1. Introduction
To drive safely, the driver must be sufficiently aware of your surroundings, pay constant attention to the road and traffic, and be alert enough to react to unexpected circumstances [
1,
2]. Tasks that are directly related to maneuvering a vehicle are called basic driving activities [
3].
The lack of concentration of drivers remains one of the crucial factors that contribute to serious accidents and deaths on the road and continues to be a problem for international road safety measures, as they affect not only the driver, but also everyone else on the road [
4,
5]. Approximately 324,000 people were injured due to driver inattention in the United States in 2020, and more than 3,000 lost their lives, representing 8.1% of all fatal accidents in the country [
6,
7].
The term “driver fatigue” refers to a particular type of inattention that occurs when a driver reverses their focus from basic vehicle navigation tasks to concentrate on another activity [
8]. These distractions may come from more common activities, such as talking to other passengers and eating, as well as using mobile phones and systems [
9]. These activities can have different effects on drivers. From the point of view of support by measurement technologies, existing research indicates two main issues:
Detect anomalies in driver behavior to prevent an accident, personalized behavior measures driving style through face detection or Internet of Things (IoT) technologies [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14],
Monitor correct cognitive and safe driver behaviors with intelligent sensors and IoT to monitor the face, eyes, or movements of a driver’s entire body for a novel driver education process [
15].
Although there are two distinct categories, they have a lot in common; for example, they are recorded and classified within the framework of currently available technologies, and many activities can be divided into more than one of them. For example, the use of a device requires participation in all of these distractions, otherwise known as secondary driving activities. The cognitive distraction that occurs in the driver’s brain is the most difficult to identify. This phenomenon is also known as “looking, but not seeing”. The attention requirements of distracting work and the prevalence of multitasking among drivers are two fundamental elements of the problem of distributed driving safety [
16,
17,
18].
Task demand is the total amount of visual, physical, and cognitive resources required to perform the activity. The second issue is the frequency with which the drivers perform the task. Even a small task, but performed frequently, can pose a safety concern [
19,
20].
According to [
21,
22], the results suggest that activities that require the driver to look away from the road or perform manual tasks significantly increase the probability of a collision. The risk of a traffic accident increases by 2.05 when using a mobile phone, especially when dialing (x12) and sending messages (x6).
The long time spent looking away from the road also has a significant impact. According to some studies, taking your eyes off the road for more than two seconds significantly increases the probability of safety-critical events [
23]. In fact, the U.S. Department of Transportation advises against taking your eyes off the road repeatedly within 12 seconds while operating a motor vehicle [
24]. Recognition of human activity based on preconstructed groups of activities is a commonly used approach [
25,
26,
27,
28].
There are many well-described activities, mainly related to basic needs and daily life, e.g., breathing, eating, sleeping, and walking [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. Among the recognition of these activities, some were divided into even more detailed (complex activities), e.g., food was divided into food preparation, and food preparation was even more separated for the preparation of breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Applying the aforementioned convention, we decided to analyze and recognize the activities and scenarios that accompany the driving of a vehicle.
Exploring the problems further, the challenge was to recognize the road conditions under which the trip is taking place and to recognize if a person is improving their ability to park their car after the trip. To recognize the driving conditions, we had to obtain a huge amount of data. In this article, we will describe how the data and basic laws of physics were incorporated into the sensors in JINS MEME ES_R glasses) and how the data were obtained for analysis and classification [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38].
Electrooculography (EOG) is a technique that is based on electrical features generated by the eye. By measuring the voltage difference between the cornea and the retina, it aims to capture the movements of the eyes [
35]. JINS MEME ES_R Glasses (JINS Inc., Tokyo, Japan) is a smart glasses device that consists of a three-point electrooculography (EOG) and a six-axis inertial measurement unit (IMU) with a gyroscope and an accelerometer. They acquire ten channels: linear and angular acceleration on the X, Y, and Z axes, and four EOG channels: electric potentials on the right (EOG
) and left (EOG
) electrodes and the vertical (EOG
) and horizontal (EOG
) difference between them [
39,
40,
41].
According to [
40], data collected with smart glasses are useful for recognizing cognitive activity. In our study, we adopted the feature machine learning approach (automatic or manual sequencing) of the data sets analyzed to recognize the cognitive activity of drivers.
2. Related works
When looking for examples of similar studies to compare, it should be noted that in a ratio of four to one, articles were found dedicated to searching for anomalies such as drowsiness, fatigue, lack of driver concentration, and external factors associated with vehicle damage and atmospheric factors associated with driving conditions [
42,
43,
44].
In another study based on data tracking the head and eyes in driving simulation conditions, the activity of 73 people who performed various secondary tasks while driving was recorded. The results of this research improved performance classification through the development of new functions, in particular to assess the context of autonomous driving [
45]. Algorithms for the classification of eye movements were divided into methods based on statistical thresholds and probabilistic methods. Algorithms based on static thresholds are usually selected for the classification of tasks assigned to the person who performs them; in other words, they are limited in quantity.
Probabilistic methods were introduced to meet the challenge of automatic adaptation of many people as a result of various behaviors, for example, individual visual cues. Drowsiness while driving is a critical issue in the context of road safety. Several approaches have been developed to reduce the risk of driver drowsiness. Fatigue and drowsiness detection techniques are divided into three broad strategies, namely vehicle-based, physiological, and driver-based approaches. The article discusses the latest research on diagnosing driver drowsiness based on behavior, in particular changes in eye movements and facial features.
Another research project turned to a traffic surveillance system developed to detect and warn the vehicle driver of a degree of drowsiness or stress [
46,
47,
48]. A smartphone with a mobile application, using the Android operating system, was used to implement a human-computer interaction system. To detect drowsiness, the most important visual indicators that reflect the driver’s condition are the behavior of the eyes, the side and front of the head, and yawning. The system works well in natural light conditions and regardless of the use of accessories supplied by the driver, such as glasses, hearing aids, or a cap.
Due to the large number of road accidents in which drivers fall asleep, this project was implemented to develop methods to prevent napping by providing a non-invasive system that is easy to operate and without the need to purchase additional specialized equipment. This method was able to detect drowsiness with an efficiency of 93.4% [
49].
Another significant educational research experiment evaluated how an educational program affected the fatigue and conduct of teenage and adult drivers, as well as their performance and behavior during simulated night driving. A 4-week sleep program and a 4-week driving program were randomly assigned to 34 volunteers (aged 18 to 26). The findings imply that the educational program increases people’s awareness of sleepiness. Sleep and driving instruction can reduce the risks of young drivers becoming fatigued and suffering related accidents, but this requires a more comprehensive evaluation of their real driving abilities [
50].
Next, we consider a second group of studies related to eliminating typical driver behavior and IoT-based traffic management to increase road safety. IoT is an innovative design paradigm designed as a network of billions to trillions of tiny sensors communicating with each other to offer innovative solutions to problems in real time [
51]. These sensors form a network called the Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) to monitor the physical environment and distribute the collected data back to the base station via multiple hops.
WSN has the ability to collect and report data for a specific application. Location information plays an important role in various wireless sensor network applications. Therefore, such systems can improve driving safety. However, real-time monitoring of driving behavior and conditions is linked to various issues, including dizziness caused by long journeys, drastic changes in lighting, and reflections in driver’s glasses.
A Deep Learning approach was presented in [
52,
53,
54,
55] to address this problem, where the authors used a near-infrared (NIR) camera sensor to detect glances, as well as head and eye movements, without the need for user calibration at first. The proposed system was evaluated on a dedicated database, as well as on Columbia’s open dataset (The Face Tracer CAVE-DB database).
The driver’s gaze turned out to be an excellent way to create a system for driving intelligent vehicles. Due to the fashion for highly autonomous vehicles, the driver’s view can be useful in determining the time of transmission of the gesture from the driver to the traffic management system. Although there have been significant improvements in the personalization of driver vision assessment systems, a universal generalized system that is immutable for different perspectives and scales has not yet been developed. We are taking a step towards this general system using convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
Four popular CNN architectures dedicated to this task provide extensive results comparisons. Furthermore, various adjustments were made to the input image, as well as the impact of the image size on performance [
56,
57]. To train and test the network, a large collection of driving data was collected, consisting of 11 long recordings of driving activities for 10 people in 2 different cars. The models that performed best achieved a recognition accuracy of 95.2% at the time the tests were compared.
Finally, the best-performing model was compared with the publicly available Columbia Gaze dataset consisting of images of 56 people with different head positions and viewing directions. Without any training, the model successfully decoded different points of view from different data sets [
58].
2.1. Objective
The main purpose of the study was to examine what activity patterns can be classified as basic activities performed while driving a car and to determine whether it is possible to “extract them” from the signals obtained from the accelerometer, the EOG and the gyroscope installed in the JINS MEME ES_R smart glasses.
3. Materials and Methods
This section presents details on the sensor modalities that were used for data acquisition, discusses the data acquisition process, and explains the experimental settings.
Figure 1 shows all the steps in the process from data acquisition to evaluation, which has been extensively described in [
38,
59,
60].
3.1. Data Acquisition
We acquired the data set using JINS MEME smart glasses, which have a six-axis inertial measurement unit (IMU) that incorporates EOG, an accelerometer and a gyroscope [
41,
61]. Participants volunteered for the study and gave their informed consent.
The experiments were carried out in a simulated environment [
9,
62] as presented in
Figure 2.
The simulator consists of the following components:
-
a central unit equipped with:
- –
an Intel Core i7 processor,
- –
XFX RADEON HD 5770 1 GB graphic card with NVIDIA processor and 3D VISION system,
- –
4 GB memory,
- –
Gigabyte’s Ultra Durable 3 motherboard
a special construction made of steel,
a two-way adjustable seat,
a Logitech set: steering wheel, pedals, and gearbox,
3 LED 27 monitors suitable for long operation,
a sound system,
dedicated software “Nauka jazdy” (English: Driver training).
The study consisted of two independent experiments that were conducted separately. Both were completed using the JINS MEME ES_R software with the default settings. The EOG sampling rate was 200 Hz, the accelerometer sampling frequency was 100 Hz, and the accelerometer measurement range was . We synchronized all frequencies to 50 Hz. The signals were recorded simultaneously for each subject while they received voice commands during the driving simulation.
Nine subjects in total (five men and four women) volunteered to participate in the study. Six individuals, all graduate students in their 20s, four men, and two women, performed the fundamental driving tasks. In total, we collected 1200 samples of primary driver activities, evenly divided into classes that represent a different activity. Half of the samples were created by one participant, while the remaining samples were evenly distributed among the other subjects. For the secondary driver activities, we recorded 700 samples that were distributed equally among all classes. Four subjects, one male and three female, with ages ranging from 23 to 57 years, participated. One participant provided 100 samples, while the other participants each contributed 25. None of the subjects had vision problems. One subject participated in both data acquisitions (primary and secondary driver activities). All participants agreed to participate in this study and use the results for research purposes. In total, 2100 samples were collected for this investigation.
3.1.1. Scenarios
The tests consisted of scenarios that serve as good representations of basic and distracting driving behaviors. Primary activity scenarios were chosen as recommended by the local Driving Exam Center (WORD) and are being evaluated while the driving test is administered.
As stated in Table 7 of the Regulation of the Minister of Transport, Construction and Marine Economy of the Republic of Poland [
63], these activities include:
Passing through uncontrolled intersections (three- and four-way),
Passing through intersections marked with signs establishing priority of passage,
Drive through intersections with traffic lights,
Drive through intersections where traffic flows around a traffic island and
Perform one of the following parking maneuvers: perpendicular, angle, and parallel.
3.1.2. Basic Driving Activities
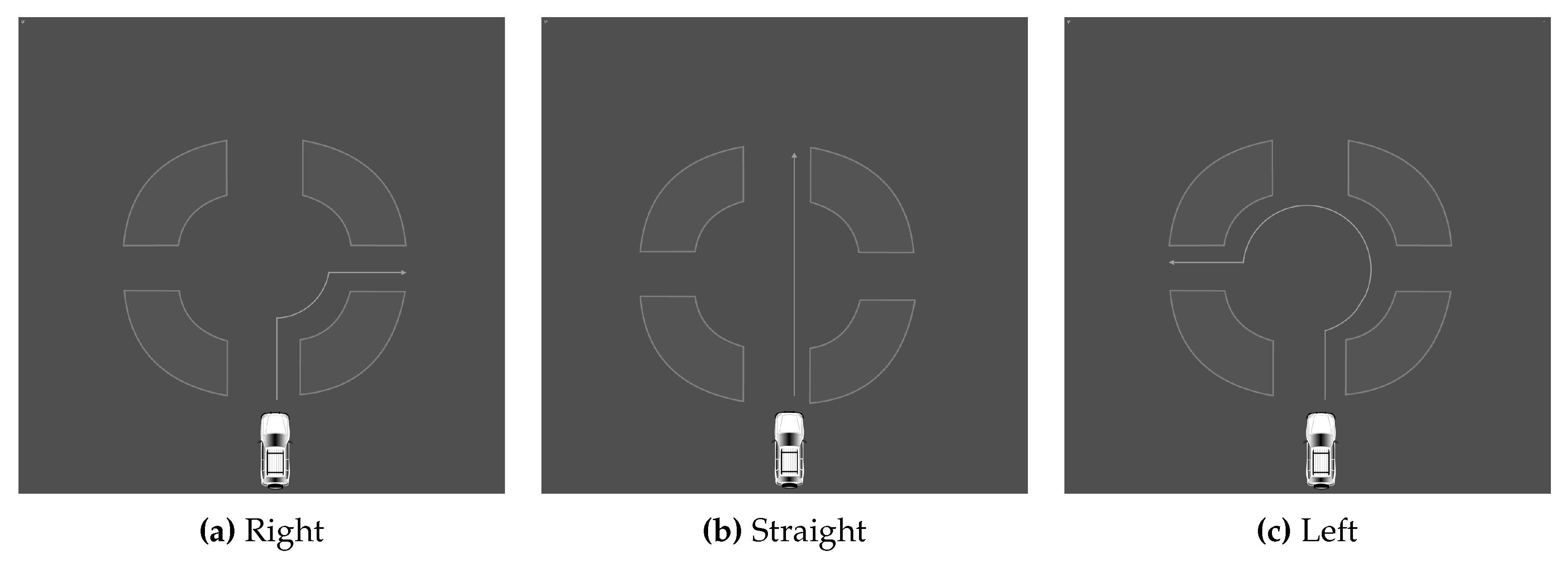
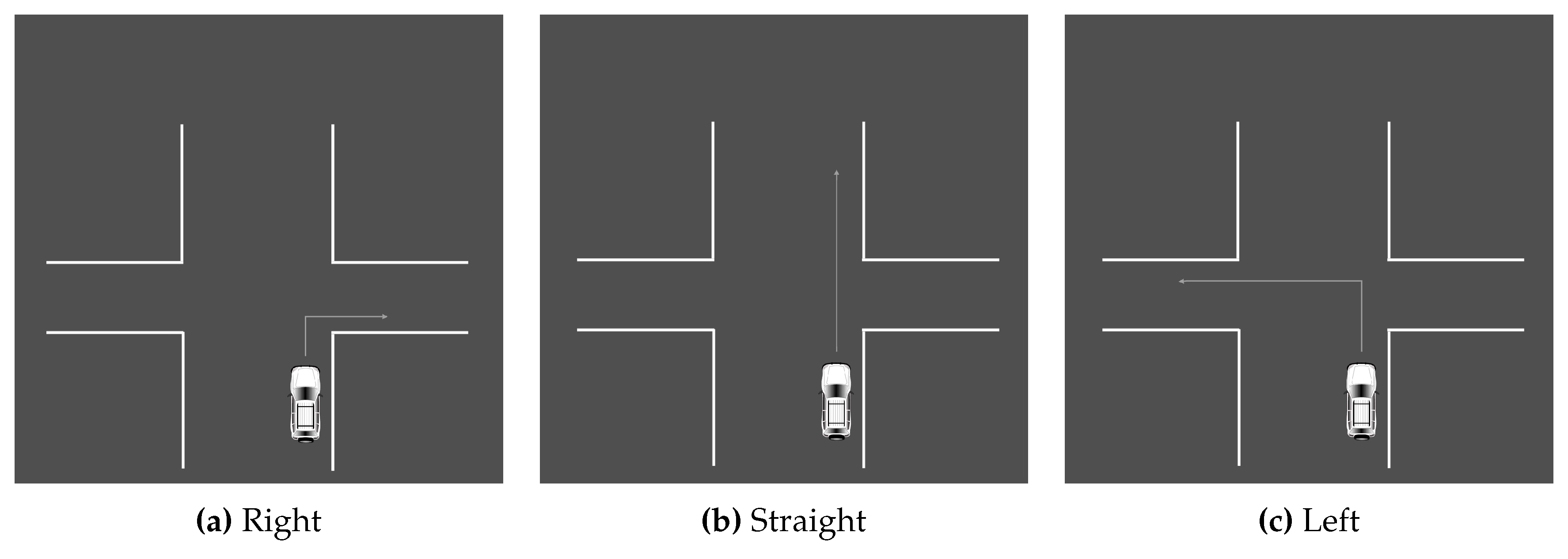
The driving simulator was used to carry out this experiment. To familiarize themselves with the machinery, each participant began with a test ride. Once they felt comfortable, a scenario was given and they were asked to complete the action while wearing JINS MEME ES_R Eyewear. To allow the participants to concentrate solely on driving, the supervisor was in charge of managing the computer program and issuing voice commands. Three types of situation were created, each of which was performed in an appropriate setting. In total, there were a total of 12 scenarios in this section. The first set of tasks was carried out in a roundabout. It involved making a left, right turn, or going straight ahead by choosing the first, second, or third exit. The actions are illustrated in
Figure 3. The second set of actions was executed at an intersection. The scenarios are similar to the roundabout. The second series of actions was carried out at a crossroad. The situations resemble those of a roundabout and are illustrated in the
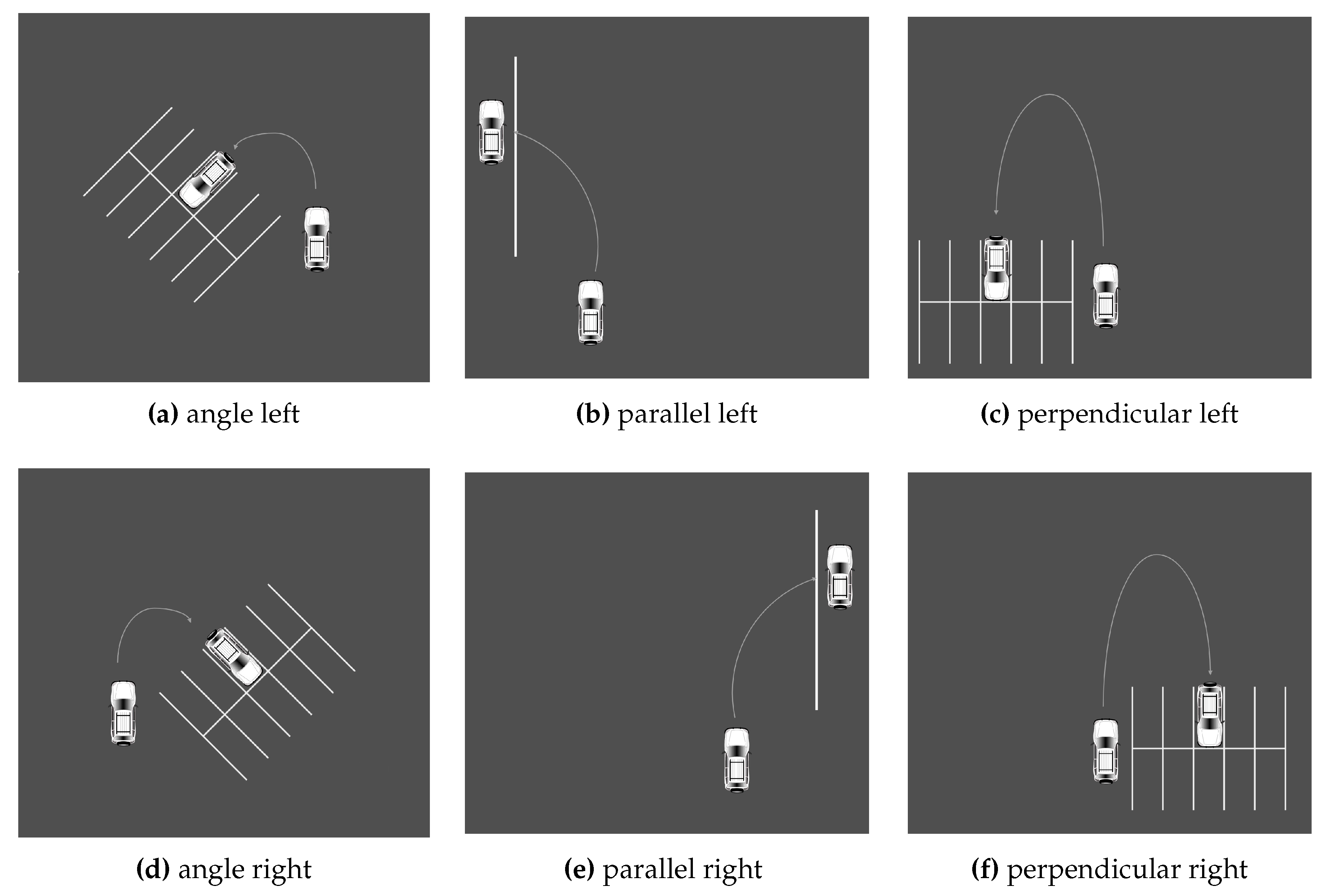
Figure 4. The final set of situations comprises various parking methods. Specifically, angle, parallel, and perpendicular parking. Every action was carried out twice, on each side of the street. All scenarios are illustrated in the
Figure 5.
3.1.3. Distracting Driving Activities
The second investigation focused on secondary or distracting driving activities. They represent all actions that are performed when operating a vehicle that is not related to actual driving. However, they affect performance quality. These actions were carried out in a setting similar to sitting behind a wheel because they do not require being in a vehicle. This section of the study introduced four scenarios: eating, drinking, turning, and bending. The actions are explained in detail in
Table 1.
3.1.4. Data format and label information
First, the data acquisition parameters are presented, followed by the header describing the content of each column that contains the sample number, the date in the format: dd.mm.rrrr:gg:mm:ss, then the 3 channel accelerometer components:
Followed by the EOG sensor components:
EOG raw EOG signal from the left and right eye, respectively,
EOG the difference between the left and right eye potential (EOG - EOG) and
EOG negative arithmetical mean of the left and right eye potential -(EOG + EOG)/2.
A list of dataframes comprising one sample signal is created by successively reading the data from the relevant path by folders. To accurately describe all signals, the rows containing the parameter specifications are removed and the header fixed. Labels for primary activities are presented in
Table 2.
3.2. Preprocessing
The data collected by smart glasses include signals from the four EOG channels (EOG, EOG, EOG, and EOG), three axes of the accelerometer (ACC, ACC, and ACC) and three axes of the gyroscope (GYRO, GYRO, and GYRO). The signals collected by these sensors are often contaminated by noise and artifacts. For example, the EOG channels may pick up electrical signals from the surrounding environment, which can cause baseline drift and power line noise. Linear and angular acceleration may be affected by vibrations or other disturbances, which can cause errors in measurements. To address these issues, various preprocessing techniques applied to the data is filtering, which involves applying mathematical operations to the signals to remove unwanted components.
A low-pass filter allows the low-frequency components of the signal to pass through, while blocking the high-frequency components. This can be useful for removing noise and smoothing out fluctuations in the signal to remove power line noise, which occurs at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz.
On the other hand, a band-pass filter allows a range of frequencies to pass through while blocking frequencies outside of that range. This can be useful for removing static or DC components of the signal, the EOG channels may pick up DC offsets due to electrode polarization, which was removed using a band-pass filter.
After pre-processing the data, it can finally be analyzed using statistical analysis and machine learning technique. The cleaned data provide valuable associations of changes in the EOG signal in the recognition of human behavior or cognition.
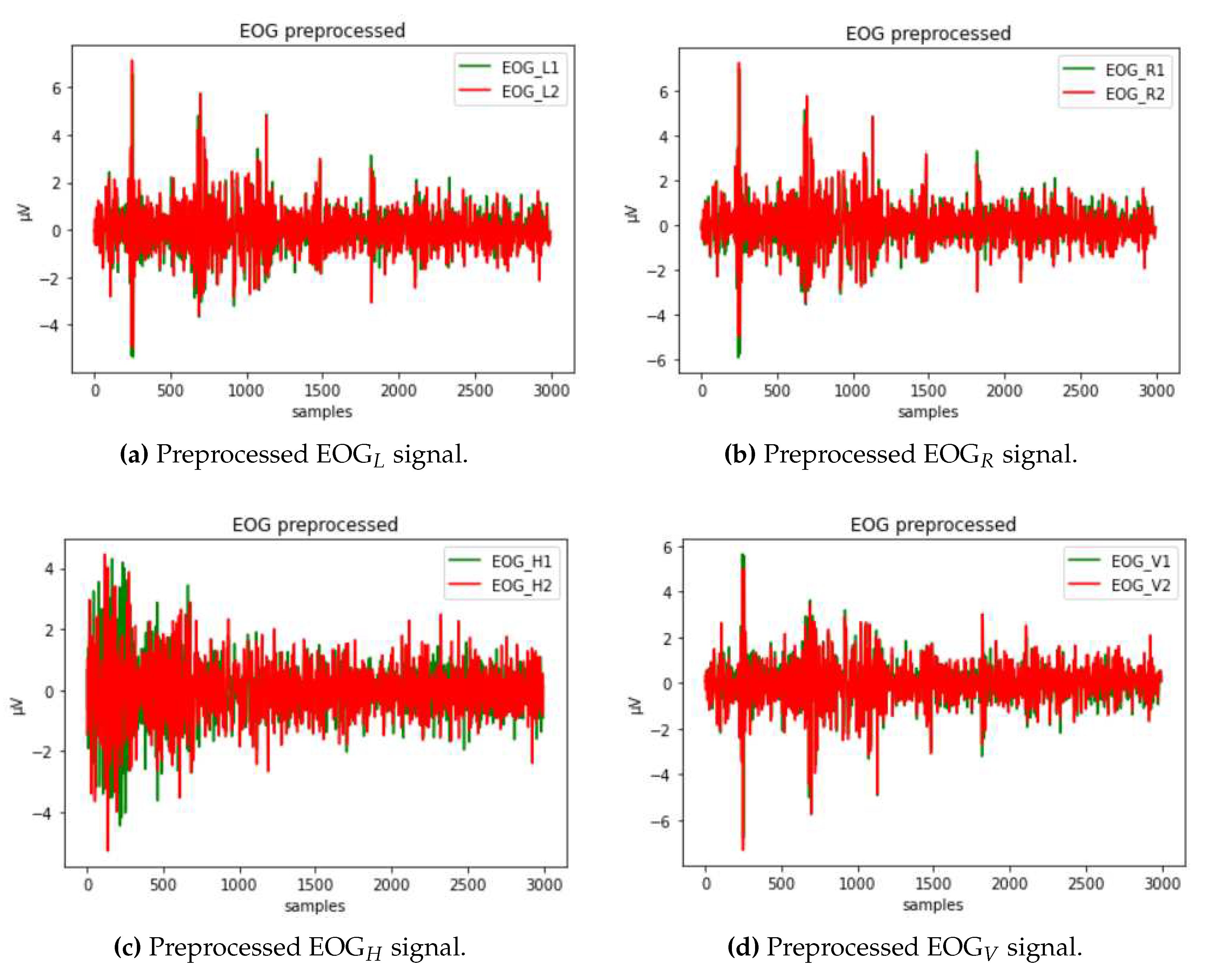
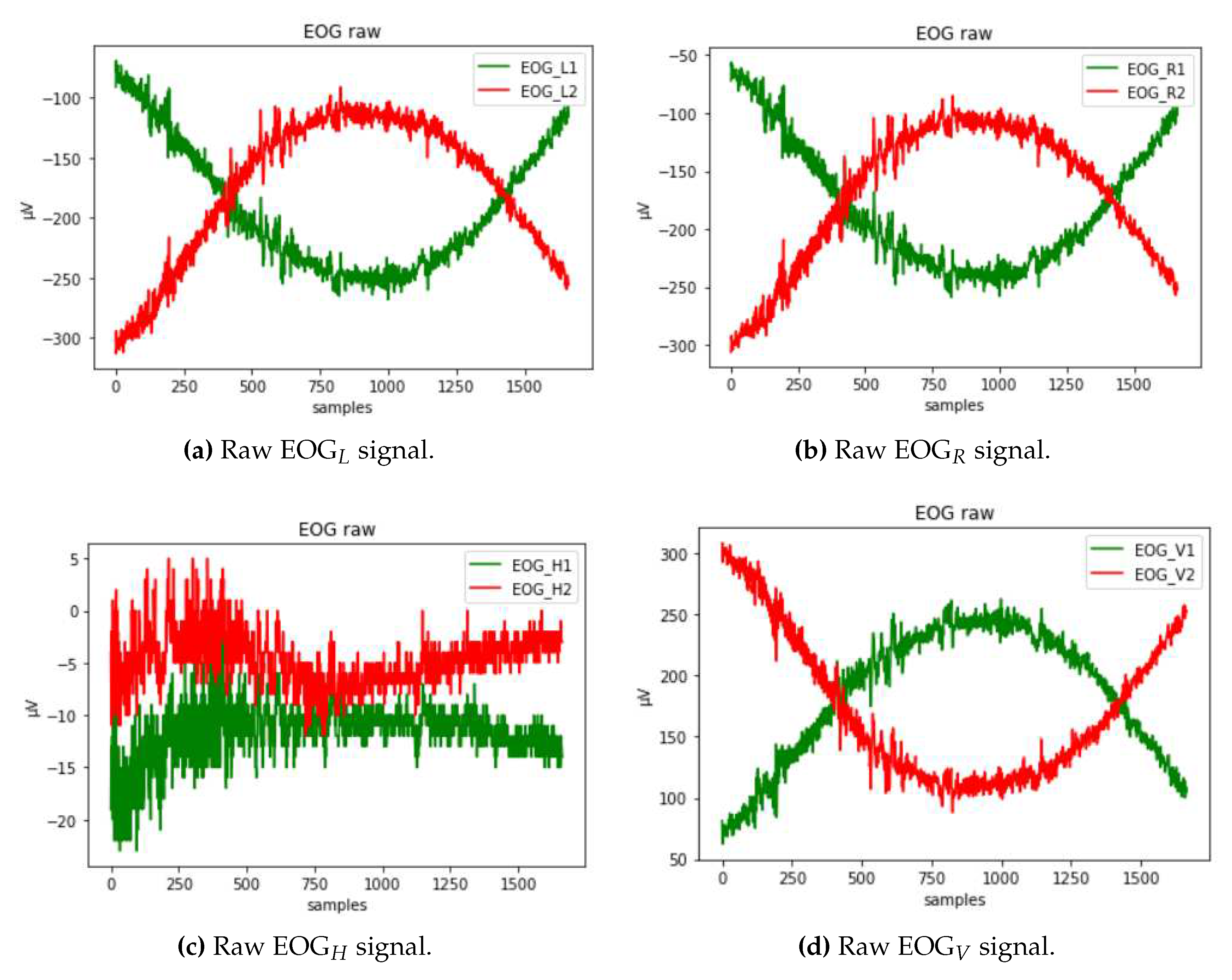
The raw EOG signal presented in
Figure 6 contains different types of artifacts that must first be filtered out. To reduce the noise of electricity lines and other potential types of noise, a second-order low-pass Butterworth filter is used to filter the EOG signal. It is applied to the signal twice: once forward and once backward. Such a filter has twice the order of the initial filter and zero phase. In addition, a slow unrelated alteration that is superimposed on the EOG signal, known as a baseline drift, might appear. It could be caused by a variety of things, including electrode polarization or interference with background signals [
64]. To eliminate this effect, we have applied detrending by differentiating.
For the acceleration signals, a median and a low-pass filter are applied to the three signals. The median filter is used to eliminate large peaks and to ignore outliers. Since the frequencies of vigorous, voluntary head rotations do not exceed 20 Hz, all frequencies over the cutoff frequency, set to 20 Hz, are blocked with the use of a low-pass filter. This kind of filter maintains low frequencies but introduces unwanted distortions. To fully utilize both strategies, they are combined by first applying the median filter and then running the resulting signal through a Hamming window-based low-pass filter. The disadvantage of this method is the attenuated values at the signal edges; however, these values were omitted because of the possibility of containing noise resulting from human control.
The entire data set was then independently normalized using Z-score normalization. The Z-score normalization helps distinguish the rest values and the values related to activities. The mean and standard deviation of each signal are calculated, and the samples values are replaced with the newly determined values using the following formula:
where
is the mean of the signal,
is the standard deviation, x is the current value of a sample and x is the new value, so that the new mean of all values is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
A sliding time window technique was used to segment all normalized sensor signals, with a window length of 5.6 s (280 samples) and a 50% stride (140 samples). The final samples were eliminated if the signal length was not divisible by 140.
Completing some tasks required more time than for the others. Also, depending on the precision of the driver, the acquired signals had different lengths. The shortest one was obtained for secondary activity Turning back and lasted 103 samples, the longest one for primary activity whereas taking a left turn at a roundabout was 3013 samples long. To be able to train the model, the data needed to be unified. Therefore, to avoid losing important data, all signals were resampled at a rate of 3000.
Figure 7.
Preprocessed EOG signals.
Figure 7.
Preprocessed EOG signals.
3.3. Classification
In this study, we used 1D CNN for feature learning and classification. Multiple convolutional operators in CNN allow automatic recognition of important features from a higher-dimensional input [
65,
66,
67,
68]. Convolutions offer the advantage of taking into account the spatial organization of the data. In doing so, additional information about the position in relation to other samples is expected to be taken into account.
The 1D CNN can be used to analyze time series with one or more variables. The latter scenario involves combining two or more concurrent signals. Based on our previous experiments, we segmented the data using the sliding window segmentation technique (SWS). Different settings were tested to select the length T and stride size ΔS of a time window and the best values were chosen empirically. In 1D CNN, the only samples with an inherent ordering are those along the time dimension. The channels for the various variables do not, in contrast to the most popular 2D CNN.
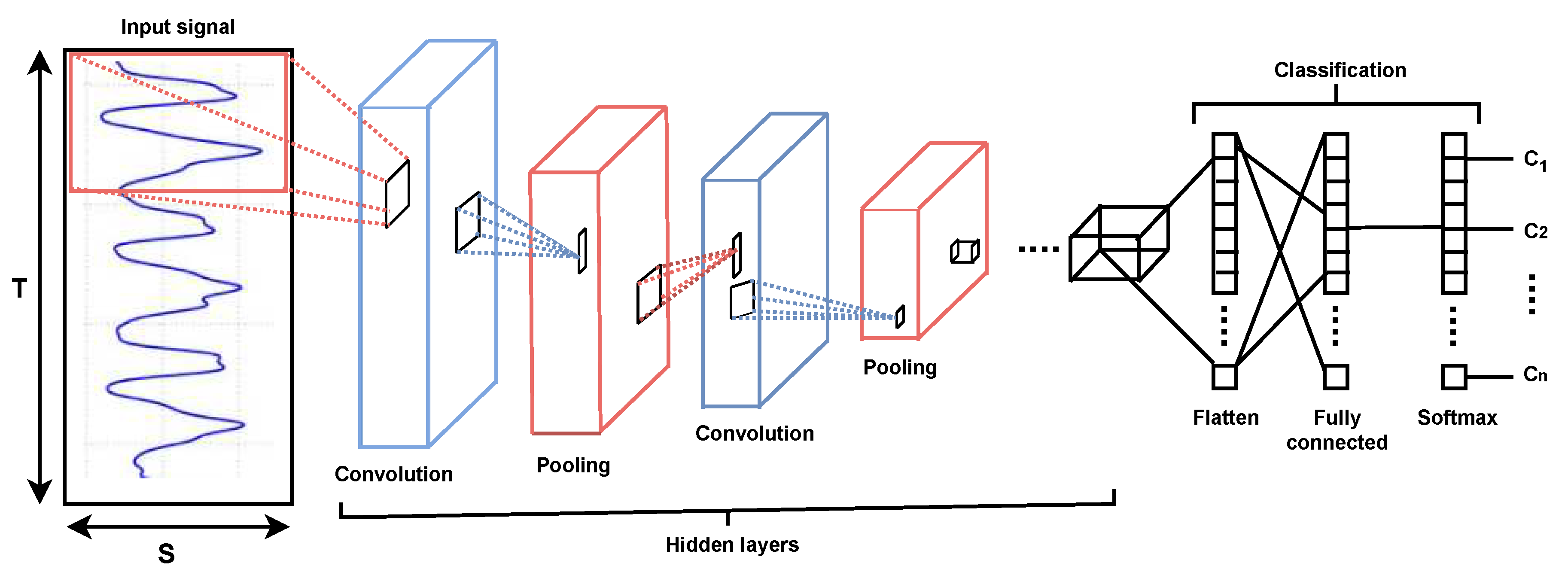
The basic architecture of a CNN model is shown in
Figure 8, and the parameters used in our proposed 1D CNN are shown in
Table 3. The first dimension of the input and output data is the batch size, the second dimension is the length of the sequence, and the third dimension is the number of features. The batch size was 32, the number of epochs was 100, and the learning rate (lr) was set to
.
In terms of functionality, the model can be divided into two parts. The first component, common for this type of network, acts as a feature extractor. It performs template matching using convolutional filtering techniques. To create the so-called “feature maps”, it uses layers and functions that include a convolutional layer, a batch normalization layer, a ReLU activation function, and a pooling layer. The network can learn higher-level features by training it on a large dataset using a suitable number of epochs and a learning rate.
The second component is the categorization into one of the output classes. The input vector values are first reshaped using the global average pooling layer, a further dropout layer to prevent the model from overfitting, and a dense layer with the “softmax” activation function, which assigns the final label representing the predicted class value by performing a matrix-vector multiplication. This process results in a new vector at the output.
3.4. Evaluation
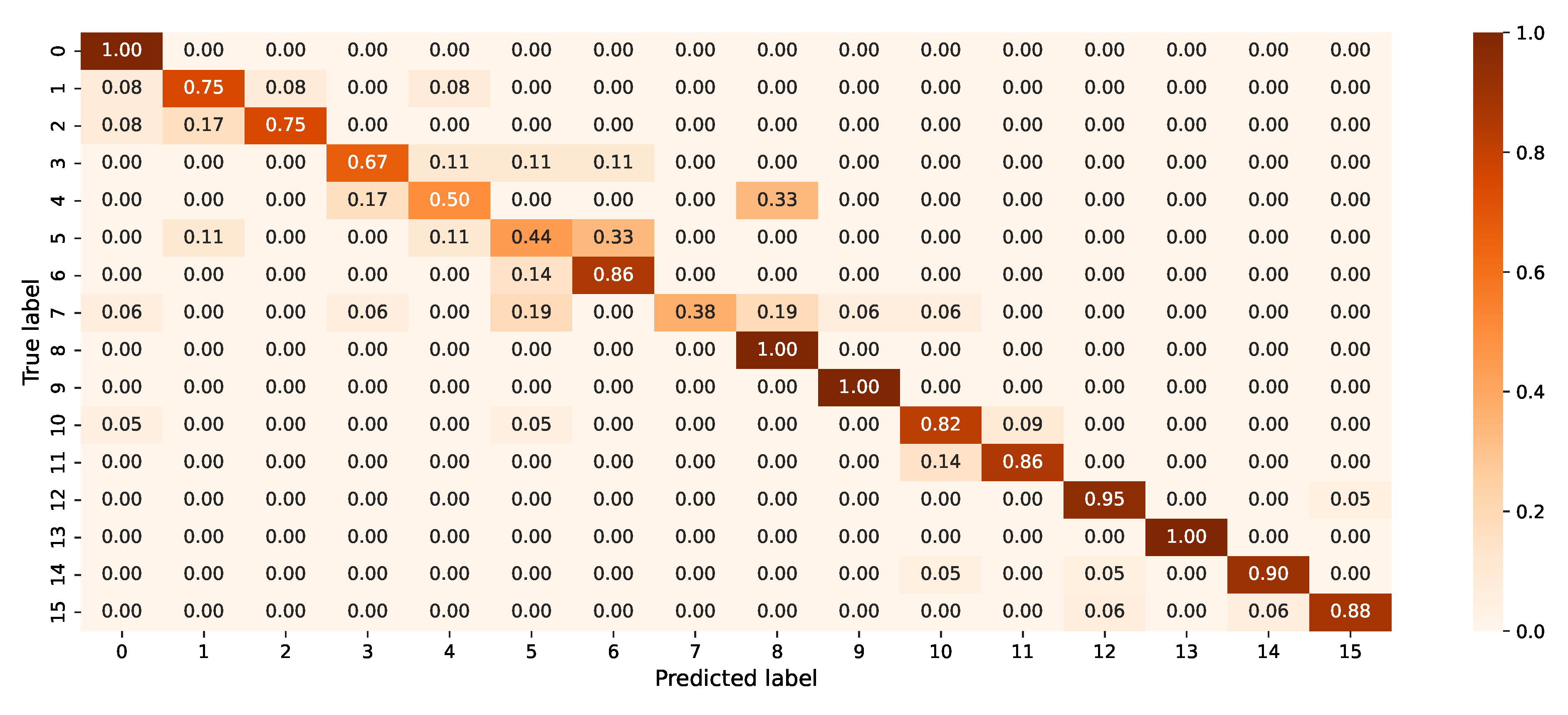
The performance of the classifier was expressed in the form of a confusion matrix (see
Figure 11), the numbers of true positives, true negatives, false positives, false negatives, accuracy, precision, F1 score, and categorical cross entropy.
Accuracy presents the percentage of correct predictions relative to all predictions made.
where:
- -
true positive () - correctly classified trials,
- -
false positive () - incorrectly classified trials,
- -
true negative () - correctly classified nonevent trials,
- -
false negative () - incorrectly classified nonevent trials.
Precision is a metric that identifies the successful predictions of all predictions made in favor of the event.
Recall presents the fraction of correctly classified predictions of a particular activity with respect to all predictions made in favor of the activity.
The F1 score is a harmonic mean of precision and recall, which, compared to accuracy, should provide a more realistic model assessment in multiclass predictions with unbalanced classes.
Categorical cross-entropy loss measures the model performance by comparing the actual and predicted labels according to the formula:
where
t is the true label,
p the predicted label and
N is the number of scalar values in the model output.
Linear acceleration and EOG signals that had already been analyzed were used to train and assess the network. A 9:1 ratio was used to divide the data into subsets for training and testing. A further division with 8:2 ratio was used on the training set to divide it into training and validation sets. Since the signals were sorted, the data had to be shuffled to train the model on signals from all possible classes.
4. Results
4.1. Accuracy and loss while training
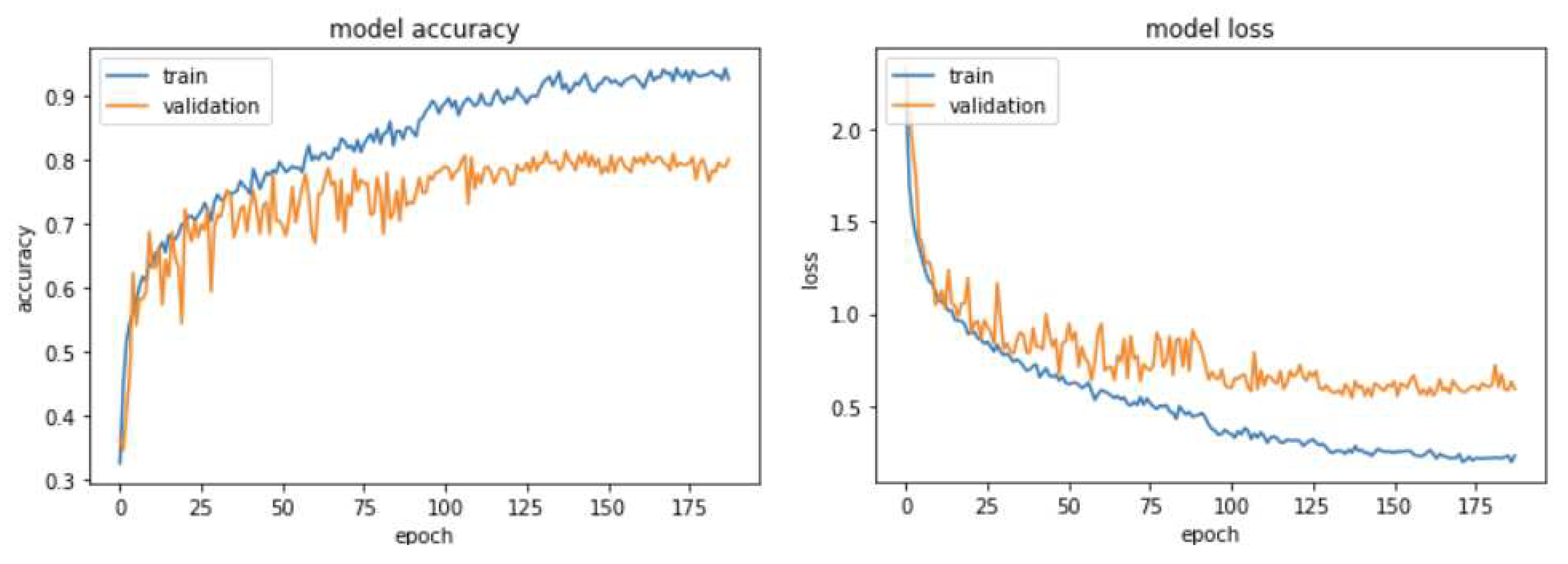
Figure 9 shows the accuracy curve for training and validation and loss of the model with respect to the number of epochs elapsed. The loss function is categorical cross-entropy. When the epoch reached 130, the training accuracy was found to be greater than 90%, providing a loss value of 0.2. The validation rate was 80% with a loss of 0.6. The model obtained the optimal parameters in 188 epochs.
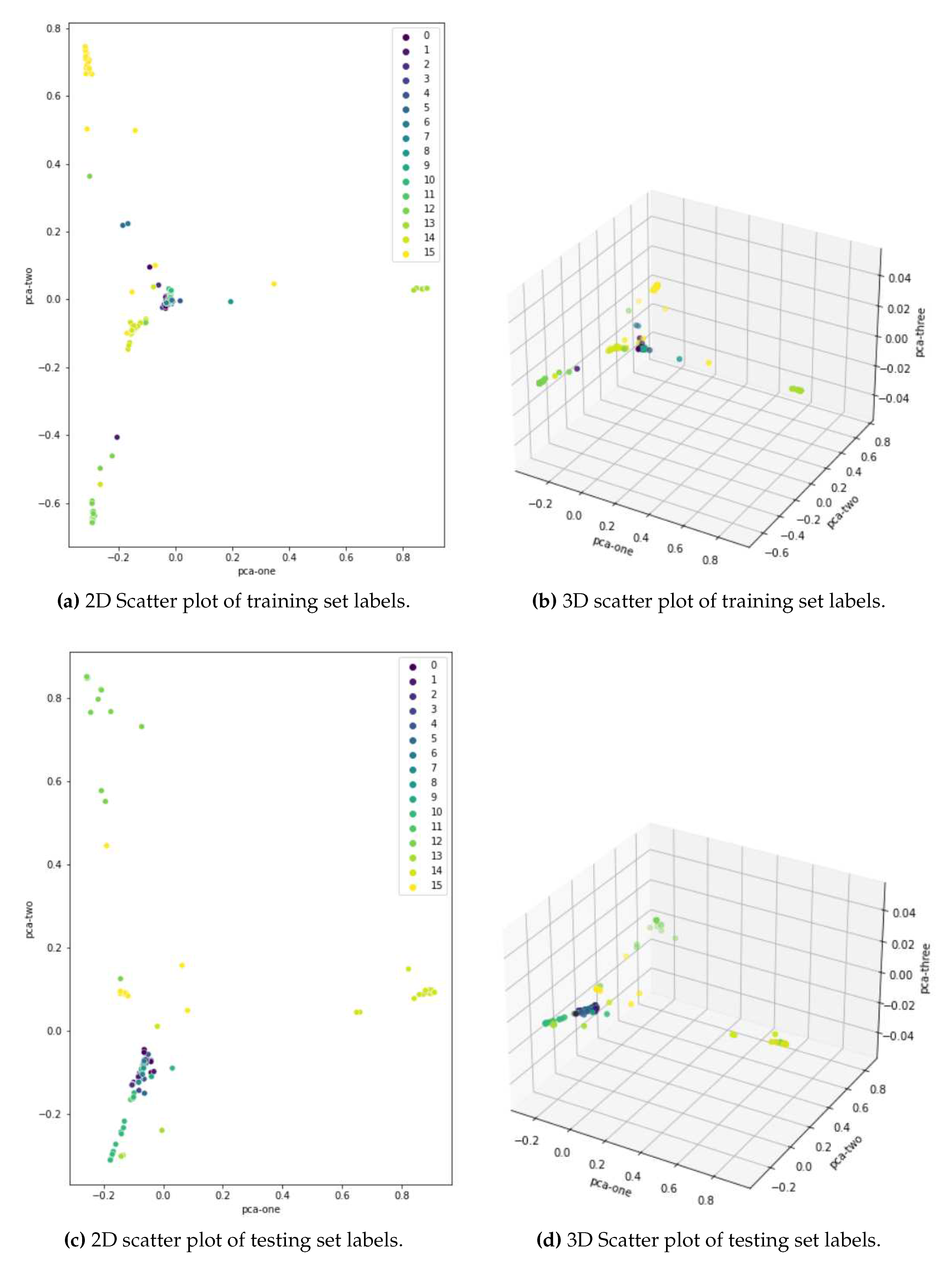
Figure 10 shows how well the classes were segregated after 188 epochs in dimensions 2 and 3. A dimensionality reduction method known as principal component analysis (PCA) was used for visualization purposes. The correlation between different dimensions is used, and the goal is to provide as few variables as possible while preserving as much variation or information about the distribution of the original data as possible.
It can be seen that the distinction between primary and secondary driving activities is very apparent. The latter are also separated in such a way that they usually do not overlap. However, the primary activities cover areas very close to each other, so the greatest misclassifications are anticipated.
The distinction between primary and secondary driving activities is readily apparent, as can be seen. The latter are divided in such a way that they do not primarily overlap. The greatest misclassifications were expected for groups of similar primary activities that covered areas that are relatively close to each other.
Table 4.
Evaluation scores of driving activities classification.
Table 4.
Evaluation scores of driving activities classification.
| Label |
Activity |
Precision |
Recall |
F1-score |
| 0 |
P_Crossroad_Left |
1.00 |
0.67 |
0.80 |
| 1 |
P_Crossroad_Right |
0.75 |
0.75 |
0.75 |
| 2 |
P_Crossroad_Straight |
0.75 |
0.90 |
0.82 |
| 3 |
P_Parking_Diagonal_Left |
0.67 |
0.75 |
0.71 |
| 4 |
P_Parking_Diagonal_Right |
0.50 |
0.50 |
0.50 |
| 5 |
P_Parking_Parallel_Left |
0.44 |
0.40 |
0.42 |
| 6 |
P_Parking_Parallel_Right |
0.86 |
0.60 |
0.71 |
| 7 |
P_Parking_Perpendicular_Left |
0.38 |
1.00 |
0.55 |
| 8 |
P_Parking_Perpendicular_Right |
1.00 |
0.29 |
0.44 |
| 9 |
P_Roundabout_Left |
1.00 |
0.88 |
0.93 |
| 10 |
P_Roundabout_Right |
0.82 |
0.86 |
0.84 |
| 11 |
P_Roundabout_Straight |
0.86 |
0.75 |
0.80 |
| 12 |
S_Bending |
0.95 |
0.90 |
0.93 |
| 13 |
S_Drinking |
1.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
| 14 |
S_Eating |
0.90 |
0.95 |
0.93 |
| 15 |
S_Turning_Back |
0.88 |
0.94 |
0.91 |
All activity predictions had a weighted average precision, recall, and F1 score of 0.83, 0.80, and 0.80, respectively. Drinking as a secondary activity is the category that has the best performance with all values equal to 1, while primary parallel parking on the left and perpendicular parking on the right are the categories that are mostly misclassified with F1 scores 0.42 and 0.44, respectively. In general, secondary driving actions performed better, all receiving F1 scores greater than 0.9.
The accuracy of the prediction of 15 driving actions is shown in
Figure 11, where the accuracy of the prediction of each class is shown on the diagonal and inaccurate classifications are shown outside the diagonal.
Figure 11.
Confusion matrix of the classifier.
Figure 11.
Confusion matrix of the classifier.
Most misclassifications occurred in a group of activities that were related to each other. Parking activities show that the model had the most trouble detecting the difference between the same action being conducted on the left and right sides due to their similarity. The binary classification between secondary and primary activities has an accuracy rate of 99.5%. Although the latter was mistakenly classified as eating, the former was consistently assigned to the appropriate group.
An investigation of classifications for a particular collection of activities, including crossroad, parking, roundabout, and secondary activities, yielded accuracy ratings of 97.9%, 96.8%, 97.4%, and 99.5%, respectively.
Table 5 displays these results together with the precision, recall, and F1 score values. Although the network received these actions as individual activities, it was still able to indicate patterns that differentiate the different types of action.
5. Discussion
We have recognized road conditions based on electrooculograms acquired from drivers wearing JINS MEME ES_R smart glasses. The highest precision, recall, and F1 score for drinking (1.00 for each metric) were observed, whereas the lowest results were observed for parallel parking on the left side (precision of 0.44, recall of 0.4, and F1 score of 0.42).
Most misclassifications occurred in a group of activities that were related to each other, e.g., parking on the left and parking on the right side due to their similarity. The binary classification between secondary and primary activities has an accuracy rate of 99.5%. Although the latter was mistakenly classified as eating, the former was consistently assigned to the appropriate group.
In this study, the recognition of primary and secondary driver activities based on the processing of EOG signals with a convolutional network achieved excellent recognition performance, but there are still some limitations. The first limitation was to obtain the EOG signals in a simulated driving experiment. Although the experimental results showed that the turn or park condition was successfully induced and verified the effectiveness of the experimental scheme, it cannot be compared with the complexity of driving in real traffic. The second limitation was a limited number of experimental data segments. This setup could be used in future studies that do not expose volunteers to the dangers of real traffic. Classification models were trained on short signal samples. The third limitation was the use of only one time window width (5.6 seconds) to calculate the EOG characteristics without fully examining the impact of other time window divisions on the classification results.
In future studies, we consider obtaining more data from real road conditions to validate our method. Such an application would be an element of the system to assist drivers, especially older drivers or drivers with disabilities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.J.D. and J.K.; methodology, R.J.D.; software, J.K. and R.J.D.; validation, R.J.D. and J.K.; formal analysis, R.J.D., J.K. and M.T.I; investigation, R.J.D and J.K.; resources, R.J.D.; data curation, J.K. and R.J.D; writing–original draft preparation, R.J.D. and J.K.; writing–review and editing, R.J.D., S.S., M.T.I., A.P., and M.G.; visualization, R.J.D., J.K., N.J.P., M.T.I., M.A.H and A.P.; supervision, R.J.D., S.S., F.L., M.A.N., and M.G.; project administration, R.J.D, M.G.; funding acquisition, R.J.D and M.G.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Medical University of Silesia on 16 October 2018 (KNW/0022/KB1/18).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kinnear, N.; Stevens, A. The battle for attention: Driver distraction - a review of recent research and knowledge; Technical report,; IAM, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hussein, W.A.; Kiah, M.L.M.; Yee, P.L.; Zaidan, B.B. A systematic review on sensor-based driver behaviour studies: coherent taxonomy, motivations, challenges, recommendations, substantial analysis and future directions. PeerJ Computer Science 2021, 7, e632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, P.; Qin, W.; Xu, Y.; Miyajima, C.; Kazuya, T. Spectral clustering based approach for evaluating the effect of driving behavior on fuel economy. 2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC); pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Jamroz, K.; Smolarek, L. Driver Fatigue and Road Safety on Poland’s National Roads. International Journal of Occupational Safety and Ergonomics 2013, 19, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurczynski, D.; Zuska, A. Analysis of the Impact of Invisible Road Icing on Selected Parameters of a Minibus Vehicle. Sensors 2022, 22, 9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Statistics and Analysis. Distracted Driving 2020; Technical report; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Arevalo-Tamara, A.; Caicedo, A.; Orozco-Fontalvo, M.; Useche, S.A. Distracted driving in relation to risky road behaviors and traffic crashes in Bogota, Colombia. Safety Science 2022, 153, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.D. Driver Fatigue. Human Factors 1994, 36, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthaus, M.; Wascher, E.; Getzmann, S. Distraction in the Driving Simulator: An Event-Related Potential (ERP) Study with Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Drivers. Safety 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, N.; Soryani, M.; Azmi, R. Computer vision-based recognition of driver distraction: A review. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience 2021, 33, e6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashevnik, A.; Shchedrin, R.; Kaiser, C.; Stocker, A. Driver Distraction Detection Methods: A Literature Review and Framework. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60063–60076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Hu, W.; Cui, G.; Wei, D.; Xu, J. Gaze dynamics with spatiotemporal guided feature descriptor for prediction of driver’s maneuver behavior. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering 2021, 235, 3051–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Eswari, R. Accident prevention and safety assistance using IOT and machine learning. Journal of Reliable Intelligent Environments 2022, 8, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozhabr Pour, H.; Li, F.; Wegmeth, L.; Trense, C.; Doniec, R.; Grzegorzek, M.; Wismuller, R. A Machine Learning Framework for Automated Accident Detection Based on Multimodal Sensors in Cars. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Si, Y.; Guo, M.; Li, S. Driver Distraction Recognition Using Wearable IMU Sensor Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Hurtig, R. Looking but not seeing. Neurology 1987, 37, 1642–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eraqi, H.M.; Abouelnaga, Y.; Saad, M.H.; Moustafa, M.N. Driver Distraction Identification with an Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks. Journal of Advanced Transportation 2019, 2019, e4125865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariansyah, D.; Pardamean, B.; Caruso, G. The effect of visual advanced driver assistance systems on a following human driver in a mixed-traffic condition. Procedia Computer Science 2023, 216, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böddeker, B.; von Wendorff, W.; Nguyen, N.; Diehl, P.; Meertens, R.; Johannson, R. Automated driving safety - The art of conscious risk taking - minimum lateral distances to pedestrians. 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), 2021, pp. 1466–1471. ISSN: 1558-1101. [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.W.; Hsu, C.M. Innovative Framework for Distracted-Driving Alert System Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 77523–77536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauer, S.G.; Dingus, T.A.; Neale, V.L.; Sudweeks, J.; Ramsey, D.J. The Impact of Driver Inattention on Near-Crash/Crash Risk: An Analysis Using the 100-Car Naturalistic Driving Study Data; Technical report; National Traffic Safety Administration, US Department of Transportation, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jomnonkwao, S.; Uttra, S.; Ratanavaraha, V. Analysis of a driving behavior measurement model using a modified driver behavior questionnaire encompassing texting, social media use, and drug and alcohol consumption. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives 2021, 9, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauer, S.G.; Guo, F.; Simons-Morton, B.G.; Ouimet, M.C.; Lee, S.E.; Dingus, T.A. Distracted Driving and Risk of Road Crashes among Novice and Experienced Drivers. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 370, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, M.J.; Tijerina, L.; Bents, F.D.; Wierwille, W.W. Using Cellular Telephones in Vehicles: Safe or Unsafe? Transportation Human Factors 1999, 1, 3–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, S.; Hoshika, K.; Kunze, K.; Kise, K.; Dengel, A. Towards reading trackers in the wild: detecting reading activities by EOG glasses and deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers; ACM, 2017; pp. 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.A.; Shirahama, K.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Grzegorzek, M. Rank Pooling Approach for Wearable Sensor-Based ADLs Recognition. Sensors 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.Z.; Soylu, A. Human activity recognition using wearable sensors, discriminant analysis, and long short-term memory-based neural structured learning. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdansepas, D.; Niazi, A.H.; Gay, J.L.; Maier, F.W.; Ramaswamy, L.; Rasheed, K.; Buman, M.P. A Multi-featured Approach for Wearable Sensor-Based Human Activity Recognition. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI); IEEE, 2016; pp. 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Intille, S.S. Activity Recognition from User-Annotated Acceleration Data. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, 2004; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hoey, J.; Nugent, C.D.; Cook, D.J.; Yu, Z. Sensor-Based ActivityRecognition. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev 2012, 42, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, S.; Natarajan, S. Recognition of EOG based reading task using AR features. International Conference on Circuits, Communication, Control and Computing; 2014; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shirahama, K.; Irshad, M.T.; Nisar, M.A.; Piet, A.; Grzegorzek, M. Sleep Stage Classification in Children Using Self-Attention and Gaussian Noise Data Augmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shirahama, K.; Li, F.; Grzegorzek, M. Sleep stage classification for child patients using DeConvolutional Neural Network. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2020, 110, 101981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doniec, R.; Piaseczna, N.; Li, F.; Duraj, K.; Pour, H.H.; Grzegorzek, M.; Mocny-Pachońska, K.; Tkacz, E. Classification of Roads and Types of Public Roads Using EOG Smart Glasses and an Algorithm Based on Machine Learning While Driving a Car. Electronics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulling, A.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G. Wearable EOG goggles: Seamless sensing and context-awareness in everyday environments. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments 2009, 1, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenewald, A.; Kroenert, D.; Poehler, J.; Brueck, R.; Li, F.; Littau, J.; Schnieber, K.; Piet, A.; Grzegorzek, M.; Kampling, H.; Niehaves, B. Biomedical Data Acquisition and Processing to Recognize Emotions for Affective Learning. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.T.; Jiang, W.L.; Chen, S.F.; Huang, K.C.; Liao, L.D. Design of a Wearable Eye-Movement Detection System Based on Electrooculography Signals and Its Experimental Validation. Biosensors 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, M.T.; Nisar, M.A.; Huang, X.; Hartz, J.; Flak, O.; Li, F.; Gouverneur, P.; Piet, A.; Oltmanns, K.M.; Grzegorzek, M. SenseHunger: Machine Learning Approach to Hunger Detection Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhuliawala, M.; Lee, J.; Shimizu, J.; Bulling, A.; Kunze, K.; Starner, T.; Woo, W. Smooth eye movement interaction using EOG glasses. In ICMI ’16: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction; 2016; pp. 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, D.; Yee, N.; Daum, C.; Stroulia, E.; Liu, L. Activity Classification in Independent Living Environment with JINS MEME Eyewear. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom); 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JINS, Inc.. JINS MEME glasses specifications. Available online: https://jins-meme.github.io/apdoc/en/ (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Aksjonov, A.; Nedoma, P.; Vodovozov, V.; Petlenkov, E.; Herrmann, M. Detection and Evaluation of Driver Distraction Using Machine Learning and Fuzzy Logic. Ieee Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2019, 20, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.; Alotaibi, B. Distracted driver classification using deep learning. Signal Image and Video Processing 2020, 14, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, H.; Jiao, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, G. Driving Fatigue Detection with Three Non-Hair-Bearing EEG Channels and Modified Transformer Model. Entropy 2022, 24, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunagel, C.; Geisler, D.; Rosenstiel, W.; Kasneci, E. Online recognition of driver-activity based on visual scanpath classification. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine 2017, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansare, D.J.; Deshpande, R.; Shingare, S.; Deokar, H.; Manwar, P. Real-time Driver Drowsiness Detection with Android. International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology 2022, 10, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-García, N.; Gil-González, A.B.; Reboredo, A.d.L.; Pérez-Lancho, B. Driver Stress Detection in Simulated Driving Scenarios with Photoplethysmography. Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence, 19th International Conference; Omatu, S., Mehmood, R., Sitek, P., Cicerone, S., Rodríguez, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2023; pp. 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, I.; Uddin, K.M.A.; Murad, S.A.; Miah, M.S.U.; Khan, T.Z.; Masud, M.; Aljahdali, S.; Bairagi, A.K. 4D: A Real-Time Driver Drowsiness Detector Using Deep Learning. Electronics 2023, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarza, E.E.; Egas, F.D.; Silva, F.M.; Velasco, P.M.; Galarza, E.D. Real Time Driver Drowsiness Detection Based on Driver’s Face Image Behavior Using a System of Human Computer Interaction Implemented in a Smartphone. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology & Systems (ICITS 2018); Springer International Publishing, 2018; pp. 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvaro, P.K.; Burnett, N.M.; Kennedy, G.A.; Min, W.Y.X.; McMahon, M.; Barnes, M.; Jackson, M.; Howard, M.E. Driver education: Enhancing knowledge of sleep, fatigue and risky behaviour to improve decision making in young drivers. Accid. Anal. Prev 2018, 112, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlZubi, A.A.; Abugabah, A.; Al-Maitah, M.; Ibrahim AlZobi, F. DL Multi-sensor information fusion service selective information scheme for improving the Internet of Things based user responses. Measurement 2021, 185, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, R.A.; Arsalan, M.; Batchuluun, G.; Yoon, H.S.; Park, K.R. Deep learning-based gaze detection system for automobile drivers using a NIR camera sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, C. Deep unsupervised multi-modal fusion network for detecting driver distraction. Neurocomputing 2021, 421, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaegae, N.K.; Pulluri, K.K.; Bagadi, K.; Oyerinde, O.O. Design of an Efficient Distracted Driver Detection System: Deep Learning Approaches. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 116087–116097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Nakano, K. Spatio-Temporal Image Representation and Deep-Learning-Based Decision Framework for Automated Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2022, 23, 24866–24875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.; Huang, C.; Ding, W.; Liu, Y.; Chiyomi, M.; Kazuya, T. Distracted driving detection based on the fusion of deep learning and causal reasoning. Information Fusion 2023, 89, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, D.; Velenis, E.; Wang, F.Y. Driver Activity Recognition for Intelligent Vehicles: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 5379–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, S.; Rangesh, A.; Trivedi, M.M. Driver Gaze Zone Estimation using Convolutional Neural Networks: A General Framework and Ablative Analysis; ArXiv180202690 Cs; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Shirahama, K.; Nisar, M.; Köping, L.; Grzegorzek, M. Comparison of Feature Learning Methods for Human Activity Recognition Using Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.T.; Nisar, M.A.; Gouverneur, P.; Rapp, M.; Grzegorzek, M. AI Approaches towards Prechtl’s Assessment of General Movements: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Khadem, N.K.; Kabir, M.M.; Jeihani, M. Driver Behavior Post Cannabis Consumption: A Driving Simulator Study in Collaboration with Montgomery County Maryland. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.12026. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gu, M.; Su, Y. Comparing the Effects of Visual Distraction in a High-Fidelity Driving Simulator and on a Real Highway. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Transport, Construction, and Maritime Economy of the Republic of Poland. Rozporządzenie Ministra Transportu, Budownictwa i Gospodarki Morskiej z dnia 13 lipca 2012 r. w sprawie szkolenia osób ubiegających się o uprawnienia do kierowania pojazdami, instruktorów i wykładowców, Dz.U. 2012 poz. 1019, 2012. Accessed 24 February 2023. 24 February.
- Gu, J.J.; Meng, M.Q.H.; Cook, A.; Faulkner, M.G. A study of natural eye movement detection and ocular implant movement control using processed EOG signals. Proceedings 2001 ICRA. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.01CH37164) 2001, 2, 1555–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, L.; Yan, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Driver Fatigue Detection Based on Convolutional Neural Networks Using EM-CNN. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2020, 2020, e7251280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Coenen, F.; Zhang, B. Driving posture recognition by convolutional neural networks. IET Computer Vision 2016, 10, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdy, M.; Fathy, M.; Berangi, R.; Sabokrou, M. Driver behavior detection and classification using deep convolutional neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications 2020, 149, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Yan, H.; Qin, L.; Ngo, T.; Manjunath, B.S. How Do Drivers Allocate Their Potential Attention? Driving Fixation Prediction via Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2020, 21, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).