Submitted:
30 April 2023
Posted:
01 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Using the same convolutional recurrent neural network, the MCG features perform better than other evaluation features in categorical emotion recognition.
- The multi-level attention network is proposed, in which channel-level and spatial-level attention modules obtain fused features from MCG features, and temporal-level attention further captures significant emotional regions from fused feature sequences, thereby improving emotion recognition performance.
- The proposed method is evaluated on Interactive Emotional Dyadic Motion Capture Database (IEMOCAP). It obtains an unweighted accuracy of 71%, showing the effectiveness of our approach.
2. Modulation-filtered cochleagram
2.1. Modulation-filtered cochleagram features
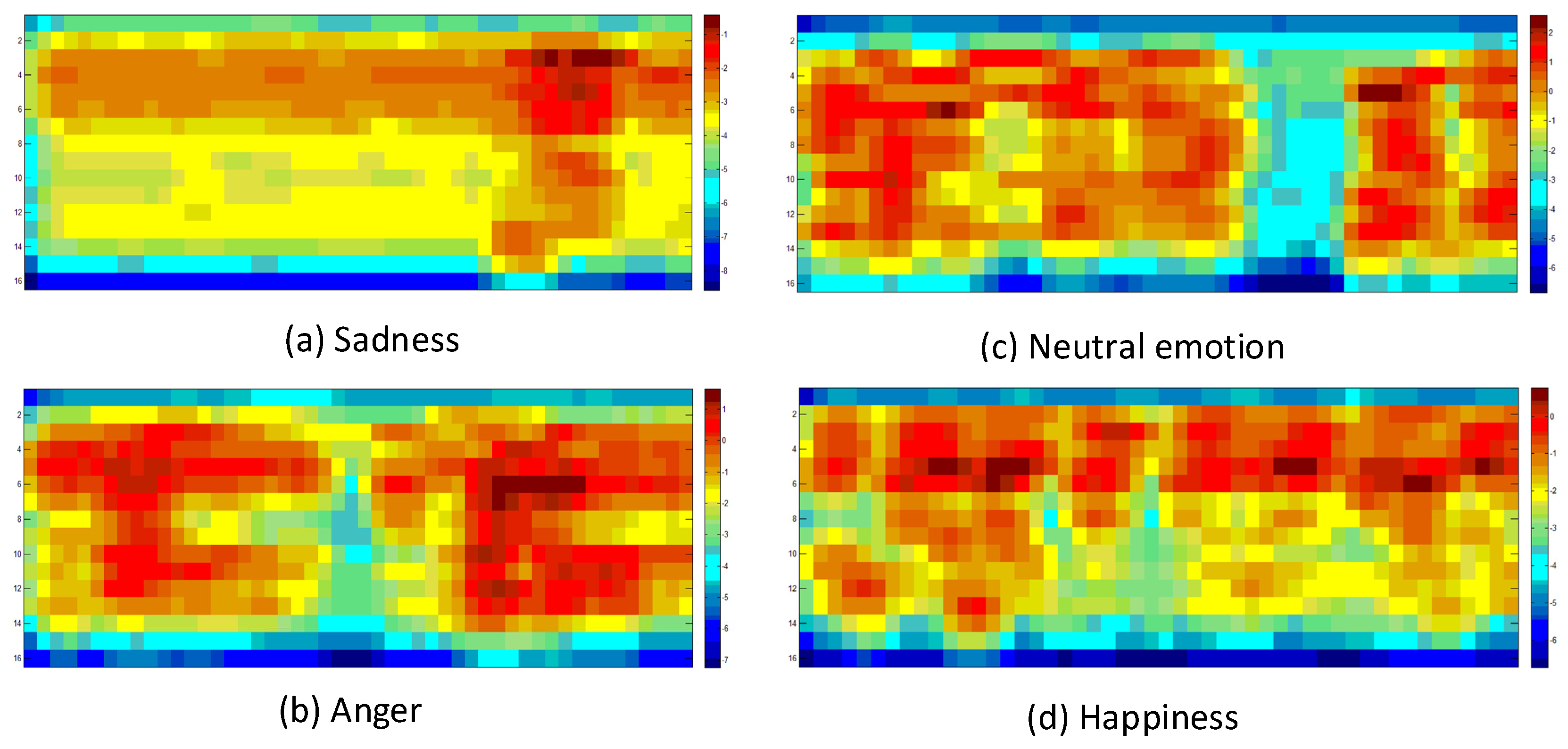
2.2. MCG feature representation of different emotions
3. Emotional recognition model
3.1. Overview of the emotion recognition model
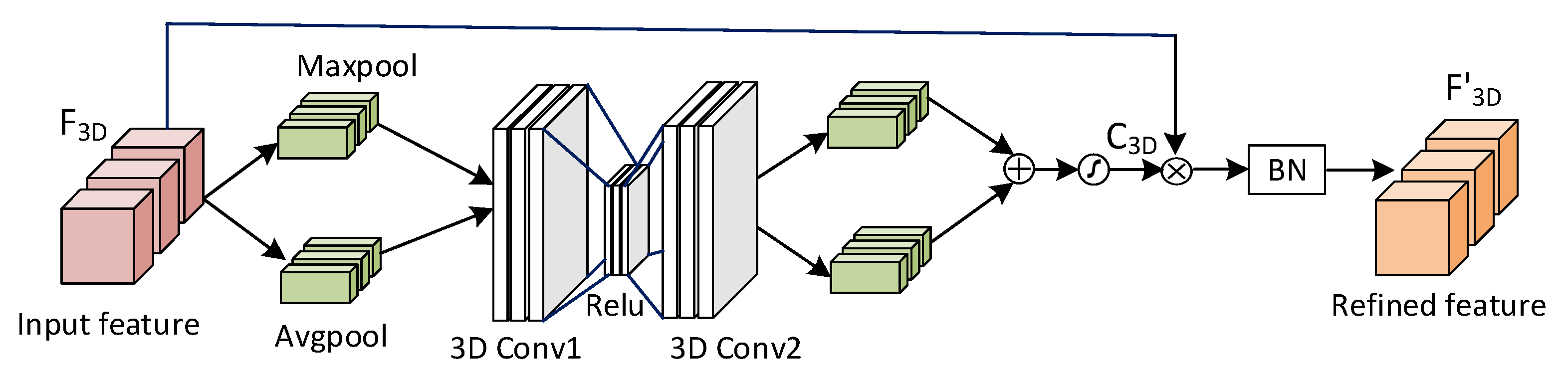
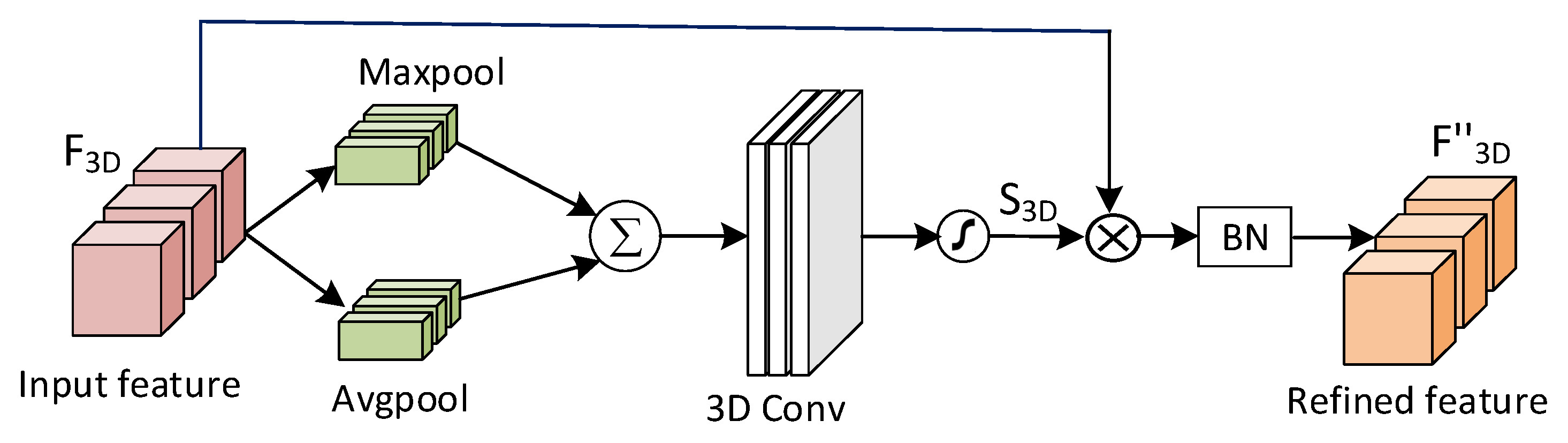
3.2. Channel-level attention
3.3. Spatial-level attention
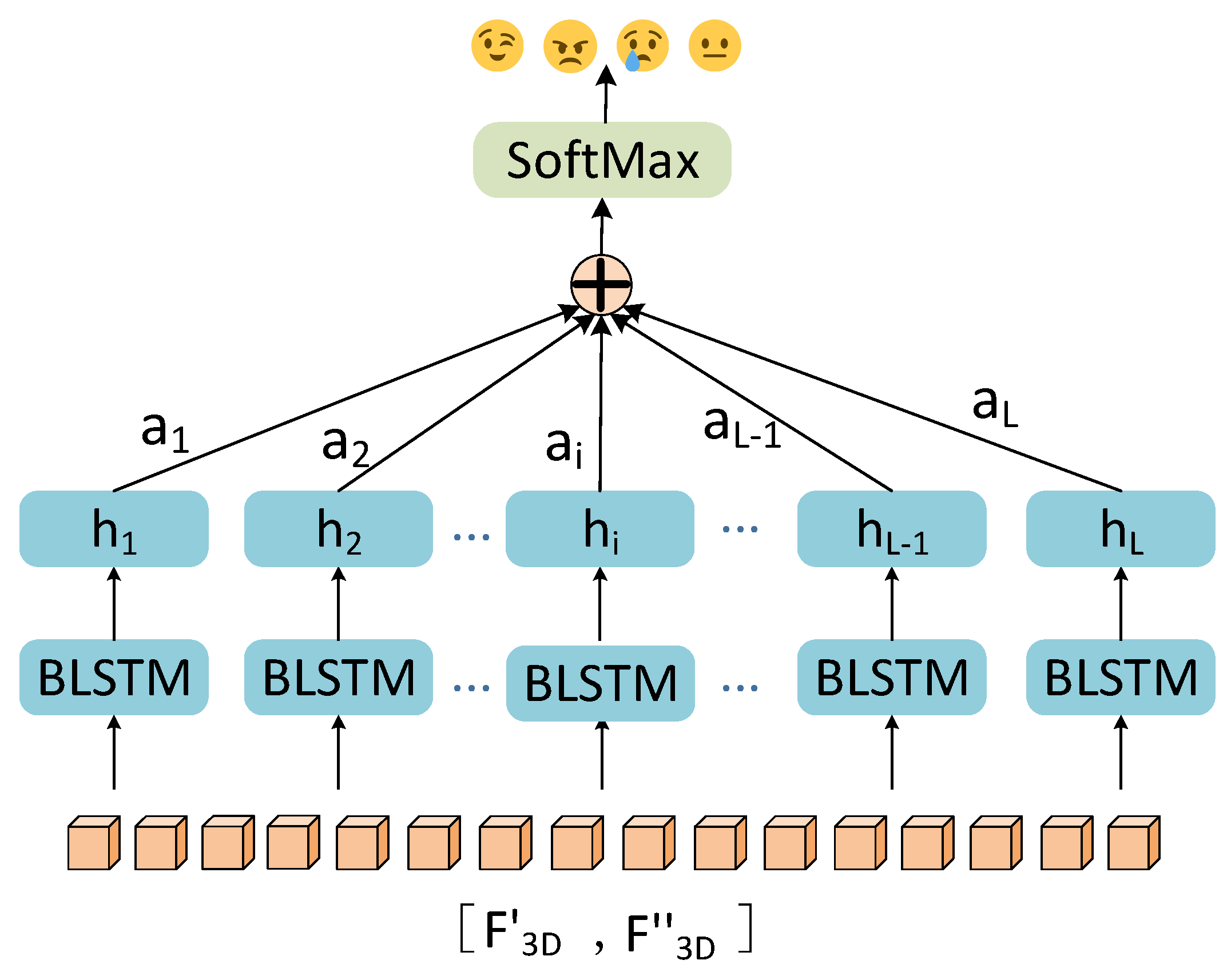
3.4. Temporal-level attention
4. Experimental results and analysis
4.1. Dataset description
4.2. Experimental setup
4.3. Experimental results analysis
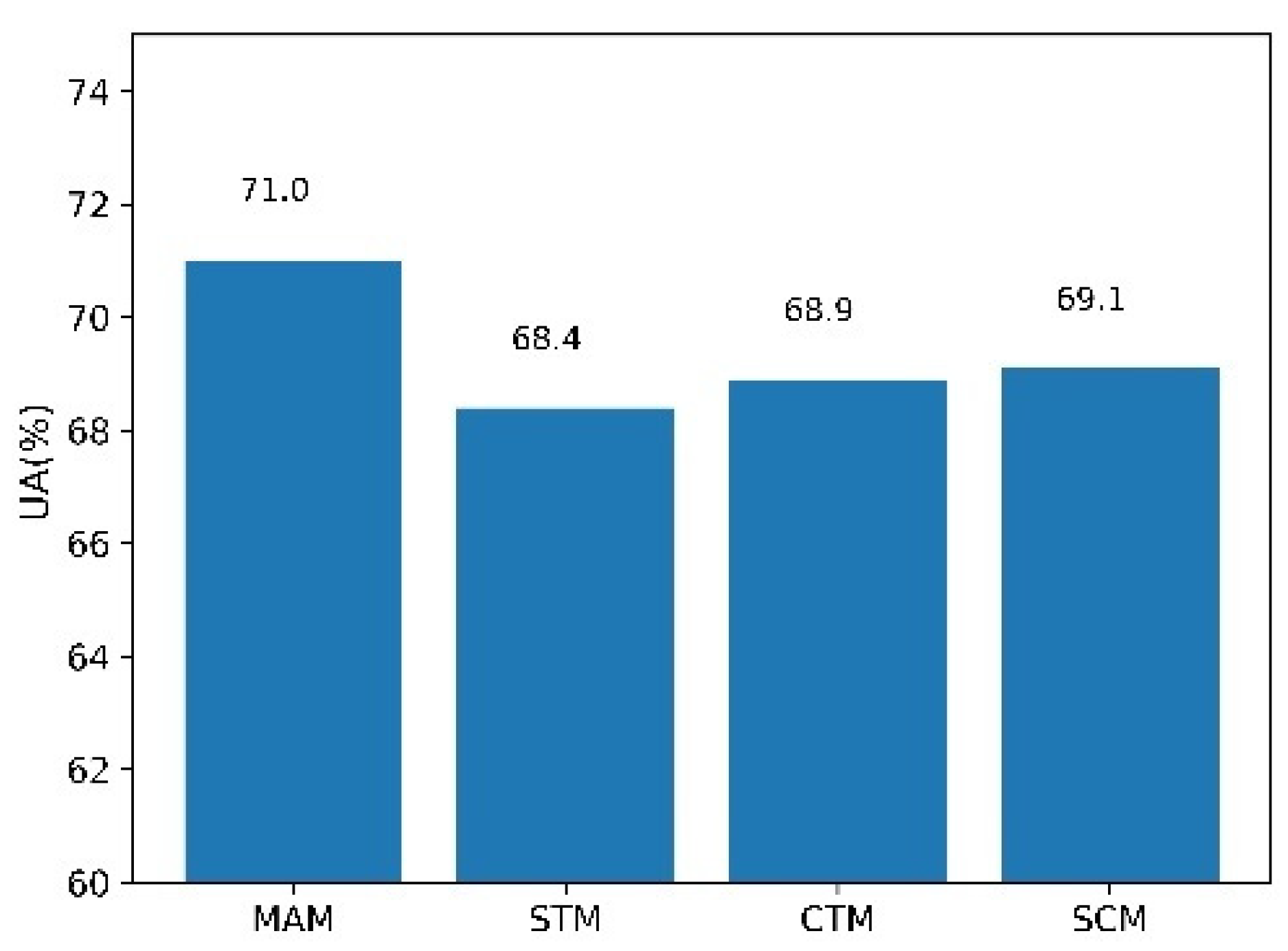
4.4. Ablation experiment
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, Y.; Lim, Y.; Tan, Y. A Novel Human Activity Recognition and Prediction in Smart Home Based on Interaction. Sensors 2019, 19, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K. Han, D. Yu, and I. Tashev, “Speech emotion recognition using deep neural network and extreme learning machine,” 2014.
- M. Neumann and N. T. Vu, “Attentive convolutional neural network based speech emotion recognition: A study on the impact of input features, signal length, and acted speech,” Proc. INTERSPEECH 2017 18th Annu. Conf. Int. Speech Commun. Assoc., vol. 2017-Augus, no. 3, pp. 1263–1267, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Dong, M.; Huang, Z.; Zhan, Y. Learning Salient Features for Speech Emotion Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2014, 16, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- W. Lim, D. Jang, and T. Lee, “Speech emotion recognition using convolutional and Recurrent Neural Networks,” Proc. 8th Asia-Pacific Signal Inf. Process. Assoc. Annu. Conf., pp. 1–4, 2016. [CrossRef]
- El Ayadi, M.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. Survey on speech emotion recognition: Features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Chen, Y. Wang, and D. Wang, “A feature study for classification-based speech separation at low signal-to-noise ratios,” IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, Lang. Process., vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 1993–2002, 2014.
- Santoro, R.; Moerel, M.; De Martino, F.; Goebel, R.; Ugurbil, K.; Yacoub, E.; Formisano, E. Encoding of Natural Sounds at Multiple Spectral and Temporal Resolutions in the Human Auditory Cortex. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Nishino, Y.; Miyauchi, R.; Unoki, M. Study on linguistic information and speaker individuality contained in temporal envelope of speech. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2016, 37, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.H.; Simoncelli, E.P. Sound Texture Perception via Statistics of the Auditory Periphery: Evidence from Sound Synthesis. Neuron 2011, 71, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Falk, T.H.; Chan, W.-Y. Automatic speech emotion recognition using modulation spectral features. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 768–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.R.; Akhtar, Z.; Santos, J.F.; Oshaughnessy, D.; Falk, T.H. Feature Pooling of Modulation Spectrum Features for Improved Speech Emotion Recognition in the Wild. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 12, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Dang, J.; Unoki, M.; Akagi, M. Multi-resolution modulation-filtered cochleagram feature for LSTM-based dimensional emotion recognition from speech. Neural Networks 2021, 140, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluhaidan, A.S.; Saidani, O.; Jahangir, R.; Nauman, M.A.; Neffati, O.S. Speech Emotion Recognition through Hybrid Features and Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. Keren and B. Schuller, “Convolutional RNN: An enhanced model for extracting features from sequential data,” Proc. Int. Jt. Conf. Neural Networks, vol. 2016-Octob, pp. 3412–3419, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Satt, S. Rozenberg, and R. Hoory, “Efficient emotion recognition from speech using deep learning on spectrograms,” Proc. Interspeech 2017, pp. 1089–1093, 2017.
- S. Mirsamadi, E. Barsoum, and C. Zhang, “Automatic speech emotion recognition using recurrent neural networks with local attention,” in in Proc. 40th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2017, pp. 2227–2231.
- Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Unoki, M.; Dang, J.; Akagi, M. Speech Emotion Recognition Using 3D Convolutions and Attention-Based Sliding Recurrent Networks With Auditory Front-Ends. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 16560–16572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Hu, L. Shen, and G. Sun, “Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks,” CoRR, vol. abs/1709.0, 2017, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507.
- Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Lei, Y. SK-Net: Deep Learning on Point Cloud via End-to-End Discovery of Spatial Keypoints. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 6422–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, B. Wu, P. Zhu, P. Li, W. Zuo, and Q. Hu, “Supplementary material for ‘ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks,” in Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020, pp. 13–19.
- Xu, K.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.C. A2-Net: Molecular Structure Estimation from Cryo-EM Density Volumes. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Xue, C. Liu, F. Wan, J. Jiao, X. Ji, and Q. Ye, “Danet: Divergent activation for weakly supervised object localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019, pp. 6589–6598.
- S. Woo, J. Park, J.-Y. Lee, and I. S. Kweon, “Cbam: Convolutional block attention module,” in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 3–19.
- W. Ma et al., “TripleNet: Triple attention network for multi-turn response selection in retrieval-based chatbots,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv1909.10666, 2019.
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, T.; Hu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X. TANet: Robust 3D Object Detection from Point Clouds with Triple Attention. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 11677–11684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xu, X.; Tao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zou, C. Convolutional-Recurrent Neural Networks With Multiple Attention Mechanisms for Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 14, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X. Li, B. Zhao, and X. Lu, “MAM-RNN: Multi-level attention model based RNN for video captioning,” IJCAI Int. Jt. Conf. Artif. Intell., pp. 2208–2214, 2017.
- H. Zou, Y. Si, C. Chen, D. Rajan, and E. S. Chng, “Speech emotion recognition with co-attention based multi-level acoustic information,” in ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2022, pp. 7367–7371.
- Glasberg, B.R.; Moore, B.C. Derivation of auditory filter shapes from notched-noise data. Hear. Res. 1990, 47, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.-C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Evaluation 2008, 42, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Schuller, S. Steidl, and A. Batliner, “The interspeech 2009 emotion challenge,” 2009.
- F. Eyben, M. Wöllmer, and B. Schuller, “Opensmile: the munich versatile and fast open-source audio feature extractor,” in Proc. 18th ACM int. conf. Multimedia, 2010, pp. 1459–1462.
- G. Ramet, P. N. Garner, M. Baeriswyl, and A. Lazaridis, “Context-aware attention mechanism for speech emotion recognition,” in 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), 2018, pp. 126–131.
- Chen, M.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. 3-D Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks With Attention Model for Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Q. Learning multi-scale features for speech emotion recognition with connection attention mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 214, 118943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| FEATURE | UA |
| MFCC | 58.5 |
| emobase2010 | 60.9 |
| IS09 | 58.4 |
| MSF | 59.7 |
| Spectrogram | 61.6 |
| Cochleagram | 62.1 |
| MCG | 63.8 |
| METHOD | UA |
| 3D CRNN-max-pooling | 67.5 |
| 3D CRNN-attention | 67.8 |
| Triple-attention | 69.4 |
| Proposed method | 71.0 |
| Literature | Features | Models | UA |
| Ramet et al.[34] | LLDs | ARNN | 63.7 |
| Mirsamadi et al.[17] | MFCC and spectrum | ARNN | 58.8 |
| Chen et al.[35] | Spectrogram | ACRNN | 64.74±5.44 |
| Peng et al. [18] | Modulation spectrum | ASRNN | 62.6 |
| Zou et al.[29] | wav2vec2 | Co-attention | 68.65 |
| Jiang et al.[27] | Mel-spectrum | CRNN-MA | 60.6 |
| Chen et al. [36] | Spectrogram and LLDs | AMSNet | 70.51 |
| Our work | MCG | MAM | 71.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





