Submitted:
27 April 2023
Posted:
27 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Participants
2.3. Calculating IR, FPIS, SPIS, and GE
- IR: 327 subjects were enrolled in the study. IR was estimated using an insulin suppression test. The r-value between the obtained and calculated GE was 0.581 (p < 0.001). This can be observed in the “Journal of Diabetes Investigation” from 2013.
- 2.
- FPIS: 186 subjects were enrolled. FPIS was measured using an intravenous glucose tolerance test via frequent sampling. The r-value between the measured and calculated GE was 0.671 (p < 0.000). The following equation was published in the “International Journal of Endocrinology” in 2015.
- 3.
- SPIS: 82 participants were enrolled. SPIS was measured using a modified glucose infusion test at a low dose. The r-value between the measured and calculated GE was 0.65 (p = 0.002). It was referred to in ”Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders” in 2016.
- 4.
- GE: 227 participants were enrolled. GE was measured using a constant sampled intravenous glucose tolerance test. The r-value between the measured and calculated GE was 0.43 (p = 0.001). It was published in “Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders” in 2016.
2.4. Laboratory Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
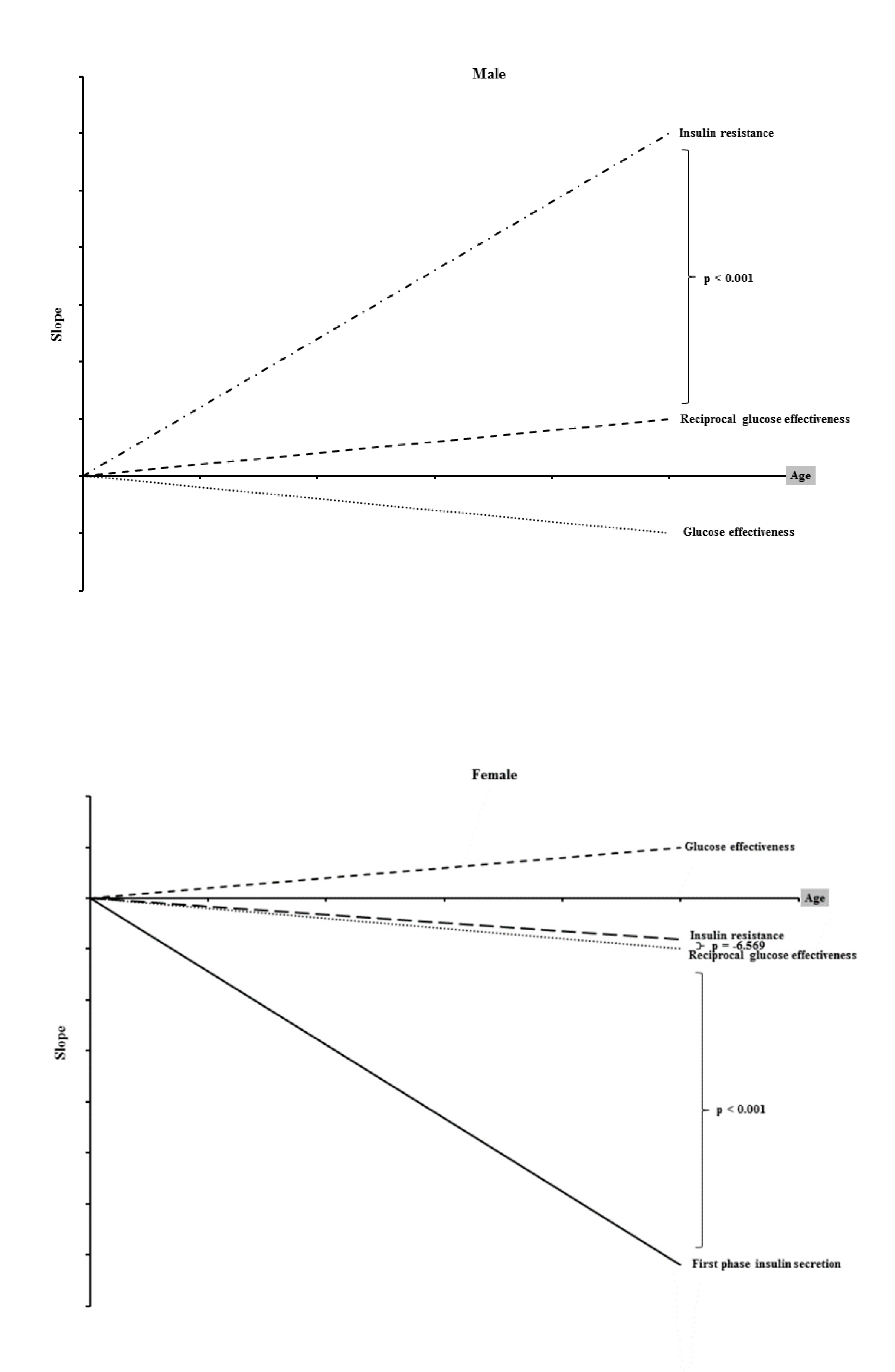
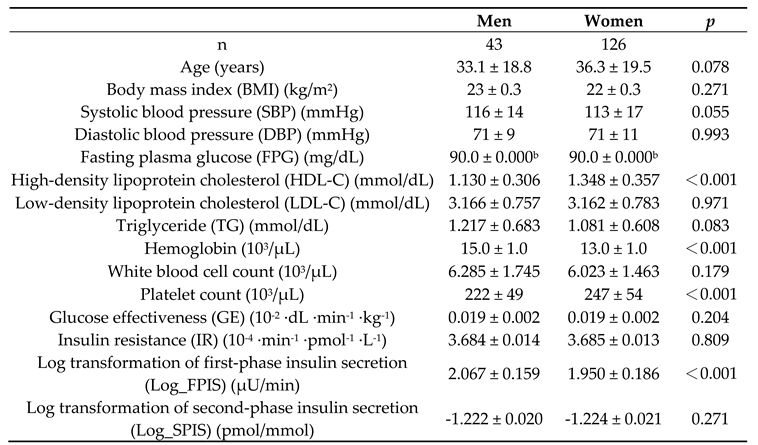
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chockalingam, N.; Gatt, A.; Formosa, C.; Nachiappan, N.; Healy, A. Provision of assistive devices for people with diabetes at risk of mobility impairment. World Health Organization 2019, 2019, 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, C.-H. The Epidemiologic Transition of Diabetes Mellitus in Taiwan: Implications for Reversal of Female Preponderance from a National Cohort. Open Diabetes J. 2009, 2, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Yeh, C.-J.; Chen, H.-H.; Huang, K.-C.; Pan, W.-H. Morbid obesity in Taiwan: Prevalence, trends, associated social demographics, and lifestyle factors. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0169577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-J.; Li, M.-L.; Chang, C.-M.; Wu, C.-H.; Tan, M.P. Disability trajectories prior to death for ten leading causes of death among middle-aged and older adults in Taiwan. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and Insulin Resistance. Clin Biochem Rev 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osei, K.; Rhinesmith, S.; Gaillard, T.; Schuster, D. Impaired insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion, and glucose effectiveness predict future development of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes in pre-diabetic African Americans: implications for primary diabetes prevention. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquin, J.C. Regulation of insulin secretion: a matter of phase control and amplitude modulation. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; DeFronzo, R.A. Contributions of β-Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance to the Pathogenesis of Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glucose. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, A.; Shah, P.; Basu, R.; Basu, A.; Holst, J.J.; A Rizza, R. Effect of glucagon-like peptide 1(7-36) amide on glucose effectiveness and insulin action in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steil, G.M.; Murray, J.; Bergman, R.N.; Buchanan, T.A. Repeatability of Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Effectiveness From the Minimal Model: Implications for Study Design. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.D.; E Kahn, S.; Ader, M.; Watanabe, R.M.; Ni, T.C.; Bergman, R.N. Role of Glucose Effectiveness in the Determination of Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes Care 1996, 19, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Rewers, M.J.; Karter, A.J.; Bergman, R.N.; Hanley, A.J.G; et al. Disposition Index, Glucose Effectiveness, and Conversion to Type 2 Diabetes. The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS) 2010, 33, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morettini, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Burattini, L.; Fioretti, S.; Göbl, C.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Pacini, G.; Tura, A. Assessment of glucose effectiveness from short IVGTT in individuals with different degrees of glucose tolerance. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Shau, W.Y.; Jiang, Y.D.; Li, H.Y.; Chang, T.J.; Sheu, W.H.; Kwok, C.F.; Ho, L.T.; Chuang, L.M. Type 2 diabetes prevalence and incidence among adults in Taiwan during 1999–2004: a national health insurance data set study. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Li, C.-I.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-S.; Yang, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-C.; Li, T.-C. Time trend analysis of the prevalence and incidence of diagnosed type 2 diabetes among adults in Taiwan from 2000 to 2007: a population-based study. BMC Public Heal. 2013, 13, 318–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akehi, Y.; Oketa, A.; Mitsuyoshi, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Ohkubo, K.; Yamashita, T.; Kawashima, H.; Anzai, K.; Ono, J. [The effects of age on insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion in Japanese subjects with normal glucose tolerance]. . 2007, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Ropelle, ER.; Pauli, JR.; Cintra, DE.; Silva, AS. ; Souza CT-D. ; Guadagnini D.; et al. Targeted disruption of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against aging, S-nitrosylation, and insulin resistance in muscle of male mice. Diabetes 2013, 62, 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Buren, J.; Lindmark, S.; Renstrom, F.; Eriksson, J.W. In vitro reversal of hyperglycemia normalizes insulin action in fat cells from type 2 diabetes patients: is cellular insulin resistance caused by glucotoxicity in vivo? Metabolism 2003, 52, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, K.C.; Chuang, L.M.; Yoon, C. Comparison of measured and estimated indices of insulin sensitivity and beta cell function: impact of ethnicity on insulin sensitivity and beta cell function in glucose-tolerant and normotensive subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86, 1620–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Cui, Q.; Yang, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. The impairment of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells caused by prolonged glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity is associated with elevated adaptive antioxidant response. Food Chem Toxicol 2017, 100, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, X.; Bouché, C.; Tatro, E.; Goldfine, A.B. Family history of diabetes impacts on interactions between minimal model estimates of insulin sensitivity and glucose effectiveness. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-Z.; Lin, J.-D.; Hsia, T.-L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chang, J.-B.; Chen, J.-S.; Pei, C.; Pei, D.; Chen, Y.-L. Accurate method to estimate insulin resistance from multiple regression models using data of metabolic syndrome and oral glucose tolerance test. J. Diabetes Investig. 2013, 5, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.D.; Hsu, C.H.; Liang, Y.J.; Lian, W.C.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wu, C.Z.; et al. The estimation of first-phase insulin secretion by using components of the metabolic syndrome in a chinese population. Int J Endocrinol 2015, 2015, 675245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-Z.; Lian, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Pei, D.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, J.-D. Measuring Second Phase of Insulin Secretion by Components of Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Diabetes Clin. Diagn. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Lee, S.-F.; Pei, C.; Pei, D.; Lee, C.-H.; He, C.-T.; Liang, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-D. Predicting Glucose Effectiveness in Chinese Participants Using Routine Measurements. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2016, 14, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stančáková, A.; Javorský, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Haffner, S. M.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Changes in insulin sensitivity and insulin release in relation to glycemia and glucose tolerance in 6,414 Finnish men. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’archivio, M.; Annuzzi, G.; Varì, R.; Filesi, C.; Giacco, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Rivellese, A.A.; Masella, R. Predominant role of obesity/insulin resistance in oxidative stress development. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 42, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołacki, J.; Matuszek, M.; Matyjaszek-Matuszek, B. Link between Insulin Resistance and Obesity—From Diagnosis to Treatment. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardado-Mendoza, R.; Jimenez-Ceja, L.; Majluf-Cruz, A.; Kamath, S.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Casiraghi, F.; Velazquez, A.O.C.; A DeFronzo, R.; Dick, E.; Davalli, A.; et al. Impact of obesity severity and duration on pancreatic β- and α-cell dynamics in normoglycemic non-human primates. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 37, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, N.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Visceral adiposity index and insulin secretion and action in first-degree relatives of subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2014, 31, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Man, C.D.; Campioni, M.; Basu, A.; Klee, G.; Toffolo, G.; et al. Effects of Age and Sex on Postprandial Glucose Metabolism : Differences in Glucose Turnover, Insulin Secretion, Insulin Action, and Hepatic Insulin Extraction. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacos, K.; Gillberg, L.; Volkov, P.; Olsson, A.H.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Gjesing, A.P.; Eiberg, H.; Tuomi, T.; Almgren, P.; et al. Blood-based biomarkers of age-associated epigenetic changes in human islets associate with insulin secretion and diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Epidemiology of Gender Differences in Diabetes and Obesity. In Sex and Gender Factors Affecting Metabolic Homeostasis, Diabetes and Obesity; Mauvais-Jarvis, F., Ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Dunstan, D.W.; Cameron, A.J.; Welborn, T.A.; Shaw, J.E. Differences in height explain gender differences in the response to the oral glucose tolerance test— the AusDiab study. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman-Gruen, D.; Barrett-Connor, E. Sex differences in the association of endogenous sex hormone levels and glucose tolerance status in older men and women. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Genugten, R.E.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Tong, J.; Gerchman, F.; Zraika, S.; Udayasankar, J.; Boyko, E.J.; Fujimoto, W.Y.; Kahn, S.E. ; the American Diabetes Association GENNID Study Group Effects of Sex and Hormone Replacement Therapy Use on the Prevalence of Isolated Impaired Fasting Glucose and Isolated Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Subjects With a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3529–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsholme, E.A.; Dimitriadis, G. Integration of biochemical and physiologic effects of insulin on glucose metabolism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2001, 109, S122–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Jia, G.; Parrish, A.R.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism 2021, 119, 154766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.; Williams, J.S.; Hopkins, P.N.; Simonson, D.C.; Williams, G.H. Familial Aggregation of Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2006, 8, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.W.; Chung, R.; Juarez, D.T. Prevalence of comorbid conditions with aging among patients with diabetes and cardiovascular disease. . 2011, 70, 209–13. [Google Scholar]
- GLumer, C.; Jørgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K. Prevalences of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation in a Danish population: the Inter99 study. Diabetes care 2003, 26, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torquato, M.T.d.C.G.; Junior, R.M.M.; Viana, L.A.L.; de Souza, R.A.H.G.; Lanna, C.M.M.; Lucas, J.C.B.; Bidurin, C.; Foss, M.C. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance in the urban population aged 30-69 years in Ribeirão Preto (São Paulo), Brazil. Sao Paulo Med J. 2003, 121, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzilai, N.; Ferrucci, L. Insulin resistance and aging: a cause or a protective response? . Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences 2012, 67, 1329–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayoso-Diz, P.; Otero-González, A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.X.; Gude, F.; García, F.; De Francisco, A.; Quintela, A.G. Insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) cut-off values and the metabolic syndrome in a general adult population: effect of gender and age: EPIRCE cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2013, 13, 47–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A. M.; Halter, J. B. Aging and insulin secretion. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2003, 284, E7–E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Vichi, S.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Laakso, M.; Paolisso, L.; Smith, G.; et al. Insulin action and age: European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Diabetes 1996, 45, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and Abuse of HOMA Modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.; Clark, P.; Hales, C.; Osmond, C. Understanding Oral Glucose Tolerance: Comparison of Glucose or Insulin Measurements During the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test with Specific Measurements of Insulin Resistance and Insulin Secretion. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjems, L.L.; Vølund, A.; Madsbad, S. Quantification of beta-cell function during IVGTT in Type II and non-diabetic subjects: assessment of insulin secretion by mathematical methods. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrakou, A.; Vuorinen-Markkola, H.; Raptis, G.; Toft, I.; Mokan, M.; Strumph, P.; Pimenta, W.; Veneman, T.; Jenssen, T.; Bolli, G. Simultaneous assessment of insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity using a hyperglycemia clamp. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, H.; Zawalich, K.C.; Ganesan, S.; Calle, R.; Zawalich, W.S. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Insulin Secretion. Diabetes Care 1990, 13, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henquin, J.-C.; Ishiyama, N.; Nenquin, M.; Ravier, M.A.; Jonas, J.-C. Signals and Pools Underlying Biphasic Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51, S60–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.P.; Ensinck, J.W. Acute-Phase Insulin Secretion and Glucose Tolerance in Young and Aged Normal Men and Diabetic Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1975, 41, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei, K.; Gaillard, T.; Schuster, D.P. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Type II Diabetes in African-Americans: The significance of insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, and glucose effectiveness. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festa, A.; Williams, K.; Hanley, A. J.; Haffner, S. M. β-Cell dysfunction in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance and early type 2 diabetes: comparison of surrogate markers with first-phase insulin secretion from an intravenous glucose tolerance test. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-D. Levels of the first-phase insulin secretion deficiency as a predictor for type 2 diabetes onset by using clinical-metabolic models. Ann. Saudi Med. 2015, 35, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Rizza, R. Glucose effectiveness: measurement in diabetic and nondiabetic humans. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2001, 109, S157–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, X.; Bouché, C.; Tatro, E.; Goldfine, A.B. Family history of diabetes impacts on interactions between minimal model estimates of insulin sensitivity and glucose effectiveness. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.J.; Osei, K.; Gaillard, T. Comparative Study of Glucose Homeostasis, Lipids and Lipoproteins, HDL Functionality, and Cardiometabolic Parameters in Modestly Severely Obese African Americans and White Americans With Prediabetes: Implications for the Metabolic Paradoxes. Diabetes Care 2014, 38, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| r | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | ||
| Log transformation of first phase insulin secretion | -0.008 | 0.929 |
| Log transformation of second phase insulin secretion | -0.028 | 0.762 |
| Insulin resistance | -0.391 | <0.001 |
| Glucose effectiveness | -0.667 | <0.001 |
| Female | ||
| Log transformation of first phase insulin secretion | -0.238 | 0.003 |
| Log transformation of second phase insulin secretion | 0.096 | 0.240 |
| Insulin resistance | -0.240 | 0.003 |
| Glucose effectiveness | -0.780 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





