1. Introduction
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an ongoing viral pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The main transmission route of this virus is inhalation of contaminated respiratory droplets; however, other modes of transmission for SARS-CoV-2 have also been described [
1]. The disease is common, as most patients are asymptomatic or may have common symptoms, such as fever, sore throat, rhinorrhea, cough, muscle aches, headache, shortness of breath, and gastrointestinal symptoms. The risk of hospitalization and mortality varies based on the virus variant, immune status, ethnicity, body mass index, gender and underlying diseases [
2,
3].
Studies on COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 infection in children are limited. The first confirmed cases of the novel coronavirus infection in children and neonates were reported in China in January 2020[
4]. Although some epidemiological studies showed that children are at lower risk of COVID-19 infection compared with adults [
5,
6], recent findings have demonstrated the existence of a similar viral load and possibly a similar secondary infection rate in children, suggesting that self-isolation and school closure may be the reason for the lower frequency of infection in this population [
7,
8,
9]. Infected households can transmit SARS-CoV-2 to children in all age groups [
10]; however, children are less affected by COVID-19, resulting in a small proportion of symptomatic infections characterized by generally milder symptoms [
11]. In the US, the overall cumulative COVID-19-associated hospitalization rate among children aged 0–17 years during March 1, 2020–August 14, 2021, was 49.7 per 100,000 population, which resulted in death in 0.7–1.8% of them [
12]. The presence of untrained T lymphocyte cells against the virus and fewer ACE2 receptors in the nose of children were suggested as reasons for the lower frequency of symptoms in children [
13,
14]. Although these findings support that children could play a role in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 into their households, their role in the household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 as the primary source was not confirmed by some other studies [
15].
Although common symptoms of COVID-19 in children are fever and cough, other complications including headache, nasal discharge, anosmia and abdominal symptoms were reported less frequently [
16]. These symptoms are self-limited and the patients recover with few hospitalizations. Risk factors for severe disease with SARS-CoV-2 among children are not well known; however, multiple co-morbidities, like cardiovascular, neurological, and gastrointestinal conditions, may be involved [
17]. In a study in Brazil, it was shown that disease severity in children was also correlated with both social and economic status [
18]. This diversity could be related to genetics, type of virus variant, immunity, and contact status. More detailed studies are needed to establish this correlation in other populations, especially in children with specific comorbidities and those in different age groups.
With 7,563,728 reported cases, including 144,744 deaths (27 January 2023), Iran is the country most affected by COVID-19 among the Eastern Mediterranean Region of the WHO, both in the number of cases and death rates [
19]. However, local and global data about the incidence and prevalence of COVID-19 are scarce among children in comparison to other age groups [
20,
21,
22]. In a serosurvey in 18 cities of Iran during the first COVID-19 wave in 2020, in which participants <19 years of age constituted only 1.7% of the sample, a population-weighted seroprevalence of 15.4% was reported [
21]. In a subsequent study conducted during the third COVID-19 wave in 16 cities of Iran, with only 5% of the participants being children ≥10–19 years of age, a higher population-weighted seroprevalence of 29.7% was reported [
20].
There are few data about the proportion of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 infections and their associations with demographics, seasonality, underlying diseases and socioeconomic status in children. Accordingly, implementation of a community-based surveillance study using both serological and molecular methods could provide valuable data. This study aimed to investigate the seroprevalence and RT-qPCR positivity of SARS-CoV-2 among children in Tehran before the introduction of the COVID-19 vaccine, between 19 September 2020 and 21 June 2021. Moreover, associations of SARS-CoV-2 infection with demographic data and the reported symptoms were analysed in this population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
To determine the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies and active SARS-CoV-2 infections in children of Tehran during autumn 2020, winter 2020–2021 and spring 2021, we used a cross-sectional design. To estimate sample size according to SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence, calculations were done with different scenarios considering the prevalence of 5 to 50 percent with a precision of 5 to 10 percent (95% confidence interval width). Accordingly, 1574 participants was determined as the maximum required sample size. Due to concerns about study participants attending public health centres and the expected low response rate during the pandemic, three different strategies were used to increase participation. For the first strategy, information on the study and a link for voluntary participation was provided to Tehran residents using “Snapp”, a ridesharing application with 2 million customers in Tehran (SNAPP strategy unit, Iran Internet Group). Upon registration, participants provided consent for participation in this study, as well as their age and gender. Clustering of the registered families was done according to their recorded addresses and their distribution in the north, south, east, west, and central areas in 21 regions of Tehran. To increase the response rate, a phone call after initial registration, two reminder messages, a transportation discount, and a charge-free serological test for one of the parents were considered for the registered families. Sampling in public health centres, as the second strategy, was carried out according to available data from the Integrated Health System (SIB), the Iranian electronic health records system, to randomly select families who had children aged ≤14 years. Phone calls and reminder messages to selected families were used to increase the response rate. The third strategy was voluntary sampling of children who referred to the pediatric surgery and dentistry clinics in Mofid Children’s Hospital and healthy children who referred to private laboratories for a general checkup. During the study period, COVID-19 vaccines had not yet been approved for use in children in Iran. Vaccination of children aged 12–18 years started in September 2021[
23].
2.2. Participants
Children residing in Tehran and aged 0 to 14 years at the time of recruitment were considered eligible to participate. Their parents or guardians signed a consent form before sampling. Families who refused to give informed consent, or declared a contraindication to venipuncture, were excluded from the study. An orally administered questionnaire was used by physicians and trained staff to collect information from children, parents, or their guardians. The questions covered demographics (age, gender), household size, exposure to either suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19, recent travelling, underlying diseases, history of positive SARS-CoV-2 tests, COVID-19 symptoms, and socioeconomic status. The existence of fever (>38 oC) and/or cough and/or diarrhea, defined as cardinal syndromes, in the presence or absence of other symptoms of COVID-19 in children (sore throat, fatigue, rhinorrhea, stomachache, headache, nausea/vomiting, wheeze, dyspnea, myalgia, chest pain, and change in smell or taste), defined as common COVID-19 symptoms, were considered as indicative for the statistical analysis [
24]. The results of the SARS-CoV-2 tests and general clinical explanations were provided to all participants 24 hours post sampling.
2.3. Sampling
Blood and nasopharyngeal swab samples were obtained from each child and transported under cold chain conditions within 6 hours to the laboratory. Blood samples were obtained by venipuncture and transferred into serum separator gel tubes. All swab samples were transported in viral transportation media. Serum samples were prepared after centrifugation and stored at -70 oC until use. RNA extraction of swab samples was done using a High Pure Viral RNA extraction kit (Roche, Germany). The RNA extracts were stored at -70 oC until use for real time PCR.
2.4. Serology tests
Infected people with SARS-CoV-2 generally develop antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 antigens within 1–2 weeks of exposure, irrespective of age [
25]. To measure history of infection with SARS-CoV-2, IgG antibody against the S1 domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was measured using an anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody kit (Euroimmun, Lübeck, Germany). Interpretation of results was done according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The collected samples with either positive or borderline results were rechecked when possible with a WANTAI SARS-CoV-2 Ab Elisa kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (WANTAI BioPharm, China).
2.5. Reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
Infection with SARS-CoV-2 during the sampling period was detected using a commercial kit (COVID-19 One step RT-qPCR, Pishtaz Teb Diagnostics, Iran). Two genomic loci of SARS-CoV-2, RdRp and N genes, and a human endogenous control gene for quality control were targeted to confirm the infection. The cycle threshold was calculated for each gene and results were interpreted according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6. Statistical analysis
For data clearance, we checked the “missing completely at random” (MCAR) assumption. The MCAR assumption was rejected according to the significant result of Little’s MCAR test. So, assuming that the pattern of data missingness matched the “Missing at random” (MAR), missing imputation was performed with the EM estimation. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (version 25; IBM Corp., Armonk, N.Y., USA) was used to carry out single imputations of variables with missing values.
The seroprevalence was estimated as the proportion of seropositive children with IgG SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. The prevalence of active SARS-CoV-2 infection was estimated as the proportion of children testing positive with RT-qPCR. For data weighting by age-gender-season (two categories for gender and three categories for age, three categories for season), we used population data from the 2016 census available from the Statistical Centre of Iran [
26]. Frequency weights were calculated by dividing the size of the actual population in Tehran in each category by the number of participants in our study in the same categories. Analysis of survey data was performed with STATA version 14.2 (College Station, TX, USA). For descriptive data analysis we report percentages with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI); however, because of intermittent epidemics over time, frequencies are reported by season. We used multivariable logistic regression analysis to evaluate associations between SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity and RT-qPCR positivity and demographics and potential risk factors. To adjust for confounding we compared results from the univariable and multivariable analysis. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
2.7. Ethics Statements
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (Code: IR.SBMU.RICH.REC.1399.050). Informed consent was confirmed by the IRB.
3. Results
Overall, 1517 children in Tehran provided pairs of sera and naso-pharyngeal swab samples and answered the questionnaire during the study period (356 children in autumn 2020, 551 during winter 2020–2021, and 610 in spring 2021). In total, 1034 (68.2%) participants were boys, and 906 (60%) children were 4 years old or younger. Characteristics and related data about socioeconomic status and household size are shown in
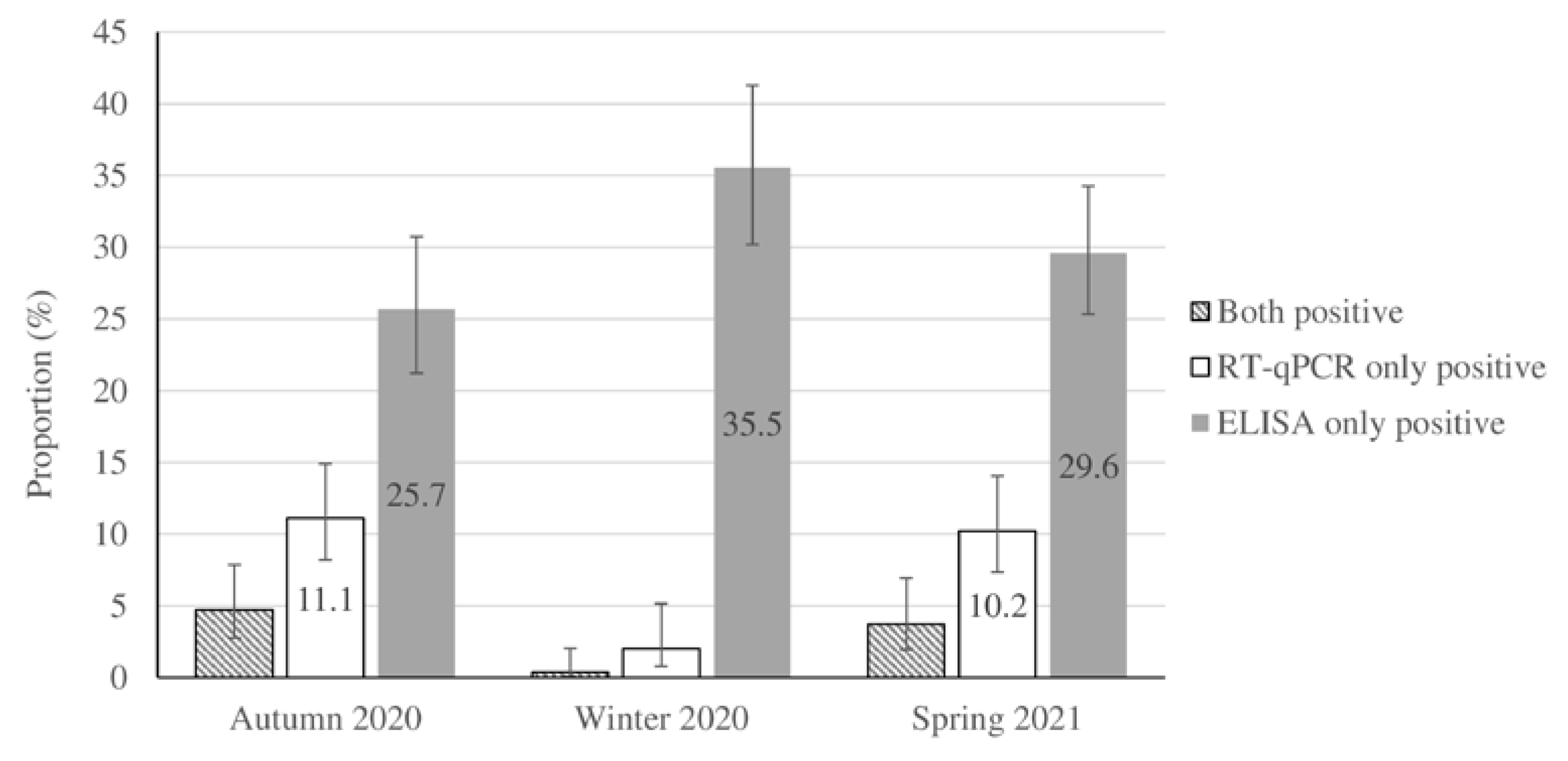
Table 1. Of the 728 participants (48% of study sample) who provided information about their geographic location, 18.8% originated from the northern, 33.2% from the southern, 36.6% from the western and 13.2% from the northern areas of Tehran. Around 13.3% of children (202/1517) recorded a history of contact with suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19. Household members constituted 60% (121/202) of the contacts in children with a positive-contact history. According to the laboratory tests, 464 cases were ELISA-only positive, 101 cases were RT-qPCR-only positive, and 34 cases presented positive ELISA and RT-qPCR results. Seropositivity and RT-qPCR positive test results accounted for 33.2% and 10.7% of the weighted population. The cardinal (fever >38 oC and/or cough and/or diarrhea) and common COVID-19 symptoms (sore throat, fatigue, rhinorrhea, stomachache, headache, nausea/vomiting, wheeze, dyspnea, myalgia, chest pain, and change in smell or taste) were detected in 44.8% and 22.4% of the population-weighted RT-qPCR-confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 respectively, while asymptomatic infection was detected in 32.9% of them (
Table 2). The seasonal distribution and population-weighted prevalence of RT-qPCR positivity and seropositivity for the studied samples are shown in
Figure 1 and supplementary material
Table S1. The results of the Euroimmun kit were confirmed by the Wantai kit with a positive predictive value of 91.2% (187/205).
In our study, the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG seropositivity was not associated with gender, season, socioeconomic status, household size, or contact with a healthcare worker who was a household family member. However, SARS-CoV-2 IgG seropositivity was associated with older age (10–14 years age) as compared to younger children (0–4 years old) (OR 1.53, 95% CI 1.08–2.17) (
Table 3).
The prevalence of RT-qPCR positivity was higher in spring 2021 compared to winter 2020–2021 (OR 6.57, 95% CI 2.60–16.57), and higher in symptomatic children compared to asymptomatic participants (OR of 4.62 and 2.11 for the cardinal and common COVID-19 symptoms, respectively) (
Table 4). According to the multivariable data analysis, RT-qPCR positivity was higher among children in the low socioeconomic group, and participants with smoking parents had lower odds of RT-qPCR positivity compared to those with non-smoking parents (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.36–1.08).
4. Discussion
This study provides data on the seroprevalence and RT-qPCR positivity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and their association with demographics (age, sex), season, socioeconomic status, and COVID-19 symptoms among children ≤14 years of age. Our findings confirm that the infection can present either as asymptomatic or symptomatic in children. These results indicate that children can play a role as a silent reservoir of SARS-CoV-2 in the community. In a similar study in Brazil in 2020, about 15% of children were reported as asymptomatic [
27]. Similarly, the pooled proportion of test-positive asymptomatic children from 13 different studies was estimated as 21.1% (95% CI: 14.0–28.1%) in a literature review [
28].
In the present study, a relative increase in seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 was observed in children in the older age groups. In a study conducted in 2021 in Italy, the seroprevalence in the age groups younger than 5 years, 6–11 and 12–17 years was reported as 18%, 37.6% and 43.7%, respectively [
29]. In the United States, a study conducted between April and May 2020 reported a seroprevalence of 0.8% and 4.5% in children >4 and 5–14 years of age, respectively [
30]. A study in Switzerland reported a higher seroprevalence in 10–19-year-old children (9.6%) compared with the 5–9-year-old group (0.8%)[
31].
In the present study, there was no difference in seropositivity or RT-qPCR positivity between girls and boys. A slightly higher frequency of infection (RT-qPCR positivity) among boys was reported in a study in China (19.5% in boys compared to 14.5% in girls) [
32]. In contrast, a relatively higher frequency of infection among girls was reported in a study in the United States (11.8% vs 10.1% in boys) [
33].
In this study, the rate of SARS-CoV-2 infection estimated using serological and molecular methods in children was not significantly associated with a larger household size; however, seropositivity was relatively higher in children from more crowded families (OR of 1.24 and 1.34 in families with 4 and >4 members). A study in Brazil in 2021 reported a higher prevalence of infection in families with more than three members (29.8%) compared to fewer members (23%) [
27]. A higher secondary attack rate was reported in a study in Norway among families with more than six family members (25% from parents to children). The study showed higher secondary transmission in larger families, with more contact with family members and more cramped living conditions favouring infection in children [
34]. In a study in Iran, 31% of affected children had a history of contact with a suspected or infected family member [
35]. In this study, a slight difference (3.8%) was observed in the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR positivity in children of medical staff compared to other occupations, although this difference was not statistically significant. According to a study conducted in Madrid among families of medical staff, a secondary attack rate of 43.7% was reported for medical staff’s children, which varied based on the infection status in their family members [
36]. Similarly, in a study in London, higher seropositivity was detected in children of medical staff (45%) compared with those belonging to non-medical staff families [
37]. Higher exposure to COVID-19 patients appears to be the main risk factor for secondary transmission of SARS-CoV-2 to family members in this population.
In the present study, the highest seroprevalence was detected in winter and spring 2021 and a significantly lower percentage of positive samples was found autumn 2020. Seasonal alteration of SARS-CoV-2 prevalence was similarly reported in a study in children <18 years of age in the United States in 2020[
33]. The increase in the number of positive serological cases during the study seems to be due to the cumulative increase in the number of infected patients in the community following the pandemic. According to the PCR results, a higher prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection was detected in spring 2021, which was consistent with the early course of a new wave of pandemic caused by the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 (Supplementary material
Figure S1) [
38].
This study had limitations. Selection bias was introduced by sampling in different settings, and assessment in private laboratories, outpatient clinics and public health centres. Dissatisfaction and unawareness of the parents resulted in missing data for some questions. Willingness to participate in this study was low, due to fear of attending hospitals/public health centres, incorrect opinions about the minor impact of COVID-19 on children during the primary course of sampling, fear of blood sampling in children despite offering incentives to the parents involving free-of-charge serological tests and a transportation discount. The greater rate of participation of symptomatic families during the peaks, issues related to self-reporting for socioeconomic status and some other variables like symptoms are among other limitations in this study.
5. Conclusion
The special feature of this SARS-CoV-2 study is its large sample size in a specific population, namely children up to 14 years of age in Tehran, which had previously been studied only to a limited extent. During the study period, both high seroprevalence and high SARS-CoV-2 prevalence were observed in children. Children in the older age group who were in contact with suspected or confirmed cases within the household and those living in families with a lower socioeconomic status were more likely to be infected with SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 infection occurred in children in the presence or absence of cardinal or common COVID-19 symptoms. Although seasonality was confirmed based on the RT-qPCR positivity results, no significant change in the seropositivity rate was detected in different seasons in this study. Further studies are needed to increase awareness regarding the control of COVID-19 in children.
Supplementary Materials
Figure S1: Reported COVID-19 cases from February 2020 to October 2022 in Iran; Table S1: Prevalence of COVID-19 positive cases in children during autumn 2020 to spring 2021 in Teheran; Table S2: Participants’ characteristics by the site of sampling in Tehran, from autumn 2020 to spring 2021.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: R.MG, I.B, A.K., M.A.; Data curation: AR.S., N.M., A.A., I.B., HR.B, M.A.; Formal analysis: AR.S., I.B., HR.B., M.A.; Investigation: R.MG., I.B., AR.S., A.K., A.A., N.M., MH.R., N.P., S.J., L.A., H.K., F.F, T.E., A.J., HR.B., M.M.O., SM., A.E., M.A.; Methodology: A.A., N.M., I.B., AR.S., MH.R., HR.B., MH.R., N.P., S.J., M.A.; Project administration: R.MG., I.B., M.A.; Resources: R.MG, I.B., M.A., A.K, T.E, A.J; Supervision: R.MG, I.B., M.A.; Validation: I.B, AR.S., M.A.; Visualization: AR.S, HR.B., M.A; Writing – original draft: M.A.; Writing – review & editing: AR.S, I.B., R.MG., M.A.
Funding
The Robert Koch Institute (Germany) supported this study by providing diagnostic material through a special COVID pandemic grant from the German Ministry of Health. The study was also supported by the Pediatric Infection Research Centre, Iran (Grant No. 563), and in part by the World Health Organization, Country Office, Islamic Republic of Iran. The APC was funded by Robert Koch Institute, Germany”.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this study would like to thank all participating children, parents and guardians of the children, and express their gratitude to the colleagues of health centres and the president and vice presidents of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences; directors and managers of the Mofid Children’s Hospital; the strategic management team of SNAP; the international unit of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences; the international unit of the Ministry of Health, Treatment and Medical Education (MoHME); Office of Global Health Cooperation in Iran; Communicable Diseases Management Department, (MoHME); colleagues of Tajrish Lab., Medical Lab., Mazda Lab. and Vahidiya Pathobiology Laboratories. The authors would also like to thank Dr. Christoph Hamelmann, former Representative, and Dr. Omid Zamani from Universal Health Coverage for Communicable Diseases (UHC:CD), World Health Organization, Country Office, Islamic Republic of Iran.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: implications for infection prevention precautions: scientific brief, 09 July 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/333114 (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Twohig, K.A.; Nyberg, T.; Zaidi, A.; Thelwall, S.; Sinnathamby, M.A.; Aliabadi, S.; Seaman, S.R.; Harris, R.J.; Hope, R.; Lopez-Bernal, J.; et al. Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study. The Lancet. Infectious diseases 2021, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijls, B.G.; Jolani, S.; Atherley, A.; Dijkstra, J.I.R.; Franssen, G.H.L.; Hendriks, S.; Yi-Wen Yu, E.; Zalpuri, S.; Richters, A.; Zeegers, M.P. Temporal trends of sex differences for COVID-19 infection, hospitalisation, severe disease, intensive care unit (ICU) admission and death: a meta-analysis of 229 studies covering over 10M patients. F1000Research 2022, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourian, M.; Ghandi, Y.; Habibi, D.; Mehrabi, S. COVID-19 infection in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical features and laboratory findings. Archives de pediatrie : organe officiel de la Societe francaise de pediatrie 2021, 28, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Helgason, A.; Jonsson, H.; Magnusson, O.T.; Melsted, P.; Norddahl, G.L.; Saemundsdottir, J.; Sigurdsson, A.; Sulem, P.; Agustsdottir, A.B.; et al. Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Icelandic Population. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 382, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, O.; Li, J.; Tang, K.; Wang, Z.; Bhutta, Z.A. Risk of infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children and adolescents in households, communities and educational settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of global health 2021, 11, 05013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald-Sargent, T.; Muller, W.J.; Zheng, X.; Rippe, J.; Patel, A.B.; Kociolek, L.K. Age-Related Differences in Nasopharyngeal Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Levels in Patients With Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA pediatrics 2020, 174, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonker, L.M.; Neilan, A.M.; Bartsch, Y.; Patel, A.B.; Regan, J.; Arya, P.; Gootkind, E.; Park, G.; Hardcastle, M.; St John, A.; et al. Pediatric Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): Clinical Presentation, Infectivity, and Immune Responses. The Journal of pediatrics 2020, 227, 45–52.e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws, R.L.; Chancey, R.J.; Rabold, E.M.; Chu, V.T.; Lewis, N.M.; Fajans, M.; Reses, H.E.; Duca, L.M.; Dawson, P.; Conners, E.E.; et al. Symptoms and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Among Children - Utah and Wisconsin, March-May 2020. Pediatrics 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, V.T.; Yousaf, A.R.; Chang, K.; Schwartz, N.G.; McDaniel, C.J.; Lee, S.H.; Szablewski, C.M.; Brown, M.; Drenzek, C.L.; Dirlikov, E.; et al. Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from Children and Adolescents. New England Journal of Medicine 2021, 385, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F. Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta paediatrica (Oslo, Norway: 1992) 2020, 109, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahoy, M.J.; Ujamaa, D.; Whitaker, M.; O’Halloran, A.; Anglin, O.; Burns, E.; Cummings, C.; Holstein, R.; Kambhampati, A.K.; Milucky, J.; et al. Hospitalizations Associated with COVID-19 Among Children and Adolescents - COVID-NET, 14 States, March 1, 2020-August 14, 2021. MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report 2021, 70, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, C.A.; Preston-Hurlburt, P.; Dai, Y.; Aschner, C.B.; Cheshenko, N.; Galen, B.; Garforth, S.J.; Herrera, N.G.; Jangra, R.K.; Morano, N.C.; et al. Immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitalized pediatric and adult patients. Science Translational Medicine 2020, 12, eabd5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Arena, C.; Sovereto, D.; Caloro, G.A.; Dioguardi, A.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Innate Immunity in Children and the Role of ACE2 Expression in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Pediatr Rep 2021, 13, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Bloxham, C.J.; Hulme, K.D.; Sinclair, J.E.; Tong, Z.W.M.; Steele, L.E.; Noye, E.C.; Lu, J.; Xia, Y.; Chew, K.Y.; et al. A Meta-analysis on the Role of Children in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Household Transmission Clusters. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2021, 72, e1146–e1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viner, R.M.; Ward, J.L.; Hudson, L.D.; Ashe, M.; Patel, S.V.; Hargreaves, D.; Whittaker, E. Systematic review of reviews of symptoms and signs of COVID-19 in children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, R.; Yan, H.; Talawila Da Camara, N.; Smith, C.; Ward, J.; Tudur-Smith, C.; Linney, M.; Clark, M.; Whittaker, E.; Saatci, D.; et al. Which children and young people are at higher risk of severe disease and death after hospitalisation with SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and young people: A systematic review and individual patient meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 44, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Filho, P.R.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; Sposato, K.B.; Souza Tavares, C.S.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Fontes Leite, D.C.; de Paiva, S.M.; Santos, H.P., Jr.; Santos, V.S. Socio-economic inequalities and COVID-19 incidence and mortality in Brazilian children: a nationwide register-based study. Public health 2021, 190, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. COVID-19 Daily Updates Archive. Islamic Republic of Iran; WHO Iran Country Office, 2022; p. 812. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/images/stories/iran/covid-19-sit-reps/COVID-19-Update-220511.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Zamani, M.; Poustchi, H.; Mohammadi, Z.; Dalvand, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Motevalian, S.A.; Eslami, S.; Emami, A.; Somi, M.H.; Yazdani-Charati, J.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibody among urban Iranian population: findings from the second large population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustchi, H.; Darvishian, M.; Mohammadi, Z.; Shayanrad, A.; Delavari, A.; Bahadorimonfared, A.; Eslami, S.; Javanmard, S.H.; Shakiba, E.; Somi, M.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroprevalence in the general population and high-risk occupational groups across 18 cities in Iran: a population-based cross-sectional study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2021, 21, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalagi, K.; Gharibzadeh, S.; Khalili, D.; Mansournia, M.A.; Mirab Samiee, S.; Aghamohamadi, S.; Mir-Mohammad-Ali Roodaki, M.; Hashemi, S.M.; Tayeri, K.; Namdari Tabar, H.; et al. Prevalence of COVID-19 in Iran: results of the first survey of the Iranian COVID-19 Serological Surveillance programme. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2021, 27, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Country Office Annual Report 2021. Iran (Islamic Republic of). Available online: https://www.unicef.org/media/120701/file/Iran-(Islamic-Republic-of)-2021-COAR (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Panaro, S.; Cattalini, M. The Spectrum of Manifestations of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) Infection in Children: What We Can Learn From Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Frontiers in Medicine 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterfield, T.; Watson, C.; Moore, R.; Ferris, K.; Tonry, C.; Watt, A.; McGinn, C.; Foster, S.; Evans, J.; Lyttle, M.D.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in children: a prospective multicentre cohort study. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2021, 106, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Center of Iran. Census 2016- Detailed Results [Website]. Available online: https://www.amar.org.ir/english/Population-and-Housing-Censuses/Census-2016-Detailed-Results (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Afonso, E.T.; Marques, S.M.; Costa, L.D.C.; Fortes, P.M.; Peixoto, F.; Bichuetti-Silva, D.C.; Aredes, N.D.A.; Rosso, C.F.W.; Oliveira, F.D.S.; Fiaccadori, F.S.; et al. Secondary household transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children and adolescents: Clinical and epidemiological aspects. Pediatric pulmonology 2022, 57, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaythorpe, K.A.M.; Bhatia, S.; Mangal, T.; Unwin, H.J.T.; Imai, N.; Cuomo-Dannenburg, G.; Walters, C.E.; Jauneikaite, E.; Bayley, H.; Kont, M.D.; et al. Children’s role in the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review of early surveillance data on susceptibility, severity, and transmissibility. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 13903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comar, M.; Benvenuto, S.; Lazzerini, M.; Fedele, G.; Barbi, E.; Amaddeo, A.; Risso, F.M.; Strajn, T.; Di Rocco, P.; Stefanelli, P.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Italian pediatric population: a regional seroepidemiological study. Italian journal of pediatrics 2021, 47, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.K.; Janowski, A.B.; Danis, J.E.; Harvey, I.B.; Zhao, H.; Dai, Y.N.; Farnsworth, C.W.; Gronowski, A.M.; Roper, S.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children and Adults in St. Louis, Missouri, USA. mSphere 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringhini, S.; Wisniak, A.; Piumatti, G.; Azman, A.S.; Lauer, S.A.; Baysson, H.; De Ridder, D.; Petrovic, D.; Schrempft, S.; Marcus, K.; et al. Seroprevalence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies in Geneva, Switzerland (SEROCoV-POP): a population-based study. Lancet 2020, 396, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Mo, X.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, S. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics 2020, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, C.V.; Drobeniuc, J.; Kittle, T.; Williams, J.; Byers, P.; Satheshkumar, P.S.; Inagaki, K.; Stephenson, M.; Kim, S.S.; Patel, M.M.; et al. Estimated SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Among Persons Aged <18 Years - Mississippi, May-September 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report 2021, 70, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telle, K.; Jørgensen, S.B.; Hart, R.; Greve-Isdahl, M.; Kacelnik, O. Secondary attack rates of COVID-19 in Norwegian families: a nation-wide register-based study. European journal of epidemiology 2021, 36, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Shervin Badv, R.; Navaeian, A.; Pourakbari, B.; Rostamyan, M.; Sharifzadeh Ekbatani, M.; Eshaghi, H.; Abdolsalehi, M.R.; Alimadadi, H.; Movahedi, Z. The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Children: A Study in an Iranian Children’s Referral Hospital. Infect Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Sainz, T.; de Felipe, B.; Alcolea, S.; Olbrich, P.; Goycochea-Valdivia, W.A.; Escosa-García, L.; Cobo, L.; Calvo, C.; Neth, O. High Rates of SARS-CoV-2 Family Transmission in Children of Healthcare Workers During the First Pandemic Wave in Madrid, Spain: Serologic Study. The Pediatric infectious disease journal 2021, 40, e185–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladhani, S.N.; Andrews, N.; Aiano, F.; Baawuah, F.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; Brown, K.E.; Amirthalingam, G.; Ramsay, M.E.; Waterfield, T. Secondary Attack Rate and Family Clustering of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in Children of Healthcare Workers With Confirmed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Clin Infect Dis 2021, 73, e260–e263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikhi, F.; Yousefian, N.; Tehranipoor, P.; Kowsari, Z. Estimation of the basic reproduction number of Alpha and Delta variants of COVID-19 pandemic in Iran. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0265489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).