Submitted:
30 April 2023
Posted:
01 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Hydrogen as a Promising Agent for Regulating the State of the Integrated-Buffer Metabolic Environment of the Local Tissue Microenvironment
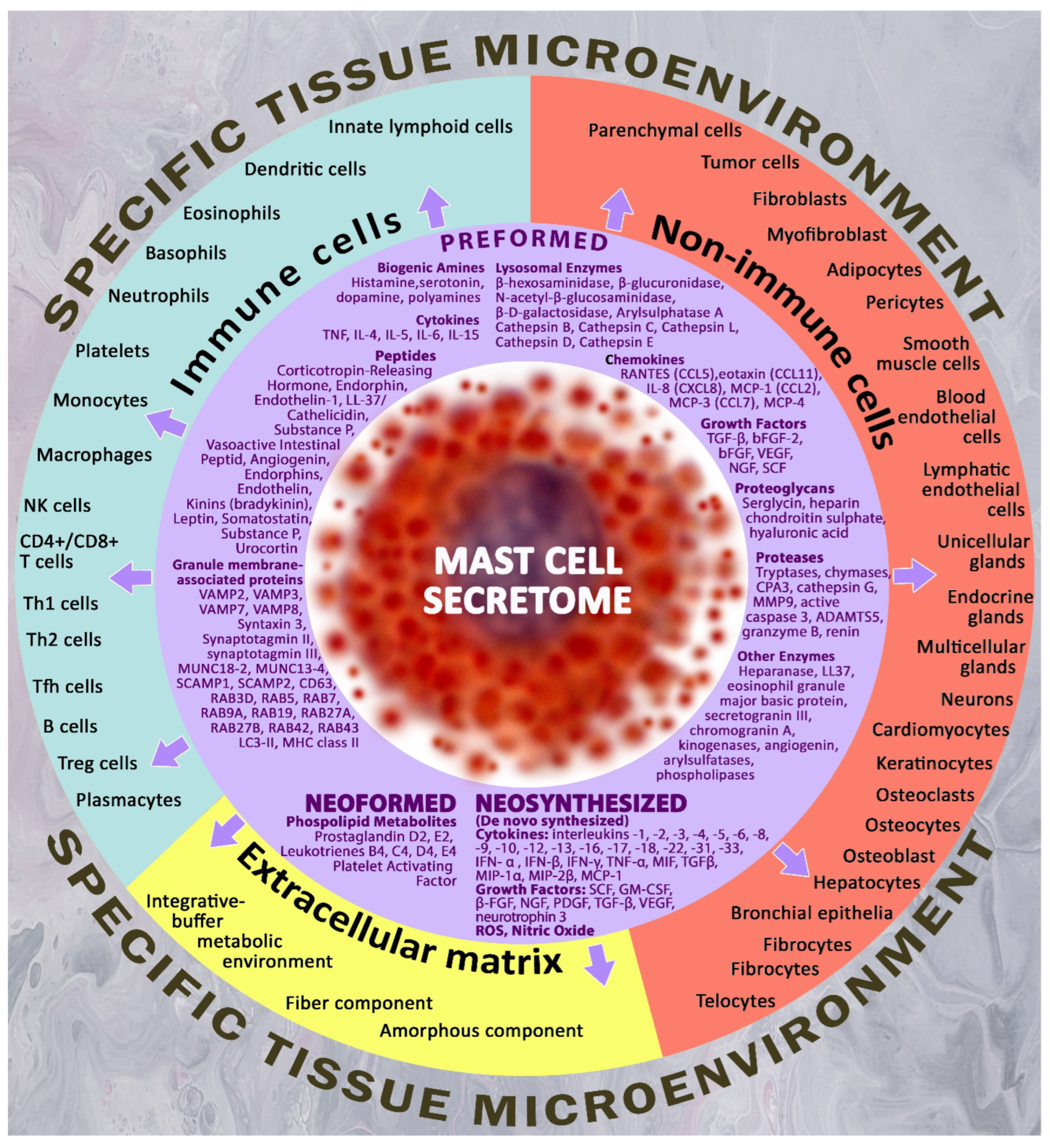
3. Mast Cells Are Key Regulatory Players in the Organ-Specific Tissue Microenvironment
4. Mast Cells and Inflammation
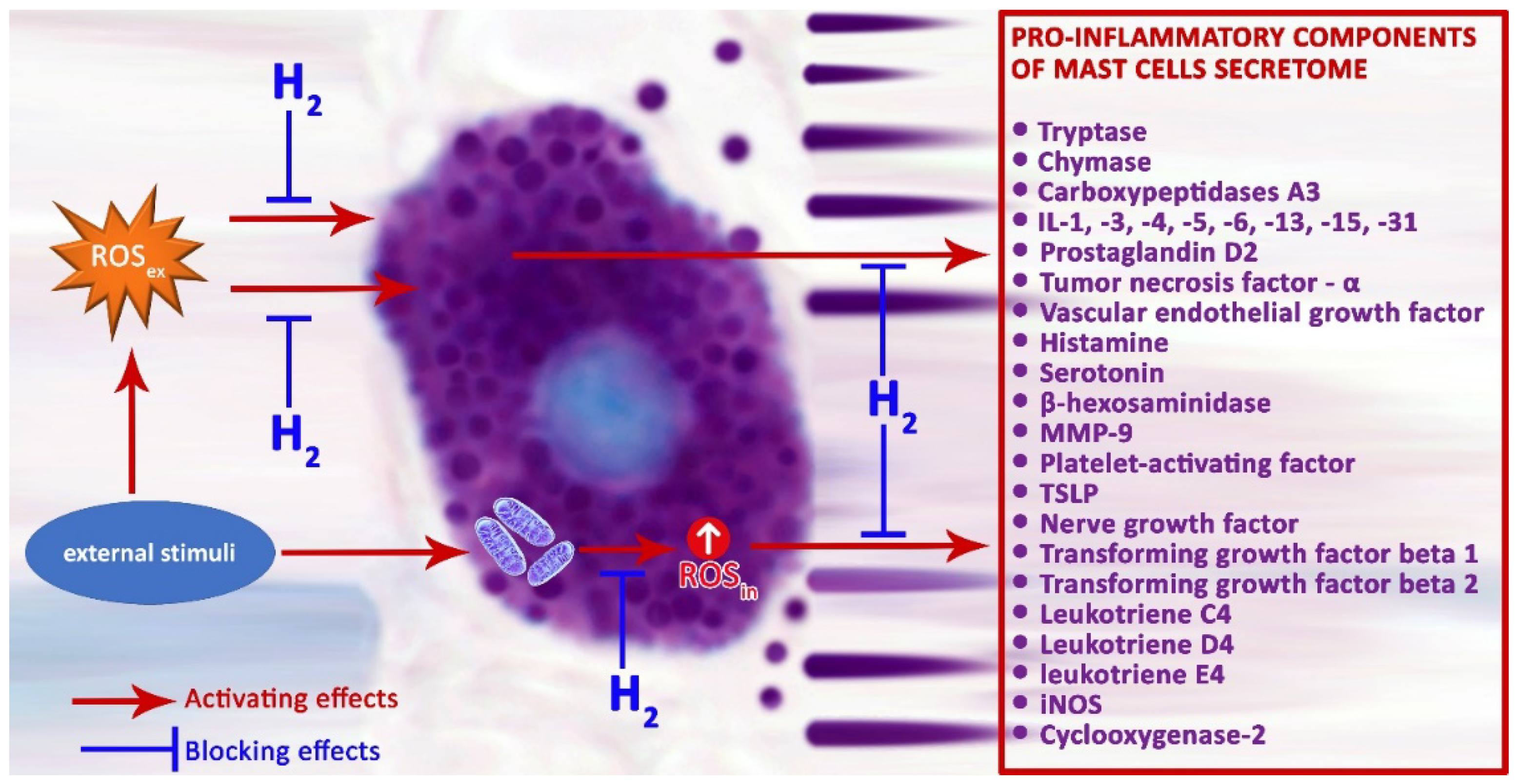
5. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Mechanisms of Activation of Mast Cell Secretory Pathways
6. Preformed Mast Cell Secretome Components - Inflammatory Stimulants
6.1. Mast Cell Specific Proteases
6.1.1. Tryptase
6.1.2. Chymase
6.1.3. Carboxypeptidase A3
7. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albano, G.D.; Gagliardo, R.P.; Montalbano, A.M.; Profita, M. Overview of the Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress: Impact in Inflammation of the Airway Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Batty, M.; Bennett, M.R.; Yu, E. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Cells 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Resiere, D.; Mehdaoui, H.; Neviere, R. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Snakebite Envenomation: A Brief Descriptive Review and Clinical Implications. Toxins (Basel) 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, A.; de Oliveira, J.; da Silva Pontes, L.V.; de Souza Junior, J.F.; Goncalves, T.A.F.; Dantas, S.H.; de Almeida Feitosa, M.S.; Silva, A.O.; de Medeiros, I.A. ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and its Implications in Aging Pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 1225578. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Garcia, V.; Estupinan-Jimenez, J.R.; Vivas-Mejia, P.E.; Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Vazquez-Guillen, J.M.; Resendez-Perez, D. A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 980694. [CrossRef]
- Wlaschek, M.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Oxidative stress in chronic venous leg ulcers. Wound Repair Regen 2005, 13, 452-461. [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, G.; Vejux, A.; Sahakyan, N. The Role of Oxidative Stress-Mediated Inflammation in the Development of T2DM-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy: Possible Preventive Action of Tannins and Other Oligomeric Polyphenols. Molecules 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Kloska, D.; Grochot-Przeczek, A.; Feelisch, M.; Cuadrado, A.; van Goor, H. Personalized redox medicine in inflammatory bowel diseases: an emerging role for HIF-1alpha and NRF2 as therapeutic targets. Redox Biol 2023, 60, 102603. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jia, S.; Ding, Y.; Xia, S.; Giunta, S. Balanced basal-levels of ROS (redox-biology), and very-low-levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (cold-inflammaging), as signaling molecules can prevent or slow-down overt-inflammaging, and the aging-associated decline of adaptive-homeostasis. Exp Gerontol 2023, 172, 112067. [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Akin, C.; Hartmann, K.; Nilsson, G.; Reiter, A.; Hermine, O.; Sotlar, K.; Sperr, W.R.; Escribano, L.; George, T.I.; et al. Mast cells as a unique hematopoietic lineage and cell system: From Paul Ehrlich's visions to precision medicine concepts. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10743-10768. [CrossRef]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Wohrl, S.; Bielory, L. Mast Cell Biology at Molecular Level: a Comprehensive Review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2020, 58, 342-365. [CrossRef]
- Caughey, G.H. Mast cell tryptases and chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol Rev 2007, 217, 141-154. [CrossRef]
- Pejler, G.; Ronnberg, E.; Waern, I.; Wernersson, S. Mast cell proteases: multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 2010, 115, 4981-4990. [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, L.; Hermine, O. Mast cells and inflammation. Joint Bone Spine 2013, 80, 141-145. [CrossRef]
- Reber, L.L.; Daubeuf, F.; Pejler, G.; Abrink, M.; Frossard, N. Mast cells contribute to bleomycin-induced lung inflammation and injury in mice through a chymase/mast cell protease 4-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 2014, 192, 1847-1854. [CrossRef]
- Reber, L.L.; Frossard, N. Targeting mast cells in inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Ther 2014, 142, 416-435. [CrossRef]
- Bonnekoh, H.; Scheffel, J.; Kambe, N.; Krause, K. The role of mast cells in autoinflammation. Immunol Rev 2018, 282, 265-275. [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Raap, U.; Rivellese, F.; Marone, G.; Gibbs, B.F. Human mast cells and basophils-How are they similar how are they different? Immunol Rev 2018, 282, 8-34. [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Marone, G. Mast Cells: Fascinating but Still Elusive after 140 Years from Their Discovery. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Gaudenzio, N.; Tsai, M. Mast Cells in Inflammation and Disease: Recent Progress and Ongoing Concerns. Annu Rev Immunol 2020, 38, 49-77. [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Unsworth, L.D. Targeting active sites of inflammation using inherent properties of tissue-resident mast cells. Acta Biomater 2023, 159, 21-37. [CrossRef]
- Swindle, E.J.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Coleman, J.W. Rodent and human mast cells produce functionally significant intracellular reactive oxygen species but not nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 48751-48759. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Inoue, T.; Niide, O.; Ra, C. Role of oxidants in mast cell activation. Chem Immunol Allergy 2005, 87, 32-42. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimaru, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Niide, O.; Ra, C. Silver activates mast cells through reactive oxygen species production and a thiol-sensitive store-independent Ca2+ influx. Free Radic Biol Med 2006, 40, 1949-1959. [CrossRef]
- Pignatti, P.; Frossi, B.; Pala, G.; Negri, S.; Oman, H.; Perfetti, L.; Pucillo, C.; Imbriani, M.; Moscato, G. Oxidative activity of ammonium persulfate salt on mast cells and basophils: implication in hairdressers' asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2013, 160, 409-419. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tung, H.Y.; Tsai, Y.M.; Hsu, S.C.; Chang, H.W.; Kawasaki, H.; Tseng, H.C.; Plunkett, B.; Gao, P.; Hung, C.H.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor controls murine mast cell homeostasis. Blood 2013, 121, 3195-3204. [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Ji, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. Food allergen--induced mast cell degranulation is dependent on PI3K-mediated reactive oxygen species production and upregulation of store-operated calcium channel subunits. Scand J Immunol 2013, 78, 35-43. [CrossRef]
- Hochman, D.J.; Collaco, C.R.; Brooks, E.G. Acrolein induction of oxidative stress and degranulation in mast cells. Environ Toxicol 2014, 29, 908-915. [CrossRef]
- Oh, B.; Lee, C.H. Nanofiber-coated drug eluting stent for the stabilization of mast cells. Pharm Res 2014, 31, 2463-2478. [CrossRef]
- Chelombitko, M.A.; Fedorov, A.V.; Ilyinskaya, O.P.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Chernyak, B.V. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mast Cell Degranulation. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2016, 81, 1564-1577. [CrossRef]
- Pavlyuchenkova, A.N.; Chelombitko, M.A.; Fedorov, A.V.; Kuznetsova, M.K.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Razin, E. The Distinct Effects of the Mitochondria-Targeted STAT3 Inhibitors Mitocur-1 and Mitocur-3 on Mast Cell and Mitochondrial Functions. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Hunter, K.D.; Crozier, R.W.E.; Braun, J.L.; Fajardo, V.A.; MacNeil, A.J. Acute activation of SERCA with CDN1163 attenuates IgE-mediated mast cell activation through selective impairment of ROS and p38 signaling. FASEB J 2023, 37, e22748. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L. Molecular hydrogen: a therapeutic antioxidant and beyond. Med Gas Res 2016, 6, 219-222. [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Yang, M.; Yang, N.N.; Yin, X.X.; Song, W.G. Molecular hydrogen: a preventive and therapeutic medical gas for various diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102653-102673. [CrossRef]
- Noda, M.; Uemura, Y.; Yoshii, Y.; Horita, T.; Takemi, S.; Sakata, I.; Sakai, T. Circulating messenger for neuroprotection induced by molecular hydrogen. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2019, 97, 909-915. [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Higashida, K.; Muraoka, I. Application of Molecular Hydrogen as a Novel Antioxidant in Sports Science. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 2328768. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Role of Molecular Hydrogen in Ageing and Ageing-Related Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 2249749. [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R.; Ohno, K. Electrolyzed-Reduced Water: Review I. Molecular Hydrogen Is the Exclusive Agent Responsible for the Therapeutic Effects. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R.; Ohno, K. Electrolyzed-Reduced Water: Review II: Safety Concerns and Effectiveness as a Source of Hydrogen Water. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, E.I.; Khlusov, I.A.; Noda, M. Homeostatic and endocrine responses as the basis for systemic therapy with medical gases: ozone, xenon and molecular hydrogen. Med Gas Res 2021, 11, 174-186. [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Fujita, Y.; Ito, M.; Masuda, A.; Ohno, K.; Ichihara, M.; Kojima, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, M. Molecular hydrogen suppresses FcepsilonRI-mediated signal transduction and prevents degranulation of mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 389, 651-656. [CrossRef]
- Manaenko, A.; Lekic, T.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, J. Hydrogen inhalation ameliorated mast cell-mediated brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Crit Care Med 2013, 41, 1266-1275. [CrossRef]
- Kajisa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hu, A.; Suetake, N.; Kobayashi, H. Hydrogen water ameliorates the severity of atopic dermatitis-like lesions and decreases interleukin-1beta, interleukin-33, and mast cell infiltration in NC/Nga mice. Saudi Med J 2017, 38, 928-933. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Soboleva, M.; Nikityuk, D.; Alexeeva, N.; Klochkova, S.; Kostin, A.; Shishkina, V.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Mast Cells in Regeneration of the Skin in Burn Wound with Special Emphasis on Molecular Hydrogen Effect. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2023, 16. [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications. Methods Enzymol 2015, 555, 289-317. [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, I.; Ishikawa, M.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimaki, K.; Yamagata, K.; Katsura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Asoh, S.; Ohta, S. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med 2007, 13, 688-694. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Dong, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhuang, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M. Hydrogen: A Novel Option in Human Disease Treatment. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 8384742. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G.; Suo, L.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in studies of molecular hydrogen in the treatment of pancreatitis. Life Sci 2021, 264, 118641. [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Antitumor Activity of Protons and Molecular Hydrogen: Underlying Mechanisms. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, J.; Qiao, J.; Wei, Y. Hydrogen, a Novel Therapeutic Molecule, Regulates Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 789507. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Z. Molecular hydrogen is a potential protective agent in the management of acute lung injury. Mol Med 2022, 28, 27. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, T. Therapeutic Efficacy of Molecular Hydrogen: A New Mechanistic Insight. Curr Pharm Des 2019, 25, 946-955. [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.I.; Yamamoto, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Molecular Hydrogen as a Novel Antitumor Agent: Possible Mechanisms Underlying Gene Expression. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Yamamoto, H.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Hydrogen in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Possible Inhibiting Role on Mitochondrial Stress. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Hirano, S.I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Sato, B.; Yamamoto, H.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Molecular Hydrogen as a Potential Clinically Applicable Radioprotective Agent. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Ichikawa, Y.; Hirano, S.I.; Sato, B.; Takefuji, Y.; Satoh, F. Molecular Hydrogen as a Novel Protective Agent against Pre-Symptomatic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Bajgai, J.; Lee, K.J.; Rahman, M.H.; Fadriquela, A.; Kim, C.S. Role of Molecular Hydrogen in Skin Diseases and its Impact in Beauty. Curr Pharm Des 2021, 27, 737-746. [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, Y.; Terasaki, M.; Shimizu, A. Protective Effects of Hydrogen against Irradiation. Curr Pharm Des 2021, 27, 679-686. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.T.; Qin, S.C. Neuroprotective Effects of Molecular Hydrogen: A Critical Review. Neurosci Bull 2021, 37, 389-404. [CrossRef]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Dileepan, K.N.; Wood, J.G. Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell. Front Immunol 2015, 6, 620. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.Z.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Mast cell function: a new vision of an old cell. J Histochem Cytochem 2014, 62, 698-738. [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Wallerman, O.; Paivandy, A.; Calounova, G.; Gustafson, A.M.; Sabari, B.R.; Zabucchi, G.; Allis, C.D.; Pejler, G. Tryptase-catalyzed core histone truncation: A novel epigenetic regulatory mechanism in mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2017, 140, 474-485. [CrossRef]
- Redegeld, F.A.; Yu, Y.; Kumari, S.; Charles, N.; Blank, U. Non-IgE mediated mast cell activation. Immunol Rev 2018, 282, 87-113. [CrossRef]
- Robida, P.A.; Puzzovio, P.G.; Pahima, H.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Bochner, B.S. Human eosinophils and mast cells: Birds of a feather flock together. Immunol Rev 2018, 282, 151-167. [CrossRef]
- Ronnberg, E.; Melo, F.R.; Pejler, G. Mast cell proteoglycans. J Histochem Cytochem 2012, 60, 950-962. [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol Rev 2018, 282, 121-150. [CrossRef]
- He, B.F.; Wu, Y.X.; Hu, W.P.; Hua, J.L.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J. ROS induced the Rab26 promoter hypermethylation to promote cigarette smoking-induced airway epithelial inflammation of COPD through activation of MAPK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 2023, 195, 359-370. [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.; Latz, E.; Mills, K.H.; Natoli, G.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; O'Neill, L.A.; Xavier, R.J. Trained immunity: A program of innate immune memory in health and disease. Science 2016, 352, aaf1098. [CrossRef]
- Suurmond, J.; Habets, K.L.L.; Tatum, Z.; Schonkeren, J.J.; Hoen, P.A.C.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Laros, J.F.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; Kurreeman, F. Repeated FcepsilonRI triggering reveals modified mast cell function related to chronic allergic responses in tissue. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016, 138, 869-880. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Kostin, A.; Trotsenko, I.; Samoilova, V.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Carboxypeptidase A3-A Key Component of the Protease Phenotype of Mast Cells. Cells 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Mast cell chymase: morphofunctional characteristics. Histochem Cell Biol 2019, 152, 253-269. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Buchwalow, I.; Samoilova, V.; Tiemann, M. Tryptase as a polyfunctional component of mast cells. Histochem Cell Biol 2018, 149, 461-477. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Buchwalow, I.; Horny, P.; Tiemann, M. Protease profile of normal and neoplastic mast cells in the human bone marrow with special emphasis on systemic mastocytosis. Histochem Cell Biol 2021, 155, 561-580. [CrossRef]
- Blank, U.; Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Danelli, L.; Claver, J.; Tiwari, N.; Sanchez-Miranda, E.; Vazquez-Victorio, G.; Ramirez-Valadez, K.A.; Macias-Silva, M.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. Vesicular trafficking and signaling for cytokine and chemokine secretion in mast cells. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 453. [CrossRef]
- Vukman, K.V.; Forsonits, A.; Oszvald, A.; Toth, E.A.; Buzas, E.I. Mast cell secretome: Soluble and vesicular components. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2017, 67, 65-73. [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C. Neuroendocrinology of mast cells: Challenges and controversies. Exp Dermatol 2017, 26, 751-759. [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, A.M.; Tkaczyk, C. Integrated signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol 2006, 6, 218-230. [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Nakae, S.; Tsai, M. Mast cells in the development of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 135-142. [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Raj, S.; Arizmendi, N.; Ding, J.; Eitzen, G.; Kwan, P.; Kulka, M.; Unsworth, L.D. Identification of short peptide sequences that activate human mast cells via Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor member X2. Acta Biomater 2021, 136, 159-169. [CrossRef]
- Wernersson, S.; Pejler, G. Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol 2014, 14, 478-494. [CrossRef]
- Sahid, M.N.A.; Kiyoi, T. Mast cell activation markers for in vitro study. J Immunoassay Immunochem 2020, 41, 778-816. [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Ra, C. Reactive oxygen species produced up- or downstream of calcium influx regulate proinflammatory mediator release from mast cells: role of NADPH oxidase and mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1783, 789-802. [CrossRef]
- Paivandy, A.; Eriksson, J.; Melo, F.R.; Sellin, M.E.; Pejler, G. Lysosomotropic challenge of mast cells causes intra-granular reactive oxygen species production. Cell Death Discov 2019, 5, 95. [CrossRef]
- Manorak, W.; Idahosa, C.; Gupta, K.; Roy, S.; Panettieri, R., Jr.; Ali, H. Upregulation of Mas-related G Protein coupled receptor X2 in asthmatic lung mast cells and its activation by the novel neuropeptide hemokinin-1. Respir Res 2018, 19, 1. [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.; Dostert, C.; Mak, T.W.; Brenner, D. TNF and ROS Crosstalk in Inflammation. Trends Cell Biol 2016, 26, 249-261. [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2018, 18, 134-147. [CrossRef]
- Chelombitko, M.A.; Chernyak, B.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Razin, E.; Paruchuru, L.B. The Role Played by Mitochondria in FcepsilonRI-Dependent Mast Cell Activation. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 584210. [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 2014, 24, R453-462. [CrossRef]
- Slimen, I.B.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Dabbebi, H.; Ben Mrad, M.; Abdrabbah, M. Reactive oxygen species, heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. Int J Hyperthermia 2014, 30, 513-523. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Lei, P.; Zhang, Q. ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2015, 35, 615-621. [CrossRef]
- Davalli, P.; Mitic, T.; Caporali, A.; Lauriola, A.; D'Arca, D. ROS, Cell Senescence, and Novel Molecular Mechanisms in Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 2016, 3565127. [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, U.S.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol 2019, 25, 101084. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Jiang, L.; Lei, L.; Fu, C.; Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Q. Crosstalk between G-quadruplex and ROS. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 37. [CrossRef]
- Checa, J.; Aran, J.M. Reactive Oxygen Species: Drivers of Physiological and Pathological Processes. J Inflamm Res 2020, 13, 1057-1073. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Song, J.; Seo, Y.; Koh, E.M.; Kim, S.H.; Jung, K.J. Inhibitory Effects of AF-343, a Mixture of Cassia tora L., Ulmus pumila L., and Taraxacum officinale, on Compound 48/80-Mediated Allergic Responses in RBL-2H3 Cells. Molecules 2020, 25. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, N.; Mao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) promotes IgE-mediated mast cell activation through ROS/Gadd45b/JNK axis. J Dermatol Sci 2021, 102, 47-57. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gan, X. Pretreatment with propofol restores intestinal epithelial cells integrity disrupted by mast cell degranulation in vitro. Physiol Res 2022, 71, 849-858. [CrossRef]
- Swindle, E.J.; Metcalfe, D.D. The role of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide in mast cell-dependent inflammatory processes. Immunol Rev 2007, 217, 186-205. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Matsui, T.; Inoue, T.; Niide, O.; Nunomura, S.; Ra, C. Fc epsilon RI signaling of mast cells activates intracellular production of hydrogen peroxide: role in the regulation of calcium signals. J Immunol 2003, 171, 6119-6127. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Inoue, T.; Ra, C. Discrete generations of intracellular hydrogen peroxide and superoxide in antigen-stimulated mast cells: reciprocal regulation of store-operated Ca2+ channel activity. Mol Immunol 2009, 46, 2200-2209. [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, H.S.; Swindle, E.J.; Kim, M.S.; Beaven, M.A.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Gilfillan, A.M. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent activation of Btk is required for optimal eicosanoid production and generation of reactive oxygen species in antigen-stimulated mast cells. J Immunol 2008, 181, 7706-7712. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Inoue, T.; Yoshimaru, T.; Ra, C. Galectin-3 but not galectin-1 induces mast cell death by oxidative stress and mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1783, 924-934. [CrossRef]
- Swindle, E.J.; Hunt, J.A.; Coleman, J.W. A comparison of reactive oxygen species generation by rat peritoneal macrophages and mast cells using the highly sensitive real-time chemiluminescent probe pholasin: inhibition of antigen-induced mast cell degranulation by macrophage-derived hydrogen peroxide. J Immunol 2002, 169, 5866-5873. [CrossRef]
- Pavlyuchenkova, A.N.; Zinovkin, R.A.; Makievskaya, C.I.; Galkin, II; Chelombitko, M.A. Mitochondria-targeted triphenylphosphonium-based compounds inhibit FcepsilonRI-dependent degranulation of mast cells by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction through Erk1/2. Life Sci 2022, 288, 120174. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Moreno, I.G.; Ibarra-Sanchez, A.; Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Blank, U.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. Mast Cells Localize in Hypoxic Zones of Tumors and Secrete CCL-2 under Hypoxia through Activation of L-Type Calcium Channels. J Immunol 2020, 204, 1056-1068. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.K. SHP-2 phosphatase controls aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated ER stress response in mast cells. Arch Toxicol 2017, 91, 1739-1748. [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Ra, C. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cytokine production in mast cells by stimulating an extracellular superoxide-mediated calcium influx. Biochem Pharmacol 2011, 82, 1930-1939. [CrossRef]
- Tagen, M.; Elorza, A.; Kempuraj, D.; Boucher, W.; Kepley, C.L.; Shirihai, O.S.; Theoharides, T.C. Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 inhibits mast cell activation and reduces histamine content. J Immunol 2009, 183, 6313-6319. [CrossRef]
- Toda, C.; Diano, S. Mitochondrial UCP2 in the central regulation of metabolism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014, 28, 757-764. [CrossRef]
- Hass, D.T.; Barnstable, C.J. Uncoupling proteins in the mitochondrial defense against oxidative stress. Prog Retin Eye Res 2021, 83, 100941. [CrossRef]
- Sismanopoulos, N.; Delivanis, D.A.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Angelidou, A.; Therianou, A.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Theoharides, T.C. Mast cells in allergic and inflammatory diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2012, 18, 2261-2277. [CrossRef]
- Trenker, M.; Malli, R.; Fertschai, I.; Levak-Frank, S.; Graier, W.F. Uncoupling proteins 2 and 3 are fundamental for mitochondrial Ca2+ uniport. Nat Cell Biol 2007, 9, 445-452. [CrossRef]
- Barnstable, C.J.; Zhang, M.; Tombran-Tink, J. Uncoupling Proteins as Therapeutic Targets for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol Cell 2012, 48, 158-167. [CrossRef]
- Csordas, G.; Hajnoczky, G. SR/ER-mitochondrial local communication: calcium and ROS. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009, 1787, 1352-1362. [CrossRef]
- Song, M.Y.; Makino, A.; Yuan, J.X. Role of reactive oxygen species and redox in regulating the function of transient receptor potential channels. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011, 15, 1549-1565. [CrossRef]
- Steiner, P.; Arlt, E.; Boekhoff, I.; Gudermann, T.; Zierler, S. Two-Pore Channels Regulate Inter-Organellar Ca(2+) Homeostasis in Immune Cells. Cells 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Huu, T.; Park, J.; Zhang, Y.; Duong Thanh, H.; Park, I.; Choi, J.M.; Yoon, H.J.; Park, S.C.; Woo, H.A.; Lee, S.R. The Role of Oxidative Inactivation of Phosphatase PTEN and TCPTP in Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Sul, O.J.; Choi, E.K.; Safdar, A.M.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, H.S. Reactive oxygen species induce the association of SHP-1 with c-Src and the oxidation of both to enhance osteoclast survival. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2014, 307, E61-70. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, D.; Fan, H.; Wu, R.; Tu, J.; Zhang, F.Q.; Wang, M.; Zheng, H.; Qu, C.K.; Elf, S.E.; et al. Cellular signals converge at the NOX2-SHP-2 axis to induce reductive carboxylation in cancer cells. Cell Chem Biol 2022, 29, 1200-1208 e1206. [CrossRef]
- Heun, Y.; Pircher, J.; Czermak, T.; Bluem, P.; Hupel, G.; Bohmer, M.; Kraemer, B.F.; Pogoda, K.; Pfeifer, A.; Woernle, M.; et al. Inactivation of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 drives vascular dysfunction in Sepsis. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 120-132. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.R.; McNagny, K.M. Preface. Mast cells. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1220, vii-viii. [CrossRef]
- Heneberg, P.; Draber, P. Regulation of cys-based protein tyrosine phosphatases via reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in mast cells and basophils. Curr Med Chem 2005, 12, 1859-1871. [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Min, J.H.; Chae, Y.H.; Baek, J.Y.; Wang, S.B.; Park, S.J.; Oh, G.T.; Lee, S.H.; Ho, Y.S.; Chang, T.S. Reactive oxygen species play a critical role in collagen-induced platelet activation via SHP-2 oxidation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2014, 20, 2528-2540. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.P.; Lin Feng, M.H.; Huang, H.L.; Huang, Y.C.; Tsou, W.I.; Lai, M.Z. Reactive oxygen species promote raft formation in T lymphocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 2007, 42, 936-944. [CrossRef]
- Kura, B.; Bagchi, A.K.; Singal, P.K.; Barancik, M.; LeBaron, T.W.; Valachova, K.; Soltes, L.; Slezak, J. Molecular hydrogen: potential in mitigating oxidative-stress-induced radiation injury (1). Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2019, 97, 287-292. [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Angelidou, A.; Delivanis, D.A.; Sismanopoulos, N.; Zhang, B.; Asadi, S.; Vasiadi, M.; Weng, Z.; Miniati, A.; et al. Mast cells and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1822, 21-33. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-de-Olano, D.; Alvarez-Twose, I. Mast Cells as Key Players in Allergy and Inflammation. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol 2018, 28, 365-378. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kurashima, Y. Two Sides of the Coin: Mast Cells as a Key Regulator of Allergy and Acute/Chronic Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- O'Connell, M.P.; Lyons, J.J. Resolving the genetics of human tryptases: implications for health, disease, and clinical use as a biomarker. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2022, 22, 143-152. [CrossRef]
- Hellman, L.; Akula, S.; Fu, Z.; Wernersson, S. Mast Cell and Basophil Granule Proteases - In Vivo Targets and Function. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 918305. [CrossRef]
- Vitte, J. Human mast cell tryptase in biology and medicine. Mol Immunol 2015, 63, 18-24. [CrossRef]
- Longo, V.; Tamma, R.; Brunetti, O.; Pisconti, S.; Argentiero, A.; Silvestris, N.; Ribatti, D. Mast cells and angiogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Exp Med 2018, 18, 319-323. [CrossRef]
- Pejler, G.; Abrink, M.; Ringvall, M.; Wernersson, S. Mast cell proteases. Adv Immunol 2007, 95, 167-255. [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, M.S.; Sunzini, F.; Fiorucci, L.; Botti, E.; Fonti, G.L.; Conigliaro, P.; Triggianese, P.; Costa, L.; Caso, F.; Giunta, A.; et al. Potential Role of Cytochrome c and Tryptase in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis: Focus on Resistance to Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2363. [CrossRef]
- Lucena, F.; McDougall, J.J. Protease Activated Receptors and Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Vita, F.; Berent-Maoz, B.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Zabucchi, G.; Pejler, G. Proteolytic histone modification by mast cell tryptase, a serglycin proteoglycan-dependent secretory granule protease. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 7682-7690. [CrossRef]
- Rabelo Melo, F.; Santosh Martin, S.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Pejler, G. Exosome-mediated uptake of mast cell tryptase into the nucleus of melanoma cells: a novel axis for regulating tumor cell proliferation and gene expression. Cell Death Dis 2019, 10, 659. [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, S.; Rabelo Melo, F.; Pejler, G. Tryptase Regulates the Epigenetic Modification of Core Histones in Mast Cell Leukemia Cells. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 804408. [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, S.; Grujic, M.; Lampinen, M.; Rollman, O.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Pejler, G.; Melo, F.R. Mast Cell beta-Tryptase Is Enzymatically Stabilized by DNA. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Pejler, G. Novel Insight into the in vivo Function of Mast Cell Chymase: Lessons from Knockouts and Inhibitors. J Innate Immun 2020, 12, 357-372. [CrossRef]
- Kosanovic, D.; Luitel, H.; Dahal, B.K.; Cornitescu, T.; Janssen, W.; Danser, A.H.; Garrelds, I.M.; De Mey, J.G.; Fazzi, G.; Schiffers, P.; et al. Chymase: a multifunctional player in pulmonary hypertension associated with lung fibrosis. Eur Respir J 2015, 46, 1084-1094. [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Walls, A.F. Human mast cell chymase induces the accumulation of neutrophils, eosinophils and other inflammatory cells in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 1998, 125, 1491-1500. [CrossRef]
- Terakawa, M.; Tomimori, Y.; Goto, M.; Fukuda, Y. Mast cell chymase induces expression of chemokines for neutrophils in eosinophilic EoL-1 cells and mouse peritonitis eosinophils. Eur J Pharmacol 2006, 538, 175-181. [CrossRef]
- Takato, H.; Yasui, M.; Ichikawa, Y.; Waseda, Y.; Inuzuka, K.; Nishizawa, Y.; Tagami, A.; Fujimura, M.; Nakao, S. The specific chymase inhibitor TY-51469 suppresses the accumulation of neutrophils in the lung and reduces silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Exp Lung Res 2011, 37, 101-108. [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Jin, D. Pathophysiological Role of Chymase-Activated Matrix Metalloproteinase-9. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Shi, G.P. Mast cell chymase and tryptase as targets for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2013, 19, 1114-1125. [CrossRef]
- Groschwitz, K.R.; Ahrens, R.; Osterfeld, H.; Gurish, M.F.; Han, X.; Abrink, M.; Finkelman, F.D.; Pejler, G.; Hogan, S.P. Mast cells regulate homeostatic intestinal epithelial migration and barrier function by a chymase/Mcpt4-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 22381-22386. [CrossRef]
- Bankova, L.G.; Lezcano, C.; Pejler, G.; Stevens, R.L.; Murphy, G.F.; Austen, K.F.; Gurish, M.F. Mouse mast cell proteases 4 and 5 mediate epidermal injury through disruption of tight junctions. J Immunol 2014, 192, 2812-2820. [CrossRef]
- Suttle, M.M.; Harvima, I.T. Mast cell chymase in experimentally induced psoriasis. J Dermatol 2016, 43, 693-696. [CrossRef]
- Puri, N.; Roche, P.A. Mast cells possess distinct secretory granule subsets whose exocytosis is regulated by different SNARE isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 2580-2585. [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, S.E.; Pejler, G.; Kleinau, S.; Abrink, M. Mast cell chymase contributes to the antibody response and the severity of autoimmune arthritis. FASEB J 2009, 23, 875-882. [CrossRef]
- Desbiens, L.; Lapointe, C.; Gharagozloo, M.; Mahmoud, S.; Pejler, G.; Gris, D.; D'Orleans-Juste, P. Significant Contribution of Mouse Mast Cell Protease 4 in Early Phases of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Mediators Inflamm 2016, 2016, 9797021. [CrossRef]
- Vibhushan, S.; Bratti, M.; Montero-Hernandez, J.E.; El Ghoneimi, A.; Benhamou, M.; Charles, N.; Daugas, E.; Blank, U. Mast Cell Chymase and Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 22. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Cen, Y. Involvement of mast cell chymase in burn wound healing in hamsters. Exp Ther Med 2013, 5, 643-647. [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Bankaitis, E.; Heimbach, L.; Li, N.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G.; An, L.; Diaz, L.A.; Werb, Z.; Liu, Z. Dual targets for mouse mast cell protease-4 in mediating tissue damage in experimental bullous pemphigoid. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 37358-37367. [CrossRef]
- Waern, I.; Lundequist, A.; Pejler, G.; Wernersson, S. Mast cell chymase modulates IL-33 levels and controls allergic sensitization in dust-mite induced airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 2013, 6, 911-920. [CrossRef]
- Dell'Italia, L.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Ferrario, C.M. Multifunctional Role of Chymase in Acute and Chronic Tissue Injury and Remodeling. Circ Res 2018, 122, 319-336. [CrossRef]
- Atiakshin, D.; Buchwalow, I.; Tiemann, M. Mast cells and collagen fibrillogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 2020, 154, 21-40. [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.; Hellman, L.; Aviles, F.X.; Wernersson, S. Analysis of the mast cell expressed carboxypeptidase A3 and its structural and evolutionary relationship to other vertebrate carboxypeptidases. Dev Comp Immunol 2022, 127, 104273. [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.; Piliponsky, A.M.; Chen, C.C.; Lammel, V.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G.; Tsai, M.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells can enhance resistance to snake and honeybee venoms. Science 2006, 313, 526-530. [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J. Snake bites and bee stings: the mast cell strikes back. Nat Med 2006, 12, 999-1000. [CrossRef]
- Asai, S.; Sato, T.; Tada, T.; Miyamoto, T.; Kimbara, N.; Motoyama, N.; Okada, H.; Okada, N. Absence of procarboxypeptidase R induces complement-mediated lethal inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-primed mice. J Immunol 2004, 173, 4669-4674. [CrossRef]
- Kokkonen, J.O.; Vartiainen, M.; Kovanen, P.T. Low density lipoprotein degradation by secretory granules of rat mast cells. Sequential degradation of apolipoprotein B by granule chymase and carboxypeptidase A. J Biol Chem 1986, 261, 16067-16072.
- Lundequist, A.; Tchougounova, E.; Abrink, M.; Pejler, G. Cooperation between mast cell carboxypeptidase A and the chymase mouse mast cell protease 4 in the formation and degradation of angiotensin II. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 32339-32344. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Takai, S.; Miyazaki, M. Significance of chymase inhibition for prevention of adhesion formation. Eur J Pharmacol 2004, 484, 357-359. [CrossRef]
- Siddhuraj, P.; Clausson, C.M.; Sanden, C.; Alyamani, M.; Kadivar, M.; Marsal, J.; Wallengren, J.; Bjermer, L.; Erjefalt, J.S. Lung Mast Cells Have a High Constitutive Expression of Carboxypeptidase A3 mRNA That Is Independent from Granule-Stored CPA3. Cells 2021, 10. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-GarciaLuna, J.L.; Chan, D.; Samberg, R.; Abou-Rjeili, M.; Wong, T.H.; Li, A.; Feyerabend, T.B.; Rodewald, H.R.; Henderson, J.E.; Martineau, P.A. Defective bone repair in mast cell-deficient Cpa3Cre/+ mice. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174396. [CrossRef]
- Balzar, S.; Fajt, M.L.; Comhair, S.A.; Erzurum, S.C.; Bleecker, E.; Busse, W.W.; Castro, M.; Gaston, B.; Israel, E.; Schwartz, L.B.; et al. Mast cell phenotype, location, and activation in severe asthma. Data from the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011, 183, 299-309. [CrossRef]
- Fricker, M.; Gibson, P.G.; Powell, H.; Simpson, J.L.; Yang, I.A.; Upham, J.W.; Reynolds, P.N.; Hodge, S.; James, A.L.; Jenkins, C.; et al. A sputum 6-gene signature predicts future exacerbations of poorly controlled asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2019, 144, 51-60 e11. [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.H.; Martin, L.J.; Wen, T.; Abonia, J.P.; Putnam, P.E.; Mukkada, V.A.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophilic Esophagitis Histology Remission Score: Significant Relations to Measures of Disease Activity and Symptoms. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2020, 70, 598-603. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, L.; Jiao, L.; Wen, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, N. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Underlying Biomarkers Potentially Linking Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma. Med Sci Monit 2020, 26, e924934. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




