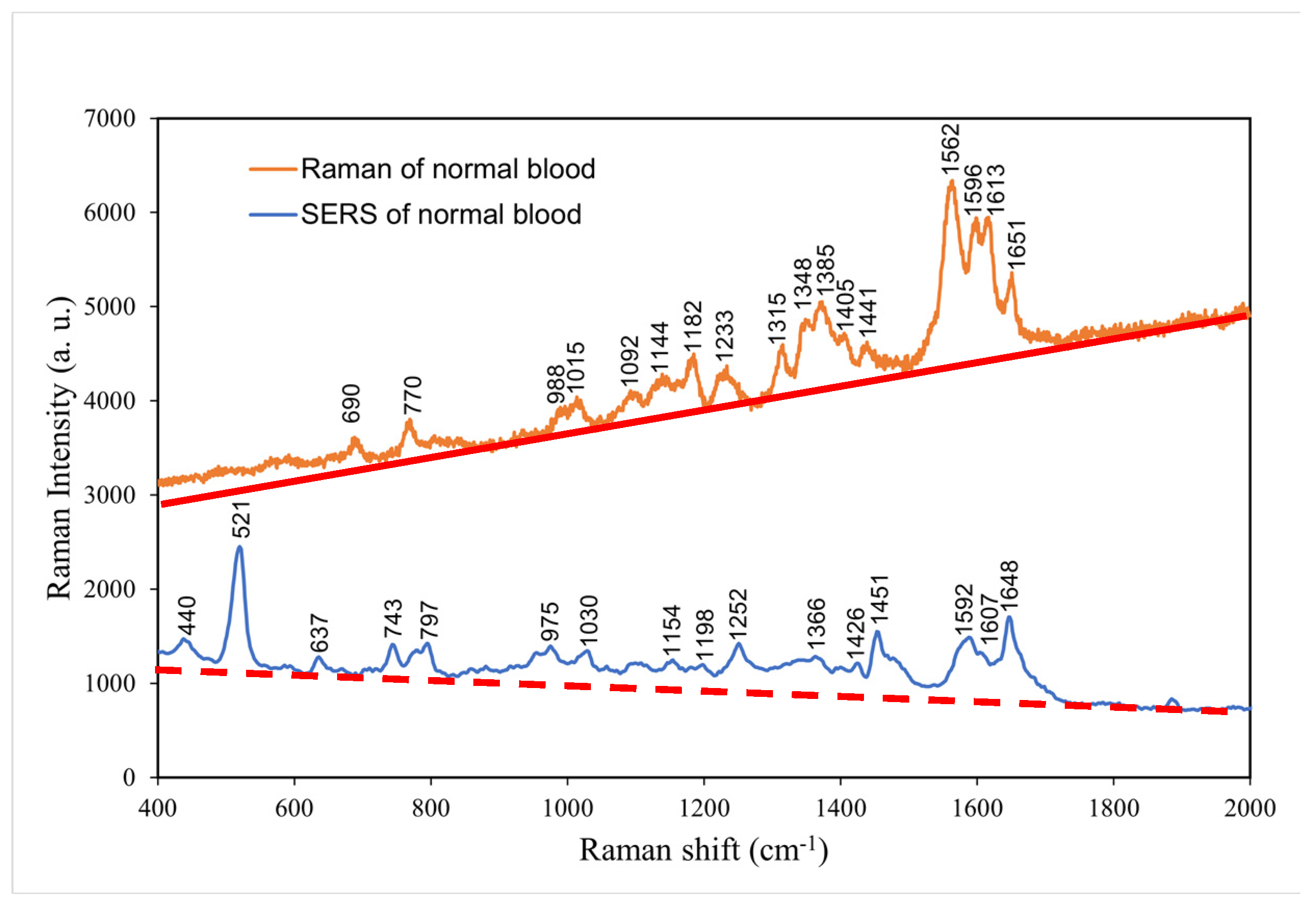
4.6. Comparison of the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant
The surface-enhanced Raman spectrum was mainly conducted to reinforce Raman spectrum at low frequency because molecular resonance at a low frequency can be achieved more easily in SERS than in Raman spectroscopy. Therefore, in
Figure 7, molecular vibration modes at high frequencies have higher intensity while in SERS, low frequency vibration modes are stronger [
24]. In the low frequency region, SERS peaks at 400–1000 cm
−1 revealed considerable additional biological information that could not be obtained through normal Raman spectroscopy, including the presence of hormone, antibody, and enzyme molecules from 440. cm
−1 to 797 cm
-1 . Above 1000 cm
−1, SERS spectrum does not reveal additional biological characteristics than that of Raman spectroscopy.
Table 5 presents the major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts [
24].
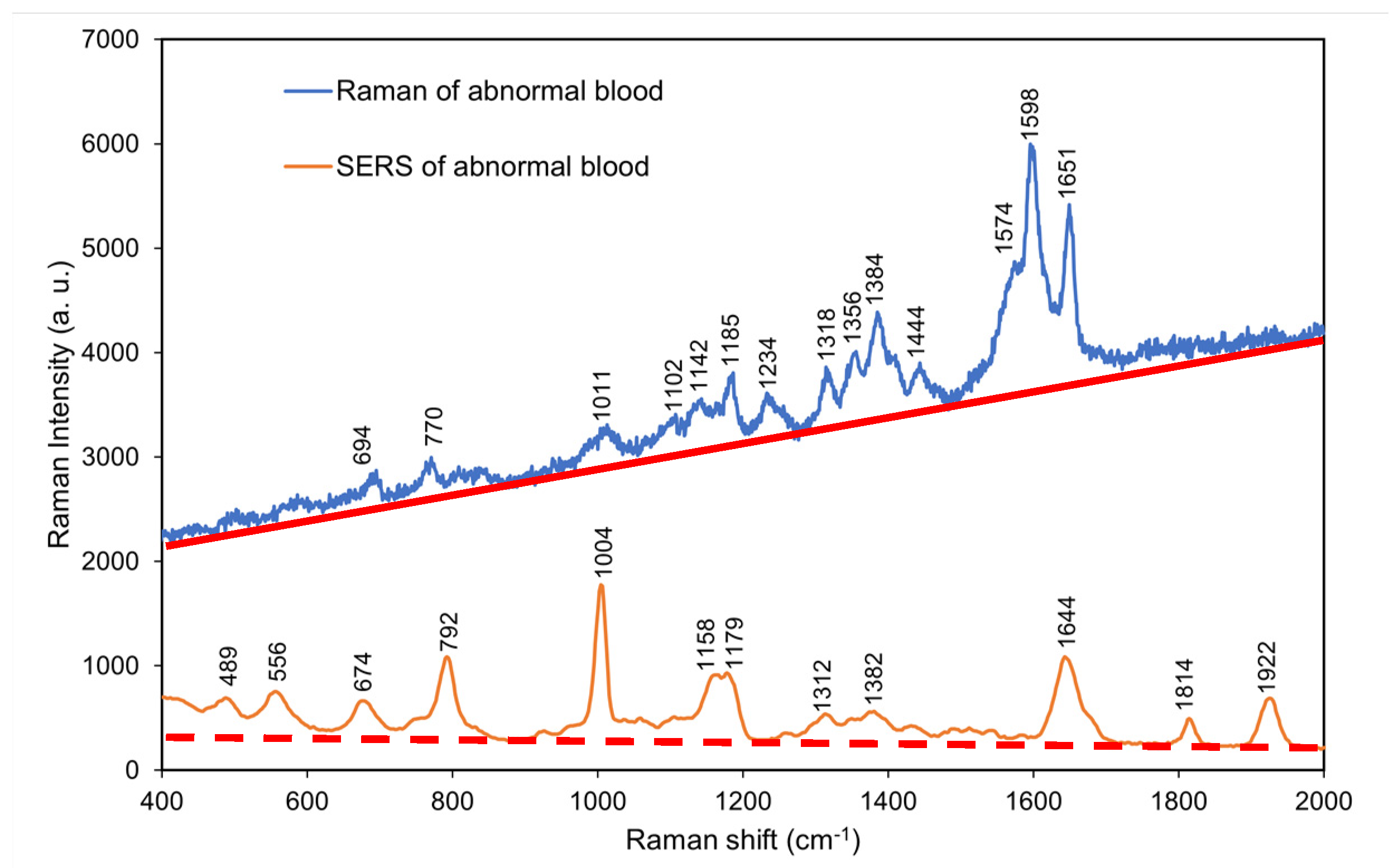
4.7. Comparison of the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant
According to
Figure 8, the surface-enhanced Raman spectrum of abnormal blood without coagulant exhibited additional peaks at 400–
800 and 1600–2000 cm
−1 (low- and high-frequency regions, respectively) that were not observed in the normal Raman spectrum of abnormal blood without coagulant. However, the surface-enhanced Raman spectrum exhibited considerably fewer peaks in the mid-frequency region of 700–1600 cm
−1 than did the normal Raman spectrum.
Comparing the SERS spectra of normal and abnormal blood at the low frequency part, the Coenzyme A characteristic peak (743 cm-1) is missing in the abnormal blood, and characteristic peak positions of L-Arginine, Cholesterol ester, and Phenylalanine shift significantly. This indicates that the abnormal blood environment probably leads to change in bond lengths in L-Arginine, Cholesterol ester, and Phenylalanine molecules. Overall, the SERS results of abnormal blood without coagulant differed from those of normal blood without coagulant (
Figure 7)
, and the strong difference at low frequency vibration modes can serve as fingerprints for diagnostics.
Table 6 presents the major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts [
25].
4.8. Comparison of the Raman spectra of whole blood, plasma, and serum
The whole blood is the normal blood that contains anticoagulant to inhibit coagulation. The characteristic peaks of whole blood had lower intensities than those of normal blood because of the lack of coagulation in whole blood, which resulted in its molecules being unable to achieve resonance. However, the overall waveforms obtained for normal blood and whole blood were similar (
Figure 9). By contrast, plasma and serum exhibited characteristic peaks only at 1016, 1153, and 1526 cm
−1 because only some small molecules remained after the removal of blood cells. A study suggested that the characteristic peaks of plasma and serum correspond to β-carotene [
26], which only exhibits molecular resonance at low frequencies. In clinical application, changes in the characteristic β-carotene peaks in the Raman spectra of serum and plasma can be used to diagnose certain diseases, such as thyroid disease and chronic renal failure. Researchers have recommended using the Raman shift of β-carotene for diagnosing chronic renal failure and thyroid disease [
27].
Table 7,
Table 8 and
Table 9 present the major Raman shifts and corresponding components for whole blood [
19], plasma [
27], and serum [
28].
5. Conclusions
Using short-wavelength Raman scattering spectroscopy and SERS, samples of normal blood, abnormal blood in whole blood, plasma, and serum were detected, and the underlying information reflected by the biological characteristics detected in each sample type were analyzed. As a result of the analysis, the following major conclusions and new finding were reached:
The addition of coagulant effectively and gradually caused the intensities and locations of the characteristic peaks of abnormal blood to approach those of the characteristic peaks of normal blood with coagulant, which indicates that the blood clotting affects the locations and intensities of characteristic peaks caused by hemoglobin.
The SERS results of abnormal blood without coagulant differed from those of normal blood without coagulant, and the strong difference at low frequency vibration modes can serve as fingerprints for diagnostics.
In serum and plasma, the main molecule that resonates in Raman spectroscopy excludes hemoglobin, but β-carotene only exhibits molecular resonance at low frequencies. Therefore, β-carotene might become crucial component in medical testing.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, Republic of China (contract numbers: MOST 109-2224-E-011 -002), for supporting the research and publication
References
- Kong, K.; Kendall, C.; Stone, N.; Notinghera, I. Raman spectroscopy for medical diagnostics — From in-vitro biofluid assays to in-vivo cancer detection. Volume. 2015, 89, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pence, I.J.; Janse, A.M. Clinical instrumentation and applications of Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1958–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, J. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy in paper and pulp analysis. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2001, 36, 139–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, S.; Umapathy, S. Raman spectroscopy explores molecular structural signatures of hidden materials in depth: Universal Multiple Angle Raman Spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.V.S.S.; Bevi, A.R. Low-Cost Pulse Oximeter & Heart Rate Measurement for COVID Diagnosis. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 1964, 62035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.W.; Yan, X.L.; Dong, R.X.; Ban, G.; Li, K. Analysis of serum from type II diabetes mellitus and diabetic complication using surface-enhanced Raman spectra (SERS). Appl. Phys. 2009, 94, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusciano, G.; Luca, A.C.D.; Pesce, G.; Sasso, A. Raman Tweezers as a Diagnostic Tool of Hemoglobin-Related Blood Disorders. Sensor. 2008, 8, 7818–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Gong, j.; Tian, Y. Analysis of Serum from Acute Leukemia Patients Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS). Spectroscopy 2022, 37, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.G.; Buckley, K.; Blades, M.W.; Turner, R.F.B. Raman Spectroscopy of Blood and Blood Components. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 71, 767–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanes, D. β-Carotene and lung cancer: a case study. Volume. 1999, 69, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Chiang, C.C.; Immanue, P.N.; Subramania, M. Point-of-Care Testing Blood Coagulation Detectors Using a Bio-Microfluidic Device Accompanied by Raman Spectroscopy. Coatings 2022, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staritzbichler, R.; Hunold, P.; Lopis, I.E.-; Hildebrand, P.W.; Isermann, B.; Kaiser, T. Raman spectroscopy on blood serum samples of patients with end-stage liver disease. PLoS One. 2021, 16, 256045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansano, A.; Navarro, R.; Arranz, A.S.; Manrique, J.A. Development of a Spectral Data Base for Exomars' Raman Instrument (RLS). LPSC. 2014, 45, 2803. [Google Scholar]
- Enejder, A.M.; Koo, T.W.; Oh, J.; Hunter, M.; Sasic, S.; Feld, M. S.; Horowitz, G.L. Blood analysis by Raman spectroscopy. Optics letters. 2002, 27, 2004–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, I.T.; Terner, J.; Pittman, R.N.; Somera, S.G. The Effect of Red Blood Cell Velocity on Oxygenation Measurements using Resonance Raman Spectroscopy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005, 289, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L. Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Common and Curable Disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013, 3, 11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Analysis, Nutrition, and Health Benefits of Tryptophan. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2018, 11, 1178646918802282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, G.A. Current concepts in lactate exchange. Med. Sci. Sports. Exerc. 1991, 23, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, S.P. Lactic Acid and Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Kumar, N.; Uppal, A.; Gupta, P.K. Visible Raman excitation laser induced power and exposure dependent effects in red blood cells. J of Biophotonics. 2016, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankapur, A.; Zachariah, E.; Chidangil, S.; Valiathan, M.; Mathur, D. Raman Tweezers Spectroscopy of Live, Single Red and White Blood Cells. PLoS ONE. 2010, 5, 10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.L.; Chiou, Y.C.; Chou, C.W.; Young, K.C.; Huang, S.J.; Liu, C.Y. Point-of-care Testing Portable Blood Coagulation Detectors Using Optical Sensors. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2013, 33, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Huang, S.J.; Chou, C.W.; Chiou, Y.C.; Lin, K.P.; Tsai, M.S.; Young, K.C. Design and evaluation of a portable optical-based biosensor for testing whole blood prothrombin time. Talanta. 2013, 116, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Gao, N.; Yue, X.; Wang, T. Establishment of a reliable scheme for obtaining highly stable SERS signal of biological serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Q.; Hung, T.M.; Chen, W.; Yu, Y.; Chang, J.T.C.; Pan, J.; Qiu, S.; Chen, R. Human blood test based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy technology using different excitation light for nasopharyngeal cancer detection. IET Nanobiotechnology. 2019, 13, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Zheng, W.; Schweitzer, M.; Hallen, H. Resonance Raman imagery of semi-fossilized soft tissues. Volume. 2018, 10753, 1075310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellaa, M.; Lucotti, A.; Tommasini, M.; Bedoni, M.; Forvi, E.; Gramaticac, F.; Zerbi, G. Raman and SERS recognition of β-carotene and haemoglobin. Volume. 2011, 79, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, K. R. M.; Maguire, A.; Bryant, J.; Arm-strong, J.; Dunne, M.; . Finn, M.; Lyng, F. M.; Meade, A. D. Development of a high throughput (HT) Raman spectroscopy method for rapid screening of liquid blood plasma from prostate cancer patients. The Analyst. 2016, 142, 3763. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Tong, D.; Chen, C.; Gao, R.; Han, H.; Lv, X. Serum Raman spectroscopy combined with multiple algorithms for diagnosing thyroid dysfunction and chronic renal failure. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 34, 34–102241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 2.
Raman spectrum obtained for normal blood at room temperature. The red solid line indicates the background of the spectrum.
Figure 2.
Raman spectrum obtained for normal blood at room temperature. The red solid line indicates the background of the spectrum.
Figure 3.
Raman spectra of normal blood and abnormal blood at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 3.
Raman spectra of normal blood and abnormal blood at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 4.
Raman spectra of normal blood with and without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 4.
Raman spectra of normal blood with and without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 5.
Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 5.
Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 6.
Raman spectra of normal blood with coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 6.
Raman spectra of normal blood with coagulant and abnormal blood with coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 7.
Normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 7.
Normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 8.
Normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 8.
Normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant at room temperature. The red solid line and orange dashed line indicate the background for each spectrum, respectively.
Figure 9.
Raman spectra of whole blood, plasma, and serum at room temperature. The red solid line indicates the background of the spectrum for whole blood.
Figure 9.
Raman spectra of whole blood, plasma, and serum at room temperature. The red solid line indicates the background of the spectrum for whole blood.
Table 1.
Characteristic peaks and corresponding vibrational modes of the components of normal blood.
Table 1.
Characteristic peaks and corresponding vibrational modes of the components of normal blood.
| Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational mode |
Component |
| 690 |
C-C-N bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 770 |
Ring vibrations |
Tryptophan |
| 989 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1015 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1092 |
C-O vibrations |
Lactic acid |
| 1144 |
CH3 rocking, C-O vibrations |
Lactate |
| 1182 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1233 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
| 1315 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1348 |
C-H bending |
Tryptophan |
| 1385 |
CH3 symmetric stretching |
Heme |
| 1405 |
C==N antisymmetric stretching |
Heme |
| 1441 |
CH2 bending |
Acetates |
| 1562 |
Pyrrole ring stretching vibrations |
Hemoglobin |
| 1596 |
C==N antisymmetric stretching and |
Hemoglobin |
| 1613 |
C-H bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 1651 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
Table 2.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood and abnormal blood.
Table 2.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood and abnormal blood.
| Normal Raman shift (cm-1) |
Abnormal blood Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| 989 |
No |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1315 |
1314 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1348 |
1356 |
C-H bending |
Tryptophan |
| 1562 |
1574 |
Pyrrole ring stretching vibrations |
Hemoglobin |
| 1596 |
1600 |
C==N antisymmetric stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1613 |
No |
C-H bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 1651 |
1651 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
Table 3.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood with and without coagulant.
Table 3.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for normal blood with and without coagulant.
| Normal blood Raman shift (cm-1) |
Normal blood (Coagulant) Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational mode |
Component |
| 770 |
769 |
Ring vibrations |
Tryptophan |
| 988 |
987 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1015 |
1014 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1315 |
1315 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1348 |
1352 |
C-H bending |
Tryptophan |
| 1562 |
1565 |
Pyrrole ring stretching vibrations |
Hemoglobin |
| 1596 |
1598 |
C==N antisymmetric stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1613 |
No |
C-H bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 1651 |
1649 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
Table 4.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for abnormal blood with and without coagulant.
Table 4.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for abnormal blood with and without coagulant.
| Abnormal blood Raman shift (cm-1) |
Abnormal blood (Coagulant) Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational mode |
Component |
| 770 |
768 |
Ring vibrations |
Tryptophan |
| 1185 |
1184 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1318 |
1315 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1356 |
1354 |
C-H bending |
Tryptophan |
| 1574 |
1577 |
Pyrrole ring stretching vibrations |
Hemoglobin |
Table 5.
Major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts.
Table 5.
Major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of normal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts.
| Normal Raman shift (cm-1) |
Normal blood (SERS) Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| No |
440 |
C-C-N bending |
L-Arginine |
| No |
521 |
S-S disulfide stretching in Proteins |
Cholesterol ester |
| No |
637 |
C-C-N bending |
Tyrosine |
| No |
743 |
C–H bending |
Coenzyme A |
| No |
797 |
Ring vibrations |
L-Serine |
| No |
975 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Phenylalanine |
| 1015 |
1030 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| No |
1154 |
CH3 rocking, C-O vibrations |
D-mannos |
| 1182 |
1198 |
C-C stretching |
L-tryptophan |
| 1233 |
1252 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
| 1348 |
1366 |
CH3 symmetric stretching |
Heme |
| 1405 |
1426 |
C==N antisymmetric streching |
Heme |
| 1441 |
1451 |
CH2 bending |
Acetates |
| 1596 |
1592 |
C==N antisymmetric stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1613 |
1607 |
C-H bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 1651 |
1648 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
Table 6.
Major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts.
Table 6.
Major Raman shifts in the normal and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of abnormal blood without coagulant and the components corresponding to these shifts.
| Abnormal blood Raman shift (cm-1) |
Abnormal blood (SERS) Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| No |
489 |
C-C-N bending |
L-Arginine |
| No |
556 |
S-S disulfide stretching in Proteins |
Cholesterol ester |
| No |
674 |
C-C-N bending |
Tyrosine |
| No |
792 |
Ring vibrations |
L-Serine |
| 1011 |
1004 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Phenylalanine |
| 1142 |
1158 |
CH3 rocking, C-O vibrations |
Lactate |
| 1185 |
1179 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1318 |
1312 |
CH3CH2 twisting |
Collagen |
| 1384 |
1382 |
C-C stretching |
L-tryptophan |
| 1648 |
1644 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
| No |
1814 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| No |
1922 |
Ring vibrations |
Hemoglobin |
Table 7.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for whole blood.
Table 7.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for whole blood.
| Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| 694 |
C-C-N bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 770 |
Ring vibrations |
Tryptophan |
| 1018 |
Aromatic ring breathing |
Hemoglobin |
| 1189 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1239 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
| 1321 |
C-C stretching |
Hemoglobin |
| 1354 |
C-H bending |
Tryptophan |
| 1384 |
CH3 symmetric stretch |
Heme |
| 1410 |
C==N antisymmetric streching |
Heme |
| 1443 |
CH2 bending |
Acetates |
| 1599 |
C-H bending |
Hemoglobin |
| 1653 |
Ferrous low spin |
Hemoglobin |
Table 8.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for plasma.
Table 8.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for plasma.
| Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| 1016 |
C-H bending |
β-Carotene |
| 1164 |
C-C stretching |
β-Carotene |
| 1526 |
C-C stretching |
β-Carotene |
Table 9.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for serum [
28].
Table 9.
Major Raman shifts and corresponding components for serum [
28].
| Raman shift (cm-1) |
Vibrational blood mode |
Component |
| 1013 |
C-H bending |
β-Carotene |
| 1172 |
C-C stretching |
β-Carotene |
| 1526 |
C-C stretching |
β-Carotene |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).