1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is among the most prevalent neurodegenerative diseases in the world. The risk of developing this condition increases in tandem with the patient’s chronological age. Alzheimer’s disease may be the underlying cause of dementia in about 6 million people in the US where most of them are of more than 65 years age group. This disease is now the sixth biggest cause of death in the US [
1]. The other causes of AD include genetic, behavioural, and environmental factors that gradually impact the brain [
2]. As Alzheimer’s disease is incurable, and early detection of this disease can be extremely beneficial. A variety of cognitive and behavioural tests are used to diagnose this disease. However, MRI images of the brain can provide important information for diagnosing this condition [
3] since Alzheimer’s disease affects a wide variety of cells and different parts of our brain, and MRI images reveal changes in the region’s structure or pattern. For this reason, researchers are now trying to develop a robust and efficient approach to analyze MRI images to detect AD through machines. They have proposed a wide range of models based on deep learning (DL), machine learning (ML), and hybrid methods. These ML and DL models need a lot of image data to train and also require high computation cost[
4]. If the dataset is not large enough, then the model may be biased towards a single class and the robustness of the models could not be provided. But, collecting data from the healthcare sector is usually challenging due to the sensitive nature of the data. The patients are also remain hesitant to share their medical information [
5]. Therefore, a secure method to train the deep learning models without collecting data has become a necessity to ensure confidentiality and integrity of medical data.
McMahan et al. [
6] proposed Federated Learning (FL) method that ensures the confidentiality and security of user data. This method involves training the model on the local server and then sending the weights of the trained model to the global server. This allowed the global server to update its weight without knowing anything about the user data. In this case, the user doesn’t need to provide any personal details to the server. As a result, the user’s privacy is secured. Using this strategy additionally guarantees that user data will not be compromised under any circumstances. In this study, a federated learning-based AD detection approach employing a pre-trained MobileNet transfer learning architecture was proposed which is robust, efficient, and privacy preserving.
MobileNet [
7] is a compact and simple model that takes less time to train, and capable of providing significant performance. In this research, MobileNet is trained in a federated way to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease from brain MRI images. In this study, we have used two distinct datasets, namely ADNI and OASIS. There are different planes of brain MRI images available in both of these datasets, and the proposed model used coronal plane images after a orientation selection procedure. For ensuring the robustness of the model, different experiments were conducted by utilizing ADNI and OASIS datasets. They were trained and tested individually, then tested on the all of the test sets of ADNI and OASIS in each of the cases. Also, these datasets were combined and named as merged set. This merged set was used in this study to explore the robustness of the model further. In the federated learning approach, each of these training processes on different datasets is performed solely on a different local server. After that, the weights of each of these trained models are forwarded to the main or central server. The global model was then took the average weights of both of the trained models. Here, the user data need not to be shared to the researchers, and the user’s privacy and data confidentiality are preserved. In addition to this, the proposed FL-based model achieved higher levels of accuracy and sensitivity than the usual approach. This further enhances the acceptability of the proposed model.
The following contributions are made in this paper.
An appropriate model and MRI image orientation selection was performed.
A federated approach was proposed to train the model. The proposed approach was found to be better performing and more privacy-preserving.
The proposed approach was validated against multiple datasets, and multiple test cases which ensures the robustness and consistency of the proposed approach.
The rest of this work is organized as follows. In
Section 2, the existing works in Alzheimers’ disease detection have been discussed.
Section 3 explains the methodology, and the results are discussed in
Section 4. Finally, in
Section 5, we have discussed the limitations of the study and provided concluding remarks and future goals.
2. Literature Review
There are many Alzheimer’s disease detection methods developed so far. Most of the techniques are implemented with ML or DL-based approaches. These approaches are extremely effective in other domain as well such as, COVID-19 chest X-ray classification [
8], brain tumor classification [
9], image quality identification from ultrasound [
10], and recognition of human activities [
11], and so on. By combining shearlet-based descriptors with deep features, Alinsaif et al. [
12] suggested a technique for the representation of characteristics that might be used for the categorization of AD. Their model can be broken down into two distinct stages. In the first place, they preprocessed the MRI images and then extracted features from them. They utilized the SVM and DTB algorithms for the classification purpose. Puente-Castro et al. [
13] developed a hybrid model for the classification of AD. They used the sagittal plane of the brain MRI images in this study. After collecting the dataset, they applied the ResNet model, extracting the features and then integrating age and sex features with them. Then, these extracted features were classified using the SVM classifier. Chui et al. [
14] proposed a three-layered model called GAN-CNN-TL. In this particular investigation, they used all three available variants of the OASIS dataset. They employed GAN to generate synthetic data. Then, feature extraction from these images was done using CNN. After that, they applied transfer learning to the classification of the images.
Folego et al. [
15] developed two different models called ADNet and ADNet-DA using 3D CNN. Here, they first preprocessed the MRI images by extracting the skull and also normalizing the images. After that, they employed 3D-CNN in these processed images for extracting features and classifying them. They used four different pre-trained architectures here. Furthermore, they employed the domain adaptation method to evaluate the robustness of their model which was evaluated against various test sets. Liu et al. [
16] suggested using a depthwise separable convolutional-based model as an alternative to the conventional CNN model in order to make the model and its parameters more simple. They implemented CNN and DSC for the purpose of AD detection. In the DSC’s convolution layer, filtering and feature extraction are kept independent from one another. Because of the potential for overfitting or underfitting with a smaller data set, they additionally relied on AlexNet and GoogleNet pre-trained models for categorization. An et al. [
17] suggested an deep ensemble learning approach for classifying AD. Their dataset includes seven distinct feature categories. A total of three layers—a voting layer, a stacking layer, and an optimizing layer—make up their model. Their proposed approach performed better considering the other ensemble approach.
By combining 3D CNN with 3D CLSTM, Xia et al. [
18] were able to develop a unique model. Its model could only do simple categorization tasks. They employed 12 layers in total (6 convolution layers, 6 max polling layers) in their CNN model. On the other hand, their CLSTM model was made up of three separate gates. This CLSTM helps improve feature extraction from images. The model’s overfitting problems were fixed by employing data augmentation techniques to make the images larger. Using Grad-cam, they also annotated the MRI images to show the area impacted by AD. Wei et al. [
19] applied an adaptive histogram technique for increasing the contrast of the images. In this study, features were selected from these images using the t-test. They employed SVM and RF for the classification of AD images.
Lin et al. [
20] proposed an Voting ensemble learning-based classification model consisting of discriminator GAN, VGG16, and ResNet50. Later, they also performed a domain adaptation task to check the robustness of the model. Kaplan et al. [
21] presented a new feed-forward method called LPQNet to reduce computational complexity with higher performance. They used a newly collected dataset in this work which contains 1070 subjects to train the model. Bringas et al. [
22] used mobility data for the detection of AD. For this purpose, they collected data from 35 patients and identified them using the CNN model. Murugan et al. [
23] developed a framework called DEMNET. This framework performed a multiclass classifier with an accuracy of 95.23%. Furthermore, they applied SMOTE to reduce the class imbalance problem. Lodha et al. [
24] proposed an ML-based model for AD classification. They illustrated a comparison among different algorithms in that study. Li et al. [
25] also proposed a hybrid model using the CNN and RNN architectures. They used DenseNet as the CNN and BGRU as the RNN model. In this hybrid model, they evaluated the hippocampus structure and classified AD.
Basheera et al. [
26] suggested a skull stripping technique in the preprocessing stages for eliminating unnecessary tissues. They also applied the HEICA method for collecting segmented grey matter from MRI images. Bi et al. [
27] developed a CAD system for AD detection using an unsupervised method. This method first extracted features from the images using a model called PCANet which is built using the CNN model. After that, K-Means clustering was performed for grouping these features as AD or normal images. Jabason et al. [
28] implemented an ensemble model for identifying different stages of AD. They first trained the hybrid CNN model separately for learning features from the images. After that, the Voting Classifier was employed for classification purposes. Helaly et al. [
29] implemented a 2D and 3D based model for AD classification. They used a CNN model for this purpose. Image preprcessing, re-sampling , data augmentation etc were also performed in their study. Venugopalan et al. [
30] proposed a multimodal DL methods to detect AD stages. They used 3DCNN for extracting features from different modalities of clinical and image data. They showed that, shallow ML algorithms are less accurate than their proposed model. They also found that integrating multimodal data enhances the performance of the proposed approach.
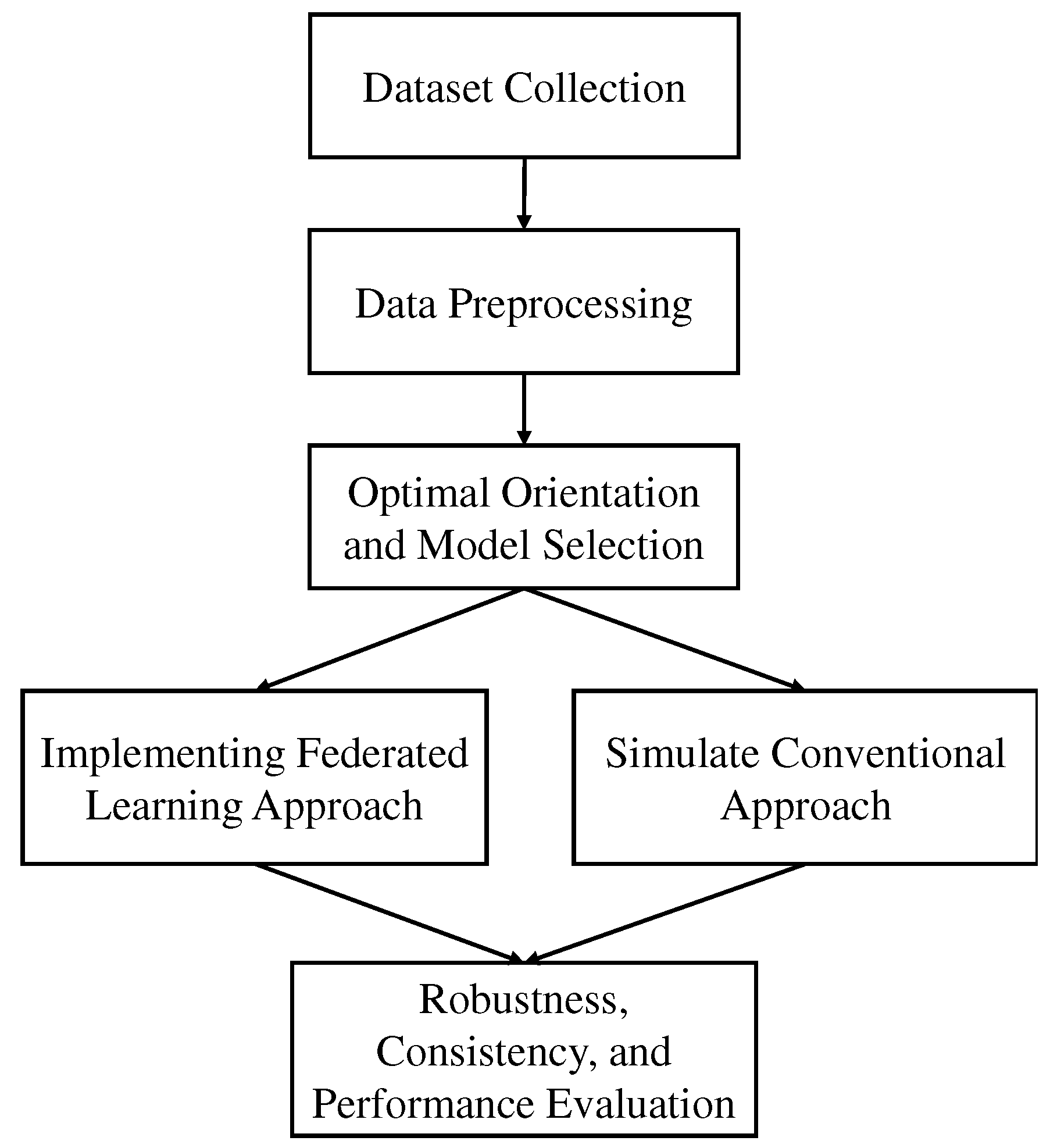
3. Methodology
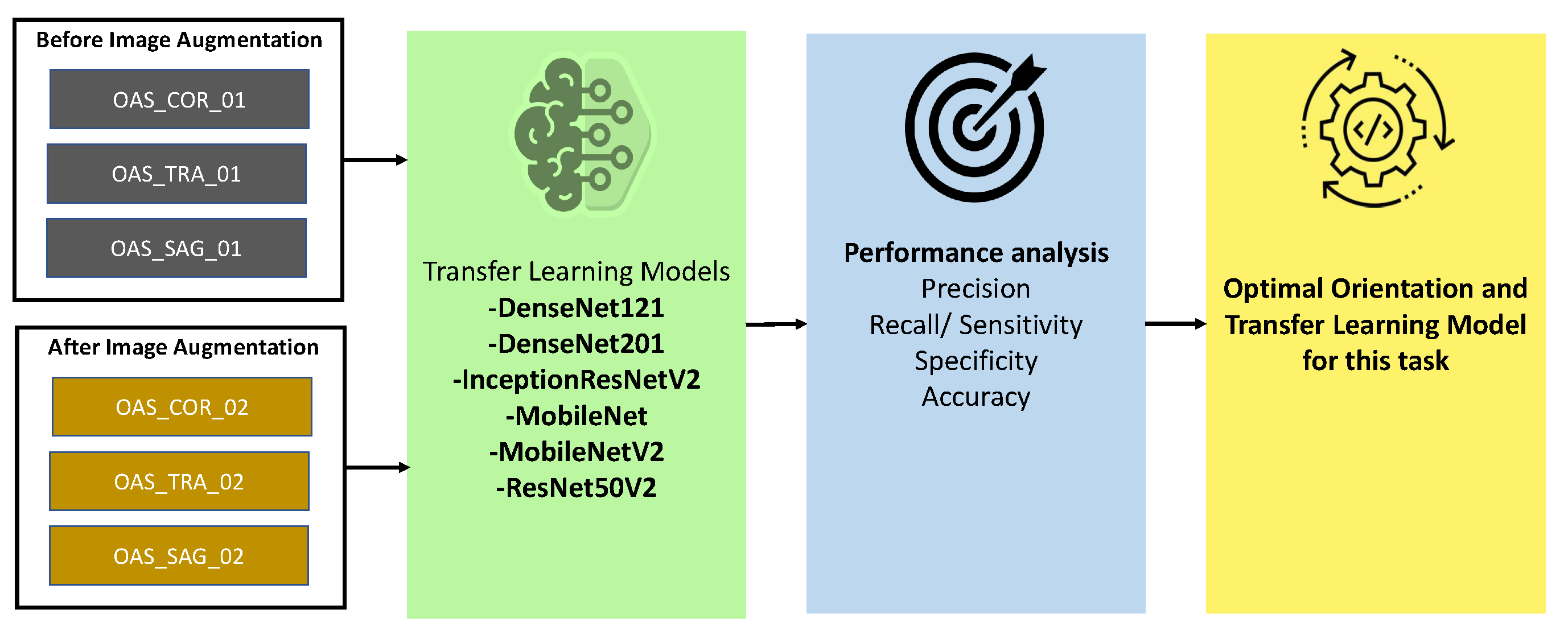
In this paper, we have tried to find out the efficacy of the federated approach in Alzheimer’s’ disease detection. For this, we have collected two datasets (ADNI and OASIS), which are available publicly. MRI images can be explored in different orientations, as they are in 3D form. Hence, we tried to find out an appropriate orientation from which our state-of-the-art transfer learning architectures can learn the patterns, and produce significant accuracy. For this reason, we have evaluated 3 different orientations of MRI images of OASIS dataset (with augmentation and without augmentation). We have trained and tested them with 6 different transfer learning architectures from which we selected the optimal orientation and model.
Figure 1 illustrates the overall workflow diagram of this study.
After the orientation and model selection procedure, a federated approach was implemented by performing multi-threading. Another dataset, ADNI, was utilized in this part to verify the robustness of the federated approach compared to the conventional approach. The whole process will be described in detail in the methodology section.
3.1. Dataset
Alzheimer’s disease can be detected in many ways, such as, brain MRI, PET scan images, neurological evaluations, and so on. In this study, we have used two different brain MRI images dataset: ADNI and OASIS. Further, these datasets are divided into many subsets including augmented sets, merged sets etc.
Figure 3 describes the overall structure of the datasets. Various orientations of MRI images are depicted in
Figure 2.
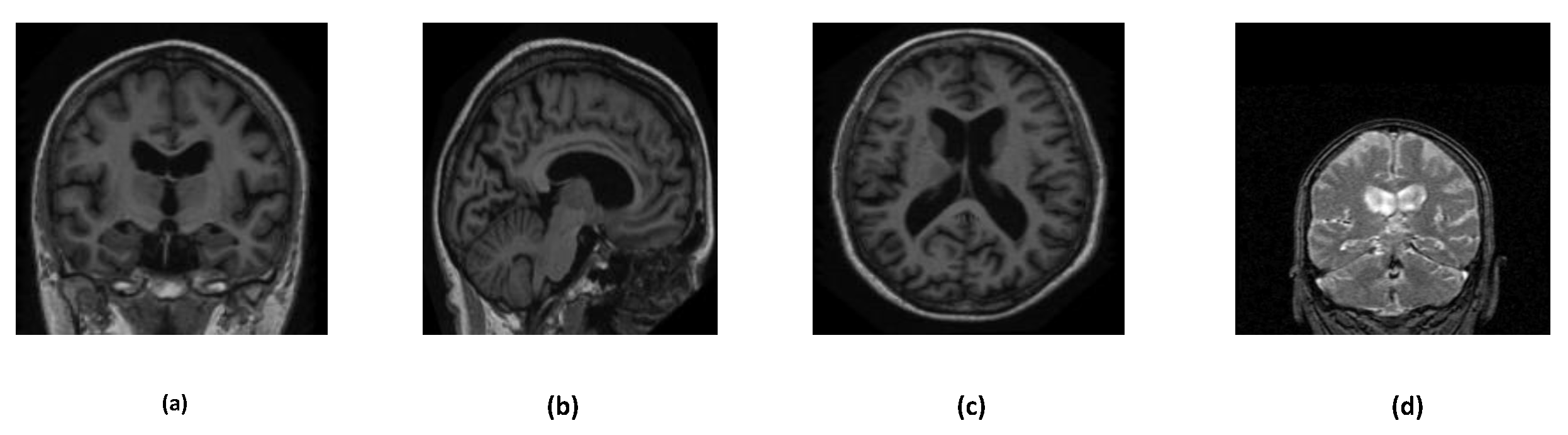
Figure 2.
Different orientations of the OASIS and ADNI dataset MRI images. (a) Coronal Plane (OASIS dataset) (b) Sagittal Plane (OASIS dataset) (c) Transverse Plane (OASIS dataset) (d) Coronal Plane (ADNI dataset)
Figure 2.
Different orientations of the OASIS and ADNI dataset MRI images. (a) Coronal Plane (OASIS dataset) (b) Sagittal Plane (OASIS dataset) (c) Transverse Plane (OASIS dataset) (d) Coronal Plane (ADNI dataset)
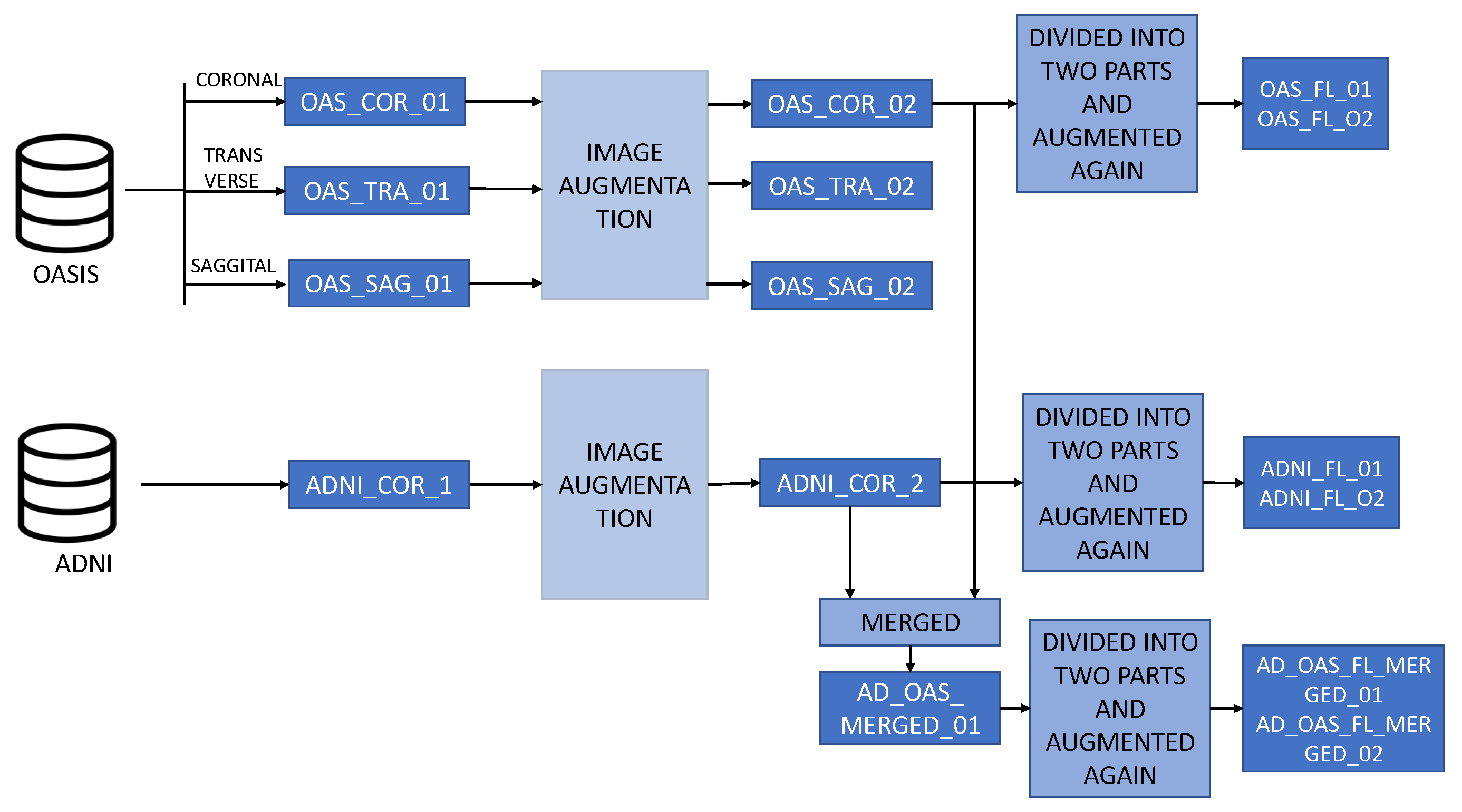
Figure 3.
Descriptions of the datasets used in this study. Three different planes of the OASIS dataset are used here which are coronal, sagittal and transverse. Only the coronal plane of the ADNI dataset is used here. These images were further augmented and then merged also. Then these images were divided into two parts and constructed datasets for the federated learning approach.
Figure 3.
Descriptions of the datasets used in this study. Three different planes of the OASIS dataset are used here which are coronal, sagittal and transverse. Only the coronal plane of the ADNI dataset is used here. These images were further augmented and then merged also. Then these images were divided into two parts and constructed datasets for the federated learning approach.
3.1.1. OASIS Dataset
The purpose of the Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS) [
31] is to make high-quality brain neuroimaging datasets available to the scientific community. By putting together neuroimaging datasets and making them available for free, they hope to speed up future scientific and clinical advances in neuroscience. For neurological, clinical, and cognitive investigations on ordinary aging and cognitive impairment, these data are widely available and assessed across a broad range of people, including neurological and genetic ranges. In this study, a total of 436 images were used of which 98 image was AD positive and 338 was normal MRI images, which were available in 3 orientations: Coronal, Sagittal, and Transverse. These images were classified into four classes: Mild demented, Very mild demented, Moderate Demented, and Cognitive Normal. As the number of images were not significant enough in all the classes, we have considered it as a binary classification problem. Therefore, Mild Demented, Very Mild Demented, and Moderated Demented classes of OASIS-1 dataset were considered as AD positive (labelled as 1), and Non Demented class has been considered as AD negative and it has been labelled as 0.
3.1.2. ADNI dataset
The findings of studies conducted by the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) [
32] can be of significant use in clinical research pertaining to the diagnosis, prevention, and management of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). It seeks biomarkers and enables precise diagnosis and tracking of AD by using its open-source data sets. ADNI has proven very beneficial for long-term MRI and PET scans of elderly patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, and other illnesses. The ADNI research started in 2004, and so far it has completed four phases. A total of 457 images were collected from their reponsitory in this study, where 136 images were of normal images and 321 images were of AD-positive class.
3.1.3. Augmentation Procedure
Data augmentation is used to increase the number of images. Deep learning-based models perform well on a huge amount of data. If the amount of data is very small, then the model can be biased and may not be able to find patter from the features of the images properly. But, collecting medical images is often a very difficult task as most hospitals do not want to share this data. In this case, data augmentation can be handy to overcome these issues. Therefore, we have performed conventional data augmentation techniques in this study for both the ADNI and OASIS datasets. These techniques include image flipping, rotation, zooming, contrast enhancement, etc. We only augmented the training dataset images for each dataset. However, testing set was kept as same as the original dataset.
3.1.4. Merging Procedure
To evaluate the performance of the models, we merged the ADNI and the OASIS datasets. In the training set of this dataset, all the training images from ADNI and OASIS are merged. On the other hand, the testing set consists of the images of the ADNI and OASIS test sets.
3.1.5. Dataset Splitting
Table 1 describes the training and testing sets used in Conventional training procedures, while
Table 2 provides the training sets used in the training of the proposed model in the federated way. Some of these datasets contain augmented images, and some of the training sets were built by combining both ADNI and OASIS datasets.
OAS_COR_01, OAS_SAG_01, OAS_TRA_01: These datasets contain a total of 436 images, all of which belong to the OASIS dataset. The training set contains a total of 352 images, and the testing set contains 84 images. In this dataset, the images are not merged and augmented. The highest number of images are from the normal class. Here, COR stands for Coronal, TRA stands for Transverse, and SAG denotes the Sagittal plane of the MRI image.
OAS_COR_02, OAS_SAG_02, OAS_TRA_02: Each of these datasets contains 2500 images. These images are augmented from the OASIS dataset. The training set contains a total of 2416 images, and the testing set remains the same as the non-augmented dataset, which has 84 images. Here, COR stands for Coronal, TRA stands for Transverse, and SAG denotes the Sagittal plane of the MRI image.
ADNI_COR_01: The ADNI_COR_01 dataset contains a total of 457 images. All the images in this dataset were collected from the ADNI dataset. Here, the training set contains 385 images and the testing set contains 72 images. The majority of the images represent the normal classes.
ADNI_COR_02: The ADNI_COR_02 dataset consists of 2756 images. These images are augmented from the ADNI dataset. After augmentation, the training set contained a total of 2648 images, of which 1453 represent the normal class and 1195 represent the AD class. On the other hand, the testing set contains 72 images.
AD_OAS_MERGED_01: This is a merged dataset that merges the ADNI and OASIS datasets together. All the training and testing images of ADNI and OASIS were merged for training and testing purposes. Here, the training set contains 5064 images and the testing set contains 156 images.
ADNI_FL_01, ADNI_FL_02: These datasets contain 1962 and 1961 images in each local client training set. These images are divided from the augmented ADNI dataset, and the number of images was increased by performing augmentation again. In the test set, both the local client have 35 test images.
OAS_FL_01, OAS_FL_02: These datasets were derived from the augmented OASIS dataset. Each local client contains 2153 images in the training set and 32 images in the local testing set.
AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_01, AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_02: This dataset is found after merging the ADNI and OASIS datasets. After merging and splitting the dataset, the two local clients contain 4115 and 4114 images in the training set after performing another layer of augmentation. On the other hand, in the local test set, each dataset contained 67 images.
LOCAL_AD_OAS_FL_01: This dataset consists of two different datasets for two local clients. Local client 1 consists of the ADNI dataset in the training and testing set, and local client 2 consists of the OASIS dataset. There are a total of 3923 images in the first local client training set and 4306 images in the second local client training set.
Table 1.
Training and testing sets used for training in conventional approach
Table 1.
Training and testing sets used for training in conventional approach
| Dataset Code |
Dataset |
Merged (Yes/No) |
Augmented (Yes/No) |
Train Image |
Test Image |
| Total |
1 |
0 |
Total |
1 |
0 |
| OAS_COR_01 |
OASIS |
No |
No |
352 |
80 |
272 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| OASIS_TRA_01 |
OASIS |
No |
No |
352 |
80 |
272 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| OASIS_SAG_01 |
OASIS |
No |
No |
352 |
80 |
272 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| OAS_COR_02 |
OASIS |
No |
Yes |
2416 |
1187 |
1229 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| OASIS_TRA_02 |
OASIS |
No |
Yes |
2416 |
1187 |
1229 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| OASIS_SAG_02 |
OASIS |
No |
Yes |
2416 |
1187 |
1229 |
84 |
18 |
66 |
| ADNI_COR_01 |
ADNI |
No |
No |
385 |
112 |
273 |
72 |
24 |
48 |
| ADNI_COR_02 |
ADNI |
No |
Yes |
2648 |
1195 |
1453 |
72 |
24 |
48 |
| AD_OAS_MERGED_01 |
ADNI + OASIS |
Yes |
Yes |
5064 |
2382 |
2682 |
156 |
42 |
114 |
Table 2.
Training and testing sets used for training in federated approach
Table 2.
Training and testing sets used for training in federated approach
| Dataset Code |
Dataset |
Merged (Yes/No) |
Augmented (Yes/No) |
Train Image Local Machine |
Test Image Local Machine |
| Total |
1 |
0 |
Total |
1 |
0 |
| ADNI_FL_01 |
ADNI |
No |
Yes |
1962 |
948 |
1014 |
35 |
10 |
25 |
| ADNI_FL_02 |
ADNI |
No |
Yes |
1961 |
948 |
1013 |
35 |
10 |
25 |
| OAS_FL_01 |
OASIS |
No |
Yes |
2153 |
1035 |
1118 |
32 |
8 |
24 |
| OAS_FL_02 |
OASIS |
No |
Yes |
2153 |
1035 |
1118 |
32 |
8 |
24 |
| AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_01 |
ADNI + OASIS |
Yes |
Yes |
4115 |
1983 |
2132 |
67 |
18 |
49 |
| AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_02 |
ADNI + OASIS |
Yes |
Yes |
4114 |
1983 |
2131 |
67 |
18 |
49 |
3.2. Orientation and Model Section
To select an optimal plane from 3 planes (Sagittal, Coronal, Transverse), we have trained and tested 6 different pretrained CNN models (DenseNet121[
33], DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2 [
34], MobileNet, MobileNetV2, and ResNet50V2) with the non augmented (OASIS_COR_01, OASIS_SAG_01, OASIS_TRA_01) and augmented (OASIS_COR_02, OASIS_SAG_02, OASIS_TRA_02) OASIS datasets. In almost all of the cases, models performed better in the Coronal plane. Again, among these transfer learning models, MobileNet was found as better performing in most of the cases. Detail performance analysis has been provided in
Section 4. Based on the findings of this analysis, we have selected MobileNet as optimal model, and Coronal as optimal plane. Therefore, MobileNet and Coronal plane has been used for further analysis in this study.
Figure 4 has described the procedure for selecting the best orientation and transfer learning model.
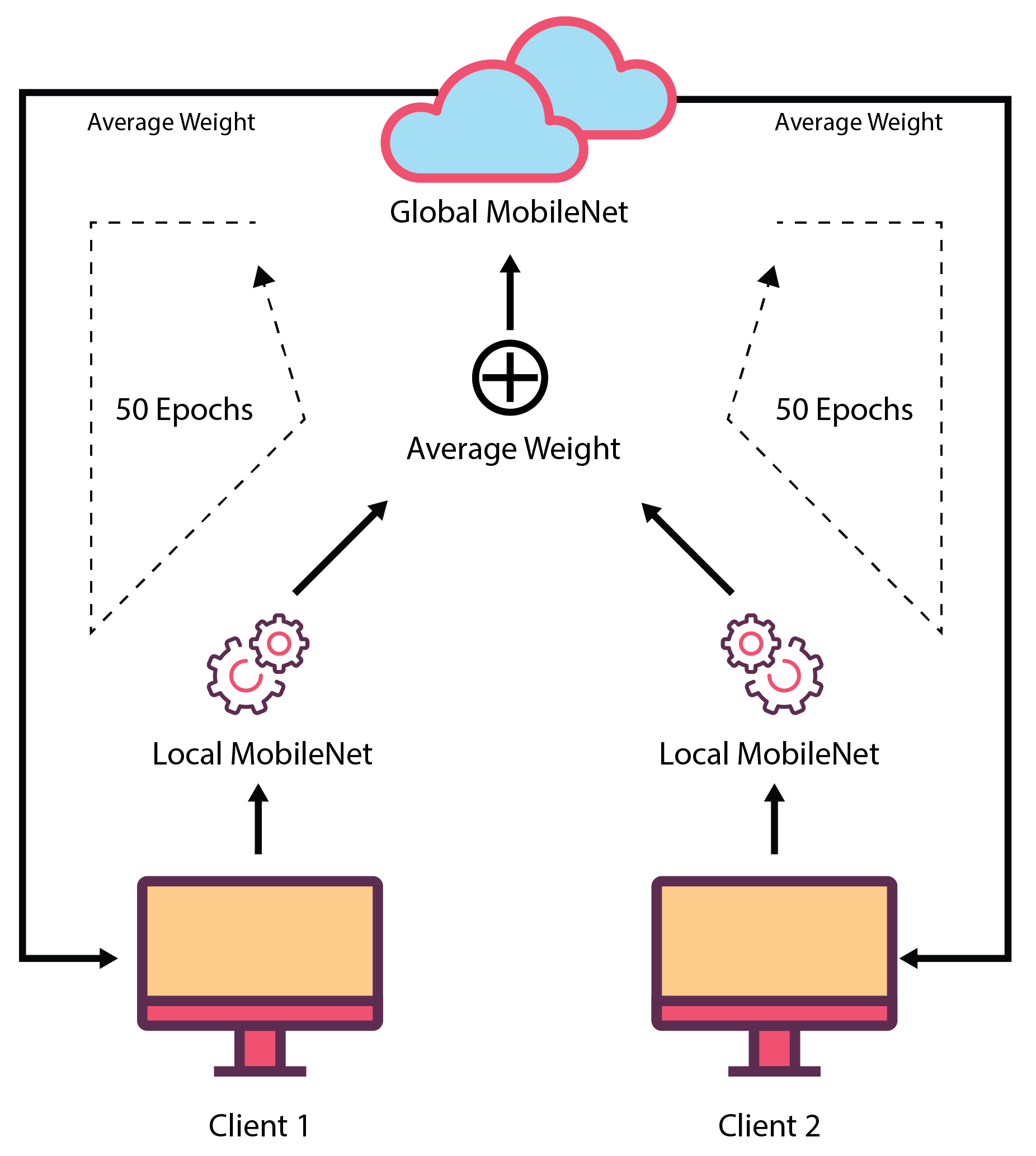
3.3. Proposed Federated Learning Framework
In our study, we have proposed to train deep learning models in federated way. Therefore, MobileNet has been trained in federated way to evaluate the performance. The MobileNet architecture is very fast and efficient for image processing-related tasks. We’ve used the MobileNet’s initial weights which was gained from training on ImageNet database. We only changed the last layer (dense layer) of the MobileNet architecture. This dense layer has two neurons and a sigmoid as an activation function. These two neurons indicate AD or normal images.
In this proposed FL-based model, two local clients were involved in its development. These two clients have different datasets for training and validation purposes. These datasets can be varied, or two local clients can use the same dataset. Both clients used the same MobileNet model. While training the models, these two local clients ran in parallel, and they sent their model’s weights for each epoch to the central server. Before transferring the weights to the global server, the local clients validated their model using the local validation dataset that evaluated the local client’s performance. In the central server, an average of both of the local client’s weights were taken, and it was considered as the weight of the global MobileNet model. Then, the global MobileNet containing this weight, was used to test the global testset which provided the global validation performance. After that, the global MobileNet weights were sent to each of the local clients for validation using their validation set. This whole set of actions were performed for 50 epochs, and after that, the found global MobileNet model was evaluated using different testing sets. In the global server, only weights of the locally trained model were available, but no local training data was available there. This ensures data security as well as confidentiality. Here, local clients do not need to share their private data as they just transfer the weights of the model. As a result, the possibility of data breaching is reduced.
Figure 5 depicts the federated learning procedure.
For example, when the MobileNet was trained in federated way using the OASIS dataset, two local machines were trained with OAS_FL_01 and OAS_FL_02 training sets, and their corresponding test set was used as a local test. After each epoch, the weights were adjusted. The final model was tested using a global test set which was the same as the conventional approach.
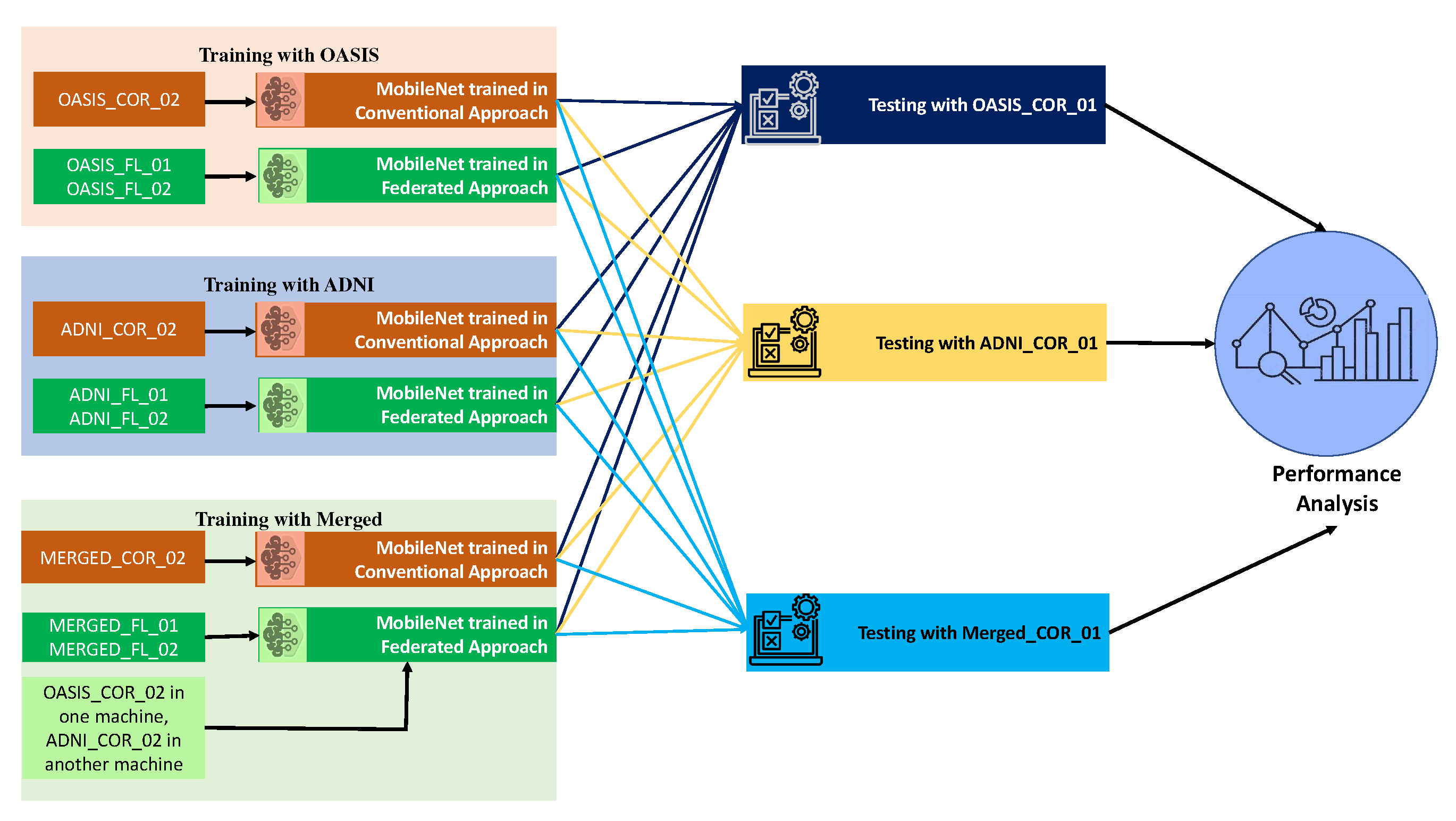
3.4. Evaluating the robustness of the current approach
We have conducted a number of tests using a variety of datasets in order to assess the robustness of our model as well as the conventional appraoch. The models were trained using the OASIS dataset, and then they were tested using the ADNI dataset, as well as vice versa. After that, we combined the datasets that had been trained, and after that, we tested them using the OASIS and ADNI datasets. Additionally, the ADNI and OASIS-trained models were utilized in an effort to validate this combined dataset. Further testing was performed on the merged dataset using the merged testing dataset. The experimental results help to evaluate the robustness of the models as well the efficacy of the federated apparoch compared to conventional appraoch.
Figure 6 shows the procedures for checking the robustness and performance of the models trained in conventional and federated appraoch.
4. Result Analysis
In this paper, our aim was to analyze the efficiency of the federated approach in detecting Alzheimer’s disease. For this, we needed to find out an optimal model and orientation of MRI images at first. Therefore, we have picked the OASIS dataset and trained the existing state-of-the-art transfer learning approaches such as MobileNet, MobileNeV2, ResNet50V2, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet121, and DenseNet201. To find out the best orientation of MRI images, we have tried out 3 different orientations that were already prepared in the OASIS-1 dataset (Coronal, Sagittal, and Transverse). As the number of images in the training images were not large enough, we enhanced the training set by doing augmentation, that largely increased the performance.
After selecting the optimal model and orientation, we tried to evaluate the robustness of the conventional training approach by using two different datasets (OASIS and ADNI). For this, we trained the optimal model with OASIS in both conventional and federated approaches, and tested with ADNI, OASIS, and Merged test sets. We also evaluated the performance of the effective deep learning architectures, by training with OASIS and merged training sets, and testing with all three test sets. In this section, all the performances has been analyzed in detail.
4.1. Selecting the Optimal Model and Orientation
At first, we trained the MobileNet, MobileNeV2, ResNet50V2, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet121, and DenseNet201 models with OASIS dataset which contained 352 images for training, and 84 images for testing (OAS_COR_01, OASIS_TRA_01, OASIS_SAG_01). These images were available in all three orientations (Coronal, Sagittal, and Transverse).
Table 3 provides a detailed comparison of the performance of the transfer learning architectures in all three orientations. In the case of the Coronal plane, MobileNet performed the best in the case of sensitivity, F1-score and accuracy (92%, 87%, and 90% respectively). Other models achieved accuracy in the range of 86%-89% with much lower sensitivity which is crucial in AD detection. DenseNet201 performed the worst among these models. In the case of the Transverse plane, the highest accuracy was 89% which was achieved by ResNet50V2. All the other models performed in the range of 81-85% which is much lower than the average performance of the Coronal Plane. In the case of the Sagittal plane, the highest accuracy was 86% by MobileNet with only 75% accuracy which is much lower than the performance achieved by MobileNet in Coronal Plane (90%). Therefore, it is evident that all the models performed well in Coronal Plane, and MobileNet provided the best performance.
As number of images in the training set was not large enough to train these deep learning architectures, we performed augmentation on the training set only (2416 total images, 1187 images labelled as AD MRI, 1229 as non AD MRI). The testing set was the same as before (18 images labelled as AD MRI, 66 as non-AD MRI (84 in total), OAS_COR_02, OASIS_TRA_02, OASIS_SAG_02 as per mentioned in section 3.1.
Table 4 provides the performance of the transfer learning architectures after image augmentation. In the case of the Coronal plane, MobileNet’s accuracy jumped to 92% from 90% after augmentation. ResNet50V2’s accuracy was increased to 92% after augmentation. In the case of the Transverse Plane, the highest accuracy was 86% by MobileNet after augmentation. MobileNet achieved the highest accuracy (85%) in the Sagittal plane. Considering the performance of all the models, the optimal model was MobileNet in this case, and all of the models performed better in the case of the Coronal plane compared to the Transverse and Sagittal plane.
Considering the performances of the transfer learning approaches before and after augmentation in various planes, it is observed that MobileNet performed the best in most of the cases, and models performed the best in the Coronal plane. Hence, we considered MobileNet as the optimal model and the Coronal plane as the selected orientation in this paper.
4.2. Training with OASIS, testing with ADNI, OASIS, Merged Dataset
From
Section 4.1, it is evident that MobileNet was the go-to model, and the Coronal plane was the selected orientation of MRI images. Now, we tried to compare the performance of the proposed federated approach with the conventional approach.
4.2.1. Conventional Approach
To check the robustness of the MobileNet in Alzheimer’s’ disease detection, at first, we trained the MobileNet model with an augmented OASIS training set (OAS_COR_02_train), and tested with ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), and merged test set (AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test) in conventional approach.
Table 5 provides the performance of the Conventional and federated approach while the models were trained with the OASIS dataset. Here, in this approach, MobileNet achieved 91.67% accuracy and 66.67% sensitivity in the OASIS test set, 65.28% accuracy and 12.50% sensitivity in the ADNI test set, and 76.92% accuracy and 28.50% sensitivity in the merged test set. In all the cases, there is a huge difference between sensitivity and specificity, which states that, models were not well generalized after training in the conventional approach.
Table 5 provides the performance between the conventional approach and the federated approach.
4.2.2. Federated Approach
To evaluate the performance of the model trained in federated approach, we trained two MobileNet models with OAS_FL_01_Local1 and OAS_FL_01_Local2 training sets in local machines, finally got the trained MobileNet model with optimal weight. This model was tested using ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), and merged test set (AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test), which was the same as conventional approach. MobileNet acquired 92.86% accuracy and 94.44% sensitivity while testing with the OASIS test set, 77.78% accuracy and 75.00% sensitivity in the ADNI test set, and 83.33% accuracy and 69.05% sensitivity in the merged test set. In all of the cases, the federated approach acquired better accuracy and sensitivity and showed better generalization capability. In this approach, the model was more capable of distinguishing between two classes compared to the conventional training procedure which can be clearly seen in
Table 5.
4.3. Training with ADNI, testing with ADNI, OASIS, and Merged Dataset
4.3.1. Conventional Approach
Here, MobileNet was trained with ADNI_COR_02_training set, and tested with ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), and merged testset
(AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test).
Table 6 provides the performance of the conventional and federated approaches while the models were trained with the ADNI dataset. MobileNet achieved 78.57% accuracy and 55.56% sensitivity in the OASIS test set, 75% accuracy and 75% sensitivity in the ADNI test set, and 75% accuracy and 66.67% sensitivity in the merged test set.
Table 5 compares the performance between the conventional approach and the federated approach.
4.3.2. Federated Approach
To evaluate the performance of the federated approach, we trained two local MobileNet models with ADNI_FL_01_Local1 and ADNI_FL_01_Local2 training sets, where we used ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), and merged test set (AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test) to test the performance of the global MobileNet model. MobileNet acquired 78.57% accuracy while testing with the OASIS test set, 81.94% in the ADNI test set, and 77.56% accuracy in the Merged test set. In the case of sensitivity, the performance was not up to the mark. But, the federated approach performed better than the conventional approach in the case of accuracy (see
Table 6).
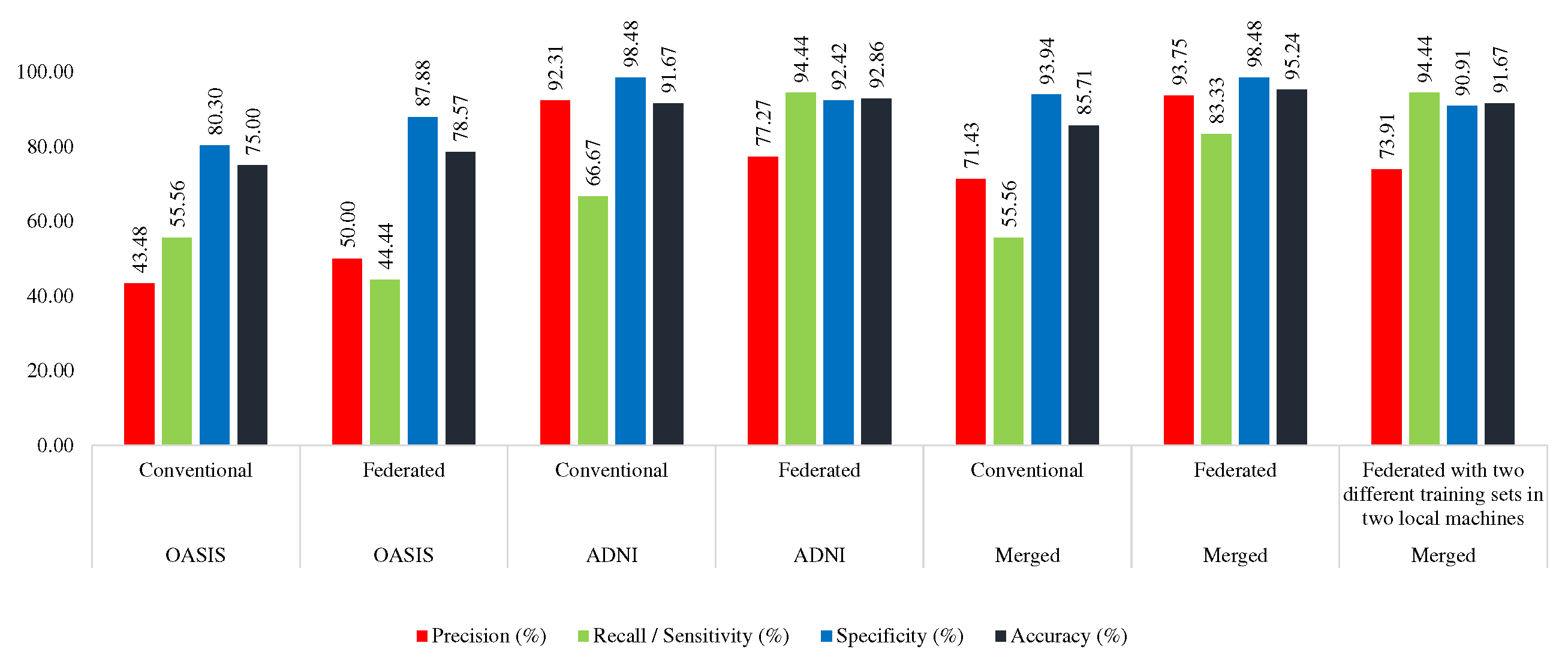
4.4. Training with Merged, testing with ADNI, OASIS, Merged Dataset
4.4.1. Conventional Approach
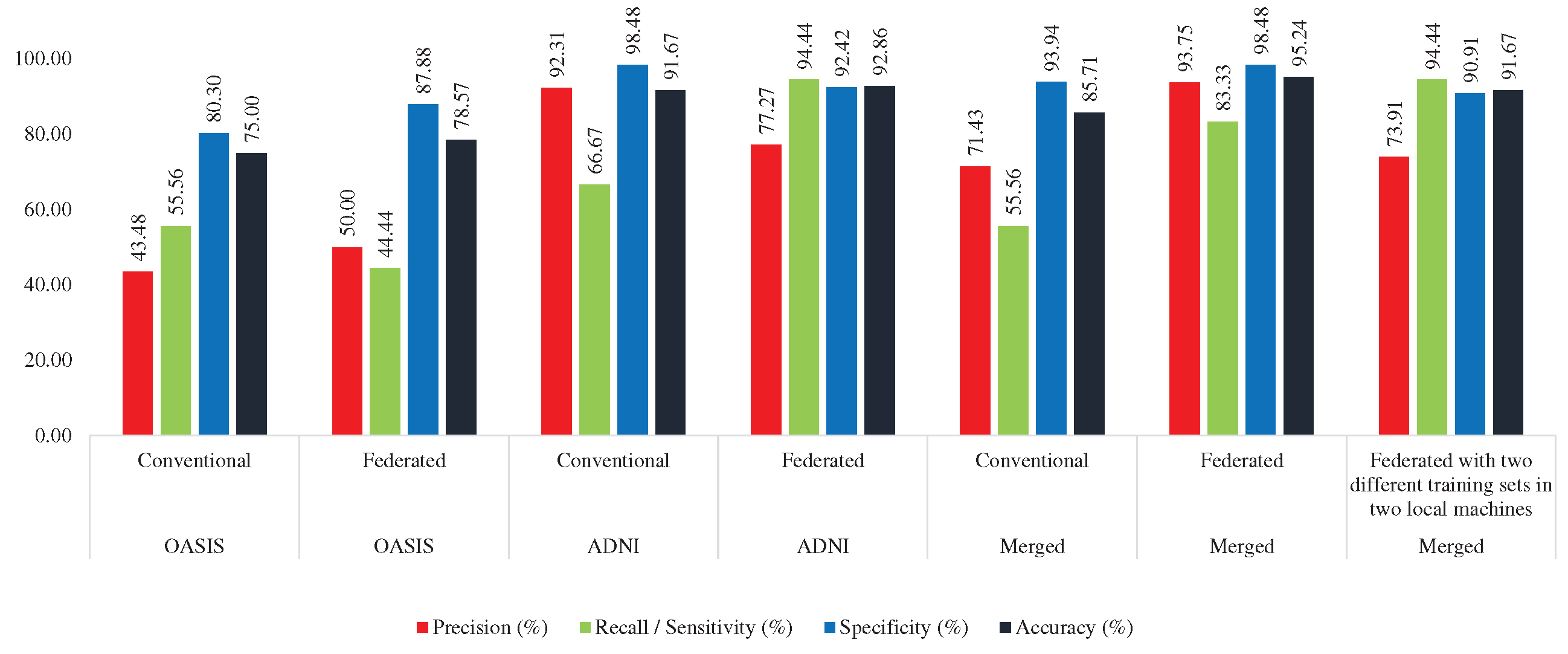
Here, the MobileNet was trained with AD_OAS_MERGED_01_train set, and tested with OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), and
merged (AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test) test set. In this case, the MobileNet acquired 85.71% accuracy and 55.76% sensitivity in the OASIS test set, 70.83% accuracy and 62.50% sensitivity in the ADNI test set, and 78.85% accuracy and 64.29% sensitivity using the merged test set.
Table 7 shows the performance of the conventional approach while trained using a merged set.
4.4.2. Federated Approach (Trained with Merged Training set)
Here, the merged training set was divided into two portions
(AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_01_Local1, AD_OAS_FL_MERGED_01_Local2) to train the two local MobileNet models. The derived global MobileNet model was tested with OASIS (OAS_COR_01_test), ADNI (ADNI_COR_01_test), and merged (AD_OAS_MERGED_01_test) test set. In the case of OASIS, it achieved the highest 95.24% accuracy and 83.33% sensitivity, 81.94% accuracy and 62.50% sensitivity, and 83.97% accuracy and 61.90% sensitivity. Almost in all the cases, the proposed federated approach performed better which can be seen in
Table 7.
4.4.3. Federated Approach (Trained with ADNI and OASIS in Two Different Machines)
Here, two MobileNet models were trained with ADNI (ADNI_COR_02_train) and OASIS (OAS_COR_02_train) separately. The found global model was tested with the same test sets which are mentioned in previous sections. This model acquired 91.67%, 77.78%, and 82.69% accuracy in OASIS, ADNI, and Merged test set respectively, which was lower than the federated approach trained with the merged set, but greater than the conventional approach. However, in this approach, the model was found as more consistent. This model was found to distinguish between two classes with more equal efficacy than the other two approaches as the gap between sensitivity and specificity is lower than the other two which can be seen in
Table 7.
Table 7.
Performance comparison between conventional and federated approach while trained with Merged dataset
Table 7.
Performance comparison between conventional and federated approach while trained with Merged dataset
| Test Set |
Approach |
Precision (%) |
Recall / Sensitivity (%) |
Specificity (%) |
Accuracy (%) |
| OASIS |
Conventional |
71.43 |
55.56 |
93.94 |
85.71 |
| Federated |
93.75 |
83.33 |
98.48 |
95.24 |
| Federated with two different training sets in two local machines |
73.91 |
94.44 |
90.91 |
91.67 |
| ADNI |
Conventional |
55.56 |
62.50 |
75.00 |
70.83 |
| Federated |
78.95 |
62.50 |
91.67 |
81.94 |
| Federated with two different training set in two local machines |
66.67 |
66.67 |
83.33 |
77.78 |
| Merged |
Conventional |
60.00 |
64.29 |
84.21 |
78.85 |
| Federated |
74.29 |
61.90 |
92.11 |
83.97 |
| Federated with two different training sets in two local machines |
67.44 |
69.05 |
87.72 |
82.69 |
4.5. Discussion
The proposed MobileNet acquired more than 95%, 78%, and 83% accuracy respectively in OASIS, ADNI, and merged tests.
Figure 7 shows that the MobileNet model acquired the highest accuracy while trained with merged dataset in federated approach. From this figure, it is also clear that the MobileNet model performed better than the Conventional approach in all the parameters in the case of training with ADNI, OASIS, or Merged training set.
In the case of testing with ADNI, the MobileNet shows a similar pattern as the previous one. Here, the model was able to distinguish better between the classes in the case of training in federated approach. While training with OASIS, the federated approach achieved 77.78% accuracy, whereas the model could acquire only 65.28% accuracy in the conventional approach. In the case of trained with ADNI and merged, the models were seen to perform better in the case of trained with the Federated approach (
Figure 8).
While testing with the merged test set, the model was found as performing better while trained in the federated approach in all the cases. If the model was trained with the OASIS dataset, it achieved 83.33% accuracy in the federated approach, while 76.92% in the Conventional approach. In the case of training with the merged training set, the model achieved 83.98% accuracy in the federated approach, while it was only 78.85% in the conventional approach.
Figure 9.
Performance analysis of Conventional and Federated approach while tested using Merged dataset
Figure 9.
Performance analysis of Conventional and Federated approach while tested using Merged dataset
Therefore, it is evident that models were found to perform better if trained in a federated approach. We also find the models to be more robust compared to the conventional approach, since performance deviation was not significant enough in case of change in the training set. Apart from that, the models acquired more consistent results in terms of sensitivity and specificity. This determines the model’s capability in distinguishing between two classes. Hence, we found the federated approach to be better performing, robust, and consistent compared to the conventional approach in all the cases.
5. Conclusion
Many researchers from all around the world are working to identify the most effective cure for AD. In this study, we pensively looked into the potential applications of federated learning for the detection of AD cases. In addition, we have used traditional DL-based methods to find this disease. Out of three distinct planes—coronal, sagittal, and transverse, we have chosen coronal to be the optimal orientation plane for MRI brain images. The MobileNet architecture was discovered to be the optimal model providing the best performance in all the cases. To avoid model bias, we used data augmentation strategies. This aids the model’s understanding of the characteristics of AD MRI images. While training with the OASIS dataset, the conventional approach achieved an accuracy of 91.67% whereas the FL approach achieved 92.86% accuracy. For the ADNI and Merged dataset, the FL approach achieved 77.78% and 83.33%, respectively. The conventional method achieved 65.28% and 76.92% accuracy in this case which was less than the FL method. Nevertheless, we also evaluated the robustness of the model by testing it in OASIS, ADNI, and Merged datasets. In most cases, the FL approach outperformed the conventional approach in terms of different evaluation parameters. Here, FL achieved 95.24%, 81.94%, and 83.97% accuracy in the OASIS, ADNI, and Merged datasets, respectively. In this study, the FL method outperformed all the conventional methods as well as it ensured the privacy of the data as it did not require the collection of any data. For further improvement of the model performance, extensive data preprocessing techniques can be exercised. In what follows, the robustness of the model might be improved by integrating more diverse datasets containing more number of samples, especially positive samples into the model. This may also enhance the efficiency of the approach. The explainabilty of the proposed model might be another important area of study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Formal analysis, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Funding acquisition, Mohammad Abu Yousuf, Md. Abdul Hamid, Muhammad Mostafa Monowar and Madini Alassafi; Investigation, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Methodology, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Supervision, Mohammad Abu Yousuf; Visualization, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Writing – original draft, Tapotosh Ghosh and Md Istakiak Adnan Palash; Writing – review & editing, Mohammad Abu Yousuf, Md. Abdul Hamid, Muhammad Mostafa Monowar and Madini Alassafi.
Funding
This research work was funded by Institutional Fund Projects under grand no. (IFPIP: 544-611-1443). The authors gratefully acknowledge technical and financial support provided by the Ministry of Education and King Abdulaziz University, DSR, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aging, N.I. Alzheimer’s disease fact sheet. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet, 2023.
- Kim, B.; Noh, G.O.; Kim, K. Behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and family caregiver burden: a path analysis. BMC geriatrics 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemuri, P.; Gunter, J.L.; Senjem, M.L.; Whitwell, J.L.; Kantarci, K.; Knopman, D.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack Jr, C.R. Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis in individual subjects using structural MR images: validation studies. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, N.; Campbell, S.; Carvalho, A.; Harapanahalli, S.; Hernandez, G.V.; Krpalkova, L.; Riordan, D.; Walsh, J. Deep learning vs. traditional computer vision. Advances in Computer Vision: Proceedings of the 2019 Computer Vision Conference (CVC), Volume 1 1. Springer, 2020, pp. 128–144.
- Hulsen, T. Sharing is caring—data sharing initiatives in healthcare. International journal of environmental research and public health 2020, 17, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. Artificial intelligence and statistics. PMLR, 2017, pp. 1273–1282.
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861 2017. arXiv:1704.04861 2017.
- Ahamed, K.U.; Islam, M.; Uddin, A.; Akhter, A.; Paul, B.K.; Yousuf, M.A.; Uddin, S.; Quinn, J.M.; Moni, M.A. A deep learning approach using effective preprocessing techniques to detect COVID-19 from chest CT-scan and X-ray images. Computers in biology and medicine 2021, 139, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurna, N.F.; Yousuf, M.A.; Taher, K.A.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. A classification of MRI brain tumor based on two stage feature level ensemble of deep CNN models. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 146, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Hasan, M.M.; Rahim, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Yousuf, M.A.; Al-Ashhab, S.; Akhdar, H.F.; Alyami, S.A.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. Particle Swarm Optimized Fuzzy CNN With Quantitative Feature Fusion for Ultrasound Image Quality Identification. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine 2022, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mim, T.R.; Amatullah, M.; Afreen, S.; Yousuf, M.A.; Uddin, S.; Alyami, S.A.; Hasan, K.F.; Moni, M.A. GRU-INC: An inception-attention based approach using GRU for human activity recognition. Expert Systems with Applications 2023, 216, 119419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinsaif, S.; Lang, J.; Initiative, A.D.N.; others. 3D shearlet-based descriptors combined with deep features for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease based on MRI data. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 138, 104879.
- Puente-Castro, A.; Fernandez-Blanco, E.; Pazos, A.; Munteanu, C.R. Automatic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on deep learning techniques. Computers in biology and medicine 2020, 120, 103764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, K.T.; Gupta, B.B.; Alhalabi, W.; Alzahrani, F.S. An MRI scans-based Alzheimer’s disease detection via convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folego, G.; Weiler, M.; Casseb, R.F.; Pires, R.; Rocha, A. Alzheimer’s disease detection through whole-brain 3D-CNN MRI. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8, 534592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Luo, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Bi, Y. Alzheimer’s disease detection using depthwise separable convolutional neural networks. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2021, 203, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, N.; Ding, H.; Yang, J.; Au, R.; Ang, T.F. Deep ensemble learning for Alzheimer’s disease classification. Journal of biomedical informatics 2020, 105, 103411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Yue, G.; Xu, Y.; Feng, C.; Yang, M.; Wang, T.; Lei, B. A novel end-to-end hybrid network for Alzheimer’s disease detection using 3D CNN and 3D CLSTM. 2020 IEEE 17th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–4.
- Koh, J.E.W.; Jahmunah, V.; Pham, T.H.; Oh, S.L.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R.; Yeong, C.H.; Fabell, M.K.M.; Rahmat, K.; Vijayananthan, A.; others. Automated detection of Alzheimer’s disease using bi-directional empirical model decomposition. Pattern Recognition Letters 2020, 135, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Lin, L.; Zhang, B.; Shen, X.; Wu, S.; Initiative, A.D.N.; others. Multi-model and multi-slice ensemble learning architecture based on 2D convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 136, 104678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.; Dogan, S.; Tuncer, T.; Baygin, M.; Altunisik, E. Feed-forward LPQNet based automatic alzheimer’s disease detection model. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2021, 137, 104828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringas, S.; Salomón, S.; Duque, R.; Lage, C.; Montaña, J.L. Alzheimer’s disease stage identification using deep learning models. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2020, 109, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Venkatesan, C.; Sumithra, M.; Gao, X.Z.; Elakkiya, B.; Akila, M.; Manoharan, S. DEMNET: a deep learning model for early diagnosis of Alzheimer diseases and dementia from MR images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 90319–90329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, P.; Talele, A.; Degaonkar, K. Diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease using machine learning. 2018 Fourth International Conference on Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–4.
- Li, F.; Liu, M.; Initiative, A.D.N.; others. A hybrid convolutional and recurrent neural network for hippocampus analysis in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of neuroscience methods 2019, 323, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheera, S.; Ram, M.S.S. A novel CNN based Alzheimer’s disease classification using hybrid enhanced ICA segmented gray matter of MRI. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2020, 81, 101713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Li, S.; Xiao, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Ma, X. Computer aided Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by an unsupervised deep learning technology. Neurocomputing 2020, 392, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabason, E.; Ahmad, M.O.; Swamy, M. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease from MRI data using an ensemble of hybrid deep convolutional neural networks. 2019 IEEE 62nd international Midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS). IEEE, 2019, pp. 481–484.
- Helaly, H.A.; Badawy, M.; Haikal, A.Y. Deep learning approach for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Cognitive computation 2021, pp. 1–17.
- Venugopalan, J.; Tong, L.; Hassanzadeh, H.R.; Wang, M.D. Multimodal deep learning models for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease stage. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, D.S.; Wang, T.H.; Parker, J.; Csernansky, J.G.; Morris, J.C.; Buckner, R.L. Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS): cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older adults. Journal of cognitive neuroscience 2007, 19, 1498–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.G.; Weiner, M.W.; Thal, L.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.; Jagust, W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Toga, A.W.; Beckett, L. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clinics 2005, 15, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 4700–4708.
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2017, Vol. 31.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).